Assessing Railway Landscape by AHP Process with GIS: A Study of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Comparison of Landscape Assessment Methods
2.2. Spatial Technologies for Landscape Assessment
2.3. AHP Method and This Research
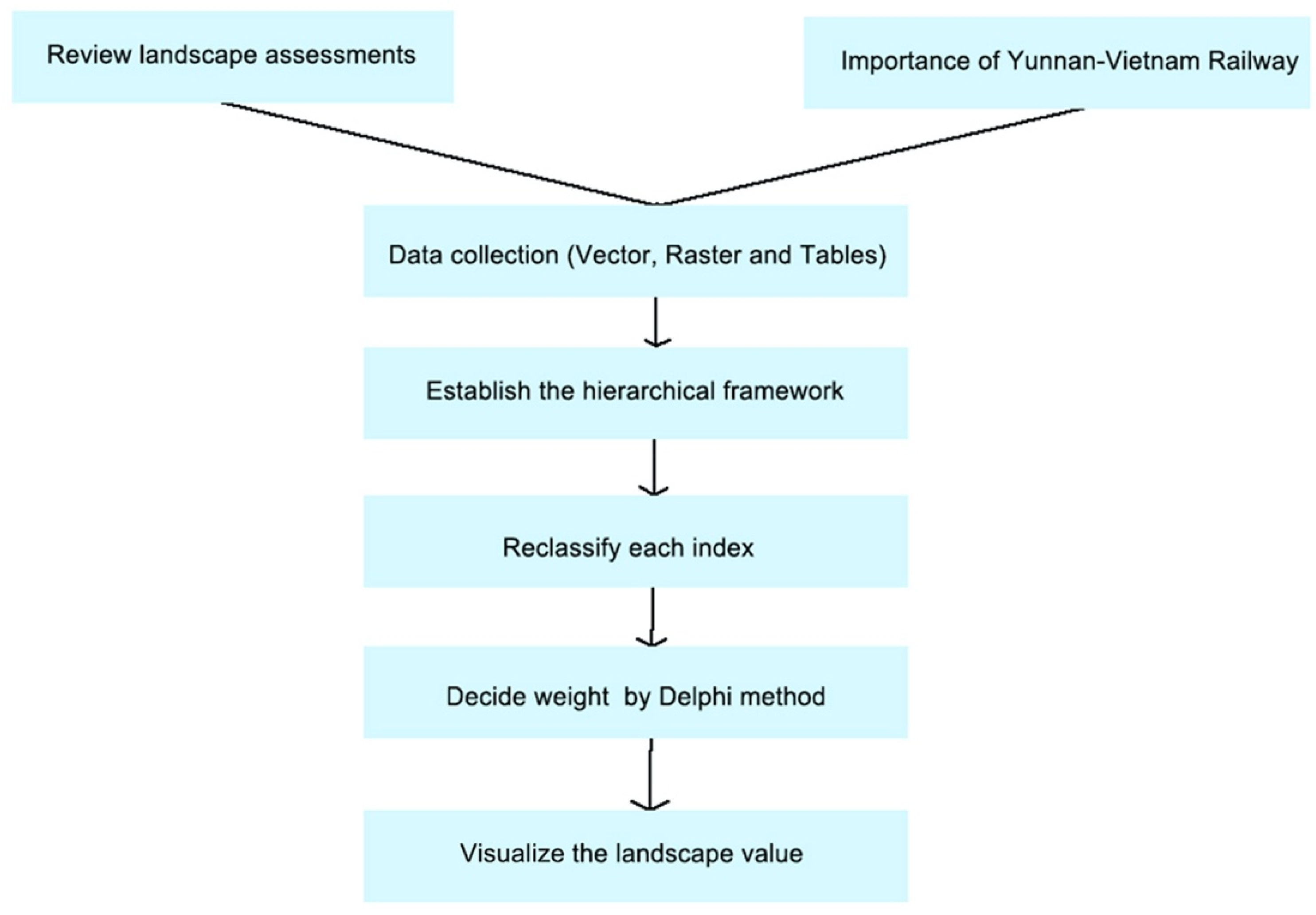
3. Materials and Methods
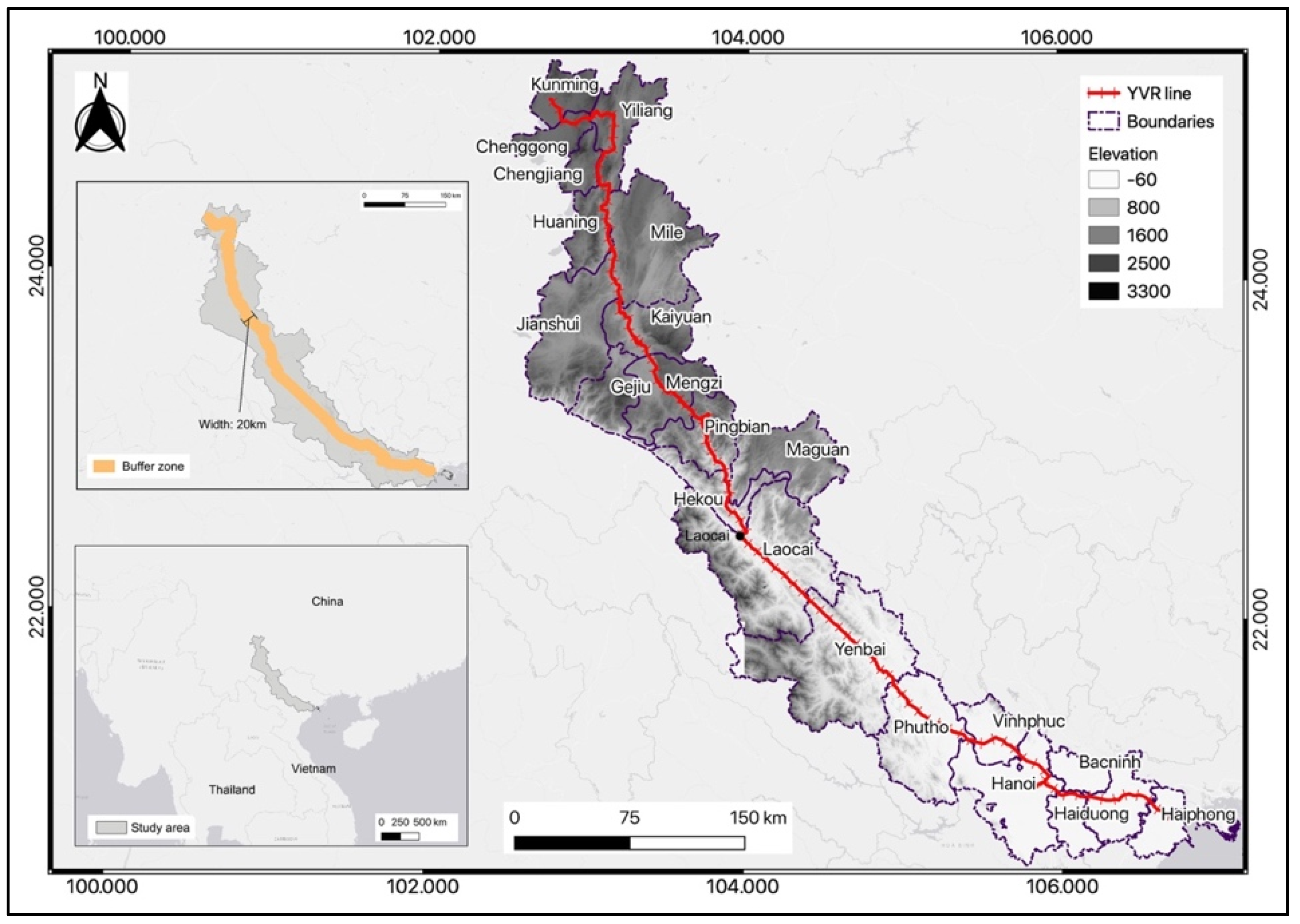
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Select Relative Indicators and Establish the Hierarchical Framework
3.3. Reclassify Each Index and Use the Delphi Method
3.4. Calculate the Landscape Value in GIS
3.5. Check the Correlation Coefficient of Landscape Value
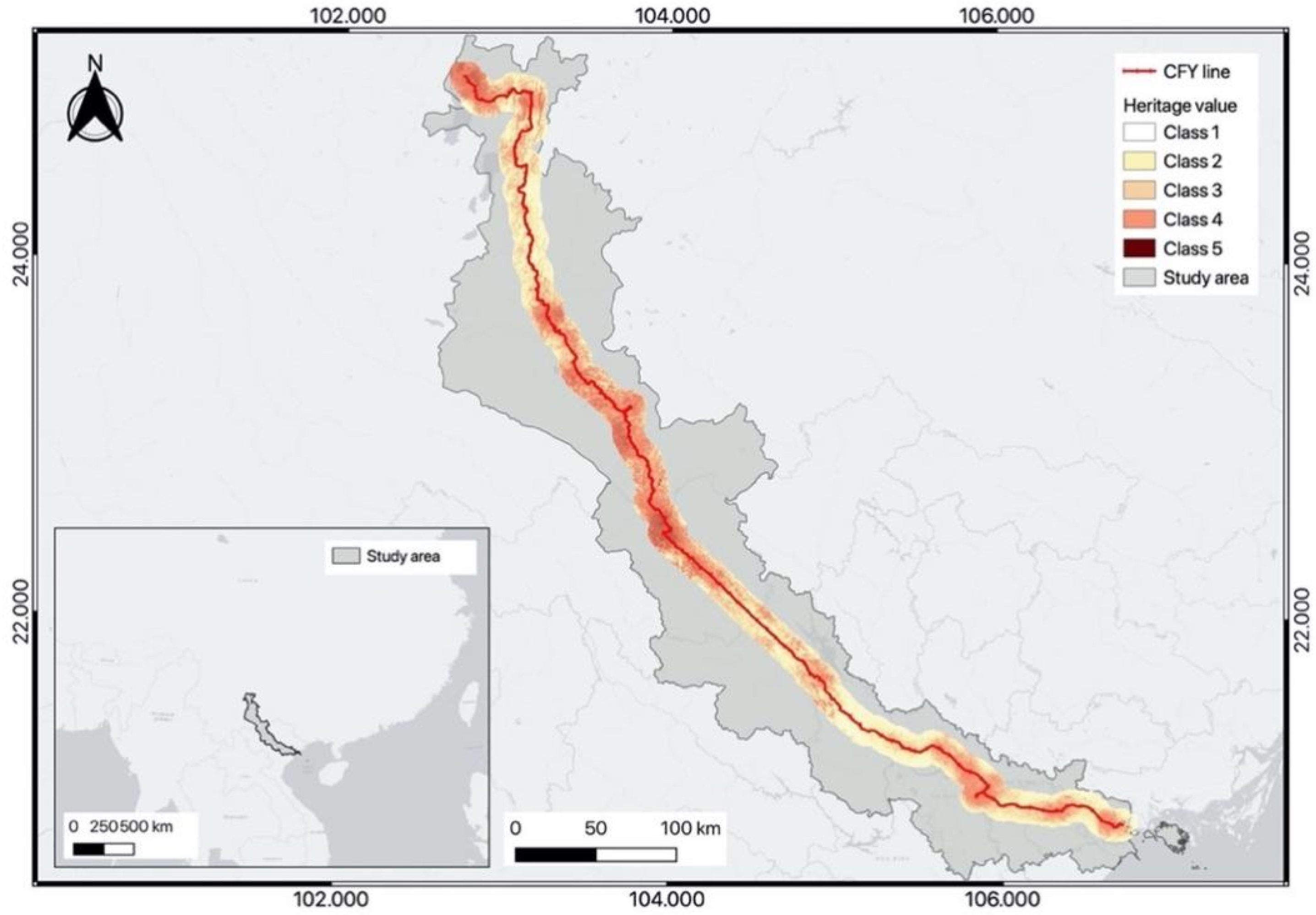
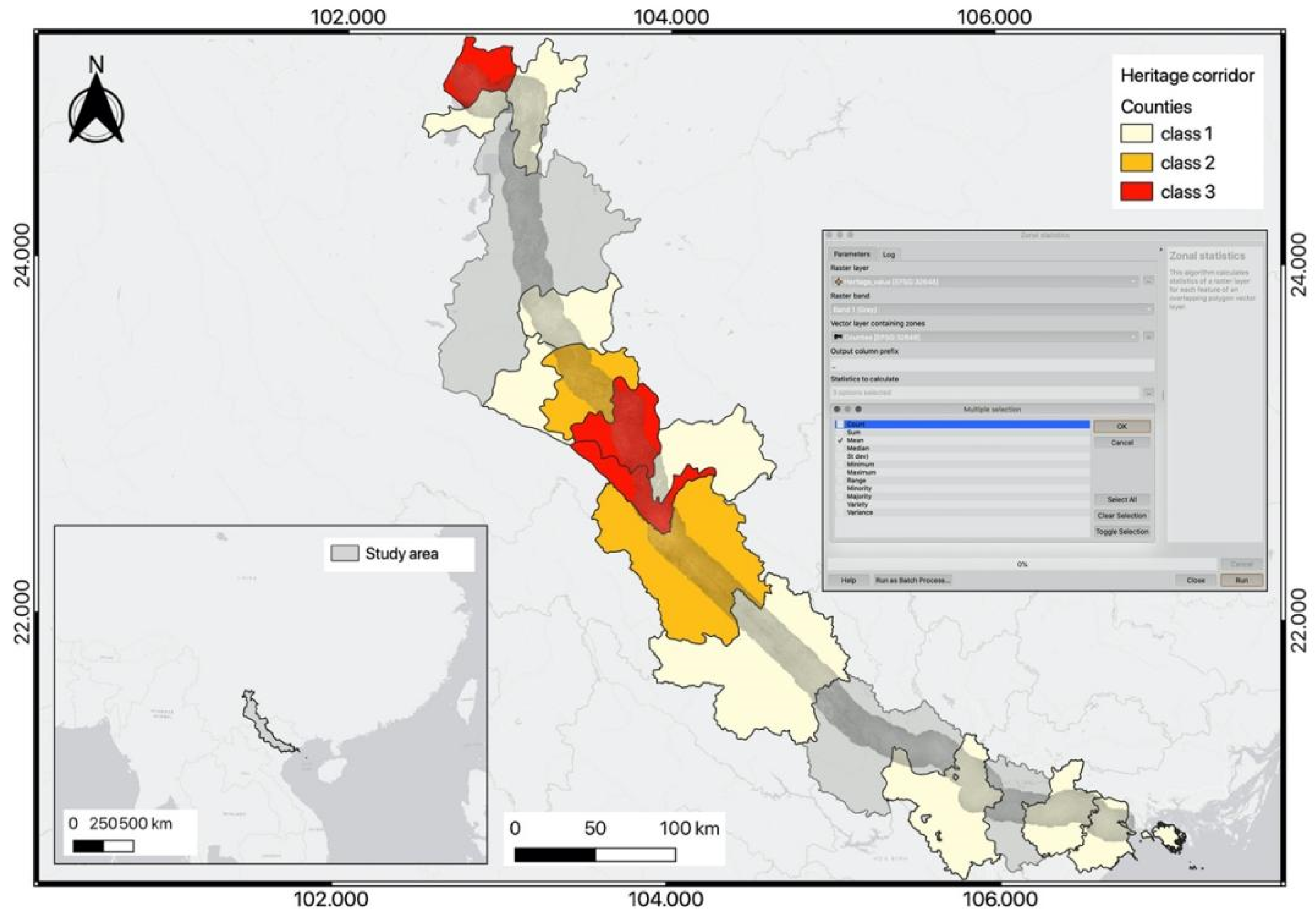
3.6. Visualize the Landscape Value in Each County
4. Results
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Council of Europe. European Landscape Convention European Treaty Series; Council of Europe: Florence, Italy, 2000; p. 176. Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/landscape (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Gulinck, H.; Múgica, M.; De Lucio, J.V.; Atauri, J.A. A framework for comparative landscape analysis and evaluation based on land cover data, with an application in the Madrid region (Spain). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 55, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, P.H. Planning at the Landscape Scale; Routledge: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.R. Conceptualising tourism transport: Inequality and externality issues. J. Transp. Geogr. 1999, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfgren, S.; Nilsson, K.L.; Johansson, C.M. Considering landscape in strategic transport planning. Transp. Res. Part. Trans. Environ. 2018, 65, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M. Modernity, anxiety, and the development of a popular railway landscape aesthetic, 1809–1879. In Trains, Literature, and Culture: Reading and Writing Rails; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bowser, R.; Croxall, B. Annihilated time, smooth surfaces, and rough edges in Steampunk and Schivelbusch’s the rail-way journey: A departure point. In Proceedings of the Interdisciplinary Nineteenth-Century Studies Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–19 April 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Blancheton, B.; Marchi, J.J. The three systems of rail tourism: French case. