A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval from Landsat-8 Top of Atmosphere Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. AERONET Data
2.2. Collection-1 and -2 Landsat-8 Data
2.3. Auxiliary Data: Atmospheric Reanalysis and Digital Elevation Data
3. Method
3.1. Training and Validation Sample Collection by Collocating Landsat-8 and AERONET Observations
3.2. Deep Neural Network AOD Retrieval and Validation
4. Results
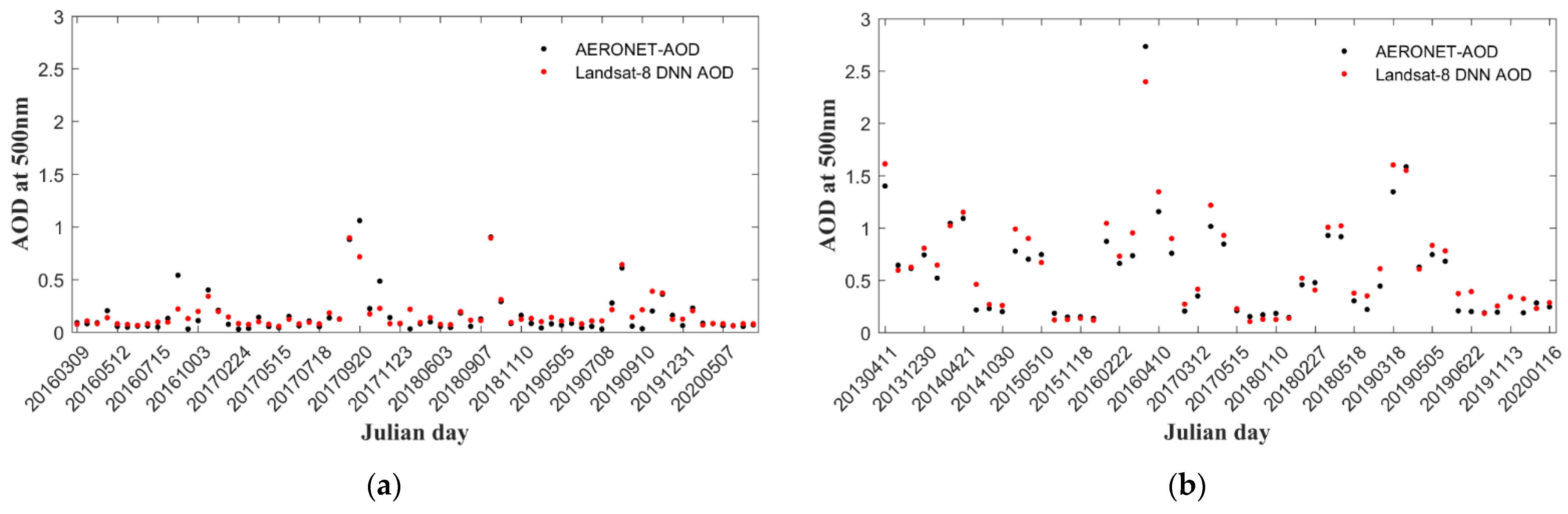
4.1. Descriptive Statistics of the Collocted Training and Validation Samples
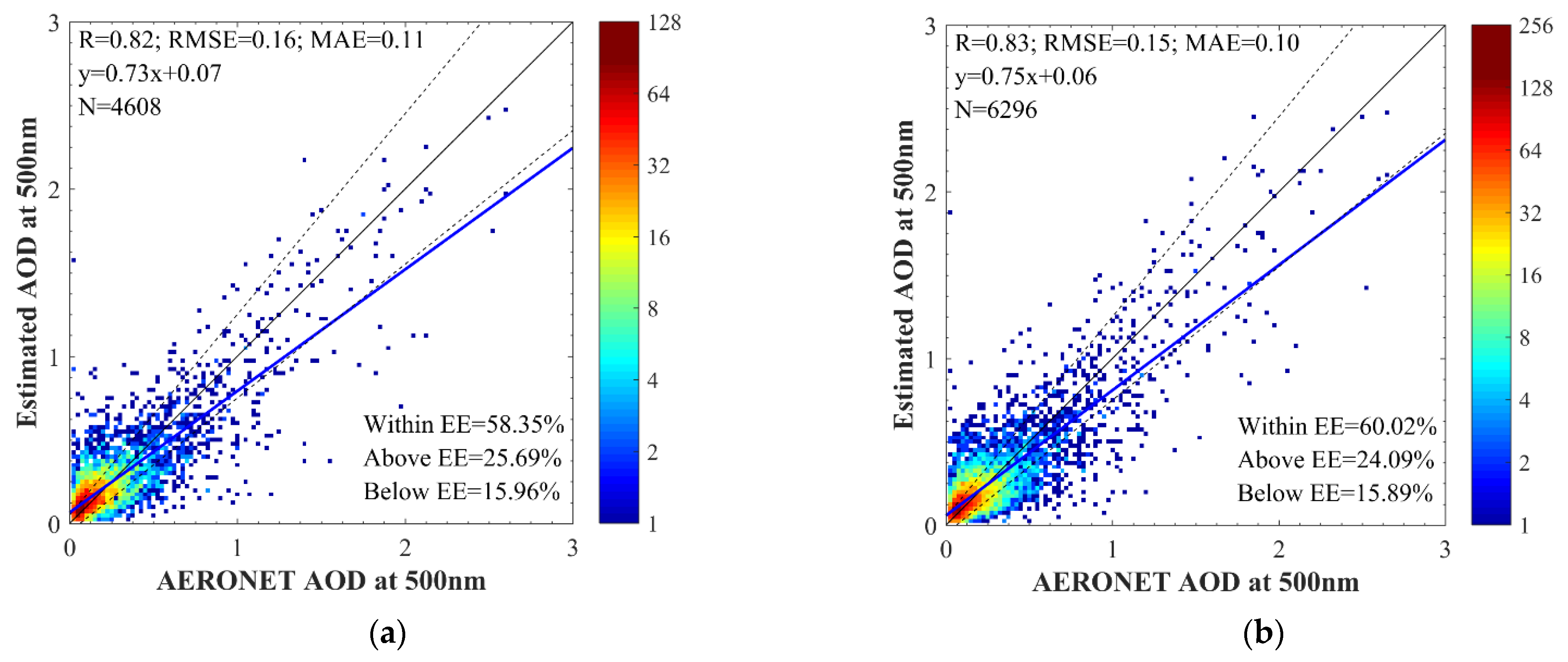
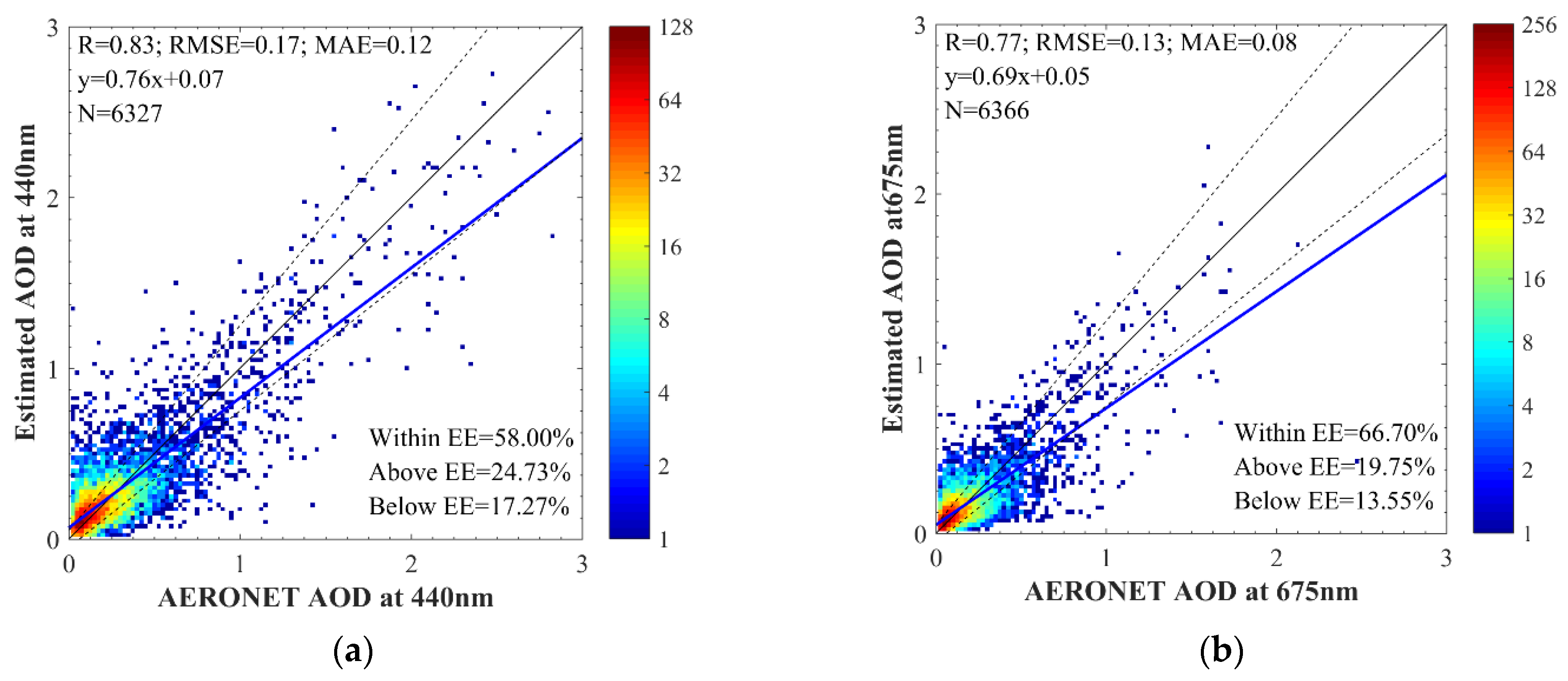
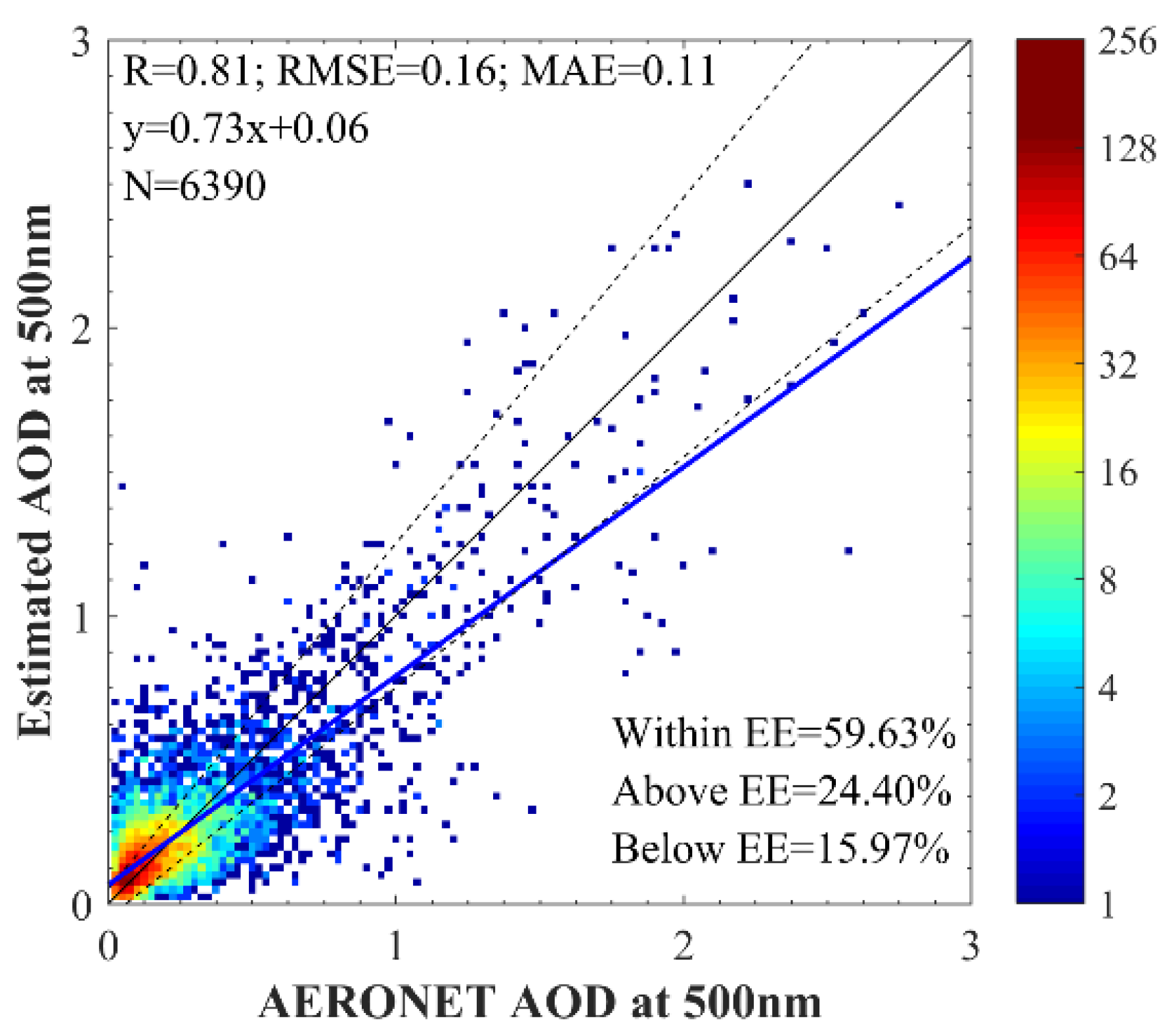
4.2. DNN AOD Validation
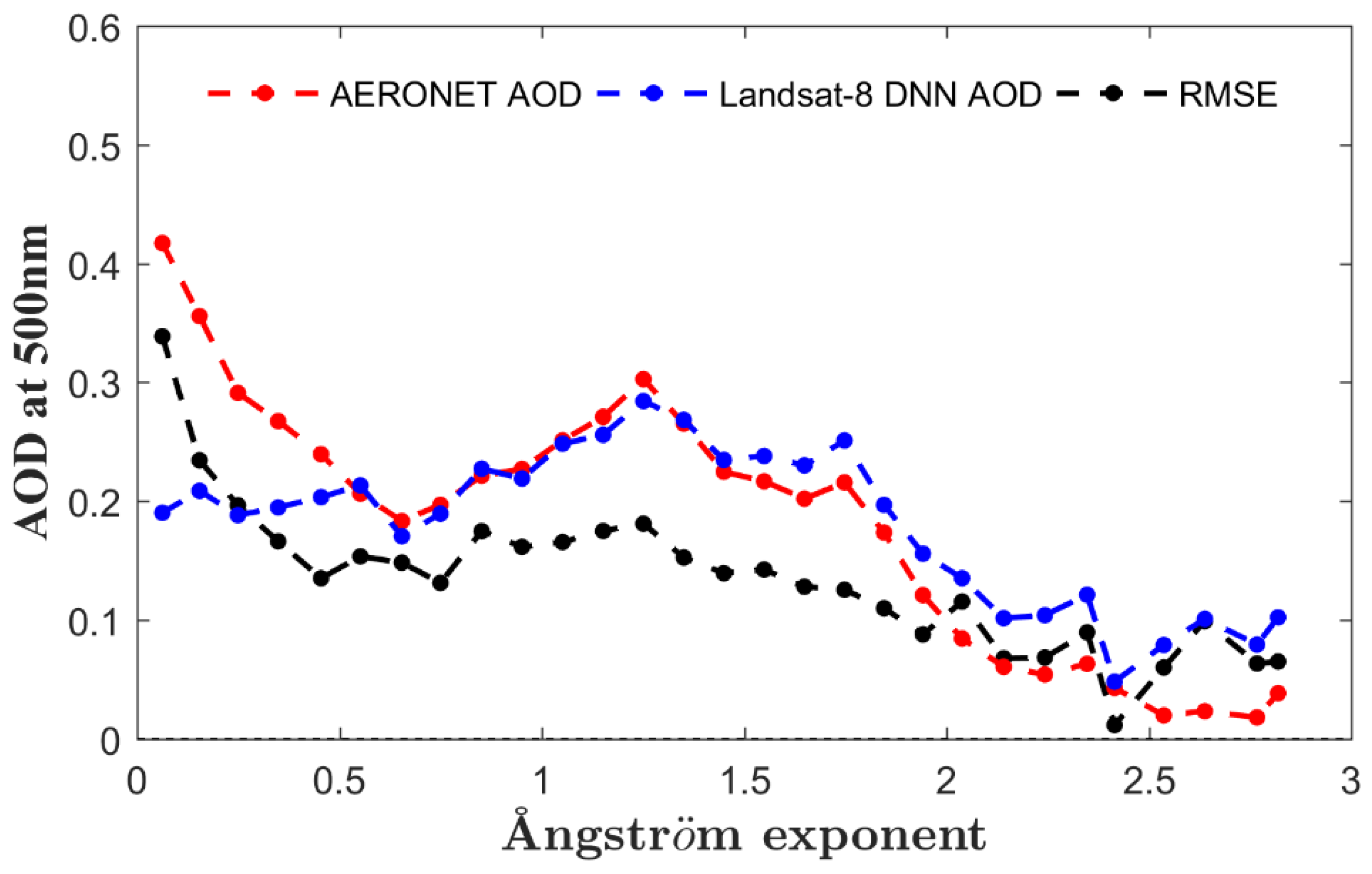
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, R.P. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T., Ed.; WMO, IPCC Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hus, N.C. The collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Garay, M.J.; Diner, D.J.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N. Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer global aerosol product assessment by comparison with the Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.E.; Carboni, E.; Sayer, A.M.; Poulsen, C.A.; Siddans, R.; Grainger, R.G. Oxford-RAL Aerosol and Cloud (ORAC): Aerosol retrievals from satellite radiometers. In Satellite Aerosol Remote Sensing over Land; Kokhanovsky, A.A., Leeuw, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 193–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Rozanov, V.; Vountas, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Levy, R.C.; Lotz, W. Retrieval of aerosol optical properties using MERIS observations: Algorithm and some first results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, M.; Murakami, H.; Suzuki, K.; Nagao, T.M.; Higurashi, A. Improved hourly estimates of aerosol optical thickness using spatiotemporal variability derived from Himawari-8 geostationary satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3442–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17051–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Near-global aerosol loading over land and ocean. