A Lightweight Model for Ship Detection and Recognition in Complex-Scene SAR Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The scenes of the SAR image are complex and changeable, which have obvious influence on target imaging and morphological changes. A large number of ships are missed and false alarms can easily occur nearshore or in areas where targets are densely distributed.
- Compared with traditional recognition models, most existing deep learning models show strong robustness and adaptability in target recognition performance. However, these methods have obvious shortcomings such as low model training efficiency, high deployment cost of embedded devices, and low real-time performance.
- In order to improve the model’s operating efficiency and reduce the cost of algorithm deployment, this paper improves and optimizes the algorithm based on the YOLOv5-n lightweight model. Combined with the fast pyramidal pooling structure, the target feature extraction efficiency of the neural network model is effectively improved.
- Aiming to improve the detection and recognition performance of ship targets in high-resolution complex-scene SAR images, this paper integrates an attention mechanism into the target feature extraction layer. The proposed attention module can improve the model’s attention to target features in complex scenes and suppress the influence of background noise.
- To optimize the performance of ship positioning and recognition in complex scenes such as nearshore or the dense distribution of ship targets, this paper introduces an angle classification module in the prediction layer of the network model to achieve the rotation detection and recognition of ship targets.
- We conducted extensive experiments on the newly released SAR ship detection and recognition dataset