SAR Image Segmentation by Efficient Fuzzy C-Means Framework with Adaptive Generalized Likelihood Ratio Nonlocal Spatial Information Embedded
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A robust unsupervised FCM framework incorporating adaptive Bayesian non-local spatial information is proposed. This non-local spatial information is measured by the log-transformed Bayesian metric which is induced by applying the log-transformed SAR distribution into the Bayesian theory.
- (2)
- To avoid undesirable properties of the log-transformed Bayesian metric, we construct the similarity between patches as the continued product of corresponding pixel similarity measured by the generalized likelihood ratio. An alternative unsupervised FCM framework is then proposed, named GLR_FCM.
- (3)
- An adaptive factor is employed to balance the original and non-local spatial information. Besides, a sample membership degree smoothing is adopted to provide the local spatial information iteratively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.1.1. The Standard FCM
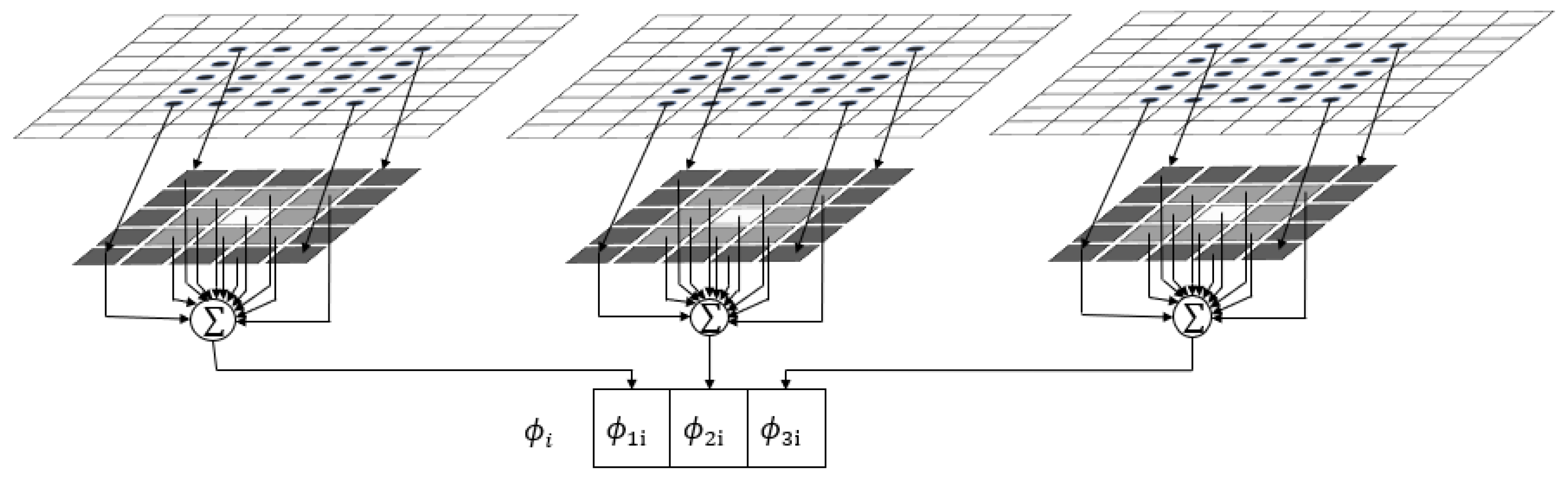
2.1.2. Nonlocal Means Method
2.1.3. Nonlocal Spatial Information Based on Bayesian Approach
2.2. The Modified FCM Based on Log-Transformed Bayesian Nonlocal Spatial Information
2.3. Some Problems on Patch Similarity Metric by Bayesian Theory
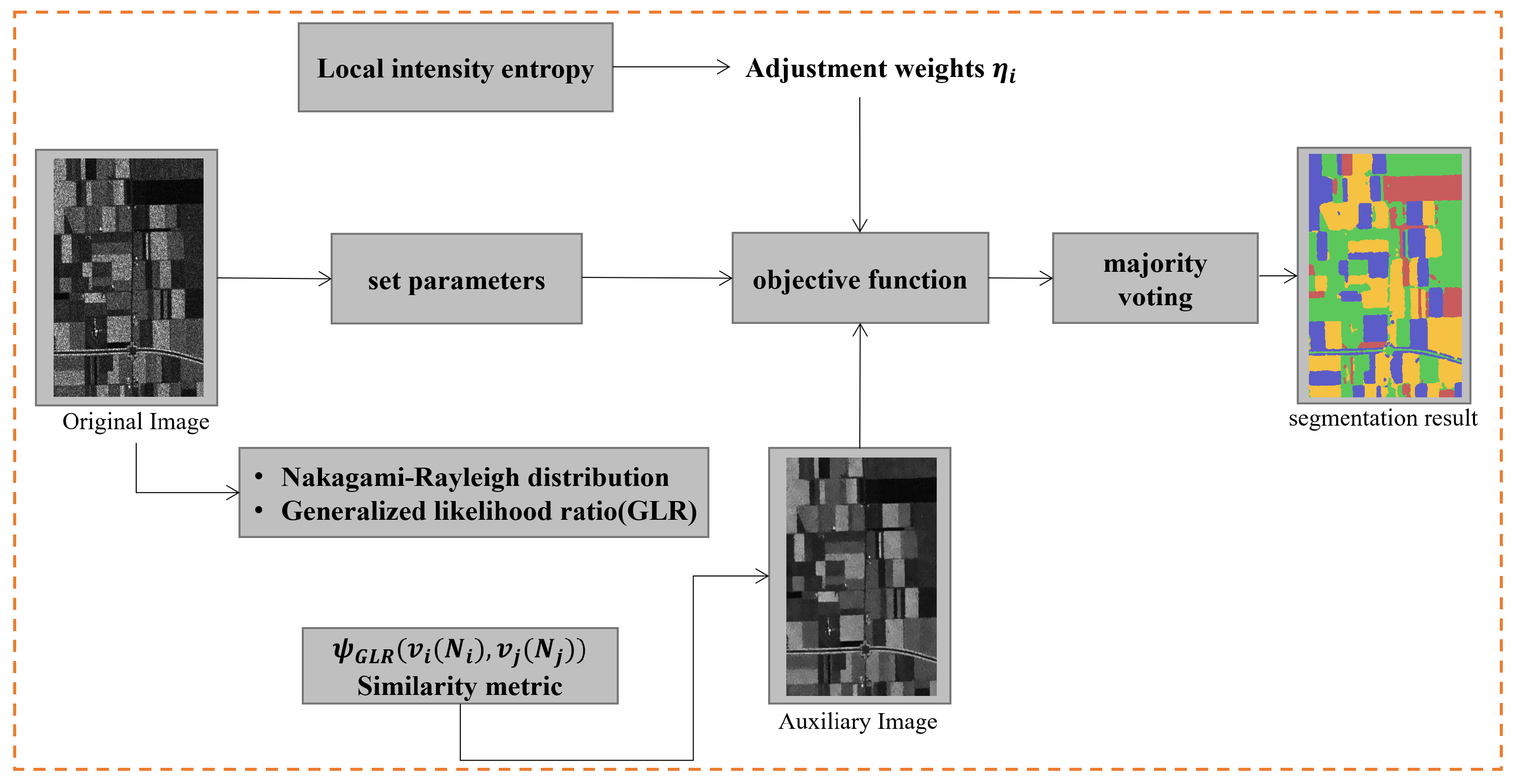
2.4. The New FCM Based on Generalized Likelihood Ratio
2.5. The Membership Degree Smoothing and Label Correction
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Setting
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
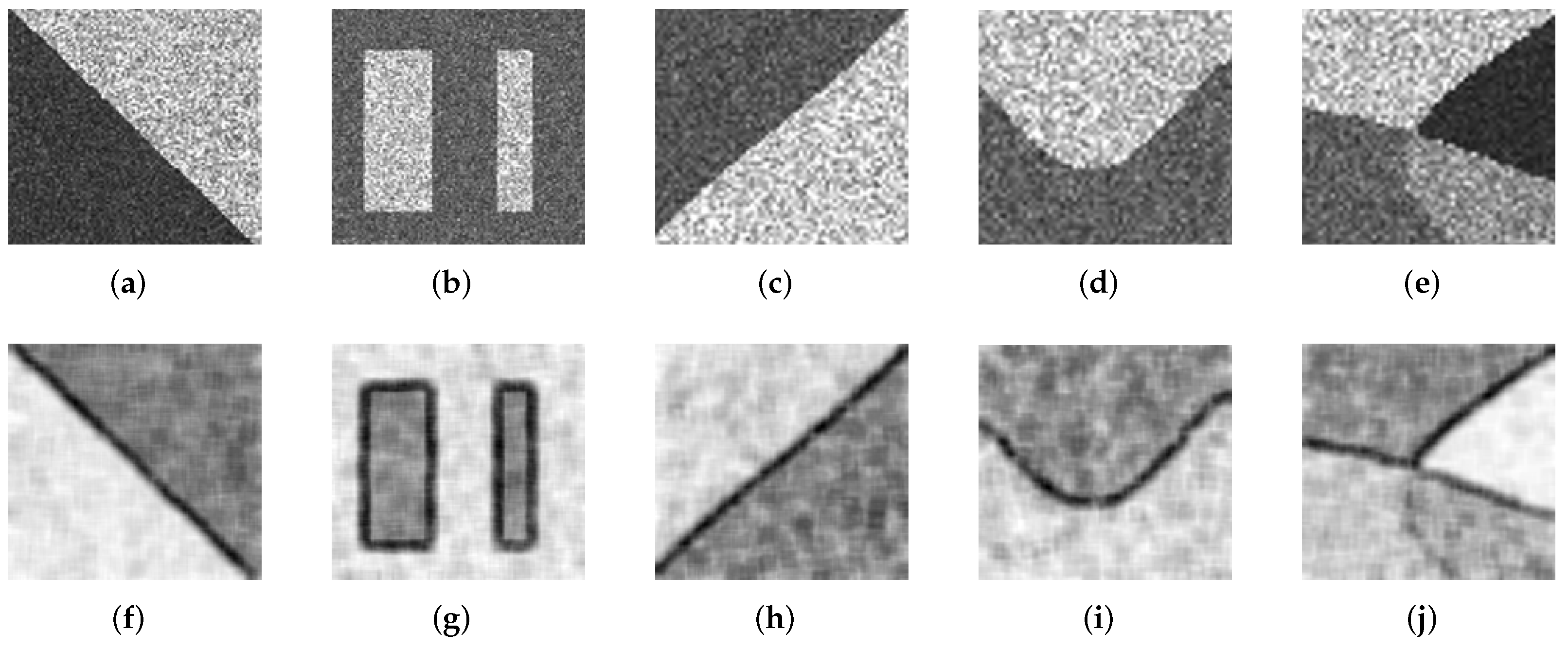
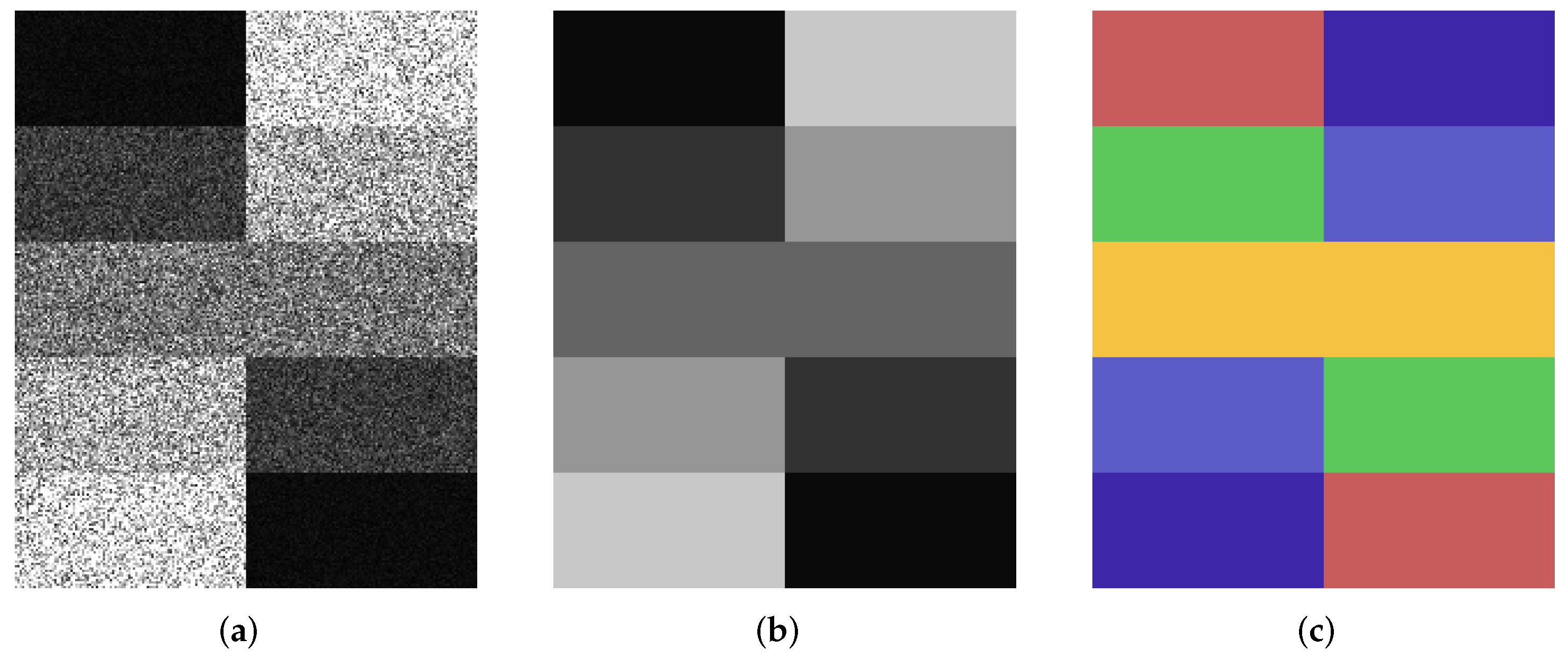
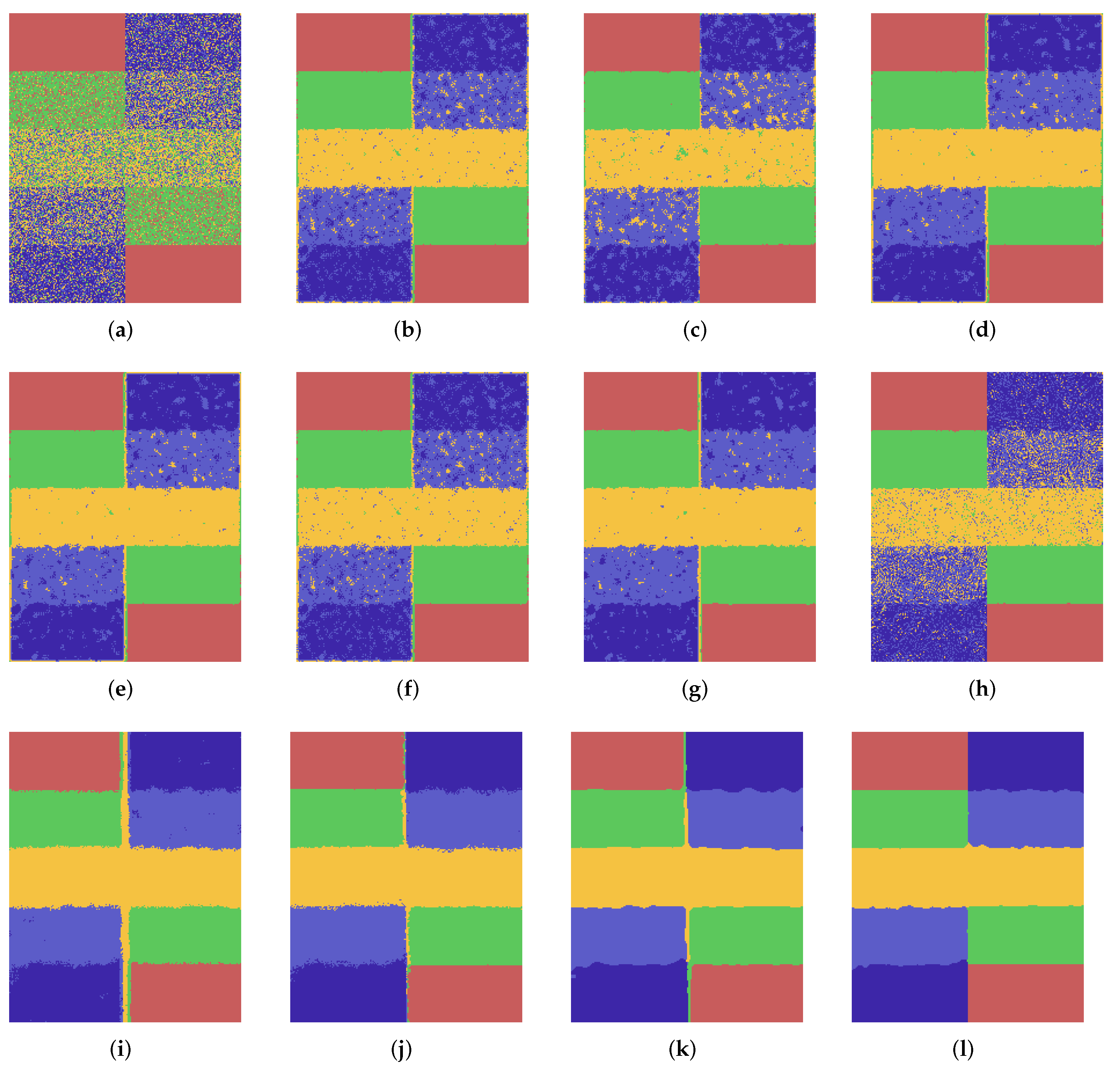
3.3. Segmentation Results on Simulated SAR Images
3.3.1. Experiment 1: Testing on the First Simulated SAR Image
