Abstract
As a common natural disaster, drought can significantly affect the agriculture productivity and human life. Compared to Southeast China, Northwest China is short of water year-round and is the most frequent drought disaster area in China. Currently, there are still many controversial issues in drought monitoring of Northwest China in recent decades. To further understand the causes of changes in drought in Northwest China, we chose Shaanxi, Gansu, and Ningxia provinces (SGN) as our study area. We compared the spatiotemporal characteristics of drought intensity and frequency in Northwest China from 2003 to 2020 showed by the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), Vegetation Condition Index (VCI), Temperature Condition Index (TCI), Vegetation Health Index (VHI), Normalized Vegetation Supply Water Index (NVSWI), Soil Moisture Condition Index (SMCI), and Soil Moisture Agricultural Drought Index (SMADI). All of these indices showed a wetting trend in the SGN area from 2003 to 2020. The wetting trend of the VCI characterization is the most obvious (R2 = 0.9606, p < 0.05): During the period 2003–2020, the annual average value of the VCI in the SGN region increased from 28.33 to 71.61, with a growth rate of 153.57%. The TCI showed the weakest trend of wetting (R2 = 0.0087), with little change in the annual average value in the SGN region. The results of the Mann–Kendall trend test of the TCI indicated that the SGN region experienced a non-significant (p > 0.05) wetting trend between 2003 and 2020. To explore the effectiveness of different drought indices, we analyzed the Pearson correlation between each drought index and the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI). The PDSI can not only consider the current water supply and demand situation but also consider the impact of the previous dry and wet conditions and their duration on the current drought situation. Using the PDSI as a reference, we can effectively verify the performance of each drought index. SPI-12 showed the best correlation with PDSI, with R values greater than 0.6 in almost all regions and p values less than 0.05 within one-half of the study area. SMADI had the weakest correlation with PDSI, with R values ranging −0.4~−0.2 and p values greater than 0.05 in almost all regions. The results of this study clarified the wetting trend in the SGN region from 2003 to 2020 and effectively analyzed the differences in each drought index. The frequency, duration, and severity of drought are continuously reduced; this helps us to have a more comprehensive understanding of the changes in recent decades and is of significance for the in-depth study of drought disasters in the future.
1. Introduction
Drought disaster is very complex and not well understood. Drought events can easily cause social and environmental problems with immeasurable economic losses [1,2,3,4,5]. In recent decades, with the frequent occurrences of global drought disasters, the international community has paid more attention to drought [6,7,8]. Although the disaster prevention management department places great importance on tracking drought disasters and records their key impact on society and the natural environment, it is difficult to accurately identify drought events because the occurrence of drought is related to changes in time, space, and natural environmental conditions [9]. Generally, there are four types of drought: meteorological, agricultural, hydrological, and socioeconomic; the causes of each type of drought are different [10]. Meteorological drought is mainly caused by a decrease of precipitation. Agricultural drought is mainly manifested in the reduction of agricultural production and the degradation of forest and grassland due to an insufficient water supply for vegetation growth. Hydrological drought refers to surface runoff decline and groundwater levels reduction. Socioeconomic drought mainly refers to the decline in economic benefits caused by insufficient water supply [11,12]. In-depth research on each type of drought will effectively promote the improvement of human society’s ability to respond to drought disasters.
In recent decades, the analysis and research on the mechanism of drought disasters and their impacts on human society and the natural environment have improved our understanding of the nature of drought disasters [13,14,15]. For a long time, the use of environmental and climate data to construct a drought index has been considered the most effective drought identification method. Presently, researchers from different countries have developed various drought indices [16]. In 1965, Palmer proposed the Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI), which considers the precipitation, evapotranspiration, runoff, and soil moisture information under the principle of water balance [17]. In 1993, Mckee et al. (1993) [18] standardized precipitation data to develop the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). In 1995, Kogan used the normalization method to construct the Vegetation Condition Index (VCI) and Temperature Condition Index (TCI) based upon the relationships between NDVI, LST, and drought [19,20]. In 2002, Kogan combined the VCI and TCI indices to propose the Vegetation Health Index (VHI) [21]. In the same year, Sandholt et al. (2002) [22] used the Thermo-Optical Trapezoidal Model to construct the Temperature Vegetation Drought Index (TVDI), which effectively characterizes the spatial characteristics of NDVI and LST and reflects the relationship between NDVI and LST under extreme drought or humid conditions [23,24]. In 2010, Vicente-Serrano et al. (2010) [25] added evapotranspiration information to the SPI to construct a Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI). In the same year, Rhee et al. (2010) [26] combined NDVI, LST, and precipitation information and developed the Scaled Drought Condition Index (SDCI). In 2013, Zhang et al. (2013) [12] referred to Kogan’s method of constructing VCI and TCI indices and used precipitation and soil moisture information to construct the Precipitation Condition Index (PCI) and Soil Moisture Condition Index (SMCI). In 2014, Abbas et al. (2014) [27] explored the inverse relationship between NDVI and LST under drought conditions (under extreme drought conditions, NDVI was usually low, and LST was usually high) and then proposed the Normalized Vegetation Supply Water Index (NVSWI). In 2016, Sanchez et al. (2016) [28] proposed the Soil Moisture Agricultural Drought Index (SMADI) based on soil moisture, NDVI, and LST data. The construction of these drought indices has facilitated our in-depth understanding of drought disasters.
Currently, many studies have used different drought indices to research the characteristics of the spatiotemporal pattern of drought under global warming conditions. However, the results obtained by different studies are often inconsistent and even opposing [29]. For example, Sheffield et al. (2012) [30] observed changes in global drought conditions and found no significant change during the past 60 years. However, Dai et al. (2013) [31] found that global drought conditions have generally increased during the same period. These contradictory results have confused the understanding of the actual characteristics of drought. The research on drought in mainland China has likewise been confounding. For example, Wu et al. (2020) [32] researched the spatiotemporal change of drought conditions in mainland China from 1961 to 2016 and found a wetting trend. Wang et al. (2017) [33] analyzed drought in mainland China from 1961 to 2009 and found that drought conditions gradually weakened in Northwest China. However, when Yu et al. (2014) [34] analyzed the frequency, severity, and duration of droughts in China from 1951 to 2010, they found that in the late 1990s, extreme droughts across China were more severe than before. Similarly, Zhao et al. (2017) [35] used the modified Temperature Vegetation Drought Index (mTVDI) to analyze the spatiotemporal pattern of droughts in mainland China and found that the frequency of droughts from 1982 to 2010 had an overall upward trend; the frequency of severe droughts increased significantly, and the frequency of mild droughts slowly rose. The existence of these controversial problems seriously hinders people’s understanding of the nature of drought disasters. Taking these problems as the starting point, further exploring the causes of these problems will greatly promote the development of drought research and effectively improve the ability of human society to cope with drought disasters.