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.; Broday, D.M.; Chatfield, R. Comparison and evaluation of MODIS Multi-angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) aerosol product over South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.M.; Liu, H.; Laszlo, I.; Kondragunta, S.; Remer, L.A.; Huang, J.; Huang, H.-C. Suomi-NPP VIIRS aerosol algorithms and data products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12673–12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Hou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Qie, L. A dark target method for Himawari-8/AHI aerosol retrieval: Application and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Sayer, A.M.; Carletta, N.; Chen, S.-H.; Tucker, C.J.; Holben, B.N.; Tsay, S.-C. Retrieving near-global aerosol loading over land and ocean from AVHRR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9968–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Nagao, T.M.; Murakami, H.; Nomaki, T.; Higurashi, A. Common retrieval of aerosol properties for imaging satellite sensors. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2018, 96B, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wang, W.; Hashimoto, H.; Xiong, J.; Vandal, T.; Yao, J.; Qian, L.; Ichii, K.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. First provisional land surface reflectance product from geostationary satellite Himawari-8 AHI. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zeng, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Point-surface fusion of station measurements and satellite observations for mapping PM2.5 distribution in China: Methods and assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Jin, Z. Estimating spatial variability of ground-level PM2.5 based on a satellite-derived aerosol optical depth product: Fuzhou, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, A.; de Leeuw, G.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Air pollution scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and ranking of extremely polluted cities using long-term concentrations of aerosols and trace gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Mei, L.; Xue, Y.; Che, Y.; Guang, J. SAHARA: A Simplified Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for Chinese gAofen data: 1. Aerosol Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T. High resolution aerosol optical depth retrieval using gaofen-1 WFV camera data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Huang, B.