Abstract
Paddy rice cropping systems play a vital role in food security, water use, gas emission estimates, and grain yield prediction. Due to alterations in the labor structure and the high cost of paddy rice planting, the paddy rice cropping systems (single or double paddy rice) have drastically changed in China in recent years; many double-cropping paddy rice fields have been converted to single-cropping paddy rice or other crops, especially in southern China. Few maps detect single and double paddy rice and cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) in China with a 30 m resolution. The Landsat-based and effective flooding signal-based phenology (EFSP) method, which distinguishes CIPR with the frequency of the effective flooding signal (EFe), was proposed and tested in China. The cloud/ice/shadow was excluded by bit arithmetic, generating a good observation map, and several non-paddy rice masks were established to improve the classification accuracy. Threshold values for single and double paddy rice were calculated through the mapped data and agricultural census data. Image processing (more than 684,000 scenes) and algorithm implementation were accomplished by a cloud computing approach with the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. The resultant maps of paddy rice from 2014 to 2019 were evaluated with data from statistical yearbooks and high-resolution images, with producer (user) accuracy and kappa coefficients ranging from 0.92 to 0.96 (0.76–0.87) and 0.67–0.80, respectively. Additionally, the determination coefficients for mapped and statistical data were higher than 0.88 from 2014 to 2019. Maps derived from EFSP illustrate that the single and double paddy rice systems are mainly concentrated in the Cfa (warm, fully humid, and hot summer, 49% vs. 56%) climate zone in China and show a slightly decreasing trend. The trend of double paddy rice is more pronounced than that of single paddy rice due to the high cost and shortages of rural household labor. However, single paddy rice fields expanded in Dwa (cold, dry winter, and hot summer, 11%) and Dwb (cold, dry winter, and warm summer, 9%) climate zones. The regional cropping intensity for paddy rice coincides with the paddy rice planting area but shows a significant decrease in south China, especially in Hunan Province, from 2014 to 2019. The results demonstrate that EFSP can effectively support the mapping of single and double paddy rice fields and CIPR in China, and the combinations of Landsat 7 and 8 provide enough good observations for EFSP to monitor paddy rice agriculture.
1. Introduction
Both globally and in China, paddy rice is an essential crop and provides approximately 19% of the consumed energy for each person on the planet, and feeds more than half of the global population [1,2]. China is ranked first in consumption and production of paddy rice in the world [3], and is of primal importance to global food security. Additionally, paddy rice agriculture substantially affects various environmental factors. For instance, paddy rice is a major water-intensive crop in Asia and plays an essential role in water resource security [4,5], and is a crucial factor for greenhouse gas (methane) emissions [6,7]. It has been generally recognized that double-cropping rice is more costly than single-cropping rice and uses more water because double-cropping is the practice of growing two rice crops in the same piece of land during one year instead of just one. To analyze the spatial distribution of paddy rice agriculture, the cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) is defined as the number of paddy rice growth cycles in one year [8]. Therefore, shedding light on the spatiotemporal distribution and CIPR is essential for food security and environmental conservation.
Since the 1980s, numerous efforts have been made to describe the regional and global spatial and temporal distributions of paddy rice [9,10,11,12]. The data sources for mapping paddy rice can be divided into two categories: visible bands (band reflectance (BR) data [13] and vegetation index (VI) data [14]), and synthetic aperture radar (RADAR) data [15]. RADAR data have higher accuracy in detecting paddy rice, given their cloud-free advantage. Nevertheless, RADAR data have some limitations compared to BR and VI, such as low data acquisition [16], so it is still challenging to continuously monitor paddy rice at a large scale. Previous studies have demonstrated that VI data are more promising than BR data in mapping paddy rice [17,18], without complex preprocessing. Therefore, VI data were adopted to map paddy rice in this study.
In addition to the data source, classification algorithms have also attracted much attention [19], including statistics-based approaches (supervised and unsupervised classifiers), temporal analysis approaches, and phenology-based approaches. The temporal analysis approaches require the construction of a time-series vegetation index profile based on field surveys, and map paddy rice using a threshold-based method (decision tree). Phenology-based approaches take advantage of the paddy rice phenology characteristics (e.g., the land surface water index is higher than the normal different vegetation index in the transplanting phase) to detect the paddy rice, and do not require a field survey, unlike temporal analysis approaches. Onojeghuo et al. [20] successfully mapped paddy rice, combining VI and RADAR data, on the Sanjiang Plain, northeastern China, using support vector machine and random forest machine learning algorithms. Bazzi et al. [21] and Guan et al. [22] detected paddy rice fields using temporal analysis approaches. In some studies, phenology-based methods were used to identify paddy rice areas, acquiring excellent results [23,24]. Statistics-based and temporal analysis approaches are able to map paddy rice planting areas with high precision and are suitable for cloudy regions and complex landscapes, but they depend on training samples and field surveys. Phenology-based approaches can interpret the phenological characteristics of paddy rice and are independent of the a priori data, and are adopted in this study to map paddy rice. However, early phenology-based approaches usually leveraged the land surface temperature (LST) to determine the time window of the rice transplanting phase [25,26,27,28] with a complex procedure [26], which can introduce accidental errors due to LST fluctuations and the difference in LST per pixel. In addition, no threshold values of the land surface water index (LSWI) and VI exist for the detection of the flooding signal (FS) in early phenology-based approaches, which means the water covers the land surface rather than vegetation, resulting in noise appearing in the FS detection. Some efforts were made in this study to address these challenges.
Maps of CIPR are sporadic and scarce despite many mapping works, especially on a large scale with good resolution. Tian et al. [29] successfully distinguished early, middle, and late rice extents using an unsupervised classifier with Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1A data in the Poyang Lake Plain, China. Peng et al. [30] developed a phenology-based method to estimate the paddy rice cropping system in the Hunan Province and quantified temporal trends in paddy rice agriculture. Zhang et al. [31] combined multisource data to monitor paddy rice areas in three provinces of China. In addition, some studies have also generated CIPR maps at a regional scale [32,33]. The existing CIPR maps provide applicable information about paddy rice agriculture for policy making and environmental issue assessment. Unfortunately, the available maps mainly explain the regional information of paddy rice agriculture and cannot provide the details of CIPR at a national scale.