Generally, the reason for the contradictory results in the study of the drought spatiotemporal patterns is believed to be the use of different drought indices [29]. In fact, different drought indices often emphasize different drought influencing factors [33]. For example, the single-factor drought index SPI uses precipitation as the impact factor [36,37]; VCI uses NDVI as the drought impact factor [38]; TCI uses LST as the drought impact factor [39]; the composite drought indices VHI and NVSWI use NDVI and LST as the drought-influencing factors [40,41]; and SMADI uses soil moisture, NDVI, and LST as drought-influencing factors [11,42]. Although there are certain correlations among different drought-influencing factors, they are very different in time and space, which leads to completely different spatiotemporal patterns. Even if the composite drought index considers a variety of drought factors, it is difficult to eliminate this difference due to the different theories and calculation methods. Therefore, using a single drought index to monitor the spatiotemporal pattern of regional drought is often inaccurate. These are the main reasons for the contradictory results obtained by existing studies. Therefore, in the study of drought disasters, considering as many natural environmental factors related to drought as possible and selecting various drought indices for comprehensive comparative analysis will achieve more convincing research results. In drought events, precipitation and temperature are the most important drivers, and both the scarcity of precipitation and extreme heat weather can easily lead to extreme drought disasters. At the same time, when the drought event occurs, the soil moisture will continue to decrease. When the soil moisture drops to a certain extent, the vegetation growth is restricted, and the ecological environment is seriously damaged, which is the most common form of drought disaster. Therefore, most of the drought conditions can be effectively identified by analyzing precipitation, temperature, soil moisture, and vegetation growth. In recent years, the study of these influencing factors and drought have continuously deepened, and a large number of drought indexes have been developed. For example, SPI-1, SPI-3, and SPI-12 consider the effects of precipitation on drought on different time scales. VCI, TCI, and SMCI consider the relationship between vegetation index, surface temperature, soil moisture, and drought, while VHI, NVSWI, and SMADI consider the combined effect of multiple factors on drought. VHI and NVSWI consider vegetation index and surface temperature, and SMADI considers vegetation, surface temperature, and soil moisture. Therefore, we chose these indices for a comparative analysis on changes in drought in the SGN area. The comparative analysis of the spatiotemporal pattern of drought characterized by these nine indices can provide us with a deeper understanding of the regional drought situation, which is conducive to the effective prevention and decision-making of the government management departments on drought disasters.
The main purposes of our study were to: (1) compare the spatiotemporal pattern of drought conditions as characterized by the SPI, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, and SMADI indices in the SGN area from 2003 to 2020 and (2) compare the reliability of different drought indices in drought monitoring by calculating the Pearson correlation between each drought index and the internationally universal PDSI. It should be noted that the CHIRPS (Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation With Station Data) used in this study is one of the source data of the FLDAS (Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET) Land Data Assimilation System) data production process, so there may be some autocorrelation between the SPI, SMCI, and SMADI indices in this study. This problem may cause some bias to the exponential comparison results; however, this bias has little effect on the study results because the calculation theory of SPI, SMCI, and SMADI is not consistent. Our findings will advance our understanding of the changing characteristics of drought in the SGN area over the past 20 years and are an important reference for prevention and management of drought.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The SGN 7800 area is in Northwest China and includes Shaanxi, Gansu, and Ningxia provinces (Figure 1a), with geographic coordinates spanning ~30–45°N and ~90–120°E (Figure 1b). It spans ~2350 km from east to west and 1000 km from north to south. The total area is 7.259 × 105 km2 (Shaanxi 2.058 × 105 km2, Gansu 4.537 × 105 km2, and Ningxia 6.64 × 104 km2) and includes 29 prefecture-level cities. The topography of the SGN is relatively undulating, with an elevation of 0~3517 m. The elevation at the junction of Southwestern Gansu and Qinghai is the highest of the study area, and Central and Southern Shaanxi are the lowest (Figure 1b).
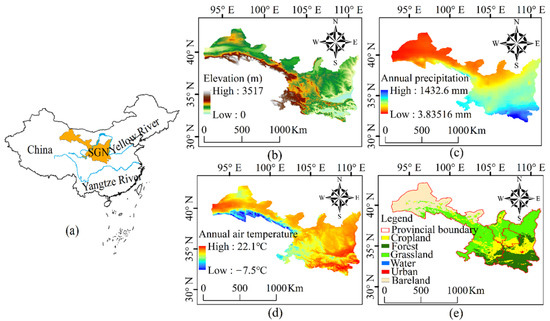
Figure 1.
(a) The location of the SGN area in China. (b) The topographical properties. (c) The spatial distribution of mean annual precipitation. (d) The spatial distribution of mean annual air temperature. (e) Distribution of terrestrial ecosystems in the study area.
The SGN region straddles the northern temperate and subtropical zone and belongs to a continental monsoon climate, and precipitation decreases gradually from southeast to northwest. The Southeast has a semi-arid and semi-humid climate, with annual precipitation above 400 mm, and the Northwest has an arid climate with an annual precipitation of less than 200 mm (Figure 1c). The annual average temperature is −7.5–22.1 °C. The temperature is lowest at the junction of Southwestern Gansu and Qinghai province and is highest in the Guanzhong Plain of Shaanxi Province (Figure 1d). The cropland is mainly distributed in the Guanzhong Plain of Shaanxi, along the Yellow River in Ningxia Province, and in the Hexi Corridor of Gansu Province (Figure 1e).
The SGN region is in the transitional area of spring wheat and winter wheat. The southeast region is mainly winter wheat, and the Northwest is mainly spring wheat and other spring crops. Irrigation infrastructure is situated around the rivers, and crops here are less affected by drought than in other areas where imperfect irrigation infrastructure is uncommon and crops mainly rely upon precipitation. The occurrence of drought disasters can easily affect agricultural production where irrigation is absent. Thus, it is very important to explore the long-term changing trends of drought in the SGN region and quantify their adverse effects on agricultural production.
2.2. Datasets and Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Precipitation Data
The precipitation data used in this study comprised the CHIRPS daily precipitation dataset [43]. This dataset contains global daily precipitation data from 1981 to 2021. Compared with commonly used precipitation datasets such as TRMM (spatial resolution 25 km) and GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement) (spatial resolution 11 km), the CHIRPS dataset has a higher spatial resolution (5 km). Here, we aggregated the CHIRPS daily precipitation data to monthly values, and we calculated the SPI, with 1 month named SPI-1, 3 months named SPI-3, and 12 months named SPI-12. The daily CHIRPS data can be obtained through the GEE platform (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/UCSBCHG_CHIRPS_DAILY; accessed on 15 October 2021).