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2013, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prideaux, B. Tracks to tourism: Queensland Rail joins the tourist industry. Int. J. Tour. Res. 1999, 1, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, J.A. Sustainability of heritage railways: An economic approach. Jap. Rail and Transp. Res. 2002, 32, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Orbaşli, A.; Woodward, S. A railway ‘route’ as a linear heritage attraction: The Hijaz Railway in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Herit. Tour. 2008, 3, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.C. Mobility, tropicality and landscape: The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, 1881–1939. J. Hist. Geogr. 2014, 44, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xi, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, Q. Evaluation of tourism dynamic landscape along Qinghai-Tibet railway based on the visual corridor. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 3320–3330. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R. Assessing values in conservation planning: Methodological issues and choices. In Assessing the Values of Cultural Heritage; Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Antonson, H. Bridging the gap between research and planning practice concerning landscape in Swedish infrastructural planning. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, G.R.; Smidt, R.K. Assessing the validity and reliability of descriptor variables used in scenic highway analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 66, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Federal Highway Administration (US FHWA). Visual Impact Assessment for Highway Projects. 1981. Available online: https://www.placer.ca.gov/DocumentCenter/View/8259/FHWA-1981-Visual-Impact-Assessment-PDF (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Smardon, R.C. Historical evolution of visual resource management within three federal agencies. J. Environ. Manag. 1986, 22, 301–317. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, B.; Ortega, E.; Otero, I.; Arce, R.M. Landscape character assessment with GIS using map-based indicators and photographs in the relationship between landscape and roads. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, B.; He, P. Aesthetics theory and method of landscape resource assessment. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 9, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, I.O.; Martínez, M.A.C.; Canalejoa, A.E.; Mariño, P.E. Landscape evaluation: Comparison of evaluation methods in a region of Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Elton, M.J.; Thompson, S. The role of GIS in landscape assessment: Using land-use-based criteria for an area of the Chiltern Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Land Use Policy 1999, 16, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.F. The contribution of a GIS-based landscape assessment model to a scientifically rigorous approach to visual impact assessment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, S.; Sakieh, Y.; Shabani, A.A.; Danehkar, A.; Nazarisamani, A.A. Landscape change assessment of reservation areas using remote sensing and landscape metrics (case study: Jajroud reservation, Iran). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 18, 1701–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.A. Geographic techniques and recent applications of remote sensing to landscape-water quality studies. Water Air and Soil Pollut. 2002, 138, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magidi, J.; Ahmed, F. Assessing urban sprawl using remote sensing and landscape metrics: A case study of City of Tshwane, South Africa (1984–2015). Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, P.K. Reconstruction of contested landscape: Detecting land cover transformation hosting cultural heritage sites from Central India using remote sensing. Land Use Policy 2013, 34, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Research on Visual Quality of the Natural Landscape Along Chinese Eastern Railway. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Evaluation of the Current Landscape Along the Chengdu-Jiuzhaigou Railway. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, Sichuan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. What is the analytic hierarchy process? In Mathematical Models for Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Linstone, H.A.; Turoff, M. The Delphi Method; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Turskis, Z.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Kutut, V. A model based on ARAS-G and AHP methods for multiple criteria prioritizing of heritage value. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2013, 12, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdjevic, Z.; Lakicevic, M.; Srdjevic, B. Approach of decision making based on the analytic hierarchy process for urban landscape management. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, G.Q.; Tang, L.; Wang, K.L.; Huang, D.Y. Combining AHP with GIS in synthetic evaluation of eco-environment quality—A case study of Hunan Province, China. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutut, V.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Lazauskas, M. Assessment of priority alternatives for preservation of historic buildings using model based on ARAS and AHP methods. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2014, 14, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention. 2012. Available online: http://whc.unesco.org/archive/opguide12-en.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, H. Suitability Analysis of Heritage Corridor Based on GIS and RS. Planners. 2015. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GHSI2015S1066.htm (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Girard, L.F.; De Toro, P. Integrated spatial assessment: A multicriteria approach to sustainable development of cultural and environmental heritage in San Marco dei Cavoti, Italy. Central Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 15, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassatella, C.; Peano, A. Landscape Indicators: Assessing and Monitoring Landscape Quality; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzari, M. Spatial modelling of potential landscape quality. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Mander, Ü.; Marja, R. Trends in the use of landscape spatial metrics as landscape indicators: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TICCIH. The Nizhny Tagil Charter for the Industrial Heritage. In the TICCIH XII International Congress. Moscow, Russia. 17 July 2003, pp. 169–175. Available online: https://www.icomos.org/18thapril/2006/nizhny-tagil-charter-e.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Jiang, P.; Shao, L.; Baas, C. Interpretation of Value Advantage and Sustainable Tourism Development for Railway Heritage in China Based on the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowińska-Świerkosz, B.; Michalik-Śnieżek, M. The Methodology of Landscape Quality (LQ) Indicators Analysis Based on Remote Sensing Data: Polish National Parks Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q. Historical