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Bilal, M. A simple and universal aerosol retrieval algorithm for Landsat series images over complex surfaces. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 13338–13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.; Vermote, E.; Saleous, N.; Wolfe, R.; Hall, F.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Gao, F.; Kutler, J.; Lim, T.-K. A Landsat surface reflectance dataset for North America, 1990-2000. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.L.; Roy, D.P.; Sauer, B.; Jenkerson, C.B.; Zhang, H.; Lymburner, L. Analysis ready data: Enabling analysis of the Landsat archive. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Roy, D.P.; Vermote, E.V.; Masek, J.; Kovalskyy, V. Continental-scale validation of MODIS-based and LEDAPS Landsat ETM+ atmospheric correction methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Roy, D.P.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Huang, H. Evaluation of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A aerosol optical depth retrievals across Chinese cities and implications for medium spatial resolution urban aerosol monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; He, T.; Yang, J. High resolution aerosol optical depth retrieval over urban areas from Landsat-8 OLI images. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, K.; Abuelgasim, A.; Alhebsi, K. Aerosol optical depth retrieval over the city of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UAE) using Landsat-8 OLI images. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, J.; He, D.; Tian, Q.; Mao, Z.; Pan, D. Retrieval of Urban Aerosol Optical Depth from Landsat 8 OLI in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q. Landsat 8-based inversion methods for aerosol optical depths in the Beijing area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; De Leeuw, G.; Huang, B. Himawari-8 Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval Using a Deep