Abstract
The echo of shipborne high-frequency surface wave radar (HFSWR) is modulated by six-degrees-of-freedom (6-DOF) motion, affecting the detection of the target and the remote sensing of ocean surface dynamics parameters. Commonly, motion compensation methods of shipborne HFSWR describe each aspect of the 6-DOF motion as the superposition of sinusoidal motion, which results in the effect of motion compensation affected by the precision of 6-DOF motion parameters. A motion compensation method based on dual reference radio frequency (RF) signals is proposed in this paper, without depending on a sinusoidal motion model to describe the 6-DOF motion. By using the motion compensation parameters, which are relevant to the motion attitude and calculated from the information of dual reference RF signals located onshore, the method realizes the compensation of shipborne HFSWR echo modulated by platform 6-DOF motion. This paper proposes the extraction of reference RF signals from radar echo and analyzes the influence of the location of the reference RF signals’ emission source on the motion compensation method. The result shows that a good motion compensation effect is achieved in eliminating the influence of 6-DOF motion modulation. In addition, a traversal of different reference RF signals’ emission source locations is conducted, and the simulation results show that the method proposed in this paper has universality.
1. Introduction
High-frequency surface wave radar (HFSWR) has been widely used in the over-the-horizon detection and the observation of marine dynamic environmental parameters for their real-time and all-weather characteristics. HFSWR is generally deployed along the coastline, monitoring the economic exclusive zone that is commonly within about 200 nautical miles (n miles). For more flexible detection, studies on vehicle-mounted portable HFSWR, buoy-based HFSWR, and shipborne HFSWR have been carried out. In addition to the advantages of shore-based HFSWR, shipborne HFSWR is more flexible and can provide a larger detection range. Therefore, it has received extensive attention in recent years [1,2,3,4,5].
The echo signal of shipborne HFSWR is modulated by the motion of the shipborne platform, resulting in additional peaks and the broadening of the first-order Bragg peaks on the echo Doppler spectrum, casting a negative influence on radar target monitoring and the remote sensing of ocean surface dynamics parameters. Wang et al. conducted a theoretical analysis and simulation experiments on the echo characteristics of HFSWR under the impact of the forward movement and the six-degrees-of-freedom (6-DOF) motion of the shipborne platform [6]. Khoury et al. derived the received signal model of the moving antenna system and analyzed the influence under forward movement and sway motion on the Doppler spectrum [7]. Xie et al. theoretically analyzed the first-order Bragg peaks in the Doppler spectrum under forward movement [2]. According to the research above, the forward movement of the shipborne platform will induce the broadening of the first-order Bragg peaks, while the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne platform will result in additional peaks (i.e., motion-induced peaks) of the first-order Bragg peaks. This paper focuses on the modulation of shipborne platform 6-DOF motion and proposes a motion compensation method to eliminate the motion-induced peaks caused by 6-DOF motion modulation.
Many researchers have studied the modulation of shipborne radar platform 6-DOF motion on radar echo, suggesting that the platform motion can be regarded as the phase modulation of radar echo [8,9,10,11]. Based on the studies above, radar cross-section (RCS) models of HFSWR under different DOF motion modulation have been proposed. According to the electric field theory, Walsh et al. proposed the first-order and second-order RCS of the ocean surface under surge motion [12,13] and pointed out that surge motion would generate additional motion-induced peaks on the range-Doppler (RD) spectrum. Following that, researchers have derived different models of shipborne HFSWR first-order RCS containing 6-DOF motion [3,14,15,16,17,18]. These models can be divided into frequency domain models and time domain models. Among these models, we adopted the time domain model proposed by Chang et al., which is based on the modulation of the radar antenna pattern and the array steering vector under 6-DOF motion [5].
According to the analysis of the modulation of 6-DOF motion and the models above, different motion compensation methods were proposed. At present, motion compensation methods are mainly divided into two categories: (1) recovering the Doppler spectrum contaminated by the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne platform to improve the capability of obtaining ocean surface dynamics parameters and target detection [19]; and (2) recovering the antenna pattern and the array steering vector modulated by the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne platform to reduce the effects on the radar-receiving antennas [20,21,22]. In the extant research, the motion attitude of the shipborne platform is generally considered to be easy to gauge, while the accuracy of the motion attitude will influence the effect of the motion compensation methods in recovering the radar echo. The more accurate the motion attitude is, the more the radar echo can be recovered to the level before modulation.
The motion attitude of the shipborne platform can be obtained not only by sensors but also from radar echo signals. Currently, the motion attitude of most shipborne platforms is obtained by using sensors, such as an inertial navigation system (INS). However, the sensors cannot measure the translation attitude with precision that is high enough for compensation, and exhibit time delay, which will severely affect the compensation effect. Based on the characteristics of the radio frequency (RF) signal modulated by 6-DOF motion, Zhu et al. proposed a method to obtain 6-DOF motion parameters by using a reference RF signal [1]. This method solves the problems of error and time delay in obtaining motion attitude by sensors but still presents some limitations. First, the method assumes that the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne platform is single-frequency sinusoidal motion, which cannot accurately describe the real platform movement. Second, the method identifies the 6-DOF motion parameters from the characteristics of motion-induced peaks generated by different degrees-of-freedom motions in the RD spectrum, which indeed have similar characteristics in the spectrum, leading to difficulties in determining the corresponding relationship of the motion-induced peaks and the degree of freedom that produces them.
To solve the problems above, this paper proposes a motion compensation method based on dual reference RF signals to obtain motion compensation parameters and to compensate for the 6-DOF motion modulation of the shipborne platform. The method proposed in this paper uses the same reference RF signal temporal model as [1]. However, the way to compensate for motion modulation is different. The motion compensation parameters proposed in this paper are the core in motion compensation. Unlike the motion parameters in [1], the motion compensation parameters are dynamic, and contain the attitude of 6-DOF motion. Therefore, the proposed method has the innovation that it is not constrained by the sinusoidal 6-DOF motion model and it can compensate for the motion modulation of all DOF simultaneously, regardless of the motion attitude. This method not only solves the limitation of sensors that have difficulties in measuring translation, but also solves the limitation of the method in [1] that fails to compensate for random motion modulation at the same time.
