Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on the Time-Frequency Constraint Joint Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Previous Work of RFI Detection
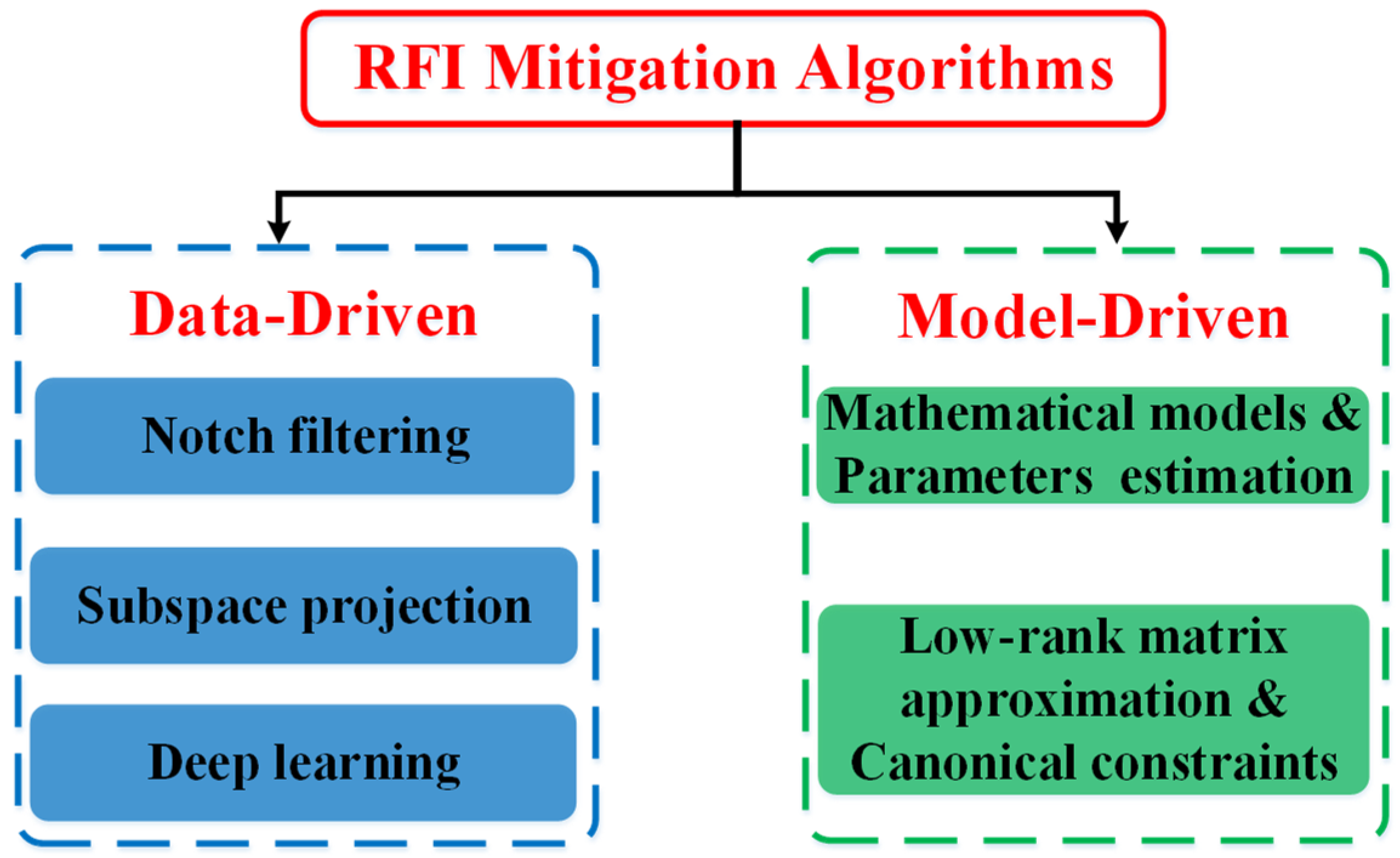
1.2. Previous Work on RFI Mitigation
- (1)
- Data-Driven RFI Mitigation Algorithms
- (2)
- Model-Driven RFI Mitigation Algorithms
1.3. Related Problems
1.4. Contributions
- (1)
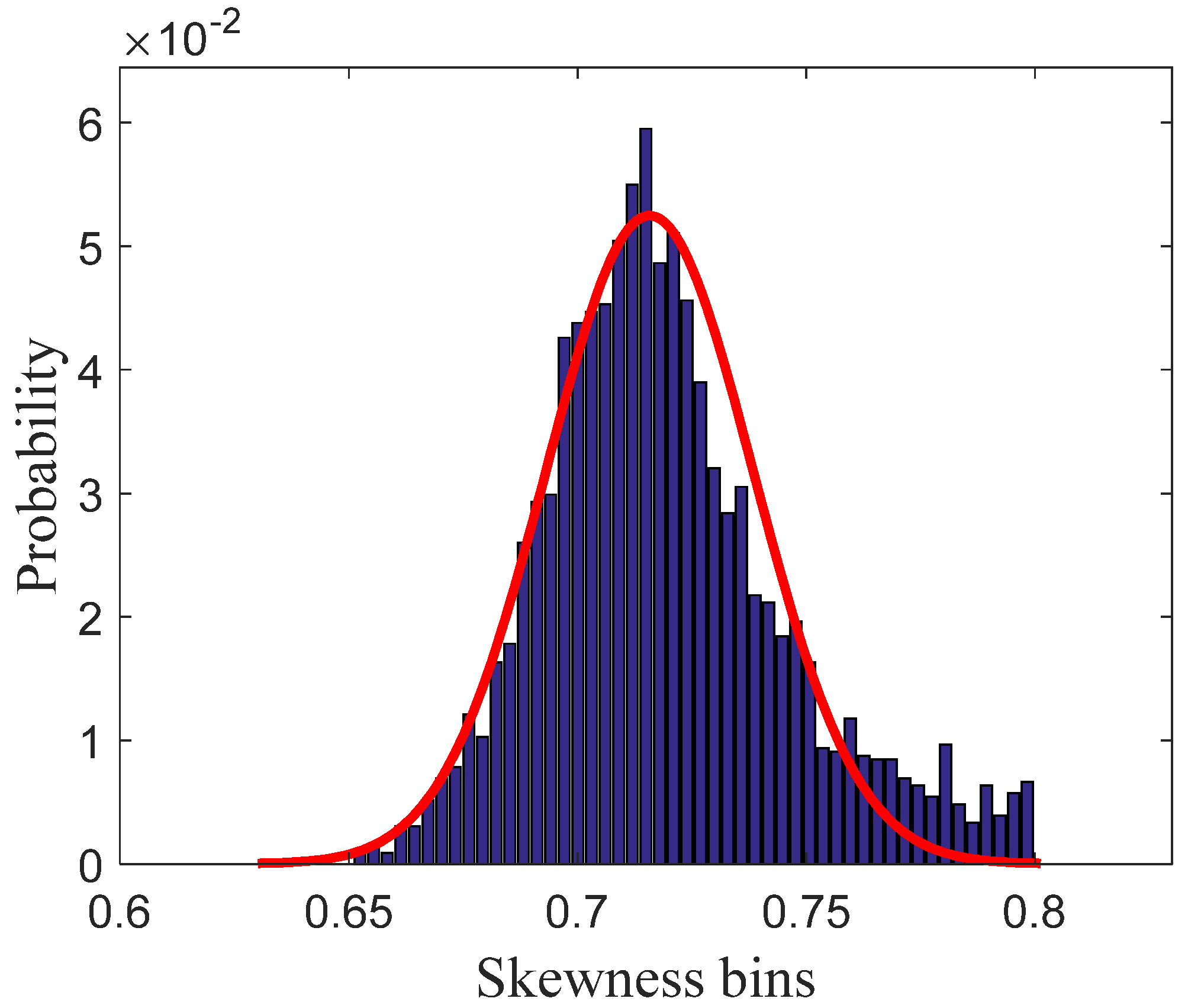
- An adaptive RFI detection method based on TF skewness is proposed. Aiming to solving the poor robustness of the existing RFI detection methods, this paper introduces TF skewness to measure the non-Gaussianity of the echo in the TF domain. It also achieves adaptive statistical detection of RFI with the Neyman–Pearson criterion, which is suitable for detecting both NBI and WBI.