2.2.2. NDVI and LST Data
The MODIS data products, MYD13A2 and MYD11A2, were from the Aqua satellite. The temporal resolution of the MYD13A2 is 16 days, which was composited using all high-quality NDVI pixels collected within 16 days. The temporal resolution of the MYD11A2 is 8 days, which was composited by averaging all LST observations within 8 days [44,45,46,47]. The MYD13A2 and MYD11A2 datasets have the high spatial resolution of 1 km. In order to keep the temporal and spatial resolution consistent with the precipitation data, we used the maximum and average values to represent the monthly NDVI and LST, respectively. We also used the bicubic method to covert the spatial resolution to 5 km. Considering the significant decrease in nighttime surface temperature and large regional differences, which increases the uncertainty in drought monitoring, only the daytime LST data in the MYD11A2 product were used [24]. These data can be obtained from the GEE platform (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/; accessed on 17 October 2021).
2.2.3. Soil Moisture Data
The soil moisture data used in this study comprised the FLDAS datasets, which contain global monthly soil moisture data in different depths from 1982 to 2020, as well as information on elevation, vegetation coverage, and albedo. These datasets were designed to promote the needs of environmental and food security assessments in developing countries where data are scarce; the spatial resolution is 0.1 degrees [48,49]. The FLDAS datasets can be obtained through the GEE platform (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/NASA_FLDAS_NOAH01_C_GL_M_V001; accessed on 20 October 2021). We selected the 0–10 cm soil moisture data in the FLDAS datasets and combined the VCI and MTCI indices to generate the SMADI. To maintain the same spatial resolution as other data, we used the bicubic method to resample the soil moisture data to 5 km resolution.
2.2.4. Other Data
The TerraClimate dataset is a global, monthly scale, high-spatial-resolution (5 km) climate dataset. This dataset contains the PDSI, which was widely recognized by the international community [50,51,52]. Therefore, the PDSI based on the TerraClimate dataset was selected as the reference data, and the reliability of each drought index was expressed by the results of the correlation analysis between this index and the PDSI. Pearson correlation analysis is a widely used mathematical method to analyze the relationship of multiple variables. This method can accurately and efficiently identify the size of correlation between different variables. The results of correlation analysis have important reference significance for us to deeply understand the essential characteristics of variables. Therefore, Pearson correlation analysis between each drought index and PDSI was selected. TerraClimate data are available through the GEE platform (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets; accessed on 10 November 2021).
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. SPI
In 1993, McKee first proposed the SPI, which was recognized as the primary index for drought research by the WMO [53]. In the past two decades, the SPI has been widely used for different drought research [54,55,56,57,58]. The calculation of the SPI can be divided into two steps. First, gamma distribution fitting of the long time series rainfall records in a specific time scale is conducted to find the precipitation probability distribution. Second, the gamma probability distribution is transformed to the normal distribution as the SPI [18,59]. Here, we calculated the SPI indices at 1 month named SPI-1, 3 months named SPI-3, and 12 months named SPI-12 in the SGN area from 1982 to 2020. When the SPI > 0, it indicated a higher precipitation than the average value, and the environmental condition was wet, and when the SPI < 0, it indicated a dry condition. The frequency distribution function is as follows:
The SPI can be calculated by Equations (2) and (3):
while F > 0.5, S = 1; while F ≤ 0.5, S = −1. , , , , , .
2.3.2. VHI
The VHI was proposed by Kogan and considers the NDVI and LST and is weighted by the VCI and TCI [60,61]. The VCI and TCI reflect the changes of vegetation and land surface temperature over time and space, respectively, and the calculation method is shown in Equations (4) and (5). Low NDVI and high LST values are usually associated with severe drought events. Combining Equations (4) and (5), it can be seen that the smaller values of VCI and TCI indicated a more severe drought. Therefore, when a severe drought event occurs, the VHI has a lower value.
where NDVImax, NDVImin, LSTmax, and LSTmin are respectively the maximum and minimum values of the NDVI and LST during the period 2003–2020; a is the weight of VCI, and b is the weight of TCI. Since the contribution of water and temperature to vegetation growth is difficult to quantify, when calculating the VHI, we selected the same weighting coefficient for the VCI and TCI indices [62].
2.3.3. NVSWI
In drought conditions, vegetation prevents water loss from leaves by closing their stomata. Therefore, the evapotranspiration decreases with the surface temperature increases. While the soil moisture sufficient, the surface temperature of the vegetation canopy is usually lower than in bare lands [27,63]. We used NDVI, LST, and Equation (7) to calculate the VSWI. Because the VSWI can only represent the inverse relationship of the NDVI and LST, it cannot characterize the changing characteristics of drought [27]. In this study, Equation (8) was used to normalize the VSWI to obtain the Normalized Vegetation Supply Water Index (NVSWI).
where VSWImax is the maximum VSWI, and VSWImin is the minimum VSWI from 2003 to 2020, respectively.
2.3.4. SMADI
The SMADI combines soil moisture, vegetation index, and surface temperature information [28,64]. The generate method is essentially considered the inverse relationship of the LST and NDVI. Both land surface temperature and vegetation response are strongly connected with soil moisture, and changes in the LST and NDVI are often used to identify soil moisture. Thus, it is necessary to consider soil moisture information when calculating the SMADI [65]. Since the NDVI, LST, and Soil Moisture (SM) have completely different dimensions, they cannot be used directly in the calculation of the SMADI. Therefore, it is necessary to normalize the NDVI, LST, and SM data to obtain the VCI, MTCI (Equation (9)), and SMCI (Equation (10)). The SMADI is calculated by Equation (11), where MTCI/VCI emphasizes the inverse relationship between the LST and NDVI, and the SMCI is the product factor [64]. From Equations (4) and (9)–(11), it can be seen that the SMADI is opposite of the SPI, VHI, and NVSWI on recognition of drought. The larger SMADI value represents a severer drought.
where LSTmax, LSTmin, SMmax, and SMmin represent the maximum and minimum values of LST and SM during the period 2003–2020, respectively.
2.3.5. Trend Analysis
We used parametric and non-parametric methods to determine the significance in changes of the time series climate data. The parameter test method requires the data to obey an independent normal distribution, while the non-parametric test method only requires the data independence [66]. Here, we used the Mann–Kendall test [67] and Sen’s slope [68] to analyze the significance of the trends in the drought indices. The Mann–Kendall test and Sen’s slope estimator are widely used to determine whether temporal trends of time series data are statistically significant [69,70,71,72,73,74].
The calculation of the variance Var(S) of the test statistic S is shown in Equation (12):
where n represents the length of the data sequence, m represents how many tie groups, and ti represents the width of the ith tie groups (the number of repeated data in the ith repeated tie group). If n > 10, the statistic Zs is obtained by Equation (13):
when Zs > 0, it represents an upward trend; when Zs < 0, it means there is a downward trend; and when Zs = 0, it means there is no obvious trend.
Sen’s slope estimator method was proposed by Sen in 1968 [68]. If there is a time series Xi, the data series Q is constructed by Equation (14):
where xj and xi are the jth and ith observations in Xi (j > i), N = n(n − 1)/2.