Neural Network Trained Using AERONET Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Laszlo, I.; Li, Z.; Wei, J.; Kalluri, S. Refining aerosol optical depth retrievals over land by constructing the relationship of spectral surface reflectances through deep learning: Application to Himawari-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; de Leeuw, G.; Arola, A.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K. Joint retrieval of the aerosol fine mode fraction and optical depth using MODIS spectral reflectance over northern and eastern China: Artificial neural network method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Sun, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Inversion of aerosol optical depth for Landsat8 OLI data using deep belief network. J. Remote Sen. 2020, 24, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y. Retrieval of regional Aerosol optical depth using deep learning. Acta Opt. Sin. 2021, 41, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the aerosol robotic network (AERONET) version 3 database–automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorov, A.V.; Roy, D.P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Huang, H. Landsat 4, 5 and 7 (1982 to 2017) Analysis Ready Data (ARD) observation coverage over the conterminous United States and implications for terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengarajan, R.; Storey, J.C.; Choate, M.J. Harmonizing the Landsat Ground Reference with the Sentinel-2 Global Reference Image Using Space-Based Bundle Adjustment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.K.; Roy, D.P.; Martins, V.S. Large Area, Single Pixel Time Series, Convolutional Neural Network Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 15, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on Imagenet Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift; Google: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 30 June 2016; p. 770778. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C. Tensorflow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. 2016. Available online: https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//pubs/archive/45166.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2019).