Reconstruction and Complementary Development: A Preliminary Study on the Heritage Protection and Tourism Development of the Yunnan Section of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway Heritage Corridor. Arch. Cult. 2011, 8, 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Brunsden, D.; Thornes, J.B. Landscape sensitivity and change. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 1979, 4, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tudor, C. An Approach to Landscape Sensitivity Assessment—To Inform Spatial Planning and Land Management. Natural England. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/natural-england (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Tveit, M.; Ode, Å.; Fry, G. Key concepts in a framework for analysing visual landscape character. Landsc. Res. 2006, 31, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, I.R.; Aničić, B.; Krklec, K.; Andlar, G.; Hrdalo, I.; Pereković, P. Cultural landscape evaluation and possibilities for future development–a case study of the island of Krk (Croatia). Acta Geogr. Slov. 2011, 51, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanapala, W.A. Tourists perception and satisfaction: Implications for destination management. Am. J. Market. Res. 2015, 1, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making—The analytic hierarchy and network processes (AHP/ANP). J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2004, 13, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, H. AHP and Fuzzy Comprehensive Method in Railway Landscape Evaluation. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain, B.C.; Meitner, M.J. A route-based visibility analysis for landscape management. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2013, 111, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.C.; Cao, D. On consistency and ranking of alternatives in fuzzy AHP. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 124, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Comparison of Values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient on the Same Sets of Data. Master Thesis, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznan, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G. Understanding statistics by using spreadsheets to generate and analyze samples. Sportscience 2007, 11, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, L.; Casado-Arzuaga, I.; Onaindia, M. Mapping