Abstract
During the last few decades, worsening air quality has been diagnosed in many cities around the world. The accurately prediction of air pollutants, particularly, particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) is extremely important for environmental management. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) P-CNN model is presented in this paper, which uses seven different pollutant satellite images, such as Aerosol index (AER AI), Methane (CH4), Carbon monoxide (CO), Formaldehyde (HCHO), Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), Ozone (O3) and Sulfur dioxide (SO2), as auxiliary variables to estimate daily average PM2.5 concentrations. This study estimates daily average of PM2.5 concentrations in various cities of Pakistan (Islamabad, Lahore, Peshawar and Karachi) by using satellite images. The dataset contains a total of 2562 images from May-2019 to April-2020. We compare and analyze AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50 and P-CNN model on every dataset. The accuracy of machine learning models was checked with Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE). The results show that P-CNN is more accurate than other approaches in estimating PM2.5 concentrations from satellite images. This study presents robust model using satellite images, useful for estimating PM2.5 concentrations.
1. Introduction
Particulate matter of a diameter of 2.5 μm (PM2.5) is hazardous for human health, leading to further damage and the destruction of lung function [1,2,3,4,5,6]. These fine particles are extremely dangerous if they get into the lungs, which might complement the seriousness of COVID-19 infection, and increases the chances of attacks and damage to the respiratory system [7]. Overall, these hazardous pollutants impact human health and produce life-threatening complications in a short period if found in the atmosphere in large concentrations [8]. The research has proven that these particulate matters can potentially affect humans at the genetic level [9].
Various methods have been presented to better explain city-wide air quality, for example, the recent Neighbor legislation and spatial averaging [10,11], to make the most of the limited data gathered by monitoring stations using spatial interpolation. The data sparsity problem is solved by adding monitoring data in most of these systems, which are based on the assumption that air pollution particles diffuse in a spatially continuous manner. However, there are two significant drawbacks of these methods. First, different estimation approaches obtain completely different results. Second, the differences in results are particularly unsatisfactory for raw data with sparse spatial distribution. The air quality detecting network has been optimized by various researchers [12]. For instance, Mei et al. [13] suggest a method to monitor air quality utilizing mobile data. Crowdsourcing computing, including the use of auxiliary sensors, is rapidly becoming the focus of academic research. Murty et al. [14] suggest a new air pollution monitoring system called CitySense for monitoring air pollutants. In order to obtain data samples using compressed sensing technology, Yu et al. [15] proposed a monitoring strategy that relies on vehicular sensor networks (VSN), which represent a paradigm shift in transportation technology. VSN has the potential to significantly enhance the transportation environment due to the vehicles’ infinite power source and the resultant low energy constraints. Li et al. [16] used portable sensors and smartphones to track particulate matter and gas pollutants. However, portable sensors still have limited capability to accomplish the accuracy of monitoring stations accurately. In addition, it takes almost 1 h to obtain the data for PM2.5 measuring equipment; as well, it is also crucial to avoid common issues due to shaking and movement.
Recently, satellite remote sensing has been used in a variety of studies to evaluate air quality [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. For the more accurate methods, an artificial neural network can be utilized as a classifier based on data from road networks and weather data [25]. The deep learning algorithms have achieved significant advancements in image feature learning and have solved numerous challenges in typical computer vision [26]. Image feature-based learning is mainly concerned with the relationships between image characteristics and the index of PM. Liuetal. [27] investigated how air quality relates to image quality. Wang et al. [28] examined air quality by incorporating the association between observed image degradation and PM2.5. Other authors used decision tree in estimating air quality [29]. For example, Zhang et al. [30] used images to calculate air pollution levels with a CNN algorithm. A CNN is a multilayer network structure, whose fundamental structure is comprised of the input layer, convolution layer, pooling layer, fully connected layer and output layer. A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of artificial neural network (ANN) that is most typically used to evaluate visual images. It is one of the most widely used types of ANN. This deep learning method can be used to recognize images and videos in a variety of contexts, including recommendation systems, image classification, segmentation, and medical image analysis. The designed CNN was employed to identify photos according to their PM2.5 index via classification. The CNN consists of multiple layers: nine convolutional layers, two pooling layers and two dropout layers, and to overcome the gradient disappearance problem, an enhanced rectified linear unit activation function can be used. Furthermore, the VGG-16CNN model was proposed to evaluate PM2.5 levels [31] on the basis of image-based PM2.5 concentration levels.
According to atmospheric chemistry and physics, the PM2.5 formations are linked to pollutants, such as PM10, CO2, NO2 and meteorological variables, also called auxiliary variables, which can be used as input variables for model prediction [32]. Song et al. [33] proposed a statistical model for the estimation of PM2.5 concentration. Their model showed that the concentration of PM2.5 is closely associated with concentrations of NO2, SO2, CO and O3 gaseous pollutants. Therefore, these contaminants can be used as input variables for PM2.5 predictions. Image detection-based air quality research is carried out by combining image processing methods and machine learning approaches, but both have certain weaknesses. For example, the color characteristics of the sky may alter the features utilized in PM2.5 and PM10 concentration detection methods based on visual features from the phone camera image. The sensitivity is excessively high and it is greatly affected by the weather. The detection of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations based on physical properties may produce pretty good results, but it is only suited for dry air images, which are impacted by meteorological factors. Taking photos from a camera phone have few disadvantages; such as, we can capture photos with high resolution camera in day time; however, in the evening and night time, the quality might be compromised, which does not lead to better results being estimated. Second, it is very inconvenient and difficult to access remotely areas with camera devices; in contrast, satellite images are better to estimate air quality.
