Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Related Literature on NTL Validation Studies
2.2. Data
2.3. Estimation Framework
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlations
3.2. Regression Results at County-Level and Prefectural-Level
3.3. Variation in GDP-Lights Relationships by Population Density
3.4. Relationships between Changes in Electricity Consumption and Changes in NTL Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.; Muller, J.P.; Morley, J.G. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T. Estimation of Gross Domestic Product at sub-national scales using nighttime satellite imagery. Int. J. Ecol. Econ. Stat. 2007, 8, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henderson, J.V.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D.N. Measuring economic growth from outer space. Am. Econ. Rev. 2012, 102, 994–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Fu, X.; Yan, L. Comparison between the Suomi-NPP Day-Night Band and DMSP-OLS for correlating socio-economic variables at the provincial level in China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. GDP spatialization and economic differences in South China based on NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Rafa, M.; Moyer, J.; Li, J.; Scheer, J.; Sutton, P. Estimation and mapping of sub-national GDP in Uganda using NPP-VIIRS imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H. Nightlight as a proxy of economic indicators: Fine-grained GDP inference around mainland China via attention-augmented CNN from daytime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.; Pinkovskiy, M.; Sala-I-Martin, X. China’s GDP growth may be understated. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S. International isolation and regional inequality: Evidence from sanctions on North Korea. J. Urban Econ. 2018, 103, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, A.; Rogers, M. Analysis of Panamanian DMSP/OLS nightlights corroborates suspicions of inaccurate fiscal data: A natural experiment examining the accuracy of GDP data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.N.; Noy, I. Measuring the impact of insurance on urban earthquake recovery using nightlights. J. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 20, 857–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocornik-Mina, A.; McDermott, T.K.; Michaels, G.; Rauch, F. Flooded cities. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2020, 12, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Hsu, F.; Samson, E.; Letu, H.; Liang, D.; Cao, G. Time series analysis of VIIRS-DNB nighttime lights imagery for change detection in urban areas: A case study of devastation in Puerto Rico from hurricanes Irma and Maria. Appl. Geog. 2020, 120, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, M.P.; Neumayer, E. The impact of the Indian Ocean tsunami on Aceh’s long-term economic growth. J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 141, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lian, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. NPP-VIIRS DNB daily data in natural disaster assessment: Evidence from selected case studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Zhizhin, M.; Bazilian, M. The dimming of lights in China during the COVID-19 pandemic. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xiu, T.; Li, X.; Liang, X.; Jiao, L. Lockdown induced night-time light dynamics during the COVID-19 epidemic in global megacities. Int. J. Appl. Earth 2021, 102, 102421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M. Tracking economic activity in response to the COVID-19 crisis using nighttime lights—The case of Morocco. Dev. Eng. 2021, 6, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard-Ruiz, A.; Moradi, A. Regional market integration in East Africa: Local but no regional effects? J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 140, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodorow-Reich, G.; Gopinath, G.; Mishra, P.; Narayanan, A. Cash and the economy: Evidence from India’s demonetization. Q. J. Econ. 2020, 135, 57–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.V.; Squires, T.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D. The global distribution of economic activity: Nature, history, and the role of trade. Q. J. Econ. 2018, 133, 357–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblatt, R.; Heilmann, K.; Vaizman, Y. Can Medium-Resolution Satellite Imagery Measure Economic Activity at Small Geographies? Evidence from Landsat in Vietnam. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2020, 34, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.; Lunt, T.; Matsuura, R.; Novosad, P. Development research at high geographic resolution: An analysis of night-lights, firms and poverty in India suing the SHRUG open data platform. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2021, 35, 845–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhaus, W.; Chen, X. A sharper image? Estimates of the precision of nighttime lights as a proxy for economic statistics. J. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 15, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. VIIRS nighttime lights in the estimation of cross-sectional and time-series GDP. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, J.; Boe-Gibson, G. Nighttime lights and county-level economic activity in the United States: 2001 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Ziskin, D. Development of a 2009 stable lights product using DMSP-OLS data. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2010, 30, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Taneja, J. Annual time series of global VIIRS nighttime lights derived from monthly averages: 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J. Better night lights data, for longer. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2021, 83, 770–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G.; Li, C. Which night lights data should we use in economics, and where? J. Dev. Econ. 2021, 149, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodler, R.; Raschky, P.A. Regional favoritism. Q. J. Econ. 2014, 129, 995–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storeygard, A. Farther on down the road: Transport costs, trade and urban growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2016, 83, 1263–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttle, B.; Anderson, S.; Sutton, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. It used to be dark here. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing. 2013, 79, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, A.; Oram, C.; Lozano-Gracia, N. Deblurring DMSP nighttime lights: A new method using Gaussian filters and frequencies of illumination. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J. Social transfers and growth: Evidence from luminosity data. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 2016, 65, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Liu, X. A simple method to improve estimates of county-level economics in China using nighttime light data and GDP growth rate. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2019, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G. Night lights in economics: Sources and uses. J. Econ. Surv. 2020, 34, 955–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). China Statistical Yearbook (County-Level) [M]; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). China City Statistical Yearbook [M]; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). Beijing Statistical Yearbook [M]; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, T.; Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.; Zhizhin, M.; Poyda, A.; Hsu, F.-C. Extending the DMSP Nighttime Lights Time Series beyond 2013. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach, 7th ed.; Cengage Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Gibson, J.; Chung, C. Using panel data to estimate income under-reporting by the self-employed. Manch. Sch. 2017, 85, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greene, W. Econometric Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q. Likelihood ratio tests for model selection and non-nested hypotheses. Econometrical 1989, 57, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Huang, X. A novel locally adaptive method for modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption based on DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Luan, G.; Song, L.; Peng, Z.; Du, Q.; Xie, Z. Estimating rural electric power consumption using NPP-VIIRS night-time light, toponym and POI data in ethnic minority areas of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Gupta, P.; Srivastav, S. Comparative analysis between VIIRS-DNB and DMSP-OLS night-time light data to estimate electric power consumption in Uttar Pradesh, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2565–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration (NES). Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/ (accessed on 5 November 2021).
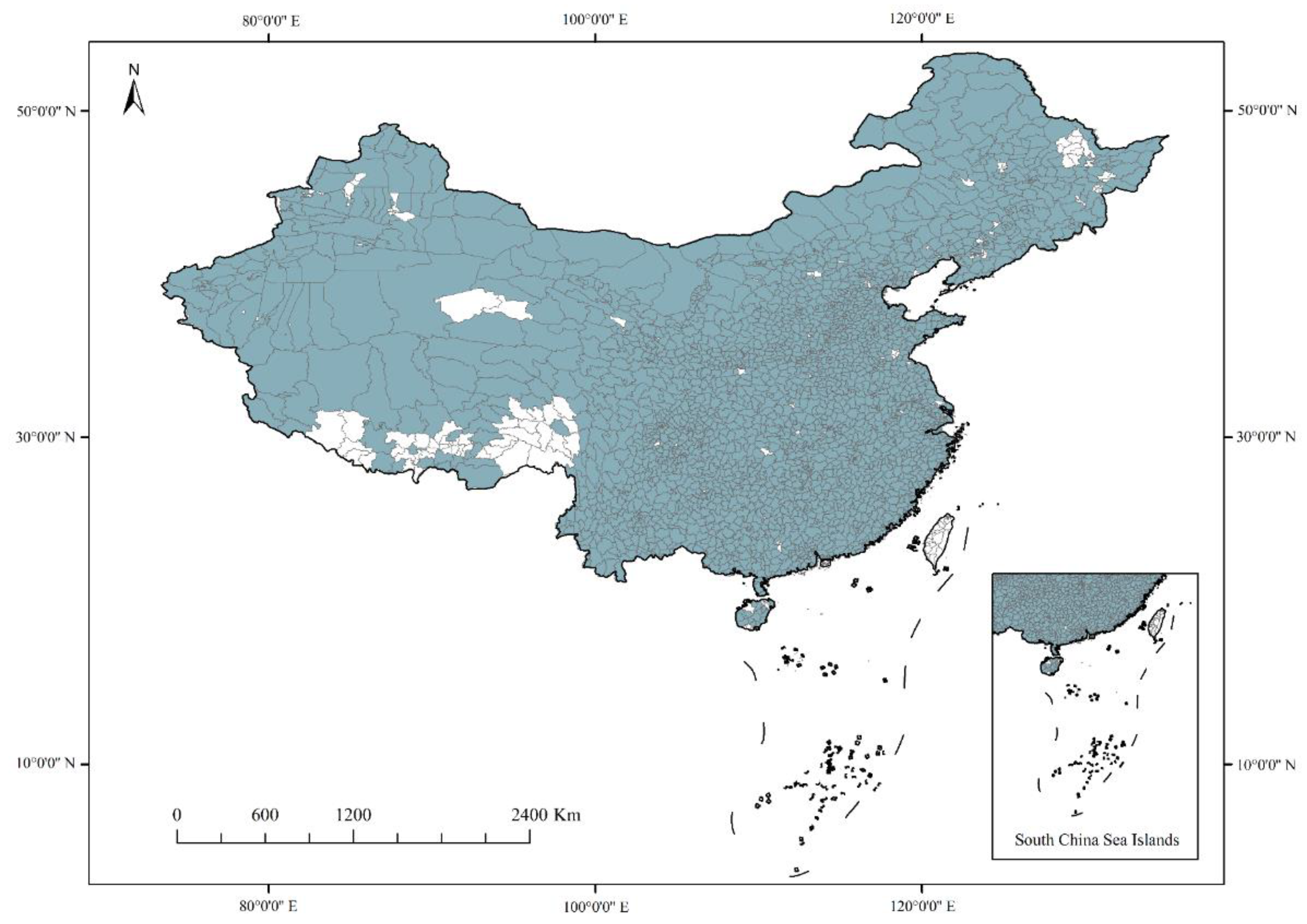