3.3.2. Experiment 2: Testing on the Second Simulated SAR Image
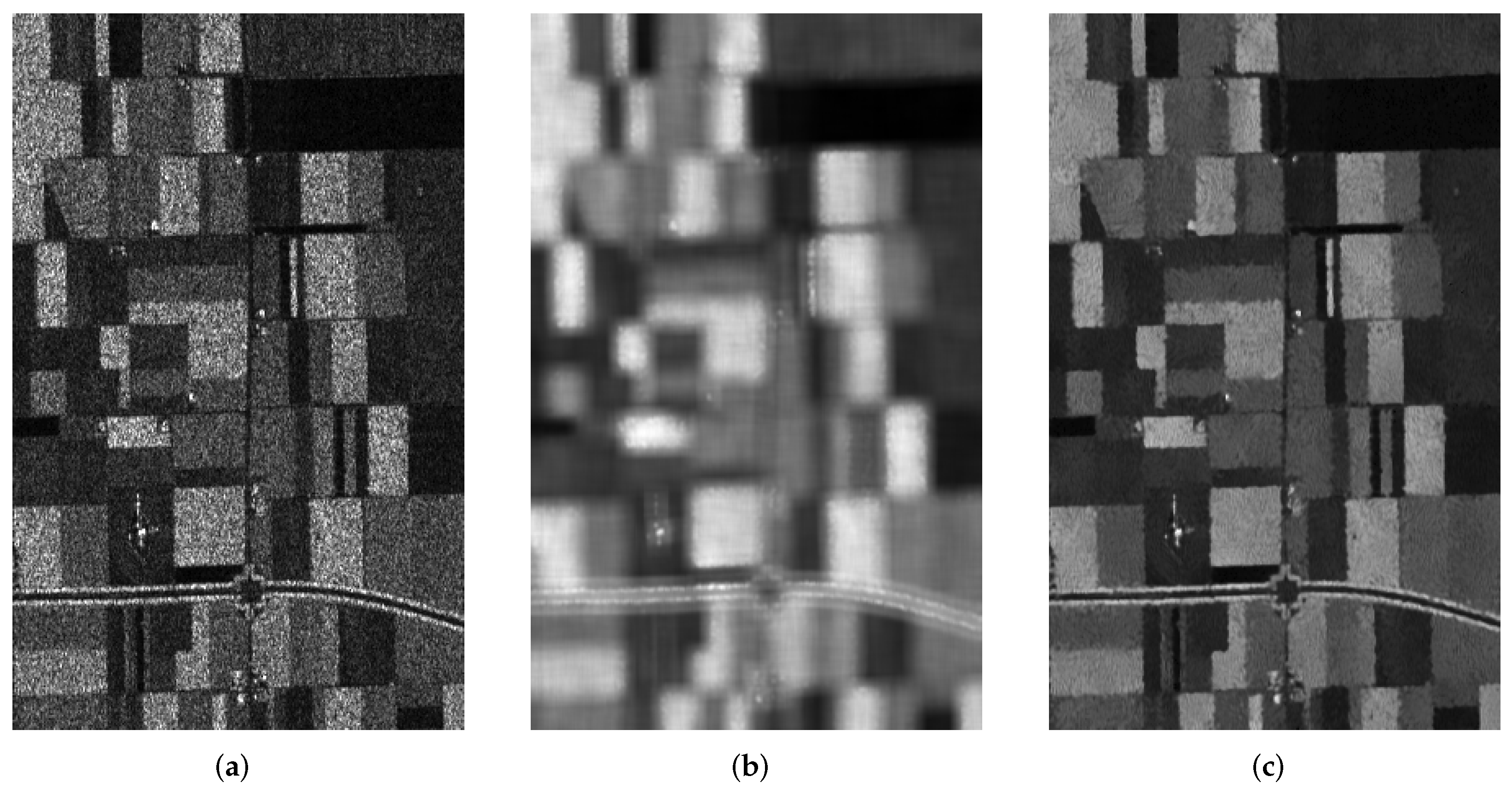
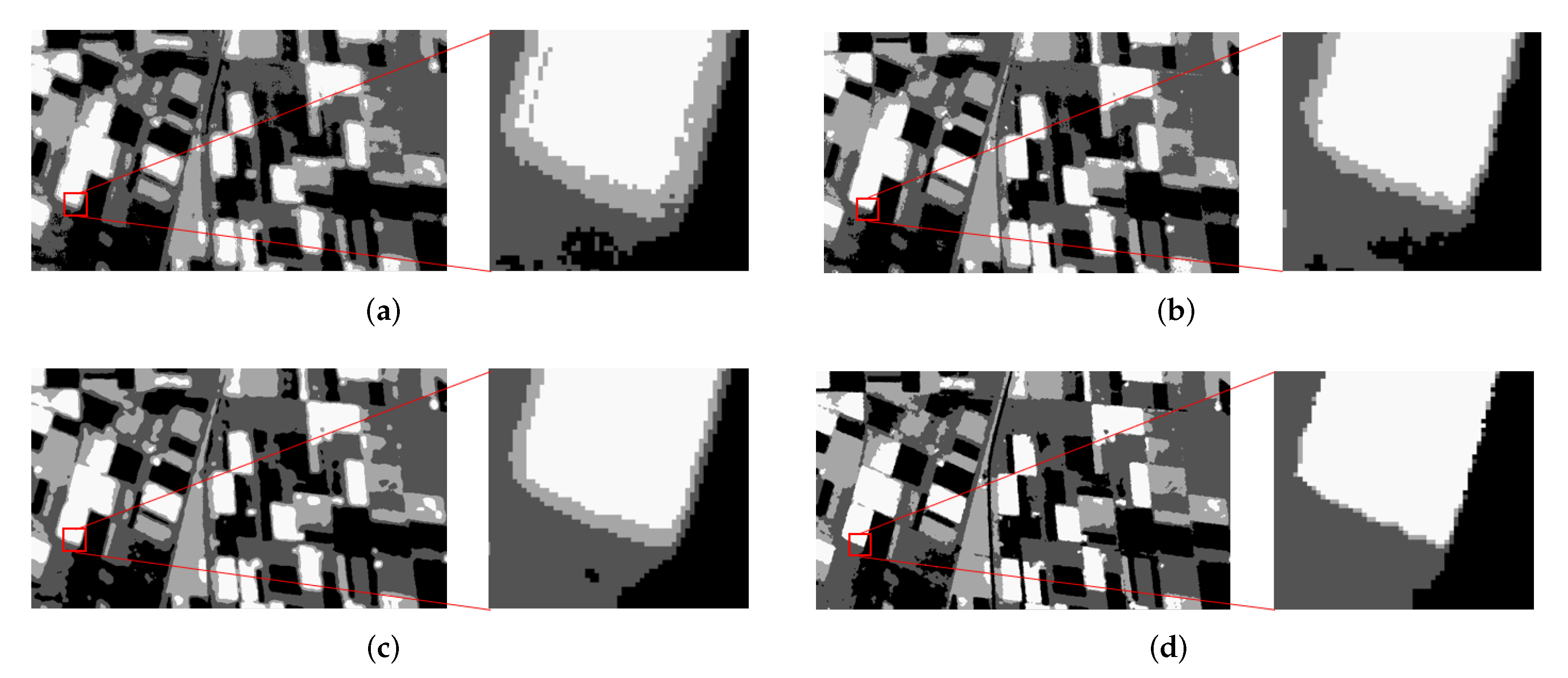
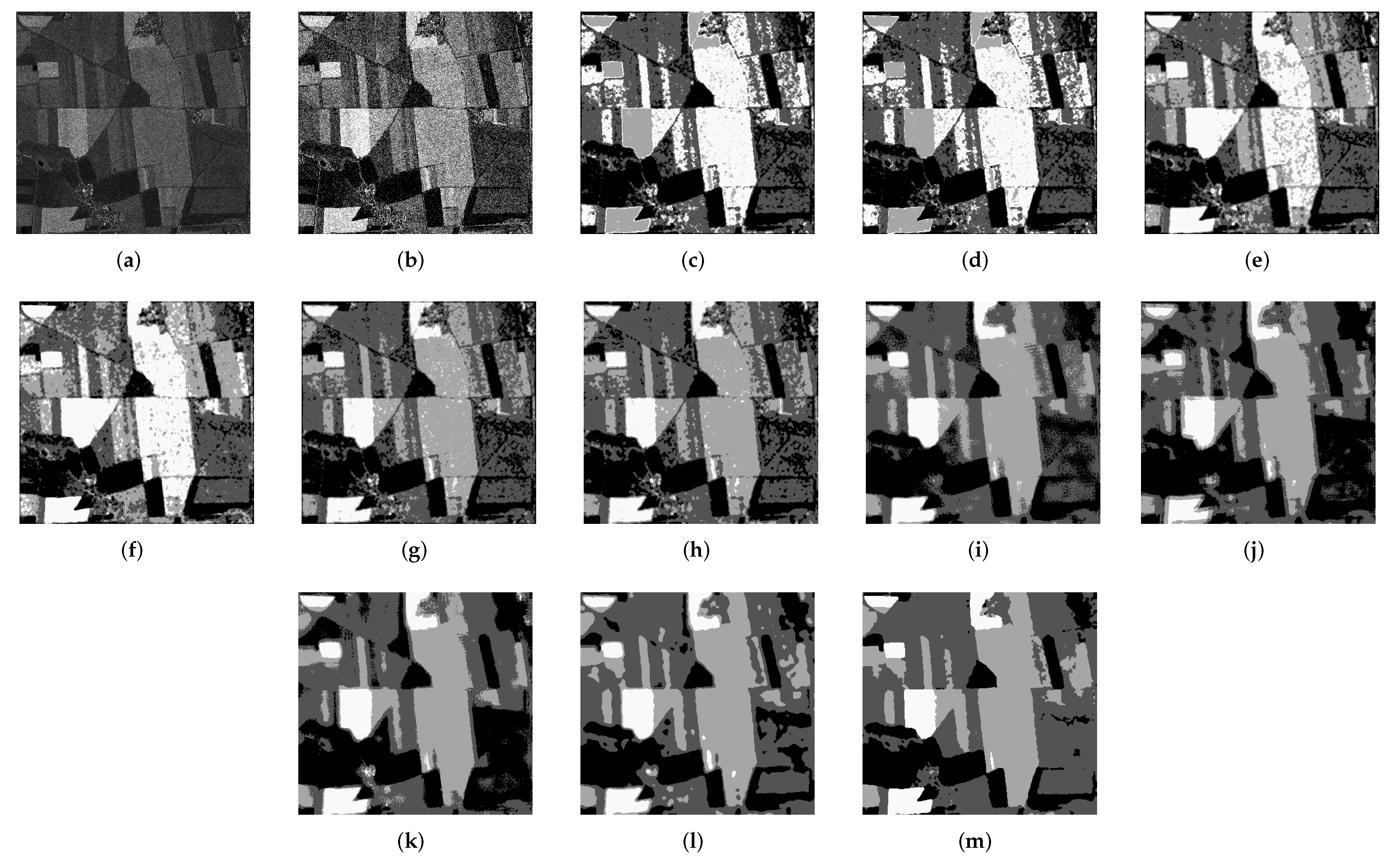
3.4. Segmentation Results on Real SAR Images
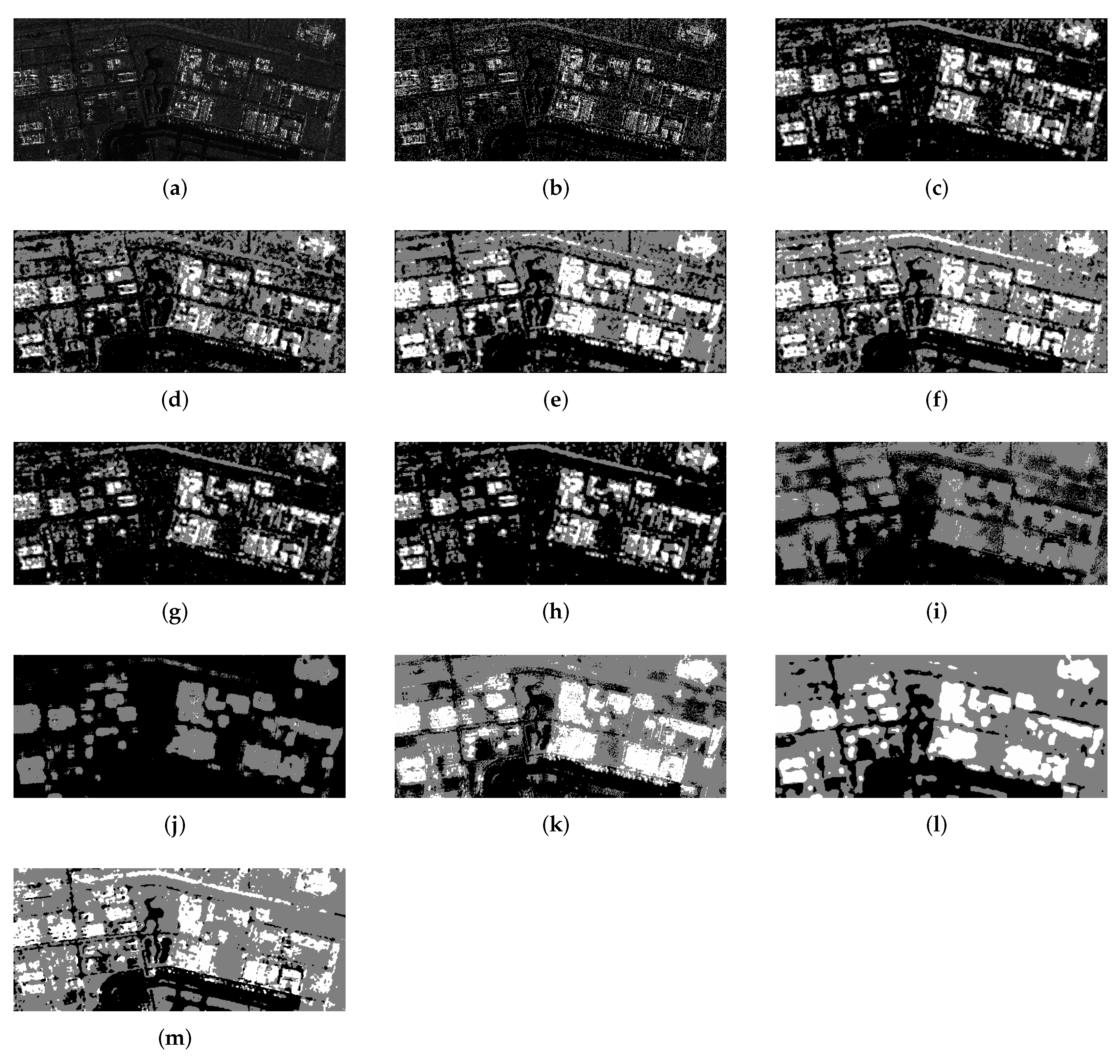
3.4.1. Experiment 1: Experiment on the First Real SAR Image
3.4.2. Experiment 2: Experiment on the Second Real SAR Image
3.4.3. Experiment 3: Experiment on the Third Real SAR Image
3.4.4. Experiment 4: Experiment on the Fourth Real SAR Image
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis to Speckle Noise
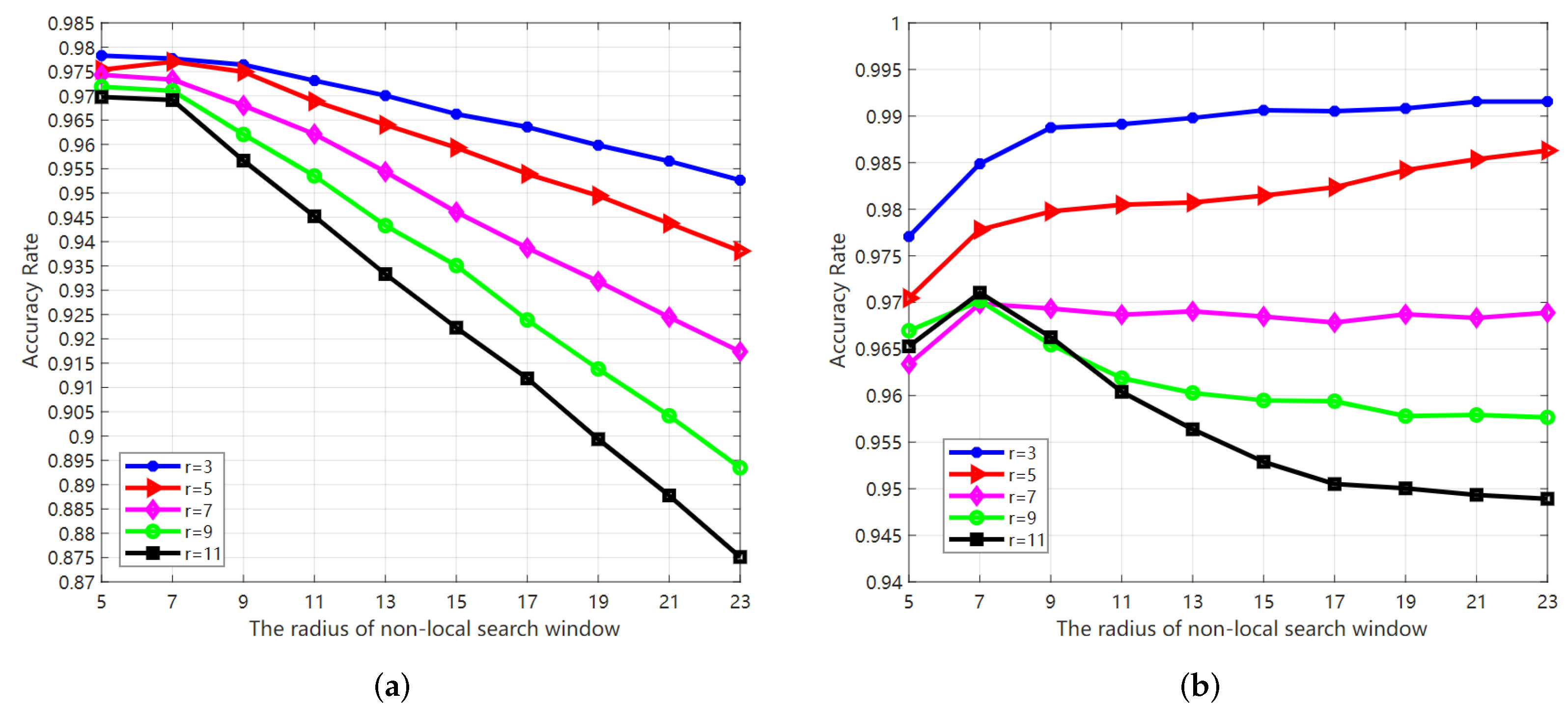
3.6. Parameters Analysis and Selection
3.7. Computational Complexity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahmani, M.; Akbarizadeh, G. Unsupervised feature learning based on sparse coding and spectral clustering for segmentation of synthetic aperture radar images. IET Comput. Vis. 2015, 9, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Li, X.; Lu, X. An Improved Ostu Method for Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2006 8th international Conference on Signal Processing, Guilin, China, 16–20 November 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Clausi, D.A. IRGS: Image Segmentation Using Edge Penalties and Region Growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 2126–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, E.A.; Ushizima, D.M.; Medeiros, F.N.; Martins, C.I.O.; Marques, R.C.; Oliveira, I.N. SAR imagery segmentation by statistical region growing and hierarchical merging. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Tang, T.; Guan, D.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y. Fast Pixel-Superpixel Region Merging for SAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9319–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Hou, B. Context-Based Hierarchical Unequal Merging for SAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, D. Optimal segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing image by combining superpixels with the minimum spanning tree. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, F.; Xiang, D.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Y. Fast Task-Specific Region Merging for SAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiang, D.; Su, Y. Fast Multiscale Superpixel Segmentation for SAR Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Bo, L.; Gong, M. Spectral Clustering Ensemble Applied to SAR Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhaya, S.; Kumar, A.; Stein, A. FCM Approach of Similarity and Dissimilarity Measures with α-Cut for Handling Mixed Pixels. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Wu, D. Multispectral image segmentation based on a fuzzy clustering algorithm combined with Tsallis entropy and a gaussian mixture model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhu, A.; Kumar, A.; Jia, P. Exploring Fuzzy Local Spatial Information Algorithms for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; He, C.; Sun, H. Integration of synthetic aperture radar image segmentation method using Markov random field on region adjacency graph. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2007, 1, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, G. SAR Image Segmentation Based on Level Set With Stationary Global Minimum. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Lv, X.; Yao, J. Water extraction in SAR Images using features analysis and dual-threshold graph cut model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zou, Z.; Liu, J.; Lin, Z. Dimensionality reduction and classification of hyperspectral image via multi-structure unified discriminative embedding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5517916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Gao, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H.; Hussain, A. Weakly supervised segmentation of SAR imagery using superpixel and hierarchically adversarial CRF. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, J. When Deep Learning Meets Multi-Task Learning in SAR ATR: Simultaneous Target Recognition and Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, A.; Fablet, R.; Tandeo, P.; Husson, R.; Peureux, C.; Longépé, N.; Mouche, A. Semantic Segmentation of Metoceanic Processes Using SAR Observations and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Guo, D. A Refined Pyramid Scene Parsing Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Semantic Segmentation in Agricultural Areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Yamany, S.M.; Mohamed, N.; Farag, A.A.; Moriarty, T. A modified fuzzy c-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, D. Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part Cybern. 2004, 34, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szilagyi, L.; Benyo, Z.; Szilágyi, S.M.; Adam, H. MR brain image segmentation using an enhanced fuzzy c-means algorithm. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37439), Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; Volume 1, pp. 724–726. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D. Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krinidis, S.; Chatzis, V. A robust fuzzy local information C-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 2, pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kong, J.; Lu, Y.; Qi, M.; Zhang, B. A modified FCM algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation using both local and non-local spatial constraints. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2008, 32, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chung, F.L.; Wang, S. Generalized fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with improved fuzzy partitions. IEEE TRansactions Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2009, 39, 578–591. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Jiao, L.; Liu, H. Fuzzy c-means clustering with non local spatial information for noisy image segmentation. Front. Comput. Sci. China 2011, 5, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jiao, L.; Liu, H.; Gao, X. A novel fuzzy clustering algorithm with non local adaptive spatial constraint for image segmentation. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Gong, M.; Sun, T. Robust non-local fuzzy c-means algorithm with edge preservation for SAR image segmentation. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, K.L. A robust nonlocal fuzzy clustering algorithm with between-cluster separation measure for SAR image segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, T.; Xiang, Y.; You, H. A robust fuzzy c-means algorithm based on Bayesian nonlocal spatial information for SAR image segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervrann, C.; Boulanger, J.; Coupé, P. Bayesian non-local means filter, image redundancy and adaptive dictionaries for noise removal. In International Conference on Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 520–532. [Google Scholar]
- Deledalle, C.A.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. How to compare noisy patches? Patch similarity beyond Gaussian noise. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 99, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Pierce, L.; Ulaby, F. Statistical properties of logarithmically transformed speckle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. JOSA 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.; Quegan, S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, R.; Lin, J.; Jiao, L.; Li, Y. SAR Image Segmentation Using Region Smoothing and Label Correction. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Chao, H. A validity index for fuzzy clustering based on bipartite modularity. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2719617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezdek, J.C. Numerical taxonomy with fuzzy sets. J. Math. Biol. 1974, 1, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Cluster Validity with Fuzzy Sets; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, R.N. Validating fuzzy partitions obtained through c-shells clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1996, 17, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, Y. A new method of choosing the number of clusters for the fuzzy c-mean method. In Proceedings of the 5th Fuzzy Systems Symposium, Kobe, Japan, 3 June 1989; pp. 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Rajendran, A.; Palanivel, K. Meticulous fuzzy convolution C means for optimized big data analytics: Adaptation towards deep learning. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 3575–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Wu, Y. Semi-supervised Fault Diagnosis Model Based on Improved Fuzzy C-means Clustering and Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing, Shaanxi, China, 8–11 October 2020; Volume 1043, p. 052043. [Google Scholar]









| Indicator | Formulation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PC (Partition Coefficient) [44] | The larger the PC value, the better the partition result | |
| PE (Partition Entropy) [45] | The smaller the PE value, the better the partition result | |
| MPC (Modified PC) [46] | The MPC eliminates the dependency on c, the large the MPC is, the better the partition result | |
| MPE (Modified PE) [46] | Similar to above that the smaller the MPE is, the better the partition result | |
| FS (Fukuyama-Sugeno Index) [47] | The first term indicates the compactness and the second term indicates the separation. And the minimum FS implies the optimal partition |
| Method | SA (%) | Time (s) | Method | SA (%) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | 60.58 | 2.16 | FGFCM | 94.65 | 5.64 |
| FCM_S1 | 90.49 | 1.11 | FCM_NLS | 83.61 | 7.27 |
| FCM_S2 | 90.49 | 1.46 | NS_FCM | 95.03 | 7.77 |
| KFCM_S1 | 92.66 | 1.27 | RFCM_BNL | 97.29 | 10.88 |
| KFCM_S2 | 91.42 | 1.20 | LBNL_FCM | 97.64 | 12.11 |
| EnFCM | 90.63 | 1.85 | GLR_FCM | 99.16 | 17.73 |
| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | 0.7994 | 0.3995 | 0.7492 | 0.3995 | |
| FCM_S1 | 0.7203 | 0.5581 | 0.6504 | 0.5582 | |
| FCM_S2 | 0.7350 | 0.5347 | 0.6688 | 0.5347 | |
| KFCM_S1 | 0.6783 | 0.6623 | 0.5978 | 0.6624 | |
| KFCM_S2 | 0.6861 | 0.6537 | 0.6076 | 0.6537 | |
| EnFCM | 0.8518 | 0.3031 | 0.8147 | 0.3031 | |
| FGFCM | 0.8750 | 0.2595 | 0.8438 | 0.2595 | |
| FCM_NLS | 0.7175 | 0.5892 | 0.6469 | 0.5893 | |
| NS_FCM | 0.6932 | 0.6342 | 0.6165 | 0.6342 | |
| RFCM_BNL | 0.8069 | 0.4165 | 0.7587 | 0.4165 | |
| LBNL_FCM | 0.9609 | 0.0792 | 0.9511 | 0.0792 | |
| GLR_FCM | 0.9855 | 0.0260 | 0.9819 | 0.0260 |
| Method | SA (%) | Time (s) | Method | SA (%) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | 73.82 | 3.47 | FGFCM | 97.88 | 9.36 |
| FCM_S1 | 95.83 | 1.16 | FCM_NLS | 95.03 | 8.85 |
| FCM_S2 | 96.55 | 1.27 | NS_FCM | 96.10 | 9.59 |
| KFCM_S1 | 96.36 | 1.02 | RFCM_BNL | 98.66 | 16.58 |
| KFCM_S2 | 96.94 | 1.22 | LBNL_FCM | 98.82 | 16.83 |
| EnFCM | 95.88 | 2.03 | GLR_FCM | 99.86 | 18.45 |
| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | 0.8354 | 0.3298 | 0.7943 | 0.3298 | |
| FCM_S1 | 0.8204 | 0.3667 | 0.7755 | 0.3667 | |
