Pulse Parameters and Peak Currents of Return Strokes Observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese Inland Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
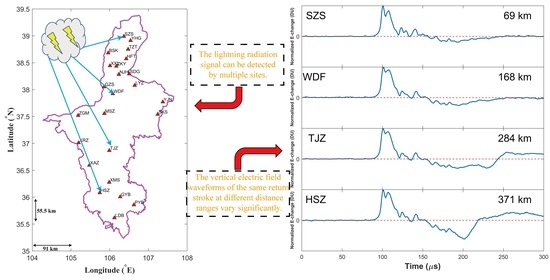
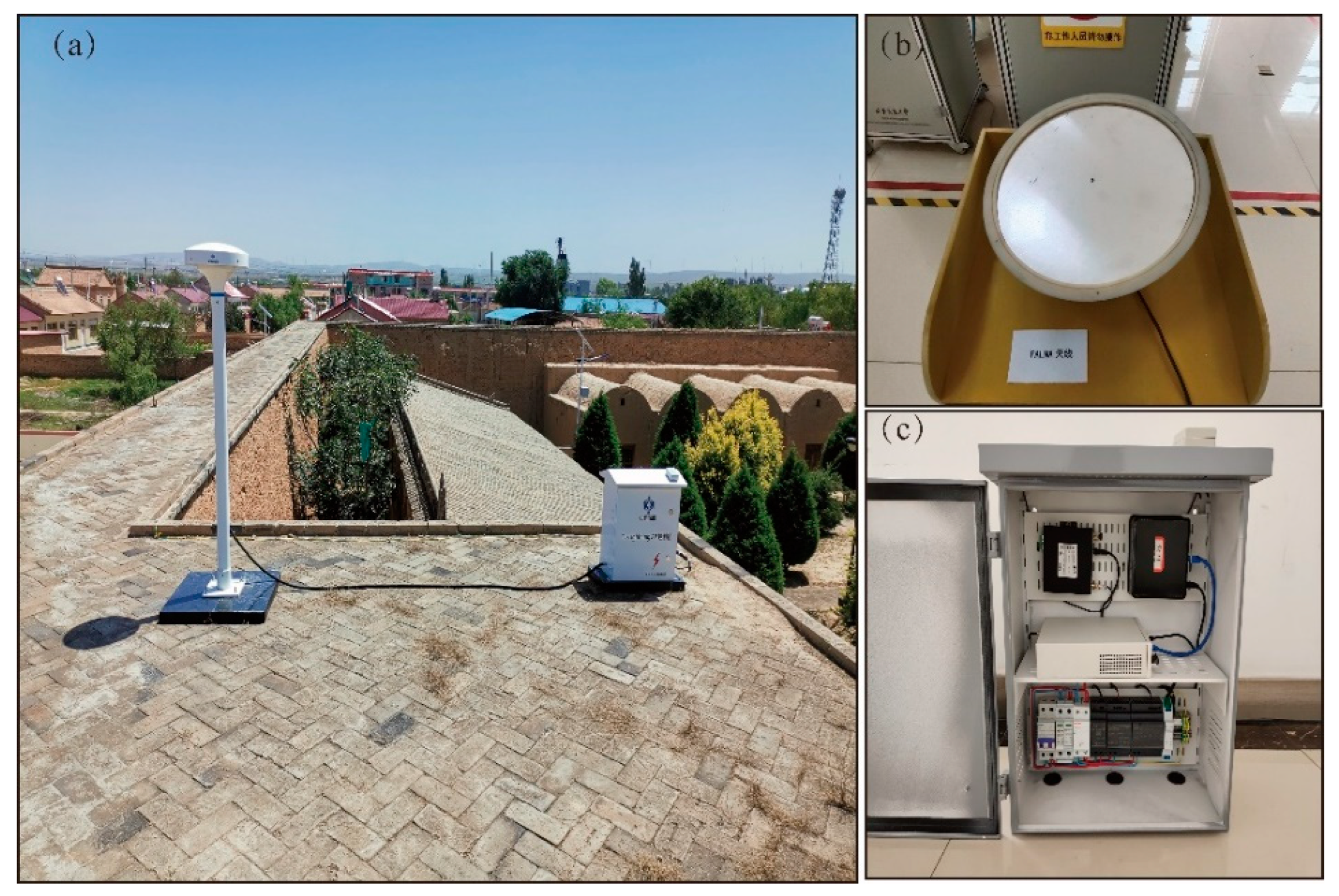
2. Observational Experiment
3. Data Processing
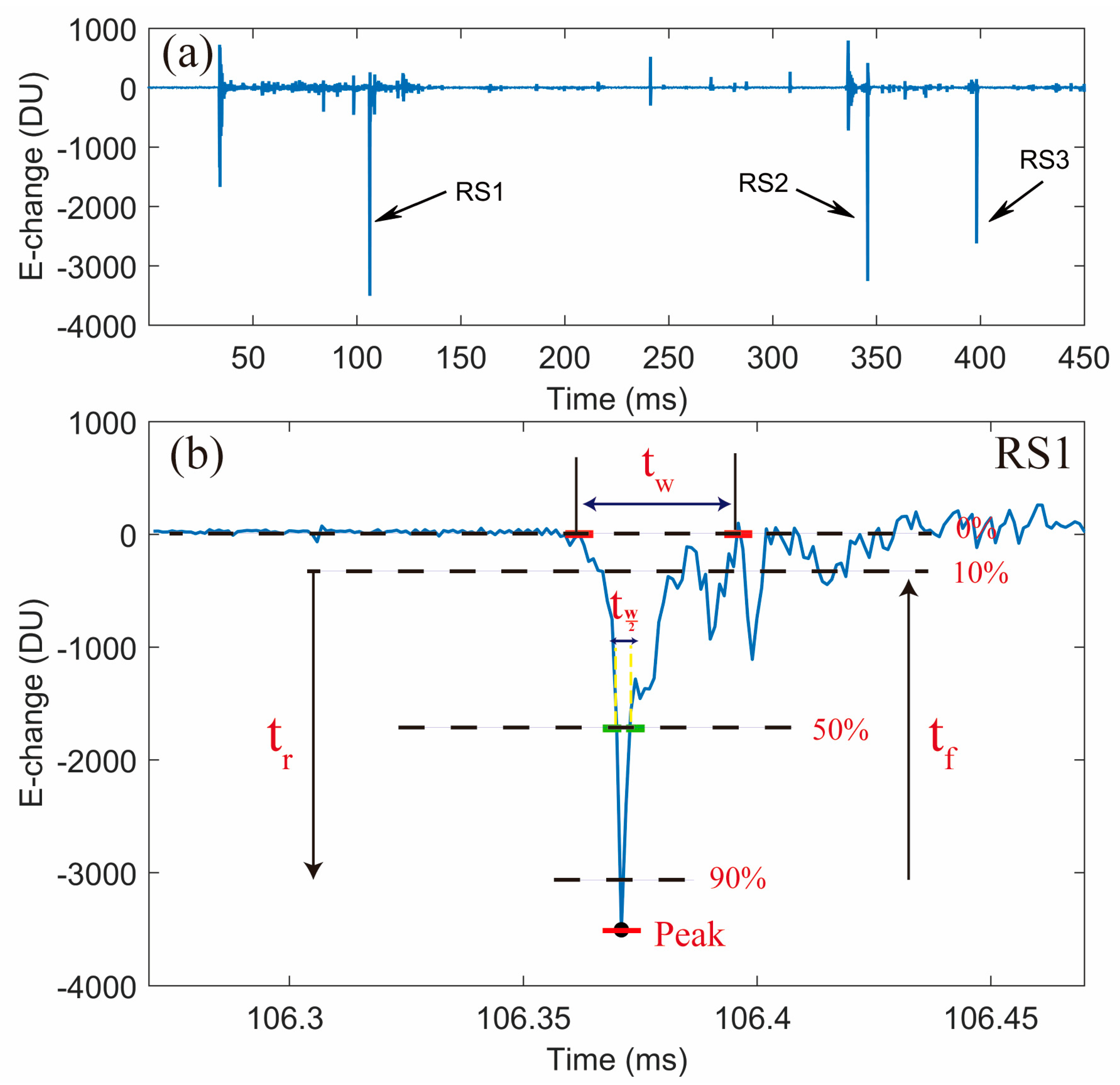
3.1. Calculation of Pulse Parameter