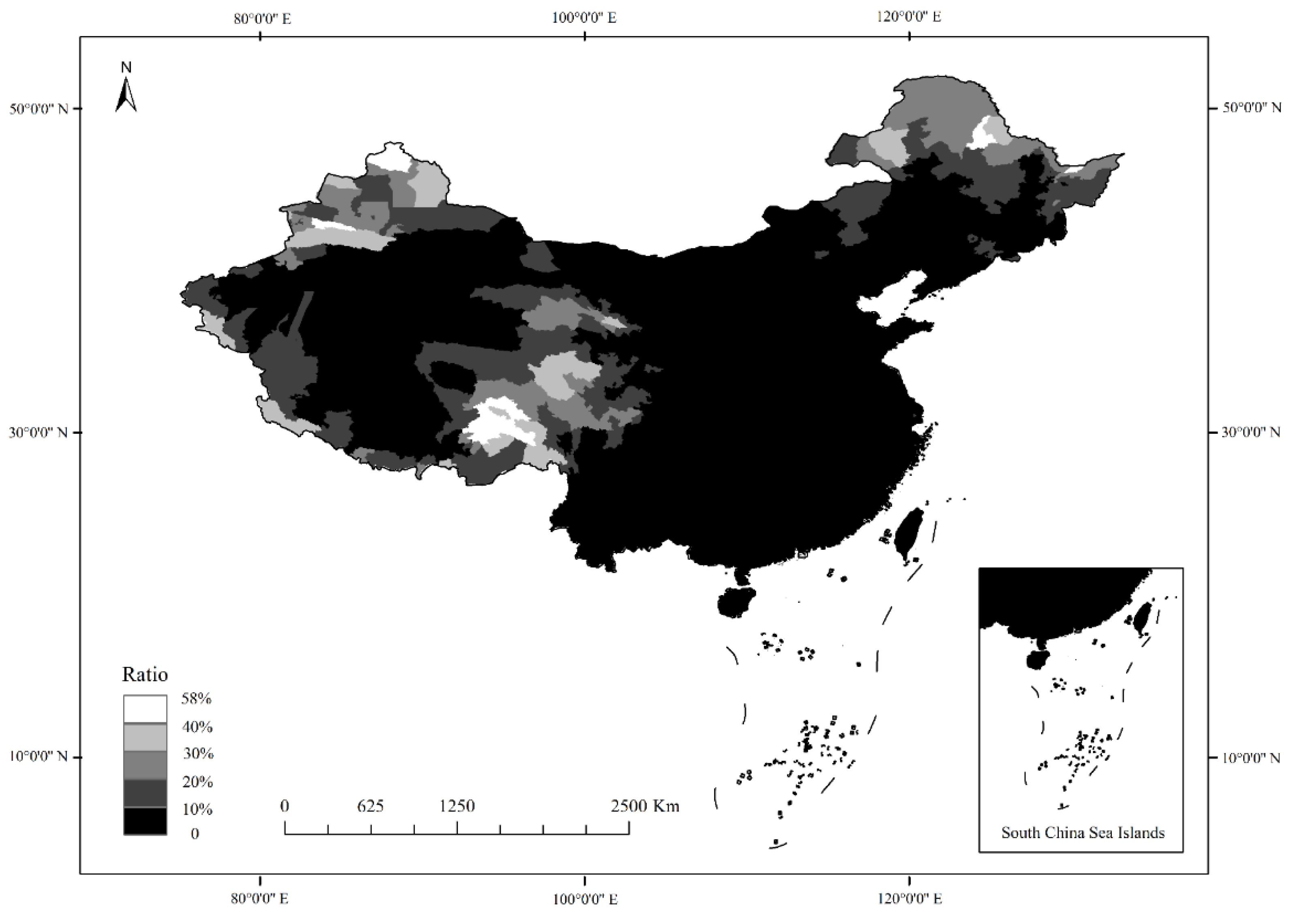
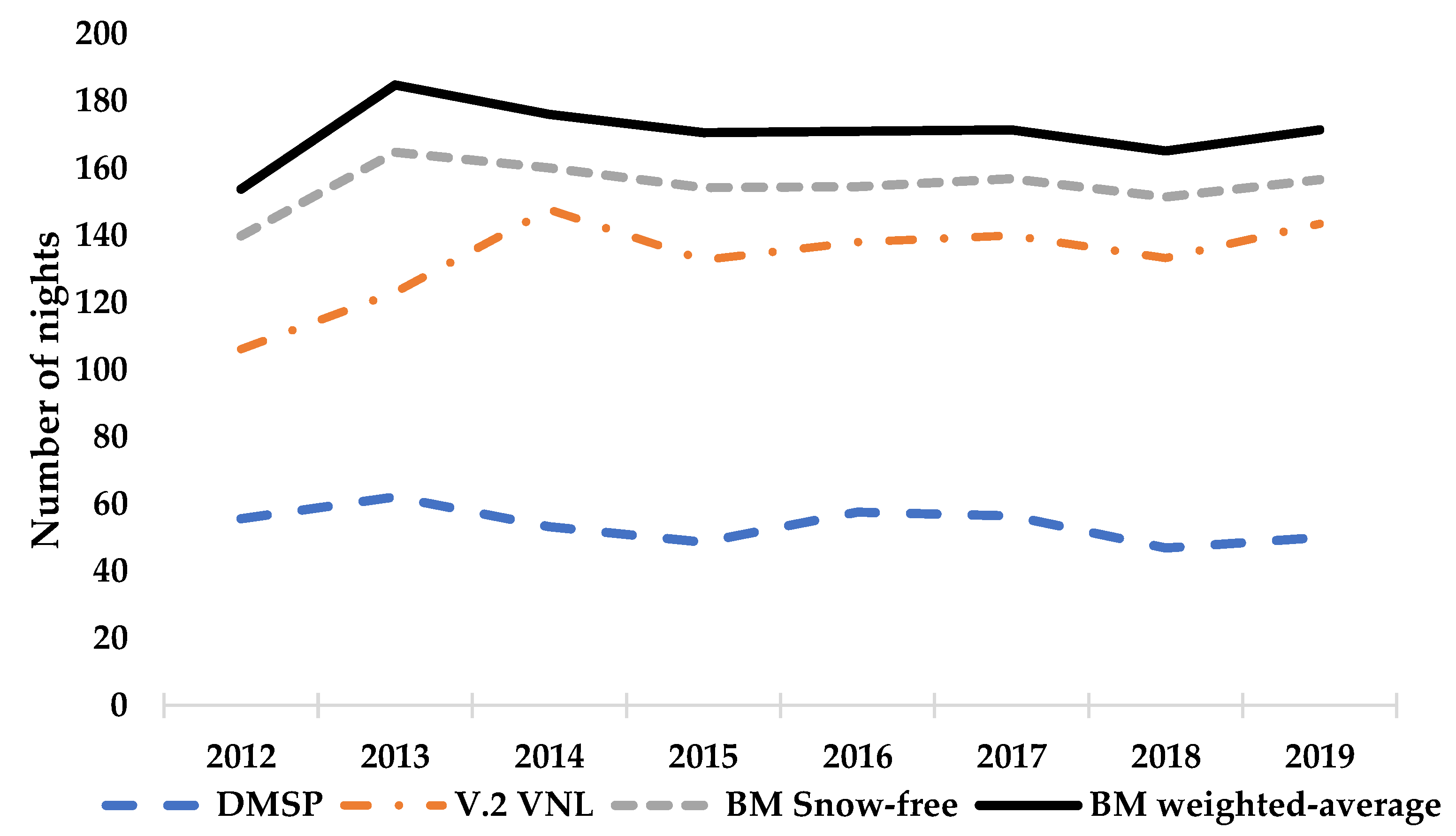
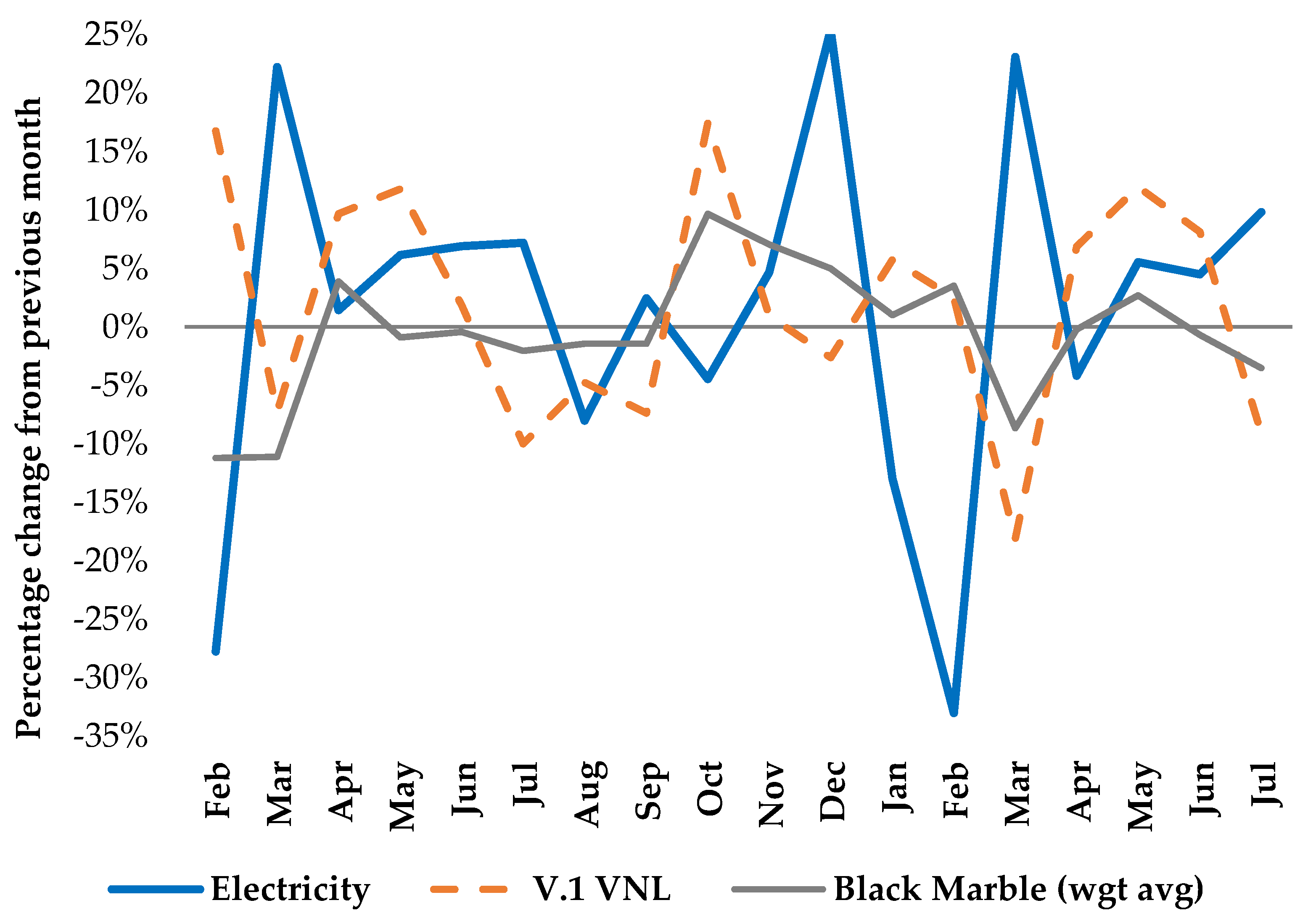
| DMSP | V.2 VNL | Black Marble | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite/Sensor Attributes | |||
| Operator | US DoD | NASA/NOAA | |
| Available years | 1992–2019 | 2012–2020 | |
| Spectral band | 0.5–0.9 μm | 0.5–0.9 μm | |
| Orbit type and altitude | Polar, 830 km | Polar, 830 km | |
| Spatial resolution at nadir | 2.7 km | 742 m | |
| Scan width | 3000 km | 3000 km | |
| Revisit time | 12 h | 12 h | |
| Pixel saturation | Saturated | Not saturated | |
| On-board calibration | No | Yes | |
| Data Products | |||
| Creator of annual composites | EOG | EOG | NASA |
| Spatial resolution | 30 arc second | 15 arc second | 15 arc second |
| Tiled | No | No | Yes, 648 tiles |
| Masking of ephemeral light sources | No | Yes | Yes |
| Stray-light correction | No | Yes, from 2014 | Yes |
| User control over angle of detection | No | No | Yes |
| Treatment of snow | No | No | Yes |
| Matrix of Correlation Coefficients | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std Dev | DMSP | V.2 VNL | BMsf | BMwa | |
| DMSP | 8.526 | 1.176 | ||||
| V.2 VNL | 7.999 | 1.247 | 0.850 | |||
| BMsf | 10.478 | 1.254 | 0.791 | 0.872 | ||
| BMwa | 10.500 | 1.226 | 0.857 | 0.964 | 0.903 | |
| GDP | 4.950 | 1.266 | 0.635 | 0.730 | 0.687 | 0.740 |
| Independent Variables and Summary Statistics | Annual NTL Data Product | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSP Stable Lights | V.2 VNL Masked Average | Black Marble Snow-Free | Black Marble Weighted Average | |
| Within-estimator, for annual GDP changes within each county | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.109 *** | 0.067 *** | 0.022 *** | 0.124 *** |
| (0.010) | (0.015) | (0.004) | (0.016) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared (Within) | 0.014 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.011 |
| Between-estimator, for average GDP differences between counties | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.786 *** | 0.764 *** | 0.834 *** | 0.780 *** |
| (0.015) | (0.013) | (0.014) | (0.013) | |
| R-squared (Between) | 0.500 | 0.560 | 0.587 | 0.579 |