- (2)
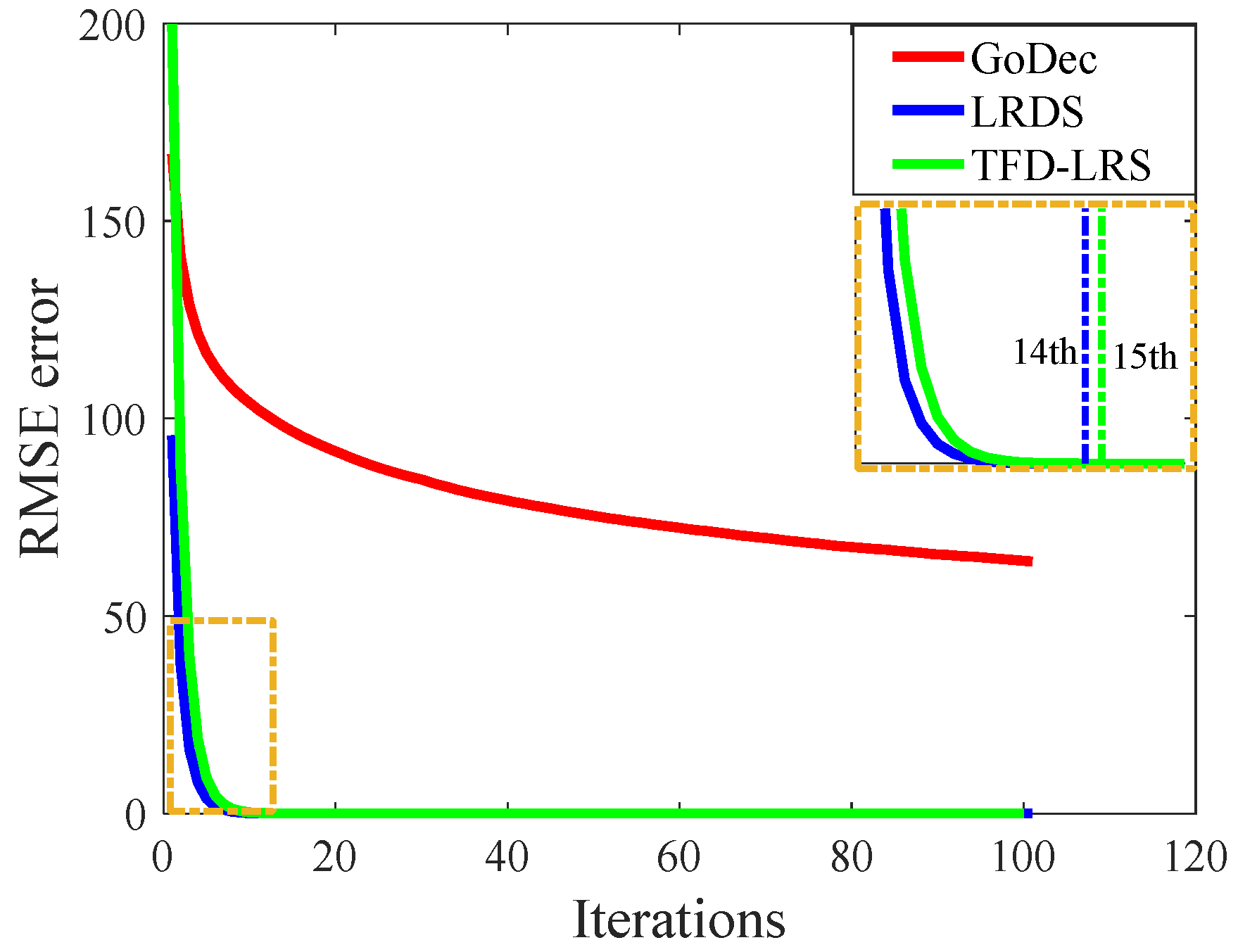
- The LRDS algorithm is proposed to improve the accuracy of the RFI mitigation model and accelerate its convergence speed. Based on the TF analysis of the measured data, this paper introduces the low-rank and sparsity characteristics for RFI. Meanwhile, a more accurate RFI reconstruction model is proposed, which restrains the sparsity and low-rank property of RFI and the sparsity of TES simultaneously. The LRDS algorithm promotes the accuracy of the RFI reconstruction model with less signal recovery error and significantly reduces the iteration number to find the optimal solution.
- (3)
- The TFC-LRS algorithm is formulated to specify the sparsity of RFI. By virtue of the aggregation property of RFI in the TF domain, the TF constraint concept is introduced to replace the sparsity of RFI. Compared with LRDS, TFC-LRS improves the model accuracy of RFI reconstruction and reduces the signal loss further without slowing down the convergence speed.