- A.
- A 10-to-90% rise time (tr): interval rising from 10% to 90% of the RS peak amplitude;
- B.
- Half-peak width (tw/2): 50%-of-peak-crossing time;
- C.
- Fall time (tf): time difference falling from 90% to 10% of the RS peak amplitude;
- D.
- Zero-crossing time (tw): the interval between the zero-crossing points.
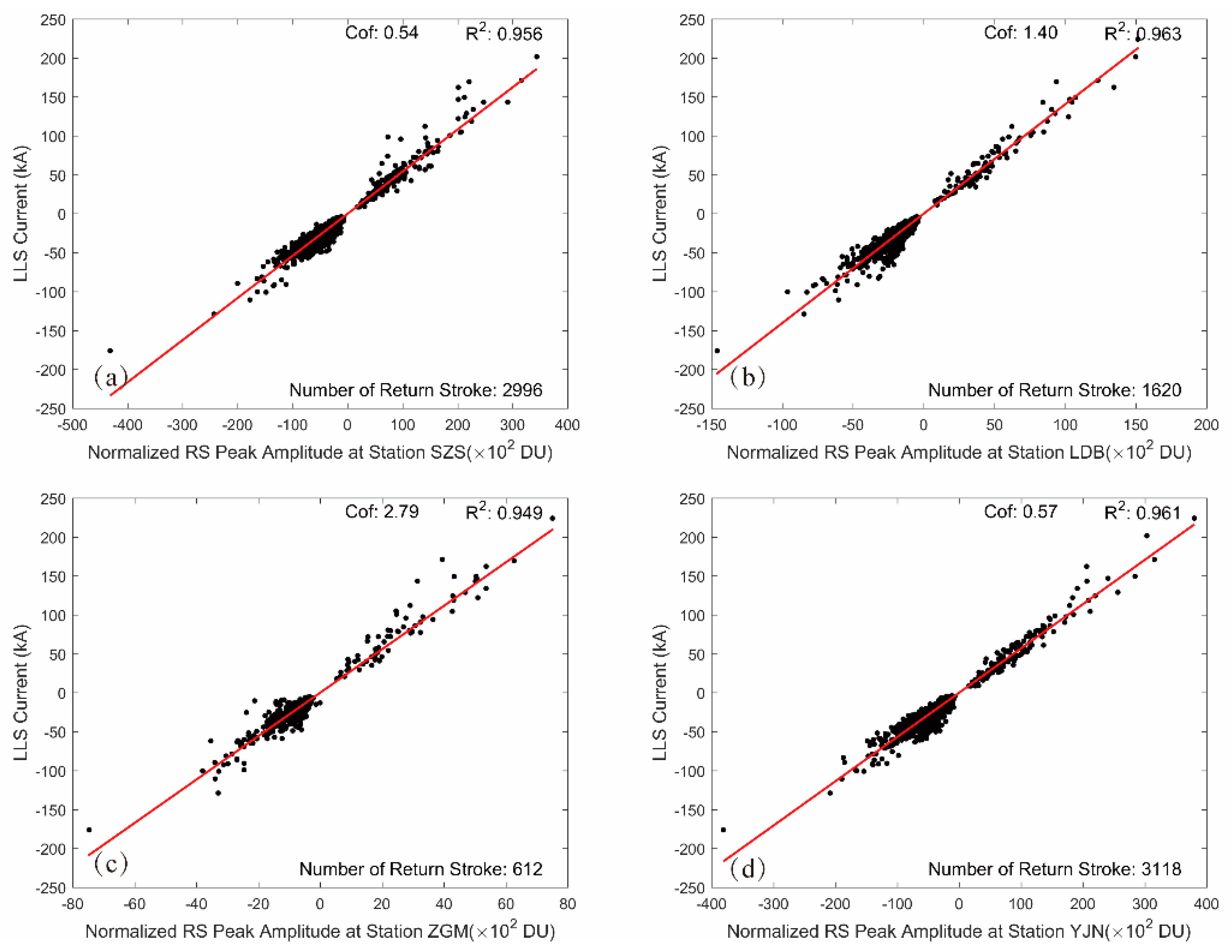
3.2. Estimation of RS Current
