From SMOS Soil Moisture to 3-hour Precipitation Estimates at 0.1° Resolution in Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ground-Based Precipitation Measurements
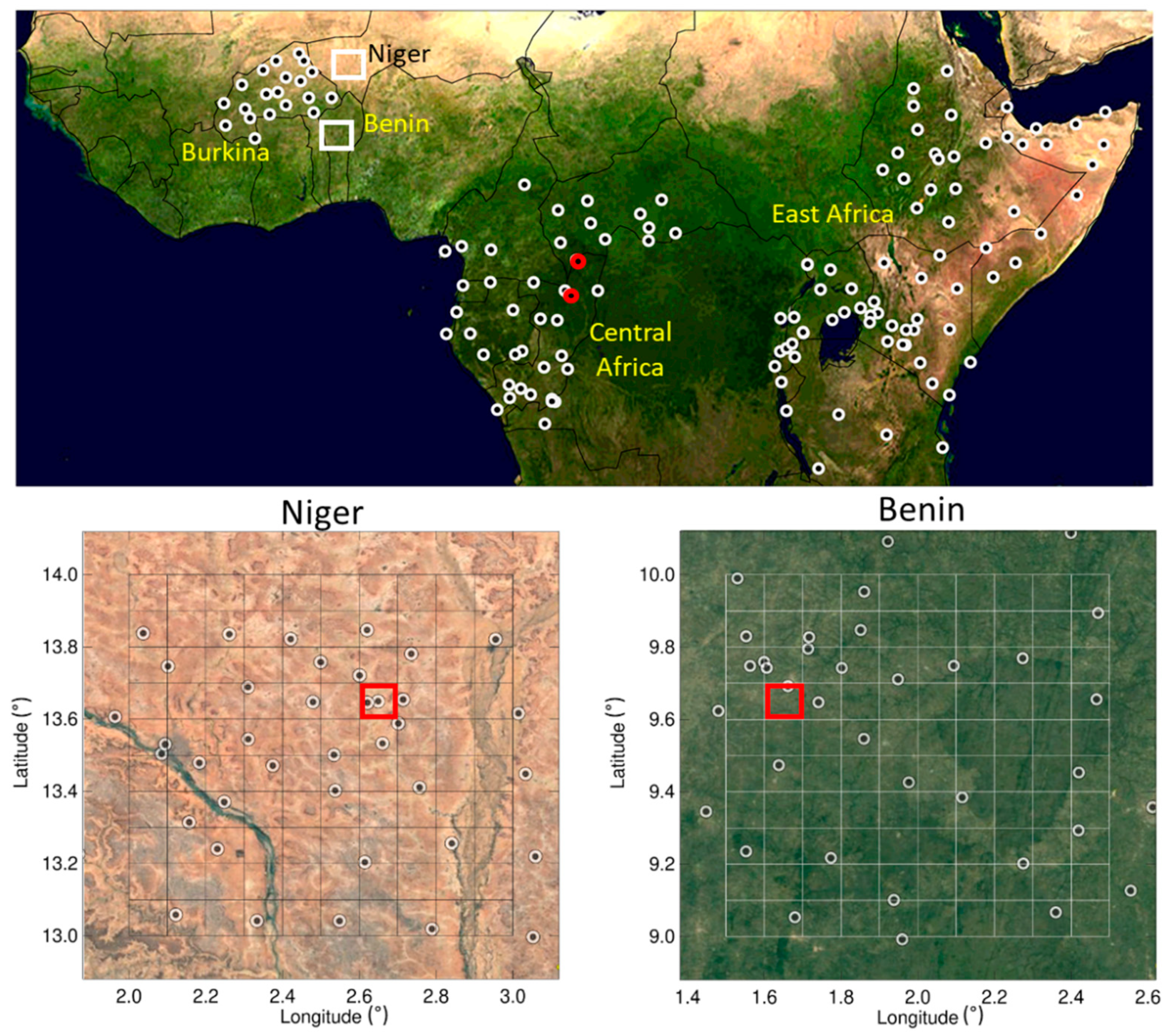
2.2. Satellite-Based Precipitation Products
2.3. SMOS Soil Moisture Datasets
2.4. The PrISM Algorithm
2.4.1. The Soil Moisture Model (S2M)
2.4.2. The Particle Filter Assimilation Scheme
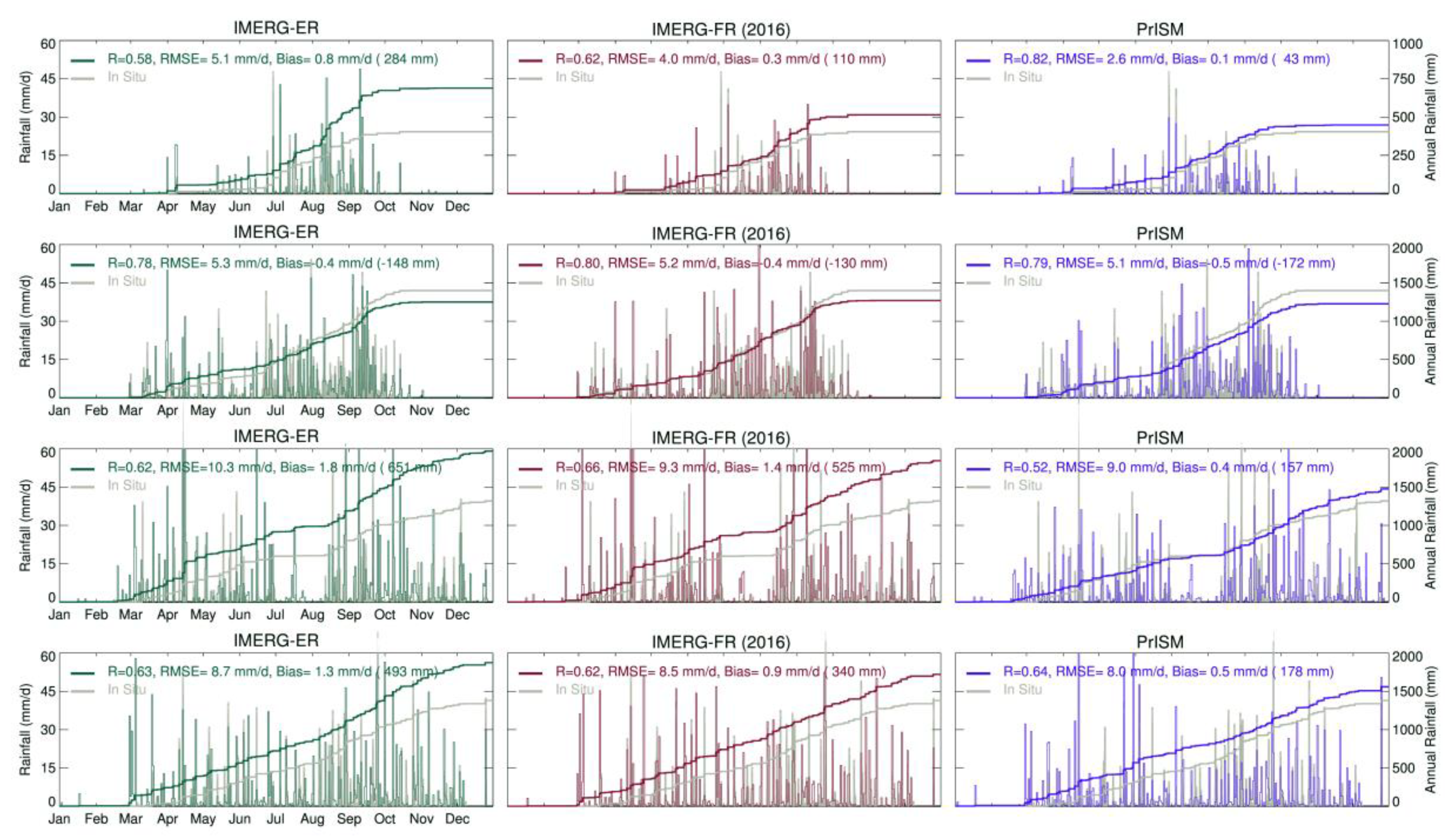
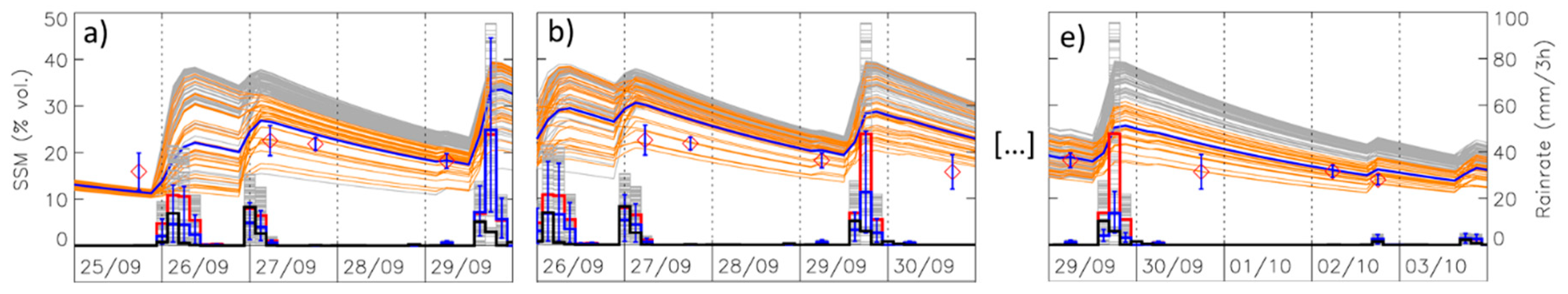
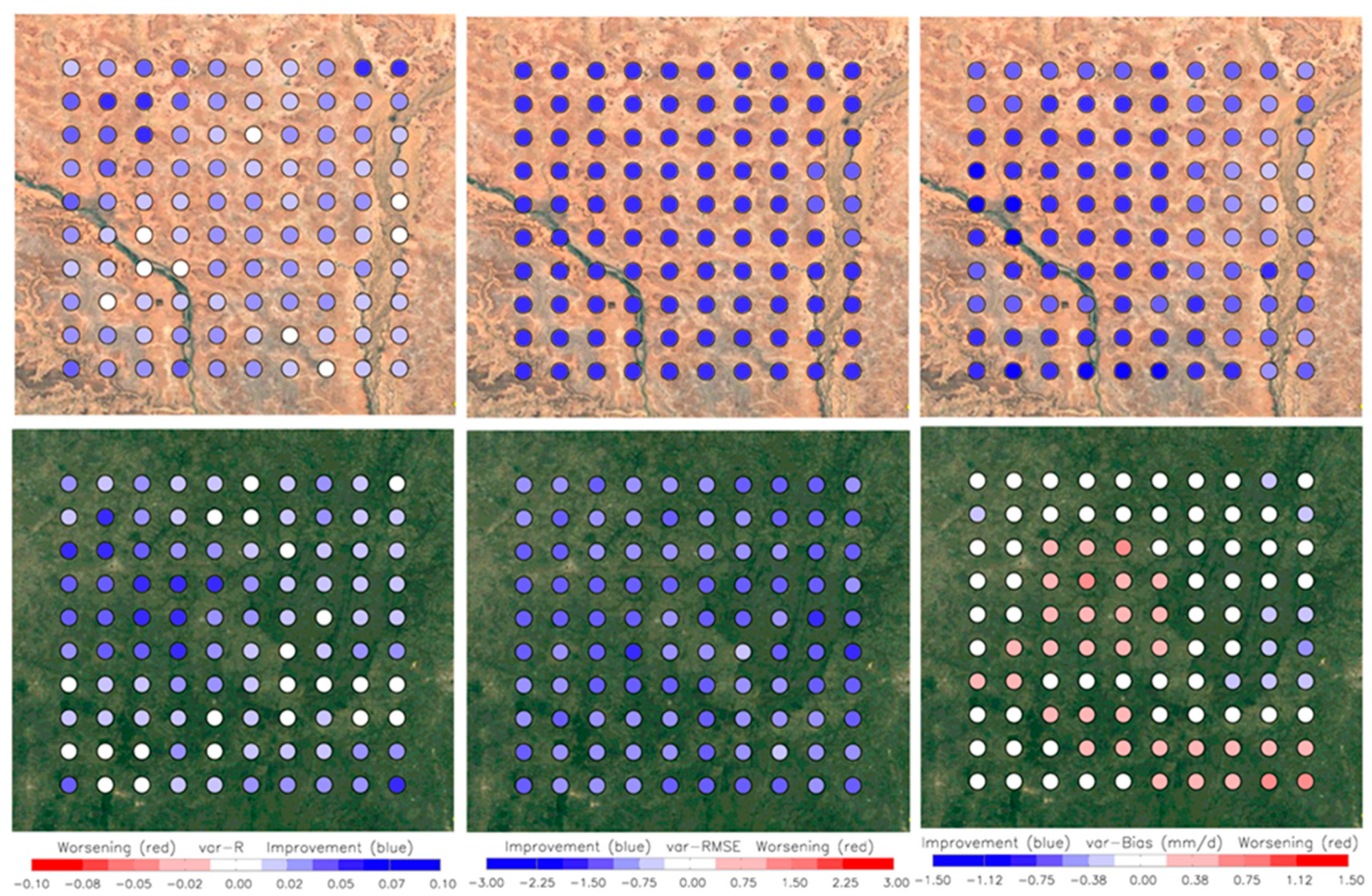
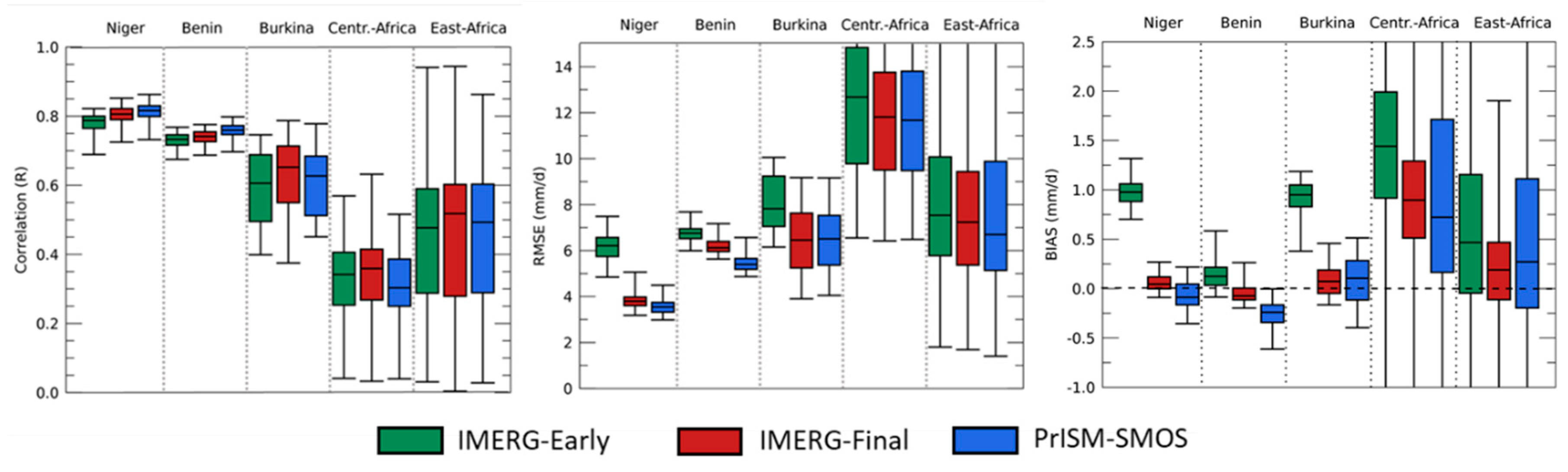
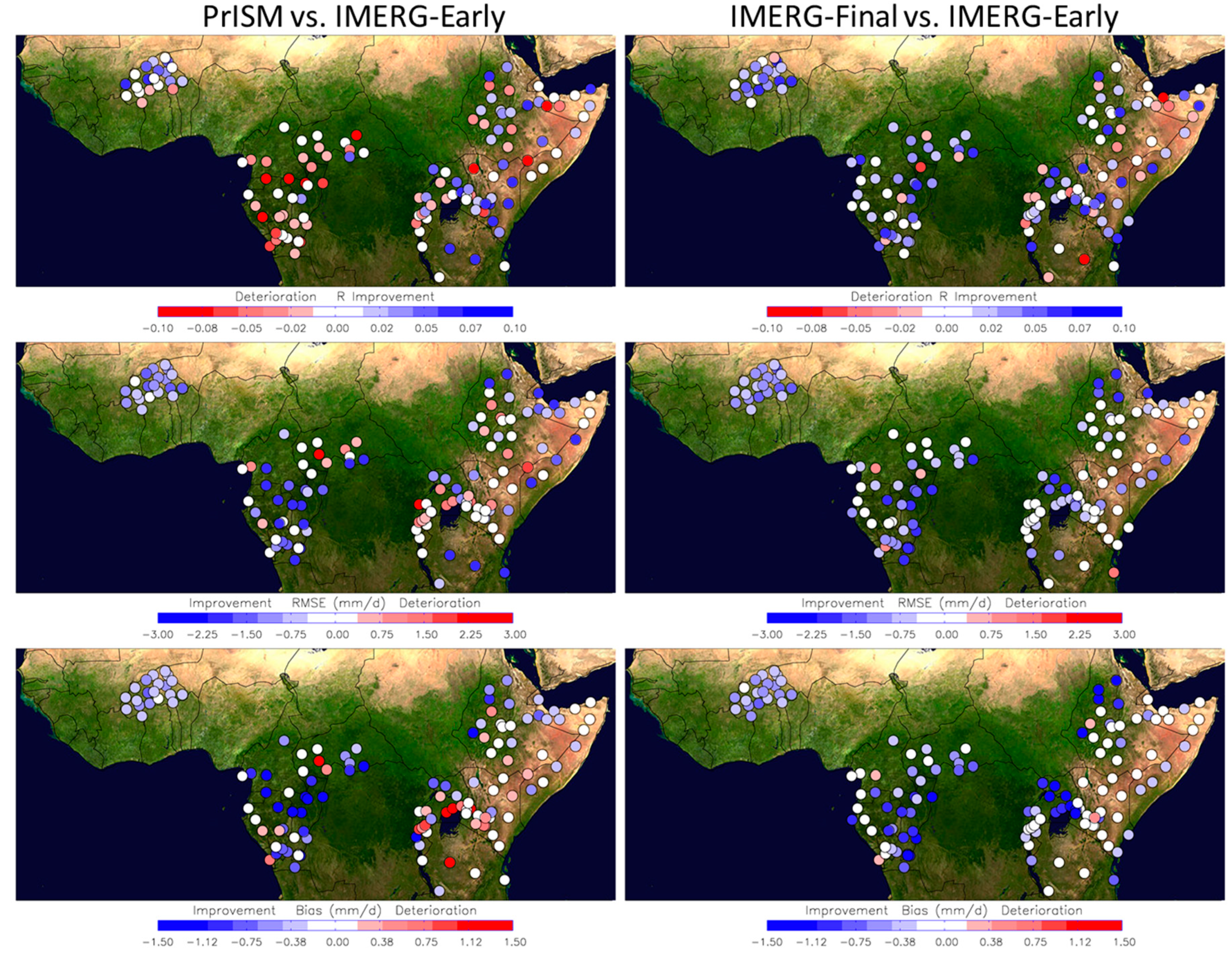
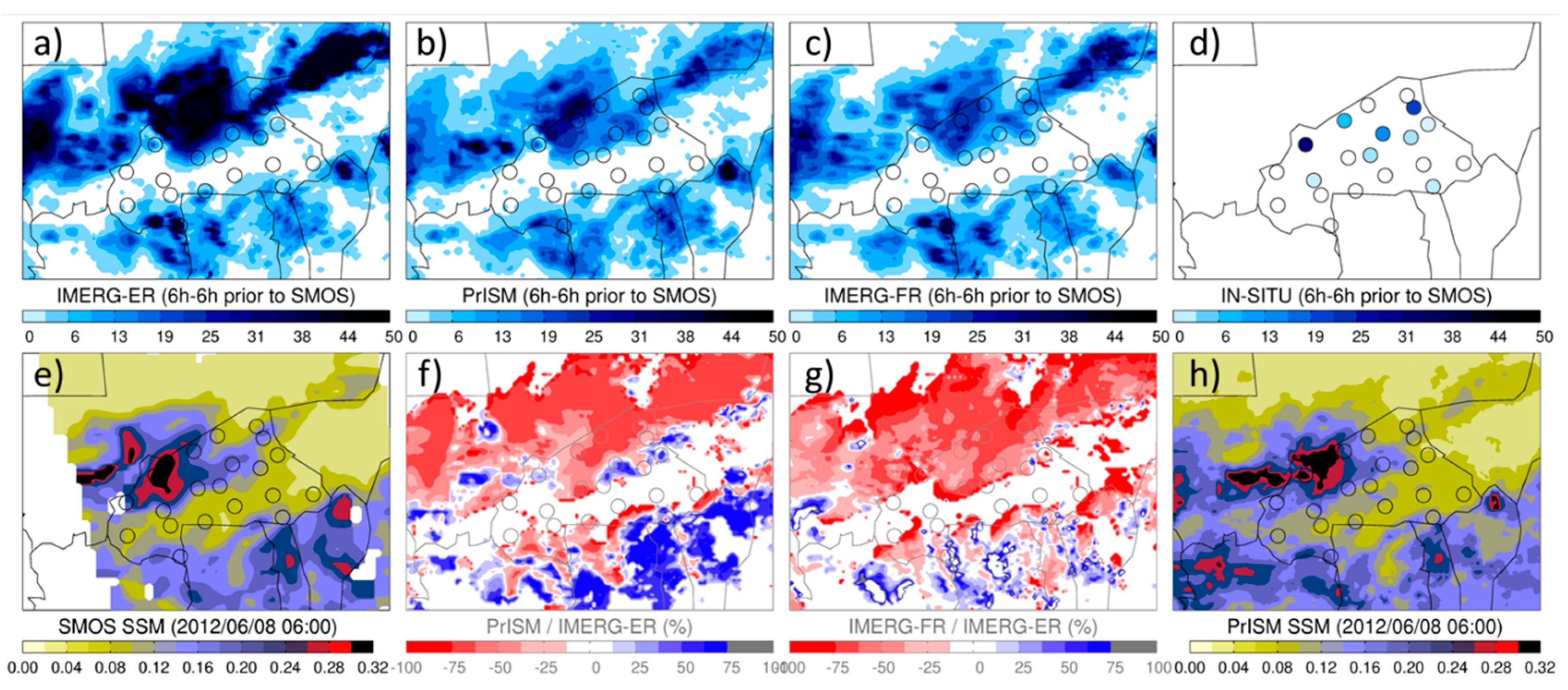
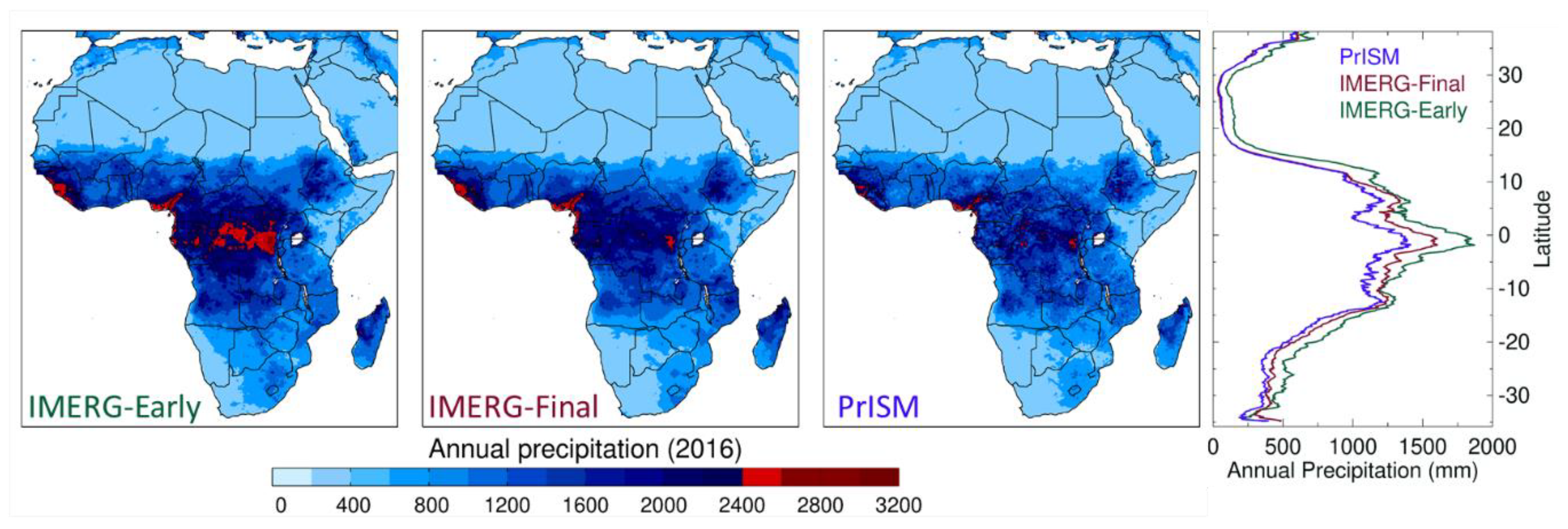
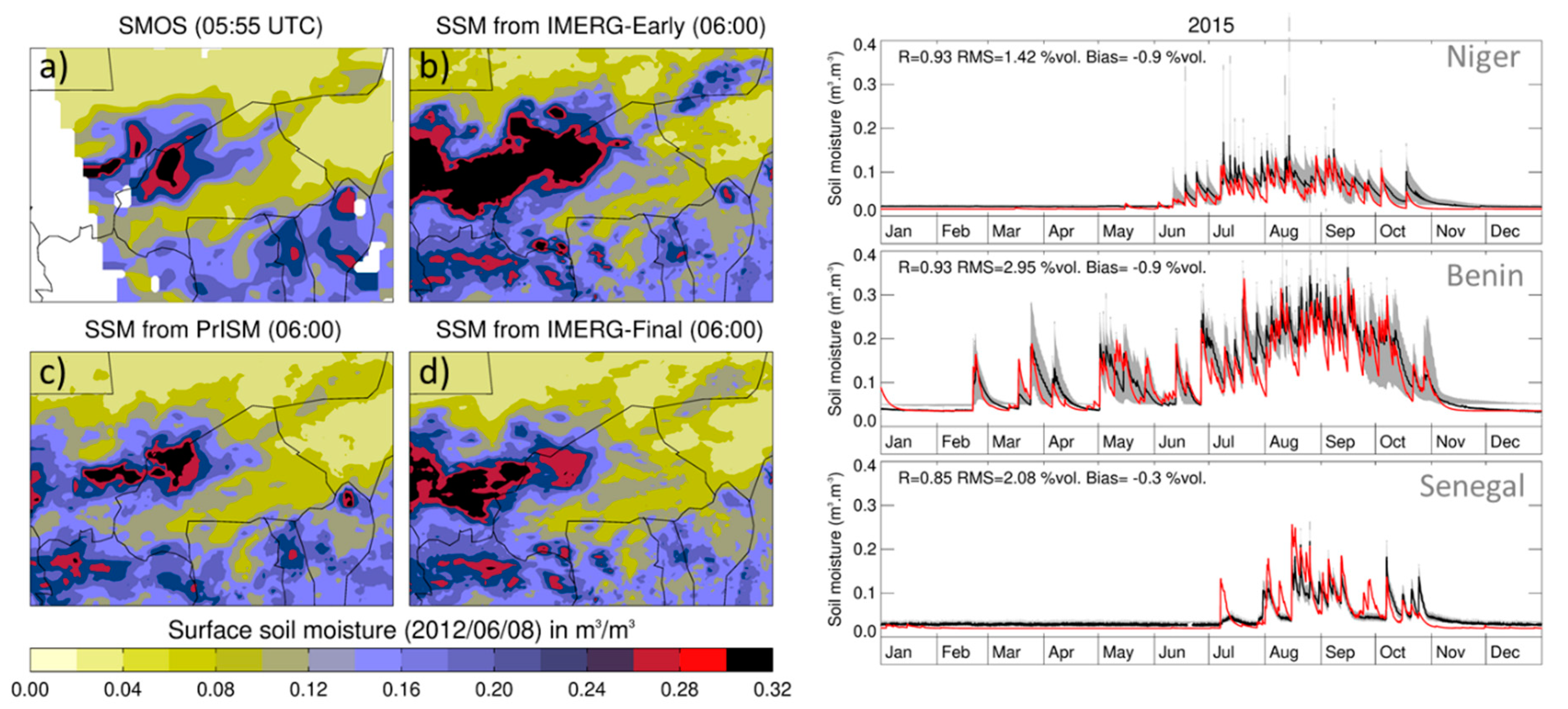
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Assessment
3.2. Spatial Modification of the Precipitation Fields
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultan, B.; Barbier, B.; Fortilus, J.; Mbaye, S.M.; Leclerc, G. Estimating the Potential Economic Value of Seasonal Forecasts in West Africa: A Long-Term Ex-Ante Assessment in Senegal. Weather. Clim. Soc. 2010, 2, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Harrison, M.; Conway, D.; Black, E.; Challinor, A.; Grimes, D.; Jones, R.; Morse, A.; Kay, G.; Todd, M. African climate change—Taking the shorter route. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Some, B.; McCollum, J.; Nelkin, E.; Klotter, D.; Berte, Y.; Diallo, B.M.; Gaye, I.; Kpabeba, G.; Ndiaye, O.; et al. Validation of TRMM and other rainfall estimates with a high-density gauge dataset for West Africa. Part I: Validation of GPCC rainfall product and pre-TRMM satellite and blended products. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrat-Capdevila, A.; Merino, M.; Valdes, J.B.; Durcik, M. Evaluation of the Performance of Three Satellite Precipitation Products over Africa. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloteau, C.; Roca, R.; Gosset, M. A Multiscale Evaluation of the Detection Capabilities of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products in West Africa. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2041–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Viarre, J.; Quantin, G.; Alcoba, M. Evaluation of several rainfall products used for hydrological applications over West Africa using two high-resolution gauge networks. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberlin, P.; Barraud, G.; Bigot, S.; Dewitte, O.; Imwangana, F.M.; Mateso, J.C.M.; Martiny, N.; Monsieurs, E.; Moron, V.; Pellarin, T.; et al. Evaluation of remotely sensed rainfall products over Central Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 2115–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeon, T.; Jackisch, D.; Diekkruger, B. Evaluating the performance of remotely sensed and reanalysed precipitation data over West Africa using HBV light. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.I.F.; Allan, R.P.; Greatrex, H.; Rojas, O.; Leo, O. Evaluation of satellite-based and model re-analysis rainfall estimates for Uganda. Meteorol. Appl. 2013, 20, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, R.; Chambon, P.; Jobard, I.; Kirstetter, P.E. Comparing Satellite and Surface Rainfall Products over West Africa at Meteorologically Relevant Scales during the AMMA Campaign Using Error Estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, I.; Chopin, F.; Berges, J.C.; Roca, R. An intercomparison of 10-day satellite precipitation products during West African monsoon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2353–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coz, C.; Van De Giesen, N. Comparison of Rainfall Products over Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 553–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Tan, J.; Xie, P. NASAGlobal Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). Algorithm Theoretical Basis Doc. Version 5.2; p. 35. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_ATBD_V5.2_0.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Crow, W.T. A novel method for quantifying value in spaceborne soil moisture retrievals. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pellarin, T.; Ali, A.; Chopin, F.; Jobard, I.; Berges, J.C. Using spaceborne surface soil moisture to constrain satellite precipitation estimates over West Africa. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W. A new method for rainfall estimation through soil moisture observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.D.; Brocca, L.; Crow, W.T.; Burgin, M.S.