This study uses satellite images and employs a novel deep learning-based method for PM2.5 predictions. This technique, such as prediction from satellite images, is not limited by locations and can be suitable to detect air quality at any location. This study uses seven satellite images (AER AI, CH4, CO, HCHO, NO2, O3 and SO2) collected by high resolution sensors (TROPOMI) from the sentinel-5p satellite. The method that we used in this study differs from existing methods. It estimates the daily average of PM2.5 concentration using satellite images collected by the TROPOMI sensor of sentinel-5p satellite every day. It can address the weaknesses of present air quality detection technologies and offer fine-grained, low-cost air quality monitoring. The proposed technique can estimate the AQI directly, which is broader and better reflects the air quality. The air quality index (AQI) is a daily indicator that measures the quality of the air at a certain location. It is a way to measure how air pollution affects a person’s health during a short period of time (less than 24 h). In short, this study investigates the relationship between PM2.5 concentrations and the concentrations of various pollutants based on satellite images. P-CNN recognizes and extracts patterns and features from input images, and it estimates the daily average of PM2.5 concentrations from these images. This study used four datasets covering Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore and Peshawar city, each dataset contains seven pollutants’ images for each day. This paper proposes a deep convolutional neural network model to estimate PM2.5 concentrations from seven given input images. In addition, we also conducted comparative analysis of our proposed model with other three deep learning models on four datasets for more robust results.
This paper is structured in the following way. The second section introduces the study area, datasets and methodology. The third section presents result and discussion of the study, followed by the conclusion and implications in the last section.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Dataset
The study area we have chosen in this paper is Pakistan. We have taken four metropolitan cities for our experiments such as Karachi, Lahore, Islamabad and Peshawar. Figure 1 shows the study areas and monitoring stations for PM2.5 in Pakistan.
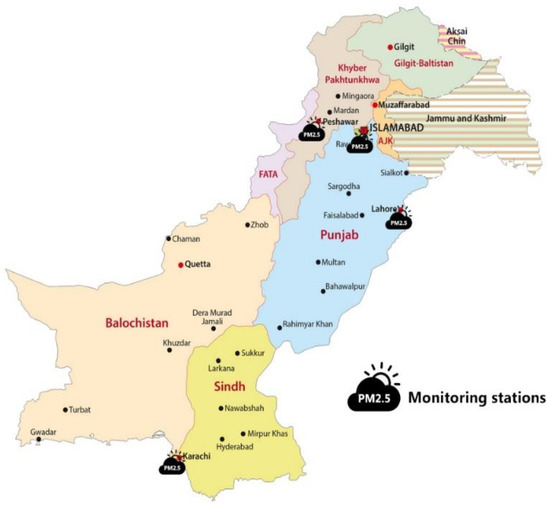
Figure 1.
Study area and the distribution of monitoring stations.
There is no openly available library to estimate PM2.5 concentrations from satellite images; therefore, based on sentinel-5p satellite, a multi-input air quality image database was built for each city (Islamabad, Lahore, Peshawar and Karachi). The library contains 2562 images with different PM2.5 levels, which are a collection of scene satellite images at different PM2.5 levels. We used the following steps to create the dataset:
- We collected scene images for each city from the official website [34] from May-2019 to April-2020. Each day contains seven different pollutant images (AER AI, CH4, CO, HCHO, NO2, O3 and SO2). Table 1 describes the information about the air quality image collection point. One Image cannot cover the concentration of various gases; therefore, each sample is described by taking at least seven satellite images in our research work. The standard single-input CNN architecture is not suitable for our research. Thus, a novel P-CNN model was built to accept seven images as input.
 Table 1. Satellite image collection information.
Table 1. Satellite image collection information.
Figure 2 shows the actual satellite images of seven air pollutants with different PM2.5 air quality levels in the image library. Figure 2, such as from A to D shows different days, while I, II, III, IV, V, VI, and VII are seven different pollutant images by sentinel-5p satellite for same day. I represents concentration of AER AI pollutant in single day, while II illustrates CH4 pollutant concentration for same day. III number image is about CO concentration. IV image is about HCHO pollutant concentration. V, VI and VII images are examples of NO, O3, and SO2, respectively.
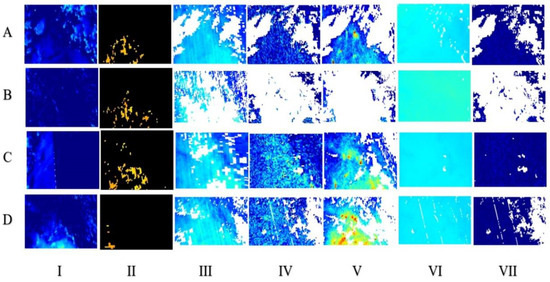
Figure 2.
Example of 4 days of seven different satellite input images in dataset.
Real-time monitoring stations across main cities of Pakistan, such as Islamabad, Lahore, Karachi and Peshawar, measure air quality levels then upload them on the website for the open access. Figure 1 shows the location of the monitoring stations. PM2.5 hourly real-time data were obtained from the official website [35]. Since PM2.5 concentration data are measured hourly by the monitoring stations for each city, we converted the 24-hour data into a daily average to train our model. For the model training, 70% of the images were randomly selected for training and 30% for testing purposes. Furthermore, to prevent the model from overfitting and improve model accuracy and robustness, we strengthened the dataset training process with the minimal number of samples in the training dataset in the following ways.
- (1)
- Randomly Image Rotation between [0, 360] degrees.
- (2)
- Scale the image at random between [0.8, 1] coefficients.
- (3)
- Size of each auxiliary input pollutant image is adjusted to 300 × 300, and then normalized to [0, 1].