After sorting the Qi data sequence from small to large, we used Equation (15) to calculate the median of Qi(Qmed):
when Qmed > 0, it represents an ascending trend; when Qmed < 0, it represents a descending trend.
2.3.6. Assessment Criterion
Table 1 shows the classification schemes of different drought indices. We divided the regional drought conditions into six categories: Extreme, Severe, Moderate, Mild, Abnormal, and Moist. The larger the SMCI and SMADI values, the more severe the drought. The smaller values of other index represents a severer drought condition.

Table 1.
Drought severity classifications by drought index.
According to the drought classification system in Table 1, we analyzed the frequency, duration, and severity of drought in the SGN area during the period 2003–2020. The calculation of drought frequency is shown in Equation (16):
where f is drought frequency, m is the number of dry months, and n is number of months during 2003–2020.
2.3.7. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
To verify the reliability of each drought index in different times and spaces, we selected the PDSI in the TerraClimate dataset as reference data and calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient of the SPI, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, and SMADI with PDSI. The Pearson correlation can effectively measure the linear correlation between two samples calculated based on sample data. For samples X and Y, the coefficient r can be calculated by the following Equation (17):
where n represents the sample numbers, xi and yi are the ith sample value of X and Y, respectively, and and represent the sample mean value of X and Y, respectively.
3. Results
To explore the spatiotemporal change of drought in the SGN region and the differences between different drought indices, we analyzed the trends of time series, spatial distribution pattern, drought intensity identification, and the correlation of each index and the PDSI. Results for all indices indicated that the SGN region was constantly wetting during the period 2003–2020. We would like to note that the CHIRPS used in this study is one of the source data to produce FLDAS data, that is, there is a certain autocorrelation between CHIRPS and FLDAS, so the SPI, SMCI, and SMADI comparison results may have some errors. However, because the computational theory of the SPI, SMCI, and SMADI is not consistent, this error is completely within the reasonable range and does not have much impact on our results.
3.1. Temporal Comparisons
3.1.1. Time Series Comparisons
To explore the temporal characteristics of drought in the recent 20 years in the SGN region, we used the Mean Value Composite method (MVC) to calculate the time series of different drought indices in the SGN area (Figure 2). We found that during 2003–2020, six drought indices had an upward trend: SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-12, VCI, VHI, and NVSWI (Figure 2a–d,f,g. The SMCI and SMADI had a downward trend (Figure 2h,i), and the only drought index based on Land Surface Temperature, TCI, had no significant trend (R2 = 0.0087) (albeit a slight upward trend (Figure 2e)). Thus, the SGN area became more humid during 2003–2020. As seen in Figure 2a–i, the drought indices VCI, VHI, NVSWI, and SMADI were related to the vegetation index (NDVI) and had the most significant trends (R2 > 0.8). The precipitation-related drought indices, SPI-1, SPI-3, and SPI-12, and the soil moisture-based drought index SMCI had significant trends (R2 < 0.6). These results indirectly indicated that during 2003–2020, the vegetation coverage in the three provinces of the SGN area increased significantly and the precipitation and soil moisture steadily increased. It also indicated that in the past 20 years, the environmental protection and governmental policies related to afforestation, windbreak, and sand fixation in the SGN area have had positive effects by reducing drought severity.
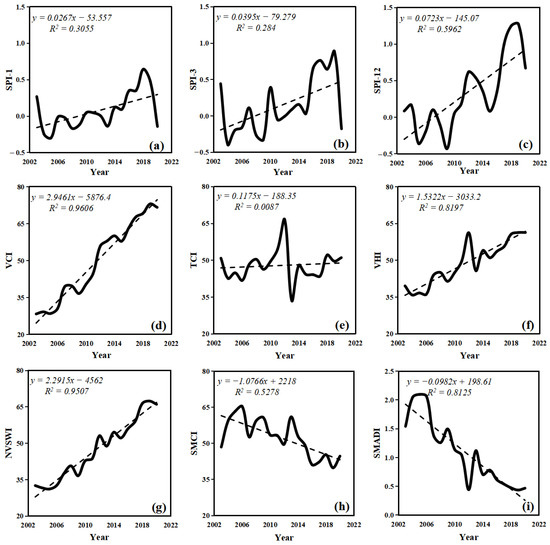
Figure 2.
Time series of different drought indices in SGN for the period 2003–2020. (a) SPI-1. (b) SPI-3. (c) SPI-12. (d) VCI. (e) TCI. (f) VHI. (g) NVSWI. (h) SMCI. (i) SMADI.
3.1.2. Trend Analysis Comparisons
Here, we used the Mann–Kendall trend test to determine the significance of the trends of the drought indices over time, which are shown in Figure 3 and Table 2. We divided the significant and non-significant trends into four types: Significant Wetting (SW) (slope > 0, p < 0.05), Non-Significant Wetting (NSW) (slope > 0, p ≥ 0.05), Significant Drying (SD) (slope < 0, p < 0.05), and Non-Significant Drying (NSD) (slope < 0, p ≥ 0.05) (because the SMCI and SMADI had a negative correlation with other indices, we used the opposite of the SMCI and SMADI in trend analysis).
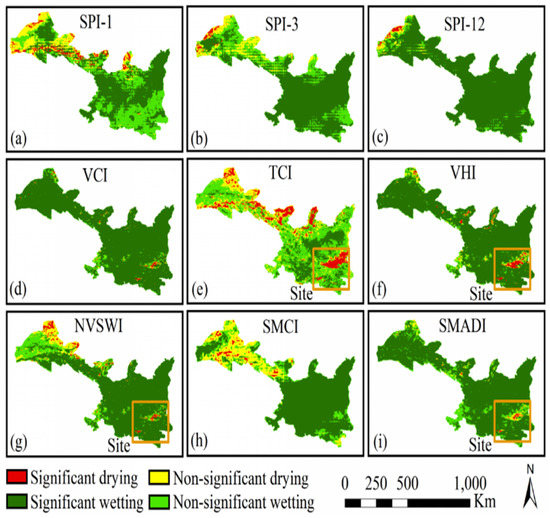
Figure 3.
Trends of different drought indices in SGN for the period 2003–2020. (a) SPI-1. (b) SPI-3. (c) SPI-12. (d) VCI. (e) TCI. (f) VHI. (g) NVSWI. (h) SMCI. (i) SMADI.

Table 2.
Area statistics of trend analysis.