Based on the scarcity of national CIPR maps and the deficiencies of old phenology-based approaches to monitor paddy rice agriculture, single and double paddy rice maps and regional CIPR maps of China from 2014 to 2019 were generated using the effective flooding signal-base phenology (EFSP) method with Landsat 7/8 data. Due to the large quantity of data (more than 114,000 images per year), the calculation was implemented with cloud-computing technology through the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. The objective of this study was threefold: (1) to improve the previous phenology-based method and generate CIPR layers in China; (2) to verify the validity of the phenology-based method in mapping paddy rice in tropical/subtropical regions of China; and (3) to analyze the temporospatial distribution of CIPR from 2014 to 2019 in China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The spatial heterogeneity of cropping systems is substantial [34,35,36] due to the complex climate and topography in China. Northern China predominantly comprises single cropping agriculture, whereas polyculture cropping systems occur in southern China [37,38] because there is sufficient rainfall, and it has a longer warm period than the north. The alluvial plains are mainly distributed in eastern China with developed river networks, and the plateau is mainly located in the western part of China. The elevation shows a decreasing trend from the southwest (Tibetan Plateau) to the east coast (Figure 1).
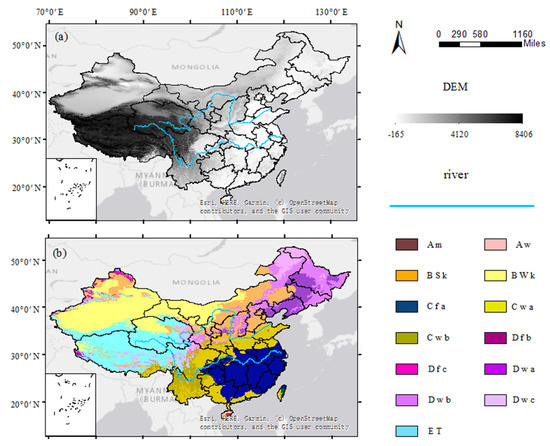
Figure 1.
Overview of the study area: (a) the digital elevation model (DEM) data, which were acquired from http://www.gscloud.cn/search (accessed on 6 September 2021); (b) the climate zone [39], in which the initial character represents the main climates (A: equatorial, B: arid, C: warm temperate, D: snow, E: polar), the second letter means the precipitation (W: desert, S: steppe, f: fully humid, w: winter dry, m: monsoonal), and the final character is the temperature (k: cold arid, a: hot summer, b: warm summer, c: cold summer, T: polar tundra).
The climates in China are widely different, with a transition from a cold temperate monsoon climate in northern China to a tropical monsoon climate in southern China, and the alpine mountain climate and subtropical monsoon climate dominate on the Tibetan Plateau (Figure 1). Precipitation decreases from more than 2000 mm on the southeast coast of China to less than 200 mm in the northwest inland area of China due to differences in climate and complex topographic variation in the different areas [40].
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Landsat Images
All the available Landsat 7/8 images (row: 22–48; path 121–163) of Collection 2, Level 2 and precision terrain-corrected from 2014 to 2019 were collected from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/) (accessed on 18 September 2021). The images provide 30 m spatial resolution with a revisit time of 16 days, including five visible and near-infrared (VNIR) bands, two shortwave infrared (SWIR) bands processed to orthorectified surface reflectance, and one thermal infrared (TIR) band processed to orthorectified surface temperature; the quality assessment (QA) band was also included.
The QA band was adopted to remove the bad observations (pixels, not the entire image), including clouds, snow/ice, cirrus, and cloud shadow. Four levels were generated by the CFmask algorithm [41]: “not determined” (algorithm did not determine the status of this condition), low confidence (0–33%), mid confidence (34–66%), and high confidence (67–100%) [16]. The mid- and high-confidence observations were excluded as bad observations to avoid the potential influence of clouds, snow/ice, cirrus, and cloud shadow (Figure 2).
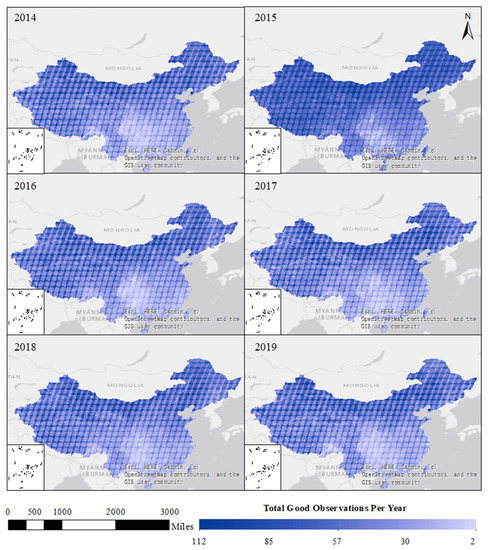
Figure 2.
Availability of good observations per year from 2014 to 2019.
2.2.2. Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Data
The 30 m Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation model (DEM) datasets were acquired from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) (https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros) (accessed on 6 July 2021) to extract the non-paddy rice field layer.
2.2.3. Validation Data
China Statistical Yearbooks report the planting areas of the paddy rice in each province, and province statistical yearbooks report the single and double paddy rice planting areas. The related data were obtained through the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) (http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/) (accessed on 10 Septerber 2021) and province-level statistics bureau, containing 31 province-level data [42]. High-resolution images were collected from Google Earth (https://earth.google.com/web/) (accessed on 22 October 2021) to acquire validation samples. In addition, field surveys were conducted in the Hubei and Jiangxi provinces in 2019. Finally, a total of 1840 regions of interest (ROIs) were generated with the stratified random sampling approach, containing paddy rice fields (1049/1840) and non-rice areas (791/1840) (Figure 3).
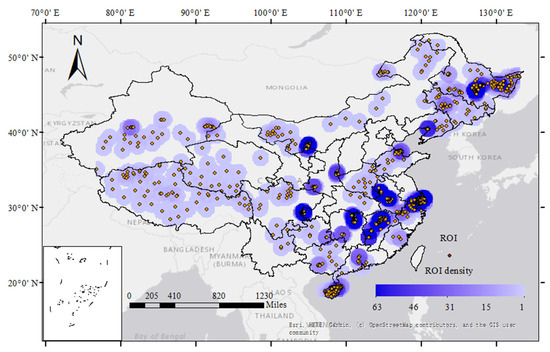
Figure 3.
The region of interest (ROI) distribution in China. The base map is from the GIS user community (https://www.esri.com/en-us/home) (accessed on 10 November 2021).
In addition to the ROIs, the National Land Cover Dataset (NLCD) of China with a 1 km spatial resolution, downloaded through the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx) (accessed on 25 November 2021), and generated by visual interpretation and digitization with Landsat TM/ETM/OLI images, was used for comparison in this study. The paddy rice layer derived from NLCD (NLCDrice) was adopted to validate the paddy rice map generated through the effective flood signal-based phenology method (EFSPrice).
