A Combined Approach for Retrieving Bathymetry from Aerial Stereo RGB Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bathymetric Retrieval Methods Review
3. A Proposed Combined Approach for Bathymetry Retrieval
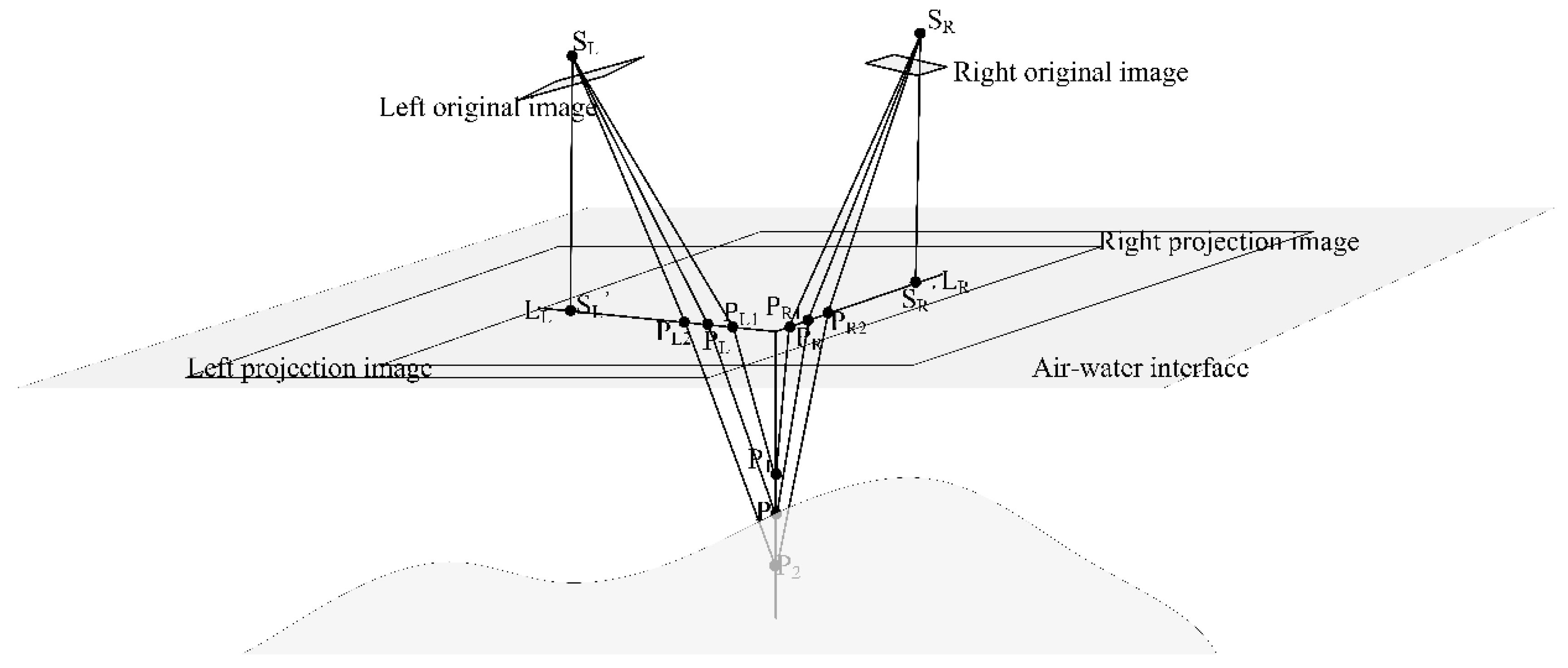
3.1. The Projection Image Based Two-Medium Stereo Triangulation Method
- All projection images are within the same spatial coordinate system;
- All projection images’ pixels have the same ground sample distance (GSD) and are not affected by any rotation angles because the rotation angles are zeros; and
- When the elevation of target point is equal to the horizontal plane elevation Z0, the projected points of the target point on the left and right projection images share the same position.
- Projecting the original images to the air-water interface to generate projection images;
- Locating the target point’s horizontal position (X, Y), obtaining a series of depth candidates for the target point within the reasonable water depth range (hmin, hmax) and depth searching increment (k), and choosing an appropriate cross correlation window size (m × n);
- Computing the candidate pairs of searching points using Equation (2);
- Computing the correlation coefficients of the candidate pairs by Equation (3); and
- Finding the pair with the maximum correlation coefficient and regarding its corresponding depth as the optimal depth position of the target point.