This paper is arranged as follows. The physical model and the principle of motion compensation are introduced in Section 2. The radar system setup and radar echo model are introduced, as well as the shipborne platform movement model, the modulation effect of shipborne platform movement on radar echo signal, and the motion compensation parameters proposed in the physical model. The feasibility of using motion compensation parameters to recover the RD spectrum is analyzed via the principle of motion compensation. The motion compensation method based on dual reference RF signals is introduced in Section 3, including the analysis of the shipside-received reference RF signals model, the method of using dual reference RF signals to work out the motion compensation parameters, and the problems needing attention in the motion compensation method. The simulation results of the motion compensation algorithm are introduced in Section 4, containing the simulation process and the effect of the motion compensation method in recovering the RD spectrum. Suggestions for improving this motion compensation method are discussed in Section 5. The conclusions of this research, as well as the direction of future work, are presented in Section 6.
2. Analysis of the Model and the Principle of Motion Compensation
2.1. System Setting and Receiving the Signal Model
The shipborne HFSWR system discussed in this paper has several receiving antennas and a transmitting antenna mounted on the same ship. To eliminate the motion-induced peaks in the RD spectrum of radar echo caused by the shipborne platform motion, two shore-based emission sources of RF signals are set up. These transmit fixed frequency RF signals, called reference RF signals. The radar system setting is shown in Figure 1. The ocean surface is divided into small patches for calculation convenience, and these patches, which we call sea patches, are considered ideal point targets. The X-axis represents the sailing direction, and the Y-axis represents the normal direction of the receiving array. and represent the distances between the center of the shipborne platform and the corresponding RF source, respectively, and and represent the included angle of the opposite extension of the Y-axis and the corresponding RF source, respectively, whose ranges are both from to , clockwise being the positive direction. represents the distance between the sea patch and the center of the shipborne platform, and represents the included angle of the Y-axis and the sea patch, whose ranges are also from to , clockwise being the positive direction.
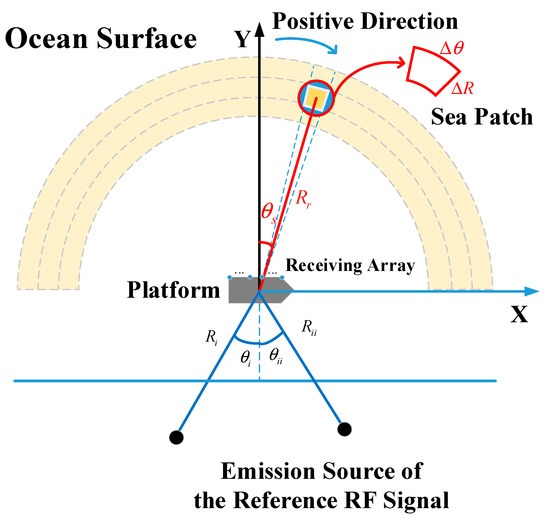
Figure 1.
The relative position of the shipborne HFSWR platform, the emission source of reference RF signals, the ocean surface, and the shore.
The shipborne HFSWR transmits a frequency-modulated interrupted continuous wave (FMICW), and its echo signal is discrete sampled data. According to [1,5], the received temporal modeled signal can be expressed as
where n denotes the n-th sweep period, and denotes the number of receiving antennas ( is an even number). is the sea-clutter temporal signal, is the reference RF temporal signal, and is the background noise.
According to the radar equation, the sea-clutter temporal signal can be expressed as
where is the radar transmitting power, and are the gains of the transmitting and receiving antennas, respectively, and denotes the wavelength. represents the ocean surface first-order RCS, denotes the receiving antenna pattern, and is the array steer vector, in which is the amplitude and is the phase. The double summation of index and extends from to and from 1 to . is the bandwidth of the transmitting radio, c is the speed of light, and is the floor function.
The reference RF temporal signal can be expressed as
Here, is the temporal modeled signal of the reference RF signal. is used for distinguishing between two reference RF signals. is the array steer vector, which is the same as that in the sea-clutter temporal signal.
2.2. The Antenna Pattern and the Array Steer Vector of Shipborne Radar-Receiving Antennas
According to [23,24], the motion of the shipborne HFSWR platform can be described as 6-DOF motion with roll , pitch , heading changes , surge , sway , and heave . In this paper, the heading change refers to the heading value at the current time relative to the starting point of the current coherent integration time (CIT), clockwise being the positive direction. The receiving antennas and the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne HFSWR platform are shown in Figure 2. Here, a transmitting antenna is located at the stem, and the receiving array composed of receiving antennas is arranged on one side of the shipborne platform, with the antenna closest to the stem called antenna No. 1, etc. The height of the receiving antenna is , and the spacing is . The gravity center of the shipborne platform is defined as the origin of coordinates for describing the changes in the antenna pattern and the array steering vector caused by the movement of the receiving antenna array, along with the shipborne platform motion. is the half-width of the shipborne platform, and is the distance between the gravity center and the deck.
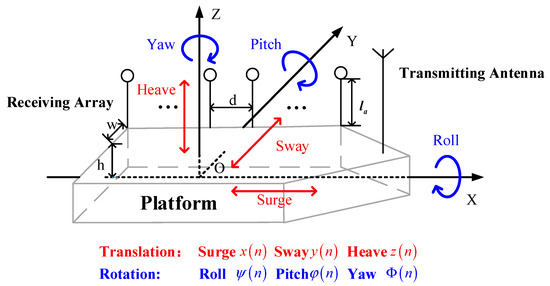
Figure 2.
The model of the shipborne HFSWR platform.
It can be gleaned from Equations (2) and (3) that the core consideration in evaluating the impact of 6-DOF motion on the received radar signal includes analyzing the antenna pattern and the array steering vector .
