A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Description
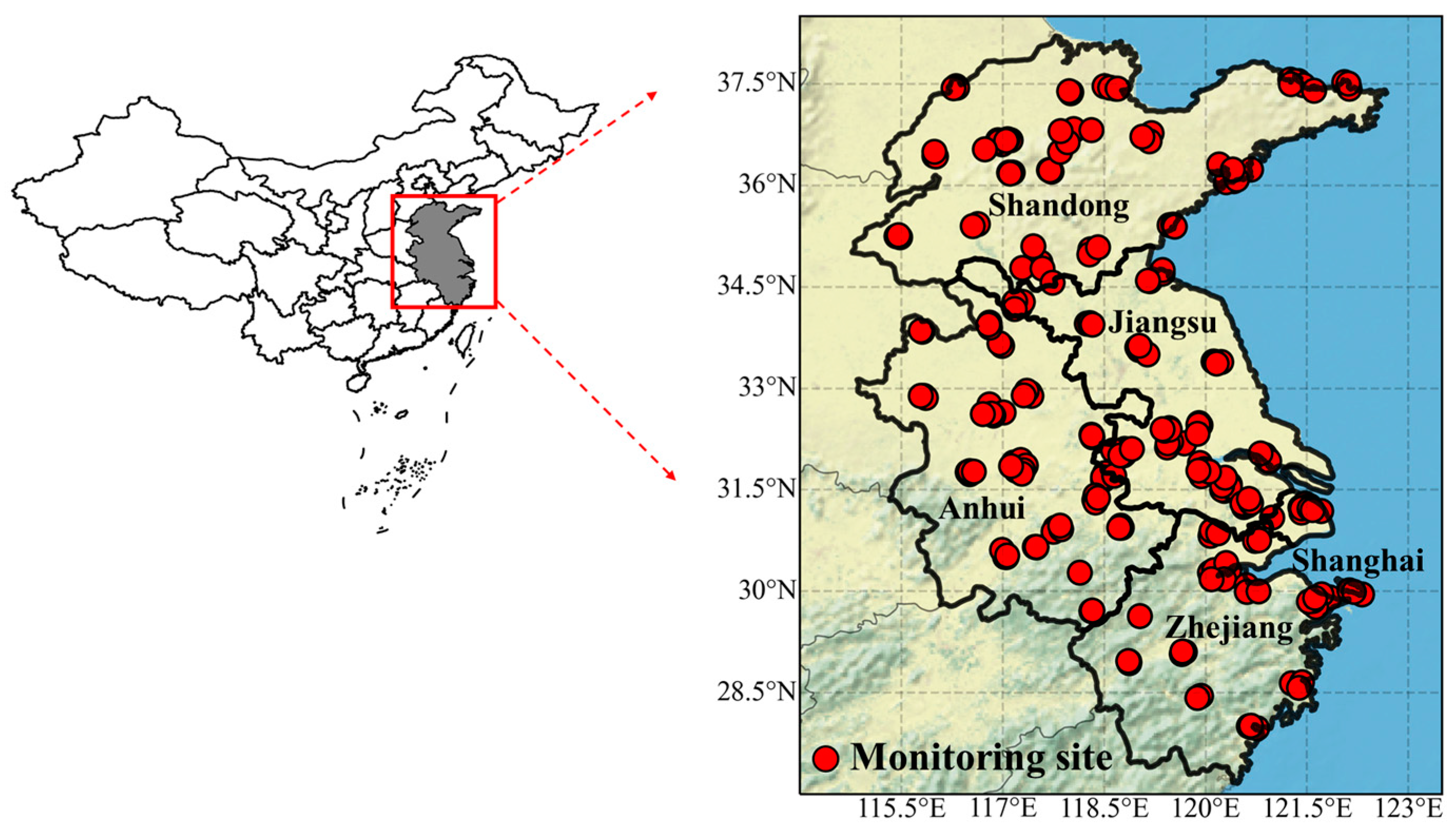
2.1.1. Study Area and Ground-Level Ozone Concentration Data
2.1.2. Satellite-Based Total Ozone Column (TOC) Data
2.1.3. Meteorological Data
2.1.4. WRF-Chem Simulations and Other Data
2.2. Data Preprocessing
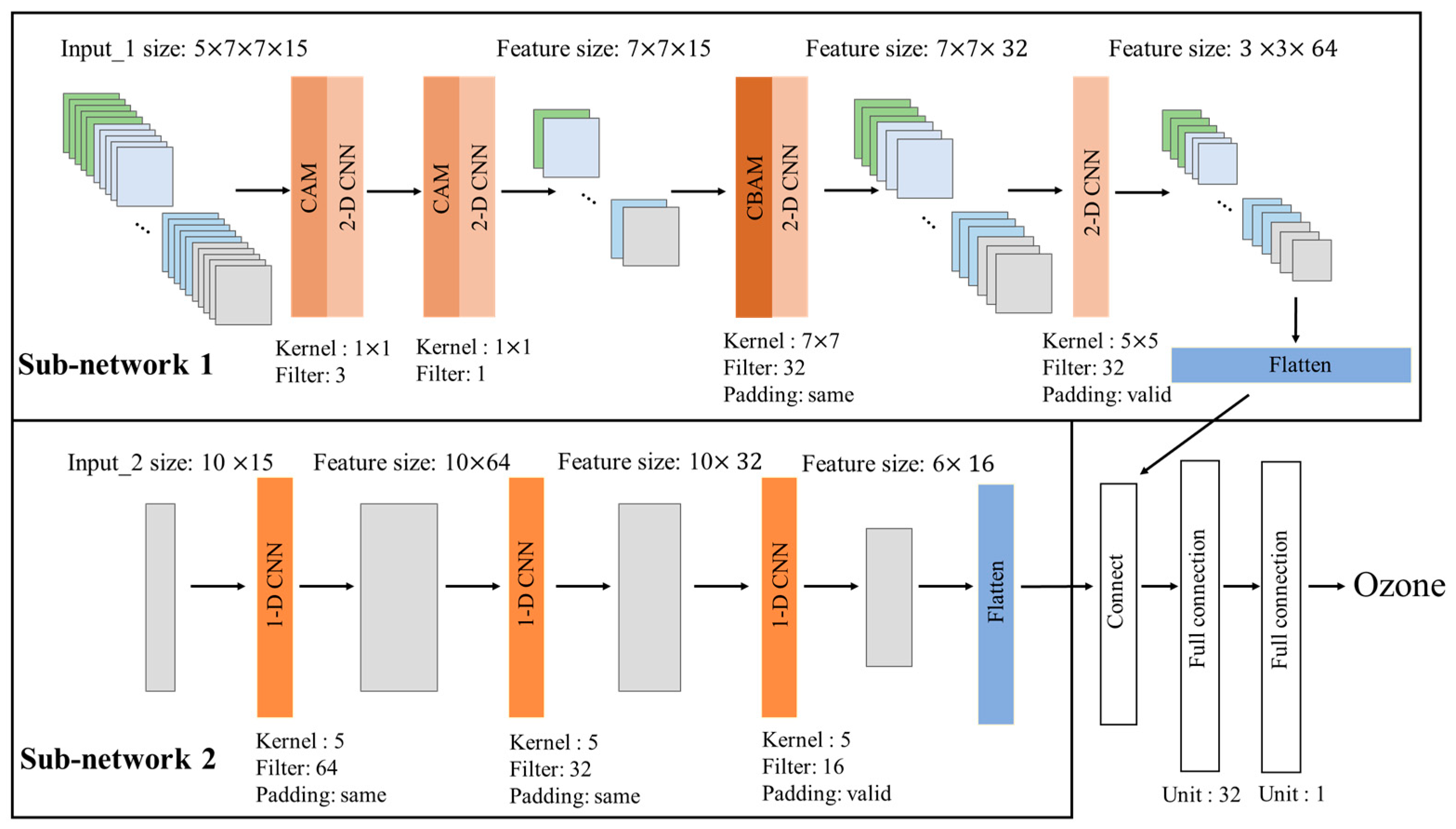
2.3. Model Development
BLH + DPT + WRF-Chem simulations + NDVI + DEM + DOY)
2.4. Model Validation
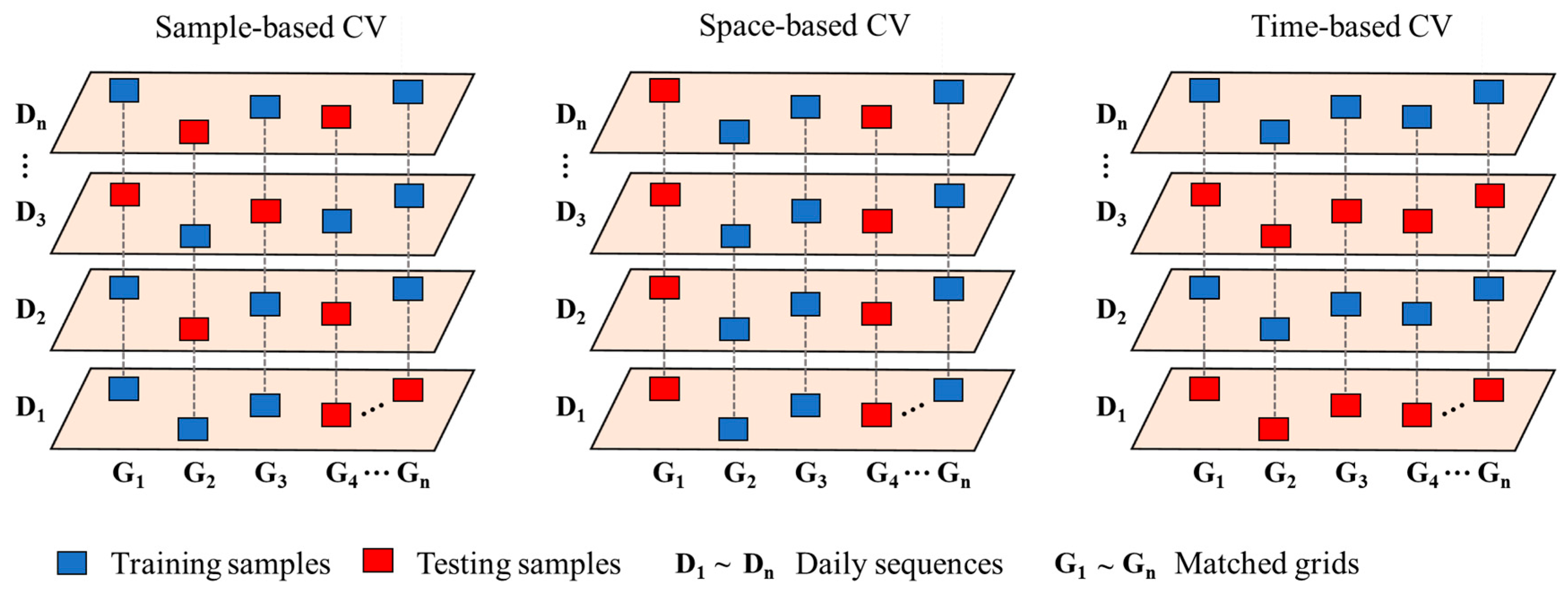
2.4.1. Cross-Validation
2.4.2. Predictive Performance for Major Cites
2.4.3. Statistical Metrics
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Statistical Description
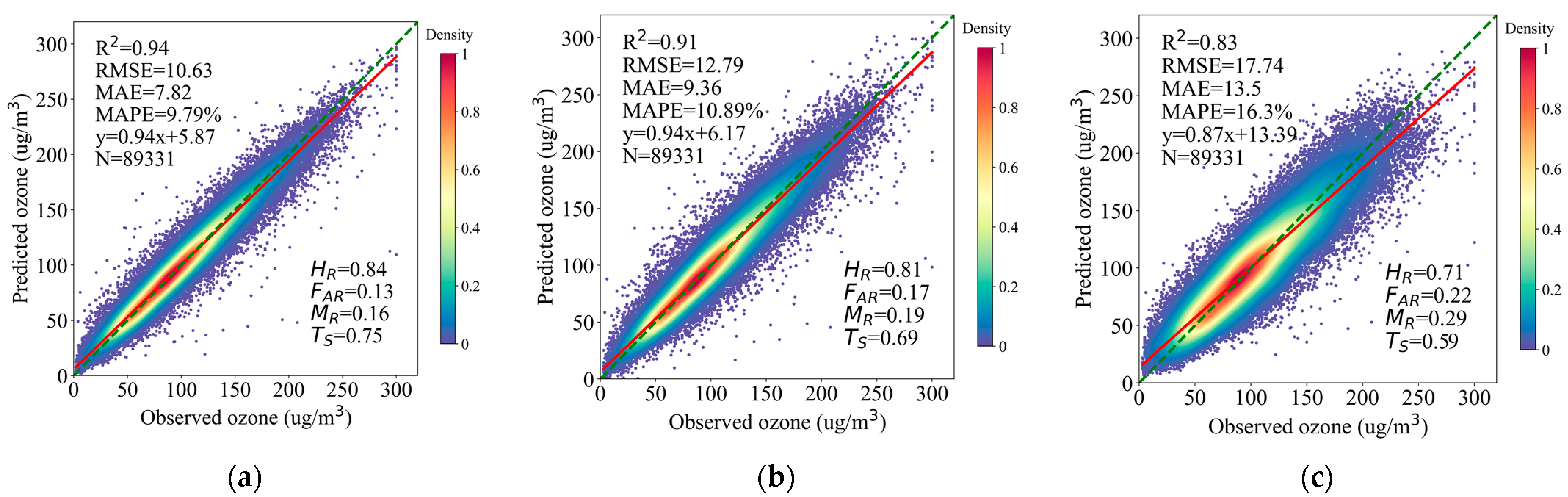
3.2. Overall Fitting Results
3.3. Spatiotemporal Variations of Model Performance
3.4. Prediction for Major Cities
4. Discussions
4.1. Comparisons
4.2. Uncertainty Analyses
4.2.1. Training Sample Size
4.2.2. Site Density
4.2.3. Spatiotemporal Sampling Size
4.2.4. Configurations of the Sub-Networks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L.; Wells, B.; Gerosa, G. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Global Ozone Metrics for Climate Change, Human Health, and Crop/Ecosystem Research. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Song, T.; Gong, Z.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, G.; Huo, Y.; et al. Contrasting Trends of PM2.5 and Surface-Ozone Concentrations in China from 2013 to 2017. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavinezhad, S.; Choi, Y.; Pouyaei, A.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Nelson, D.L. A Comprehensive Investigation of Surface Ozone Pollution in China, 2015–2019: Separating the Contributions from Meteorology and Precursor Emissions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chu, C. Assessing the Health Impacts Attributable to PM2.5 and Ozone Pollution in 338 Chinese Cities from 2015 to 2020. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, S.; Gong, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y. Regionalization Based on Spatial and Seasonal Variation in Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations across China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yi, K.; Yang, H.; Xiang, S.; Ma, J.; Tao, S. Spatiotemporal Variability and Driving Factors of Ground-Level Summertime Ozone Pollution over Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 265, 118686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Yung, Y.L. Spatial Representativeness of PM2.5 Concentrations Obtained Using Observations From Network Stations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3145–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.; Nassar, R.; Baxter, M. Estimating Power Plant CO2 Emission Using OCO-2 XCO2 and High Resolution WRF-Chem Simulations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jiménez, R.; Belalcázar, L.C.; Rojas, N.Y. Application of WRF-Chem Model to Simulate PM10 Concentration over Bogota. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1206–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henze, D.K.; Hakami, A.; Seinfeld, J.H. Development of the Adjoint of GEOS-Chem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2413–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; He, L.Y.; Huang, X.F. Development of a High-Performance Machine Learning Model to Predict Ground Ozone Pollution in Typical Cities of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Zhang, M.; Di, B. Spatiotemporal Prediction of Daily Ambient Ozone Levels across China Using Random Forest for Human Exposure Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, P.; Crippa, P.; de Marco, A.; Castruccio, S.; Giani, P.; Cuesta, J.; Paoletti, E.; Feng, Z.A. High Spatial Resolution WRF-Chem Model over Asia: Physics and Chemistry Evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 118004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.; Hongbo, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Satellite-Based Estimation of Full-Coverage Ozone (O3) Concentration and Health Effect Assessment across Hainan Island. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; Kos, G.; Dijkema, M.; der Zee, S.C.V.; Fischer, P.H.; Brunekreef, B. Land Use Regression Model for Ultrafine Particles in Amsterdam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.B.; Beckerman, B.; Jerrett, M.; Brauer, M. Application of Land Use Regression to Estimate Long-Term Concentrations of Traffic-Related Nitrogen Oxides and Fine Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P. Geographically Weighted Regression with Parameter-Specific Distance Metrics. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Mi, Z.; Georgopoulos, P.G. Comparison of Machine Learning and Land Use Regression for Fine Scale Spatiotemporal Estimation of Ambient Air Pollution: Modeling Ozone Concentrations across the Contiguous United States. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Dong, G.H.; Yang, B.Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, T.; Yu, P.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Improving Satellite-Based Estimation of Surface Ozone across China during 2008–2019 Using Iterative Random Forest Model and High-Resolution Grid Meteorological Data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silibello, C.; Carlino, G.; Stafoggia, M.; Gariazzo, C.; Finardi, S.; Pepe, N.; Radice, P.; Forastiere, F.; Viegi, G. Spatial-temporal prediction of ambient nitrogen dioxide and ozone levels over Italy using a Random Forest model for population exposure assessment. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Fu, H. Long-Term Trends of Ambient Nitrate (NO3) Concentrations across China Based on Ensemble Machine-Learning Models. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nadry, M.; Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; Awad, M.A.; Mostafa, A.R. Urban Health Related Air Quality Indicators over the Middle East and North Africa Countries Using Multiple Satellites and AERONET Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, M.; Amanollahi, J.; Tzanis, C.G. Evaluation of linear, nonlinear, and hybrid models for predicting PM2.5 based on a GTWR model and MODIS AOD data. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Di, B. Satellite-based estimates of daily NO2 exposure in China using hybrid random forest and spatiotemporal kriging model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shen, H.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Geographically and temporally weighted neural networks for satellite-based mapping of ground-level PM2.5. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal Estimation of Hourly 2-Km Ground-Level Ozone over China Based on Himawari-8 Using a Self-Adaptive Geospatially Local Model. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinow, R.R. Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks. Science 2006, 313, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional Networks for Images, Speech, and Time-Series. In The Hand Book of Brain Theory and Neural Netwok; Arbib, M.A., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 255–258. ISBN 0-262-51102-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, F.; Li, Z. Air big data outlier detection based on infinite Gauss Bayesian and CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, Zhuhai, China, 22–24 February 2019; pp. 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Sayeed, A.; Choi, Y.; Eslami, E.; Lops, Y.; Roy, A.; Jung, J. Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Predict 2017 Ozone Concentrations, 24 Hours in Advance. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jin, M.; Li, H. Exploring spatial influence of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration using a developed deep convolutional neural network model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Kong, P.; Jiang, P.; Wu, Y. Estimation of PM2.5 Concentration Using Deep Bayesian Model Considering Spatial Multiscale. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Qu, K.; Ding, J.; Shang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, M. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution, Regional Distribution and Causes during 2014–2018 in Shandong Province, East China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/ (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Technical Specifications for Operation and Quality Control of Ambient Air Quality Continuous Automated Monitoring System for SO2, NO2, O3 and CO. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/dqhj/202009/W020200922483880824988.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Technical Regulation for Selection of Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Stations. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/dqhj/201311/W020181008687878171473.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Di, Q.; Rowland, S.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. A hybrid model for spatially and temporally resolved ozone exposures in the continental United States. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Lou, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Huang, S.; Du, H. Satiotemporal distribution of ground-level ozone in mid-east China based on OMI observations. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. A Machine Learning Model to Estimate Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations in California Using TROPOMI Data and High-Resolution Meteorology. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garane, K.; Koukouli, M.E.; Verhoelst, T.; Lerot, C.; Heue, K.P.; Fioletov, V.; Zimmer, W. TROPOMI/S5P total ozone column data: Global ground-based validation and consistency with other satellite missions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5263–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copernicus Open Access Hub. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- CLDAS-V2.0 Real-Time Product Datasets. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/data/detail/dataCode/NAFP_CLDAS2.0_RT.html (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- CLDAS v2.0 Atmospheric Product Description Document. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/article/showPDFFile.html?file=/pic/static/doc/F/CLDAS-V2.0/CLDAS-V2.0_ADP.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- CLDAS v2.0 Surface Temperature Product Description Document. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/article/showPDFFile.html?file=/pic/static/doc/F/CLDAS-V2.0/CLDAS-V2.0_GST.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1979 to Present. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.; Xiao, J. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2015, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, C.G.; Spero, T.L.; Bowden, J.H.; Sarofim, M.C.; Martinich, J.; Mallard, M.S. Regional temperature-ozone relationships across the US under multiple climate and emissions scenarios. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, M.A.; Savastru, R.S.; Dan, M.S.; Tautan, M.N. Assessing the relationship between ground levels of ozone (O3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) with coronavirus (COVID-19) in Milan, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Banerjee, T.; Aneja, V.P. Trend and variability of atmospheric ozone over middle Indo-Gangetic Plain: Impacts of seasonality and precursor gases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wang, T.; Kasoar, M.; Mansfield, L. A study of the effect of aerosols on surface ozone through meteorology feedbacks over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 21, 5705–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yao, G.; Guo, J.; Bai, K. Distinct spatiotemporal variation patterns of surface ozone in China due to diverse influential factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Li, G.H.