3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) Model
3.3. Bathymetric Accuracy Assessment Criteria
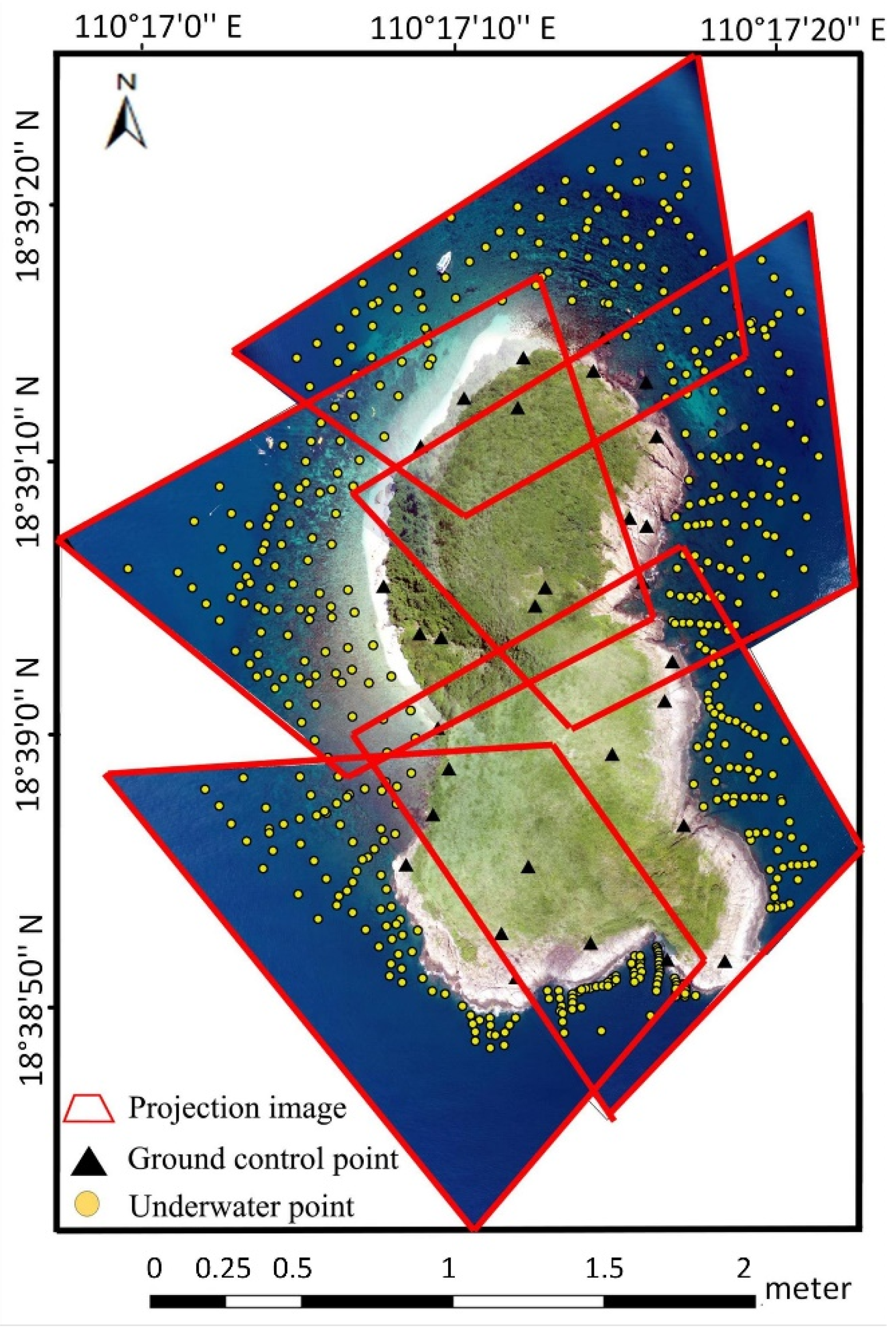
4. The Experiments of Retrieving Bathymetry Using the Combined Approach
4.1. Bathymetry Determination Using the Combined Approach
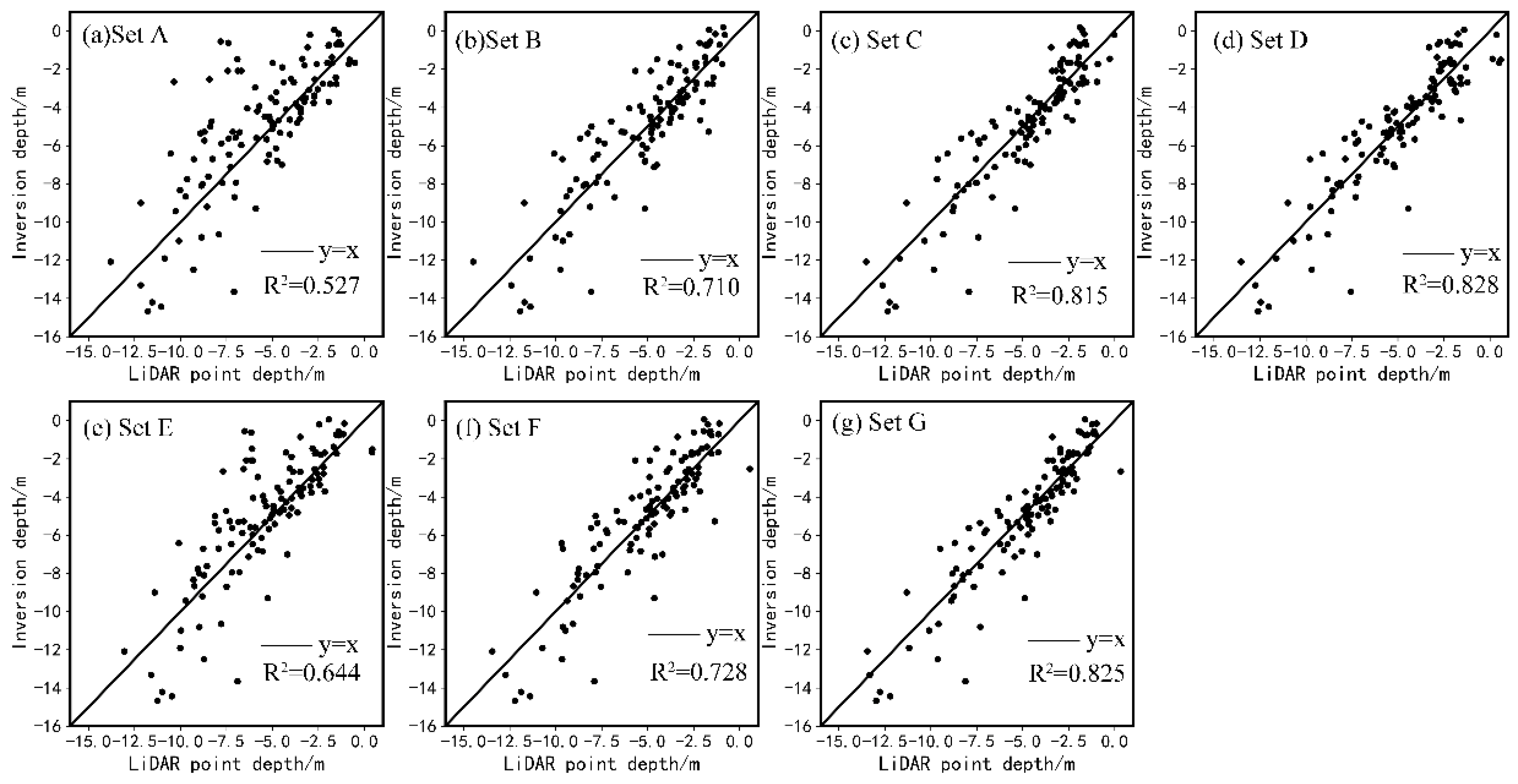
4.2. Evaluation of the Combined Approach
5. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Zhao, J. Underwater navigation based on topographic contour image matching. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 25–27 June 2010; pp. 2494–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Badejo, O.; Adewuyi, K. Bathymetric survey and topography changes investigation of Part of Badagry Creek and Yewa River, Lagos State, Southwest Nigeria. J. Geogr. Environ. Earth Sci. Int. 2019, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Koehl, M.; Piasny, G.; Thomine, V.; Garambois, P.-A.; Finaud-Guyot, P.; Guillemin, S.; Schmitt, L. 4D GIS for montoring river bank erosion at meander bend scale case of Moselle River. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIV-4/W1-2020, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Wen, H.; Ruan, H.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, K.; Zhong, F. High-resolution monitoring of beach topography and its change using unmanned aerial vehicle imagery. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 160, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, S.; Randazzo, G. Improvements to a Coastal Management Plan in Sicily (Italy): New Approaches to borrow sediment management. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Senet, C.; Seemann, J.; Flampouris, S.; Ziemer, F. Determination of Bathymetric and Current Maps by the Method DiSC Based on the Analysis of Nautical X-Band Radar Image Sequences of the Sea Surface (November 2007). Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2008, 46, 2267–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westaway, R.M.; Lane, S.N.; Hicks, D.M. Remote sensing of clear-water, shallow, gravel-bed rivers using digital photogrammetry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Mandlburger, G. Through-Water dense image matching for shallow water bathymetry. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, N.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Satellite-derived bathymetry using the ICESat-2 lidar and Sentinel-2 imagery datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legleiter, C. Mapping river depth from publicly available aerial images. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 760–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzirafuti, A.; Barreca, G.; Crupi, A.; Faina, G.; Paltrinieri, D.; Lanza, S.; Randazzo, G. The contribution of multispectral satellite image to shallow water bathymetry mapping on the coast of Misano Adriatico, Italy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Quilleuc, A.; Collin, A.; Jasinski, M.; Devillers, R. Very high-resolution satellite-derived bathymetry and habitat mapping using pleiades-1 and ICESat-2. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlatos, D.; Agrafiotis, P. A novel iterative water refraction correction algorithm for use in Structure from Motion photogrammetric pipeline. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, B.; Deng, R.; Zhu, S. Universal algorithm for water depth refraction correction in through-water stereo remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 91, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partama, I.G. A simple and empirical refraction correction method for UAV-based shallow-water photogrammetry. Int. J. Environ. Chem. Ecol. Geol. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 11, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Mandlburger, G.; Kölle, M.; Nübel, H.; Soergel, U. BathyNet: A deep neural network for water depth mapping from multispectral aerial images. PFG—J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2021, 89, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tani, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Ohkawa, N.; Ishiguro, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Kayanne, H.; Yamano, H. A photogrammetric correction procedure for light refraction effects at a two-medium boundary. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J. Relative orientation for two-media photogrammetry. Photogramm. Rec. 2006, 14, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Karantzalos, K.; Georgopoulos, A.; Skarlatos, D. Correcting image refraction: Towards accurate aerial image-based bathymetry mapping in shallow waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Holderied, K.; Sinclair, M. Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramante, J.; Kumaran Raju, D.; Sin, T. Multispectral derivation of bathymetry in Singapore’s shallow, turbid waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2070–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Harborne, A.; Mumby, P. Technical note: Simple and robust removal of sun glint for mapping shallow-water benthos. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2107–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Digital surface model refinement based on projection images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2021, 87, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M. True Orthophoto Generation; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Principle of Photogrammetry (with Remote Sensing); Publishing House of Surveying and Mapping: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gruen, A. Multi-image matching for DSM generation from IKONOS imagery. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2006, 60, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial non-stationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, A.; Long, F.; Farber, S. Moving window approaches for hedonic price estimation: An empirical comparison of modelling techniques. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noresah, M.S.; Ruslan, R. Modelling urban spatial structure using Geographically Weighted Regression. In Proceedings of the Combined IMACS World Congress/Modelling and Simulation Society-of-Australia-and-New-Zealand (MSSANZ)/18th Biennial Conference on Modelling and Simulation, Cairns, Australia, 13–17 July 2019; pp. 1950–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Windle, M.J.S.; Rose, G.A.; Devillers, R.; Fortin, M.