recreation supply and demand using an ecological and a social evaluation approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 13, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, X.; Cao, Y.; Xie, J.; Gong, J. High-resolution urban land-cover mapping and landscape analysis of the 42 major cities in China using ZY-3 satellite images. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenweg, K.; Williams, K.; Cerveny, L.; Styers, D. Is recreation a landscape value? Exploring underlying values in landscape values mapping. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 185, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Content | Format | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIVA-GIS | Administrative divisions; rivers; roads; railroads; ethnic groups | Vector | |
| World Clim | Monthly temperature | Raster | 1000 m |
| CIESIN 1 | Economic and population data | Excel table | |
| Earth Explorer | Sentinel-2 satellite images; DEM | Raster | 500 m |
| Global Forest Watch | Biodiversity significance | Raster | 100 m |
| Earth data | MODIS Land Cover-MCD12Q1 (2001; 2018) | Raster | 500 m |
| Online Map (Baidu map and open street map) | Scenic spots (parks, mountains, historical monuments, scenic resorts) | Vector | |
| Social media (Flickr) | Popular photo-shooting sites | Vector | |
| Archive of Mulhouse | Historical photo sites by YVR | Vector |
| Indicator | Index | ID | References | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual quality (B1) | Scenic spots | C1 | [46] | Baidu and open street map |
| Visibility | C2 | Archive of Mulhouse | ||
| Stream density | C3 | DIVA-GIS | ||
| Ecology (B2) | NDVI 2 | C4 | [47] | Earth Explorer |
| Naturalness | C5 | Earth Explorer | ||
| Biodiversity | C6 | Global Forest Watch | ||
| Technology (B3) | Historical richness | C7 | [48] | Archive |
| Engineering difficulty | C8 | Earth Explorer | ||
| Climate suitability | C9 | World Clim | ||
| Social culture (B4) | Population density | C10 | [49] | CIESIN |
| Cultural diversity | C11 | DIVA-GIS | ||
| Economy growth | C12 | CIESIN | ||
| Tourism (B5) | Touristic services | C13 | [50] | Baidu and open street map |
| Accessibility | C14 | DIVA-GIS | ||
| Popularity | C15 | Flickr |
| Index | Class (Score) |
|---|---|
| C1 | 5, Distance < 50 4, 50 m < Distance < 150 3, 150 m < Distance < 1000 2, 1000 m < Distance < 5000 1, Distance > 5000 (m) [52] |