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, R.; Garcia, A.R.; Lee-Taylor, J.; Liu, Y. Characterizations of Chemical Oxidants in Mexico City: A Regional Chemical Dynamical Model (WRF-Chem) Study. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1989–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multi-Resolution Emission Inventory for China Model. Available online: http://meicmodel.org/ (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Zhou, G.; Xu, J.; Xie, Y.; Chang, L.; Gao, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, J. Numerical Air Quality Forecasting over Eastern China: An Operational Application of WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MODIS Vegetation Index Products (NDVI and EVI). Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod13.php (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- SRTM 90 m DEM Digital Elevation Database. Available online: https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/ (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Technical Specification for Environmental Air Quality Assessment. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/dqhj/201706/P020181010540072997802.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521v2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Estimating Daily Full-Coverage near Surface O3, CO, and NO2 Concentrations at a High Spatial Resolution over China Based on S5P-TROPOMI and GEOS-FP. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-Coverage Mapping and Spatiotemporal Variations of Ground-Level Ozone (O3) Pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Meng, X.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, T. Estimating Spatiotemporal Variation in Ambient Ozone Exposure during 2013–2017 Using a Data-Fusion Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14877–14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078v3. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
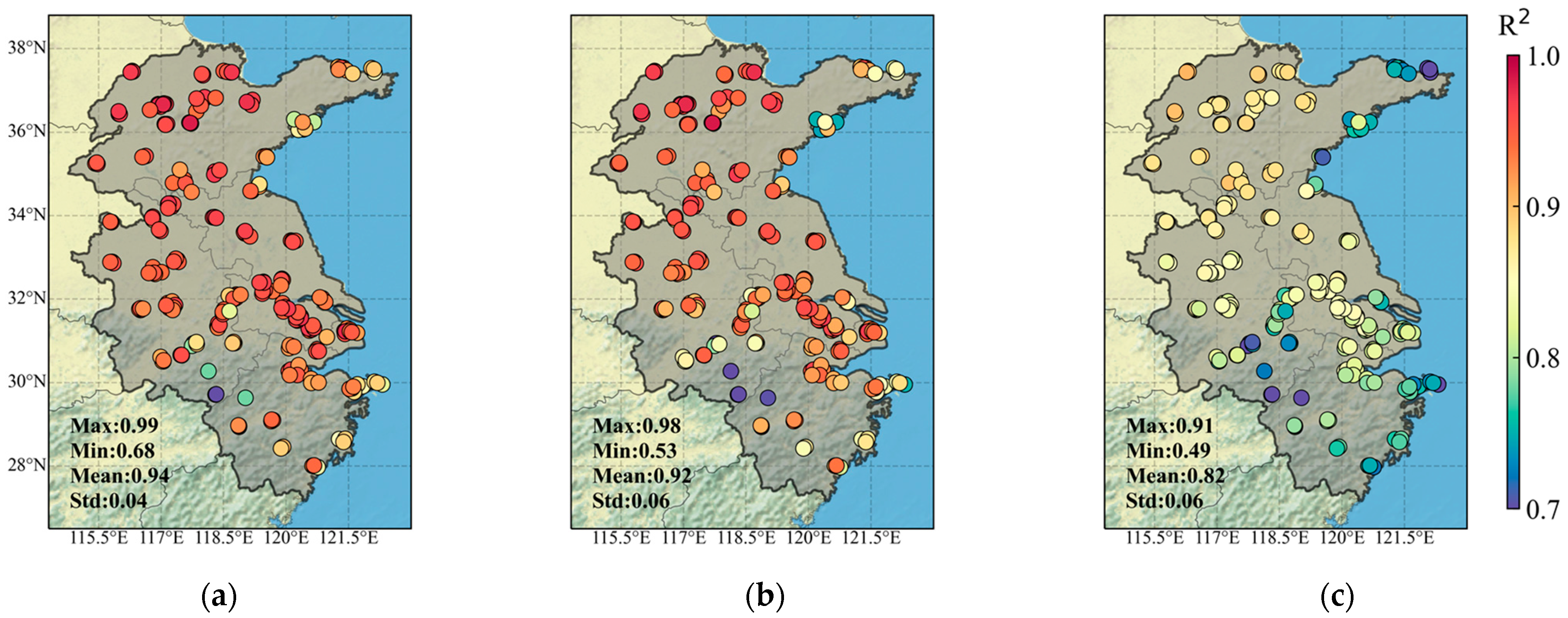
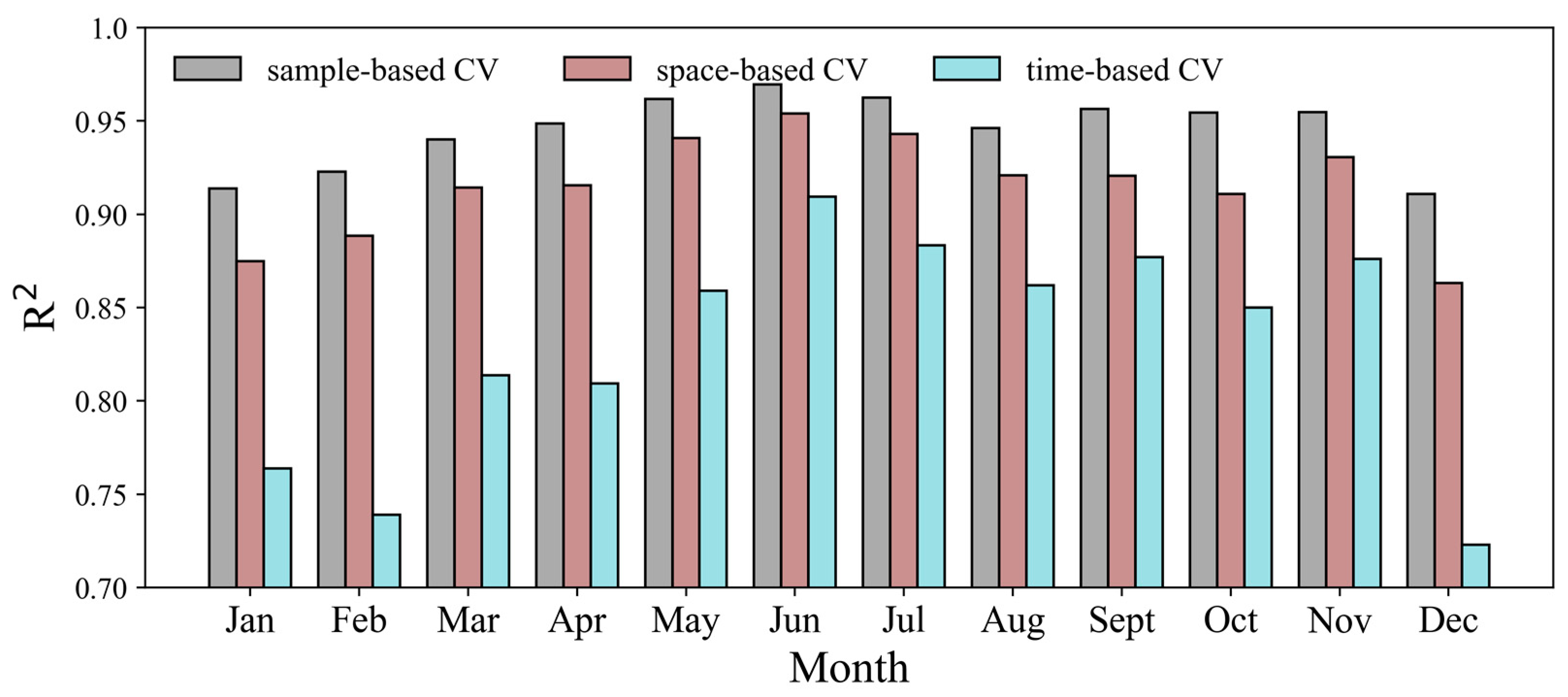
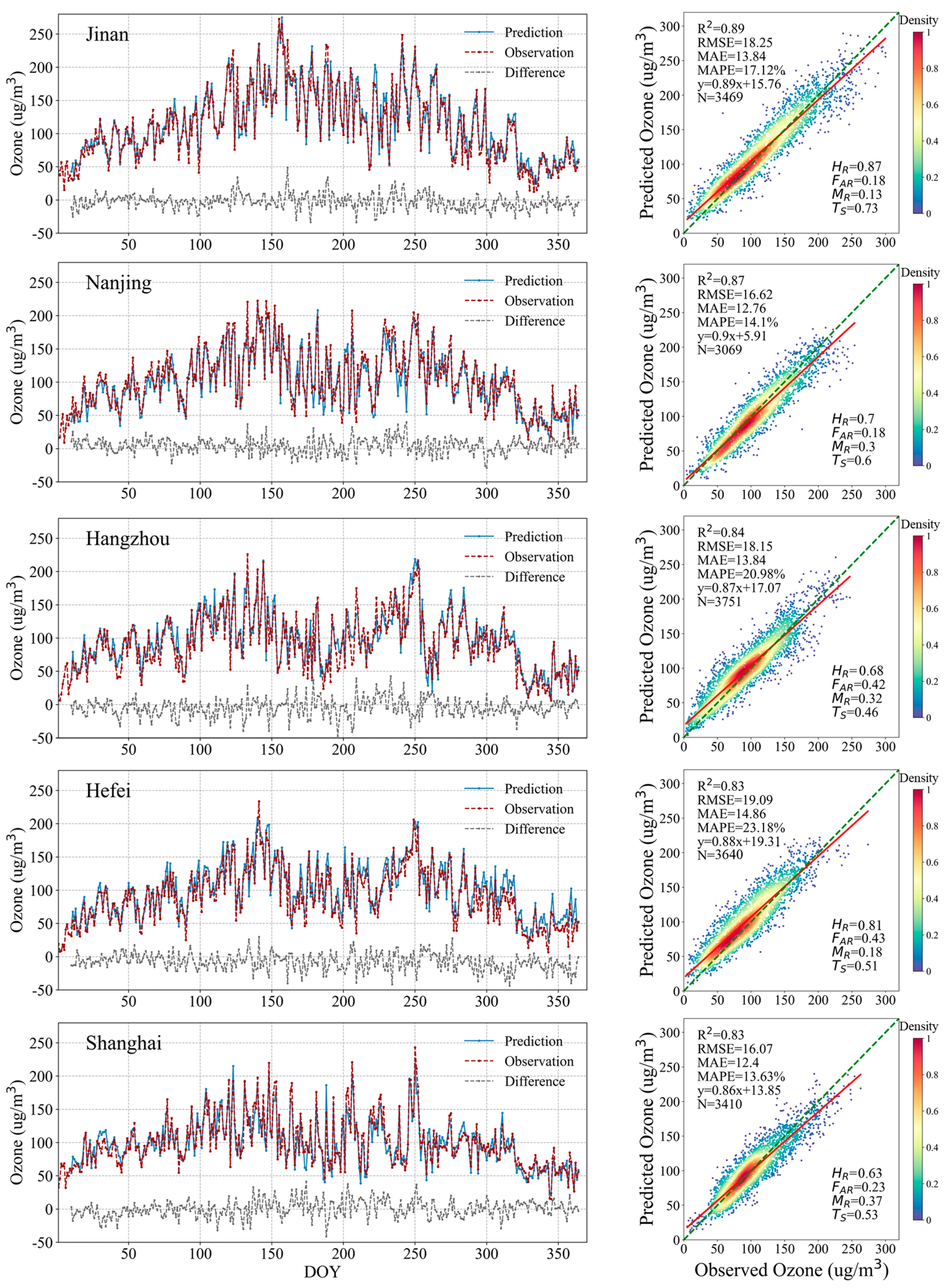
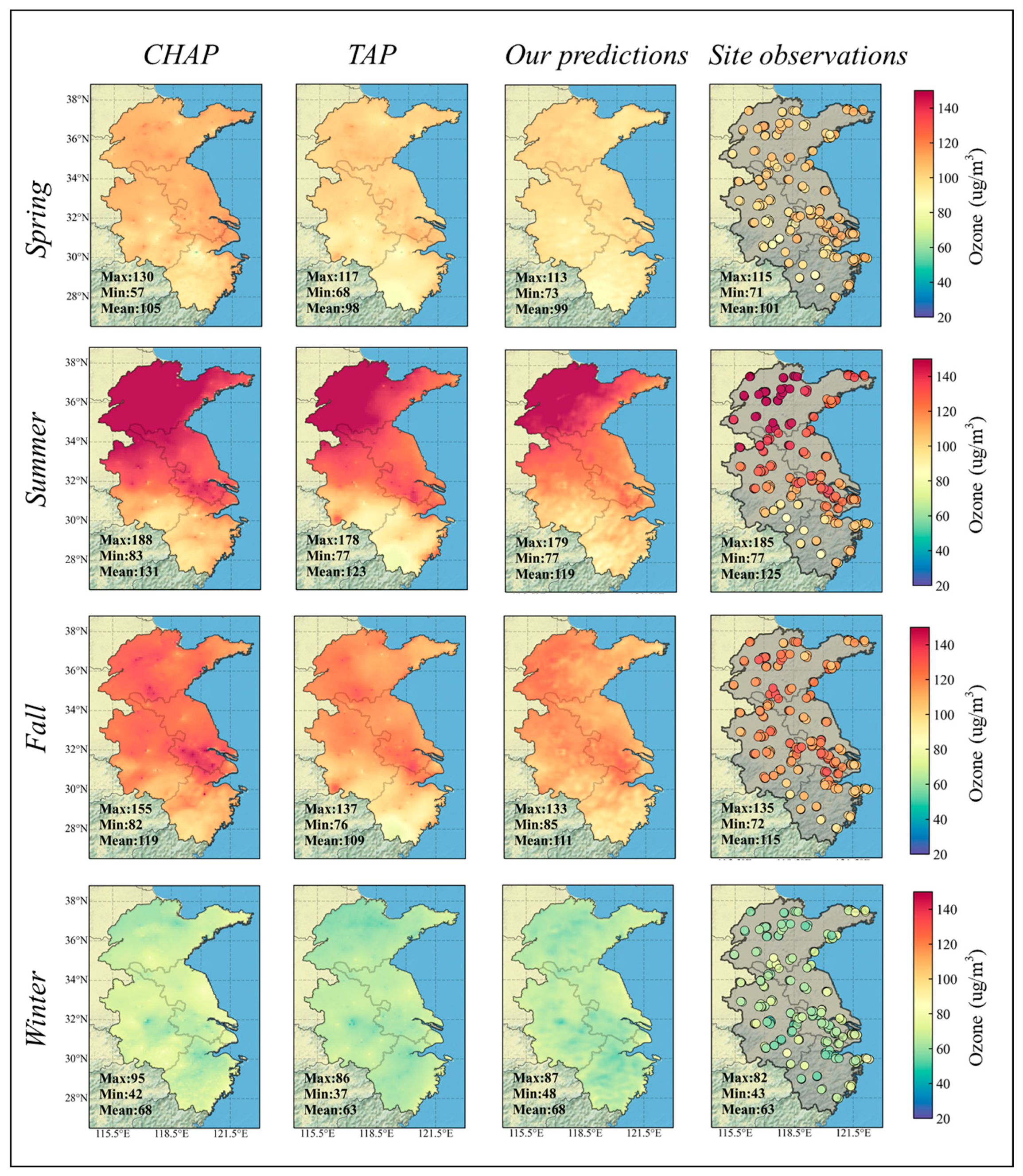
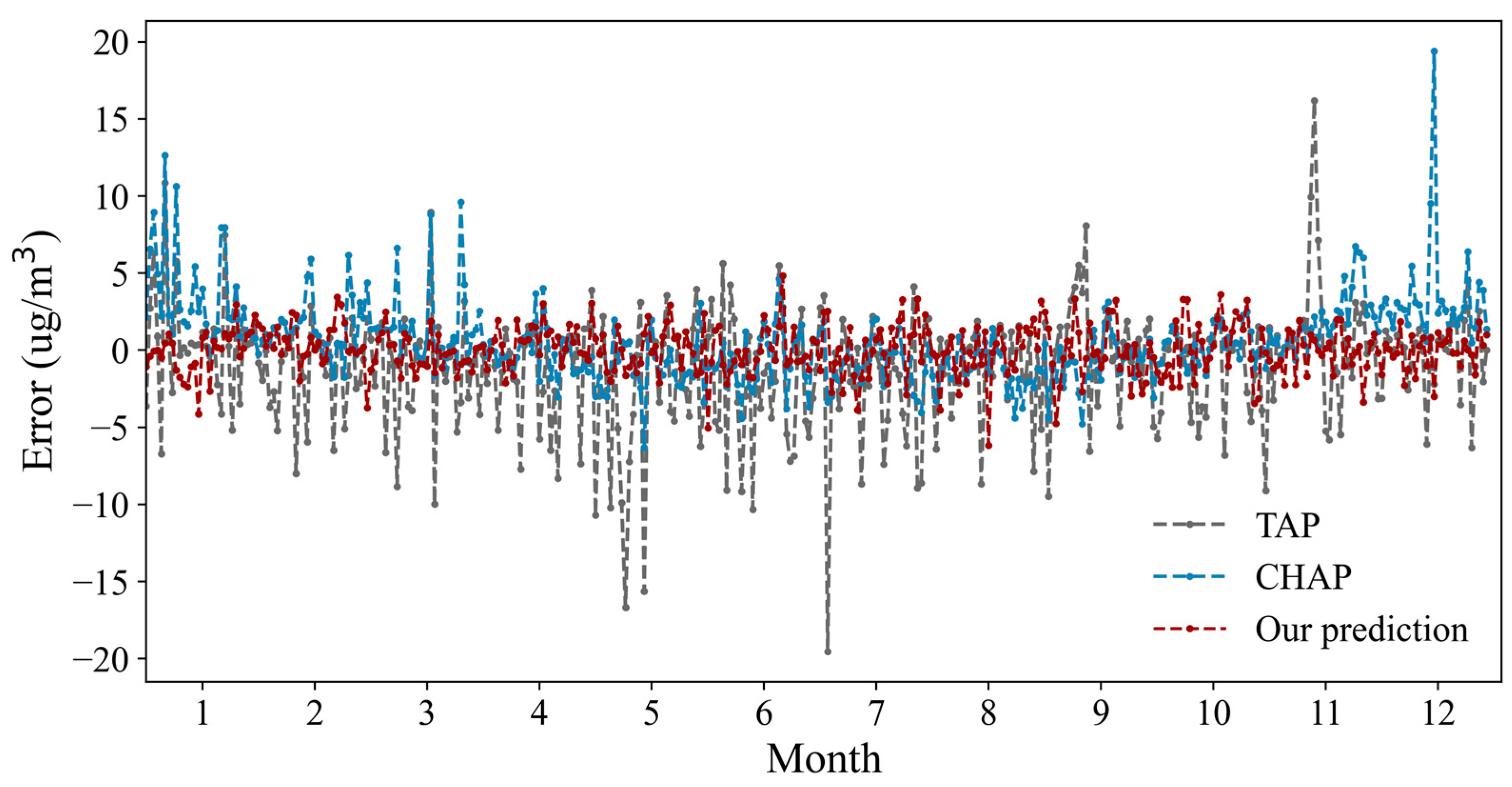
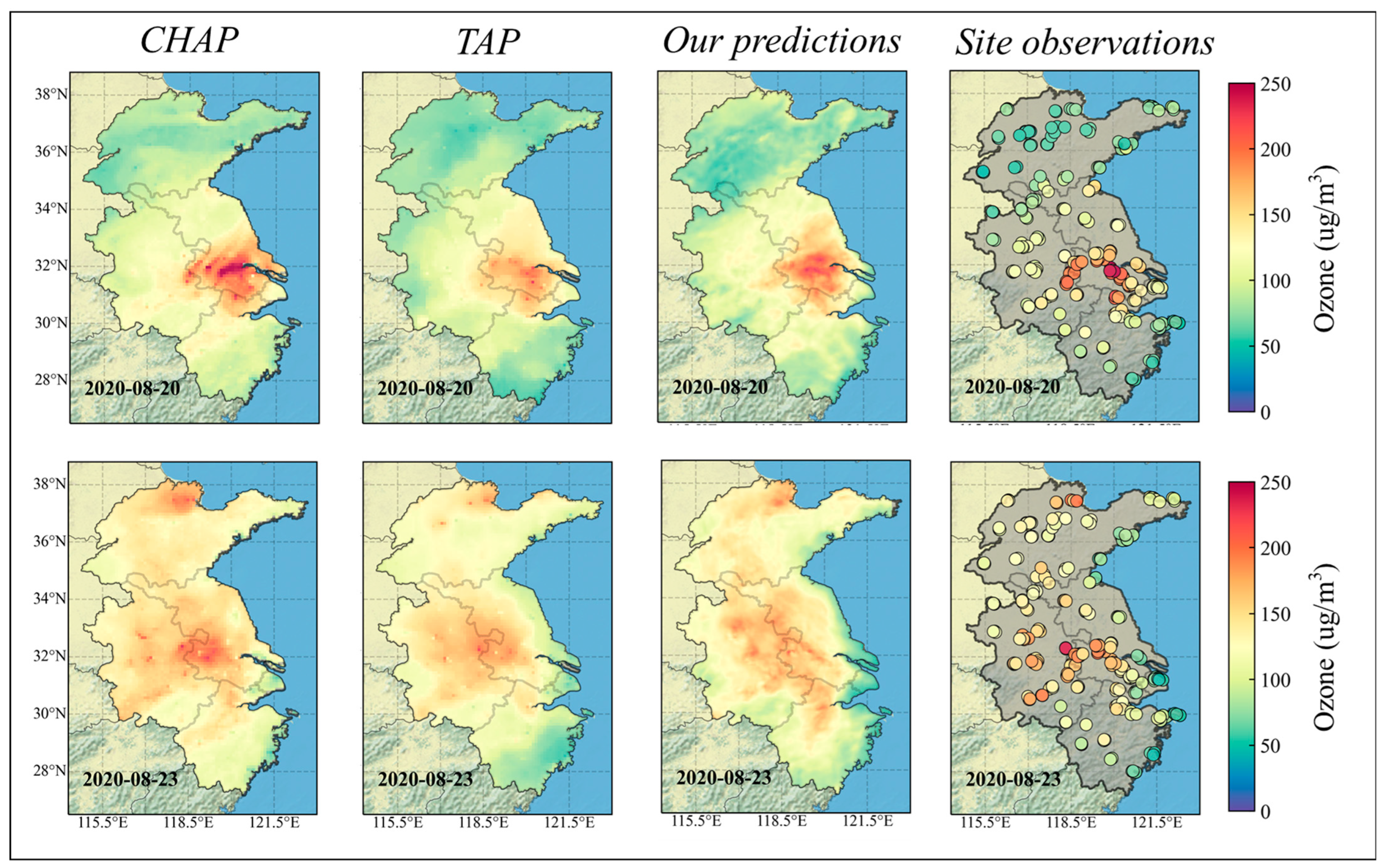
| Model | Parameters 1 | Sample-Based CV | Space-Based CV | Time-Based CV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | TS | R2 | RMSE | TS | R2 | RMSE | TS | ||
| RF | 350/31/1/2 | 0.87 | 15.56 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 15.58 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 18.68 | 0.67 |
| LGBM | gbdt/800/26/0.04/21 | 0.91 | 12.78 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 13.99 | 0.73 | 0.80 | 19.58 | 0.65 |
| DNN | 512/128/80/32/1 | 0.87 | 15.57 | 0.72 | 0.86 | 16.08 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 19.02 | 0.68 |
| Sub-network 1 | - | 0.92 | 12.29 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 15.07 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 18.88 | 0.71 |
| Sub-network 2 | - | 0.91 | 12.72 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 13.40 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 19.33 | 0.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Huo, Y.; Mu, X.; Jiang, P.; Xun, S.; He, B.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071640
Wang S, Huo Y, Mu X, Jiang P, Xun S, He B, Wu W, Liu L, Wang Y. A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071640
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sichen, Yanfeng Huo, Xi Mu, Peng Jiang, Shangpei Xun, Binfang He, Wenyu Wu, Lin Liu, and Yonghong Wang. 2022. "A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071640
APA StyleWang, S., Huo, Y., Mu, X., Jiang, P., Xun, S., He, B., Wu, W., Liu, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). A High-Performance Convolutional Neural Network for Ground-Level Ozone Estimation in Eastern China. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071640