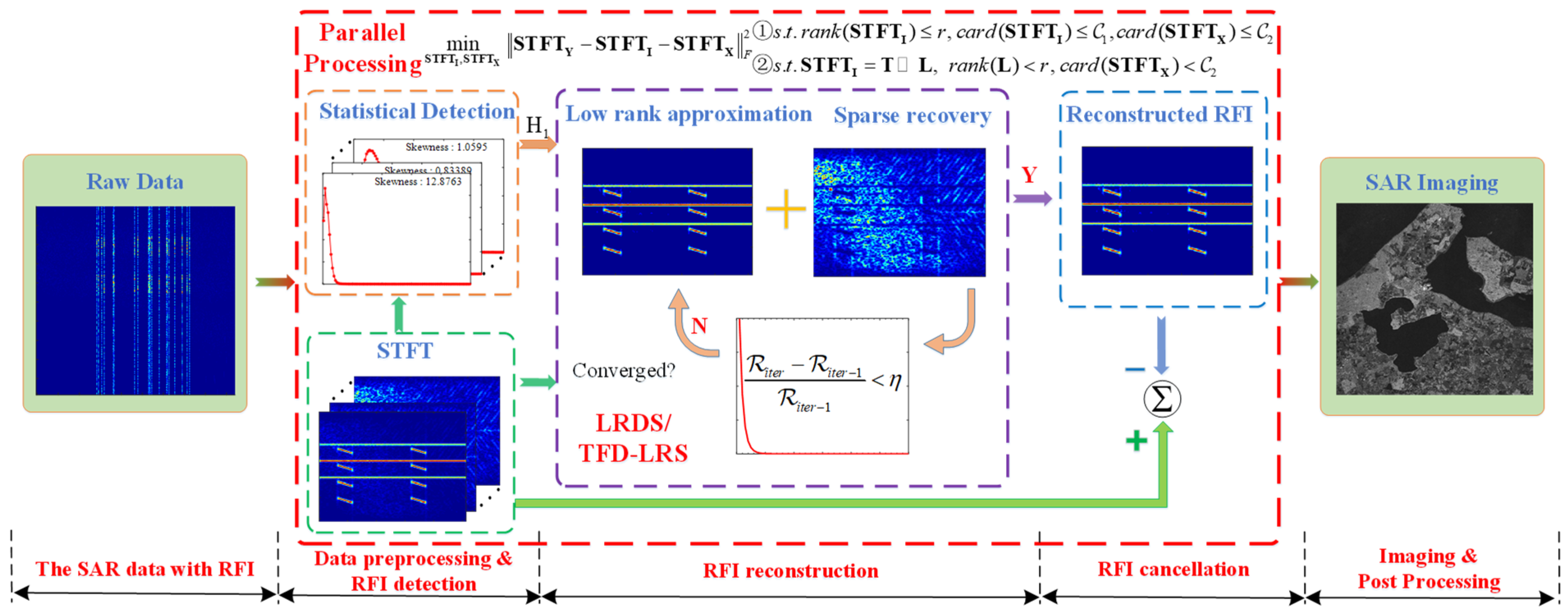
2. Algorithm Model Formulation
2.1. Flowchart of the Proposed Algorithms
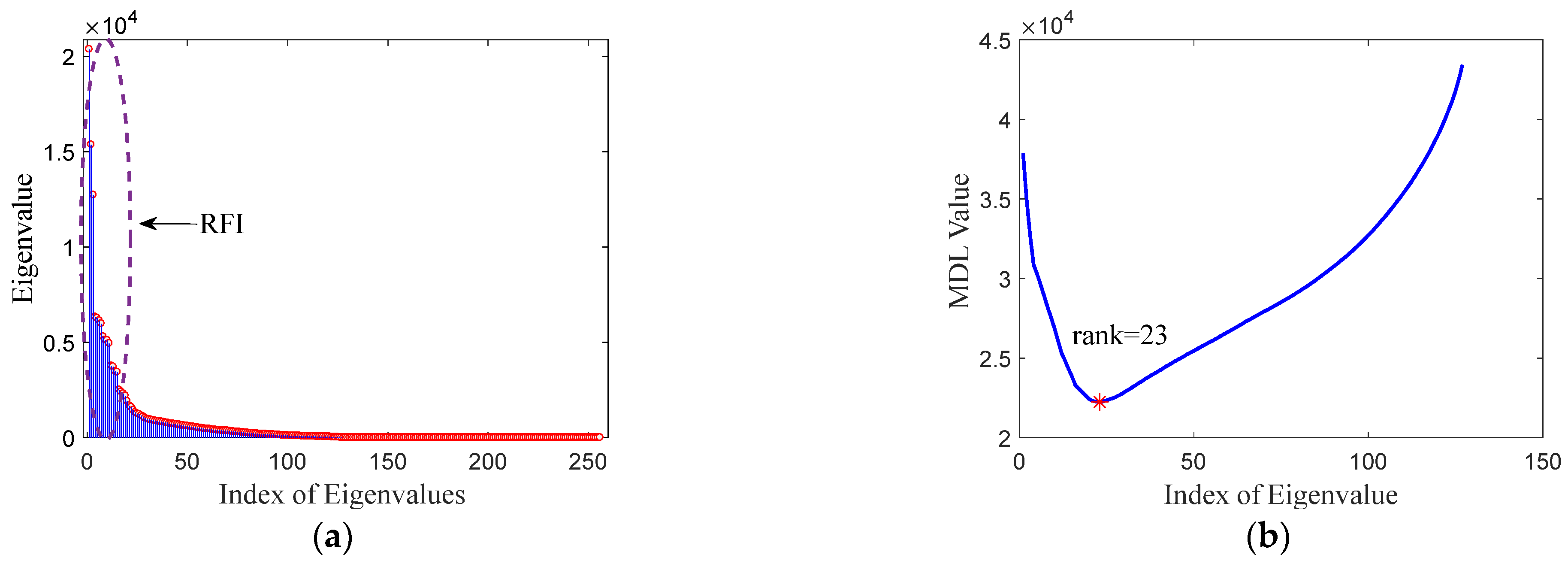
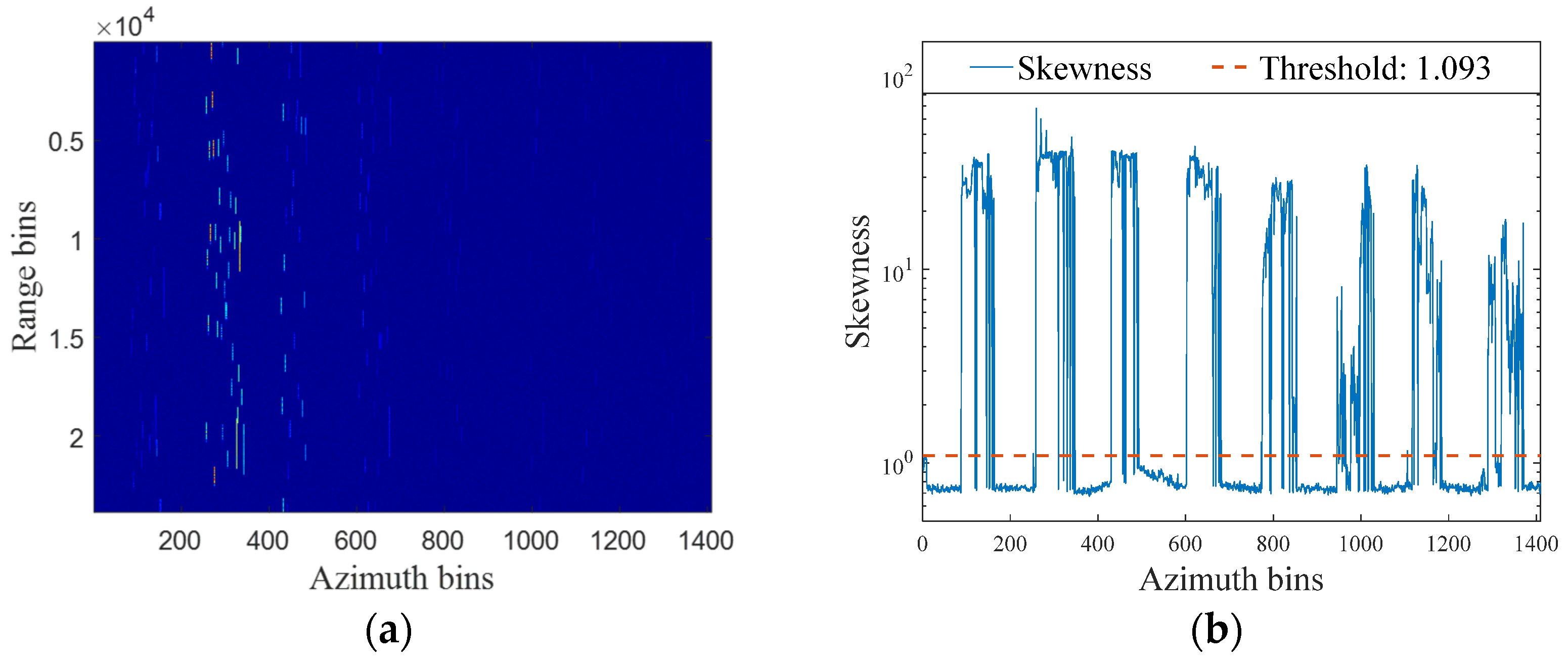
2.2. RFI Formulation and Detection
2.3. The RFI Reconstruction Model
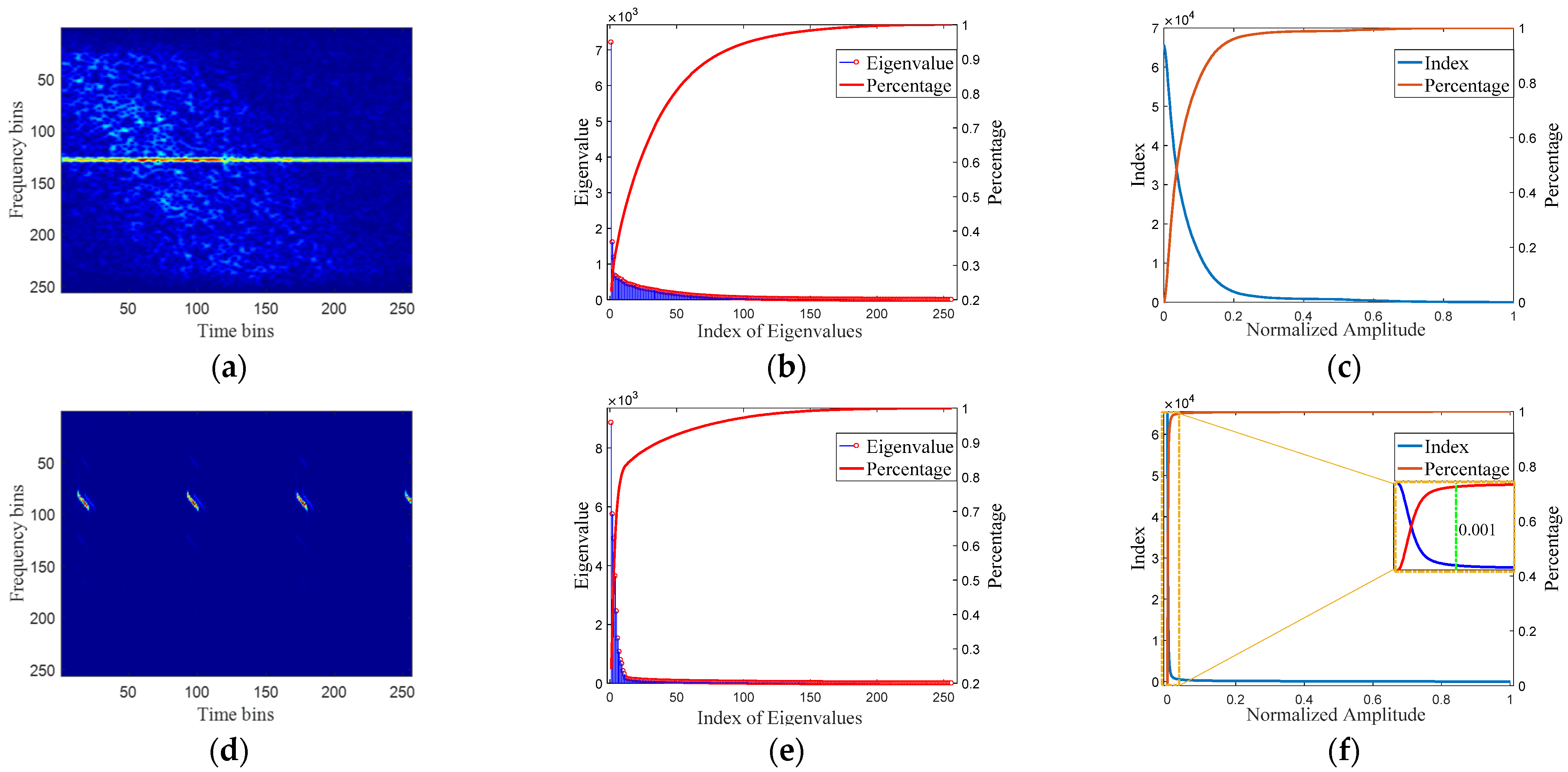
2.3.1. The Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties of RFI
2.3.2. The Sparsity of TES
3. Theory and Methodology
3.1. LRDS Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. The Proposed LRDS Algorithm |
| Input: , , , , |
| Initialization: , , , |
| While do |
| Low rank approximation: ; |
| RFI reconstruction: ; |
| TES recovery: ; |
| End while. |
| Output: , |
3.2. TFC-LRS Algorithm
3.3. Analysis of the Prior Parameters
| Algorithm 2. The Proposed TFC-LRS Algorithm |
| Input: , , , |
| Initialization: , , , |
| While do |
| RFI reconstruction: ; |
| TES recovery: ; |
| ; |
| End while. |
| Output , |
4. Performance Analysis and Evaluation
4.1. Computational Complexity
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
5. Experimental Results
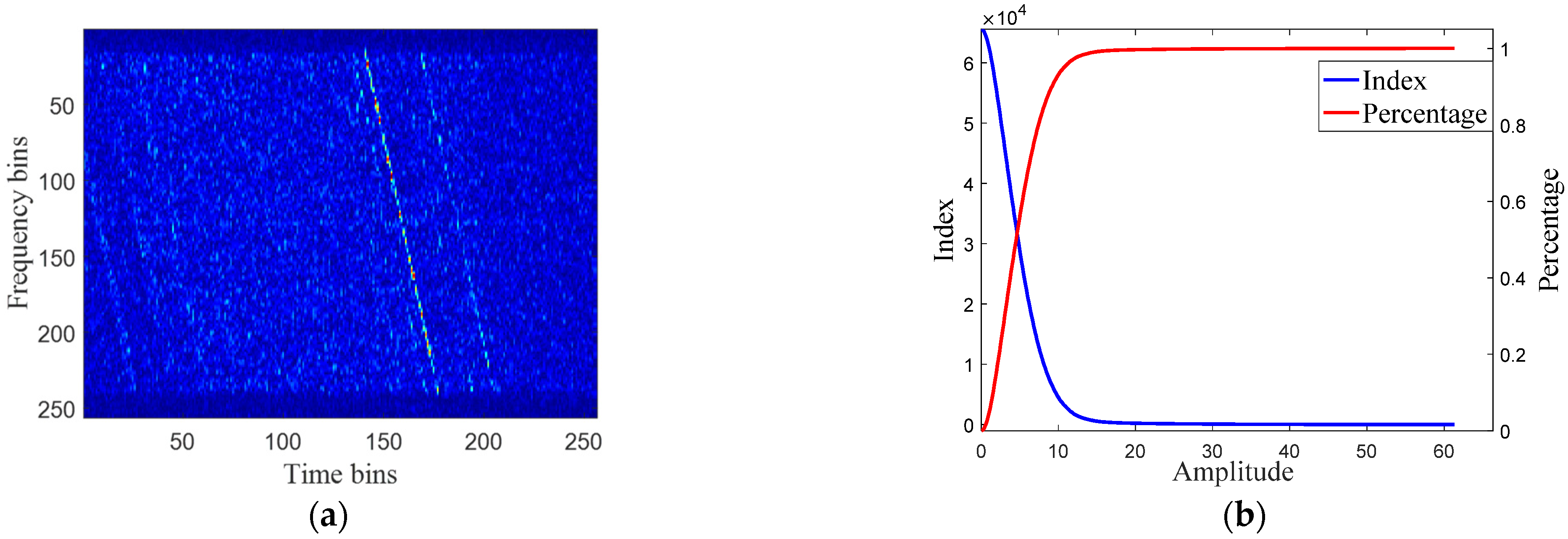
5.1. RFI Mitigation Results of the Simulated Single Snapshot
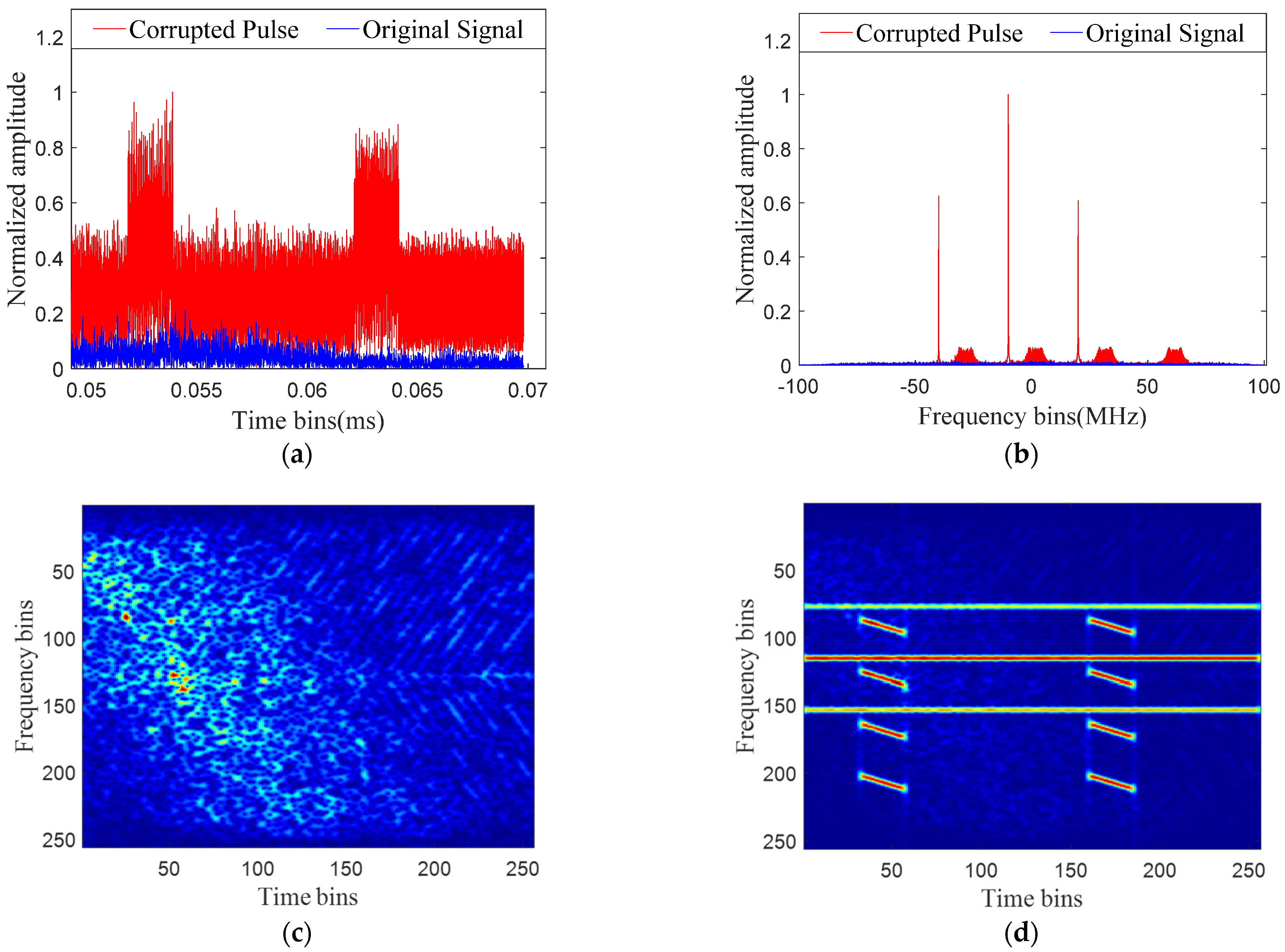
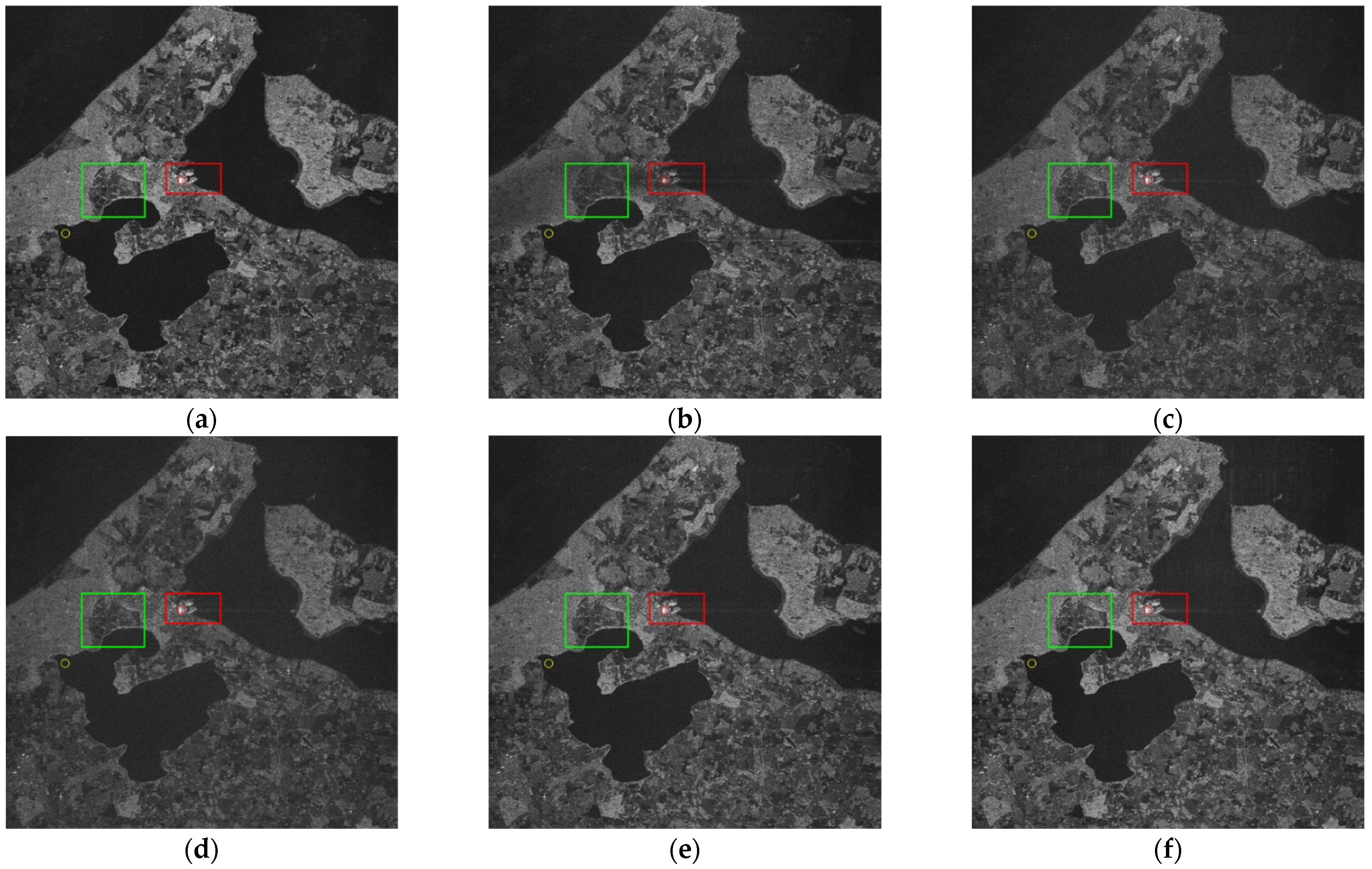
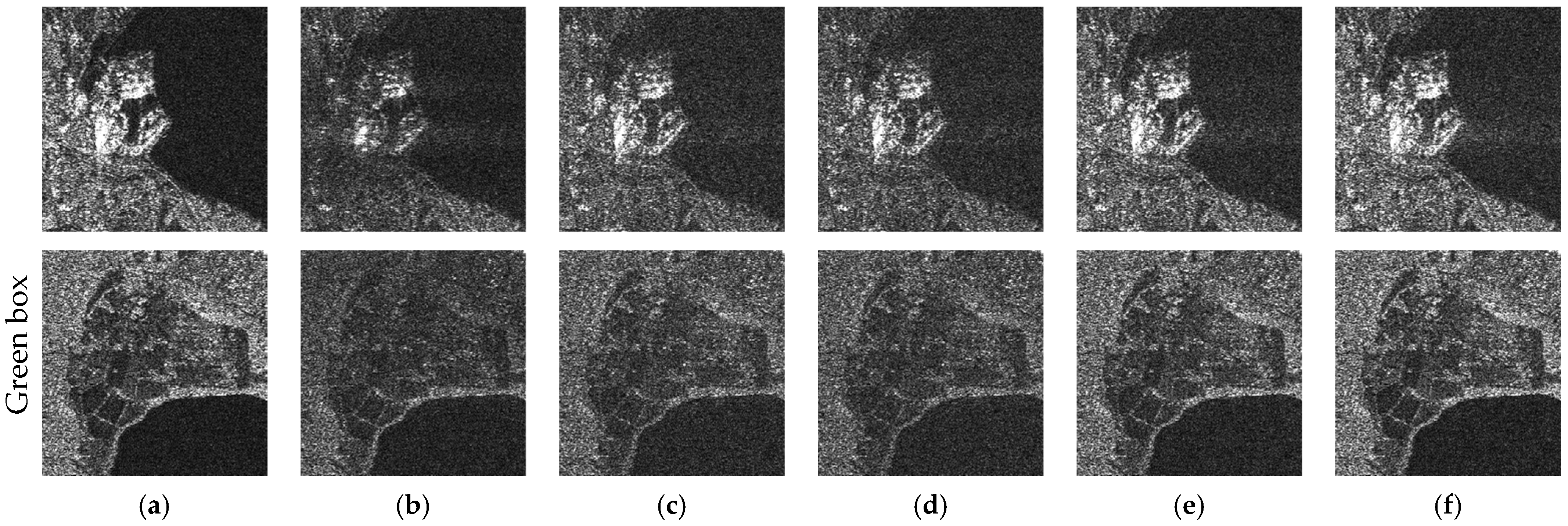
5.2. Mitigation Results of the Measured SAR Data Corrupted with Simulated RFI
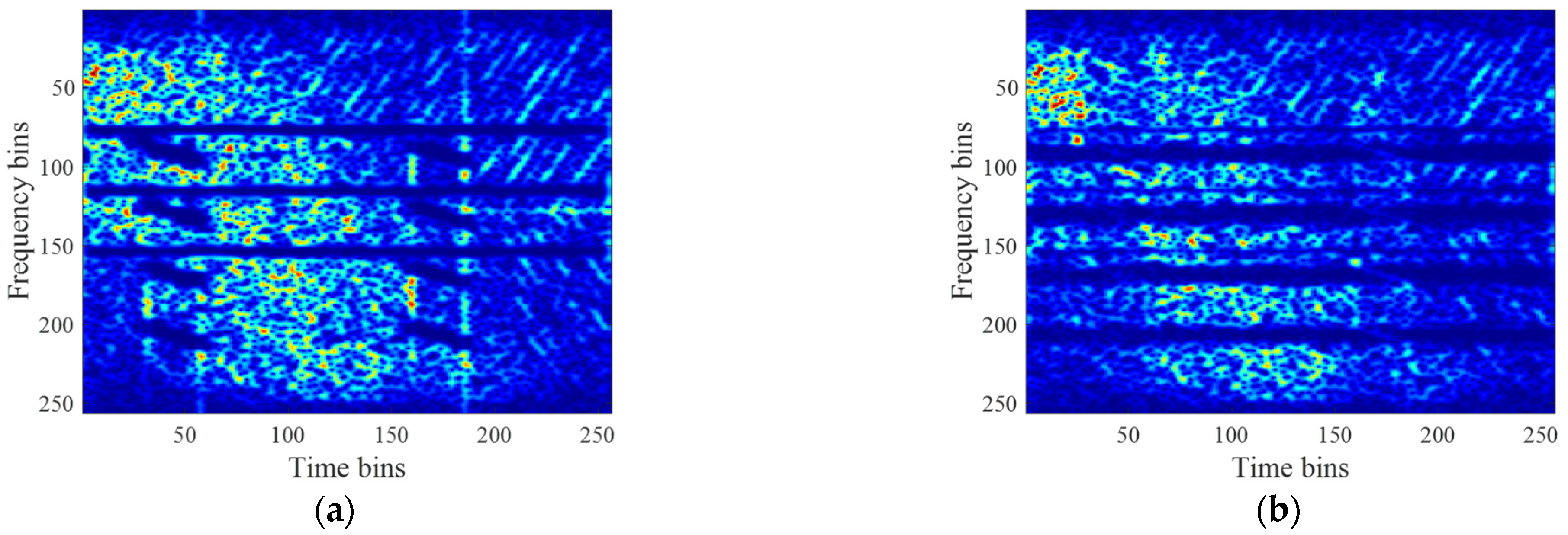
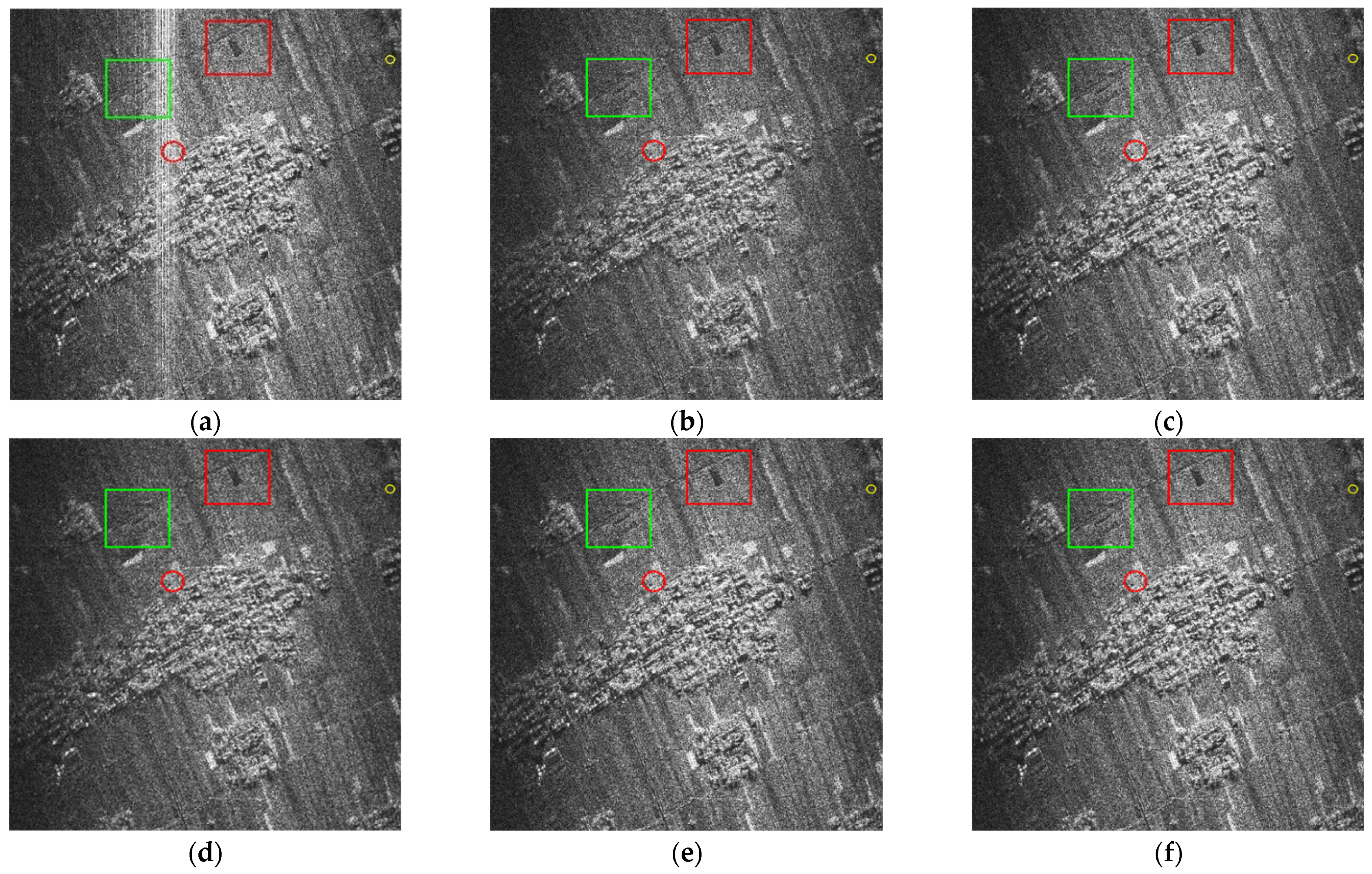
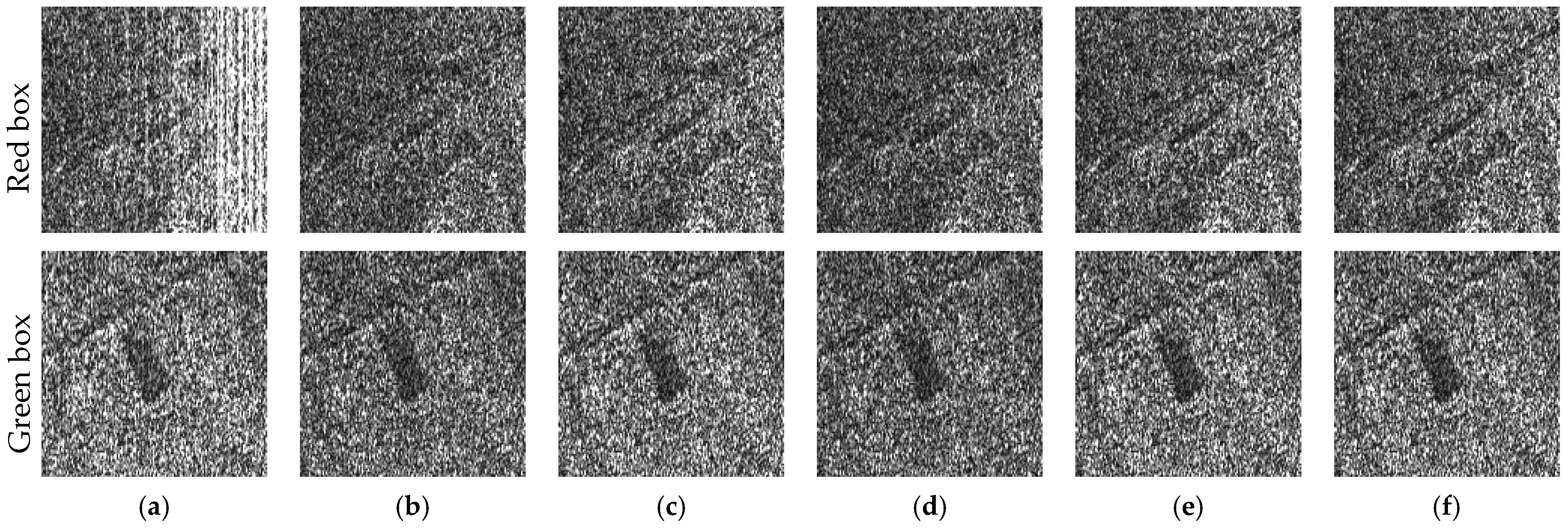
5.3. Mitigation Results of the Measured SAR Data Corrupted with NBI
5.4. Mitigation Results of the Measured SAR Data Corrupted with WBI
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A Strategy for Active Remote Sensing Amid Increased Demand for Radio Spectrum; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, M.; Ulaby, F. Spectrum issues faced by active remote sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J. Introduction to Ultra-Wideband Radar Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.J. Performance requirements for ionospheric correction of low-frequency SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3694–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skriver, H. Crop classification by multitemporal C- and L-band single- and dual-polarization and fully polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I. Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.E. Frequency allocation challenges for ultra-wideband radars. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2013, 28, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigber, A.; Scheiber, R.; Jager, M.; Pau, P.; Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Bai, X.; Liu, J. Narrow-band interference suppression for SAR based on independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4952–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, Z. Narrow-band interference mitigation for SAR using independent subspace analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5289–5301. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Tao, H.; Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, J. Narrow-band interference suppression via RPCA-based signal separation in time-frequency domain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5016–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Z. Wideband interference mitigation in high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Bai, X.; Rong, P.; Yang, S.; Tian, T. Interference mitigation for synthetic aperture radar based on deep residual network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lord, R. Radio frequency interference suppression applied to synthetic aperture radar data. In Proceedings of the 28th General Assembly of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI), New Delhi, India, 23–29 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dakovic, M.; Thayaparan, T.; Djukanovic, S.; Stankovic, L. Time–frequency-based non-stationary interference suppression for noise radar systems. IEE Radar Sonar Navig. 2008, 2, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgamel, S.; Soraghan, J. Using EMD-FrFT filtering to mitigate very high-power interference in chirp tracking radars. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2011, 18, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natsuaki, R.; Watanabe, M.; Motohka, T.; Suzuki, S. RFI detection and removal in Range-time Azimuth-frequency domain. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liao, G.; Yang, Z. Time variant RFI suppression for SAR using iterative adaptive approach. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, R.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. Eigensubspace-based filtering with application in narrow-band interference suppression for SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, J.; Li, C. Multiclass radio frequency interference detection and suppression for SAR based on the single shot multibox detector. Sensors 2018, 18, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Li, J.; Su, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L. Extraction and Analysis of RFI Signatures via Deep Convolutional RPCA. In Proceedings of the General Assembly of the International Union of Radio Science, URSI GASS, Rome, Italy, 28 August–4 September 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Ton, T.; Wong, D.; Soumekh, M. Adaptive coherent suppression of multiple wide-bandwidth RFI sources in SAR. In Proceedings of the SPIE 5427, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XI, Orlando, FL, USA, 2 September 2004; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liang, D. Gradual RELAX algorithm for RFI suppression in UWB-SAR. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 1916–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R.T.; Inggs, M.R. Efficient RFI suppression in SAR using LMS adaptive filter integrated with range/Doppler algorithm. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Sheng, M. A new method for SAR radio frequency interference mitigation based on maximum a posterior estimation. In Proceedings of the General Assembly of the International Union of Radio Science, URSI GASS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Tran, T.; Do, T. Sparse models and sparse recovery for ultra-wideband SAR applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 940–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D. RFI suppression based on sparse frequency estimation for SAR imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Gu, H.; Su, W. Wide-band interference mitigation algorithm for SAR based on time-varying filtering and sparse recovery. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Narrowband RFI suppression for SAR system via efficient parameter-free decomposition algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3311–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Li, J.; Nehorai, A. Fast narrowband RFI suppression algorithms for SAR systems via matrix-factorization techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, S.; Nguyen, L.; Tran, T.D. Radio frequency interference suppression in ultra-wideband synthetic aperture radar using range-Azimuth sparse and low-rank model. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.; Tran, T. A comprehensive performance comparison of RFI mitigation techniques for UWB radar signals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Process, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 3086–3090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Tao, D. GoDec: Randomized low-rank & sparse matrix decomposition in noisy case. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Bellevue, WA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2011; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, F. Wideband Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Data Based on Variational Bayesian Inference. In Proceedings of the General Assembly of the International Union of Radio Science, URSI GASS, Rome, Italy, 29 August–5 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhou, F. Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation Method for Synthetic Aperture Radar Using Joint Low Rank and Sparsity Property. In Proceedings of the General Assembly of the International Union of Radio Science, URSI GASS, Rome, Italy, 28 August–4 September 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.; Potter, L.; McCorkle, J. RFI suppression for ultra wideband radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1997, 33, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shi, X. FM interference suppression for PRC-CW radar based on adaptive STFT. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Microwave, Antenna, Propagation and EMC Technologies for Wireless Communications (MAPE), Beijing, China, 27–29 October 2009; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xing, M.; Guo, R.; Zhang, L.; Bao, Z. Interference suppression algorithm for SAR based on time–frequency transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3765–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandawate, A.V.; Giannakis, G.B. Asymptotic properties and covariance expressions of kth-order sample moments and cumulants. In Proceedings of the Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1–3 November 1993; pp. 1186–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, M.A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mertins, A.; Mertins, D.A. Signal Analysis: Wavelets, Filter Banks, Time–Frequency Transforms and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rajapakse, J.C. Adaptive Blind Signal and Image Processing: Learning Algorithms and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, T.; Ng, M. Multi-Dimensional Visual Data Completion via Low-Rank Tensor Representation Under Coupled Transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3581–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnik, M.I. Radar Handbook, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]







| Abbr. | Full Name | Abbr. | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | Synthetic aperture radar | TES | Target echo signal |
| RFI | Radio frequency interference | TF | Time–frequency |
| GoDec | Go decomposition | WBI | Wideband interference |
| LRDS | Low-rank and double sparsity | NBI | Narrowband interference |
| TFC-LRS | TF constraint joint low-rank and sparsity | SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier transform | SVT | Singular value threshold |
| SVD | Singular value decomposition | BRP | Bilateral random projection |
| MDL | Minimum description length | SDR | Signal distortion ratio |
| SSIM | Structural similarity index measure | MNR | Multiplicative noise ratio |
| ISNF | Instantaneous-spectrum notch filtering | ESP | Eigenspace projection |
| Algorithm | Computational Complexity |
|---|---|
| GoDec | |
| LRDS | |
| TFC-LRS |
| Carrier Frequency | X Band | The Pulse Repetition Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Velocity | ||
| The pulse width | Resolution (Range × Azimuth) |
| Carrier Frequency | C Band | The Pulse Repetition Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Velocity | ||
| The pulse width | Resolution (Range × Azimuth) |
| Metric | SDR (dB) | SSIM | Time (ms) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | ||||