It can be seen from Figure 3 and Table 2 that during 2003–2020, the SGN area continued to become more humid. All indices showed that the wetting area (combined of significant and non-significant wetting area) exceeding 70% of the study area (Table 2). The SPI-12, VCI, VHI, and SMADI indices had a significant wetting trend over 80% of the study area (Figure 3c,d,f,i, Table 2), and the TCI had the lowest significant wetting trend with the area of SW, only 21.21% (Figure 3e, Table 2). SPI-1 indicated that Ningxia and the southern part of Shaanxi Province had a non-significant wetting trend (Figure 3a), and SPI-3 indicated that the northern part of the study area had a non-significant wetting trend and that the southern part of the study area had a significant wetting trend (Figure 3b). The NVSWI indicated that the northwestern part of Gansu had a non-significant wetting or drying trend and that other areas had a significant wetting trend (Figure 3g). The SMCI, which was based on soil moisture, indicated that the northern part of Gansu had a non-significant drying trend and that the southern part of Gansu and the provinces of Ningxia and Shaanxi had significant wetting trends (Figure 3h). It is worth noting that all drought indices that were related to Land Surface Temperature (TCI, VHI, NVSWI, and SMADI) had significant drying trends in the central part of Shaanxi Province (boxed area in Figure 3e–g,i. Thus, the extreme drought in this region may be directly caused by the higher temperature.
3.2. Spatial Comparisons
To compare the similarities and differences of the spatial distribution of different indices, we mapped the spatial distribution of the nine drought indices (SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-12, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, SMADI) in four different months (February, May, August, and November) of 2004, 2009, and 2015 (Figures S1–S3 in Supplementary Materials).
According to the spatial distribution of the three meteorological drought indices, SPI-1, SPI-3, and SPI-12, drought severity in the SGN area was relatively low, and there are few areas of extreme and severe drought. SPI-1 indicated severe droughts in November 2004 and August 2015, and extreme moisture was observed in August and November 2004; February, May, August, and November 2009; and November 2015. SPI-3 indicated severe droughts in February and May 2004; February, May, and August 2009; and February and August 2015, and moist conditions were present in November 2009 and May and November 2015. SPI-12 indicated severe drought only in 2009 and indicated that conditions were moist in February and May 2004 and February, May, and August 2015.
Compared with the three different time scales for the SPI indices, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, and SMADI indicated that there were extreme droughts almost every month. Each of these six indices showed more severe drought conditions than the SPI indices. Because these indices consider vegetation condition, and because vegetation growth is closely related to temperature and soil moisture, these indices are more conducive for monitoring agricultural drought than the SPI indices. According to Figures S1–S3, the entire SGN area encountered extreme and severe droughts in 2004. In 2009, except for the SMCI, the areas of extreme and severe droughts monitored by other indices were significantly lower than in 2004. In 2015, the area of extreme and severe drought further decreased.
These findings agree with the wetting trend described in Section 3.1. Among all drought indices, the drought conditions represented by the SMCI were more severe than that of other indices. Except for November 2015, the SMCI detected extreme drought conditions in the entire study area. The spatial distributions of the two single factor drought indices, VCI and TCI, were the same in February and May, and there were significant differences in August and November. For the two multi-factor drought indices that were based on temperature and the NDVI, VHI, and NVSWI, the drought severity as indicated by the NVSWI was more severe than that indicated by the VHI. Comparing the spatial distribution of the VCI, TCI, VHI, and NVSWI in Figures S1–S3, the NVSWI and VCI and VHI and TCI were strongly consistent, respectively.
3.3. Drought Assessment Comparisons
We analyzed the frequency, duration, and severity of drought in the SGN area during the period 2003–2020. The results are shown in Figure 4 and Figure S4. Figure 4 shows the temporal characteristics of SPI-3, SPI-12, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, and SMADI in the study area from 2003 to 2020. Figure 4b,c,e,f,h shows that during 2003–2020, the average drought in the SGN area characterized by SPI-12, VCI, VHI, NVSWI, and SMADI gradually weakened, and the frequency, duration, and severity of droughts clearly decreased. From 2003 to 2011, the SGN area suffered from a severe drought that lasted for many years. From 2012–2020, the SGN area was generally moist. As shown in Figure 4a,g, the changes in SPI-3 and the SMCI were not obvious, but the frequency, duration, and severity of droughts still decreased. In Figure 4d, the TCI was very stable during 2003–2020, and the frequency, duration, and severity of the drought conditions represented by them did not change significantly. This result indicated that the drought in the SGN area was less affected by temperature.
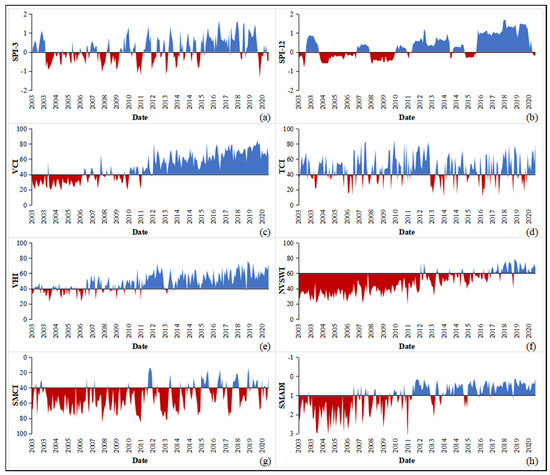
Figure 4.
Drought indices in the regions of SGN from 2003 to 2020. (a) SPI-3. (b) SPI-12. (c) VCI. (d) TCI. (e) VHI. (f) NVSWI. (g) SMCI. (h) SMADI.
Figure S4 shows drought frequency maps of all nine drought indices in three different time periods (2003–2011, 2012–2020, 2003–2020) in the SGN area. According to Figure S4, the frequency of drought as determined by the NVSWI and SMCI was highest in the three time periods. During 2003–2011, the frequency of droughts as indicated by the TCI, VHI, and SMADI in the entire study area was low (<0.5), the frequency of droughts as indicated by SPI-1 and SPI-3 in the entire study area was moderate (0.5–0.6), and the frequency of drought as indicated by SPI-12 was very low (<0.4) in Central Gansu and Southern Shaanxi. The VCI had a high drought frequency in the entire study area (>0.7), and the NVSWI and SMCI indicated that the entire study area had high drought frequency.
During 2012–2020, the drought frequency as indicated by SPI-12, VCI, VHI, and SMADI was very low (<0.4) in all regions of the study area, and the drought frequencies as indicated by SPI-1, SPI-3, and TCI were lower than 0.5 in the entire study area. The NVSWI had the highest drought frequency (>0.7) in Northwest Gansu, a low drought frequency (0.4–0.5) in Southeast Gansu and Ningxia, and the lowest drought frequency in Shaanxi (<0.4). The SMCI had the highest drought frequency (>0.7) in the northwest of the study area and a moderate drought frequency (0.4–0.6) in the southeast of the study area. During 2012–2020, the frequency of droughts for all indices was lower than the frequency of droughts during 2003–2011. The frequency of droughts as indicated by SPI-12 and the VCI decreased the most substantially, and the frequency of droughts as indicated by the TCI decreased the least.