4. Statistics of RS Pulse Parameters
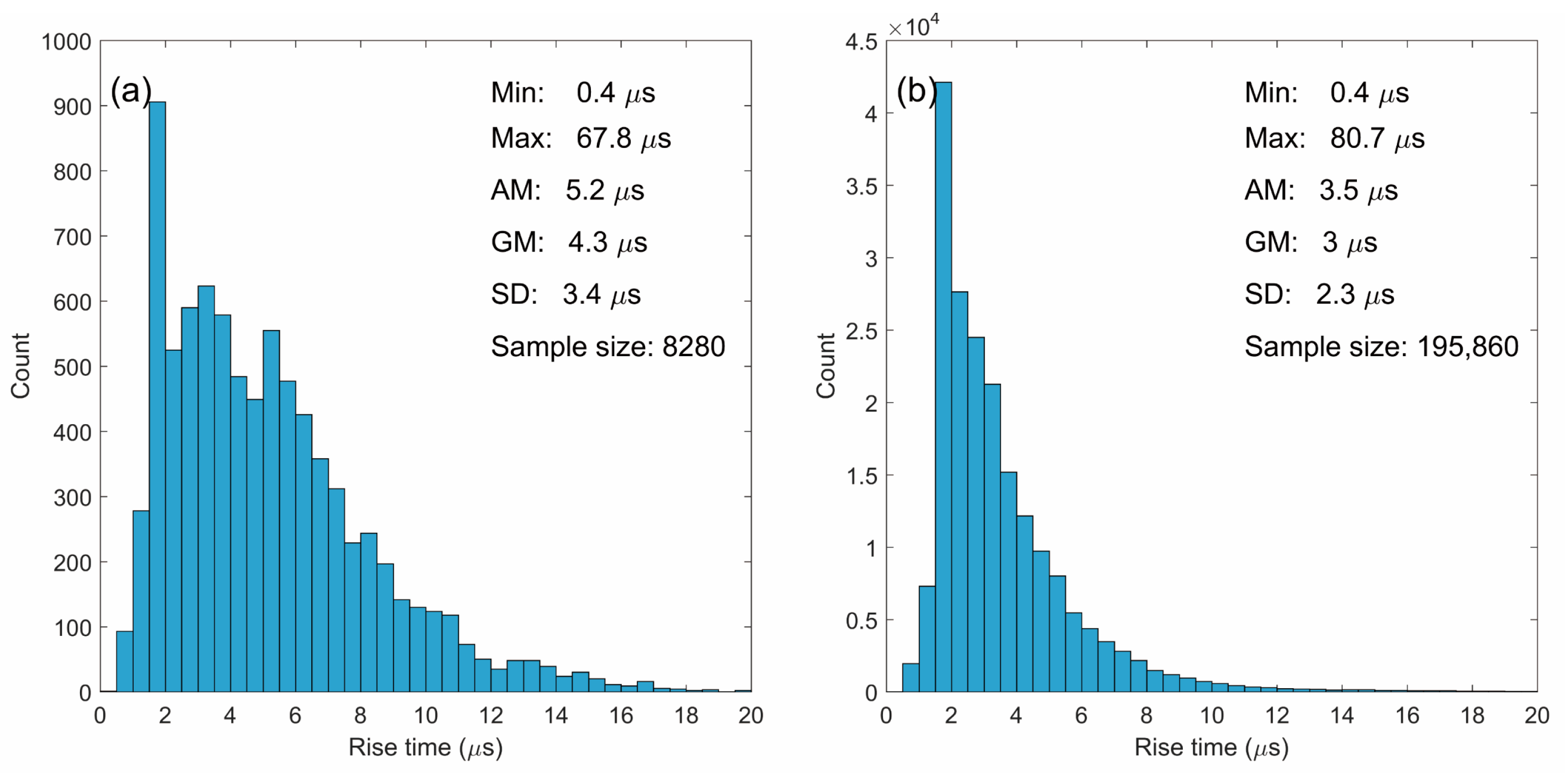
4.1. 10-to-90% Rise Time
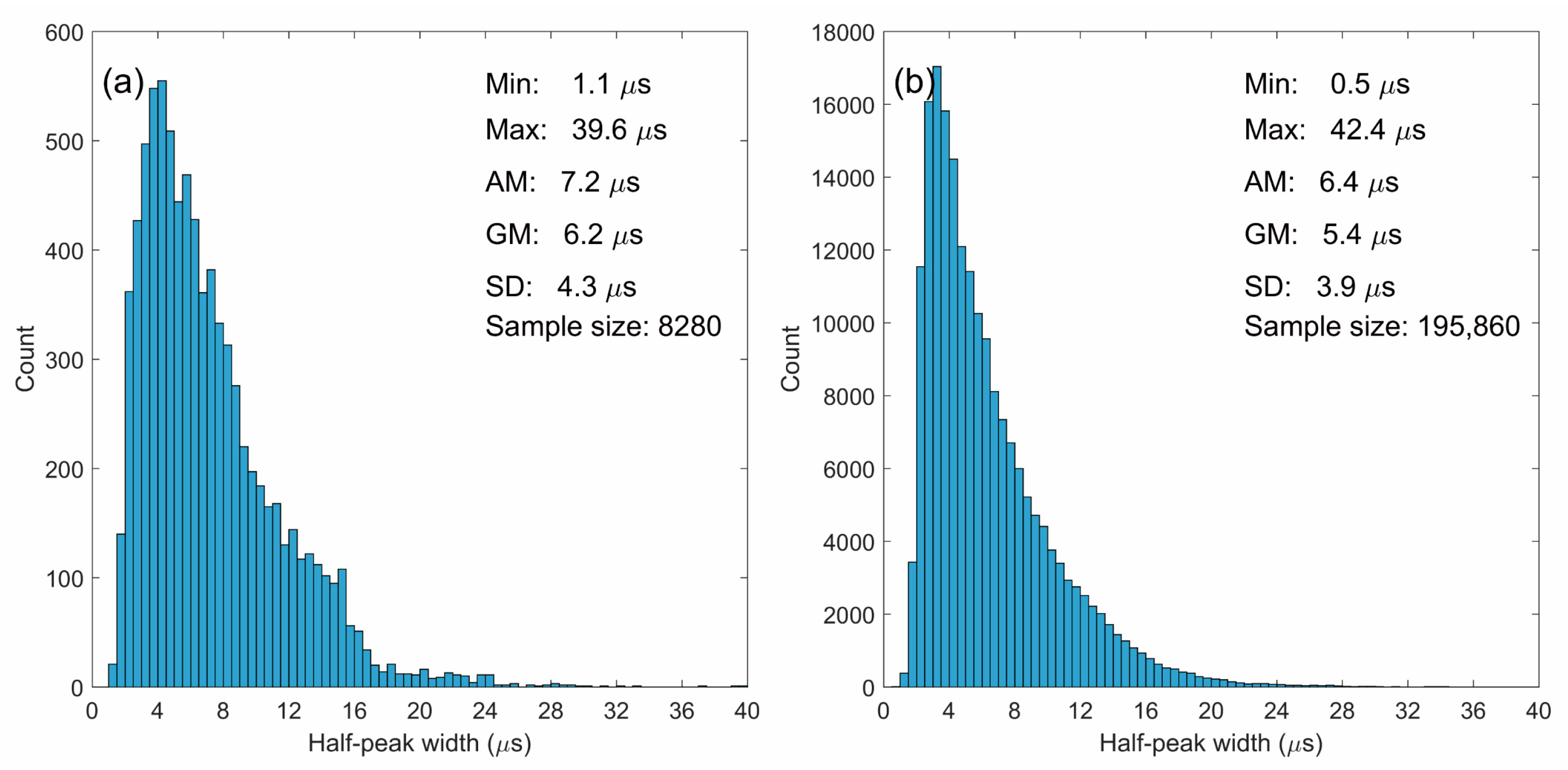
4.2. Half-Peak Width
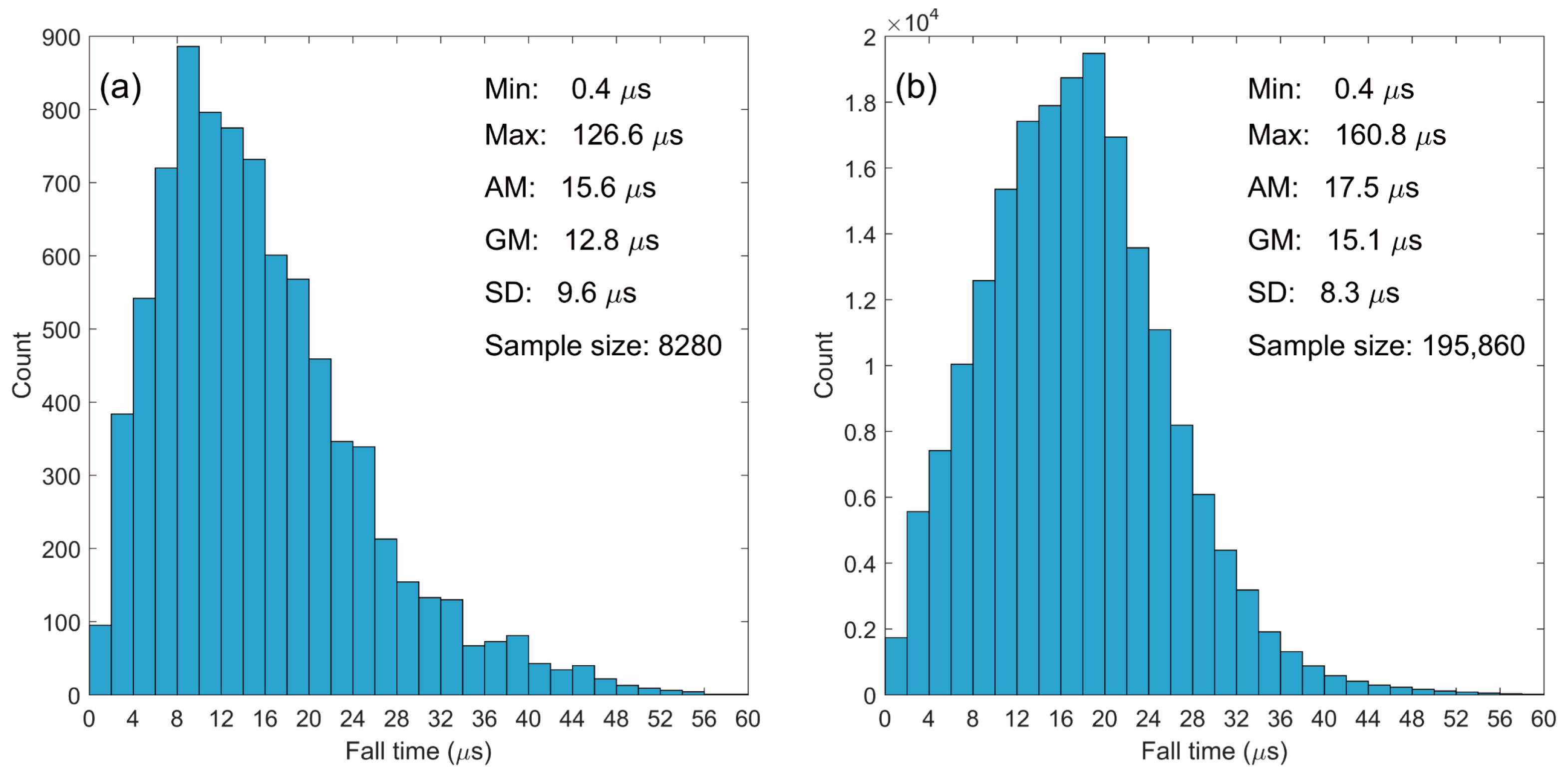
4.3. 90-to-10% Fall Time
4.4. Zero-Crossing Time
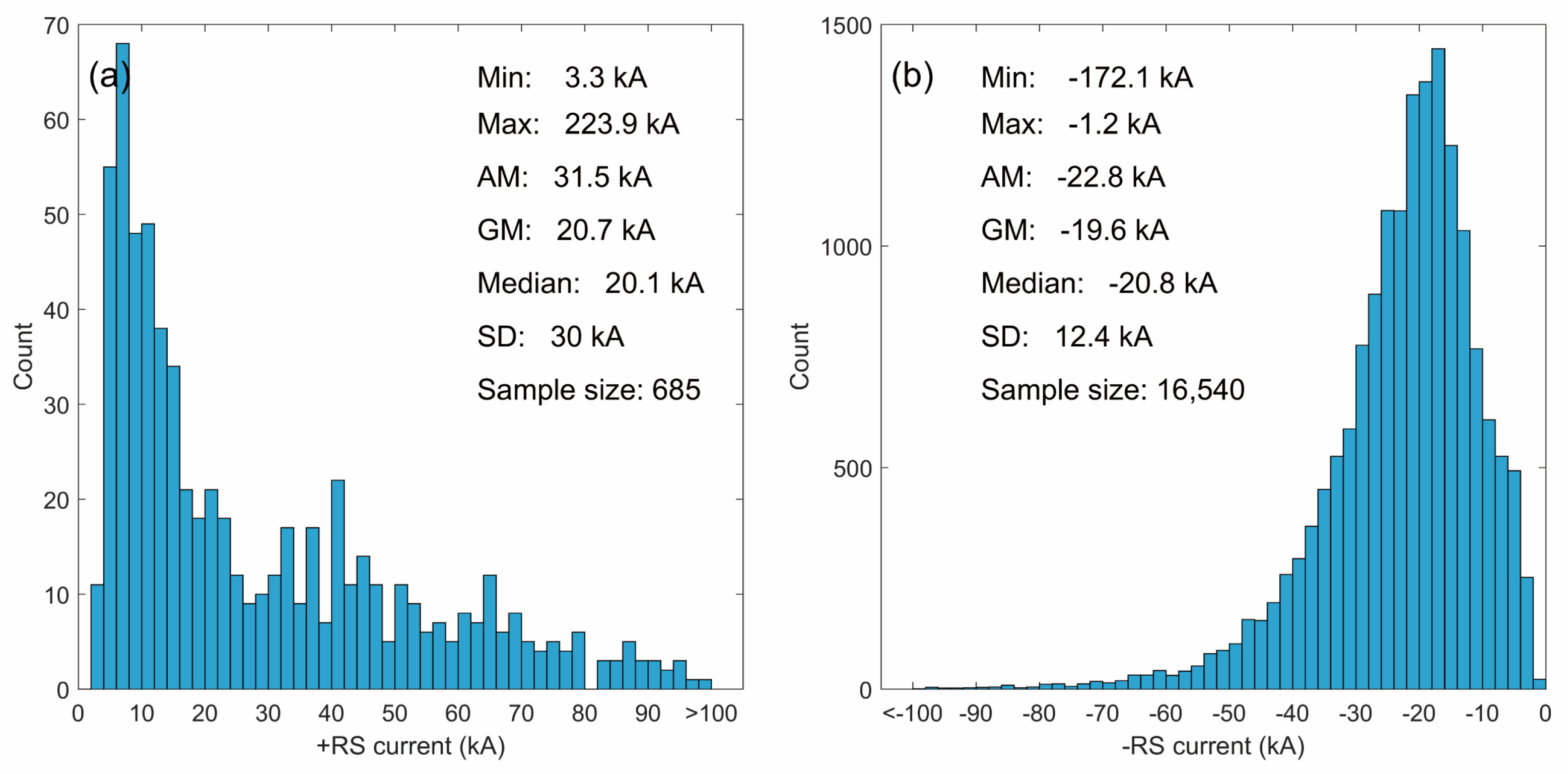
5. Statistics of RS Peak Currents
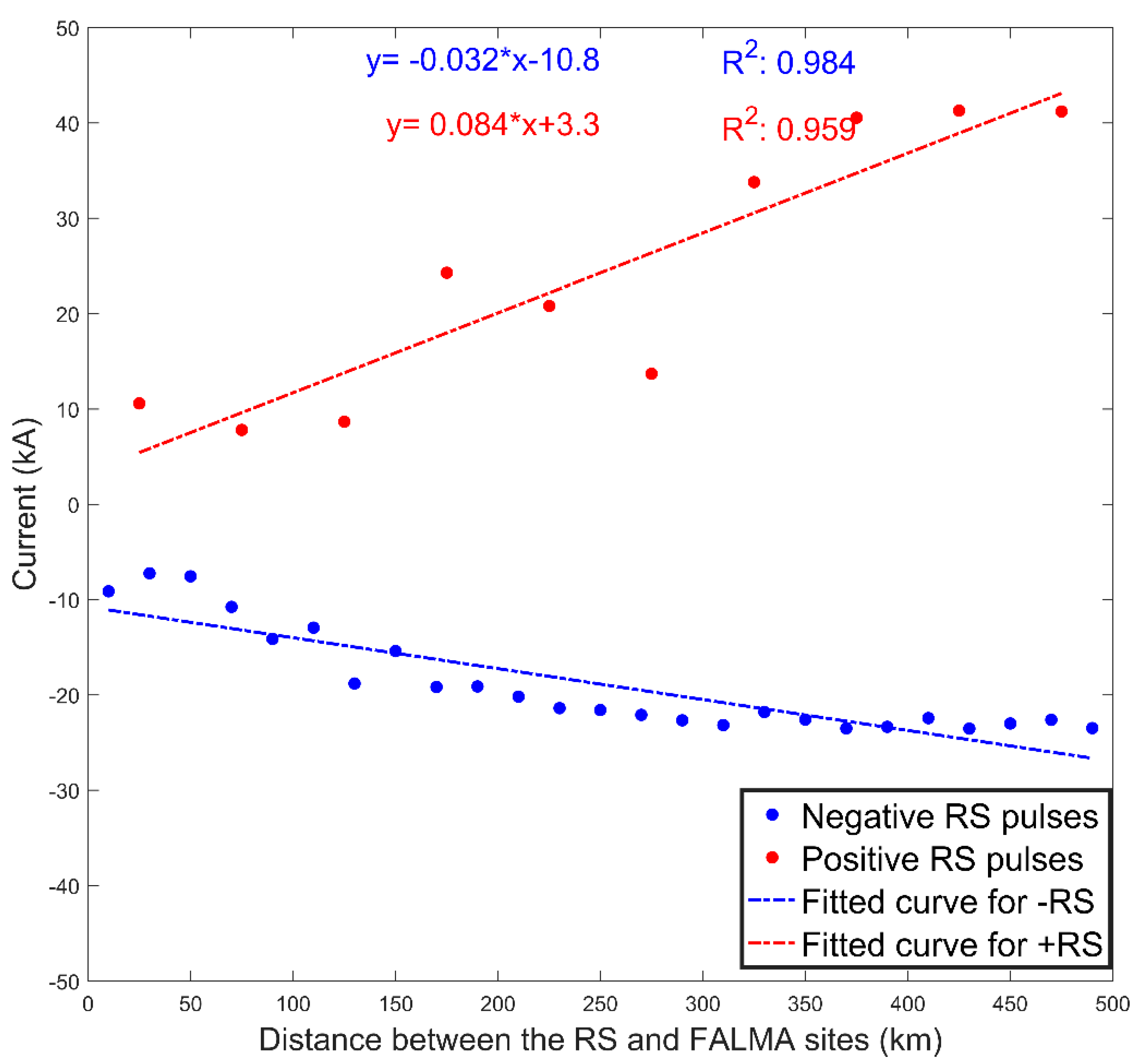