| Independent Variables and Summary Statistics | Annual NTL Data Product | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSP Stable Lights | V.2 VNL Masked Average | Black Marble Snow-Free | Black Marble Weighted Average | |
| Within-estimator, for annual GDP changes within each prefecture | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.275 *** | 0.038 | 0.025 * | 0.135 ** |
| (0.061) | (0.046) | (0.013) | (0.068) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared (Within) | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| Between-estimator, for average GDP differences between prefectures | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.965 *** | 0.924 *** | 0.995 *** | 0.947 *** |
| (0.054) | (0.047) | (0.047) | (0.046) | |
| R-squared (Between) | 0.479 | 0.527 | 0.562 | 0.552 |
| Independent Variables and Summary Statistics | Annual NTL Data Product | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSP Stable Lights | V.2 VNL Masked Average | Black Marble Snow-Free | Black Marble Weighted Average | |
| Within-estimator, for annual GDP changes within each county | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.111 *** | 0.078 *** | 0.021 *** | 0.139 *** |
| (0.011) | (0.015) | (0.004) | (0.016) | |
| ln (sum of lights) × density | 0.005 | 0.041 *** | 0.004 ** | 0.063 *** |
| (0.011) | (0.011) | (0.002) | (0.018) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| County fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared (Within) | 0.014 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.012 |
| Between-estimator, for average GDP differences between counties | ||||
| ln (sum of lights) | 0.767 *** | 0.736 *** | 0.805 *** | 0.753 *** |
| (0.014) | (0.013) | (0.014) | (0.013) | |
| ln (sum of lights) × density | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.013 |
| (0.020) | (0.019) | (0.022) | (0.019) | |
| R-squared (Between) | 0.558 | 0.574 | 0.599 | 0.592 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Gibson, J. Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051282
Zhang X, Gibson J. Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051282
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoxuan, and John Gibson. 2022. "Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051282
APA StyleZhang, X., & Gibson, J. (2022). Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051282