2.2. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
CNN, firstly proposed by LeCun et al. [36] for recognition of handwritten digits, has been widely successful in the areas of image detection, segmentation, and identification tasks [37,38,39,40,41,42]. CNN has shown its remarkable capacity to classify large-scale images. It consists of three-layers: convolutional layers, pooling layers and fully connected layers. The essential layers in CNN are the convolutional and pooling layers. The convolution layers are used to extract features with numerous filters by convolving image regions. As the layers expand, the CNN gradually understands the image. The pooling layers lower the dimensions of output maps from the convolutional layers and avoid overfitting. The number of neurons, parameters and connections in the CNN model is substantially less through these two levels. Thus, CNNs are much more effective than Backpropagation (BP) neural networks with correspondingly sized layers.
2.3. Architecture of P-CNN
Based on the standard CNN architecture, we have proposed a model named P-CNN. The model is employed to estimate PM2.5 concentrations and acquire a preferable result on the dataset. Figure 3 shows the entire model of CNN architecture.
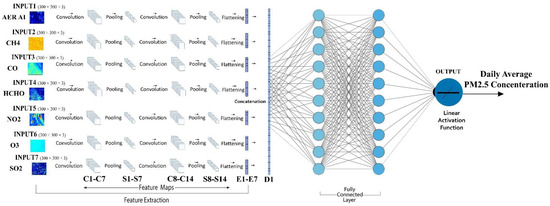
Figure 3.
PM2.5 Concentration Estimation Model.
The convolutional layers C1–C7 filter seven 300 × 300 × 3 input images with 32 kernels of size 4 × 4 × 3 with the stride of 1 pixel. The stride of pooling layers S1–S7 is 2 pixels. C8–C14 filter with 16 kernels of size 4 × 4 × 3 with the stride of 1 pixel. The stride of pooling layers S8–S14 is 2 pixels, and the dropout is applied to the output of S8–S14, which has been flattened (E1–E4). D1 is the concatenation of the previous flattened E1–E4. The fully connected layer FC1 has ten neurons, FC2 has ten neurons, and FC3 has one. The activation of the output layer is a linear function.
A high-level neural networks API called “Keras” is used to implement the model [16]. All of the experiments were carried out on an Ubuntu Kylin 14.04 server equipped with a 3.40 GHz i7-3770 CPU (16 GB RAM) and a GTX 1070 graphics card (8 GB memory). The original image has a resolution of 3310 × 1575 pixels, which needs be lowered in order to fit into the GPU memory. All of the original images are scaled to 300 × 300 pixels, and then the value of per-pixel is divided by 255. In addition, images should be normalized and standardized before being fed into model in order to achieve rapid convergence. A randomization process is used to ensure that the model is not influenced by the sequence in which photographs are input. Both the sequence of samples and the seven images corresponding to each sample should be randomized. The convolutional neural network training procedure is divided into two steps. The first is called forward propagation, and the second is called backward propagation.
2.4. Forward Propagation
Data are transmitted from the input layer to the output layer by a sequence of operations that include convolution, pooling and fully connected. Each convolutional layer employs trainable kernels in order to filter the results of the preceding layer followed by activation function to build the output feature map.
In a general way, the procedure is as follows:
where denotes the collection of input maps we choose. is the bias that is applied to all output map. indicates the kernels, the weight of the row “” and column “” in each kernel is represented by the . Using a kernel map, the outputs of surrounding neurons are summarized by the pooling layer, which is the operation of the pooling layer.
where denotes multiplicative bias and indicates additive bias, “” is a subsampling function that uses the max-pooling algorithm [43]. The reason why we chose max-pooling over mean pooling is that the latter makes it impossible to identify critical information such as the edges of objects, whereas the former selects the most active neuron of each region in feature maps, which is more efficient [44]. As a result, it is easier to extract useful features when using max-pooling. In a multilayer perceptron, the fully connected layer is equivalent to the hidden layer. The activation function “linear” for output layer was employed for regression [45], which is given below by
Any constant value can be for variable “”. A derivative of f(x) in this case is not zero, but is equal to the constant employed. Notably, the gradient does not equal zero, but rather a constant number that is independent of the input value x, which indicates that the weights and biases will be updated throughout the backpropagation phase, despite the fact that the updating factor will remain the same.
2.5. Backward Propagation
Backward propagation adjusts parameters by using stochastic gradient descent (SGD) in order to reduce the disparity between the anticipated outcome and the actual outcome. For the purpose of avoiding overfitting, and regularization is used.
where represents loss in the formula (4). The formula for is given by below
This paper uses a weight of 0.0001 for L1 and L2 regularization. Dropout is also used to prevent overfitting [46], and its value is set to 0.1. The SGD algorithm calculates the gradients and modifies the coefficients or weights. It can be stated in the following way:
where denotes the sensitivities of each unit to fluctuations of the bias b, and represents the element-wise multiplication. An upsampling procedure is represented by the , and subsampling operation is represented by the . The updated weight is denoted by , and represents the learning rate.
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
The following evaluation measures, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), were employed in this work to complete the quantitative assessment of the constructed P-CNN model’s capabilities.
MAE is a model assessment statistic that is commonly employed in regression models. It is a metric for estimating the average discrepancy between estimates and actual results. It is used to estimate the machine learning model’s accuracy.
The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is a commonly used metric for determining how well a model predicts quantitative data. Here, RMSE calculates the error between actual (station value) and predicted value (model’s predicted value).
MAPE means absolute percentage error and is a statistical indicator used for prediction. The “accuracy” of this measurement is expressed as a percentage. It is possible to determine for each period the average absolute percent error, which is deducted from the actual numbers, and then the outcome is divided by actual values. However, the larger the concentration, the bigger the absolute inaccuracy in the forecast. As a result, we anticipate that the MAPE will be able to offer the most accurate forecasts among models.