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
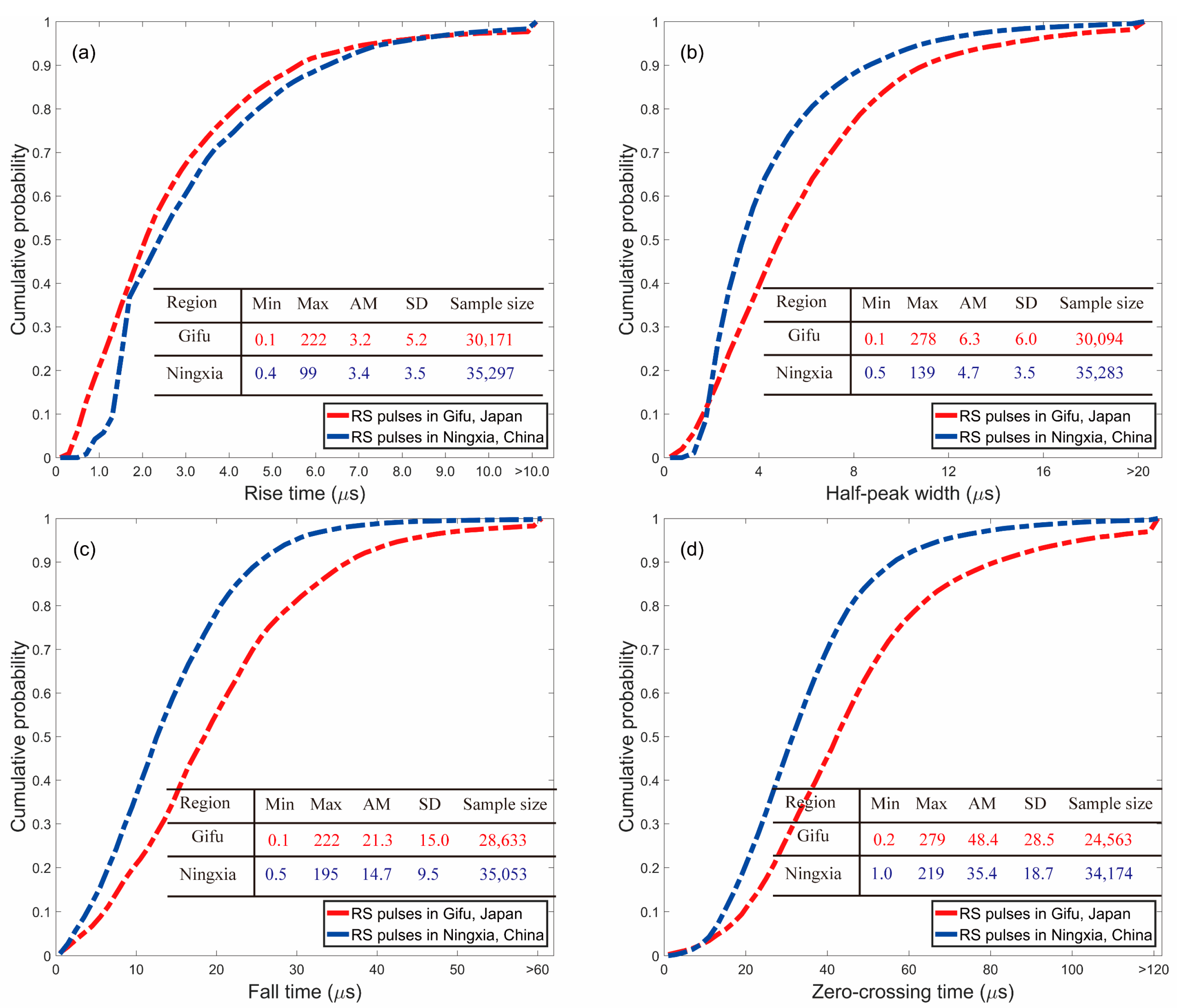
- All of the statistical histograms of RS pulse parameters in this study apparently follow the normal distribution. The comparison between the positive and negative RSs shows that on average, the positive RS tends to have a longer rise time (AM: 5.3 versus 3.6 μs), wider half-peak width (AM: 7.3 versus 6.4 μs), shorter fall time (AM: 15.8 versus 17.5 μs), and longer zero-crossing time (AM: 42.8 versus 38.5 μs). Compared to the results in other studies, the fall time and zero-crossing time in this study appear to be shorter, and we suggest that the two parameters should be underestimated due to the limitation of the short time constant of the fast antenna used in the FALMA.
- The AM positive and negative RS currents are 31.5 and 22.8 kA, respectively. Compared to the previously reported results, the RS peak currents in the Chinese inland areas seem to be relatively larger. In our dataset, the positive RSs with peak currents below 10 kA account for up to 27% (182/685), indicating that small positive discharge pulses should be taken into account.