| FCM_S2 | 0.8298 | 0.3524 | 0.7872 | 0.3524 | |
| KFCM_S1 | 0.7880 | 0.4492 | 0.7351 | 0.4492 | |
| KFCM_S2 | 0.7923 | 0.4448 | 0.7404 | 0.4448 | |
| EnFCM | 0.9060 | 0.1971 | 0.8825 | 0.1971 | |
| FGFCM | 0.9307 | 0.1511 | 0.9134 | 0.1511 | |
| FCM_NLS | 0.8171 | 0.3890 | 0.7714 | 0.3890 | |
| NS_FCM | 0.8085 | 0.4102 | 0.7607 | 0.4103 | |
| RFCM_BNL | 0.8939 | 0.2414 | 0.8674 | 0.2414 | |
| LBNL_FCM | 0.9882 | 0.0208 | 0.9852 | 0.0208 | |
| GLR_FCM | 0.9972 | 0.0051 | 0.9965 | 0.0051 |
| Method | Computational Complexity | Method | Computational Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | FGFCM | ||
| FCM_S1 | FCM_NLS | ||
| FCM_S2 | NS_FCM | ||
| KFCM_S1 | RFCM_BNL | ||
| KFCM_S2 | LBNL_FCM | ||
| EnFCM | GLR_FCM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; You, H. SAR Image Segmentation by Efficient Fuzzy C-Means Framework with Adaptive Generalized Likelihood Ratio Nonlocal Spatial Information Embedded. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071621
Zhu J, Wang F, You H. SAR Image Segmentation by Efficient Fuzzy C-Means Framework with Adaptive Generalized Likelihood Ratio Nonlocal Spatial Information Embedded. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(7):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071621
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jingxing, Feng Wang, and Hongjian You. 2022. "SAR Image Segmentation by Efficient Fuzzy C-Means Framework with Adaptive Generalized Likelihood Ratio Nonlocal Spatial Information Embedded" Remote Sensing 14, no. 7: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071621
APA StyleZhu, J., Wang, F., & You, H. (2022). SAR Image Segmentation by Efficient Fuzzy C-Means Framework with Adaptive Generalized Likelihood Ratio Nonlocal Spatial Information Embedded. Remote Sensing, 14(7), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071621