According to the radar electric field theory analyzed by Walsh et al., the motion component in the vertical direction (i.e., the Z-axis) will not produce additional Doppler effects, while the motion component in other directions (i.e., the X-axis and the Y-axis) will influence the antenna pattern and the array steering vector of the receiving antennas. Therefore, what should be under consideration are the surge, the sway, the heading changes, and the horizontal component of roll and pitch, while the heave and the vertical component of roll and pitch can be ignored. The model of the change of radar antenna pattern and the array steering vector modulated by 6-DOF motion, proposed by Chang et al. [5], is used in this paper.
According to the work of Zhu et al. [1], when the amplitude of roll and pitch are within , the antenna pattern hardly changes. This can be described as a constant .
where is the wave number and is the height of the receiving antenna. According to the work of Chang et al. [5], the motion modulation of the shipborne platform hardly changes the amplitude of the array steering vector, which can be expressed as a constant :
The preliminary study shows that when the amplitude of roll and pitch are within 5°, the 6-DOF motion has little influence on the antenna pattern or the amplitude of the array steering vector. The analysis of the phase of the array steering vector is derived below.
The receiving antenna array of shipborne HFSWR is a linear array composed of receiving antennas laid along one side of the shipborne platform. The phase of the array steering vector can be expressed as in the absence of motion, and when there is modulation by other 5-DOF motions, excluding heave. The specific expression of and are shown in Appendix A.
Unlike roll and pitch, which are reciprocating motions, the heading changes slowly and generally changes clockwise or counterclockwise under the influence of ocean surface current. The heading changes can be measured by sensors. In the case of the roll, pitch, and heading changes being within 5°, is defined as the phase of the array steering vector containing the heading changes only, whose specific expression is also shown in Appendix A.
By substitution, the phase of the array steering vector can be expressed as
The specific derivation of Equation (6) is seen in Appendix B. It can be seen from Equation (6) that and are the X-axis and Y-axis projections of the 6-DOF motion of the array on the n-th sweep period, respectively—that is, the translation on the X-axis and Y-axis. For simplicity, let and ; then, Equation (6) can be further arranged as
2.3. Principle of Motion Compensation
For convenient expression, define ; in other words, the phase of the array steering vector of antenna No. 1 under motion modulation is . In a similar way, and represent the phases of the array steering vector without motion modulation and modulated only by heading changes, respectively.
Take antenna No. 1 as an example. According to the work of Chang et al. [5], when ignoring the propagation attenuation, the temporal sea-clutter signal under motion modulation can be expressed as
Based on Equation (7), Equation (8) can be rewritten as
Additionally, the temporal sea-clutter signal in the absence of motion modulation can be expressed [1] as
Therefore, the sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion may be compensated for, to the level of the absence of motion modulation, by
It can be seen from Equation (11) that, when the heading of the shipborne platform is measurable, the sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion can be compensated as long as the displacements along the X-axis and Y-axis (i.e., and ) are available. Therefore, and are named as the motion compensation parameters discussed in this paper.
3. Motion Compensation Method Based on Dual Reference RF Signals
Based on the analysis in Section 2, the sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion can be compensated for, once the motion compensation parameters and can be determined. According to Zhu et al. [1], the sea-clutter signal and the reference RF signals are modulated in the same way. Since the waveform of the reference RF signal is easy to obtain and dual reference RF signals contain more information regarding motion modulation, the motion compensation parameters and can be determined using dual reference RF signals.
3.1. The Model of Shipborne HFSWR Receiving the Reference RF Signal
According to the work of Zhu et al. [1] and the features of the radar system used in this project, assuming the transmitting signal and local oscillator signal of the radar are the same, the reference RF signal in the radar-receiving antenna is a fixed-frequency sinusoidal signal. The q-th reference RF signal in the n-th sweep period can be expressed as
Here, , , and represent the amplitude, frequency, and phase of this reference RF signal, respectively. needs to be within the radar bandwidth to ensure that the reference RF signal can be received by the radar. In other words, , where is the carrier frequency of the radar signal.
The reference RF signal is multiplied by the complex conjugate of the radar local oscillator signal and then passed through a low-pass filter . After that, the first fast Fourier transformation (FFT) is performed for range separation. The temporal modeled signal of the reference RF signal can be expressed as
Here, is the Fourier transformation operator, and and represent the sweep period and the sweep slope, respectively. , where is the start frequency of radar local oscillator signal. .
According to the work of Zhou et al. and Equation (13), the reference RF signal forms a sinusoidal sequence over different sweep periods, creating strips that are distributed parallel to the distance axis in the RD spectrum after the second FFT is performed. The Doppler frequency of the reference RF signal is
where .
3.2. Calculation of Motion Compensation Parameters
Take antenna No. 1 as an example; according to the work of Zhu et al. [1] and Equations (8) and (9), the reference RF signal modulated by 6-DOF motion can be expressed as
Equation (15) can be rewritten so that terms containing motion compensation parameters are on the left-hand side.
Equation (16) can be extended to all distance units and all receiving antennas of the temporal modeled signal.
Here, refers to the different array elements, with being the total number of elements. refers to different distance units, with as the maximal detection range.
Defining , the left-hand side of Equation (17) can be rewritten using the Euler formula to
It can be determined, based on the real motion amplitude on the ocean and the radar system parameters, that . Therefore, can be uniquely calculated. That is, values containing motion compensation parameters and may be available. The specific process of determining uniquely is shown in Appendix A.
With the help of dual reference RF signals, the motion compensation parameters and of the n-th sweep period can be calculated by simultaneous equations.
The sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion may be compensated to the level of the absence of motion modulation. Equation (11) can then be used to work out the motion-compensation parameters.