- Rodriguez, J.D.; Perez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity analysis of k-fold cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G., Jr.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the Southeastern United States using MAIAC AOD retrievals and a two-stage model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, B. Satellite-based mapping of daily high-resolution ground PM2.5 in China via space-time regression modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Nordio, F.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J. Incorporating local land use regression and satellite aerosol optical depth in a hybrid model of spatiotemporal PM2.5 exposures in the Mid-Atlantic states. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, L. Investigating the performance of satellite-based models in estimating the surface PM2.5 over China. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Levy, R.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Martins, J.V.; Ichoku, C.; Koren, I.; Yu, H.; et al. Global aerosol climatology from the MODIS satellite sensors. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.; Zhang, H.; Ju, J.; Gomez-Dans, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Kovalskyy, V. A general method to normalize Landsat reflectance data to nadir BRDF adjusted reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V. Optimal solar geometry definition for global long-term Landsat time-series bidirectional reflectance normalization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. A Robust Deep Learning Approach for Spatiotemporal Estimation of Satellite AOD and PM 2.5. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witthuhn, J.; Hünerbein, A.; Deneke, H. Evaluation of satellite-based aerosol datasets and the CAMS reanalysis over the ocean utilizing shipborne reference observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, C.; Zhou, S. Simulation and evaluation of dust emissions with WRF-Chem (v3. 7.1) and its relationship to the changing climate over East Asia from 1980 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, H.; Lei, T.; Liu, P.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhao, H. Effects of natural and anthropogenic factors and their interactions on dust events in Northern China. Catena 2021, 196, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Lapyonok, T.; Litvinov, P.; Herman, M.; Fuertes, D.; Ducos, F.; Federspiel, C. GRASP: A versatile algorithm for characterizing the atmosphere. SPIE Newsroom 2014, 25, 2-1201408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for sentinel-2. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 10427, p. 1042704. [Google Scholar]
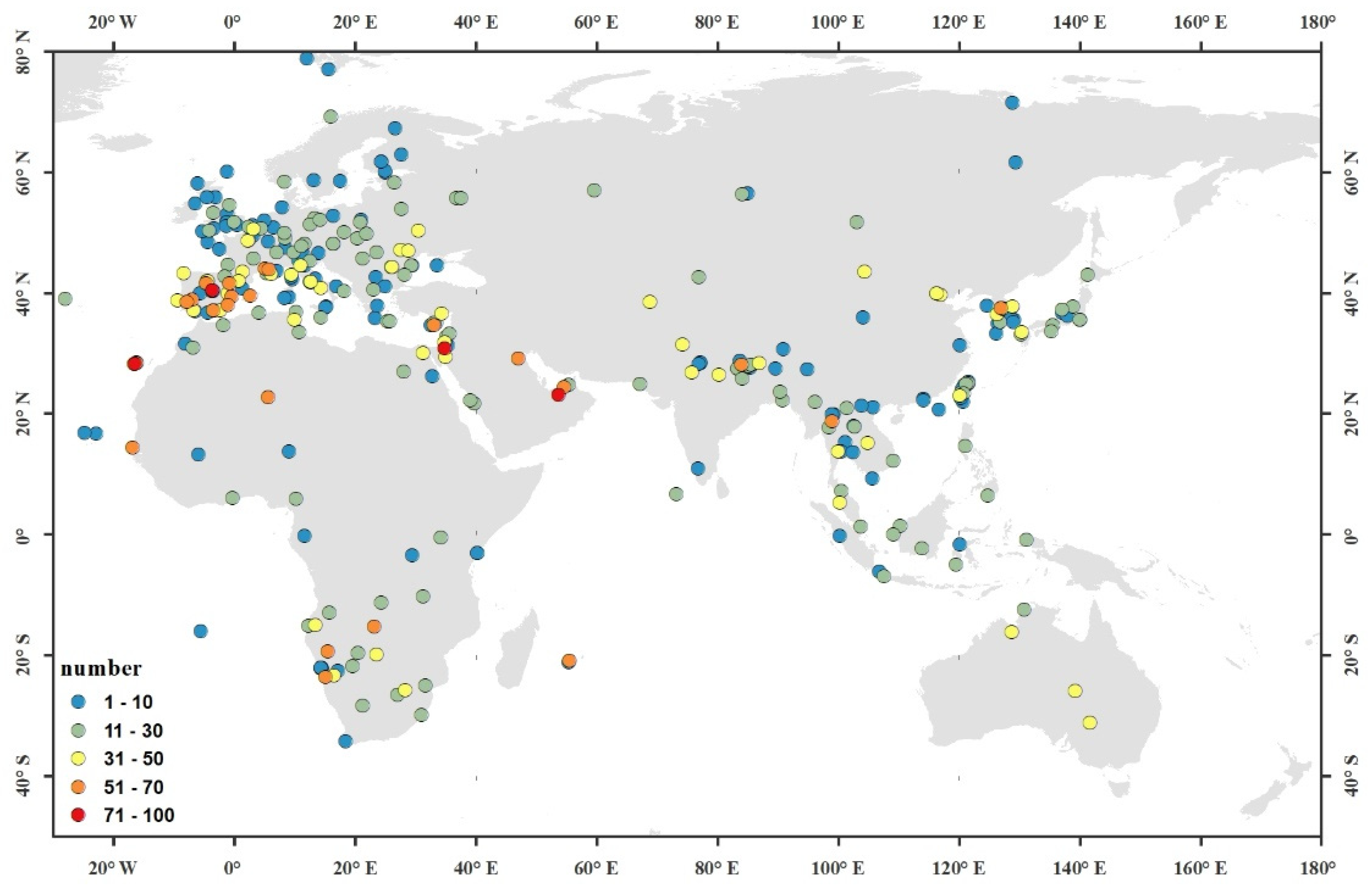