named SRSDD [28] to validate the proposed improvements. The experimental results show that the proposed method in this paper not only outperforms several other deep learning methods in terms of detection and recognition performance, but also has significant advantages in terms of algorithm parameters, model size, and operation efficiency.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lightweight Models
2.2. Embedding Attention Mechanism Models
2.3. Rotation Detection Models
3. Proposed Method
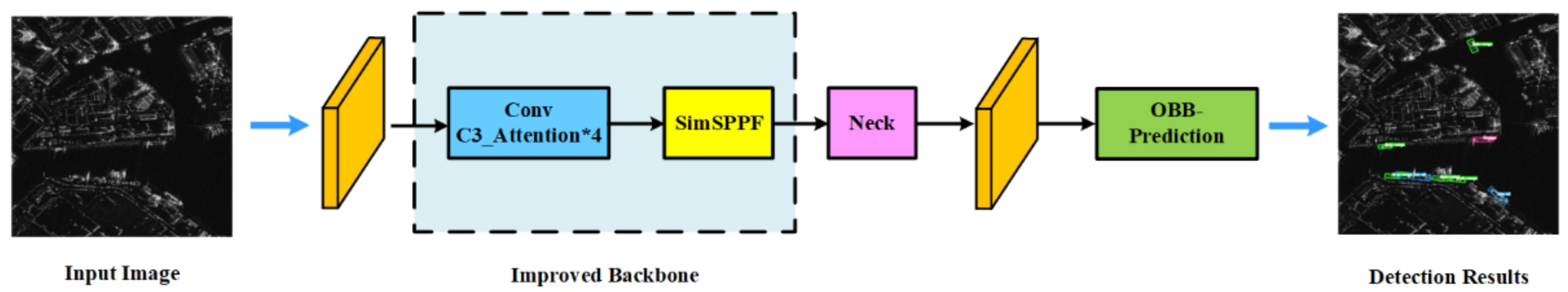
3.1. Overall Framework
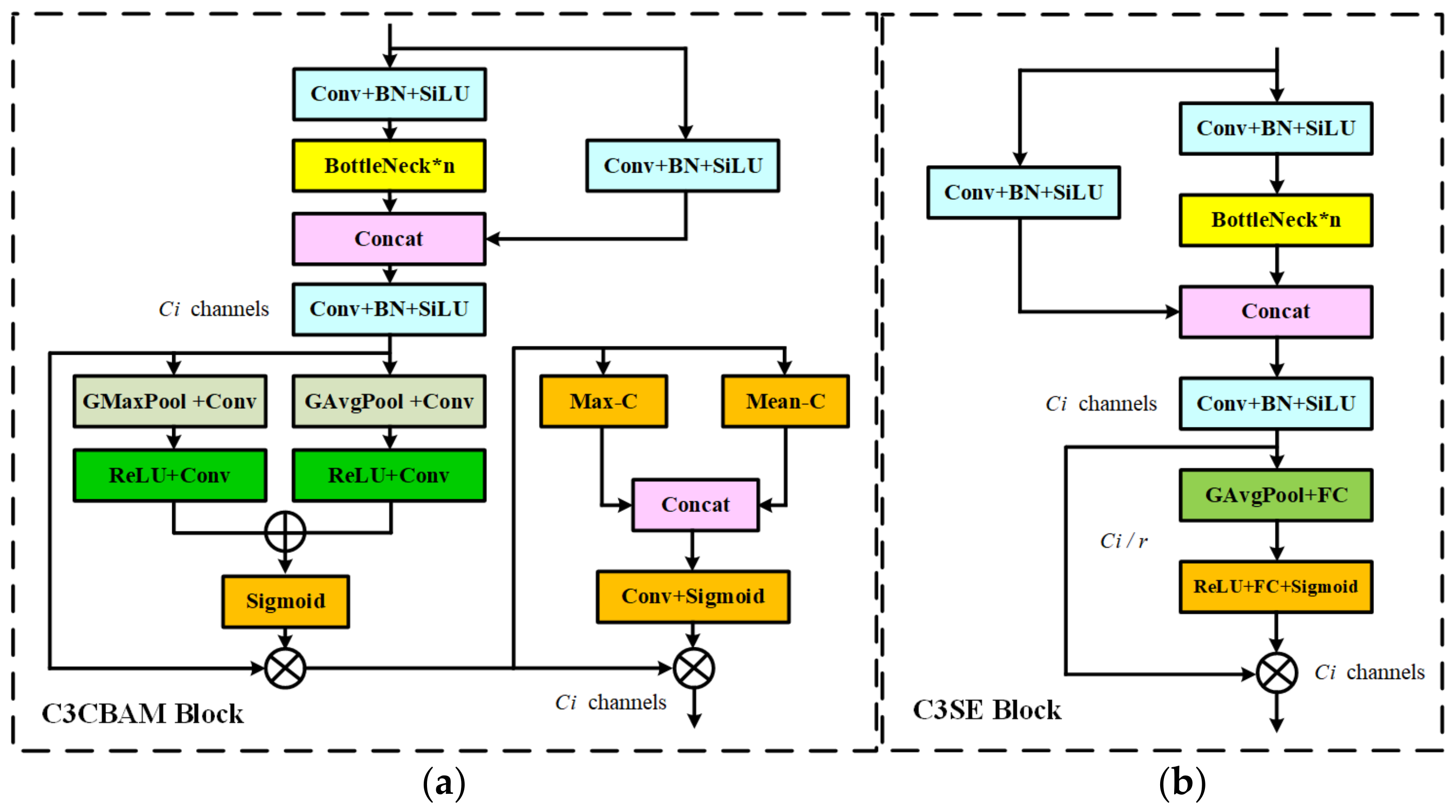