3.3. Several Key Problems of Motion Compensation Based on Dual Reference RF Signals
3.3.1. Extraction of Dual Reference RF Signals
Section 3.1 mentions that two reference RF signals need to be used separately when calculating the motion compensation parameters. In the real radar system, however, multiple reference RF signals will be received simultaneously by radar-receiving antennas, and they perform as a sum of multiple fixed-frequency sinusoidal signals in receiving antennas. The reference RF signal in the n-th sweep period can be expressed as
Here, , and the same is true below. By using the linear properties of Fourier transform, the temporal modeled signal of reference RF signals can be expressed as
After operating the second FFT on Equation (21), the reference RF signals form several strips distributed parallel to the distance axis in the RD spectrum, with Doppler frequency obeying Equation (14). Since the frequency demarcation of the reference RF signal is clear, a band-pass filter may be used to extract one of the reference RF signals. The reference RF signal extracted by the filter can be expressed as
where represents the q-th reference RF signal extracted by the filter and represents the filter used for extracting the q-th reference RF signal. With a properly designed filter, the frequency components outside the passband will be attenuated greatly; then, Equation (22) may be simplified as
To ensure that the reference RF signals can be extracted entirely, and to avoid reference RF signals appearing in the low-speed target area, the Doppler frequency of reference RF signals in the RD spectrum is recommended to obey the inequality , where the Doppler frequency of the reference RF signals obey Equation (14). The filter pass band is recommended to be larger than 1 Hz.
3.3.2. The Influence of Reference RF Signal Locations on Motion Compensation
It can be seen in Figure 1 that the reference RF signals are mounted onshore; therefore, the influence of the locations of reference RF signals on calculating the motion compensation parameters should be considered. According to Equation (20), the distance from the emission source of reference RF signals to the shipborne platform and the azimuth of the emission source of reference RF signals will not influence the calculation of motion compensation parameters. When and only when the two reference RF signals are in line with the shipborne platform will the motion compensation method fail, as the motion compensation parameters cannot be calculated in principle.
There are two situations when the two reference RF signals are in line with the shipborne platform, shown in Figure 3. The black dots in the figure represent the emission source of the reference RF source.
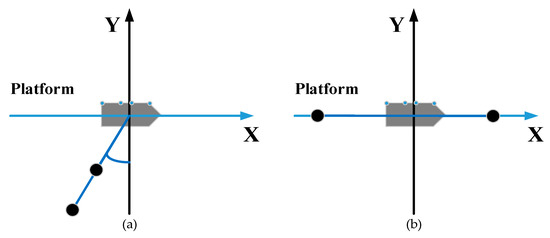
Figure 3.
The situations when the two reference RF signals are in line with the shipborne platform. (a) The reference RF signals are mounted on the same side of the shipborne platform; (b) The reference RF signals are mounted on different sides of the shipborne platform.
In the first case, as shown in Figure 3a, the reference RF signals are both mounted on one side of the shipborne platform. In this case, the known condition is insufficient for Equation (19); the simultaneous equations have no solution, resulting in the motion compensation parameters being unavailable. As such, the motion compensation fails. As for the other case, shown in Figure 3b, the reference RF signals are on opposite sides of the shipborne platform. In this case, since , motion compensation parameter is solvable, while is unsolvable from Equation (19), leading to a failure of motion compensation.
To sum up, the azimuth of the emission source of the dual reference RF signals only needs to satisfy the following condition:
In other words, avoid the emission source of the dual reference RF signals being in line with the shipborne platform. Apart from this, all of the other azimuths can be deployed in relation to the reference RF signals.
3.3.3. The Influence of Initial Phase of Reference RF Signals on Motion Compensation
It can be seen from Equation (13) that the initial phase of reference RF signals at the receiving end, in the absence of motion modulation, will be affected by the distance between the shipborne platform and the reference RF signals as well as by some other factors that are usually difficult to determine. Therefore, while calculating the motion compensation parameters, the initial phase deviation of the theoretical reference RF signals and the actual receiving reference RF signals should be taken into consideration. Assuming that the initial phase of is and that the initial phase of is , then their deviation is . In a field experiment, the initial deviation phase at the shipborne receiving end would be affected by the distance error between the emission source of reference RF signals and the shipborne platform. The phase deviation can be expressed as
where is the error of the distance between the emission source of the reference RF signal and the shipborne platform and is the wavelength of the reference RF signal.
From formula deduction, a fixed deviation exists between the motion compensation parameters that are determined, which we name and , and the actual motion compensation parameters, which we name and . The deviation and can be expressed as
Additionally, it can be proven that the fixed deviation introduced by the initial phase will only lead to limited influence on the RD spectrum and will not influence the radar target-detection and remote sensing capability. The details of the deduction of Equation (26) and the process of proof are shown in Appendix C.
4. Simulation Results
The simulation results of the proposed motion compensation algorithm are presented in detail in this section, including the simulation environment parameters, the process of the simulation, the results of motion compensation, and the ergodic experiment of the location of the reference RF signals’ emission source.
The simulation environment was set according to the real ship and radar parameters in a field experiment conducted in July 2019. The detailed parameters are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters.
In the 6-DOF motion attitude of the shipborne platform, the roll, pitch, and heading changes used the data recorded by sensors in the actual sea experiment. The unit was degree. Due to the limitation of conditions, surge and sway failed to record. Therefore, the PM wave spectrum model proposed by Pierson and Moskowitz was used to simulate surge and sway, and the unit was meter. The 6-DOF motion attitude is shown in Figure 4. Curves plotted by data of surge, sway, roll, and pitch are shown in Figure 4a. Curves plotted by heading changes are shown in Figure 4b. Since the precision of the sensor for measuring yaw is , a random error of was introduced in the yaw data measured by sensor.
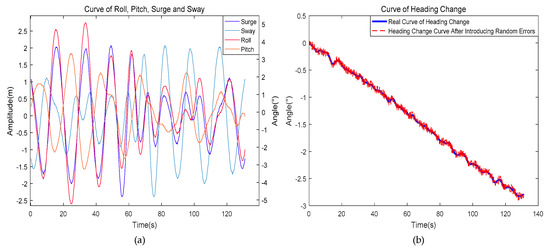
Figure 4.
6-DOF motion attitude. (a) Curve of surge, sway, roll, and pitch; (b) Curve of heading changes.
The purpose of the simulation process is to set the radar system’s parameters and the shipborne platform’s parameters, as well as the motion and attitude data of the shipborne platform. The reference RF signal and the sea-clutter signal are generated in the time domain. After this, the motion modulation of the shipborne platform is introduced into the reference RF signal and the sea-clutter signal, and the motion compensation parameters are calculated using the proposed method. Finally, the motion compensation parameters are used to compensate for the motion modulation, and the RD spectrum before and after the compensation is plotted. The simulation process is shown in Figure 5.