3. Results
AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50 and P-CNN were all evaluated for their prediction abilities using three different indicators. They are Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE). Table 2 displays MAE results for Lahore, Karachi, Peshawar and Islamabad after applying different machine learning models. When we applied AlexNet on the datasets, a 34.464 average value was achieved, which was reduced 5.113 using ResNet50. VGG16 also decreased the 7.723 MAE value after ResNet50. After applying the P-CNN model on the datasets, 6.475 MAE reduced, and its average value for each city was calculated as 15.152, which is a really good result. Table 3 shows the RMSE values for different cities with different models. AlexNet achieved a 49.445 RMSE average value for all cities, and 12.082 was reduced after applying ResNet50. VGG16 also helped to reduce the 9.079 RMSE value, and 8.726 RMSE decreased after applying P-CNN, and its average value was 19.557. Table 4 reveals results for MAPE. For the average value for all cities after using the AlexNet model, we achieved 43.932. After employing ResNet50, the 7.373 MAPE value decreased. VGG16 also decreased the 11.990 MAPE value. Lastly, P-CNN reduced 9.403 MAPE after VGG16, and its average value for all cities was 15.167. All of these metrics show that P-CNN is superior to other models.

Table 2.
MAE results for all cities using AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50 and P-CNN.

Table 3.
RMSE results for all cities using AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50 and P-CNN.

Table 4.
MAPE results for all cities using AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50 and P-CNN.
Figure 4 depicts a comparison of the actual values and projected values in a time series graph obtained by applying AlexNet (a), VGG16 (b), ResNet50 (c) and our proposed model P-CNN (d) to a testing dataset for Karachi city. In this figure, the P-CNN obtained values that were more closely aligned with the observed values than AlexNet, VGG16 and ResNet50. According to performance indicators, our P-CNN performs much better than other models in terms of predicting of PM2.5 concentrations. When AlexNet was used to the Karachi testing dataset, it produced the following results: MAE (32.343), RMSE (56.322) and MAPE (45.954). The ResNet50 model obtained the following metrics: MAE (28.187), RMSE (37.299) and MAPE (40.223). VGG16 achieved MAE (19.554), RMSE (29.368) and MAPE (22.838). In the same testing dataset for Karachi, we implemented our proposed model P-CNN and obtained the best results, such as MAE (17.123), RMSE (22.084) and MAPE (14.149). Figure 5 shows the difference between the actual and predicted values after applying the same models to Lahore city. The graphs clearly demonstrate that P-CNN (d) outperformed the other models. AlexNet (a) determined the MAE, RMSE and MAPE for Lahore city (29.843, 47.917 and 42.390). ResNet50 (c) achieved (30.214, 39.239 and 37.901). VGG16 attained (b) (21.240, 24.431 and 24.431). However, while assessing the performance of models for predicting PM2.5 concentration, P-CNN (d) achieved the lowest MAE, RMSE and MAPE (14.205, 20.835 and 12.394). The actual and estimated outcomes for Peshawar city are depicted in Figure 6. The graph clearly demonstrates that the P-CNN (d) estimated values more accurate than AlexNet (a), ResNet50 (c) and VGG16 (b). In addition, performance metrics revealed too that P-CNN (d) outperformed all other models. AlexNet computed MAE, RMSE and MAPE (37.449, 50.329 and 47.987), ResNet50 (27.345, 32.302 and 35.025), VGG16 (22.145, 31.502 and 21.494) and P-CNN (18.280, 18.743 and 17.200). Figure 7 provides a time series graph of the observed and predicted values for Islamabad city. It shows that P-CNN (d) is more accurate in predicting PM2.5 concentrations when compared with the other deep learning models (a), (b) and (c). Testing dataset for Islamabad contains three months of daily average of PM2.5 concentration. After applying performance indicators on Islamabad city, MAE, RMSE and MAPE achieved 38.221, 43.215 and 39.399 by AlexNet; 31.657, 40.611 and 33.092 by ResNet50; 23.572, 27.834 and 28.001 by VGG16; and 11.003, 16.566 and 16.657 by P-CNN. All of these figures and performance metrics clearly demonstrate that P-CNN outperforms other deep learning models, such as AlexNet, ResNet50 and VGG16, in terms of predicting PM2.5 concentrations accurately in Karachi, Lahore, Peshawar and Islamabad.
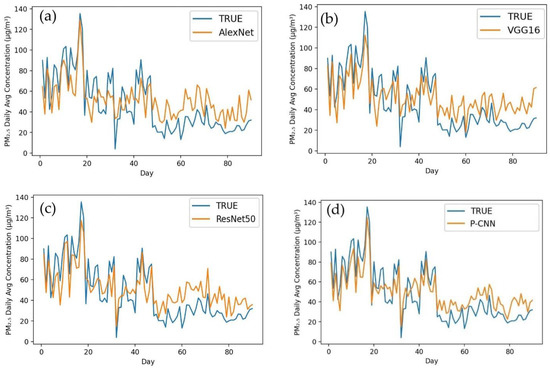
Figure 4.
Time series of observed values and predicted values of models for Karachi. (a) AlexNet, (b) VGG16, (c) ResNet50, (d) P-CNN.
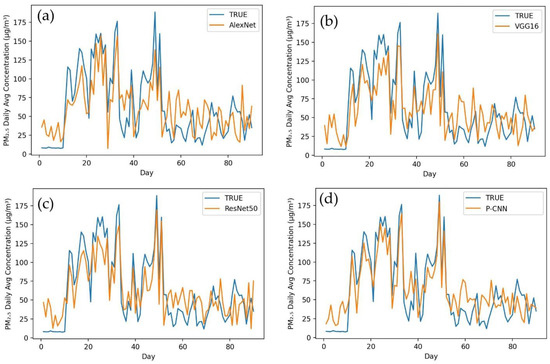
Figure 5.