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Images Preprocessing
According to the QA band code mentioned above, bad observations were removed. Because the surface reflectance and land surface temperature (LST) were stored in an integer coding, scaling factors were applied to limit the surface reflectance between 0 and 1 and obtain the LST, which can be calculated as in Equation (1):
where Bri is the i surface reflectance of band I or the LST of each pixel, α and β are the scaling factors of each band [43], and BDNi is the digital number of bands i used in the Landsat images.
The vegetation indices—normalized vegetation index (NDVI) [44] and land surface water index (LSWI) [45]—were derived as follows:
where Brred, BrNIR, and BrSWIR are the surface reflectance values of the red, near-infrared, and shortwave-infrared bands calculated using Equation (1). Image preprocessing was conducted through the GEE platform, which supports parallel computing and combines a multi-petabyte catalog of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets with planetary-scale analysis capabilities. The subsequent calculation was also conducted using cloud-computation technology in the GEE platform.
2.3.2. Effective Flood Signal
An apparent phenology characteristic of paddy rice is that it grows on flooded soils. The growth stage of paddy rice can be divided into three periods: (i) the flooding and rice transplanting period; (ii) the growing period (vegetative growth, reproductive, and ripening stages); and (iii) the fallow period after harvest [9]. Due to the physical feature of the period (i), the phenology-based algorithm was proposed by Xiao et al. [46], which uses the flood signal and night surface temperature to determine the time window for the transplanting phase of paddy rice:
where FS is the flood signal, SOT and EOT are the starting and ending points of the transplanting phase, respectively, and the others are consistent with the above.
In practice, commission errors will occur when the LSWI and NDVI are exceptionally small (for example, equal to 0). The determination approach of the time window for the rice transplanting phase has not been proven to be effective in subtropical and tropical regions [26]. To avoid calculating the time window and diminishing the misclassification errors, an effective flood signal was proposed in this study, which is described as follows:
where FSe is the effective flood signal, ε is the difference between LSWI and NDVI, δ is the threshold of LSWI, which is used to avoid the misclassification of paddy rice and other land covers, and LST is the land surface temperature.
Applying the restriction of LST > 10 °C can avoid the need to calculate the time window and eliminate the introduced errors. ε has been shown to range from 0 to 0.21 in different studies [27,47]. By comparing the mapping result and referring to other works, the study area was partitioned into three parts, taking a nonidentical ε value [30]. The variance cropping system and field water management resulting in δ are diverse in the province-level district. The details are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The effective flood signal parameter in different province-level districts.
2.3.3. Noncropland Masks
In addition to the effect of meteorology and sensors, paddy rice detection can be restricted by other land covers, including water bodies (e.g., rivers and lakes) and natural wetlands, which can also show flood signals. Additionally, miscellaneous non-cropland noise can pollute paddy rice maps. Therefore, the non-cropland masks were generated by modifying the algorithm used in previous studies [10,11,30,48] to eliminate noise.
Permanent water mask: This mask includes wetlands, ponds, lakes, and rivers. These land cover types always have a high LSWI value, and can be mixed with vegetation (e.g., ponds), but with a low NDVI value. Therefore, the permanent water pixels were identified with a mean LSWI value > 0.35 and a mean NDVI value < 0.20 in a whole year.
Sparse vegetation mask: The sparse vegetation mask contains built-up land, saline and alkaline land, and other low-vegetation lands. These land types have very low greenness throughout the entire growing season, and have high reflectance in the visible and shortwave infrared bands; thus, a sparse vegetation mask was established through the rule of a maximum NDVI value < 0.50 in all good observations.
Evergreen vegetation mask: Evergreen plants have foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. The mask was used to remove the evergreen vegetation with low reflectance in the red band and high reflectance in the near-infrared band. Thus, the criteria mean NDVI > 0.70 in a whole year was selected to map evergreen vegetation pixels.
Topography mask: Little paddy rice is planted in high-altitude localities due to climate limitations. In addition, small amounts of paddy rice are grown on sloping land due to the unique paddy rice planting condition, i.e., flooding. Therefore, the rule of elevation > 2000 m or slope > 6° was applied to exclude the areas with low probabilities of growing paddy rice through the SRTM DEM data.
2.3.4. Algorithm for Mapping Single and Double Paddy Rice
Paddy rice can be identified by its unique FSe after the non-cropland areas are masked using the above masks. However, some FSe will be missed due to the exclusion of bad observations, leading to omission errors. Potential noise can occur due to accidental factors (e.g., mixture pixels), which decreases the classification accuracy; thus, the frequency-based method was adopted to detect the paddy rice. The FSe frequency can be calculated using the equation:
where F is the FEe frequency of each pixel, ∑FSe is the total effective flooding signals of each pixel in one year, and ∑Ng is the total number of good observations of each pixel in one year.
To avoid paddy rice omissions, 5% was set as a threshold to generate the potential paddy rice layer. Rice canopies cover most of the rice fields approximately 50 to 60 days after transplanting [9], so 33% (2 × 60/365) was selected as an upper limit to map the paddy rice planting area.
Double paddy rice has two transplanting phases, whereas single paddy rice has one; thus, the F of double paddy rice is higher than that of single paddy rice. According to the statistical data of double and single paddy rice planting areas, the threshold was set to distinguish the single and double paddy rice. The workflow of mapping single and double paddy rice is shown in Figure 4.
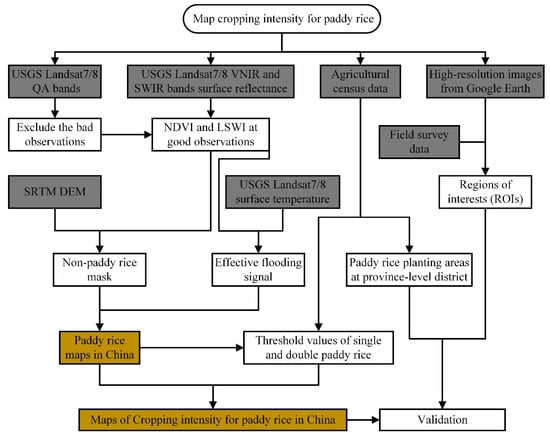
Figure 4.
The workflow for Landsat-based and the effective flooding signal-based phenology (EFSP) method to map cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) in China. Four modules comprise the method, namely, Landsat image preprocessing, effective flood signal calculation, threshold value determination for single and double paddy rice, and validation based on agricultural census data, field survey, and high-resolution images.