3.4. Correlation Comparisons
We also analyzed the Pearson correlations between SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-12, VCI, TCI, VHI, NVSWI, SMCI, SMADI, and PDSI (Figure 5). We found that all drought indices had a significant correlation with the PDSI. SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-12, VCI, TCI, VHI, and NVSWI had a positive correlation with the PDSI, and the SMCI and SMADI had a negative correlation with PDSI. As shown in Figure 5, SPI-12 had the strongest positive correlation with the PDSI, and the SMCI had the strongest negative correlation with the PDSI. SPI-1, SPI-3, and SPI-12 had stronger positive correlations with the PDSI than did the VCI, TCI, VHI, and NVSWI. The correlations for the NDVI-based drought indices (VCI, VHI, and NVSWI) were stronger during the growing season (April to September) than during other months. The TCI, based on the LST, had a stable correlation with the PDSI in all months. The negative correlation between the SMCI and PDSI was stronger than that for the SMADI.
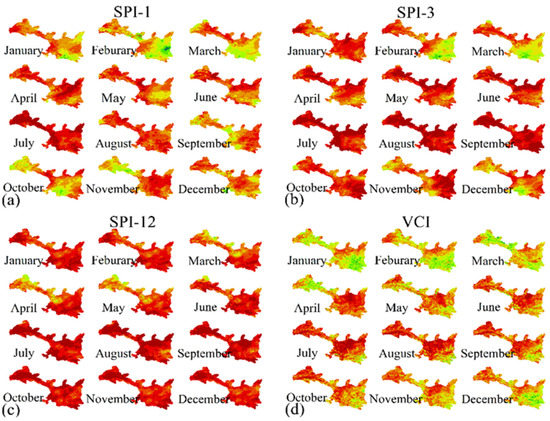
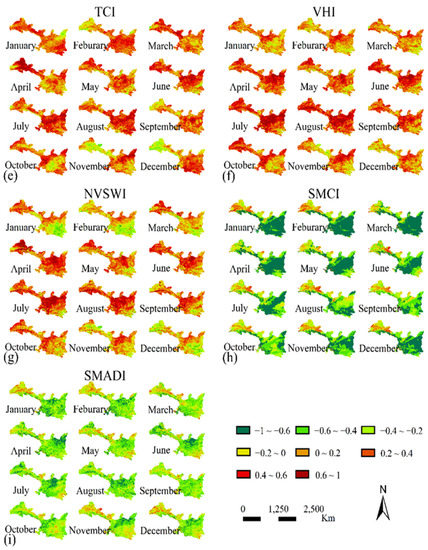
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of Pearson’s correlation between the PDSI and different drought indices in the SGN region. (a) SPI-1. (b) SPI-3. (c)SPI-12. (d) VCI. (e) TCI. (f) VHI. (g) NVSWI. (h) SMCI. (i) SMADI.
4. Discussion
4.1. Trends of Drought in SGN Area
The spatiotemporal pattern contrast results of nine different drought indices clearly clarified that the SGN region continued to be humidified during 2003–2020, the VCI showed the most significant wetting trend (R2 = 0.9606, p < 0.05), and the TCI showed the weakest wetting trend (R2 = 0.0087, p > 0.05), which is highly consistent with many previous studies. For example, Wang et al. used the self-calibrating PDSI (scPDSI) to analyze the drought changes in mainland China from 1961 to 2009 and found a wetting trend [33]. Zheng et al. concluded that the degree of drought in Northwest China declined by analyzing the changes in precipitation and temperature from 1959 to 2019 [75]. Xu et al. used the SPI, SPEI, and scPDSI to research the seasonal drought in mainland China and found that the drought continued to weaken in the period 2000–2019 [14].
Generally, changes in drought frequency and severity are closely related to the climate changes including precipitation, temperature, evapotranspiration, soil moisture, and vegetation status [76]. In recent years, due to global warming, global mean annual air temperature has risen significantly, which has accelerated the melting of glaciers and snow in the Qilian Mountains, increased surface runoff, and gradually increased soil moisture in the SGN area. Under the influence of West Pacific Subtropical High (WPSH) and North America Subtropical High (NASH), the annual precipitation also has a positive trend [77].
Moreover, the sea surface temperature anomalies, such as the El Niño and La Niña phenomena, have been also widely attributed as factors that drive changes in drought frequency and severity [29,31,33]. During El Niño, due to abnormal sea surface temperatures, the atmospheric thermal field changes, which leads to changes in weather conditions in various places. Generally, the occurrence of El Niño will increase the drought level in South China, the North China Plain, and Northwest China [78,79,80]. Presently, analyses of the driving factors of changes in global drought frequency and severity are insufficient. To explore the root causes of drought is more important. The continuous deepening of these studies will effectively promote a deep understanding of the nature of drought disasters in human society.
4.2. Advantages of Comparing Various Drought Indices
Although there are also many findings that indicate increased drought in Northwest China in recent decades, these studies may not be comprehensive, and they often ignore the differences between different drought indices. For example, Gong et al. (2021) [81] used the SPI and SPEI to analyze the spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in China and found that drought in Northwestern China intensified with global warming. Yu et al. (2014) [34] used the PDSI to analyze the frequency, severity, and duration of droughts in China from 1951 to 2010 and found that in the late 1990s, extreme droughts became more severe. Zhao et al. (2017) [35] used the modified Temperature Vegetation Drought Index (mTVDI) to analyze the spatiotemporal pattern of drought in China and found that the frequency of droughts from 1982 to 2010 had an overall upward trend; the frequency of severe droughts increased significantly, and the frequency of mild droughts gradually increased. Compared with these results, our study selected more drought indices, considered more of the influencing factors related to drought, and compared the differences of all these drought indices in the spatiotemporal pattern. Although the autocorrelation problem arising from the use of CHIRPS and FLDAS data to calculate the SPI, SMCI, and SMADI is ignored in our study and the study time frame is shorter and more inconsistent than existing studies, our study still provides more comprehensive and convincing results, which have important reference significance for us to reasonably solve the controversial problems in drought research.
4.3. Limitations
Our findings have clarified the drought changing trends in the SGN area from 2003 to 2020, but there are still some uncertainties. First, the duration of our study is not long enough, so our results have better reference significance for the understanding of short-term drought conditions and not much reference value for longer-term drought trends [82,83]. Second, because we removed cloud contaminated pixels from the satellite data, the resultant gaps in the NDVI and LST data and the subsequent gap filling and smoothing of these data resulted in a small number of abnormal values and data discontinuities in the input data used to calculate the drought indices. Even if these conditions have a small impact on the research results, these problems may cause errors in the index calculation results and further affect the accurate identification of drought conditions. Third, since CHIRPS is used in the production of FLDAS data, there may be some autocorrelation between SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-3, SPI-12, and the SMCI and the SMDI and SMADI, and there may be some uncertainty in the spatial and temporal pattern contrast between the SPI and SMCI and SMADI. Finally, although we analyzed the differences of various drought indices, the inherent nature of their differences remains unclear. Additional analyses are needed to explore the essential differences between different drought indices. It is helpful to construct a drought index that is more accurate and more in line with actual conditions.