| C2 | 5, Distance < 50 4, 50 m < Distance < 150 3, 150 m < Distance < 1000 2, 1000 m < Distance < 5000 1, Distance > 5000 (m) [53] |
| C3 | 1, Density < 0.079 2, 0.079 < Density < 0.098 3, 0.098 < Density < 0.117 4, 0.117 < Density < 0.145 5, Density > 0.145 (/km2) |
| C4 | 1, NDVI < 0.155 2, 0.155 < NDVI < 0.244 3, 0.244 < NDVI < 0.338 4, 0.338 < NDVI < 0.481 5, NDVI > 0.481 |
| C5 | 1, Urban area; 2, Bare area 3, Grassland; 4, Shrubland; 5, Forest |
| C6 | 1, value: 0–1; 2, value: 1–4 3, value: 4–5; 4, value: 5–7 5, value > 7 |
| C7 | 1, Density < 0.307 2, 0.307 < Density < 1.539 3, 1.539 < Density < 5.233 4, 5.233 < Density < 19.395 5, Density > 19.395 (/km2) |
| C8 | 1, slope < 4.696 2, 4.696 < slope < 10.531 3, 10.531 < slope < 17.442 4, 17.442 < slope < 25.855 5, slope > 25.855 (degree) |
| C9 | 1, Temp < 20.091 2, 20.091 < Temp < 21.590 3, 21.590 < Temp < 25.782 4, 25.782 < Temp < 27.984 5, Temp > 27.984 (°C) |
| C10 | 1, Density < 20 2, 20 < Density < 150 3, 150 < Density < 500 4, 500 < Density < 1000 5, Density > 1000 (person/km2) |
| C11 | 1, Density < 0.082 2, 0.082 < Density < 0.306 3, 0.306 < Density < 0.621 4, 0.621 < Density < 1.068 5, Density > 1.068 (/km2) |
| C12 | 1, Rate < 12.96% 2, 12.96% < Rate < 13.11% 3, 13.11% < Rate < 13.46% 4, 13.46% < Rate < 13.89% 5, Rate > 13.89% |
| C13 | 1, Density < 0.290 2, 0.290 < Density < 0.871 3, 0.871 < Density < 3.192 4, 3.192 < Density < 16.831 5, Density > 0.621 (/km2) |
| C14 | 1, Density < 0.048 2, 0.048 < Density < 0.071 3, 0.071 < Density < 0.092 4, 0.092 < Density < 0.118 5, Density > 0.118 (/km2) |
| C15 | 1, Density < 2.361 2, 2.361 < Density < 2.721 3, 2.721 < Density < 5.443 4, 5.443 < Density < 21.775 5, Density > 21.775 (/km2) |
| Indicator | Comparison of Two Indexes | Result (Experts) | Weight (The First Index) | Consistency 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | Scenic spots VS Visibility | 1/1 | 42.86% | 0.0000 |
| Visibility: VS Stream density | 3/1 | 42.86% | ||
| Stream density VS Scenic spots | 1/3 | 14.29% | ||
| B2 | NDVI VS Naturalness | 1/3 | 10.0% | 0.0000 |
| Naturalness VS Biodiversity | 1/2 | 30.0% | ||
| Biodiversity VS NDVI | 6/1 | 60.0% | ||
| B3 | Historical richness VS Engineering difficulty | 1/3 | 26.50% | 0.0372 |
| Engineering difficulty VS Climate suitability | 5/1 | 63.33% | ||
| Climate suitability VS Historical richness | 1/3 | 10.62% | ||
| B4 | Population density VS Cultural diversity | 1/4 | 12.26% | 0.0176 |