- The RS pulse characteristics versus distance ranges and regions are verified. The results show that with increasing distance ranges, pulse parameters and currents for both positive and negative RSs significantly exhibit an increasing tendency. Take the rise time as an example, for each 100 km increase in distance, the rise time of positive (negative) RS increases by 0.6 (0.2) μs. Furthermore, a simple comparison between Gifu, Japan and Ningxia, China has indicated that pulse parameters differed significantly in different regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simpson, S.G.; Robinson, G.D. The distribution of electricity in thunderclouds. II. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1941, 177, 281–329. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, S.G.; Scrase, F.J. The distribution of electricity in thunderclouds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1937, 161, 309–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. A preliminary analysis of the characteristics of ground discharges in thunderstorms near Zhongchuan, Gansu province. Plateau Meteorol 1990, 9, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.S.; Guo, C.M.; Wang, C.W. The surface electrostatic field-change produced by lightning flashes and the lower positive charge layer of the thunderstorm. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1987, 45, 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, X.S.; Liu, X.S.; Zhang, G.S.; Yu, Y.; Guo, C.M.; Wang, D.H.; Ushio, T.; Watanabe, T. Characteristics of lightning discharge to ground in Zhongchuan area. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1998, 56, 312–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Dong, W.S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, H.F.; Chen, C.P.; Zhang, T. Study of charge structure and radiation characteristic of intracloud discharge in thunderstorms of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Takagi, N.; Watanabe, T.; Yuan, T.; Qie, X.; Zhang, Y. Observed characteristics of lightning occurred in Lhasa city, Tibet Plateau region of China. J. Atmos. Electr. 2007, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.M.; Liu, X.S. A preliminary analysis of intracloud lightning flashes and lower positive charge of thunderclouds. Plateau Meteorol. 1987, 6, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, X.; Kong, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, A. The possible charge structure of thunderstorm and lightning discharges in northeastern verge of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2005, 76, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, X.S.; Zhang, T.L.; Chen, C.P.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, T.; Wei, W.Z. The lower positive charge center and its effect on lightning discharges on the Tibetan-Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L05814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qie, X.S.; Zhang, T.L.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, T.; Kong, X.Z. Electrical characteristics of thunderstorms in different plateau regions of China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.K.; Qie, X.S.; Zhang, T.L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Y.; She, Y.; Sun, B.L.; Wang, H.B. Electric field soundings and the charge structure within an isolated thunderstorm. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zhang, G.S.; Wen, J.; Wang, D.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, T.; Fan, X.P.; Fan, X.P.; Wu, B. Electrical structure of a Qinghai–Tibet Plateau thunderstorm based on three-dimensional lightning mapping. Atmos. Res. 2013, 134, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, J. Observation and analysis of electrical structure change and diversity in thunderstorms on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2017, 194, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N. Correlation between the first return stroke of negative CG lightning and its preceding discharge processes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 8501–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Lightning mapping with an array of fast antennas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Takagi, N. The Strongest Negative Lightning Strokes in Winter Thunderstorms in Japan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. A negative cloud-to-ground lightning flash initiating at a high altitude and starting without classic preliminary breakdown pulses. J. Atmos. Electr. 2020, 39, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Multiple-stroke positive cloud-to-ground lightning observed by the FALMA in winter thunderstorms in Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Upward negative leaders in positive upward lightning in winter: Propagation velocities, electric field change waveforms, and triggering mechanism. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Velocities of positive leaders in intracloud and negative cloud-to-ground lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 9983–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Intracloud lightning flashes initiated at high altitudes and dominated by downward positive leaders. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6982–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Takagi, N. Compact lightning strokes in winter thunderstorms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Preliminary Breakdown Pulses in Intracloud Lightning Flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 12901–12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, T.; Takagi, N. A comparison on the E-change pulses occurring in the bi-level polarity-opposite charge regions of the intracloud lightning flashes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wu, T.; Wang, D. Initial Results of Long-term Continuous Observation of Lightning Discharges by FALMA in Chinese Inland Plateau Region. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bitzer, P.; Rakov, V.; Ding, Z. A Machine-Learning Approach to Classify Cloud-to-Ground and Intracloud Lightning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Sunjerga, A. Multiple-Station Measurements of a Return-Stroke Electric Field from Rocket-Triggered Lightning at Distances of 68–126 km. IEEE Trans. EMC 2018, 61, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Rakov, V.A. Characterization of far electric field waveforms produced by rocket-triggered lightning. In Proceedings of the 32th International Conference on Lightning Protection, Shanghai China, 13–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, M.A.; Rakov, V.A.; Cummer, S.A. New measurements of lightning electric fields in Florida: Waveform characteristics, interaction with the ionosphere, and peak current estimates. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, Z. Performance evaluation for a lightning location system based on observations of artificially triggered lightning and natural lightning flashes. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2012, 29, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Rakov, V.A. Parameters of Electric Field Waveforms Produced by Positive Lightning Return Strokes. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, J.; Ishii, M.; Kawamura, T.; Suzuki, F.; Funayama, R. The fine structure in the field change produced by positive ground strokes. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 6139–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, C.; Saba, M.M.F.; Da Silva, R.B.G.; Schulz, W. Electric fields changes produced by positives cloud-to-ground lightning flashes. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 92, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Xuan, Y. Characteristics of positive cloud-to-ground lightning in Da HingganLing forest region at relatively high latitude, northeastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13393–13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, M.J.; Uman, M.A.; Beasley, W.; Darveniza, M. Lightning induced voltages on power lines: Experiment. IEEE Trans. PAS 1984, 103, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, S.; Rakov, V.A.; Kereszy, I.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of Far Electric Field Waveforms Produced by Rocket-Triggered Lightning Strokes and Subsequent Strokes in Natural Lightning. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Lightning Protection, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 30 August–4 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uman, M.A.; Swanberg, C.E.; Tiller, J.A.; Lin, Y.T.; Krider, E.P. Effects of 200 km propagation on lightning return stroke electric fields. Radio Sci. 1976, 11, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Rakov, V.A.; Hill, J.D.; Ngin, T.; Gamerota, W.R.; Pilkey, J.T.; Biagi, C.J.; Jordan, D.M.; Uman, M.A.; Cramer, J.A.; et al. Performance characteristics of the NLDN for return strokes and pulses superimposed on steady currents, based on rocket-triggered lightning data acquired in Florida in 2004–2012. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 3825–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Qie, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of cloud-to-ground lightning return strokes in Beijing based on high temporal resolution data of fast electric field change. Clim. Environ. Res. 2017, 22, 231–241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Dong, W.; Wang, T.; Qiu, S. A time-domain analysis on waveform changes of lightning electric field and identification of discharge types. Meteorol. Mon. 2009, 35, 49–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Uman, M.; Tiller, J.A.; Brantley, R.D.; Beasley, W.; Krider, E.; Weidman, C.; Merril, J.; Grant, J.R.; Platt, U.; et al. Characterization of lightning return stroke electric and magnetic fields from simultaneous two-station measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 6307–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Hojo, J. Statistics on fine structure of cloud-to-ground lightning field waveforms. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 13267–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.L.; Murphy, M.J.; Bardo, E.A.; Hiscox, W.L.; Pyle, R.B.; Pifer, A.E. A Combined TOA/MDF Technology Upgrade of the U.S. National Lightning Detection Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 9035–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Weitao, L. Temporal distribution and waveform characteristics of positive cloud-to-ground lightning in Beijing area. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2010, 21, 442–449. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, K.; Anderson, R.B.; Kröninger, H. Parameters of lightning flashes. Electra 1975, 41, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nag, A.; Rakov, V.A.; Cummins, K.L. Positive Lightning Peak Currents Reported by the U.S. National Lightning Detection Network. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Eichenbaum, A.S. The Impact of Cloud-To-Ground Lightning Type on the Differences in Return Stroke Peak Current Over Land and Ocean. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174774–174781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Cummins, K.L. Negative first stroke leader characteristics in cloud-to-ground lightning over land and ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Azadifar, M.; Rachidi, F.; Rubinstein, M.; Diendorfer, G.; Sheshyekani, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Analysis of lightning electromagnetic field propagation in mountainous terrain and its effects on TOA-based lightning location systems. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, W.; Chen, S.; Yan, X. Low-frequency E-field Detection Array (LFEDA)—Construction and preliminary results. Sci. China 2017, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Jing, X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Propagation effect of a fractal rough ground boundary on the lightning-radiated vertical electric field. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.F.R.; Rakov, V.A. Characterization of lightning electric field waveforms using a large database: 2 Analysis and results. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.; Li, Q. Electrical Field Parameters of Natural Return Strokes at Different Distances. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2022. in print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Polarity | Reference | Distance (km) | Number | AM (μs) | GM (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Nag and Rakov [32] (NL) | 7.8–157 | 62 | 4.0 | 3.4 |
| Qi et al. [35] (NL) | / | 196 | 7.77 | 7.27 | |
| Hoko et al. [33] (NL) | / | 44 | 6.7 | / | |
| Schumann et al. [34] (NL) | 3–80 | 72 | 5.7 | 5.2 | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 8280 | 5.2 | 4.3 | |
| Negative | Master et al. [36] (NL) | 1–20 | 220 | 1.5 | / |
| Ding et al. [37] (NL) | 35–55 | 184 | 2.5 | 2.2 | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 195,860 | 3.5 | 3 |
| Polarity | Reference | Distance (km) | Number | AM (μs) | GM (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Li et al. [40] (NL) | / | 304 | 6.2 | 4.8 |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 8280 | 7.2 | 6.2 | |
| Negative | Mallick et al. [39] (RTL) | 645 | 69 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| Li et al. [40] (NL) | / | 1467 | 5.3 | 3.7 | |
| Wang et al. [28] (RTL) | 68–126 | 38 | 2.9 | 2.9 | |
| Ding et al. [37] (NL) | 35–55 | 184 | 6.3 | 5.4 | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 195,860 | 6.4 | 5.4 |
| Polarity | Reference | Distance (km) | Number | AM (μs) | GM (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Li et al. [40] (first RS in NL) | / | 304 | 14.5 | / |
| Li et al. [40] (subsequent RS in NL) | / | 29 | 12.6 | / | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 8280 | 15.6 | 12.8 | |
| Negative | Liu et al. [41] (NL) | / | 750 | 89 | / |
| Li et al. [40] (first RS in NL) | / | 1467 | 23.9 | / | |
| Li et al. [40] (subsequent RS in NL) | / | 4109 | 19.5 | / | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 195,860 | 17.5 | 15.1 |
| Polarity | Reference | Distance (km) | Number | AM (μs) | GM (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Nag and Rakov [32] (first RS in NL) | 7.8–157 | 42 | 69 | 45 |
| Ishii and Hojo [43] (NL) | 100–300 | 34 | 151 | / | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 8280 | 42.8 | 37.3 | |
| Negative | Lin et al. [42] (NL) | 200 | 77 | 36 | / |
| Haddad et al. [30] (subsequent RS in NL) | 10–330 | 197 | 67.6 | 61.5 | |
| Wang et al. [28] (RTL) | 68–126 | 12 | 50 | 47 | |
| Ding et al. [37] (NL) | 35–55 | 145 | 58 | 53 | |
| This study (NL) | 0.6–500 | 195,860 | 38.5 | 35.3 |
| Polarity | Reference | Number | Median(kA) | AM (kA) | GM (kA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Berger et al. [46] | 26 | 35 | / | / |
| Zhang et al. [45] (NL) | 8184 | / | 29.7 | / | |
| Nag et al. [47] (NL) | 48 | / | 88 | 75 | |
| This study (NL) | 685 | 20.1 | 31.5 | 20.7 | |
| Negative | Berger et al. [46] (subsequent RS in NL) | 135 | 12 | / | / |
| Zhang et al. [45] (NL) | 67,022 | / | 9.5 | / | |
| Nag and Cummins. [49] (first RS in NL) | 28,328 | 20 | 27 | / | |
| Cummins et al. [48] (subsequent RS in NL) | 886 | 14.5 | 18.6 | / | |
| This study (NL) | 16,540 | 20.8 | 22.8 | 19.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, D.; Gao, P.; Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Jiang, W. Pulse Parameters and Peak Currents of Return Strokes Observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese Inland Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081838
Shi D, Gao P, Wu T, Wang D, Jiang W. Pulse Parameters and Peak Currents of Return Strokes Observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese Inland Areas. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(8):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081838
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Dongdong, Panliang Gao, Ting Wu, Daohong Wang, and Wei Jiang. 2022. "Pulse Parameters and Peak Currents of Return Strokes Observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese Inland Areas" Remote Sensing 14, no. 8: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081838
APA StyleShi, D., Gao, P., Wu, T., Wang, D., & Jiang, W. (2022). Pulse Parameters and Peak Currents of Return Strokes Observed by the Ningxia FALMA in the Chinese Inland Areas. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081838