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. Precipitation estimation using L-band and C-band soil moisture retrievals. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 7213–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Crow, W.; Brocca, L. An assessment of the performance of global rainfall estimates without ground-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4347–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Correction of real-time satellite precipitation with multi-sensor satellite observations of land surface variables. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, S.; Pellarin, T.; Al Bitar, A.; Cappelaere, B.; Galle, S.; Grippa, M.; Gruhier, C.; Kerr, Y.; Lebel, T.; Mialon, A.; et al. SMOS soil moisture product evaluation over West-Africa from local to regional scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Pan, M.; Wanders, N.; Wood, E.F. Correction of real-time satellite precipitation with satellite soil moisture observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4275–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.G.; Wang, G.L.; Qiu, J.X.; Liao, W.L. Use of SMAP Soil Moisture and Fitting Methods in Improving GPM Estimation in Near Real Time. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellarin, T.; Román-Cascón, C.; Baron, C.; Bindlish, R.; Brocca, L.; Camberlin, P.; Fernández-Prieto, D.; Kerr, Y.H.; Massari, C.; Panthou, G.; et al. The Precipitation Inferred from Soil Moisture (PrISM) near Real-Time Rainfall Product: Evaluation and Comparison. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, S.; Grippa, M.; Peugeot, C.; Moussa, I.B.; Cappelaere, B.; Demarty, J.; Mougin, E.; Panthou, G.; Adjomayi, P.; Agbossou, E.K.; et al. AMMA-CATCH, a Critical Zone Observatory in West Africa Monitoring a Region in Transition. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, T.; Cappelaere, B.; Galle, S.; Hanan, N.; Kergoat, L.; Levis, S.; Vieux, B.; Descroix, L.; Gosset, M.; Mougin, E.; et al. AMMA-CATCH studies in the Sahelian region of West-Africa: An overview. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberlin, P. Temperature trends and variability in the Greater Horn of Africa: Interactions with precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Day 1 IMERG Final Run Release Notes. NASA Doc. 2015; p. 9. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_FinalRun_Day1_release_notes.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Martinuzzi, J.M.; Font, J.; Berger, M. Soil moisture retrieval from space: The Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Al-Yaari, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Parrens, M.; Molero, B.; Leroux, D.; Bircher, S.; Mahmoodi, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P.; et al. Overview of SMOS performance in terms of global soil moisture monitoring after six years in