-J. Exploring spatial non-stationarity of fisheries survey data using geographically weighted regression (GWR): An example from the Northwest Atlantic. Ices J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, L.; Xue, F. Spatial epidemiology and spatial ecology study of worldwide drug-resistant tuberculosis. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Baek, D.; Seo, I.W.; Shin, J. Retrieving shallow stream bathymetry from UAV-assisted RGB imagery using a geospatial regression method. Geomorphology 2019, 341, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, A.; Wheeler, D.C. Geographically weighted regression. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography; Kitchin, R., Thrift, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C. Geographically weighted regression: A natural evolution of the expansion method for spatial data analysis. Environ. Plan. A 1998, 30, 1905–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P.; Fotheringham, A.S. Geographically weighted regression with a non- Euclidean distance metric: A case study using hedonic house price data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 660–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. An iterative approach for self-calibrating bundle adjustment. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B2-2020, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, H. Ordinary kriging. Multivar. Geostat. 1995, 7, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kanade, T.; Okutomi, M. A stereo matching algorithm with an adaptive window: Theory and experiment. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. IEEE Trans. 1994, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


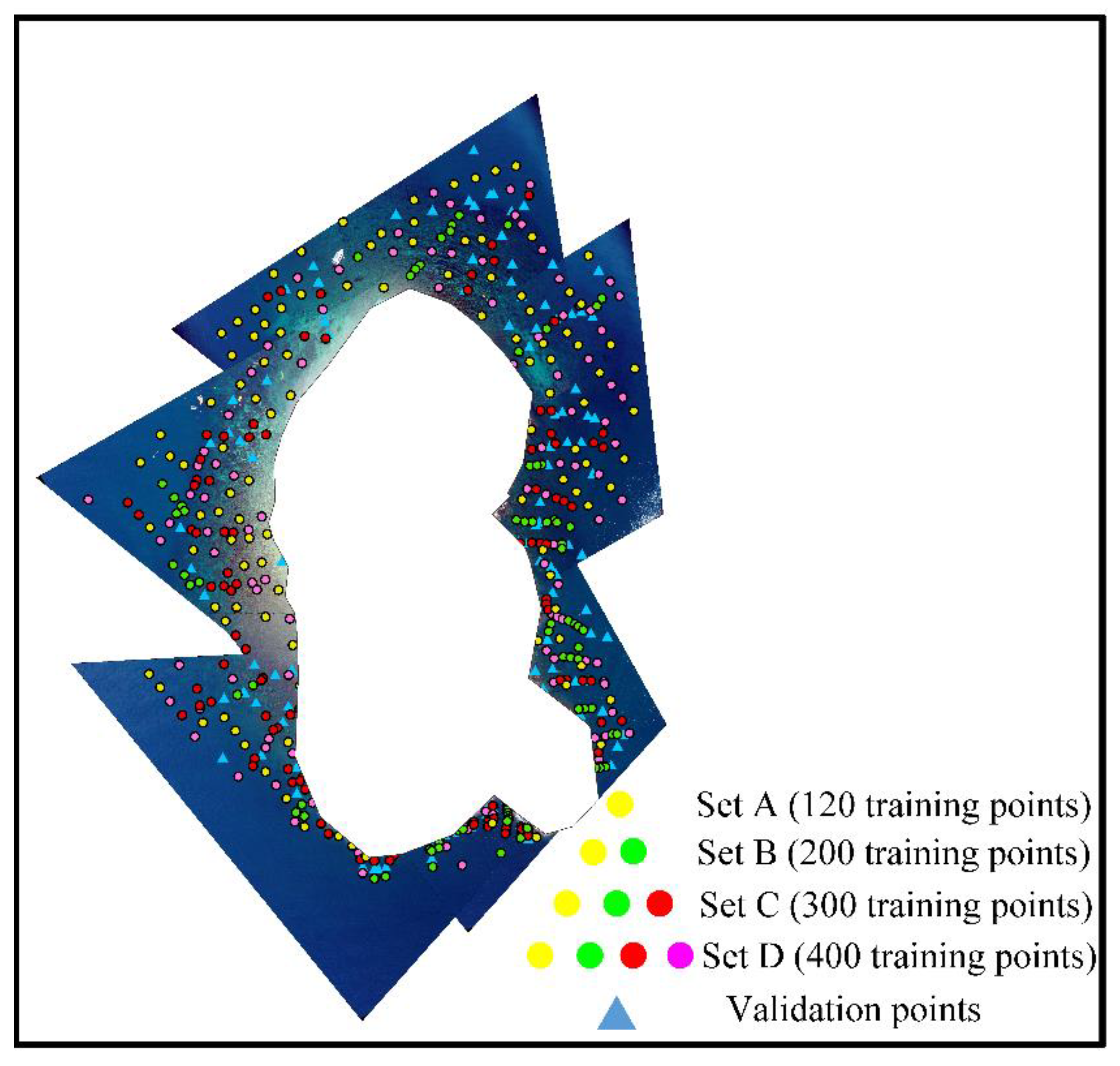

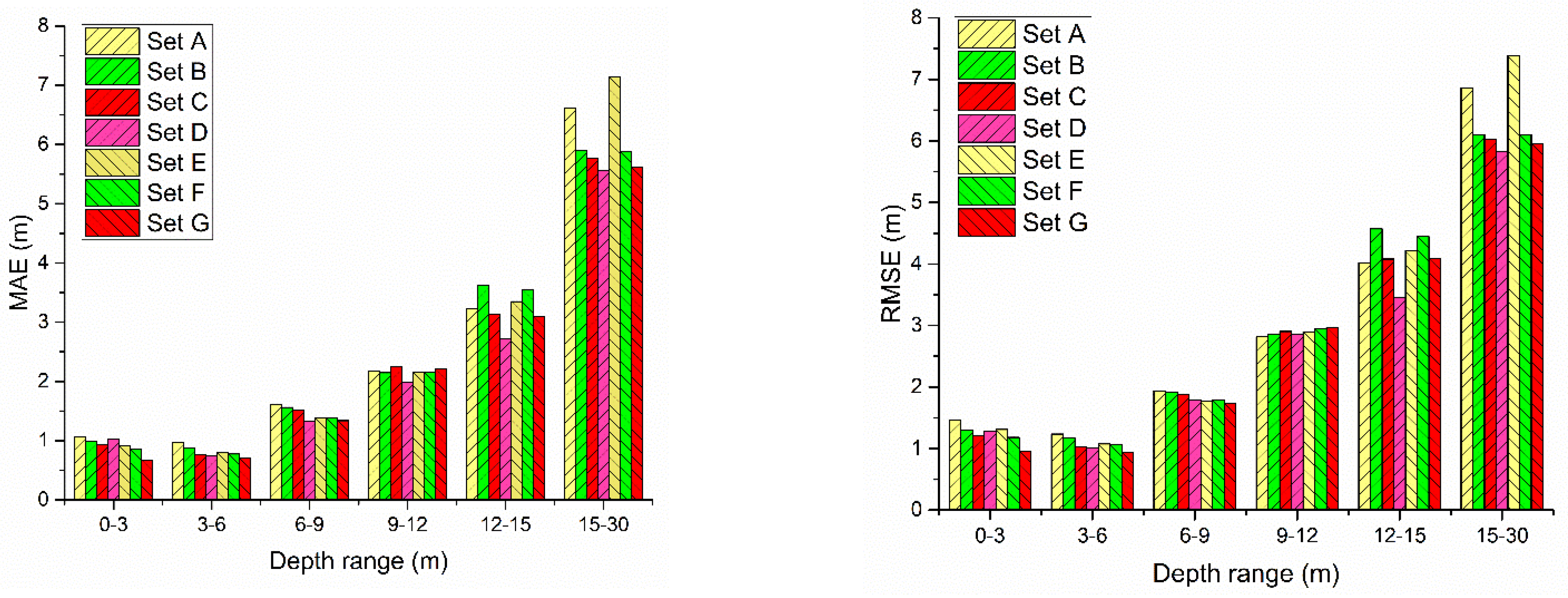