2.3.5. Regional Cropping Intensity for Paddy Rice
To analyze the regional paddy rice cropping system, the regional cropping intensity for paddy rice (RCIPR) was proposed based on single and double paddy rice maps. RCIPR can be calculated using Equation (7):
where α and β are weight coefficients for single and double paddy rice (1 and 2); Ssi is the planting area of single paddy rice in the target region; Sdi is the planting area of double paddy rice in the target region; and Sr is the area of the target region. In this study, the province-level regions are set as target regions. A simple example is used to illustrate the PCIPR: planting areas of single and double paddy rice are 1 and 2 ha in a district, where the total area is 100 ha, in one year; thus, the PCIPR of the district is 0.05 ((1 × 1 + 2 × 2)/100 = 0.05).
2.3.6. Validation
The paddy rice planting areas obtained from the China Statistical Yearbooks and the province statistical yearbooks were used to validate the single paddy rice, double paddy rice, and total paddy rice planting areas at the province level. Unfortunately, the Statistical Yearbooks do not contain the data of Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Aomen. In addition, the confusion matrix was also adopted in this study to calculate the evaluation index to assess the classification accuracy, including producer accuracy (PA), user accuracy (UA), overall accuracy (OA), and kappa coefficient (KC). These parameters can be calculated as follows.
where Sd represents the total number of correctly classified pixels, n represents the total number of validation pixels, and Xij represents an observation in row i and column j in the confusion matrix; Xi represents the marginal total of row i, and Xj represents the marginal total of column j in the confusion matrix.
3. Results
3.1. Paddy Rice Map and Accuracy
Because Nansha Islands has few paddy rice planting areas and the land area is minimal, it was not contained in this study. Figure 5 shows the distribution of paddy rice derived from Landsat data and EFSP in China from 2014 to 2019 (hereafter referred to as EFSPrice). Paddy rice is mainly distributed in southern China and northeastern China, with abundant water resources (e.g., Yangtze River, Poyang Lake, Doingting Lake) and extensive alluvial plains (e.g., Sanjiang Plain, Chengdu Plain). However, little paddy rice agriculture is scattered in western China, where the latitude and topography prohibit rice growth.
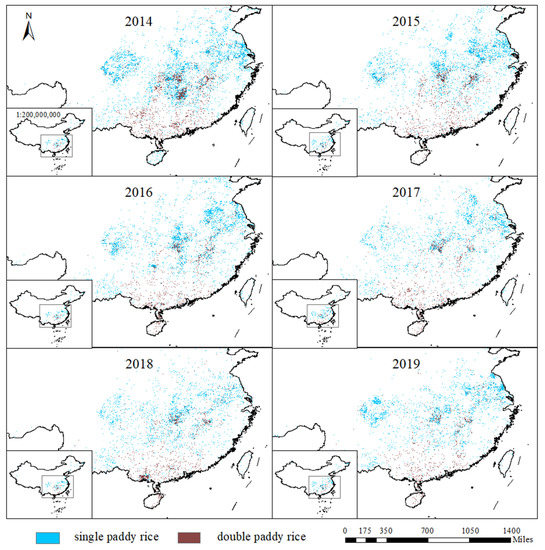
Figure 5.
Paddy rice maps derived from Landsat images with the effective flood signal-base phenology (EFSP) method in China (excluding the Nansha Islands) from 2014 to 2019.
From Figure 6b, it can be seen that half of the paddy rice area was located in Cfa (warm, fully humid and hot summer, 49%, more than 14,000 Kha), followed by Cwa (warm, winter dry and hot summer, 25%), Dwa (cold, dry winter and hot summer, 11%), and Dwb (cold, dry winter and warm summer 9%). From the spatial distribution of paddy rice fields in different climate zones, paddy rice agriculture always occurs in hot summer areas.
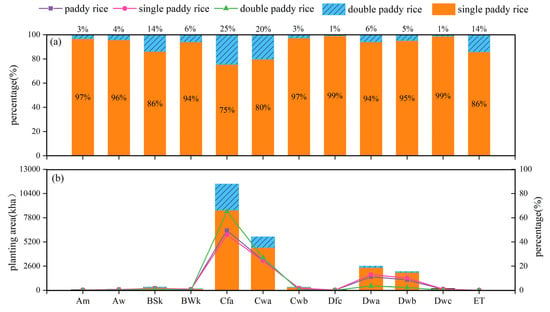
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of paddy rice planting area along with the climate zone: (a) percentage of single and double paddy rice in different climate zones; (b) paddy rice planting area in different climate zones. The bars represent the planting area of paddy rice and lines represent the percentage of paddy rice in different climate zones.
The EFSPrice was validated with statistical data at the province level and ROI data collected from high-resolution images and field surveys. Figure 7 illustrates that the mapped paddy rice planting areas were close to the statistical data. The coefficient of determination (R2) was higher than 0.88 from 2014 to 2019, which shows a remarkable correlation between the two, and EFSPrice can reflect the actual paddy rice planting area.
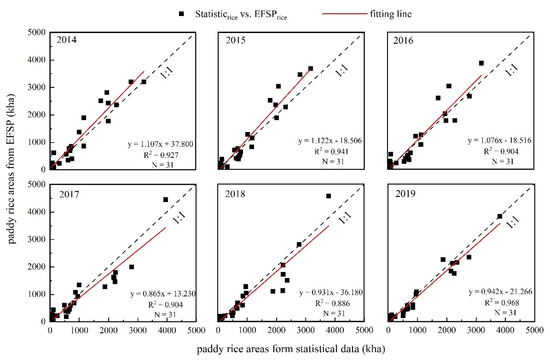
Figure 7.
Paddy rice planting area from the map compared with Statistical Yearbooks at the province level in China from 2014 to 2019.
The confusion matrix of paddy rice and non-paddy rice showed that the UA, PA, OA, and KE were higher than 0.76, 0.93, 0.83, and 0.66 from 2014 to 2019, respectively (Table 2). The excellent value of the evaluation index demonstrated that the spatial distribution of EFSP rice was close to reality. The accuracy was mainly affected by the misclassification of non-paddy rice and paddy rice agriculture.

Table 2.
The evaluation index derived from the confusion matrix from 2014 to 2019.
3.2. Single and Double Paddy Rice Distribution and Accuracy
According to the statistical data from the 2019 Statistical Yearbooks, the threshold value was set to distinguish single and double paddy rice. For example, when the planting areas (from Statistical Yearbooks) of single cover accounts for 51% of total paddy rice planting areas in Jiangxi province, the threshold (8.0%) of single and double paddy rice can be determined through the 51% accumulated frequency of FSe. Given the circumstances of various irrigation methods in different regions, the threshold was calculated at the province level to improve the identification precision. Guangxi (GX), Guangdong (GD), Hunan (HN), and Jiangxi (JX) provinces, where double paddy rice agriculture predominates the paddy rice cropping system, were selected for analysis, and the results are shown in Figure 8. The threshold values of FSe frequency to distinguish the single and double paddy rice in GX (GD), JX, and HN were 5.9%, 8.0%, and 10.3%, respectively. According to the agricultural census data, double paddy rice planting areas are small in other province-level districts, so 16% (60/365) was used as the threshold for single and double paddy rice.