3.2. C3_Attention Block
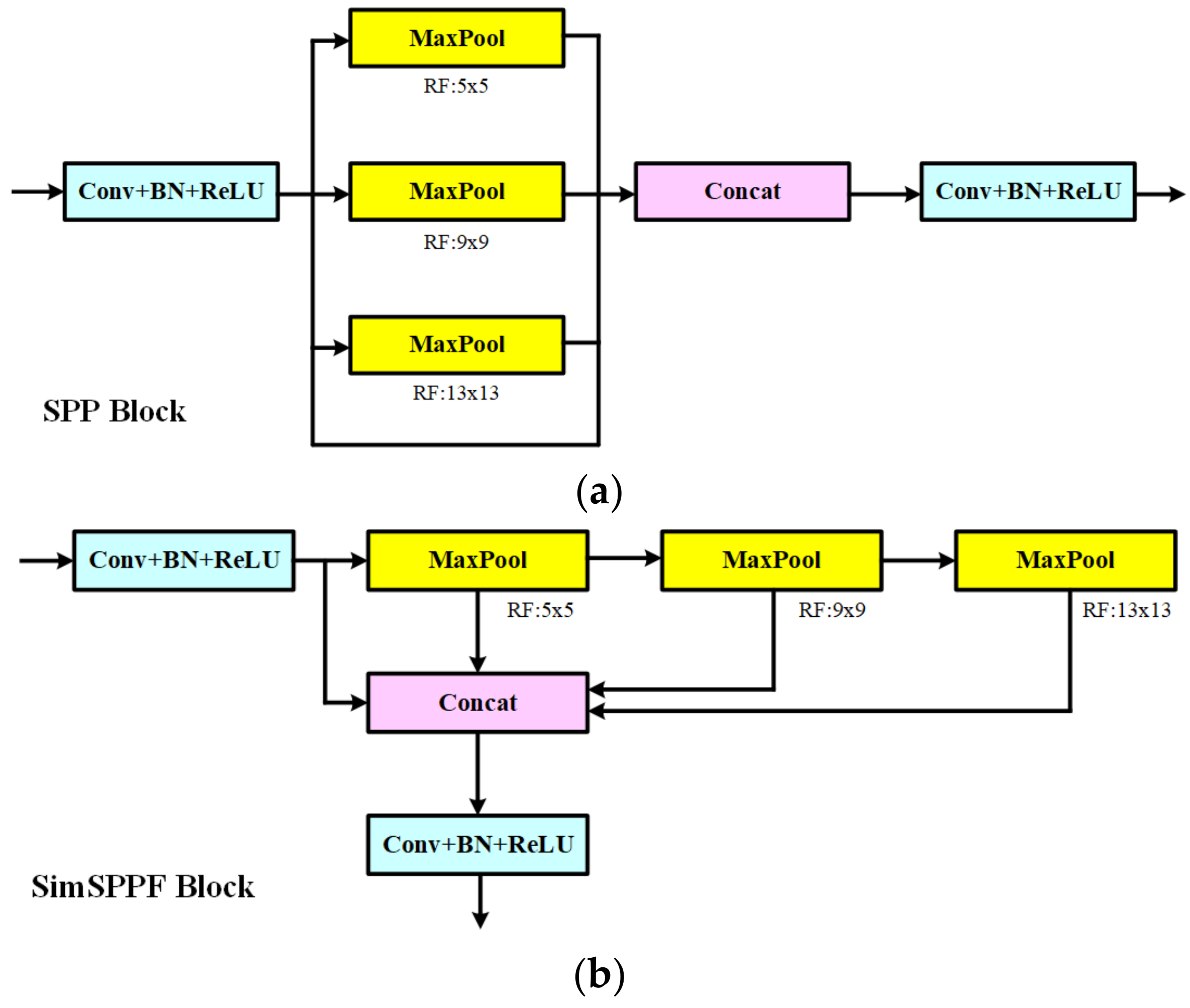
3.3. SimSPPF Block
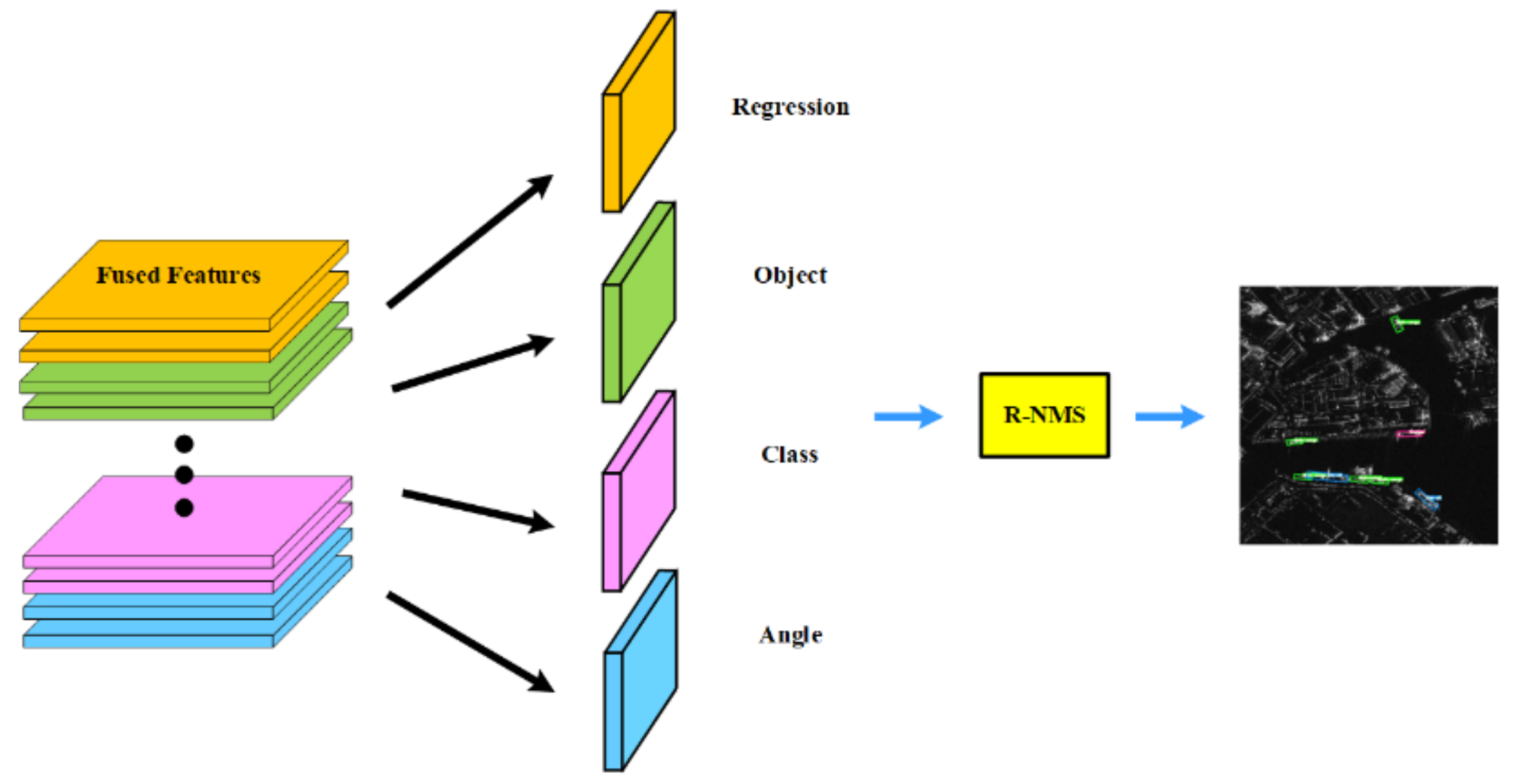
3.4. OBB Prediction Block
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Effect of C3_Attention Block
4.4.2. Effect of SimSPPF Block
4.4.3. Effect of OBB Prediction Block
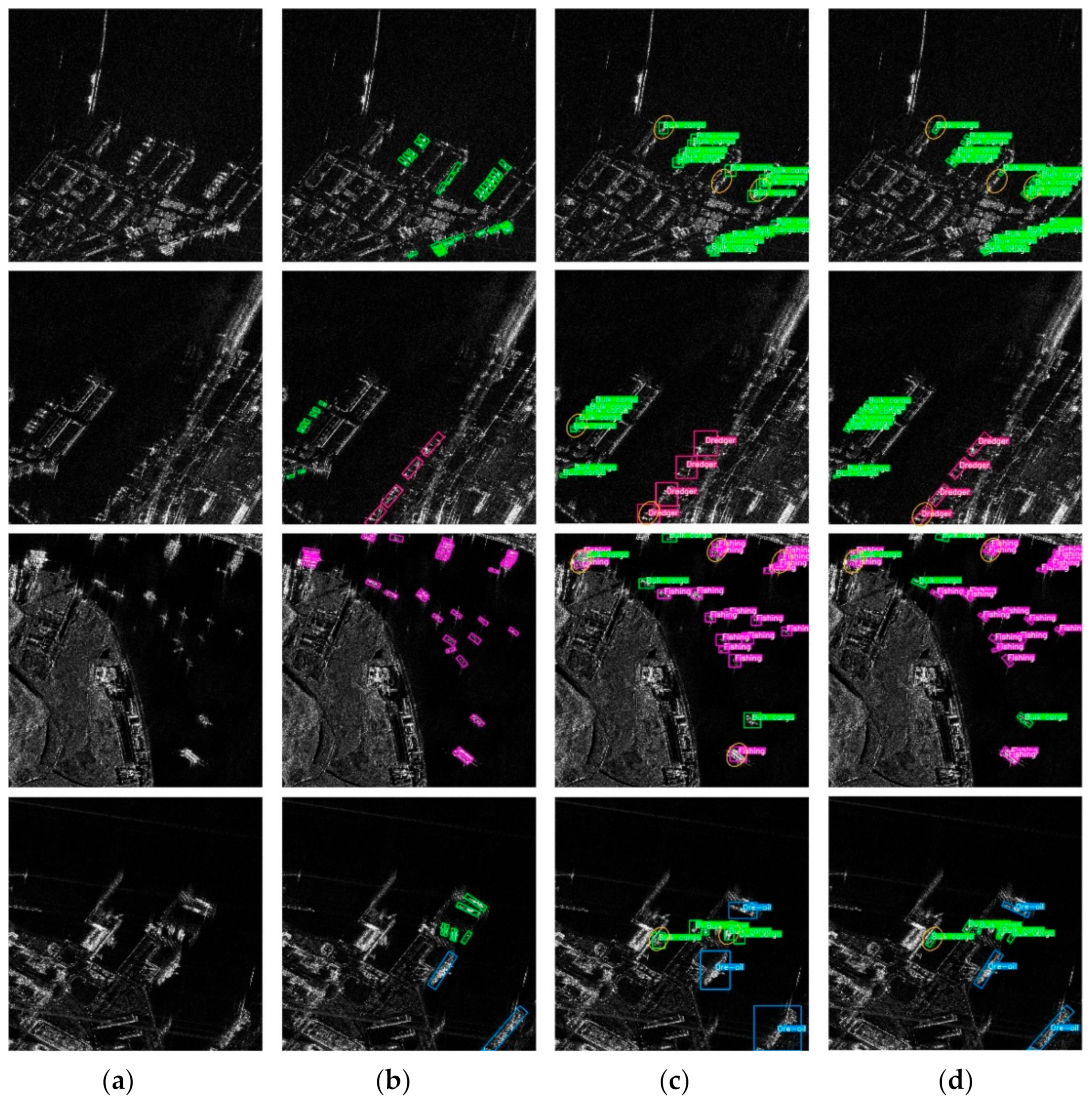
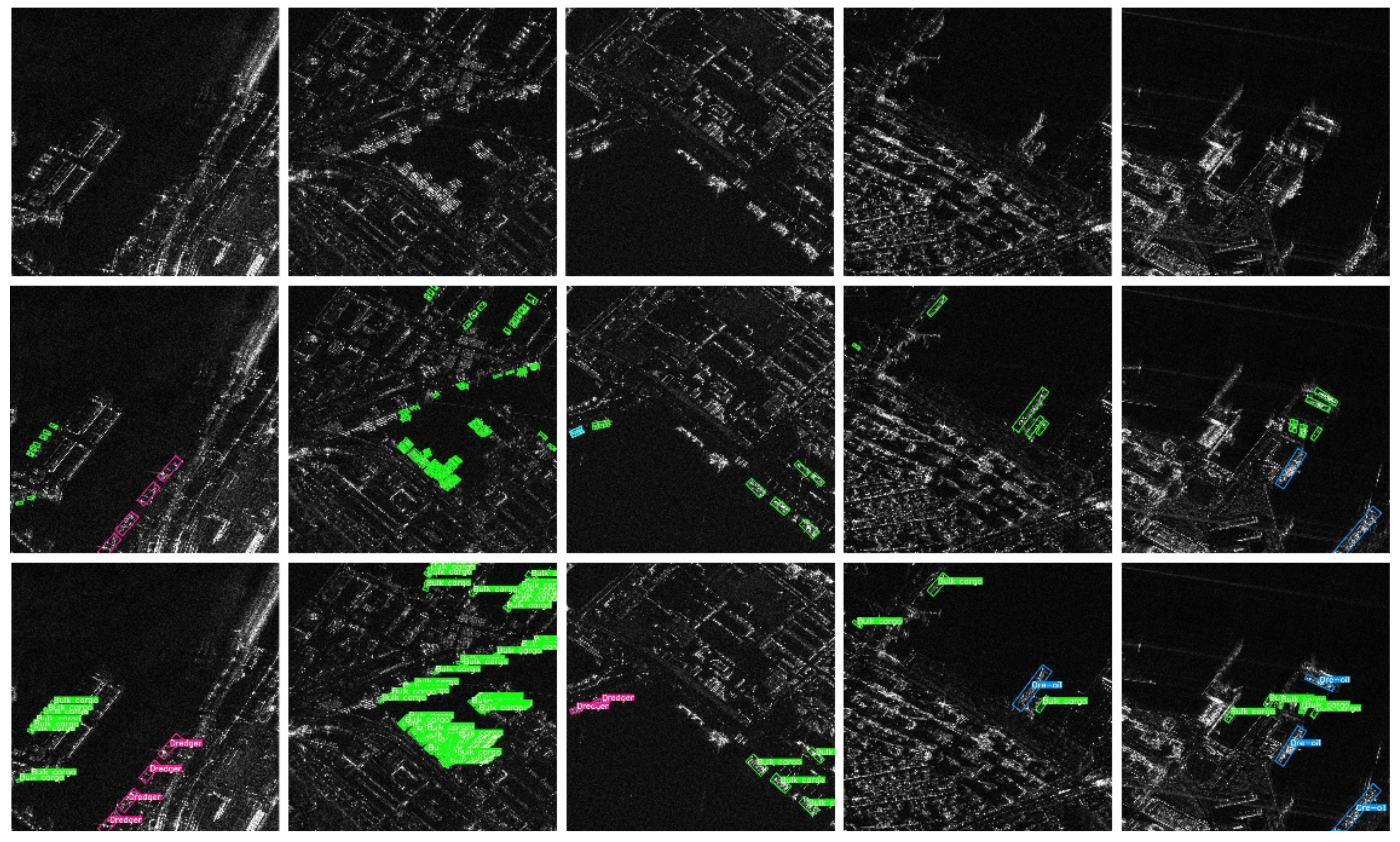
4.5. Comparison with Other Methods
| Model | Category | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 | FPS | Model (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-O [28] | Two-stage | 57.12 | 49.66 | 53.13 | 8.09 | 315 |