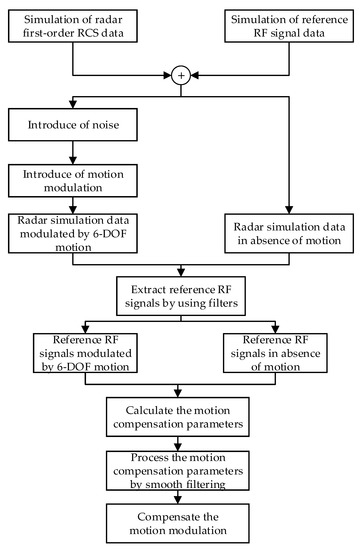
Figure 5.
Process of simulation.
4.1. Extraction of Reference RF Signals in Simulation
Since only two reference RF signals are used, the band-pass filters for extracting reference RF signals can be replaced with a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter, and digital filters are used to extract reference RF signals. As the frequency response curve of the Butterworth filter in the pass band displays maximum flatness without fluctuation and gradually drops to zero in the stopband, this type of filter is adopted in the extraction of the reference RF signals. According to Equation (14) and the radar parameters used in the simulation, the frequency range of the RD spectrum is from −3.90625 Hz to 3.90625 Hz, and the Doppler frequencies of the reference RF signals are 1 Hz and −2.8125 Hz, respectively. The filters are both designed as zero-phase digital filters, with no phase shift in extracting reference RF signals.
To verify whether the filter will change the motion information of the reference RF signals, which further affects the calculation of motion compensation parameters and the motion compensation’s effects, 6-DOF motion modulation is introduced before and after the filter, respectively, exploring the consistency of motion modulation in the spectrum. The result is shown in Figure 6. It can be seen from the figure that the filter will not change the modulation effect of the 6-DOF motion on the reference RF signals.
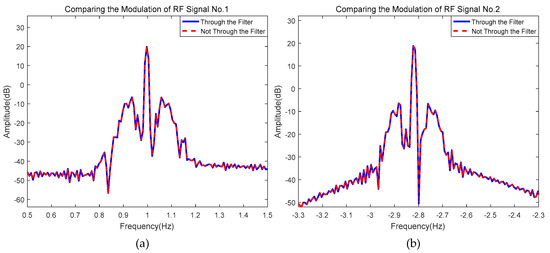
Figure 6.
Comparison of motion modulation introduced before and after filter. (a) Comparison of low-pass filter (i.e., the reference RF signal No. 1); (b) Comparison of high-pass filter (i.e., the reference RF signal No. 2).
4.2. Calculation Result of Motion Compensation Parameters and Effect of Motion Compensation
According to the analysis in Section 3, the effect of motion compensation depends on the calculation result of the motion compensation parameters. The higher the accuracy of the motion compensation parameters, the better the effect of motion compensation in restoring the radar RD spectrum modulated by 6-DOF motion. Additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) is introduced to simulate the noise in the received radar signal in the simulation, as shown in Figure 7. The red curve represents the spectrum before introducing the noise, and the blue curve represents the spectrum after introducing the noise. The power of the noise is approximately 20 dB. After introducing the noise, the motion-induced peaks caused by motion modulation increase, especially in the low-speed target area, which negatively influences the target detection capability.
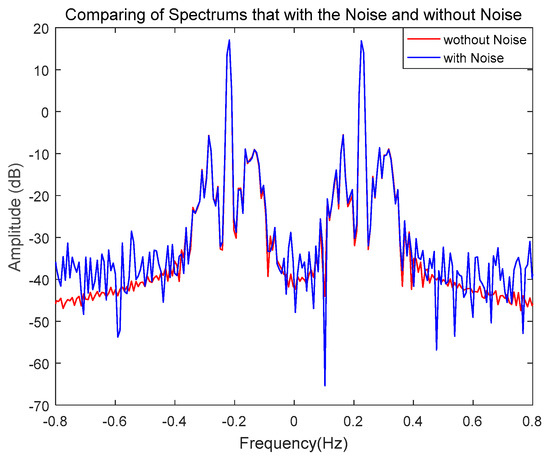
Figure 7.
RD spectrum of sea-clutter before and after introducing the noise.
After introducing the noise, many singular values appear in the calculation result of the motion compensation parameters, as shown in Figure 8a. Although the envelope of the motion compensation parameter curve can still reflect the curve variation trend, these singular values will make it difficult for the motion compensation to eliminate the motion-induced peaks generated by motion modulation and will even generate fake peaks when restoring the sea-clutter to the level in absence of motion modulation. The motion compensation parameters are shown in Figure 8b, after being smoothed via a locally weighted regression (Lowess) algorithm. The singular values generated by noise are completely eliminated, the correlation coefficients between the motion compensation parameters and the real values are both greater than 0.95, and the root mean squared error (RMSE) values are both less than 0.12.
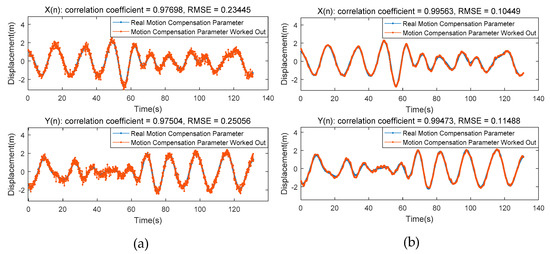
Figure 8.
Calculation result of motion compensation parameters after introducing the noise. (a) Before smoothing; (b) After smoothing.
Figure 9 shows the results of motion compensation using the motion compensation parameters. The magenta curve is the sea-clutter in the absence of motion, the blue curve is the sea-clutter modulated by 6-DOF motion, and the red curve is the sea-clutter after motion compensation. It can be seen that after motion compensation, the motion-induced peaks generated by motion modulation are greatly eliminated, the SNR corresponds to that in the absence of motion, the radar detection capability is greatly improved, and the compensation effect is good.