| 4 Triangulation Sets | Set A | Set B | Set C | Set D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference points’ number | 120 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| MAE (m) | 0.997 | 1.244 | 1.371 | 1.595 |
| RMSE (m) | 1.165 | 1.488 | 1.631 | 1.843 |
| Reference Points’ Number | Set A | Set B | Set C | Set D | Set E | Set F | Set G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triangulation Points as Reference Points | LiDAR Points as Reference Points | ||||||
| 120 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 120 | 200 | 300 | |
| 120 Validation points’ MAE (m) | 1.713 | 1.341 | 1.118 | 1.059 | 1.471 | 1.275 | 1.09 |
| 120 Validation points’ RMSE (m) | 2.329 | 1.824 | 1.455 | 1.406 | 2.021 | 1.765 | 1.417 |
| Set A | Set B | Set C | Set D | Set E | Set F | Set G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The experimental area’s MAE (m) | 2.31 | 2.247 | 2.129 | 1.986 | 2.293 | 2.157 | 1.997 |
| The experimental area’s RMSE (m) | 3.287 | 3.211 | 3.064 | 2.876 | 3.432 | 3.164 | 3.019 |
| The Number of Reference Points | 120 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 validation points’ MAE (m) | 2.045 | 1.98 | 1.894 | 1.948 |
| 120 validation points’ RMSE (m) | 2.609 | 2.573 | 2.506 | 2.515 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Zhu, W.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y. A Combined Approach for Retrieving Bathymetry from Aerial Stereo RGB Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030760
Wang J, Chen M, Zhu W, Hu L, Wang Y. A Combined Approach for Retrieving Bathymetry from Aerial Stereo RGB Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030760
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiali, Ming Chen, Weidong Zhu, Liting Hu, and Yasong Wang. 2022. "A Combined Approach for Retrieving Bathymetry from Aerial Stereo RGB Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030760
APA StyleWang, J., Chen, M., Zhu, W., Hu, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). A Combined Approach for Retrieving Bathymetry from Aerial Stereo RGB Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030760