operation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.J.; Aires, F.; Richaume, P.; Kerr, Y.H.; Prigent, C.; Kolassa, J.; Cabot, F.; Jimenez, C.; Mahmoodi, A.; Drusch, M. Soil Moisture Retrieval Using Neural Networks: Application to SMOS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5991–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, N.J.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Richaume, P.; Rosnay, P.D.; Kerr, Y.H.; Albergel, C.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S. SMOS near-real-time soil moisture product: Processor overview and first validation results. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5201–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, N.; de Rosnay, P.; Albergel, C.; Richaume, P.; Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Kerr, Y. SMOS neural network soil moisture data assimilation in a land surface model and atmospheric impact. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Cascón, C.; Pellarin, T.; Gibon, F.; Brocca, L.; Cosme, E.; Crow, W.; Fernandez-Prieto, D.; Kerr, Y.H.; Massari, C. Correcting satellite-based precipitation products through SMOS soil moisture data assimilation in two land-surface models of different complexity: API and SURFEX. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; Godsill, S.; Andrieu, C. On sequential Monte Carlo sampling methods for Bayesian filtering. Stat. Comput. 2000, 10, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Gupta, H.; Sorooshian, S. Uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model states and parameters: Sequential data assimilation using the particle filter. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, P.J. Particle Filtering in Geophysical Systems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2009, 137, 4089–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.X.; DeChant, C.M.; Moradkhani, H. Improving Soil Moisture Profile Prediction With the Particle Filter-Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6134–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Anterrieu, E.; Rouge, B.; Boutin, J.; Picard, G.; Pellarin, T.; Escorihuela, M.-J.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Mialon, A.; et al. SMOS-HR: A high resolution l-band passive radiometer for earth science and applications. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 8392–8395. [Google Scholar]
- Tagesson, T.; Fensholt, R.; Guiro, I.; Rasmussen, M.; Huber, S.; Mbow, C.; Garcia, M.; Horion, S.; Sandholt, I.; Holm-Rasmussen, B.; et al. Ecosystem properties of semi-arid savanna grassland in West Africa and its relationship to environmental variability. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Set | Nb Stations | Period | Time-Scale | Missing Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niger | 41 | 2010–2021 | 3 h | 0% |
| Benin | 40 | 2010–2021 | 3 h | 0% |
| Burkina Faso | 20 | 2010–2015 | Daily | 13% |
| Central Africa | 55 | 2010–2015 | Daily | 48% |
| East Africa | 65 | 2010–2013 | Daily | 53% |