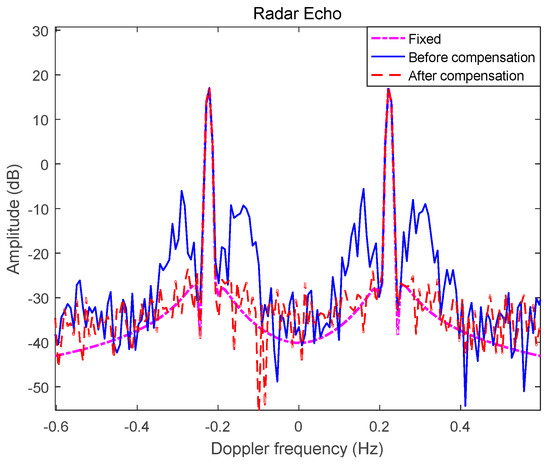
Figure 9.
Motion compensation effect of the sea-clutter.
4.3. Influence of the Reference RF Signals’ Emission Source Location on the Motion Compensation Effect
In practice, the location of the two reference RF signals’ emission source changes and is usually affected by the coastline. According to the principle derivation above, except for the situation where the reference RF signal emission source is in line with the shipborne platform and the motion compensation parameters cannot be calculated accurately, the reference RF signal source can be arranged in any other position. Below, traversal is used to investigate the relationship between the placement position of the reference RF signal transmitter and the compensation effect. The standard of evaluation is the RMSE between the sea-clutter signal after motion compensation and in the absence of motion.
4.3.1. Traversal of the Azimuth of the Dual Reference RF Signals’ Emission Source
First, a traversal is conducted of the azimuth of the reference RF signals’ emission source. The parameters of the reference RF signals are set as in Table 1. The distance from the reference RF signals’ emission source to the shipborne platform is fixed at 50 km; the azimuth of both reference RF signals’ emission source is from to , with a traversal step of . The traversal result is shown in Figure 10.
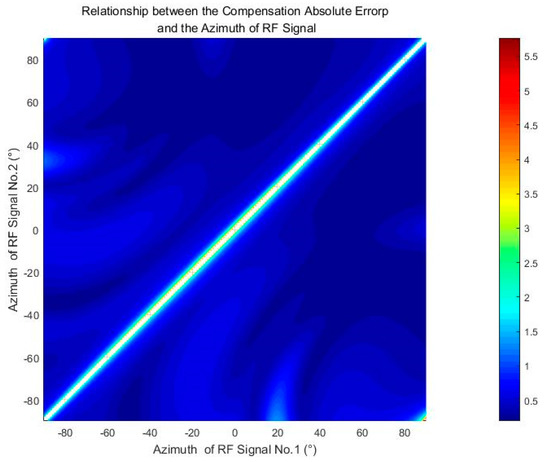
Figure 10.
Traversal result of azimuth.
The axes in the figure are the azimuths of the reference RF signals No. 1 and No. 2, respectively. The color represents the amplitude of the RMSE, and the color bar refers to the value of the RMSE corresponding to the color. It can be seen from the figure that, while two reference RF signals are not located in line with the shipborne platform, the effect of the motion compensation is generally the same; the RMSEs are no more than 1 dB. In addition, when the difference of the azimuths of the reference RF signals is less than , the compensation effect may decline, with the RMSE rising to 3 dB corresponding to an SNR decline of about 5 dB.
4.3.2. Traversal of Azimuth of the Dual Reference RF Signals’ Emission Source with Phase Deviation
According to Equation (26), when the azimuth of the reference RF signals’ emission source is fixed, the deviation of motion compensation parameters and is related to the phase deviation; that is, when the phase deviation increases, the deviation of motion compensation parameters increases, leading to a negative impact on the motion compensation effect. Therefore, a traversal of the azimuth of the reference RF signals’ emission source can be conducted to study the motion compensation effect under the largest phase deviation. From Equation (25), a bad positional accuracy may lead to a large phase deviation. For generality, a positional error of 10 m is used in the traversal, and the other parameters are set as the traversal in Section 4.3.1. The traversal result is shown in Figure 11.
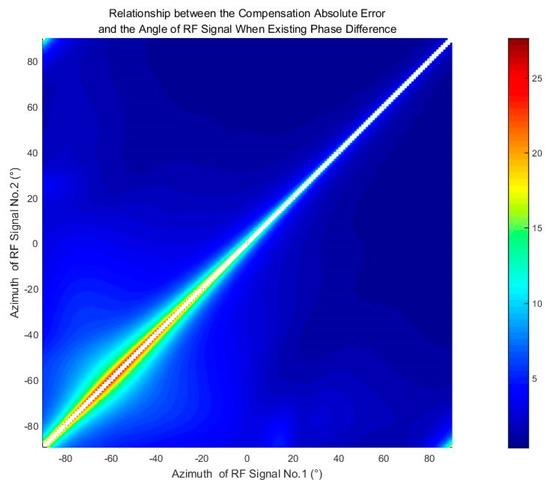
Figure 11.
Traversal result with phase deviation.
It can be seen from this result that the RMSEs increase. When the azimuth of the reference RF signals is particularly close, the RMSEs reach the maximum 25 dB. The RMSE on the other azimuth is around 5 dB, which can still present a significant motion compensation effect. Therefore, it is suggested that the azimuth difference of two reference RF signals should be larger than . Additionally, with a more precise positioning accuracy, the deviation of motion compensation parameters will decline greatly, leading to a better compensation effect. Thus, higher positioning accuracy is suggested, if permitted.
4.4. Method Comparison
The method proposed in this paper is compared to the method proposed in [1]. The method proposed in [1] can only compensate the 6-DOF motion of a single frequency sinusoidal model, and the method proposed in this paper can compensate the 6-DOF motion of any form. A sinusoidal motion model is introduced in the comparison. The motion of all DOF is in the form of
where n still refers to the n-th sweep period, refers to the attitude of different DOF motion, and a and are the motion parameters, referring to the amplitudes and the angular frequencies, respectively. The motion parameters are what the method proposed in [1] needs to identify, and they can determine the motion of each DOF. The motion parameters of each DOF are necessary for the method proposed in [1] when operating, and the motion parameters for the comparison are set as in Table 2, which is set the same as the simulation in [1].