Time series of observed values and predicted values of models for Lahore. (a) AlexNet, (b) VGG16, (c) ResNet50, (d) P-CNN.
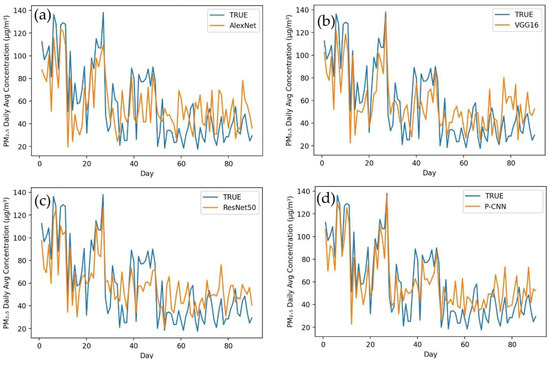
Figure 6.
Time series of observed values and predicted values of models for Peshawar. (a) AlexNet, (b) VGG16, (c) ResNet50, (d) P-CNN.
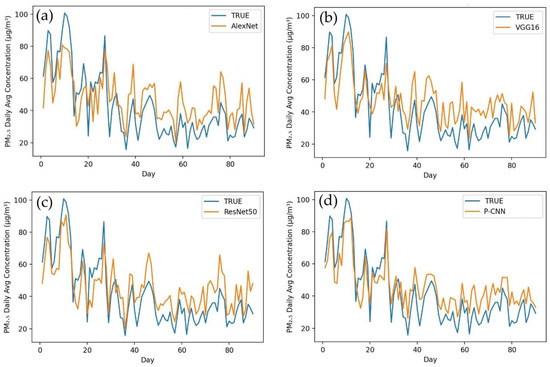
Figure 7.
Time series of observed values and predicted values of models for Islamabad. (a) AlexNet, (b) VGG16, (c) ResNet50, (d) P-CNN.
Consequently, to conduct further testing efficiency of our developed model, P-CNN, we trained a model on one city dataset, and tested on all remaining cities. After training the model on Islamabad, as seen in Figure 8, it can be used to predict PM2.5 concentrations in a number of different cities, such as Karachi, Lahore and Peshawar. Figure 8 clearly demonstrates that the P-CNN predicted values for Karachi, Lahore and Peshawar are extremely close to the real values. The proposed model for predicting PM2.5 concentrations was also trained on a dataset from Karachi and evaluated on datasets from other cities such as Lahore, Peshawar and Islamabad (as shown in Figure 9). The results indicated that the model, which was trained on the Karachi dataset, can be applied to Lahore, Peshawar and Islamabad. It was also found that training a model with Lahore data, can accurately predict PM2.5 concentrations for other cities such as Islamabad, Karachi and Peshawar (see Figure 10). According to Figure 11, using Peshawar as a training dataset, our model is able to predict the concentrations of PM2.5 in other cities such as Islamabad, Lahore and Karachi. These results proved that our proposed P-CNN model also can be applied to other cities after being trained on a single city. Overall, these results demonstrate that P-CNN model is useful in predicting PM2.5 concentrations with satellite images.
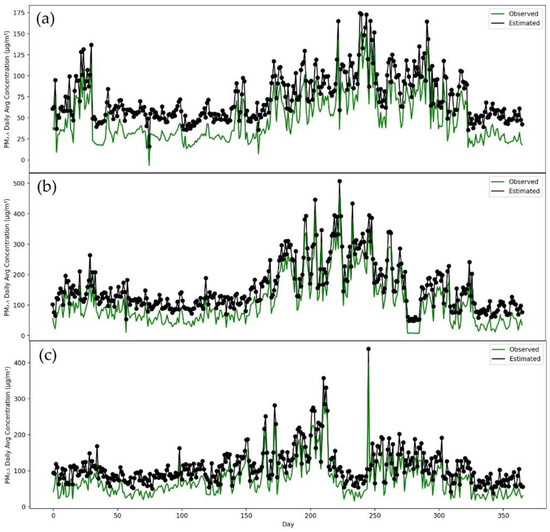
Figure 8.
Time series of station values and predicted values by P-CNN model (a) Karachi, (b) Lahore, (c) Peshawar.
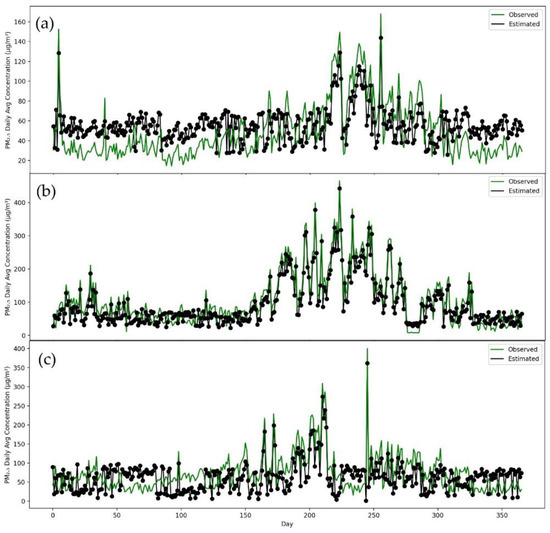
Figure 9.
Time series of station values and predicted values by P-CNN model. (a) Islamabad, (b) Lahore, (c) Peshawar.