| ISNF | −5.09 | 0.75 | 49.02 | |
| ESP | −3.74 | 0.56 | 43.74 | |
| GoDec | −3.56 | 0.54 | 416.63 | |
| LRDS | −6.72 1 | 0.843 | 144.08 | |
| TFD-LRS | −7.10 | 0.844 | 194.17 | |
| Improvement (%) 2 | 32.02/79.68/88.76 39.49/89.84/99.44 | 12.40/50.54/56.11 12.53/50.71/56.30 | -/-/65.42 -/-/53.40 | |
| Metric | SSIM | MNR (dB) | Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | ||||
| ISNF | 0.61 | −10.22 | 26.38 | |
| ESP | 0.56 | −11.23 | 24.99 | |
| GoDec | 0.51 | −11.00 | 215.63 | |
| LRDS | 0.75 1 | −12.80 | 71.19 | |
| TFD-LRS | 0.81 | −13.73 | 85.48 | |
| Improvement (%) 2 | 22.95/33.93/47.06 32.79/44.64/58.82 | 25.24/13.98/16.36 34.34/22.26/24.82 | -/-/66.99 -/-/60.36 | |
| Method | ISNF | ESP | GoDec | LRDS | TFC-LRS | Improvement (%) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | |||||||
| MNR (dB) | −7.05 | −7.89 | −7.44 | −7.97 1 | −7.94 | 13.05/1.01/7.12 12.62/0.63/6.72 | |
| Time (s) | 23.18 | 23.50 | 237.97 | 66.95 | 55.68 | -/-/71.87 -/-/76.60 | |
| Method | ISNF | ESP | GoDec | LRDS | TFC-LRS | Improvement (%) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | |||||||
| MNR (dB) | −11.72 | −10.28 | −11.43 | −11.86 1 | −12.19 | 1.19/15.37/3.76 4.01/18.58/6.65 | |
| Time (s) | 19.45 | 27.02 | 101.90 | 35.97 | 51.58 | -/-/64.70 -/-/49.38 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Lu, B. Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on the Time-Frequency Constraint Joint Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030775
Ding Y, Fan W, Zhang Z, Zhou F, Lu B. Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on the Time-Frequency Constraint Joint Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030775
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yi, Weiwei Fan, Zijing Zhang, Feng Zhou, and Bingbing Lu. 2022. "Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on the Time-Frequency Constraint Joint Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030775
APA StyleDing, Y., Fan, W., Zhang, Z., Zhou, F., & Lu, B. (2022). Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation for Synthetic Aperture Radar Based on the Time-Frequency Constraint Joint Low-Rank and Sparsity Properties. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030775