Table 2.
Motion parameters for method comparison.
AWGN is also introduced as the background noise in the comparison. Therefore, the precision of the motion parameters identified by the method in [1] may decline. The precision of the motion compensation parameters calculated by the method proposed in this paper may also decline. However, the smoothing algorithm mentioned in Section 4.2 can improve the precision, and the noise has little influence on the method proposed in this paper.
The motion compensation effects of both methods are shown in Figure 12. The difference between the curve after the compensation and the curve in the absence of the motion modulation of both methods is also compared, as shown in Figure 13. It can be seen in the comparison that when using the method proposed in this paper, the amplitude of the motion-induced peaks is about 10 dB lower than that of using method proposed in [1]. The difference in the curve of the method proposed in this paper is especially lower in the position of motion-induced peaks.
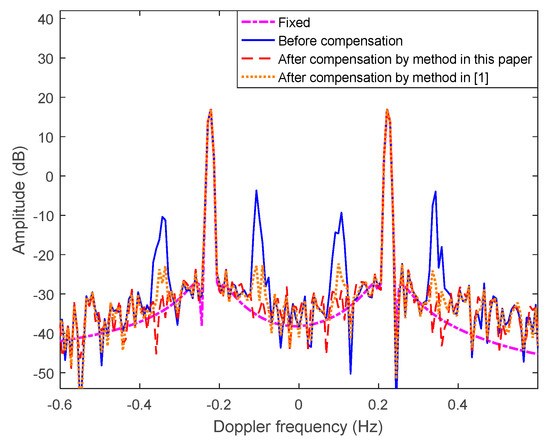
Figure 12.
The compensation effects of both methods.
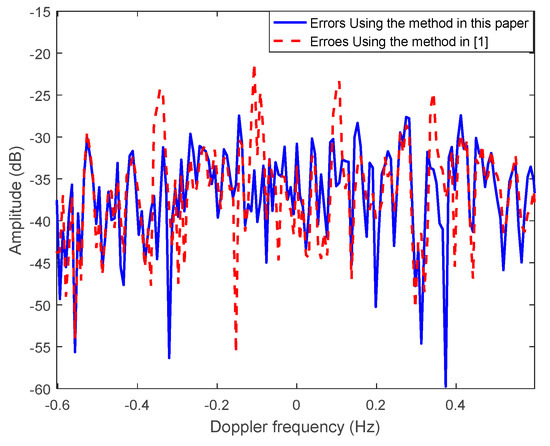
Figure 13.
The difference in the curve of both methods.
The comparison above shows that the method proposed in this paper provides a slightly better motion compensation effect than that proposed in [1] when the platform is under sinusoidal 6-DOF motion, especially in eliminating the motion-induced peaks. Furthermore, for the more realistic scene when the platform motion is arbitrary, the method proposed in [1] fails, while the method proposed in this paper can still work. Above all, the method proposed in this paper has a better performance in compensating for the 6-DOF motion.
5. Discussion
According to the extant analysis in this field, the motion compensation parameters calculated by a dual reference RF signal can recover the sea-clutter signal of HFSWR modulated by 6-DOF motion. Motion compensation methods are usually based on 6-DOF motion with an accurate sinusoidal model. Therefore, the motion attitude should be fitted by the sum of the sine curve, which may present inaccuracies. The problems above are inevitable in most of the existing motion compensation methods. A 6-DOF motion compensation method for arbitrary motion (i.e., the motion does not need to be described by a specific model) is proposed in this paper. In this compensation method, four 6-DOF motions, which are the main influencing factors, are projected in two directions, and the displacement of the array in these two directions, which we call the motion compensation parameters, is calculated by using the information of the dual reference RF signal. This method can calculate the motion compensation parameters in a real ocean environment, achieving a better motion compensation effect.
This research also suggests problems for further study. First, this paper only includes research on motion compensation under the 6-DOF motion of the shipborne platform, excluding that on a shipborne platform under a forward-movement state. In future work, the characteristics of a reference RF signal under a forward-movement state will be studied in depth, and a corresponding motion compensation method based on the reference RF signal will be proposed, in combination with the characteristics of the radar echo signal, to improve the complete motion compensation algorithm of the shipborne platform.
Second, the phase difference, as analyzed in this paper, will cause a fixed deviation on the motion compensation, leading to a decline in the motion compensation. According to prior analysis, to avoid the influence of the phase difference, the best method is to choose an appropriate location of the reference RF signals’ emission source and adopt a positioning system with high precision. In the future, a more detailed analysis may be carried out regarding the phase deviation, and a more effective method may be proposed in eliminating the decline it causes.
In addition, virtual targets and wind direction have not been considered in the current simulation model. Future models will take these factors into account to build a more realistic radar simulation. The effect of motion compensation under the conditions of a virtual target and different wind directions will be analyzed in further study.
Finally, a dual reference RF signal with a single frequency is currently used to realize motion compensation. Further study of the characteristics of different reference signal waveforms under the 6-DOF movement and conditions will be conducted to design a motion compensation method based on the special waveform reference signal with a lesser number of reference RF signals. This will also improve the ability of motion compensation in recovering the motion-modulated RD spectrum.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposed a method of calculating motion compensation parameters and compensating for 6-DOF motion modulation by using dual reference RF signals. Dual reference RF signals were added into the shipborne HFSWR echo model. Moreover, the principle and the feasibility of the motion compensation based on dual reference RF signals were analyzed. Several key problems were proposed according to the calculation of the motion compensation parameters and the principle of the motion compensation, including the extraction of reference RF signals from radar echo, the location of dual reference RF signals’ emission source, and the influence of the reference RF signal phase deviation on the motion compensation effect. This paper also presented simulation results. The simulation results show that the sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion can be recovered to the level of the absence of motion by using motion compensation parameters calculated by dual reference RF signals.
