Data-Driven Seismic Impedance Inversion Based on Multi-Scale Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
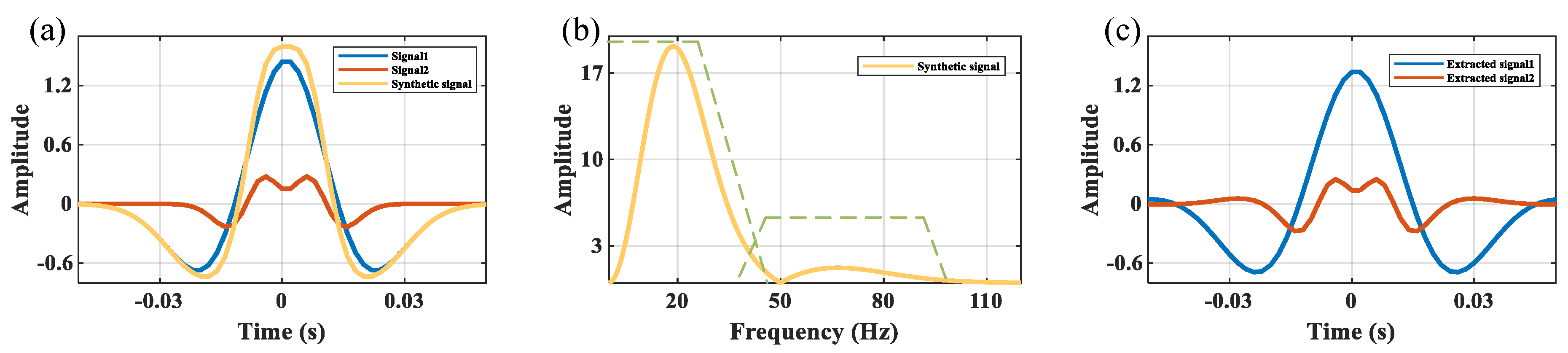
2.1. Forward Model
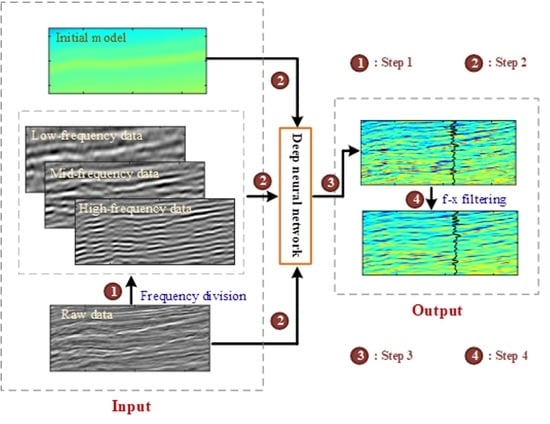
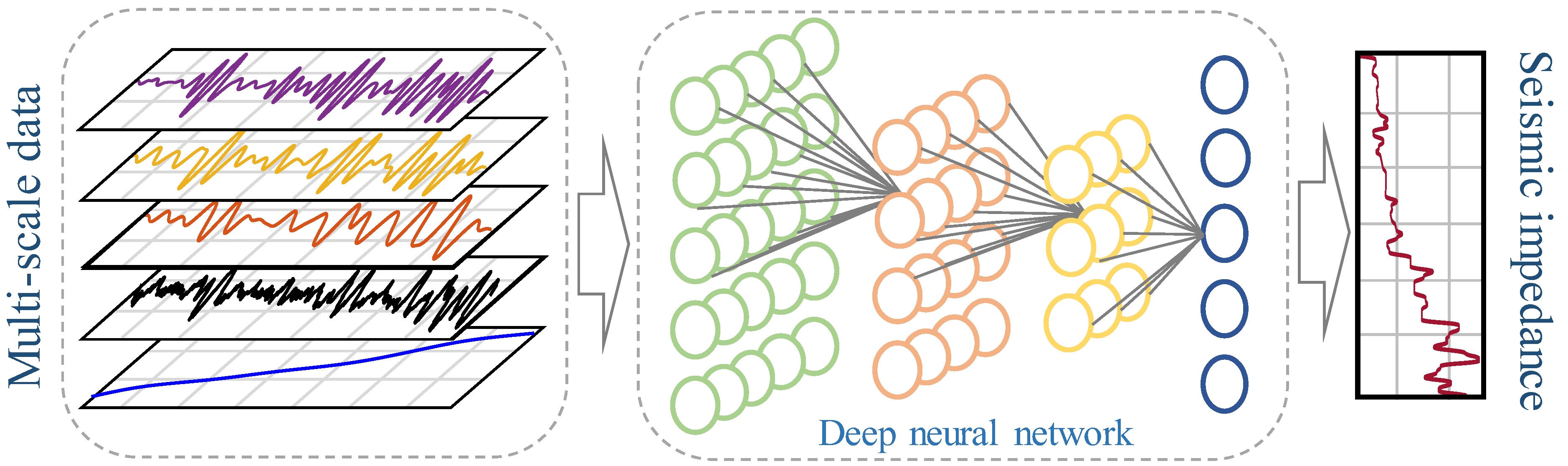
2.2. Inversion Framework of Multi-Scale Strategy
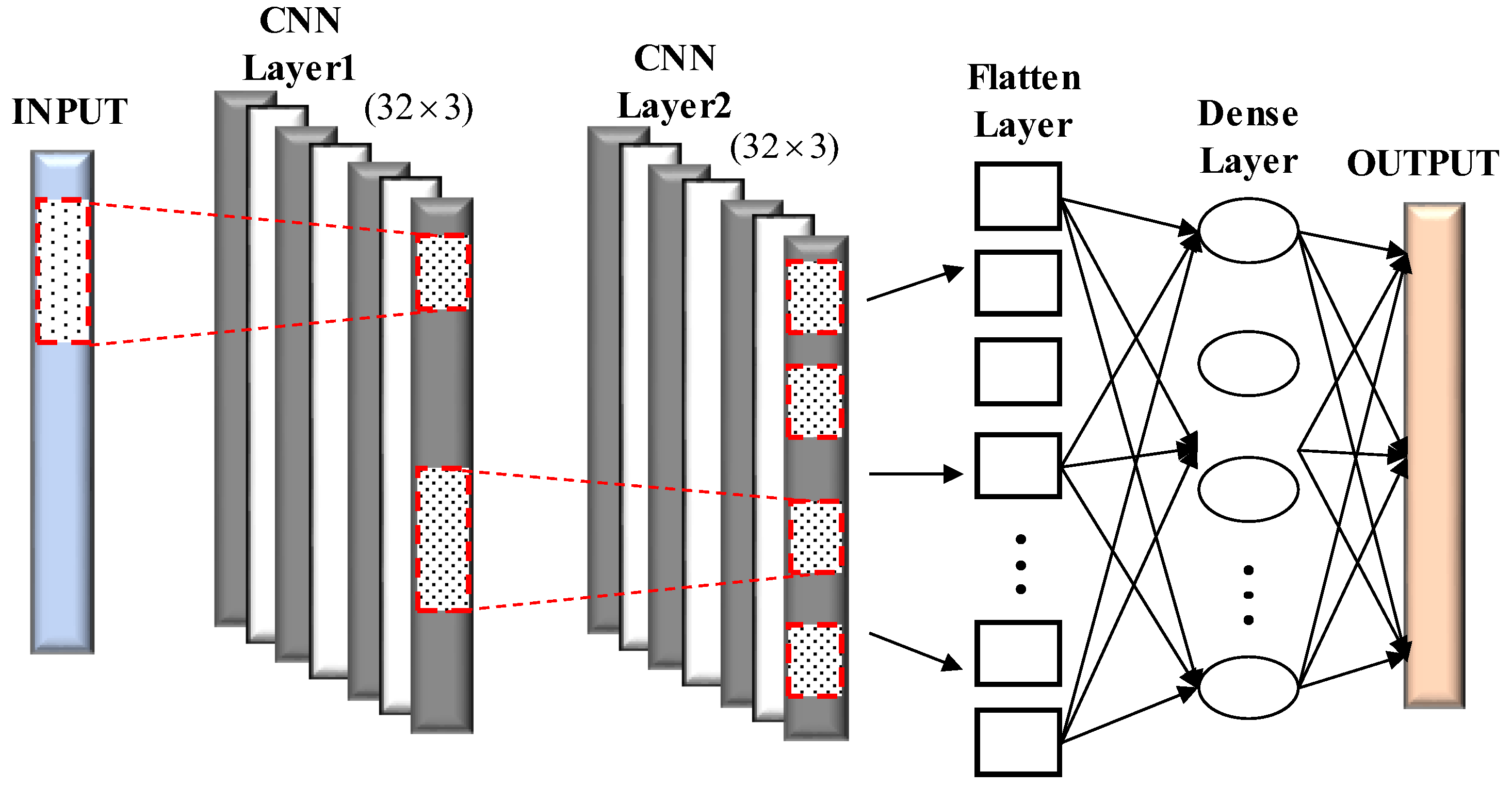
2.3. Convolutional Neural Network
2.4. Transfer Learning Strategy
2.5. f-x Filtering Technique
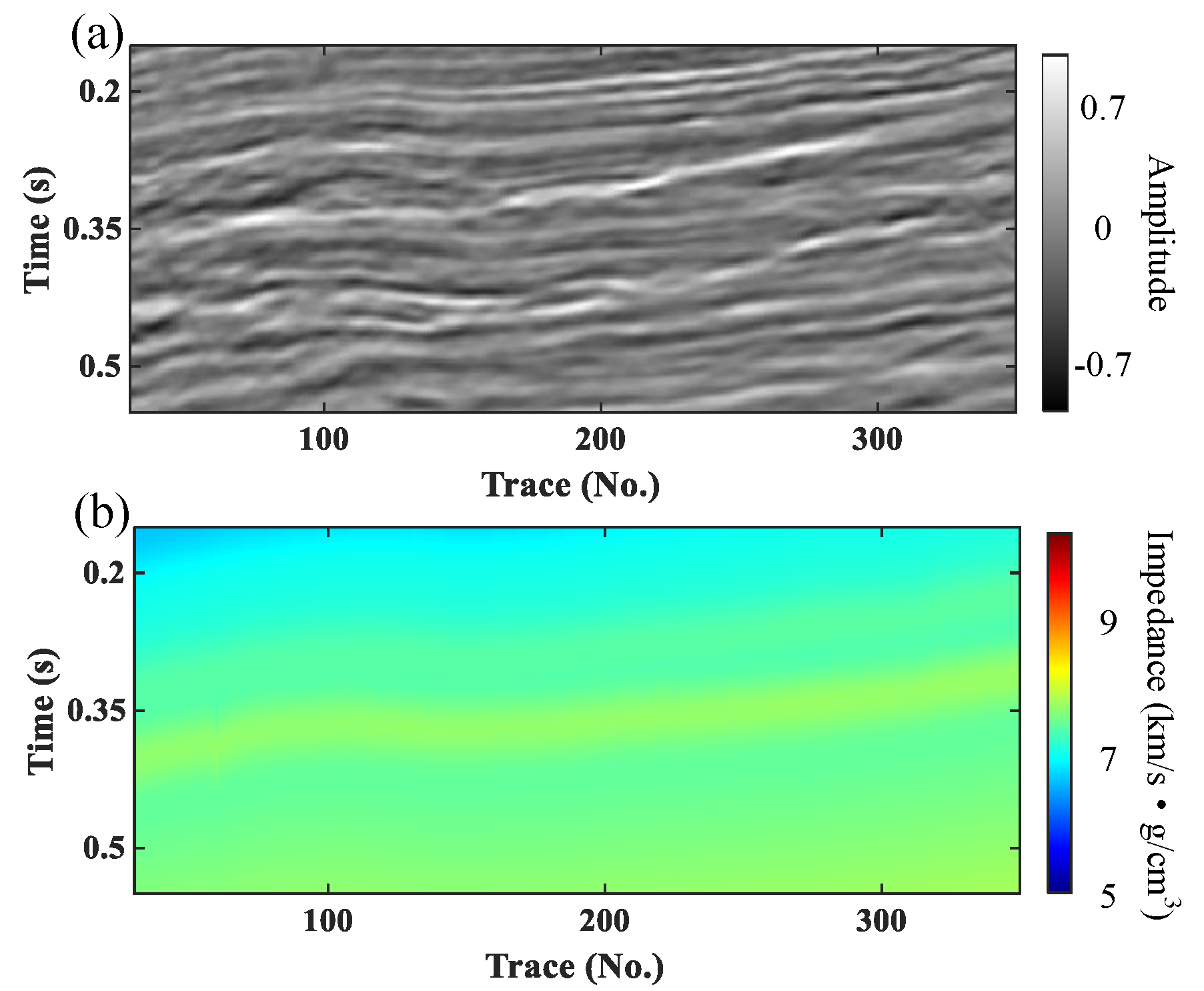
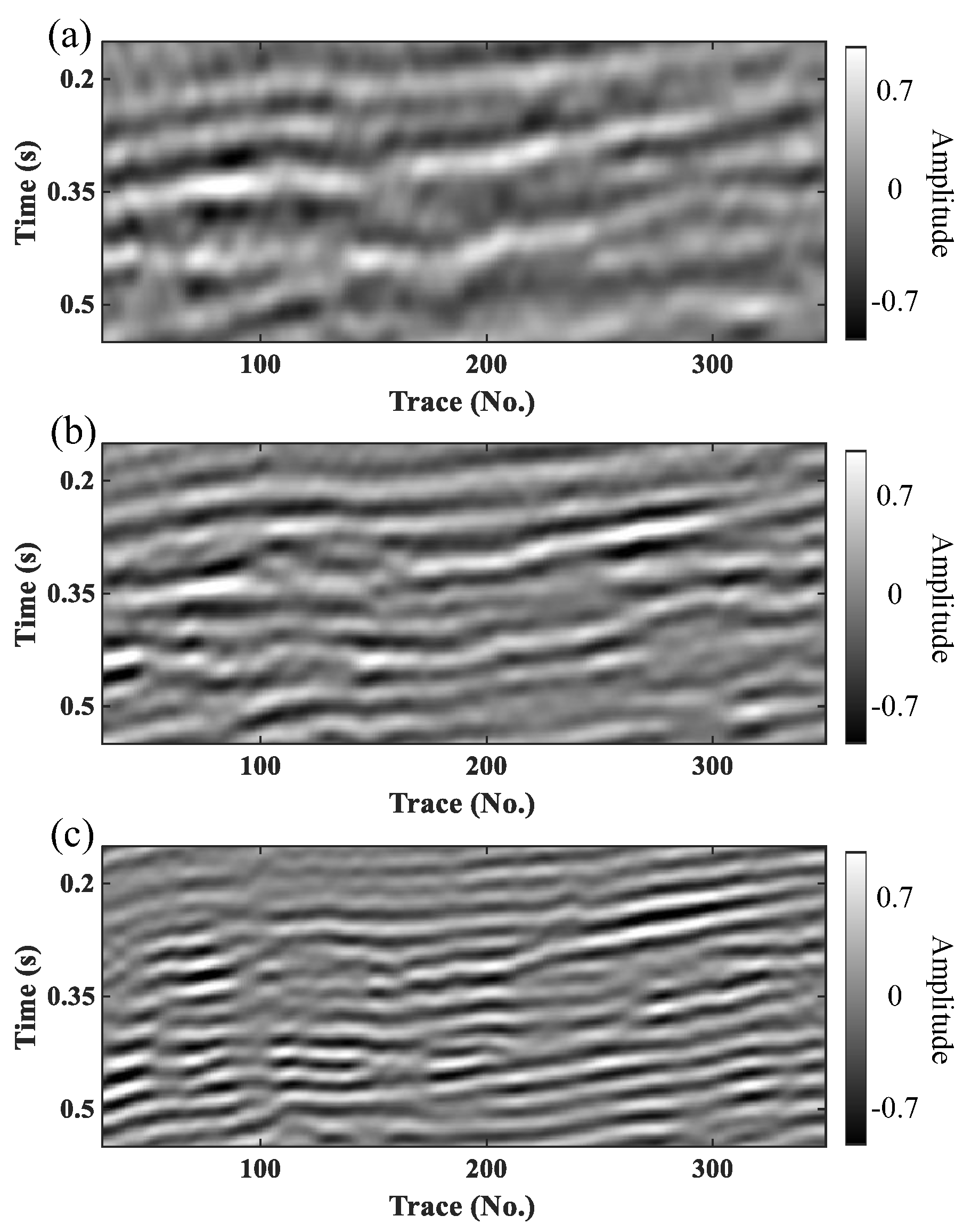
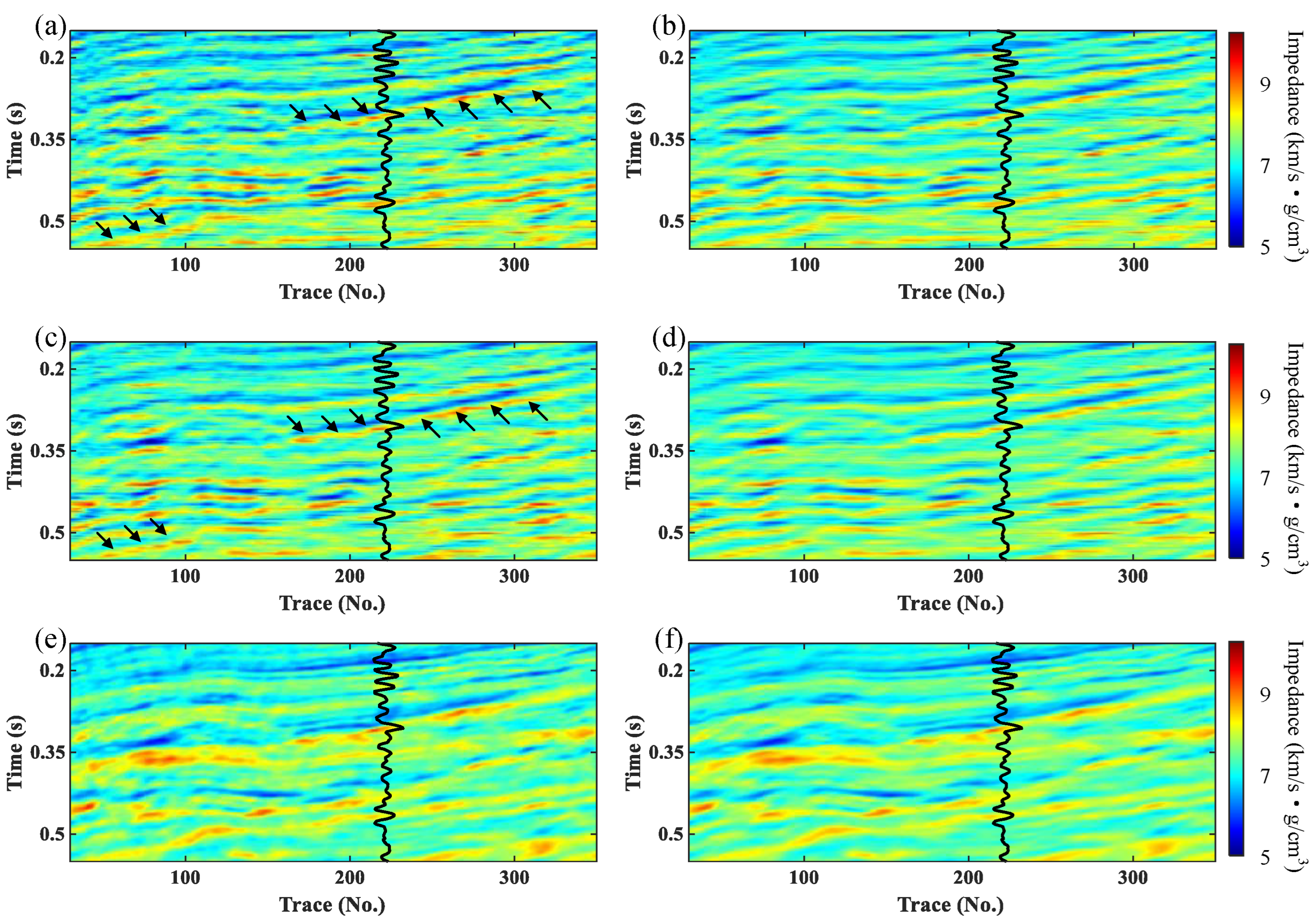
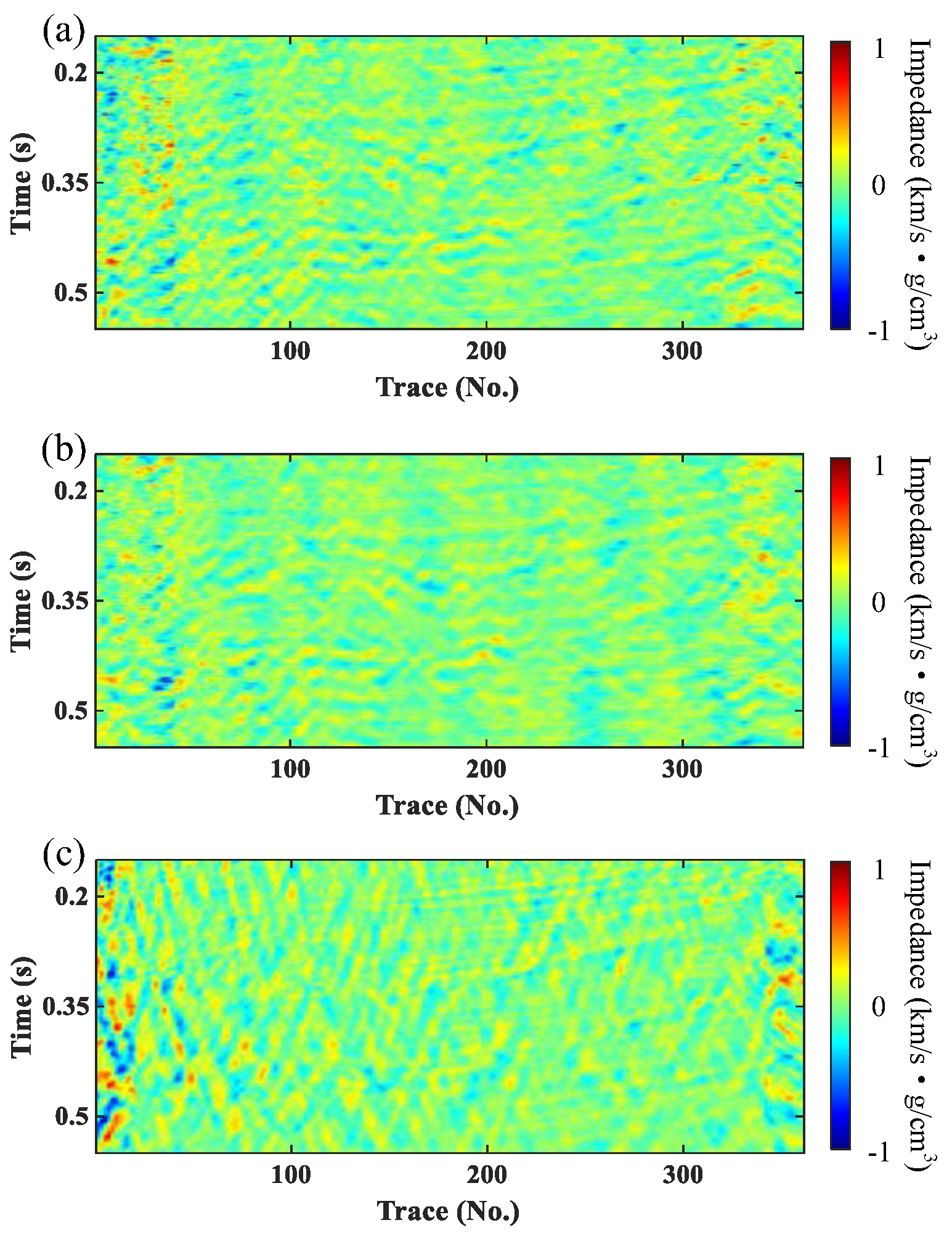
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Data Test
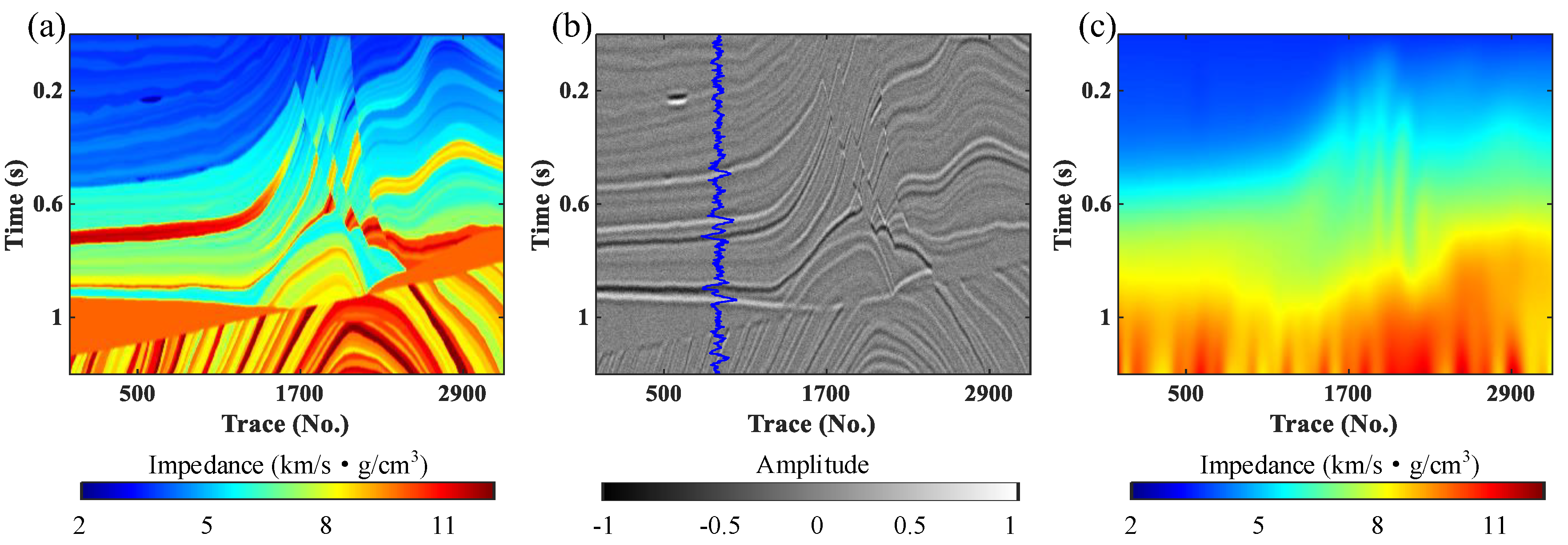
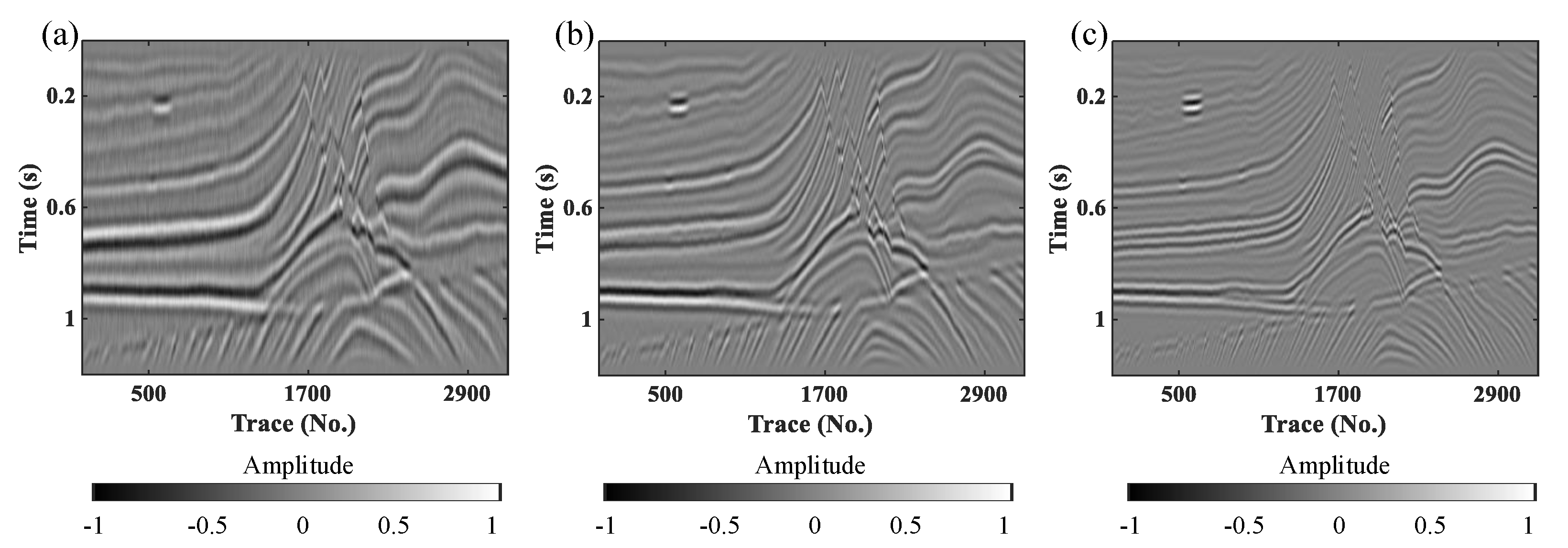
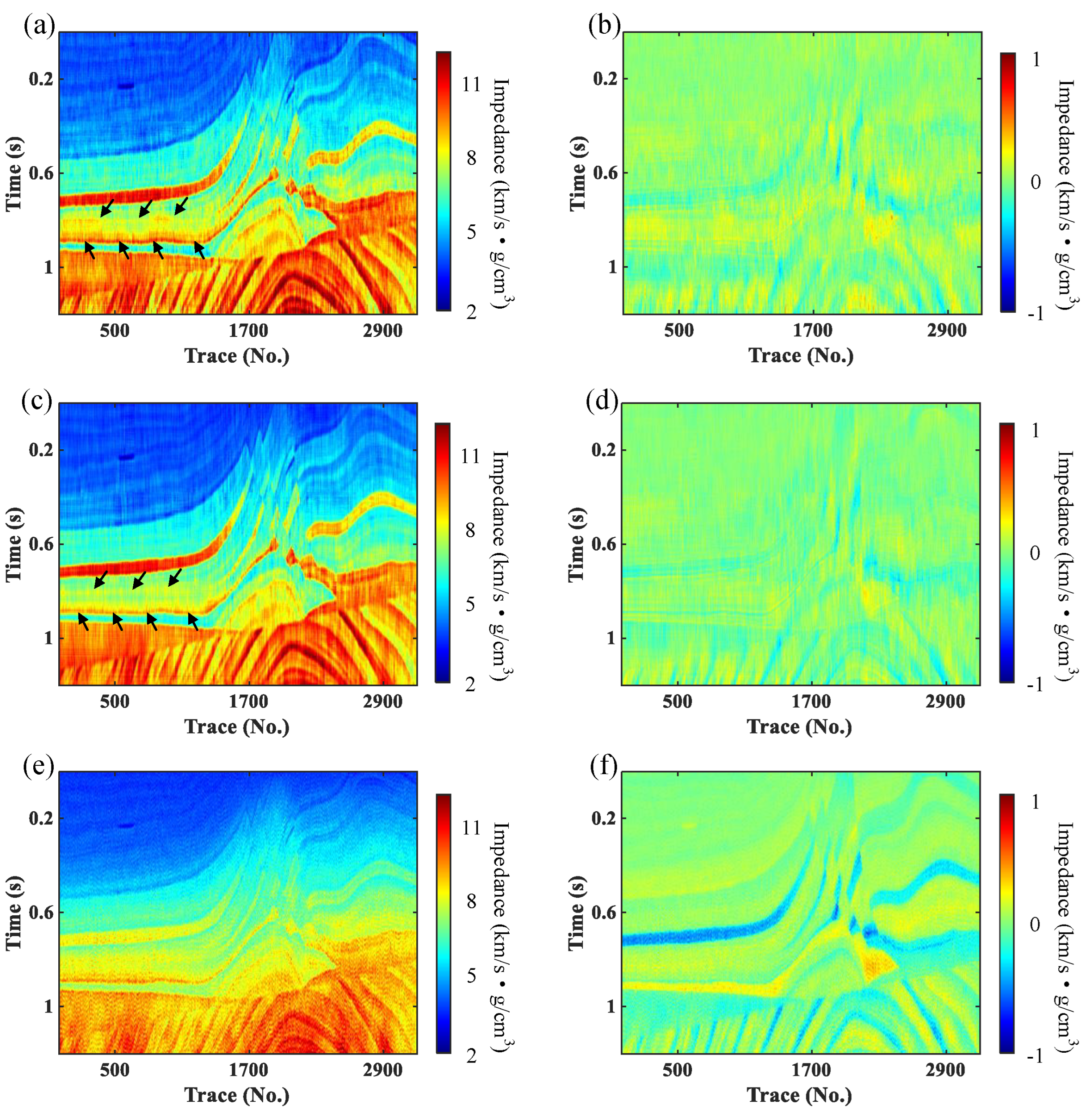
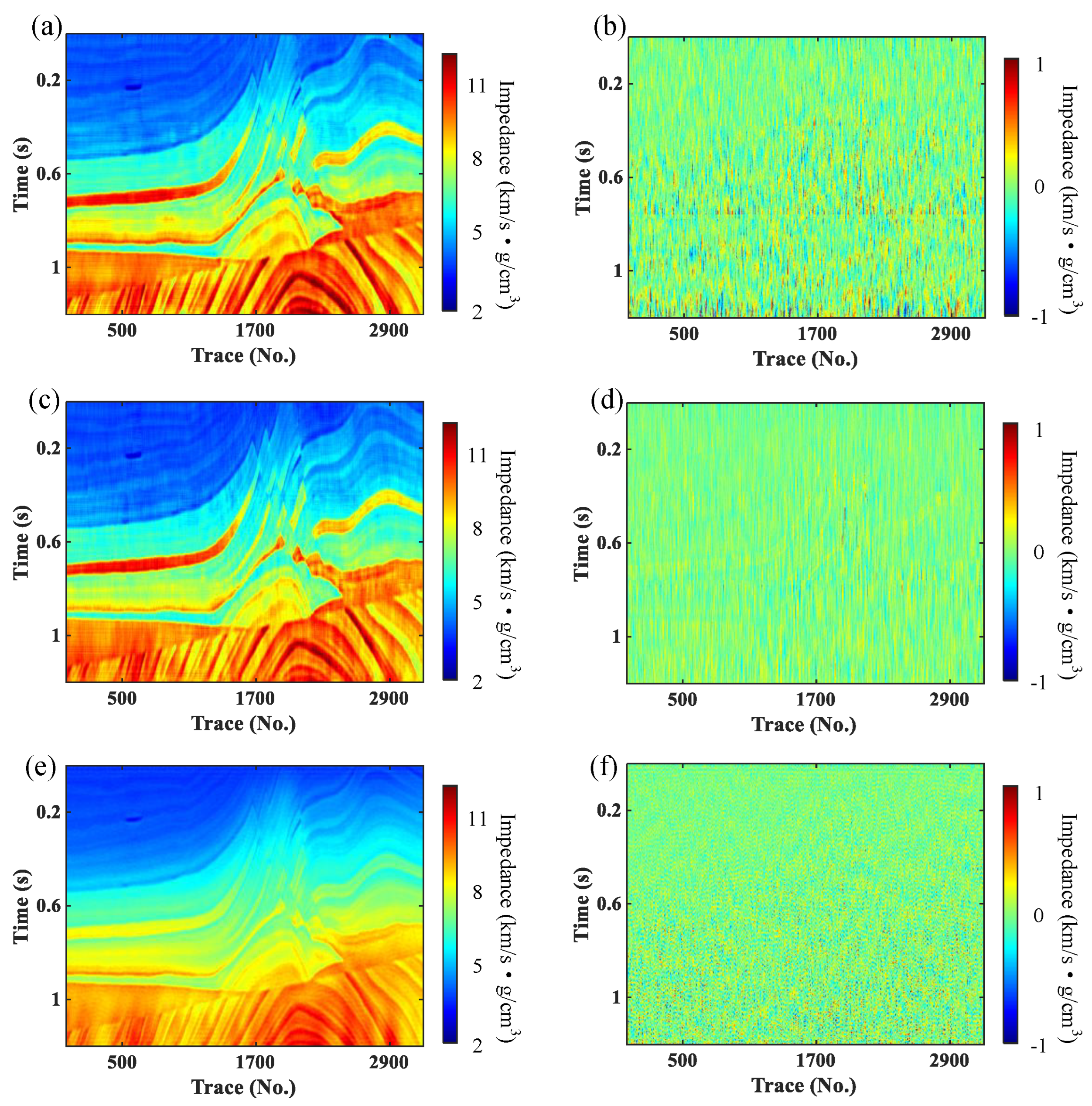
3.2. Field Data Example
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamid, H.; Pidlisecky, A. Multitrace impedance inversion with lateral constraints. Geophysics 2015, 80, M101–M111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Geological structure-guided hybrid MCMC and Bayesian linearized inversion methodology. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 199, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xing, G.; Zhu, T.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Y. Propagating Seismic Waves in VTI Attenuating Media Using Fractional Viscoelastic Wave Equation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfour, M.; Yoon, W.J.; Kim, J. Seismic attributes and acoustic impedance inversion in interpretation of complex hydrocarbon reservoirs. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 114, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, M.; Gunning, J. Joint impedance and facies inversion–seismic inversion redefined. First Break 2014, 32, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, X.; Liu, J.; Zong, Z. An improved stochastic inversion for joint estimation of seismic impedance and lithofacies. J. Geophys. Eng. 2019, 16, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madiba, G.B.; McMechan, G.A. Seismic impedance inversion and interpretation of a gas carbonate reservoir in the Alberta Foothills, western Canada. Geophysics 2003, 68, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M.; Bellefleur, G.; Mair, S.; Brent, T.A.; Dallimore, S.R. Acoustic impedance inversion and seismic reflection continuity analysis for delineating gas hydrate resources near the Mallik research sites, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Geophysics 2009, 74, B125–B137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, H.; Liu, W.; Hu, G. Seismic impedance inversion using dictionary learning-based sparse representation and nonlocal similarity. Interpretation 2019, 7, SE51–SE67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Liao, J. Robust AVO inversion for the fluid factor and shear modulus. Geophysics 2021, 86, R471–R483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Yuan, C.; Liao, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, S. Bayesian Deterministic Inversion Based on the Exact Reflection Coefficients Equations of Transversely Isotropic Media With a Vertical Symmetry Axis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5915715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, B.B.; Kamsu-Foguem, B.; Tangara, F. Deep convolution neural network for image recognition. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 48, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Lu, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Convolutional neural network architectures for matching natural language sentences. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Rahmani, H.; Shah, S.A.A.; Bennamoun, M. A Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer Vision. In Synthesis Lectures on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Deep learning for seismic lithology prediction. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 215, 1368–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, W. A spatially coupled data-driven approach for lithology/fluid prediction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5526–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shi, Y.; Fomel, S.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yusifov, A. FaultNet3D: Predicting Fault Probabilities, Strikes, and Dips With a Single Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9138–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Wu, X.; Geng, Z.; Li, H. Deep Relative Geologic Time: A Deep Learning Method for Simultaneously Interpreting 3-D Seismic Horizons and Faults. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB021882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, O.M.; Chen, Y. A fully unsupervised and highly generalized deep learning approach for random noise suppression. Geophys. Prospect. 2021, 69, 709–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Pham, N.; Fomel, S. Seismic data interpolation using deep learning with generative adversarial networks. Geophys. Prospect. 2021, 69, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Pollack, A.; Wollner, U.; Mukerji, T. Convolutional neural network for seismic impedance inversionCNN for seismic impedance inversion. Geophysics 2019, 84, R869–R880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, B.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P. Deep-learning inversion of seismic data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.07733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzyrev, V.; Egorov, A.; Pirogova, A.; Elders, C.; Otto, C. Seismic inversion with deep neural networks: A feasibility analysis. In Proceedings of the 81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019, London, UK, 3–6 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, Y. Robust deep learning seismic inversion with a priori initial model constraint. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 225, 2001–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazei, V.; Ovcharenko, O.; Plotnitskii, P.; Peter, D.; Zhang, X.; Alkhalifah, T. Mapping full seismic waveforms to vertical velocity profiles by deep learning. Geophysics 2021, 86, R711–R721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Su, Y.; Cui, R. Multi-parameter pre-stack seismic inversion based on deep learning with sparse reflection coefficient constraints. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 209, 109836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, X. Deep Learning Seismic Inversion Based on Prestack Waveform Datasets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4511311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyasiriwat, C.; Valasek, P.; Routh, P.; Cao, W.; Schuster, G.T.; Macy, B. An efficient multiscale method for time-domain waveform tomography. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCC59–WCC68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunks, C.; Saleck, F.M.; Zaleski, S.; Chavent, G. Multiscale seismic waveform inversion. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Multiscale frequency-domain seismic inversion for fracture weakness. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Multiscale viscoacoustic waveform inversion with the second generation wavelet transform and adaptive time–space domain finite-difference method. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 197, 948–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.; Zoph, B.; Le, Q.V. Searching for activation functions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:.05941. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J. A survey of optimization methods from a machine learning perspective. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 3668–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Luo, J.-H.; Wei, X.-S.; Wu, J. In defense of fully connected layers in visual representation transfer. In Proceedings of the Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia, Harbin, China, 28–29 September 2017; pp. 807–817. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Sacchi, M.D. Making Fx Projection Filters Robust to Erratic Noise. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2014; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 4371–4375. [Google Scholar]
| Without f-x Filtering | With f-x Filtering | |
|---|---|---|
| SSII | 0.59 | 0.50 |
| MSII | 0.48 | 0.44 |
| MDII | 0.90 | 0.85 |
| Without f-x Filtering | With f-x Filtering | |
|---|---|---|
| SSII | 1.41 | 1.25 |
| MSII | 1.27 | 1.22 |
| MDII | 1.51 | 1.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, G.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Guo, K. Data-Driven Seismic Impedance Inversion Based on Multi-Scale Strategy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236056
Zhu G, Chen X, Li J, Guo K. Data-Driven Seismic Impedance Inversion Based on Multi-Scale Strategy. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236056
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Guang, Xiaohong Chen, Jingye Li, and Kangkang Guo. 2022. "Data-Driven Seismic Impedance Inversion Based on Multi-Scale Strategy" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236056
APA StyleZhu, G., Chen, X., Li, J., & Guo, K. (2022). Data-Driven Seismic Impedance Inversion Based on Multi-Scale Strategy. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236056