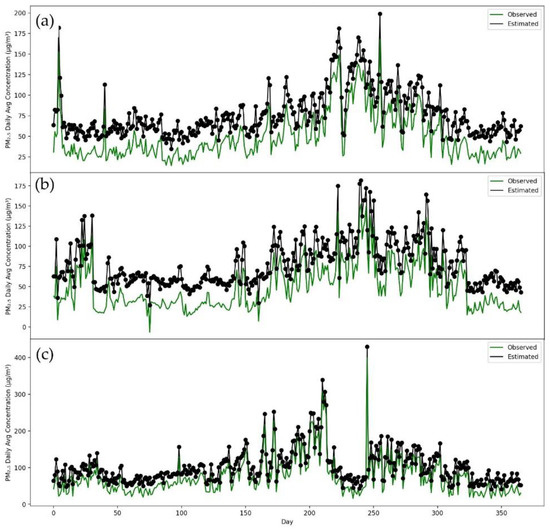
Figure 10.
Time series of station values and predicted values by P-CNN model. (a) Islamabad, (b) Karachi, (c) Peshawar.
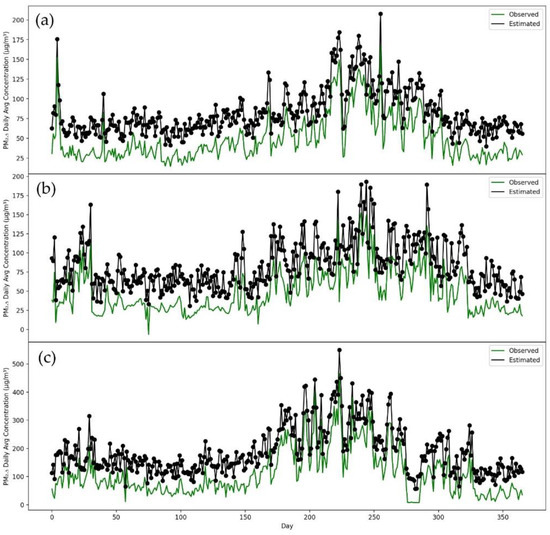
Figure 11.
Time series of station values and predicted values by P-CNN model. (a) Islamabad, (b) Karachi, (c) Lahore.
4. Discussion
This study adopts seven inputs to estimate PM2.5 concentrations in four cities, namely, Pakistan, Islamabad, Lahore, Karachi and Peshawar. The findings revealed that seven input pollutants (AER AI, CH4, CO, HCHO, NO2, O3 and SO2) are closely linked with PM2.5. The existing studies have used different approaches for PM2.5 estimation. Li et al. [47] uses transmission and depth matrices to estimate haze levels. As a proxy for PM2.5, two datasets were utilized for the evaluation. The authors used 8761 photographs in the PM2.5 datasets, and the stated Absolute Spearman correlation is 40.83%. PM2.5’s dataset contains three classes: HeavyHaze, LightHaze and NonHaze and the stated correlation is 89.05%. Zhang et al. [48] proposed deep learning method to classify the camera images according to AQI-levels; there were six classes: good, moderate, Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups, Unhealthy, Very Unhealthy and Hazardous. The applied method was tested on the dataset and achieved 74.0% accuracy. Both these studies have developed deep learning models for classification purpose; however, we proposed a novel P-CNN approach, which uses seven auxiliary input satellite images and estimates actual real number, PM2.5 concentrations. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations differs from classifying, segmenting or recognizing objects based on attributes such as color or texture. We tested P-CNN model on four different datasets using statistics metrics. We achieved satisfactory values of MAE (15.152), RMSE (19.557) and MAPE (15.167) using P-CNN model. Furthermore, in estimating PM2.5 concentrations, the results showed that the P-CNN method provides better results. For instance, the advantage of using this model helps to cover remote areas for estimating air quality.
There are various reasons that compared to Islamabad and Peshawar, the air quality in Lahore and Karachi is far worse. Peshawar and Islamabad are smaller and less populated than Lahore and Karachi city. Islamabad and Peshawar city have less public transit than Lahore and Karachi. The number of industries and construction sites are also less in Islamabad and Peshawar. Lahore and Karachi have a greater ratio of growing urbanization than Peshawar and Islamabad. On the other hand, Lahore is one of second-largest metropolitan city of Pakistan, with a population of 11 million residents, and has topped the daily rankings of the world’s most polluted cities for the second time this year. Tree cover in Lahore has declined significantly over the previous 15 years as a result of an ambitious effort to develop highways, bridges and tunnels. Increasing population, industry, deplorable conditions of municipal utilities, and traffic congestion are the primary sources of air pollution in Karachi city. Furthermore, environmental issues have increased as a result of rapid urbanization such as sewage system inadequacies, overcrowding, inadequate transportation and uncontrolled growth, particularly in Karachi. Air pollution is also exacerbated by industrial pollutants, waste burning, house fires, and other particulates. However, it appears that neither the government nor environmental organizations are taking this matter seriously or responding quickly enough. Similarly, an increase in population accelerates agriculture and industrial production, resulting an increase in waste [49]. Government can help relevant industries by providing green credit funds for the eco-friendly environment, which helps the business community to accelerate green technology and research and development. Pakistan, being a developing economy, suffers huge losses due to environmental problems. During the period between 1999 and 2018, the country spent around USD 3.8 billion to fight against environmental issues in Karachi, Lahore and Peshawar [50]. The water- and land-based ecosystems are being demolished, and unplanned urban structure have damages environment badly. This implies that poor socioeconomic systems cause environmental degradation. Lahore city is the second metropolitan city in Pakistan, covering 2233 manufacturing firms [51]. Lahore is regarded as one of the most developed cities in socioeconomic perspectives. However, some factors, such as industrial waste, poor sanitation systems and lack of urban planning, are barriers to environmental quality. Compared to Karachi and Lahore city, Islamabad is a well-planned city, with the transportation and construction sectors having been developed. On the other hand, Peshawar city is also one of the important hubs in Pakistan. Urban sprawl, deforestation and the burning of contaminated fuel have proved to be the drivers of greenhouse gas emissions [52,53].