The analysis of the principle and the simulation results show that the proposed method is robust to some extent. The motion compensation parameters can still be worked out under the situation of background noise; the effect of the motion compensation will not be affected significantly, with the fake peaks caused by shipborne platform 6-DOF motion modulation eliminated. In addition, although the calculation of the motion compensation parameters may be influenced (such as through the appearance of a fixed deviation) when the initial phase of reference RF signals is difficult to confirm, the influence on recovering the sea-clutter signal modulated by 6-DOF motion is limited. According to the traversal of the reference RF signals’ emission source location, the method proposed in this paper has no special requirements. Except for a few situations (i.e., when the reference RF signals are in line with the shipborne platform) in which the motion compensation method proposed in this paper fails in principle, locations will not significantly affect the motion compensation.
Some problems are worth further study in the future. First, motion compensation can be extended to the situation containing forward movement. Next, the motion compensation method can be optimized under the influence of noise. Finally, a more realistic simulation can be built. In addition, a field experiment will be carried out at sea using a variation of the motion compensation method based on dual reference RF signals proposed in this paper.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and J.N.; methodology, M.L. and Q.M.J.W.; software, M.C.; validation, M.C. and J.N.; formal analysis, M.C.; data curation, M.C. and W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C.; writing—review and editing, J.N., M.L. and L.Z.; visualization, M.C.; supervision, J.N. and L.Z.; project administration, J.N., Y.J. and L.Z.; funding acquisition, J.N., Y.J. and L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFC1405202) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51979256).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The expression of the phase of the array steering vector in absence of motion is
The expression of the phase of the array steering vector modulated by other 5-DOF motions, excluding heave, is [5]
The expression of the phase of array steering vector containing the heading changes only is
where represents the changing radian of heading.
The specific process of working out uniquely is
where refers to the real part and refers to the imaginary part.
Appendix B
The derivation of Equation (6) is as follows. The phase of the array steering vector is
While the amplitude of the roll , pitch , and heading changes of the shipborne platform are no more than , the approximation as follows is appropriate: . Then, Equation (A5) can be simplified as
The component containing the heading changes can be defined as , which can be expressed as
In this way, may be rewritten as
Appendix C
The influence of the initial phase on the motion compensation parameters is as follows.
Assuming the initial phase of is and that of is , the phase deviation is . Then, and can be respectively expressed as
and
Therefore, . According to Equation (17), the equation containing the motion compensation parameters can be expressed as
Let . Equation (A11) can be rewritten as follows when the imaginary part of is more than 0.
Define , where and refer to the motion compensation parameters calculated by reference RF signals’ existing phase deviation. Then
From Equation (A13), we have
In can be easily proved in the same way that, when the imaginary part of is less than 0, and also obey Equation (A14). That is, the phase deviation will only lead to a fixed deviation in the motion compensation.
References
- Zhu, D.; Niu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Y.; Wu, Q.M.J. Motion Parameter Identification and Motion Compensation for Shipborne HFSWR by Using the Reference RF Signal Generated at the Shore. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Sun, M.; Ji, Z. First-order ocean surface cross-section for shipborne HFSWR. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Xie, J.; Huang, W. First-order ocean surface cross-section for shipborne HFSWR incorporating a horizontal oscillation motion model. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Y.; Xie, J. Measurements of ocean surface currents using shipborne High-Frequency radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, G.; Li, M.; Xie, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Ji, Y. Ocean Surface Current Measurement Using Shipborne HF Radar: Model and Analysis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dizaji, R.; Ponsford, A.M. An analysis of phase array radar system on a moving platform. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, AG, USA, 9–12 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- El, K.J.; Guinvarc’H, R.; Gillard, R.; Uguen, B. Sea-echo doppler spectrum perturbation of the received signals from a floating high-frequency surface wave radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Lipa, B.J.; Barrick, D.E.; Isaacson, J.; Lilleboe, P.M. CODAR wave measurements from a North Sea semisubmersible. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 1990, 15, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y. Experimental analysis of sea clutter in shipborne HFSWR. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2001, 148, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, K.W.; Essen, H.H. On the performance of a shipborne current mapping HF radar. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 2000, 25, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, R.; Walsh, J. Measurement of Ocean Wave Spectra Using a Ship-Mounted HF Radar. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 1993, 18, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Huang, W.; Gill, E. The First-Order High Frequency Radar Ocean Surface Cross Section for an Antenna on a Floating Platform. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 2010, 58, 2994–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.; Huang, W.; Gill, E. The Second-Order High Frequency Radar Ocean Surface Cross Section for an Antenna on a Floating Platform. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 2012, 60, 4804–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Xie, J.; Ji, Z.; Sun, M. The first-order ocean surface cross section for shipborne HFSWR with rotation motion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, DC, USA, 8–12 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Xie, J.; Ji, Z.; Yao, G. Ocean surface cross sections for shipborne HFSWR with sway motion. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Gill, E.W.; Huang, W. High Frequency Radar Cross Sections of the Ocean Surface Incorporating Pitch and Roll Motions of a Floating Platform. In Proceedings of the 2018 OCEANS-MTS/IEEE Kobe Techno-Oceans (OTO), Kobe, Japan, 28–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Gill, E.W.; Huang, W. Bistatic High-Frequency Radar Ocean Surface Cross Section Incorporating a Dual-Frequency Platform Motion Model. IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 2018, 43, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Xie, J.; Huang, W. Ocean Surface Cross Section for Bistatic HF Radar Incorporating a Six DOF Oscillation Motion Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, E.W.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W. Motion compensation for high-frequency surface wave radar on a floating platform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, A.; Guinvarc’h, R.; Uguen, B.; Gillard, R. High-frequency surface wave radar based on a sea floating antenna concept. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2009, 3, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, A.; Guinvarc’H, R.; Uguen, B.; Gillard, R. Swell Compensation for High Frequency antenna array on buoys. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 9–14 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Study on Some Problems of Signal Processing in Buoys-based HF Surface Wave Radar. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.N.; Shiraishi, S.; Das, S.K. Mathematical modeling of sway, roll and yaw motions: Order-wise analysis to determine coupled characteristics and numerical simulation for restoring moment’s sensitivity analysis. Acta Mech. 2010, 213, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahar, A.; Kim, M.H. Hull/mooring/riser coupled dynamic analysis and sensitivity study of a tanker-based FPSO. Appl. Ocean Res. 2003, 25, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).