| Data Set | Spatial Resolution | Time-Scale | Period | Latency | Ground Calibration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMERG-Early | 0.1° | 0.5 h -> 3 h | 2000-present | ~4 h | no |
| IMERG-Final | 0.1° | 0.5 h -> 3 h | 2000-present | ~2.5 month | yes |
| PrISM | 0.1° | 3 h | 2010-present | ~24 h | no |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellarin, T.; Zoppis, A.; Román-Cascón, C.; Kerr, Y.H.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Panthou, G.; Philippon, N.; Cohard, J.-M. From SMOS Soil Moisture to 3-hour Precipitation Estimates at 0.1° Resolution in Africa. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030746
Pellarin T, Zoppis A, Román-Cascón C, Kerr YH, Rodriguez-Fernandez N, Panthou G, Philippon N, Cohard J-M. From SMOS Soil Moisture to 3-hour Precipitation Estimates at 0.1° Resolution in Africa. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030746
Chicago/Turabian StylePellarin, Thierry, Alexandre Zoppis, Carlos Román-Cascón, Yann H. Kerr, Nemesio Rodriguez-Fernandez, Geremy Panthou, Nathalie Philippon, and Jean-Martial Cohard. 2022. "From SMOS Soil Moisture to 3-hour Precipitation Estimates at 0.1° Resolution in Africa" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030746
APA StylePellarin, T., Zoppis, A., Román-Cascón, C., Kerr, Y. H., Rodriguez-Fernandez, N., Panthou, G., Philippon, N., & Cohard, J.-M. (2022). From SMOS Soil Moisture to 3-hour Precipitation Estimates at 0.1° Resolution in Africa. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030746