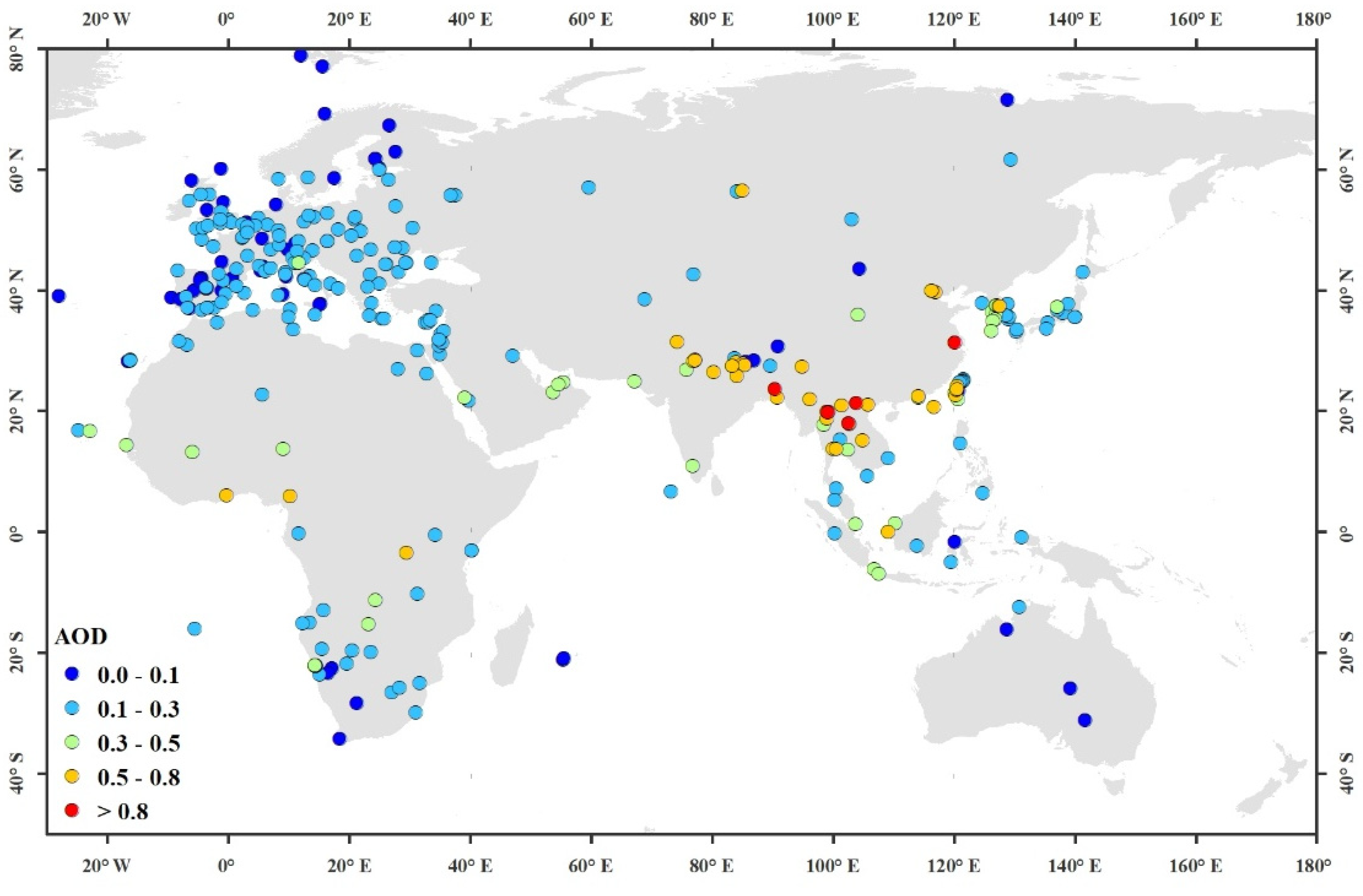
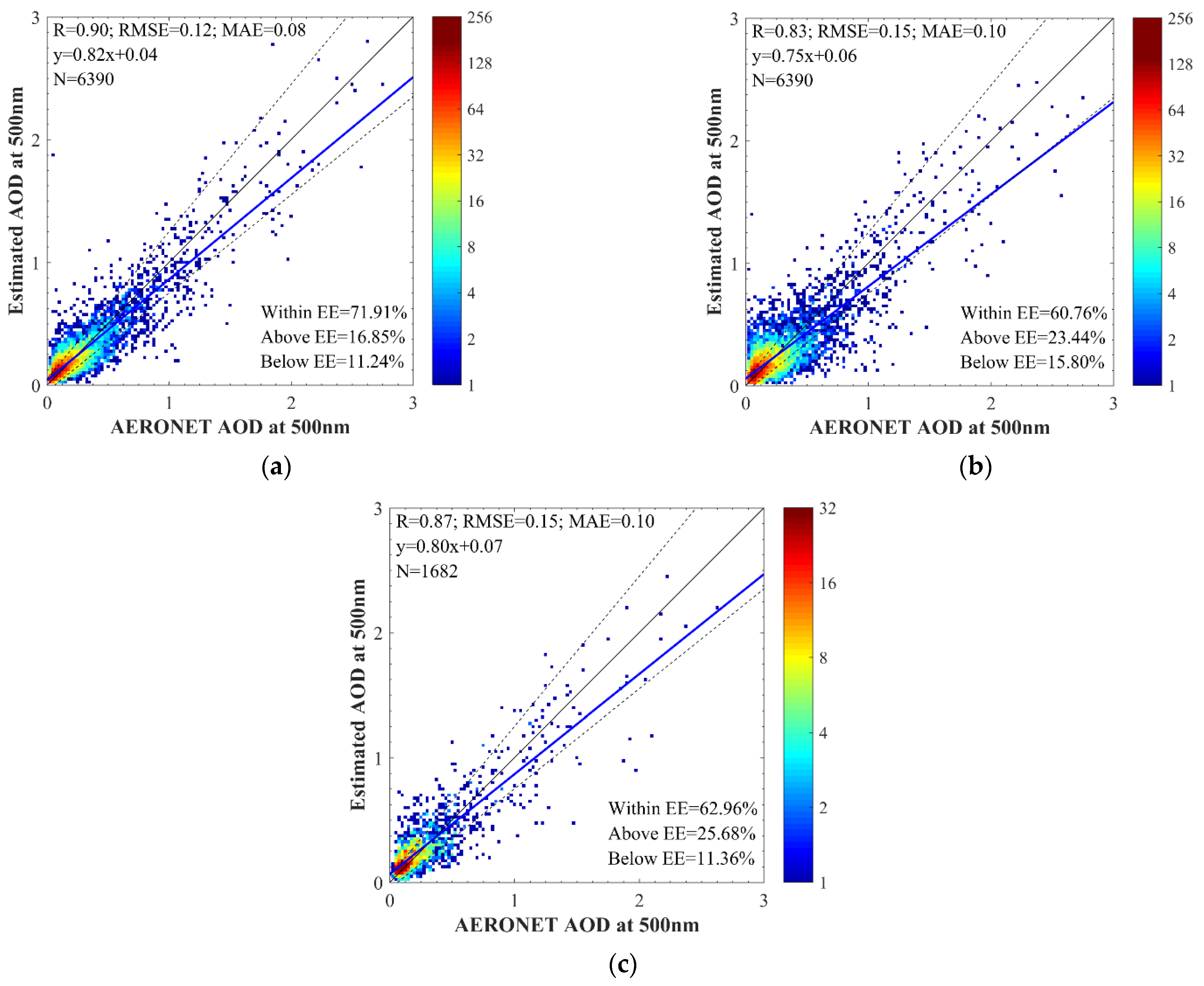
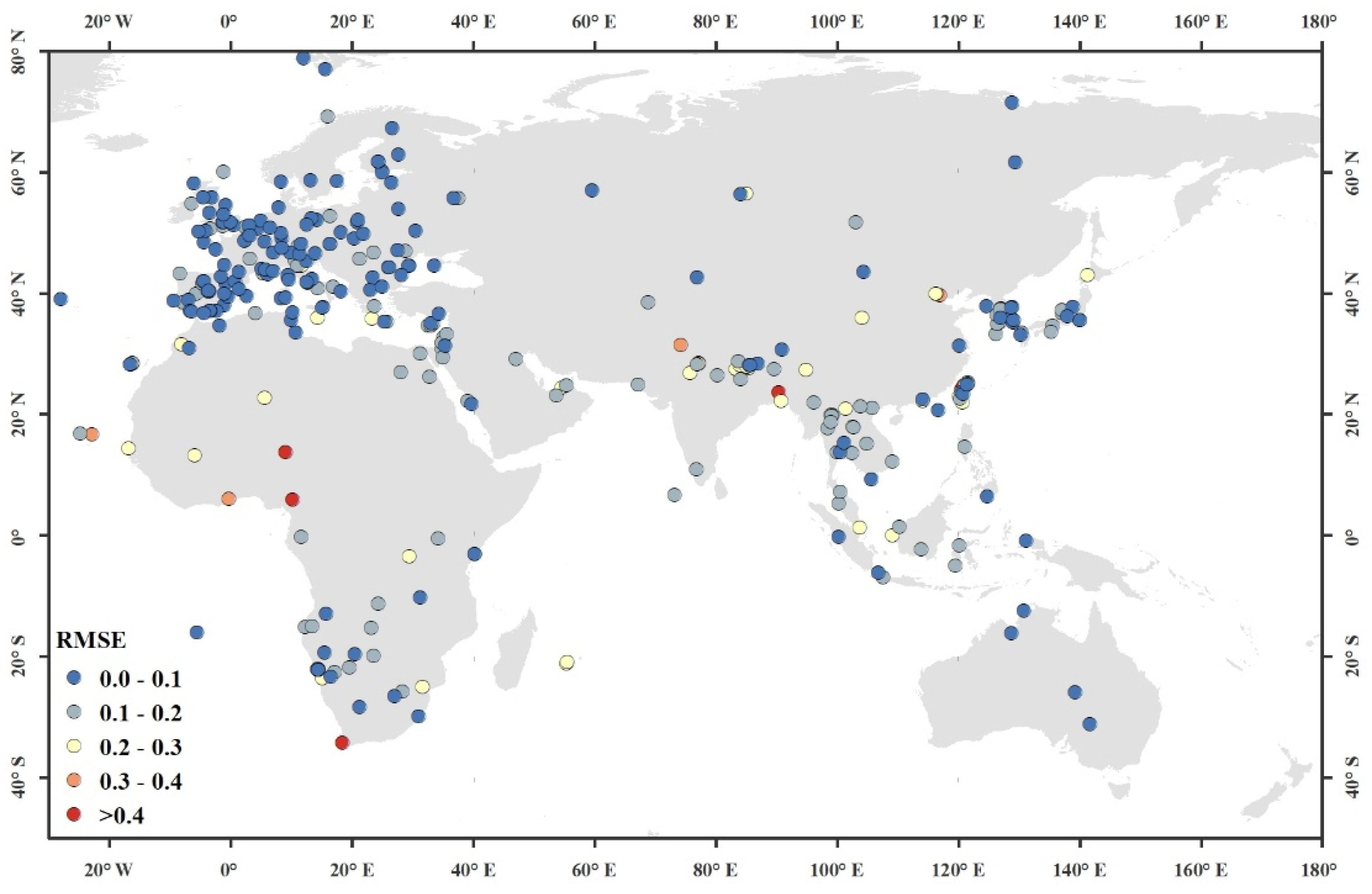
| Band Number | Band Width (μm) | Band Description | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.435–0.451 | Coastal aerosol | 30 |
| 2 | 0.452–0.512 | Blue | 30 |
| 3 | 0.533–0.590 | Green | 30 |
| 4 | 0.636–0.673 | Red | 30 |
| 5 | 0.851–0.879 | Near infrared (NIR) | 30 |
| 6 | 1.566–1.651 | Short wavelength infrared (SWIR) 1 | 30 |
| 7 | 2.107–2.294 | SWIR 2 | 30 |
| 8 | 0.503–0.676 | Panchromatic | 15 |
| 9 | 1.363–1.384 | Cirrus | 30 |
| 10 | 10.60–11.19 | Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) 1 | 100 |
| 11 | 11.50–12.51 | TIRS 2 | 100 |
| Variable | Mean | Std | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AERONET AOD 500 nm | 0.234 | 0.277 | 0.003 | 2.735 |
| TOA band 1 | 0.164 | 0.030 | 0.087 | 0.330 |
| TOA band 2 | 0.149 | 0.035 | 0.071 | 0.335 |
| TOA band 3 | 0.143 | 0.047 | 0.047 | 0.415 |
| TOA band 4 | 0.151 | 0.069 | 0.027 | 0.509 |
| TOA band 5 | 0.258 | 0.082 | 0.012 | 0.61 |
| TOA band 6 | 0.241 | 0.097 | 0.002 | 0.629 |
| TOA band 7 | 0.178 | 0.089 | 0.001 | 0.504 |
| BT band 10 (K) | 298.7 | 9.2 | 262.0 | 327.7 |
| BT band 11 (K) | 296.4 | 8.5 | 262.5 | 325.8 |
| View zenith angle (°) | 3.6 | 2.3 | 0.2 | 17.48 |
| Solar zenith angle (°) | 39.2 | 12.8 | 20.2 | 69.8 |
| View azimuth angle (°) | 55.4 | 87.2 | −161.2 | 140.2 |
| Solar azimuth angle (°) | 127.7 | 36.3 | −180.0 | 178.9 |
| Scattering angle (°) | 142.2 | 13.7 | 99.8 | 166.2 |
| Water vapor content (kg m−2) | 19.4 | 11.8 | 0.3 | 67.9 |
| Ozone content (kg m−2) | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.011 |
| DEM (m) | 473.2 | 737.0 | −350.0 | 4901.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
She, L.; Zhang, H.K.; Bu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J. A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval from Landsat-8 Top of Atmosphere Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061411
She L, Zhang HK, Bu Z, Shi Y, Yang L, Zhao J. A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval from Landsat-8 Top of Atmosphere Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061411
Chicago/Turabian StyleShe, Lu, Hankui K. Zhang, Ziqiang Bu, Yun Shi, Lu Yang, and Jintao Zhao. 2022. "A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval from Landsat-8 Top of Atmosphere Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061411
APA StyleShe, L., Zhang, H. K., Bu, Z., Shi, Y., Yang, L., & Zhao, J. (2022). A Deep-Neural-Network-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrieval from Landsat-8 Top of Atmosphere Data. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061411