| ROI [28,69] | Two-stage | 59.31 | 51.22 | 54.97 | 7.75 | 421 |
| Gliding Vertex [28,70] | Two-stage | 57.75 | 53.95 | 55.79 | 7.58 | 315 |
| O-RCNN [28,65] | Two-stage | 64.01 | 57.61 | 60.64 | 8.38 | 315 |
| R-RetinaNet [28,68] | One-stage | 53.52 | 12.55 | 20.33 | 10.53 | 277 |
| R3Det [28,71] | One-stage | 58.06 | 15.41 | 24.36 | 7.69 | 468 |
| BBAVectors [28,66] | One-stage | 50.08 | 34.56 | 40.90 | 3.26 | 829 |
| R-FCOS [28,67] | One-stage | 60.56 | 18.42 | 28.25 | 10.15 | 244 |
| Ours | One-stage | 59.70 | 62.90 | 61.26 | 68.02 | 4.52 |
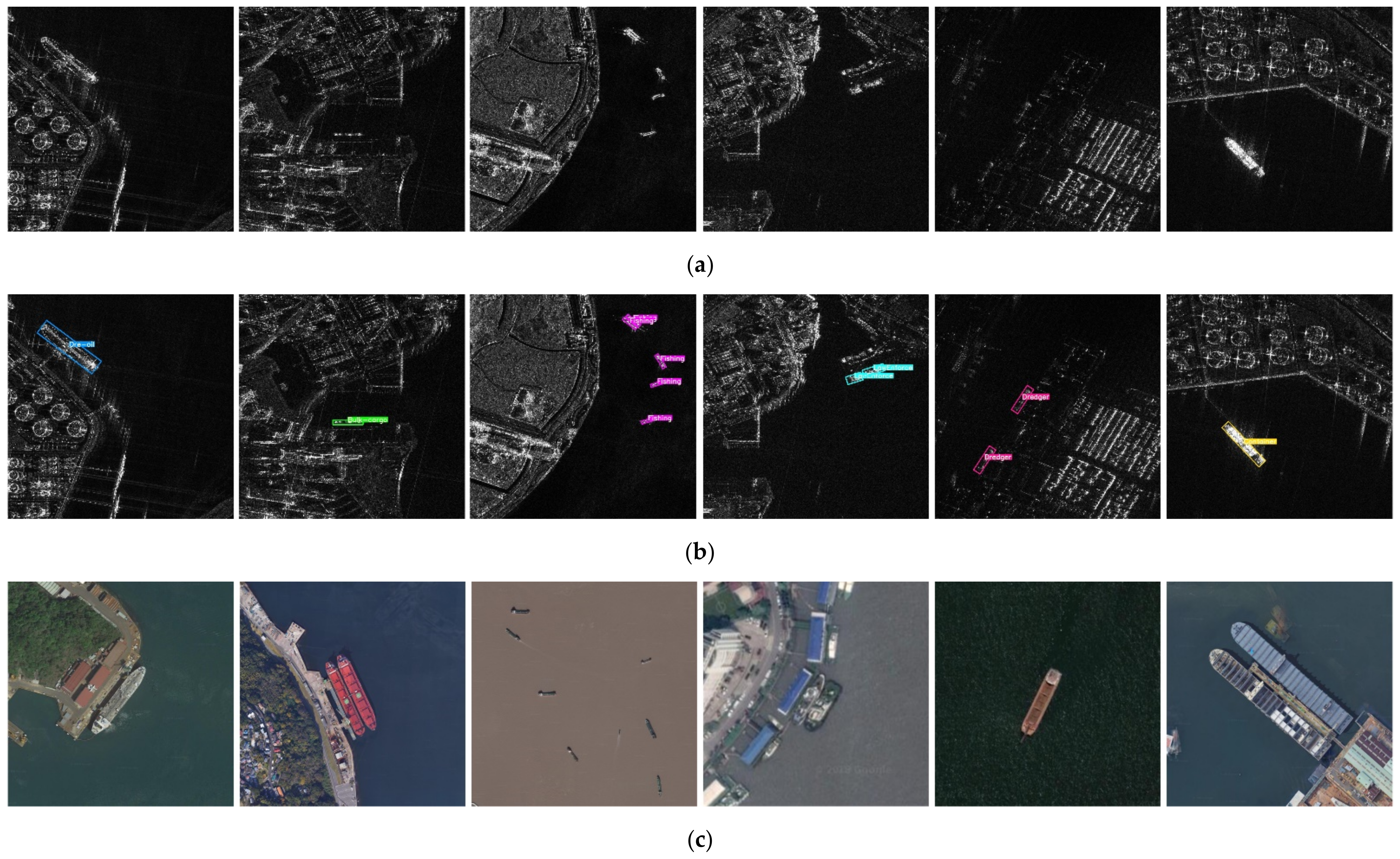
