Mapping the Northern Limit of Double Cropping Using a Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets and Pre-processing
2.2.1. Satellite Data and Pre-Processing
2.2.2. Cropland Extent Data
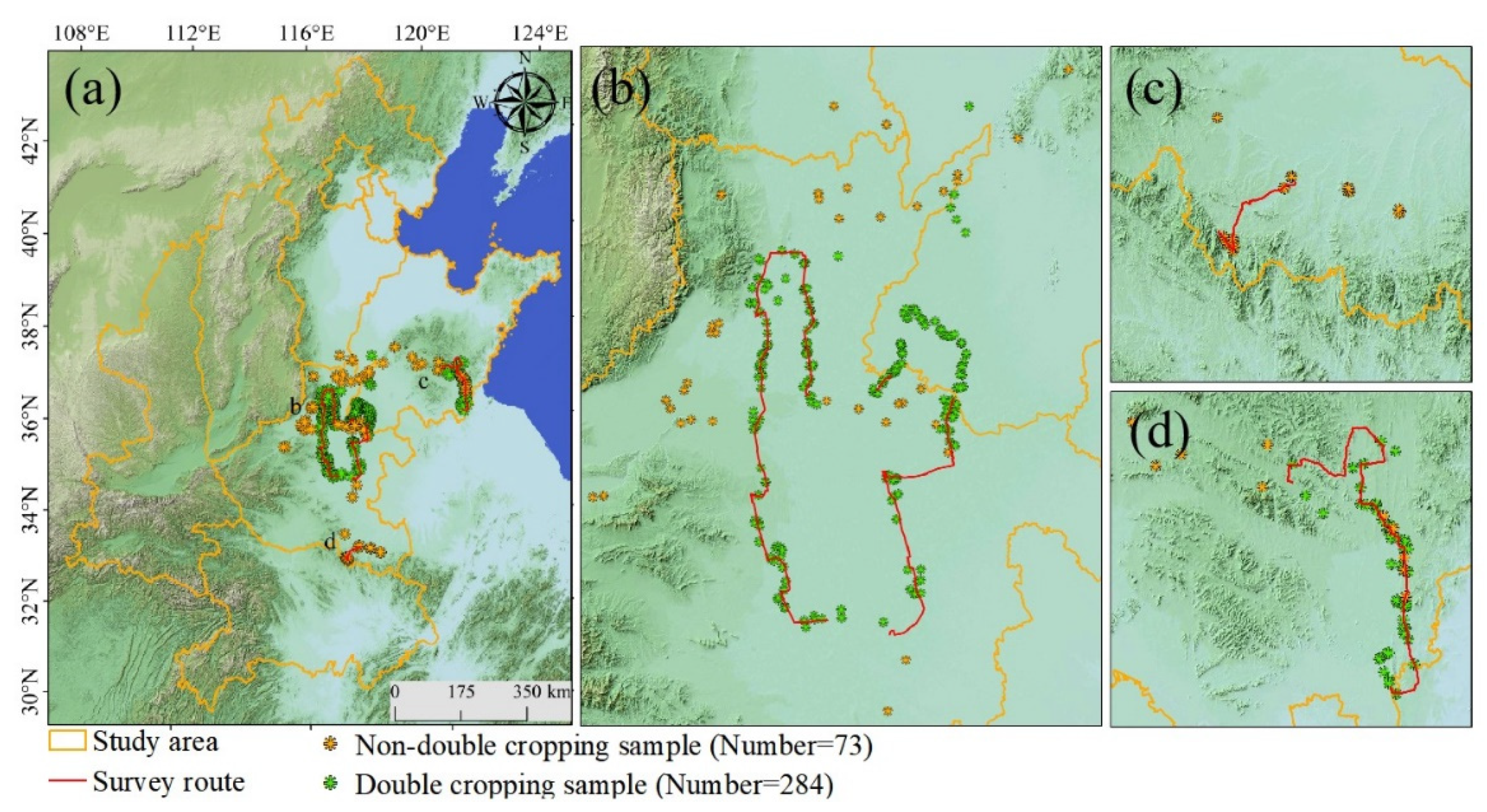
2.2.3. Ground Reference Datasets
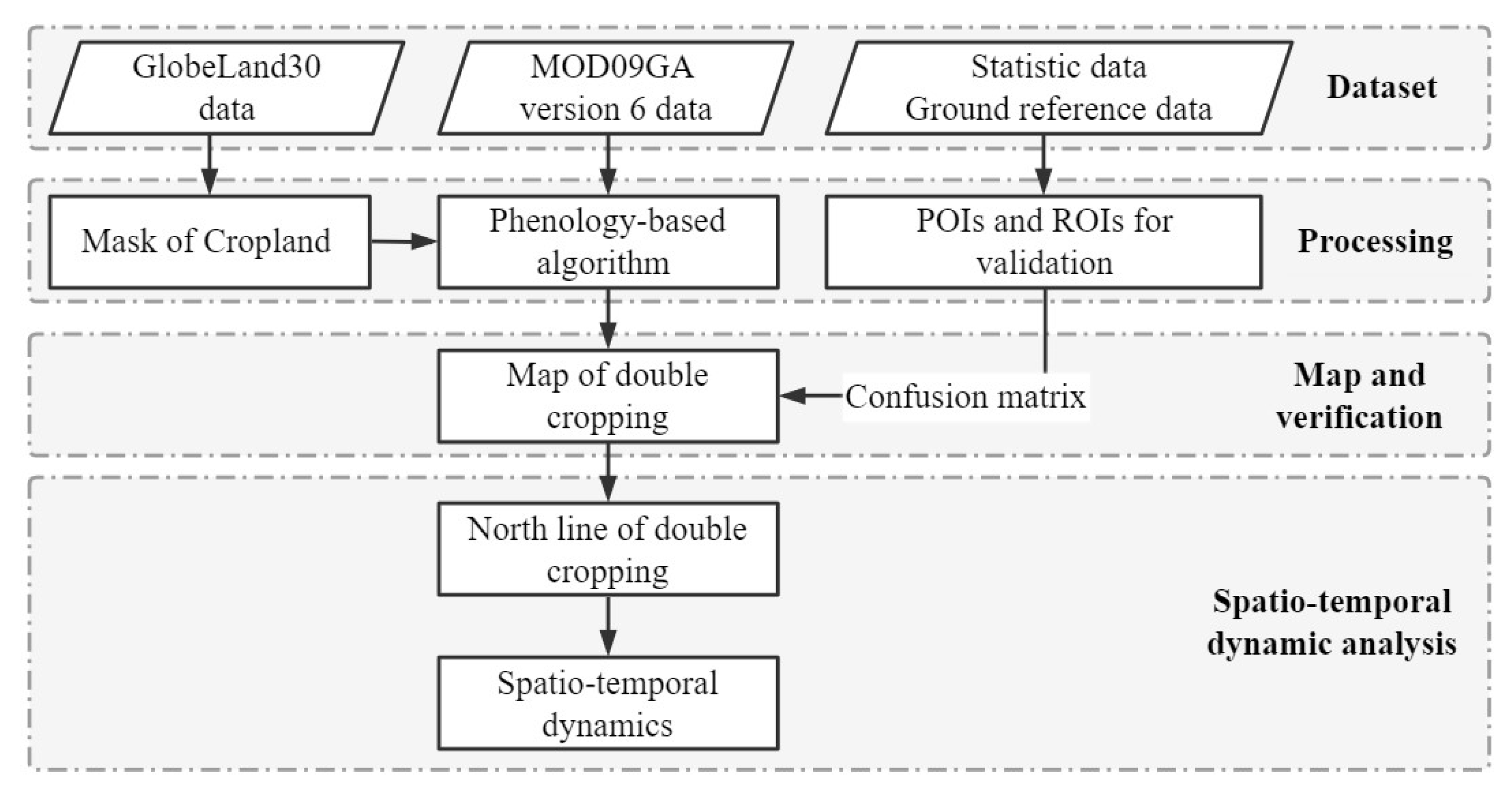
2.3. Methods
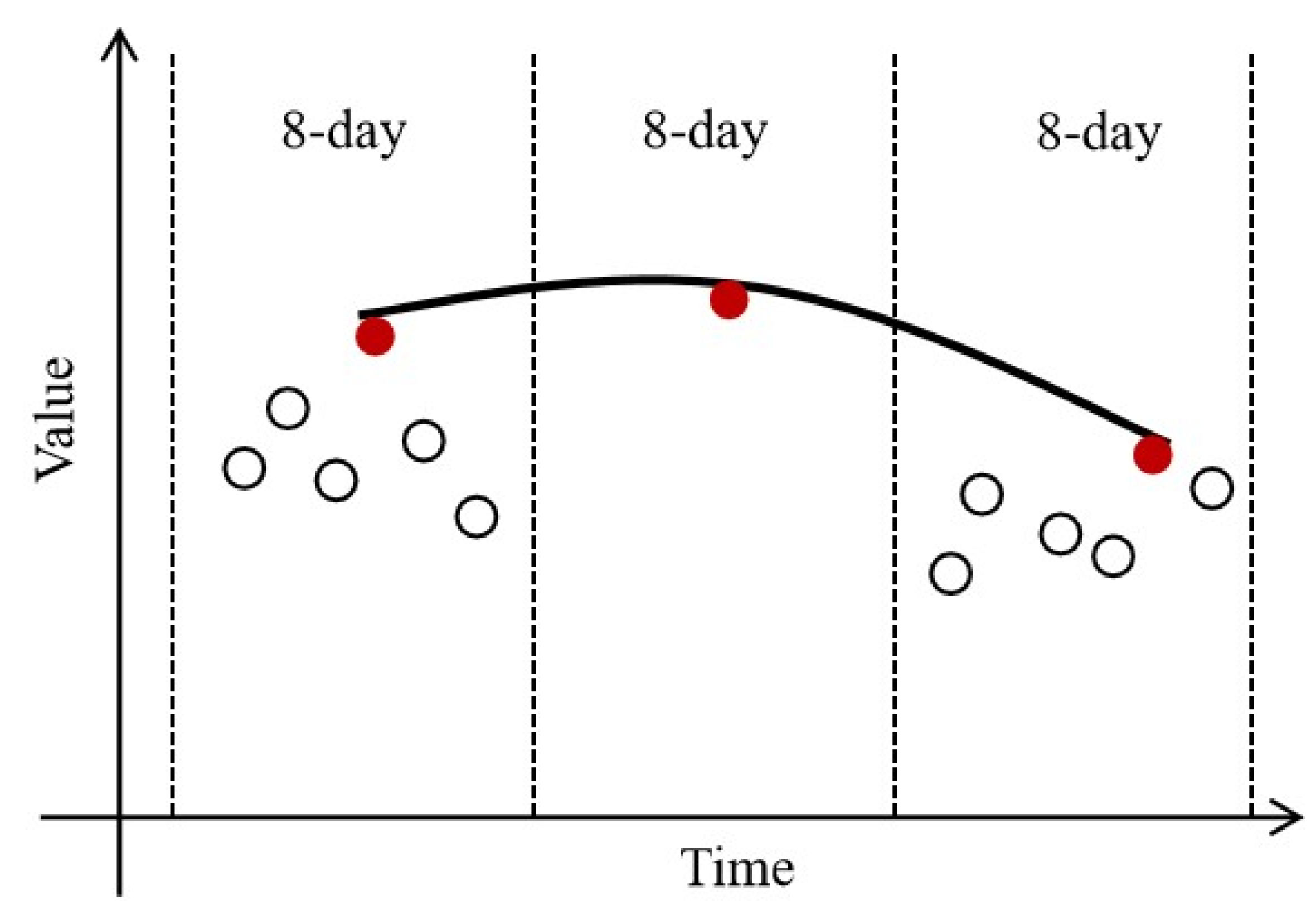
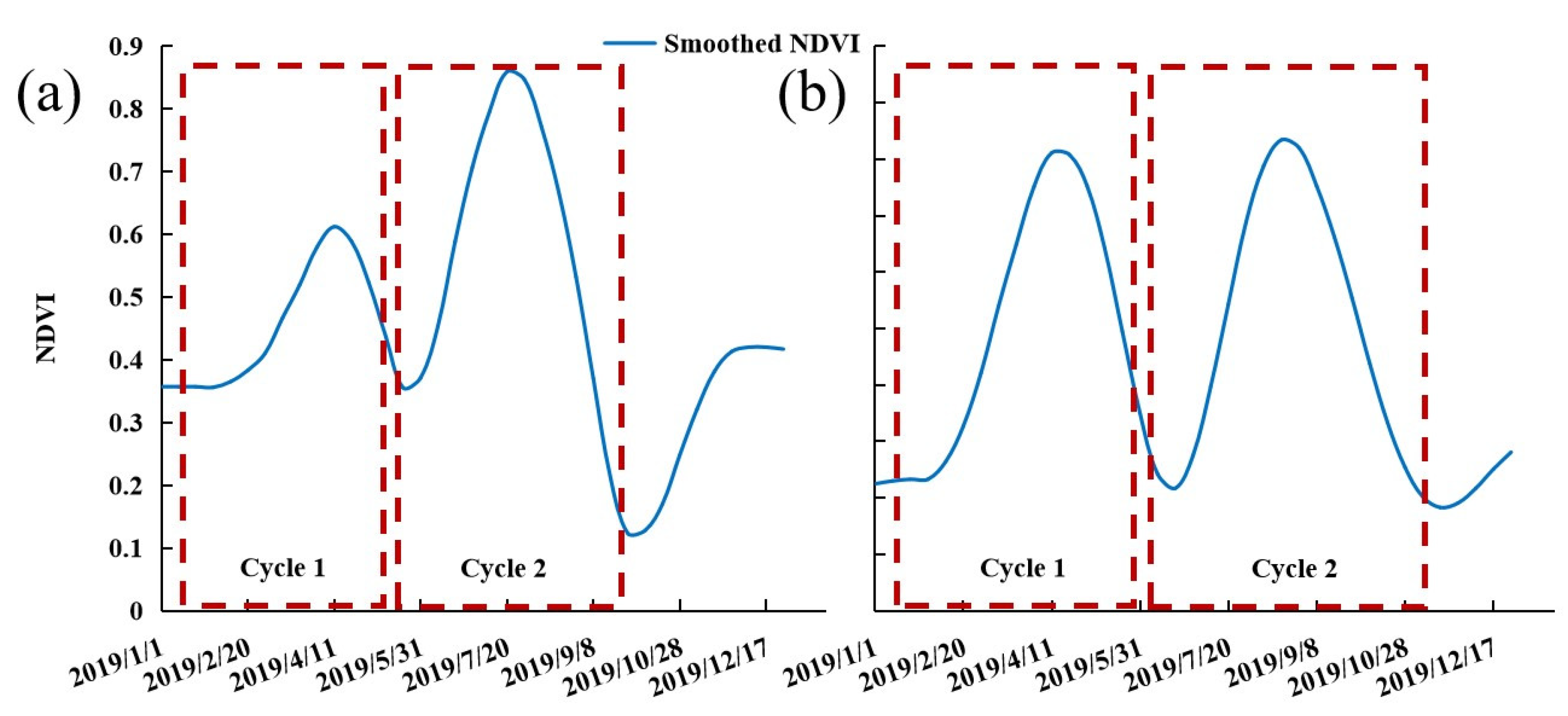
2.3.1. Annual Double-Cropping Map
2.3.2. Accuracy Assessment of the Resultant Annual Maps
2.3.3. Extraction of the NLDC
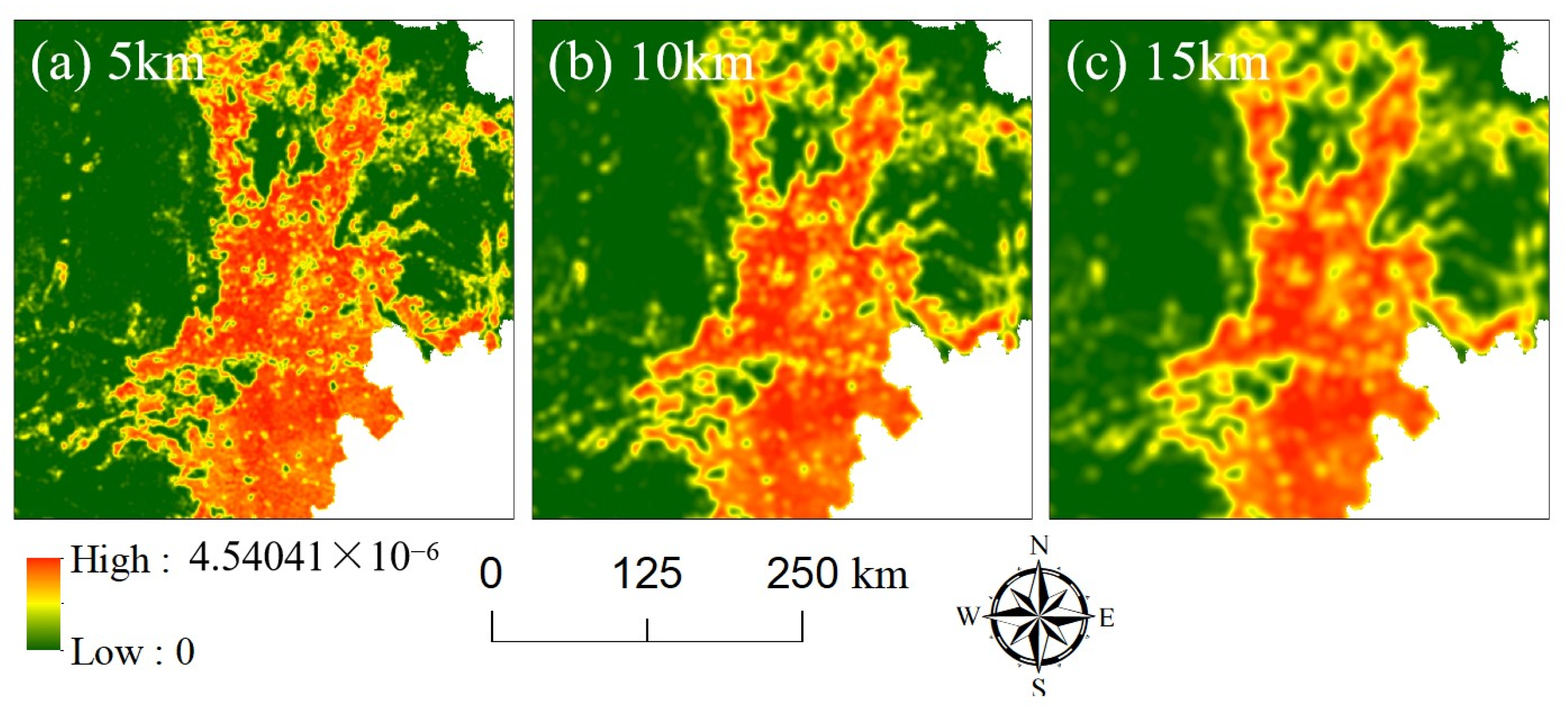
2.3.4. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of the NLDC
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of Double-Cropping Maps
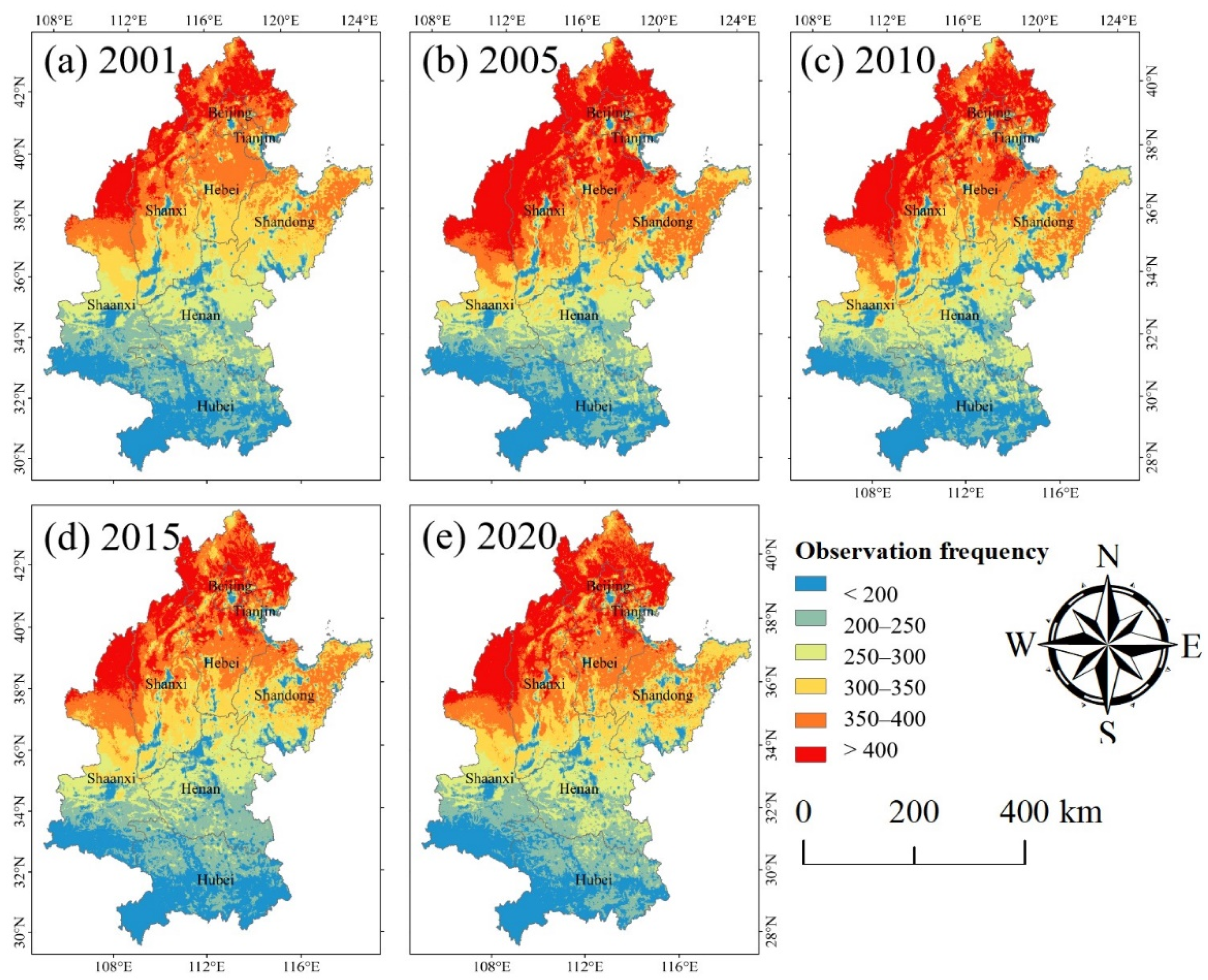
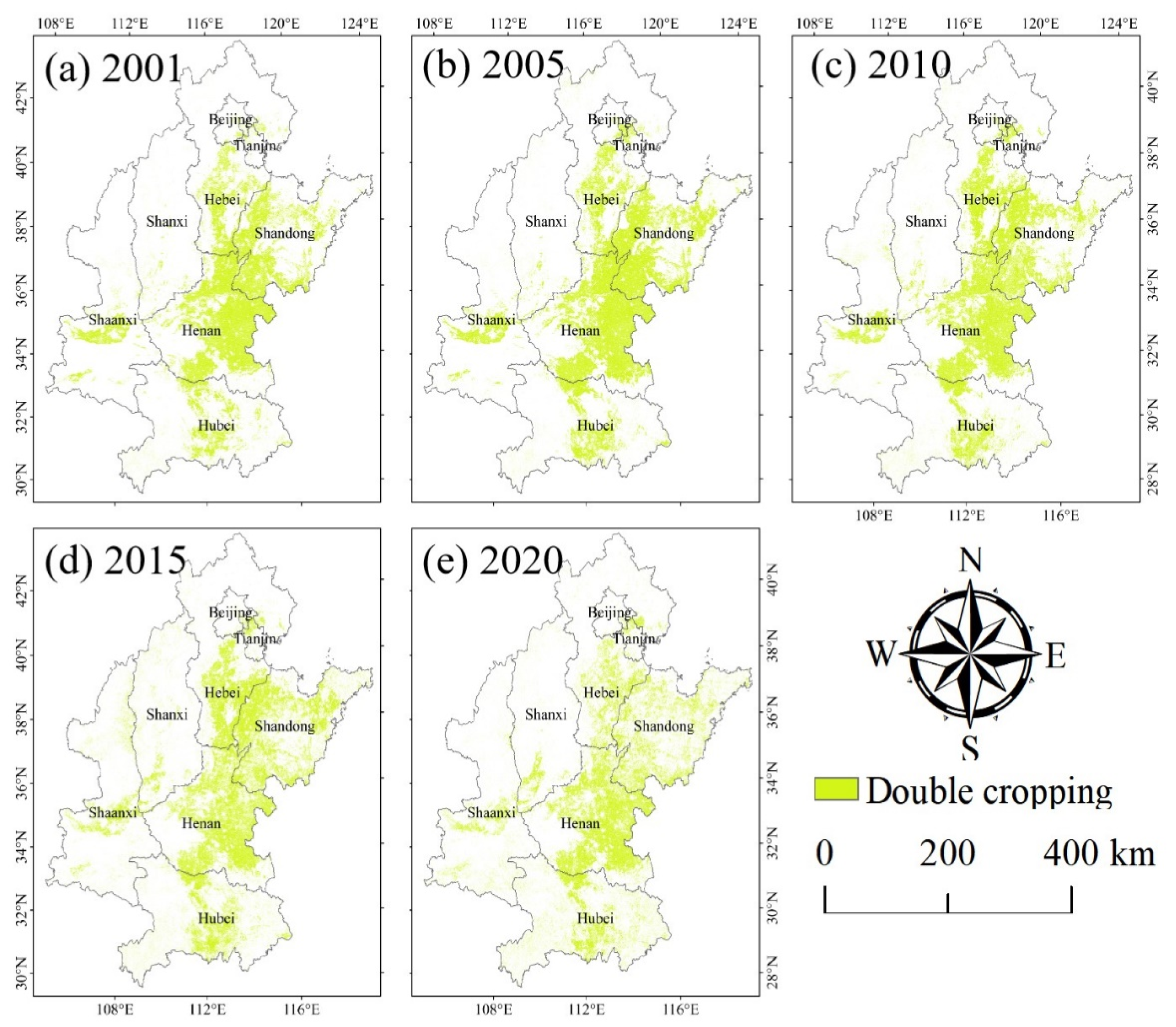
3.2. Maps of Double Cropping
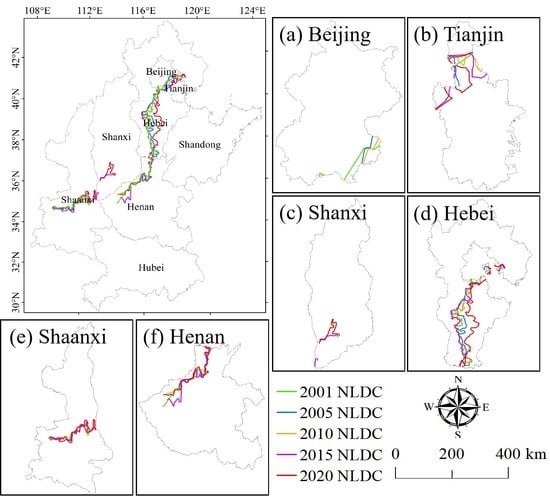
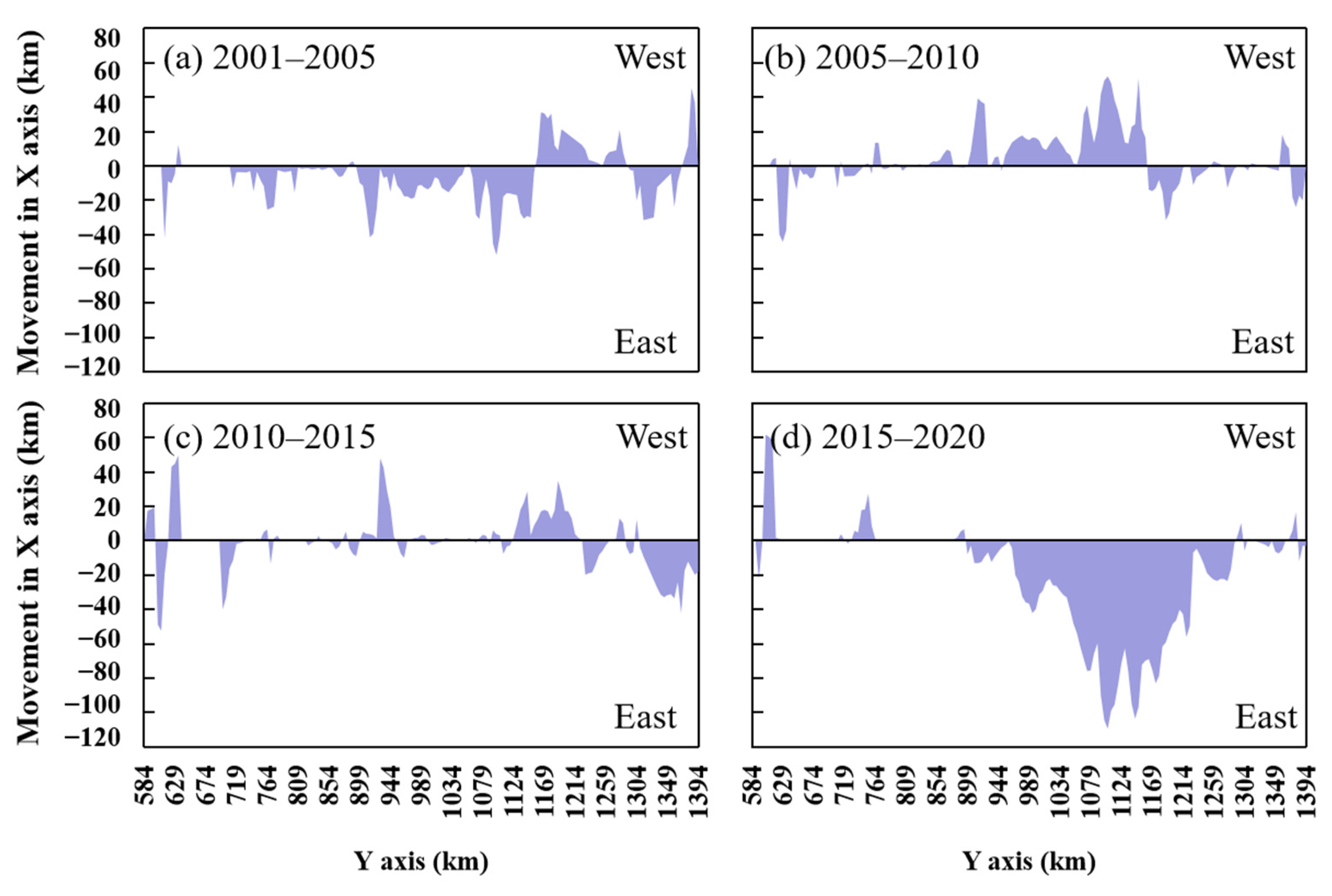
3.3. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of the NLDC
4. Discussion
4.1. Annual Map of Double-Cropping Croplands over Large Spatial Domains
4.2. Analysis of Driving Factors for Shifts of the NLDC
4.3. Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; You, L.; Chen, K.; Tang, H.; Liu, J. Global cropping intensity gaps: Increasing food production without cropland expansion. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, T.; Rivas, M.J.I.; Koch, W.; Nonhebel, S. Global changes in diets and the consequences for land requirements for food. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6868–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Amour, C.B.; Reitsma, F.; Baiocchi, G.; Barthel, S.; Güneralp, B.; Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Creutzig, F.; Seto, K.C. Future urban land expansion and implications for global croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8939–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Liu, F.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.; Xiao, X. Tracking the spatio-temporal change of cropping intensity in China during 2000–2015. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Yi, L.; Liu, B. Developing grain production policy in terms of multiple cropping systems in China. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauser, W.; Klepper, G.; Zabel, F.; Delzeit, R.; Hank, T.; Putzenlechner, B.; Calzadilla, A. Global biomass production potentials exceed expected future demand without the need for cropland expansion. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löw, F.; Biradar, C.; Dubovyk, O.; Fliemann, E.; Akramkhanov, A.; Narvaez Vallejo, A.; Waldner, F. Regional-scale monitoring of cropland intensity and productivity with multi-source satellite image time series. GISci. Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 539–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhuang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, S. Changes in the potential multiple cropping system in response to climate change in China from 1960–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chen, Q.; Xin, L.; Li, L.; Li, X. Spatial and temporal variations of multiple cropping index in China based on SPOT-NDVI during 1999–2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Lin, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, K.; Ye, Q.; Li, Y.; Lv, S. Potential benefits of climate change for crop productivity in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 208, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-B.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Peter, V.H.; You, L.-Z.; Peng, Y.; Tang, H.-J. How could agricultural land systems contribute to raise food production under global change? J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Yao, F. Improved maize cultivated area estimation over a large scale combining MODIS–EVI time series data and crop phenological information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dong, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, H.; Xiao, X. Increasing cropping intensity in response to climate warming in Tibetan Plateau, China. Field Crops Res. 2013, 142, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. Impacts of climatic warming on cropping system borders of China and potential adaptation strategies for regional agriculture development. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Friedl, M.A.; Xin, Q.; Gray, J.; Pan, Y.; Frolking, S. Mapping crop cycles in China using MODIS-EVI time series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Xiao, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Bai, X. Multiple cropping intensity in China derived from agro-meteorological observations and MODIS data. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Batistella, M.; Dutra, L.V.; Sanches, I.D.A.; da Silva, R.F.B.; Huang, J.; Luiz, A.J.B.; de Oliveira, M.A.F. Mapping croplands, cropping patterns, and crop types using MODIS time-series data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, C.M.; Xiao, X. Quantifying the area and spatial distribution of double-and triple-cropping croplands in India with multi-temporal MODIS imagery in 2005. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galford, G.L.; Mustard, J.F.; Melillo, J.; Gendrin, A.; Cerri, C.C.; Cerri, C.E. Wavelet analysis of MODIS time series to detect expansion and intensification of row-crop agriculture in Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, W. From multiple cropping index to multiple cropping frequency: Observing cropland use intensity at a finer scale. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P. Farmland cropping system identification in China based on a sliding segmentation algorithm. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Canisius, F.; Turral, H.; Molden, D. Fourier analysis of historical NOAA time series data to estimate bimodal agriculture. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5503–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, S.; Upadhyay, G.; Ray, S.S.; Parihar, J.S. Mapping of cropping system for the Indo-Gangetic plain using multi-date SPOT NDVI-VGT data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Mondal, P.; DeFries, R.S.; Small, C.; Galford, G.L. Mapping cropping intensity of smallholder farms: A comparison of methods using multiple sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Robinson, G.M.; Li, X.; Xin, L. Spatial and temporal variability of farm size in China in context of rapid urbanization. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, S.; Qi, J.; Ding, M.; Guan, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Nabil, M.; Tian, F. A new framework to map fine resolution cropping intensity across the globe: Algorithm, validation, and implication. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore III, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Nendel, C.; Hostert, P. Intra-annual reflectance composites from Sentinel-2 and Landsat for national-scale crop and land cover mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Baret, F.; Verger, A.; Neveux, P.; Weiss, M. A comparison of methods for smoothing and gap filling time series of remote sensing observations–application to MODIS LAI products. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Mapping Winter Crops Using a Phenology Algorithm, Time-Series Sentinel-2 and Landsat-7/8 Images, and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Ban, Y.; Li, S. Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 2014, 514, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Alfieri, J.G.; Kustas, W.P.; Mueller, R.; Johnson, D.M.; Prueger, J.H. Toward mapping crop progress at field scales through fusion of Landsat and MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, H.; Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Bian, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, C. Development of a New Phenology Algorithm for Fine Mapping of Cropping Intensity in Complex Planting Areas Using Sentinel-2 