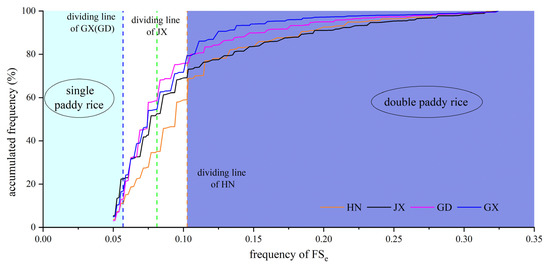
Figure 8.
The accumulated frequency of FSe to determine the threshold of single and double paddy rice according to EFSPrice and the 2019 statistical data, GX, GD, HN, and JX.
Figure 5 and Figure 6b illustrate that the double paddy rice was mainly distributed in southern and central China (Cfa and Cwa; 56% and 25%), where the lasting warm temperatures are conducive to the growth of thermophilic crops such as paddy rice. In addition, little double paddy rice is grown in other climate zones (Figure 6a).
EFSPrice was compared with statistical data to validate the classification accuracy of single and double paddy rice in GD, GX, JX, and HN from 2014 to 2019. The R2 values between EFSPrice data and statistical data were 0.73 and 0.55 for single and double paddy rice (Figure 9), respectively, and the correlation was significant at the level of p < 0.01 (n = 24). Compared with the single paddy rice result, the double paddy rice exhibits low consistency with agricultural census data and underestimation. This may be because the upper limits of F (33%) excluded some double paddy rice planting areas, which can be further studied in future research.
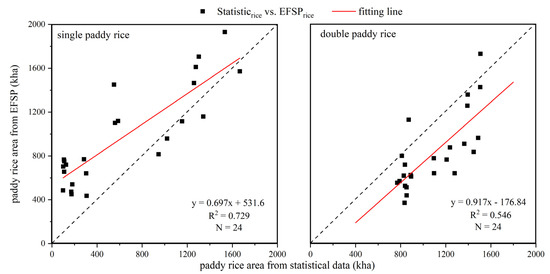
Figure 9.
Province-level comparisons of area estimates of single and double paddy rice planting areas in China between the statistical data and Landsat-based estimates.
3.3. Dynamics of the Paddy Rice Planting Area from 2014 to 2019
From 2014 to 2019, the interannual paddy rice planting area shows a slightly decreasing trend in China (Figure 10c), particularly in southern China (Figure 5), and an apparent increasing trend in northeastern China (Figure 11c).
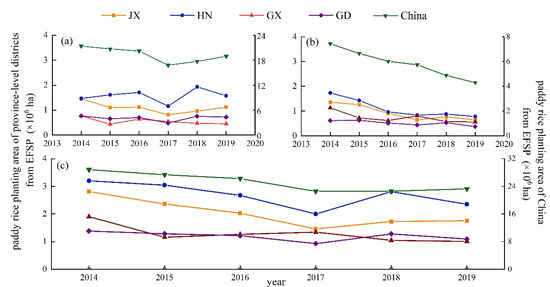
Figure 10.
Variations in paddy rice planting area from EFSPrice in China and typical provinces from 2014 to 2019. (a–c) single paddy rice, double paddy rice, and total paddy rice planting area, respectively, from 2014 to 2019.
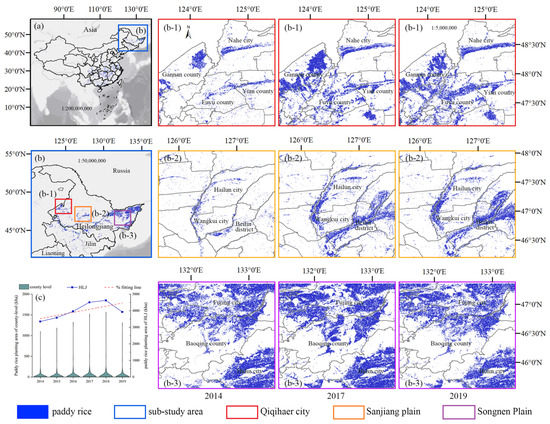
Figure 11.
Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice in the sub-study area (Heilongjiang province, HLJ) from 2014 to 2019: (a,b) spatial distribution of paddy rice of study area (China) and sub-study area (HLJ) in 2019, respectively; (c) paddy rice planting area of HLJ at prefectural level. Magnification of figures in map (b) shows the remarkable expansion area of paddy rice in the HMaps of regional cropping intensity for paddy rice.
Based on data from Statistical Yearbooks, the four provinces that are the leading double paddy rice agriculture areas in China were selected to analyze the paddy rice cropping dynamics. The single paddy rice planting area fluctuated within a given range (0.30–1.20) and did not show an evident trend in some provinces (HN and GX), whereas it showed a decreasing trend then increased in China overall (Figure 10a). Compared with single paddy rice, the double paddy rice field area sharply dropped since 2014, especially in JX and HN (Figure 10b). Given the conflict between grain production and economic development, including the development of secondary and tertiary industries, and urbanization, some paddy rice agriculture has been lost in recent years [49]. Due to the high cost of irrigation energy, a shortage of water resources, and rural household labor poverty, the double paddy rice cropping system has been converted to single paddy rice cropping or other systems [49,50]; thus, shrinkage of double paddy rice planting areas is more pronounced than that of single paddy rice planting areas.
For the spatial variation, Figure 5 clearly shows the shrinkage of the paddy rice planting area in China from 2014 to 2019, especially in South China (e.g., Chengdu Plain, Yangtze River Basin). The variations coincide with the trend from 2000 to 2015 recorded in a previous study [51], which confirms that the paddy rice planting area continued to drop from 2000 to 2019 in China. The decrease in the paddy rice planting area in southern China may be attributed to urbanization, a shortage of agricultural labor, and increases in labor wages [52,53]. The expansion of paddy rice in northeastern China should also be noted, and can be attributed to the increase in rice prices and abundant water resources, mainly concentrated in Heilongjiang Province (HLJ) (Figure 11b). In HLJ, the escalating trend of the paddy rice planting area was stable and moderate. However, the increasing trend was not continuous in some local areas. From Figure 11b, the planting area of paddy rice was reduced in 2019 compared with 2017 on the Qiqihaer and Songnen Plains. Figure 11c shows that the paddy rice planting area in HLJ, where the expansion of paddy rice agriculture occurred from 2014 to 2019, shows an increasing trend but receded slightly in 2019.
The cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) at the parcel level is shown in Figure 5, and the regional CIPR (RCIPR) maps (Figure 12) were generated for better analysis of the regional agriculture system and water management.
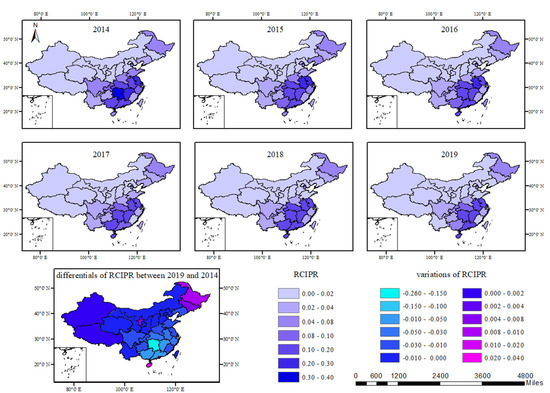
Figure 12.
Regional cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) in China from 2014 to 2019.
In southeastern China, the RCIPR was higher than that of northwestern China due to the climate factors and topographical characteristics. In southeastern China, due to its flat topography, warm climate, and adequate rainfall, paddy rice cropping system was a mixture of single- and double-cropping and the RCIPR was consistently higher than 0.1. However, there are few paddy rice planting areas in northern China, and the cropping system was dominated by single cropping due to a lack of water and the relatively cold weather in winter.
The RCIPR increased in northeastern China, western China, Hainan Province (HAN), and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NX), but dropped in other regions, especially in south China. In northeastern China, the increase in the price for rice and abundant water resources accelerated the expansion of single paddy rice, leading to the rise in RCIPR. In western China and NX, the paddy rice planting area was small in 2014, so the RCIPR showed a fluctuation. There was a significant increase in RCIPR from 2014 to 2019 in HAN due to the conversion of single-cropping paddy rice to double-cropping paddy rice. Regions with decreased RCIPR were concentrated in south China due to a rural labor shortage and a conflict between grain production and economic development. The RCIPR for Hunan Province dropped by 0.26 (Figure 13), followed by Jiangxi Province (0.09), Guangxi Province (0.07), and Guangdong Province (0.06), where the double paddy rice dominated the paddy rice cropping system. This is because some double paddy rice systems were converted to the single paddy rice system.
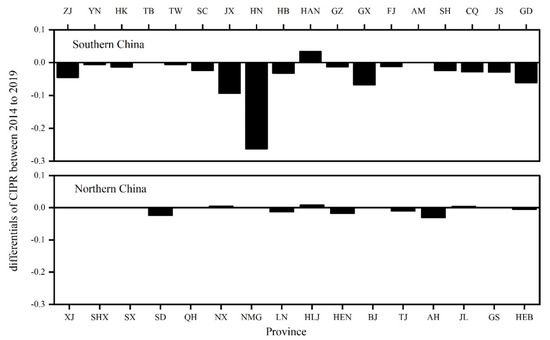
Figure 13.
Variation in RCIPR in China from 2014 to 2019 at province level. ZJ is Zhejiang Province; YN is Yunnan province; HK is Hong Kong; TB is Tibet; TW is Taiwan Province; SC is the Sichuan Province; JX is Jiangxi Province; HN is Hunan Province; HAN is Hainan Province; GZ is Guizhou Province; GX is Guangxi Province; FJ is Fujian Province; MC is Macao Special Administrative Region; SH is Shanghai City; CQ is Chongqing City; JS is Jiangsu Province; GD is Guangdong Province; XJ is Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; SHX is Shaanxi Province; SX is Shanxi Province; SD is Shandong Province; QH is Qinghai Province; NX is Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region; NMG is Inner Mongolia; LN is Liaoning Province; HLJ is Heilongjiang Province; HEN is Henan Province; BJ is Beijing city; TJ is Tianjin City; AH is Anhui City; JL is Jilin Province; GS is Gansu Province; HEB is Heibei Province.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison between Other Datasets and CIPR Maps Based on EFSP
The EFSPrice in 2019 was compared with the paddy rice layer of the national land cover dataset (NLCD) from the Institution of Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research (hereafter referred to as NLCDrice). In Figure 14a,b, the paddy rice area of EFSPrice is more nuanced than that of NLCDrice. Note that pixels for EFSPrice have a spatial resolution of 1 km × 1 km, and the binary paddy rice map was generated with fractional coverage of more than 20% (20,000 m2); however, the pixels for EFSPrice are 30 m × 30 m. Therefore, the paddy rice coverage for EFSPrice is smaller than that for NLCDrice. From the magnified charts shown in Figure 14, NLCDrice and EFSPrice share a similar spatial distribution of paddy rice area, but EFSPrice has more details (the roads between paddy rice fields) due to the finer resolution of the EFSPrice data source.
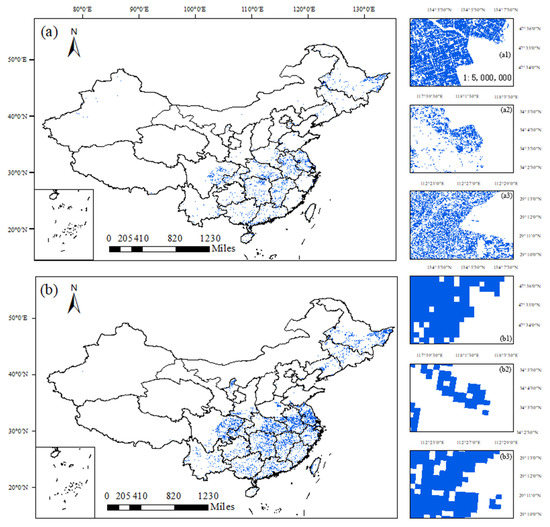
Figure 14.
Comparison of the paddy rice map derived from EFSP(EFSPrice) and Geographic Science and Natural Resources Research (NLCDrice): (a,b) EFSPrice and NLCDrice, respectively; (a1), (a2), (a3), (b1), (b2), and (b3) are the magnified areas from the corresponding charts.
Three regions that are major paddy rice agriculture areas were selected randomly to compare the details of the two maps at the same spatial scale. The two maps also have high spatial consistency in the magnified region. The comparison of the magnified charts of Figure 14a shows that the southern paddy fields (a3 and a2) are more fragmented than that of northern China (a1), where alluvial plains (Sanjiang Plain, Songen Plain) are located.
4.2. Identification of Paddy Rice Using the Effective Flood Signal
The results revealed the operability and reliability of annual mapping of paddy rice and distinguishing between single and double paddy rice in China using effective flood signal-based phenology (EFSP) methods with Landsat images. Compared with the previous phenology-based method [28,54,55], the EFSP has improved paddy rice identification, attributed to the better data source, the FSe algorithm, and the threshold value of single and double paddy rice.