Overall, the poor socioeconomic status of these cities has prevented efforts to maintain the ecosystem. Poor infrastructure, dense population and dependency on traditional cook stoves can increase the CO2, PM2.5 and other greenhouse gas emissions. The findings of Mehmood et al. [53] revealed that most of the households in rural areas of Pakistan burn wood, straw, animal dung and crops for cooking purpose, indicating that the most of the households are dependent on contaminated fuels. Moreover, cooking practices with contaminated fuel have the direct association with PM2.5 concentrations [54]; thus, the government should promote clean energy, provide modern cook stoves and reduce fossil fuel consumption to mitigate PM2.5 and other greenhouse gas emissions in Pakistan.
All four cities (Lahore, Peshawar, Islamabad and Karachi) from 1 January to 31 December 2017, had PM2.5 concentrations above than the standard recommendation (10 mg/m3). According to AQI rankings of the world’s most polluted cities, Lahore was ranked at number six, while Karachi was ranked at number sixteen, with AQI levels of 170 and 155, respectively [55]. Most recently, Lahore ranked as world’s most polluted city [56]. Hence, we need immediately the finest and most effective tools and methods to analyze, understand and estimate air quality properly. Our proposed deep learning model for estimating PM2.5 concentrations is efficient and cost saving. We do not need to deploy physical measurement tools in each city to calculate air quality. Using portable devices (laptops, mobiles, etc.), PM2.5 concentrations for any city can be estimated using our deep learning model. Pudasaini et al. [57] had proposed a model to estimate PM2.5 concentration from photographs. However, in order to estimate PM2.5 concentrations, we would need to travel to the site area and snap a picture of it using a mobile phone. However, in our method, we need only chose a city to predict PM2.5 concentrations on portable device anywhere. Thus, this study suggests a reliable and effective way of estimating PM2.5 concentrations.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a deep learning P-CNN model for PM2.5 concentrations. This model mainly uses deep convolutional neural networks to extract feature representation information related to PM2.5 in satellite images to estimate PM2.5 concentration levels. We also performed comparative analysis of our constructed model with other deep learning models such as AlexNet, VGG16 and ResNet50 on four different datasets (Karachi, Lahore, Peshawar and Islamabad). The study performed different measures to analyze the model’s accuracy. In this regard, MAE, RMSE and MAPE were used as accuracy metrics. The experimental results demonstrated that the P-CNN model is more suitable for predicting PM2.5 concentrations than other models. The results confirmed that the PM2.5 concentrations our model predicts from satellite images are closely related with actual results. Any future research should focus on finding ways to make the model more accurate, as well as to focus on seasonal-wise PM2.5 estimations. Although, the model provides better results, some limitations cannot be avoided. Based on available datasets, we used the samples between May-2019 to April-2020. This study focuses on four cities of Pakistan; future study should find large datasets and use more cities, which will give better results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.; methodology, M.A.; software, M.A.; validation, M.A.; formal analysis, Y.S.; investigation, Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.; writing—review and editing, Z.X. and Y.S.; visualization; supervision, Z.X. and Y.S.; funding acquisition, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is jointly supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No.: 2020YFB2103403), and the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xing, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.-H.; Shi, M.-H.; Lian, Y.-X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.C.; Robins, T.G.; Dvonch, J.T.; Keeler, G.J.; Yip, F.Y.; Mentz, G.B.; Lin, X.; Parker, E.A.; Israel, B.A.; Gonzalez, L. Air pollution–associated changes in lung function among asthmatic children in Detroit. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, I.; Jacobs, L.; Nawrot, T.S.; De Geus, B.; Torfs, R.; Panis, L.I.; Degraeuwe, B.; Meeusen, R. No exercise-induced increase in serum BDNF after cycling near a major traffic road. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, L.; Nawrot, T.S.; De Geus, B.; Meeusen, R.; Degraeuwe, B.; Bernard, A.; Sughis, M.; Nemery, B.; Panis, L.I. Subclinical responses in healthy cyclists briefly exposed to traffic-related air pollution: An intervention study. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatnagar, A. Environmental cardiology: Studying mechanistic links between pollution and heart disease. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valavanidis, A.; Fiotakis, K.; Vlachogianni, T. Airborne particulate matter and human health: Toxicological assessment and importance of size and composition of particles for oxidative damage and carcinogenic mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2008, 26, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mishra, S.; Singh, S.K. Deep Transfer Learning-based COVID-19 prediction using Chest X-rays. J. Health Manag. 2021, 23, 730–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.; Dockery, D.W.; Neas, L.M. Is daily mortality associated specifically with fine particles? J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 1996, 46, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, D.W.; Schmitt, M.T.; Dailey, L.A.; Duvall, R.M.; Karoly, E.D.; Devlin, R.B. Assessing the role of particulate matter size and composition on gene expression in pulmonary cells. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Lung function and chronic exposure to air pollution: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES II. Environ. Res. 1989, 50, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chestnut, L.G.; Schwartz, J.; Savitz, D.A.; Burchfiel, C.M. Pulmonary function and ambient particulate matter: Epidemiological evidence from NHANES I. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1991, 46, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhai, C.Z.; YU, J.Y. A Review of Domestic and Overseas Research on Air Quality Monitoring Networks Designing. Environ. Monit. China 2012, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, S.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Zhu, X.; Dyer, C.R. Inferring air pollution by sniffing social media. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM 2014), Beijing, China, 17–20 August 2014; pp. 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Murty, R.N.; Mainland, G.; Rose, I.; Chowdhury, A.R.; Gosain, A.; Bers, J.; Welsh, M. Citysense: An urban-scale wireless sensor network and testbed. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security, Waltham, MA, USA, 12–13 May 2008; pp. 583–588. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhang, L.; Rashvand, H.F.; Li, V.O.K. Efficient sampling and compressive sensing for urban monitoring vehicular sensor networks. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2012, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L. Demonstration abstract: PiMi air box—A cost-effective sensor for participatory indoor quality monitoring. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Berlin, Germany, 15–17 April 2014; pp. 327–328. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Gehrig, R.; Lee, Y.C.; Kumar, N. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayachi, Y.R. Satellite Remote Sensing of Particulate Matter and Air Quality Assessment in the Western Cape, South Africa. 2016. Available online: https://ukzn-dspace.ukzn.ac.za (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Chung, Y.S. Air pollution detection by satellites: The transport and deposition of air pollutants over oceans. Atmos. Environ. 1986, 20, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.; Laxen, D.P.H. Black smoke as a surrogate for PM10 in health studies? Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Atkinson, D.B. A portable pulsed cavity ring-down transmissometer for measurement of the optical extinction of the atmospheric aerosol. Analyst 2001, 126, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgeson, J.A.; McClenny, W.A.; Hanst, P.L. Air Pollution Monitoring by Advanced Spectroscopic Techniques: A variety of spectroscopic methods are being used to detect air pollutants in the gas phase. Science 1973, 182, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Hu, Y.; Shao, J.; Chi, T. Deep learning architecture for air quality predictions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22408–22417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Zheng, G.; Pan, J.Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, N. Big smog meets web science: Smog disaster analysis based on social media and device data on the web. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web, Seoul, Korea, 7–11 April 2014; pp. 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Y.L.; Cai, M.; Xu, W.J.; Li, L. Characteristic analysis on uneven distribution of air pollution in cities. Environ. Monit. China 2011, 27, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, F.; Xu, F.; Lu, H. The evaluation of air quality using image quality. Chin. J. Image Graph. 2011, 16, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. Real-time air quality estimation based on color image processing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing Conference, Valletta, Malta, 7–10 December 2014; pp. 326–329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Fu, H.; Wang, X. Outdoor air quality inference from single image. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Sydney, Australia, 5–7 January 2015; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Li, C.; Rui, X.; Liu, L.; Bie, R. On estimating air pollution from photos using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Chakma, A.; Vizena, B.; Cao, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J. Image-based air quality analysis using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 3949–3952. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; Suo, M. PM2.5 concentration modeling and prediction by using temperature-based deep belief network. Neural Netw. 2021, 133, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-Z.; Yang, H.-L.; Peng, J.-H.; Song, Y.-R.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Xi’an City using a generalized additive model with multi-source monitoring data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sentinel Sentinel-Hub. Available online: https://apps.sentinel-hub.com/ (accessed on 13 February 2022).
- AirNow Air Quality Data. Available online: https://www.airnow.gov/ (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1989, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, R.; Monrocq, C.; Le Cun, Y. Original approach for the localisation of objects in images. IEE Proc.-Vis. Image Signal Process 1994, 141, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; LeCun, Y. Overfeat: Integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6229. [Google Scholar]
- Nowlan, S.J.; Platt, J.C. A convolutional neural network hand tracker. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1995, 1, 901–908. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L.; Tsoi, A.C.; Back, A.D. Face recognition: A convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariharan, B.; Arbelaez, P.; Girshick, R.; Malik, J. Object instance segmentation and fine-grained localization using hypercolumns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Delakis, M. Convolutional face finder: A neural architecture for fast and robust face detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1408–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesenhuber, M.; Poggio, T. Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciregan, D.; Meier, U.; Schmidhuber, J. Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3642–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Xu, Y.-P.; Ramezani, E. Optimal long-term prediction of Taiwan’s transport energy by convolutional neural network and wildebeest herd optimizer. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlgren, N.; Feldman, M.; Gehan, M.A.; Wilson, M.S.; Shyu, C.; Bryant, D.W.; Hill, S.T.; McEntee, C.J.; Warnasooriya, S.N.; Kumar, I. A versatile phenotyping system and analytics platform reveals diverse temporal responses to water availability in Setaria. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Luo, J. Using user generated online photos to estimate and monitor air pollution in major cities. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Zhangjiajie, China, 19–21 August 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, F.; Tian, R. A deep learning and image-based model for air quality estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, D.; Li, F.; Guan, X.; Chen, P. Development of a new framework to identify pathways from socioeconomic development to environmental pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakistan, U. Available online: https://www.pk.undp.org/content/pakistan/en/home/library/development_policy/dap-vol7-issue2-environmental-sustainability-in-pakistan.html (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Rana, I.A.; Bhatti, S.S. Lahore, Pakistan–Urbanization challenges and opportunities. Cities 2018, 72, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziq, A.; Xu, A.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q. Monitoring of land use/land cover changes and urban sprawl in Peshawar City in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: An application of geo-information techniques using of multi-temporal satellite data. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2016, 5, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, R.; Mehmood, S.A.; Butt, M.A.; Younas, I.; Adrees, M. Spatiotemporal analysis of urban sprawl and its contributions to climate and environment of Peshawar using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shupler, M.; Godwin, W.; Frostad, J.; Gustafson, P.; Arku, R.E.; Brauer, M. Global estimation of exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from household air pollution. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IQAir Air Quality in Lahore. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/pakistan/punjab/lahore (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- IQair IQAIR. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/world-air-quality-ranking (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Pudasaini, B.; Kanaparthi, M.; Scrimgeour, J.; Banerjee, N.; Mondal, S.; Skufca, J.; Dhaniyala, S. Estimating PM2.5 from photographs. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 5, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).