and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xiao, X.; Ye, H.; Ma, J.; Doughty, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Z.; Sun, R.; Dong, J. Mapping forest and their spatial–temporal changes from 2007 to 2015 in tropical hainan island by integrating ALOS/ALOS-2 L-Band SAR and landsat optical images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986–2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Qin, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ge, S. Summer Maize Mapping by Compositing Time Series Sentinel-1A Imagery Based on Crop Growth Cycles. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L. Identifying the urban-rural fringe using wavelet transform and kernel density estimation: A case study in Beijing City, China. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 83, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wu, W.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Fan, L.; You, L.; Yang, P. Climate-mediated dynamics of the northern limit of paddy rice in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 064008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, K.M.; Thakur, G.; Sparks, K.A.; Urban, M.L.; Rose, A.N.; Stewart, R.N. Dynamically-Spaced Geo-Grid Segmentation for Weighted Point Sampling on A Polygon Map Layer; Oak Ridge National Lab(ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; González-Zamora, A.; Sánchez, N.; Gumuzzio, A.; Herrero-Jiménez, C. Satellite soil moisture for agricultural drought monitoring: Assessment of the SMOS derived Soil Water Deficit Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, G.; Adams, B. Juxtaposing thematic regions derived from spatial and platial user-generated content. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on spatial information theory (COSIT 2017), L’Aquila, Italy, 4–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilø, L.; Finstad, E.; Ramsey, C.B.; Martinsen, J.R.P.; Nesje, A.; Solli, B.; Wangen, V.; Callanan, M.; Barrett, J.H. The chronology of reindeer hunting on Norway’s highest ice patches. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Development of quantitative methods for detecting climate contributions to boundary shifts in farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Lu, D.; Tang, Z.; Song, D.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, N.; Huang, H.; Xu, W. Mapping cropping intensity trends in China during 1982–2013. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Wang, R.; Song, H.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Mapping cropping intensity in Huaihe basin using phenology algorithm, all Sentinel-2 and Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Shi, W. Review on boundary shift of farming-pastoral ecotone in northern China and its driving forces. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Anthropogenic contributions dominate trends of vegetation cover change over the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, M.; Chang, R.; Zhan, Q.; Li, Z.L. Surface warming trend analysis based on MODIS/Terra land surface temperature product at Gongga Mountain in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Lowry, A.L.; Alexander, L.V.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Maher, N. More extreme precipitation in the world’s dry and wet regions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wen, F.; Wang, Q.; Sanchez, N.; Piles, M. Seamless downscaling of the ESA CCI soil moisture data at the daily scale with MODIS land products. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tao, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Dong, J.; Shi, X. Has climate change driven spatio-temporal changes of cropland in northern China since the 1970s? Clim. Chang. 2014, 124, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Sun, L. Drivers of cropland abandonment in mountainous areas: A household decision model on farming scale in Southwest China. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Li, X. Global understanding of farmland abandonment: A review and prospects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1123–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Berry, J. Urban expansion or poor productivity: Explaining regional differences in cropland abandonment in China during the early 21st century. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Xu, X. Analysis of farmland abandonment at parcel level: A case study in the mountainous area of China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Cao, G.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S. An estimation of the extent of cropland abandonment in mountainous regions of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Rozelle, S. The subsidization of farming households in China’s agriculture. Food Policy 2013, 41, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, X.; Liang, S.; Cui, X.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Xia, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, W. Characterization of locations and extents of afforestation from the Grain for Green Project in China. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W. Accuracy assessment of GlobeLand30 2010 land cover over China based on geographically and categorically stratified validation sample data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wen, F.; Yin, G. DSRC: An Improved Topographic Correction Method for Optical Remote-Sensing Observations Based on Surface Downwelling Shortwave Radiation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Duan, S.-B. Reconstruction of daytime land surface temperatures under cloud-covered conditions using integrated MODIS/Terra land products and MSG geostationary satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Year | Period | Percentage | Year | Period | Percentage | Year | Period | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | T1 | 89.08% | 2009 | T3 | 94.58% | 2018 | ||
| 2001 | 2010 | 2019 | T5 | 95.38% | ||||
| 2002 | 2011 | 2020 | ||||||