5. Conclusions
The occurrence of drought disasters not only has an important impact on the current ecological environment, agricultural production, people’s life, and economic development but also may cause the deterioration of climate conditions and land desertification for many years. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the nature of drought disasters, deeply analyze the spatiotemporal characteristics of drought disasters, and prevent and control drought disasters through scientific methods. The exploration of drought disasters is still incomplete, as they often consider only a single drought index and rarely explore the combined effects of multiple drought influencing factors. Different from the previous studies, this study took the SGN, the most important population gathering area in Northwest China, and analyzed the spatial and temporal changes of various drought indices when considering precipitation, vegetation index, surface temperature, and soil moisture information. Our results clarified that during the period of 2003–2020, the SGN area was generally wetting, and the frequency, duration, and severity of drought have continuously reduced. The growth trend of the VCI is the most obvious, which shows that a large number of index afforestation projects in Northwest China have played a very important role in the improvement of the natural environment in the past 20 years. The increase in the SPI-1, SPI-3, and SPI-12 indices and the decreasing SMCI and SMADI indices indicate increasing precipitation and soil moisture in the SGN. The lack of significant changes in the TCI indicates that the surface temperature has not changed significantly in the past 20 years and is not the main reason for the continuous wetting of the SGN area. Overall, the wetting trend of the SGN area in the past 20 years is mainly closely related to the increased precipitation and soil moisture and the index afforestation activities strongly promoted by the government sector. The results of this study are important for our deep understanding of the nature of drought in Northwest China, our research method is fully applicable to other wider regions, and future research can be further deepened.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs14071570/s1, Figure S1: Spatial pattern of different drought indices in the SGN for the year 2004; Figure S2: Spatial pattern of different drought indices in the SGN for the year 2009; Figure S3: Spatial pattern of different drought indices in the SGN for the year 2015; Figure S4: Drought frequencies in the SGN region for 2003–2011, 2012–2020, and 2003–2020.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; methodology, X.Z., H.X.; software, X.Z.; validation, X.Z., H.X. and W.J.; formal analysis, X.Z., H.X. and W.J.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, X.Z.; data curation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z. and H.X.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., H.X., B.L. and W.J.; visualization, X.Z. and H.X.; supervision, H.X.; project administration, H.X.; funding acquisition, H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by “National Natural Science Foundation Project of China (32130066)”, “Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Research Project (212102310019)”, “Natural Science Foundation of Henan (202300410531)”, and “Youth Science Foundation Program of Henan Natural Science Foundation (202300410077)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
CHIRPS, MODIS, FLDAS, and TerraClimate data are openly available via the Google Earth Engine.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers whose constructive suggestions have improved the quality of this study. We also wish to express our gratitude to the USGS and GEE platform for supplying CHIRPS, MODIS, FLDAS, and TerraClimate data. We are grateful to the data support from the Data Center of Middle & Lower Yellow River Regions, the National Earth System Science Data Center, and the National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. (http://henu.geodata.cn, accessed on 14 October 2021). We also wish to express our gratitude to the Dabieshan National Observation and Research Field Station of Forest Ecosystem at Henan for supplying the computer platform.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Doughty, R.; Xiao, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bajgain, R.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zou, Z.; McCarthy, H.; Friedman, J. Responses of gross primary production of grasslands and croplands under drought, pluvial, and irrigation conditions during 2010–2016, Oklahoma, USA. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Yu, M. Drought assessment using a multivariate drought index in the Luanhe River basin of Northern China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, M.; Wang, H.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Yu, M. Drought assessment using a multivariate drought index in the Huaihe River basin of Eastern China. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 369, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Y.; Li, Q.F.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Li, P.C.; Zhang, J.X. Analysis of spatio-temporal evolution of droughts in Luanhe River Basin using different drought indices. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Tong, Q. Studying drought phenomena in the Continental United States in 2011 and 2012 using various drought indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Keyantash, J.A.; Dracup, J.A. An aggregate drought index: Assessing drought severity based on fluctuations in the hydrologic cycle and surface water storage. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelmi, O.V.; Wilhite, D.A. Assessing vulnerability to agricultural drought: A Nebraska case study. Nat. Hazards 2002, 25, 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Lü, A.; Wu, Z. Comparison of remotely sensed and meteorological data-derived drought indices in mid-eastern China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1755–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Quiring, S.M.; Papakryiakou, T.N. An evaluation of agricultural drought indices for the Canadian prairies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 118, 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dracup, J.A.; Lee, K.S.; Paulson, E.G., Jr. On the statistical characteristics of drought events. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.G.S.S.; Neto, A.R.; de Souza, L.L. Soil moisture-based index for agricultural drought assessment: SMADI application in Pernambuco State-Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Jia, G. Monitoring meteorological drought in semiarid regions using multi-sensor microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R. Multi-scale assessments of droughts: A case study in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J.; Wang, X.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Shan, S.Y.; Guo, J. Seasonal and aridity influences on the relationships between drought indices and hydrological variables over China. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2021, 34, 100393. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Huete, A.; Cleverly, J.; Eamus, D.; Chevallier, F.; Joiner, J.; Poulter, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guanter, L.; Meyer, W. Drought rapidly diminishes the large net CO2 uptake in 2011 over semi-arid Australia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.J.; Wang, X.P.; Zhao, C.Y. Drought sensitivity of vegetation photosynthesis along the aridity gradient in northern China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102418. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 30.