Surface reflectance product (SR) data were used rather than top-of-atmosphere reflectance (TOA) data, which can avoid the potential atmospheric conditions affecting the classification results and can reflect the actual land cover [56]. Unfortunately, the TOA was extensively adopted in the preview study due to data limitations. Landsat SR data were first used to map paddy rice on a national scale.
EFSP considers the daily LST to determine the effective flood signal (FSe), rather than the LST of one or several days, to specify the time window for the paddy rice transplanting phase, which results in moving the time window forward or backward, avoiding the occasional error introduced due to the LST fluctuation. δ (the threshold of LSWI, which is used to avoid the misclassification of paddy rice and other land cover types) was adopted in EFSP, which can diminish commission errors. In the previous phenology-based method for identifying paddy rice (Equation (4)), the raw value of LSWI is not considered, leading to the misclassification occurring when the LSWI and NDVI are small. A notable example of this can be given: although there is no paddy rice agriculture when LSWI and NDVI are close to 0, the previous method will still map it. Furthermore, three categories of FSe were established to map paddy rice better by adjusting δ and ε in China.
The FEe frequency (F) was used to identify the paddy rice. The threshold of paddy rice (5–33%) was set according to the time during which rice canopies covered most of the land surface area after transplanting. After statistical analysis based on agricultural census data and the map of paddy rice, the threshold of single and double paddy rice was generated. Introducing the frequency of FEe to distinguish single and double paddy rice simplified the procedure of traditional classification, by relying on the time-series curve of the vegetation index. Additionally, it is independent of the ground truth data and only needs the statistical data of one year, solving the labor intensity and data dependency problems.
4.3. Uncertainty of Mapping CIPR in China
Although the EFSPrice has high accuracy (validated by ROI and agricultural census data) and is consistent with other products, mapping CIPR in macro-regions (especially the considerable distance from north to south) can still be a challenging task for various reasons.
The scarcity of good observations over a year will lead to the misclassification and omission of paddy rice. In the humid tropical and subtropical areas, approximately 4% of the region had fewer than ten good observations throughout the year in China due to cloudy conditions, although the Landsat 7 and Landsat 8 data were combined in this study. Consequently, the flooding signal (FS) may not be detected by EFSP, resulting in the omission of paddy rice. Cloud-free SAR data may be applied in monitoring paddy rice agriculture, but it is still an arduous task to survey land surfaces continuously on a large scale.
The mixed pixels of paddy rice and other land cover types may weaken the FS, especially in southern China, where the fragmented fields are concentrated. The 30 m resolution may be insufficient for mapping CIPR in tiny fields close to other ground features, where smallholders constitute the majority of paddy rice agriculture [57]. To provide a more acceptable resolution, the 10 m resolution Sentinel-2 is expected to provide improved data.
Although EFSP contains rules to avoid confusion caused by ponds or wetlands, some misclassification also occurs due to similar phenology characteristics, and flood signals exist in paddy rice and other aquatic plant planting areas. Additionally, the floodplain of rivers can generate flood signals due to flooding in the transplanting stage of paddy rice (rainy season). If heavy precipitation occurs before one day of the satellite revisit, noise will be produced by the ponding water, weakening the FSe, and resulting in commission errors. Therefore, the distinction of these false flood signals with FSe from paddy rice should be further considered in future studies. In addition, the reasons for the three categories of FSe were not explained in this study and needed to be further developed in future research.
The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) is a persistent problem in spatial analysis when spatially aggregated data are used [58]. Paddy rice maps for the different spatial scale levels or different zonal systems for the same study may not show consistent results. To explain the distribution of paddy rice in China, the distribution and variations in paddy rice in China with the geographic position (north or south) were generally described. Moreover, paddy rice is a thermophilic crop affected by temperature and rainfall. The climate zone classified through the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system can reflect the physical features of temperature and rainfall. Depicting the distribution and change in the paddy rice planting area based on the climate zone is reliable and feasible. Only two zonal systems were applied in this study, which should be further studied in future research.
5. Conclusions
This study developed the Landsat-based and effective flooding signal-based phenology (EFSP) method to map cropping intensity for paddy rice (CIPR) in China from 2014 to 2019, using cloud computing on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, and the results were assessed using data from multiple sources. EFSP is independent of the ground data, uses a threshold to distinguish single and double paddy rice, and is able to monitor CIPR on a large scale. Combining Landsat 7 and Landsat 8, EFSP has been shown to be feasible in China, including in cold and tropical regions.
CIPR maps derived from Landsat data and EFSP (EFSPrice) demonstrated that paddy rice agriculture chiefly occurred in Cfa, Cwa, and Dwb climate zones, and the double paddy rice planting area in the Cfa climate zone covered 56% of the area in China, followed by Cwa (25%). Both paddy rice and double paddy rice showed a slight decreasing trend from 2014 to 2019 due to the high cost and shortage of rural households in China, but single paddy rice expanded in northeastern China due to the increase in the rice price. The RCIPR coincides with the parcel-level CIPR but shows a sharp decrease in south China due to the decrease in double paddy rice. Further research is encouraged; of particular interest are the multi-source and time-series data applied globally to map paddy rice agriculture, and determination of the drivers of changes in cropping systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C. and J.W.; methodology, J.W.; validation, J.W., W.L. and Y.L.; formal analysis, J.W.; investigation, J.W.; resources, Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.C., Y.L. and J.W.; visualization, W.L. and J.W.; project administration, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was financially supported by the NSFC-MWR-CTGC Joint Yangtze River Water Science Research Project (No. U2040213).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their time and their thoughtful comments and efforts towards improving our manuscript. The authors would like to thank the United States Geological Survey for the open data and Google Earth Engine for providing technical support. We also thank National Bureau of Statistics for providing free statistical data and the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center for validation data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, W.; Sui, H.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halder, D.; Saha, J.K.; Biswas, A. Accumulation of essential and non-essential trace elements in rice grain: Possible health impacts on rice consumers in West Bengal, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elert, E. Rice by the numbers: A good grain. Nature 2014, 514, S50–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuenzer, C.; Knauer, K. Remote sensing of rice crop areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2101–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.A.U.R.; Ashfaq, M.; Razzaq, A.; Ali, Q. Comparison of water use efficiency, profitability and consumer preferences of different rice varieties in Punjab, Pakistan. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Onwuka, M.; Song, T. Methane and Nitrous Oxide Flux after Biochar Application in Subtropical Acidic Paddy Soils under Tobacco-Rice Rotation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Qian, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Acclimation of methane emissions from rice paddy fields to straw addition. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Friedl, M.A.; Xin, Q.; Gray, J.; Pan, Y.; Frolking, S. Mapping Crop Cycles in China Using MODIS-EVI Time Series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Ke, Y.; Chen, X. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Northeastern China Using Spatiotemporal Data Fusion and Phenology-Based Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Mapping Ratoon Rice Planting Area in Central China Using Sentinel-2 Time Stacks and The Phenology-Based Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloy, K.R.; Smith, F.R.; Robinson, M.R. Monitoring rice areas using LANDSAT MSS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wu, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, X. Using NOAA AVHRR and Landsat TM to estimate rice area year-by-year. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Wen, N.; Tao, Q. County-level rice area estimation in southern China using remote sensing data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Mapping Paddy Rice Using Weakly Supervised Long Short-Term Memory Network with Time Series Sentinel Optical and SAR Images. Agriculture 2020, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panigrahy, S.; Parihar, J.S. Role of middle infrared bands of Landsat thematic mapper in determining the classification accuracy of rice. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennakoon, S.B.; Murty, V.V.N.; Eiumnoh, A. Estimation of cropped area and grain yield of rice using remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, M.K.; Hassan, Q.K.; Chowdhury, E.H. Application of Remote Sensors in Mapping Rice Area and Forecasting Its Production: A Review. Sensors 2015, 15, 769–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M.; Kindred, D.; Miao, Y. Mapping paddy rice fields by applying machine learning algorithms to multi-temporal Sentinel-1A and Landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1042–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Minh, D.H.T.; Ndikumana, E.; Courault, D.; Belhouchette, H. Mapping Paddy Rice Using Sentinel-1 SAR Time Series in Camargue, France. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, K.; Li, Z.; Rao, L.N.; Gao, F.; Xie, D.; Hien, N.T.; Zeng, Z. Mapping Paddy Rice Area and Yields Over Thai Binh Province in Viet Nam from MODIS, Landsat, and ALOS-2/PALSAR-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2238–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Guan, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. Phenology-Based Rice Paddy Mapping Using Multi-Source Satellite Imagery and a Fusion Algorithm Applied to the Poyang Lake Plain, Southern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, G.; Jin, C.; Kou, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Mapping paddy rice planting area in cold temperate climate region through analysis of time series Landsat 8 (OLI), Landsat 7 (ETM+) and MODIS imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandra Paul, G.; Saha, S.; Hembram, T.K. Application of phenology-based algorithm and linear regression model for estimating rice cultivated areas and yield using remote sensing data in Bansloi River Basin, Eastern India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 19, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Menarguez, M.A.; Biradar, C. Mapping paddy rice planting areas through time series analysis of MODIS land surface temperature and vegetation index data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Evolution of regional to global paddy rice mapping methods: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986–2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z. Mapping Early, Middle and Late Rice Extent Using Sentinel-1A and Landsat-8 Data in the Poyang Lake Plain, China. Sensors 2018, 18, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, D.; Huete, A.R.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Sun, H. Detection and estimation of mixed paddy rice cropping patterns with MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Ponce-Campos, G.E.; Zhang, M.; Chang, S.; Tian, F. Mapping up-to-Date Paddy Rice Extent at 10 M Resolution in China through the Integration of Optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Wang, R.; Song, H.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y. Mapping cropping intensity in Huaihe basin using phenology algorithm, all Sentinel-2 and Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lei, H. Fifteen-year Variations of Water Use Efficiency over a Wheat-Maize Rotation Cropland in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 306, 108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Yan, H.; Liu, F. Decreasing Cropping Intensity Dominated the Negative Trend of Cropland Productivity in Southern China in 2000–2015. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, H.; Ojara, M.A.; Lukali, A. Estimation and mitigation of greenhouse gases in typical paddy-upland rotation systems in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Tang, H.; Frolking, S.; Boles, S.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Qin, X. Mapping Single-, Double-, and Triple-crop Agriculture in China at 0.5° × 0.5° by Combining County-scale Census Data with a Remote Sensing-derived Land Cover Map. Geocarto Int. 2003, 18, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, A.D.; Takeuchi, W. A Data-Intensive Approach to Address Food Sustainability: Integrating Optic and Microwave Satellite Imagery for Developing Long-Term Global Cropping Intensity and Sowing Month from 2001 to 2015. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubel, F.; Brugger, K.; Haslinger, K.; Auer, I. The climate of the European Alps: Shift of very high resolution Köppen-Geiger climate zones 1800–2100. Meteorol. Z. 2017, 26, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Lian, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, X. Drought monitoring utility of satellite-based precipitation products across mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. Landsat Collection 2 Quality Assessment Bands. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/nli/landsat/landsat-collection-2-quality-assessment-bands (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- United States Geological Survey. USGS Landsat 8 Level 2, Collection 2, Tier 1. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/LANDSAT_LC08_C02_T1_L2#bands (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Landscape-scale characterization of cropland in China using Vegetation and Landsat TM images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3579–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-S.; Huang, J.-F.; Huete, A.R.; Peng, D.-L.; Zhang, F. Mapping paddy rice with multi-date moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cai, X.; Tan, J.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Luo, Y. Mapping paddy rice using Landsat time series data in the Ganfu Plain irrigation system, Southern China, from 1988−2017. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 1556–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Mo, C.; Yang, J. Double paddy rice conversion to maize–paddy rice reduces carbon footprint and enhances net carbon sink. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y. Detection of paddy rice cropping systems in southern China with time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 733–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Biradar, C.M.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice croplands in China and India from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Tan, M. Paddy rice multiple cropping index changes in Southern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M. Inter-provincial Differences in Rice Multi-cropping Changes in Main Double-cropping Rice Area in China: Evidence from Provinces and Households. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, C.; Liu, H.-J.; Fu, Q.; Guan, H.-X.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, X.-L.; Kong, F.-C. Mapping the fallowed area of paddy fields on Sanjiang Plain of Northeast China to assist water security assessments. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohka, T.; Nasahara, K.N.; Miyata, A.; Mano, M.; Tsuchida, S. Evaluation of optical satellite remote sensing for rice paddy phenology in monsoon Asia using a continuous in situ dataset. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4343–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanov, N.; Vargas, M.; Miura, T.; Sei, A.; Danial, A. Evaluation of the performance of Suomi NPP VIIRS top of canopy vegetation indices over AERONET sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yamauchi, F.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S. What constrains mechanization in Chinese agriculture? Role of farm size and fragmentation. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W. Modifiable Areal Unit Problem. Int. Encycl. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 2009, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).