| 2003 | 2012 | 2021 | ||||||
| 2004 | T2 | 93% | 2013 | |||||
| 2005 | 2014 | T4 | 94.58% | |||||
| 2006 | 2015 | |||||||
| 2007 | 2016 | |||||||
| 2008 | 2017 |
| Error Matrix (Pixels) | Accuracy (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Double | Others | Total | UA | PA | OA | Kappa |
| Double | 959 | 81 | 1040 | 96.58 | 92.21 | 95.97 | 0.91 |
| Others | 34 | 1783 | 1817 | 95.65 | 98.13 | ||
| Total | 993 | 1864 | 2857 | / | / | / | / |
| Double-Cropping Fields/km2 | 2001 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 777.72 | 895.74 | 637.8750 | 506.82 | 300.99 |
| Tianjin | 764.4 | 1614.34 | 1759.37 | 1746.27 | 1504.95 |
| Hebei | 24,122.97 | 24,552.58 | 29,010.59 | 32,788.19 | 21,388.05 |
| Shaanxi | 12,431.18 | 13,241.76 | 11,633.79 | 14,450.15 | 11,903.73 |
| Shanxi | 2817.24 | 2971.20 | 4078.79 | 7779.98 | 6765.53 |
| Shandong | 44,237.51 | 53,377.09 | 44,768.53 | 51,512.28 | 34,426.19 |
| Henan | 71,661.99 | 75,854.59 | 68,087.11 | 60,217.61 | 63,979.69 |
| Hubei | 20,417.76 | 22,722.65 | 21,717.67 | 26,691.77 | 27,090.54 |
| Total area | 177,154.46 | 206,402.33 | 191,464.90 | 195,108.64 | 166,909.70 |
| Percentage of total farmland area | 70.17% | 76.89% | 69.33% | 78.27% | 66.15% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Xia, H.; Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, R. Mapping the Northern Limit of Double Cropping Using a Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14041004
Guo Y, Xia H, Pan L, Zhao X, Li R. Mapping the Northern Limit of Double Cropping Using a Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14041004
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yan, Haoming Xia, Li Pan, Xiaoyang Zhao, and Rumeng Li. 2022. "Mapping the Northern Limit of Double Cropping Using a Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14041004
APA StyleGuo, Y., Xia, H., Pan, L., Zhao, X., & Li, R. (2022). Mapping the Northern Limit of Double Cropping Using a Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14041004