| Cultural diversity VS Economy growth | 2/1 | 55.71% | ||
| Economy growth VS Population density | 3/1 | 32.02% | ||
| B5 | Touristic services VS Accessibility | 1/3 | 27.21% | 0.0713 |
| Accessibility VS Popularity | 4/1 | 11.99% | ||
| Popularity VS Touristic services | 1/3 | 60.80% |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | −0.19 | |||||||||||||
| C3 | −0.03 | −0.14 | ||||||||||||
| C4 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| C5 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.12 | ||||||||||
| C6 | −0.13 | −0.10 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.15 | |||||||||
| C7 | 0.12 | 0.07 | −0.24 | −0.26 | 0.13 | 0.20 | ||||||||
| C8 | −0.02 | 0.16 | −0.13 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.52 | |||||||
| C9 | −0.05 | −0.12 | 0.52 | 0.22 | −0.12 | −0.05 | −0.73 | −0.38 | ||||||
| C10 | 0.22 | −0.16 | 0.24 | −0.32 | −0.17 | −0.44 | −0.37 | −0.68 | 0.37 | |||||
| C11 | 0.17 | −0.15 | 0.46 | −0.19 | −0.06 | −0.22 | −0.18 | −0.44 | 0.40 | 0.72 | ||||
| C12 | 0.06 | 0.08 | −0.51 | −0.36 | 0.05 | −0.29 | 0.65 | 0.21 | −0.83 | −0.12 | −0.14 | |||
| C13 | 0.34 | −0.14 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.04 | −0.32 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.18 | ||
| C14 | 0.17 | −0.10 | 0.31 | −0.03 | −0.12 | 0.03 | −0.25 | −0.38 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.48 | −0.35 | 0.31 | |
| C15 | 0.42 | −0.02 | 0.21 | −0.25 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.10 | −0.18 | 0.05 | 0.47 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 0.62 | −0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, K.; Fontana, G.L.; Piovan, S.E. Assessing Railway Landscape by AHP Process with GIS: A Study of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030603
Sang K, Fontana GL, Piovan SE. Assessing Railway Landscape by AHP Process with GIS: A Study of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030603
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Kun, Giovanni Luigi Fontana, and Silvia Elena Piovan. 2022. "Assessing Railway Landscape by AHP Process with GIS: A Study of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030603
APA StyleSang, K., Fontana, G. L., & Piovan, S. E. (2022). Assessing Railway Landscape by AHP Process with GIS: A Study of the Yunnan-Vietnam Railway. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030603