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, F.N. Droughts of the late 1980s in the United States as derived from NOAA polar-orbiting satellite data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 655–668. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, F.N. Application of vegetation index and brightness temperature for drought detection. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 15, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, F. World droughts in the new millennium from AVHRR—Based vegetation health indices. Eos. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2002, 83, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, M.; Babaeian, E.; Tuller, M.; Jones, S.B. The optical trapezoid model: A novel approach to remote sensing of soil moisture applied to Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, H.; Pan, L.; Song, H.; Niu, W.; Wang, R.; Li, R.; Bian, X.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Drought monitoring over Yellow River basin from 2003–2019 using reconstructed MODIS land surface temperature in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3748. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, J.; Im, J.; Carbone, G.J. Monitoring agricultural drought for arid and humid regions using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, S.; Nichol, J.E.; Qamer, F.M.; Xu, J. Characterization of drought development through remote sensing: A case study in Central Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4998–5018. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; González-Zamora, Á.; Piles, M.; Martínez-Fernández, J. A new Soil Moisture Agricultural Drought Index (SMADI) integrating MODIS and SMOS products: A case of study over the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Van Der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global warming and changes in drought. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F.; Roderick, M.L. Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 2012, 491, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A. Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, W.; Yao, N.; Li, L.; Liu, D.L. Spatiotemporal variability of standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index in mainland China over 1961–2016. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4781–4799. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. Does drought in China show a significant decreasing trend from 1961 to 2009? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 314–324. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Guo, R.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J. Spatial and temporal analysis of drought risk during the crop-growing season over northeast China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Cong, D.; He, K.; Yang, H.; Qin, Z. Spatial-temporal variation of drought in China from 1982 to 2010 based on a modified temperature vegetation drought index (mTVDI). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Dai, S.; Ma, J. Evolution characteristics of seasonal drought in the south of China during the past 58 years based on standardized precipitation index. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, Y. Combined use of meteorological drought indices at multi-time scales for improving hydrological drought detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Goswami, S.; Matin, S.; Sarup, J. Analyzing the extent of drought in the Rajasthan state of India using vegetation condition index and standardized precipitation index. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 601–610. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Xie, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. Comparative evaluation of drought indices for monitoring drought based on remote sensing data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20408–20425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ali, S.; Ma, Q.; Sun, L.; Jiang, N.; Jia, Q.; Hou, F. Remote sensing strategies to characterization of drought, vegetation dynamics in relation to climate change from 1983 to 2016 in Tibet and Xinjiang Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21085–21100. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Haixing, Z.; Qi, M.; Liang, S.; Ning, J.; Jia, Q.; Hou, F. Monitoring drought events and vegetation dynamics in relation to climate change over mainland China from 1983 to 2016. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21910–21925. [Google Scholar]
- Salvia, M.; Sanchez, N.; Piles, M.; Ruscica, R.; Gonzalez-Zamora, A.; Roitberg, E.; Martinez-Fernandez, J. The added-value of remotely-sensed soil moisture data for agricultural drought detection in Argentina. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6487–6500. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; He, J.; Yin, G.; Wen, F.; Wu, H. Spatiotemporal variability in land surface temperature over the mountainous region affected by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake from 2000 to 2017. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1975–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, S.-B. Reconstruction of daytime land surface temperatures under cloud-covered conditions using integrated MODIS/Terra land products and MSG geostationary satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111931. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Mapping winter crops using a phenology algorithm, time-series Sentinel-2 and Landsat-7/8 images, and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2510. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, H.; Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, R. Mapping the northern limit of double cropping using a phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Perera, S.; Linstead, E.; Thomas, R.; El-Askary, H.; Piechota, T.; Struppa, D. Investigating decadal changes of multiple hydrological products and land-cover changes in the Mediterranean Region for 2009–2018. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 285–302. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, A.; Arsenault, K.; Kumar, S.; Shukla, S.; Peterson, P.; Wang, S.; Funk, C.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Verdin, J.P. A land data assimilation system for sub-Saharan Africa food and water security applications. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Parks, S.A.; Hegewisch, K.C. TerraClimate, a high-resolution global dataset of monthly climate and climatic water balance from 1958–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Gao, H. Estimating reservoir evaporation losses for the United States: Fusing remote sensing and modeling approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Divergent shifts in peak photosynthesis timing of temperate and alpine grasslands in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111395. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G.; Wang, H.; Leng, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y. Probabilistic assessment of remote sensing-based terrestrial vegetation vulnerability to drought stress of the Loess Plateau in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111290. [Google Scholar]
- Alami, M.M.; Hayat, E.; Tayfur, G. Proposing a popular method for meteorological drought monitoring in the Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 4, 237199. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.R.; Nikoo, M.R. A fusion-based methodology for meteorological drought estimation using remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 229–247. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, T.; Li, Y.; Rashid, S.; Li, F.; Hu, Q.; Feng, H.; Chen, X.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, F.; Pulatov, B. Performance and relationship of four different agricultural drought indices for drought monitoring in China’s mainland using remote sensing data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Tian, C.; Chang, Q.; Novick, K.A.; Wang, L. A new multi-sensor integrated index for drought monitoring. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, O.; Kim, S. Copula-based Joint Drought Index using SPI and EDDI and its application to climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140701. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, F.N. Operational space technology for global vegetation assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Kogan, F.N. Global drought watch from space. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 621–636. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q. Evaluating the performance of eight drought indices for capturing soil moisture dynamics in various vegetation regions over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147803. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, D.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Duan, Z. Characterization of droughts during 2001–2014 based on remote sensing: A case study of Northeast China. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 39, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; González-Zamora, Á.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Piles, M.; Pablos, M. Integrated remote sensing approach to global agricultural drought monitoring. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, T. An overview of the “triangle method” for estimating surface evapotranspiration and soil moisture from satellite imagery. Sensors 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.O.; Abubaker, S.R. Trend analysis using Mann-Kendall, Sen’s slope estimator test and innovative trend analysis method in Yangtze river basin, China. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 8, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Long-term trends and seasonality detection of the observed flow in Yangtze River using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s innovative trend method. Water 2019, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Andrews, E.; Bigi, A.; Martucci, G.; Romanens, G.; Vogt, F.; Vuilleumier, L. Effects of the prewhitening method, the time granularity, and the time segmentation on the Mann–Kendall trend detection and the associated Sen’s slope. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6945–6964. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M. Spatio-statistical analysis of temperature fluctuation using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s slope approach. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 783–797. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, R.M.; Santos, C.A.; Moreira, M.; Corte-Real, J.; Silva, V.C.; Medeiros, I.C. Rainfall and river flow trends using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in the Cobres River basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Panchal, C.; Chandrawanshi, S.; Thanki, J. Analysis of rainfall by using Mann-Kendall trend, Sen’s slope and variability at five districts of south Gujarat, India. Mausam 2017, 68, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, B.; Peng, D.; Yu, L.; Lin, B.; Pan, Y.; Xie, Q. The trend towards a warmer and wetter climate observed in arid and semi-arid areas of northwest China from 1959 to 2019. Environ. Res. Commun. 2021, 3, 115011. [Google Scholar]
- Tramblay, Y.; Koutroulis, A.; Samaniego, L.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Volaire, F.; Boone, A.; Le Page, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Albergel, C.; Burak, S.; et al. Challenges for drought assessment in the Mediterranean region under future climate scenarios. Earth-Science Reviews. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103348. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, H.; Lian, L. Why does precipitation in northwest China show a significant increasing trend from 1960 to 2010? Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Bai, W.; Wang, J. Relationships between drought disasters and crop production during ENSO episodes across the North China Plain. Reg. Environ. Change 2015, 15, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Menzel, L.; Dong, C.; Fang, R. Temporal dynamics and spatial patterns of drought and the relation to ENSO: A case study in Northwest China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Turner, A. Increasing autumn drought over southern China associated with ENSO regime shift. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4020–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Du, S.; Li, F.; Ding, Y. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Mesoscale Drought in China under Future Climate Change Scenarios. Water 2021, 13, 2761. [Google Scholar]
- Collados-Lara, A.J.; Pulido-Velazquez, D.; Pardo-Igúzquiza, E. A statistical tool to generate potential future climate scenarios for hydrology applications. Sci. Program. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro-Monzonís, M.; Solera, A.; Ferrer, J.; Estrela, T.; Paredes-Arquiola, J. A review of water scarcity and drought indexes in water resources planning and management. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).