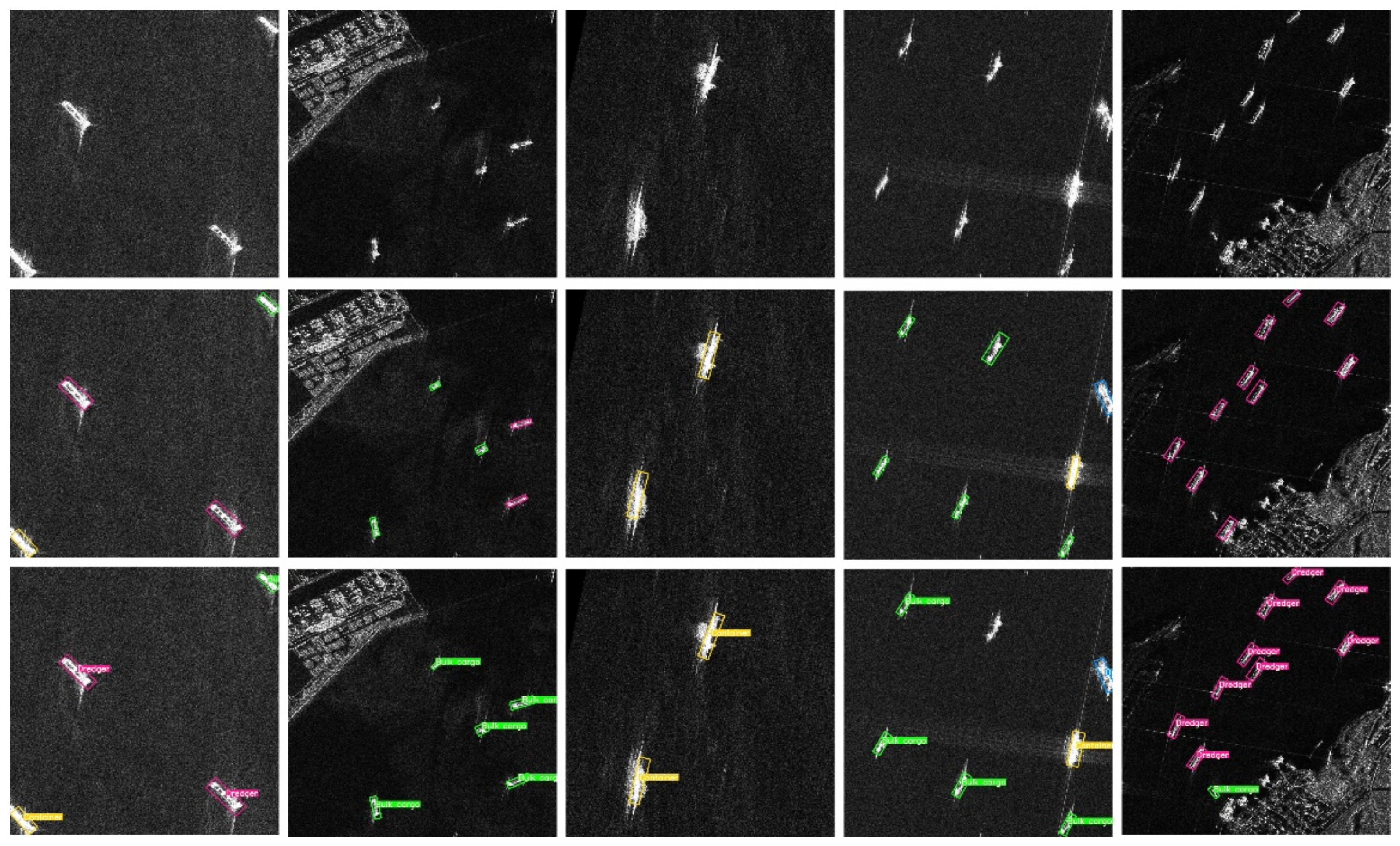
4.6. Detection and Recognition Results on SRSDD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, B. Study of Registration and Change Detection in SAR Images; National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, X.; Ji, K.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Complex Signal Kurtosis—Indicator of Ship Target Signature in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Dai, M.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. An Anchor-Free Detection Method for Ship Targets in High-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7788–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, G.; Gao, G.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, J.; Jia, C. Theory, Algorithm and Application for Target Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar; Press of National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, W. R-CNN-Based Ship Detection from High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, F. Intelligent Ship Detection in Remote Sensing Images Based on Multi-Layer Convolutional Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, W.; Deng, D. Improved YOLOv3 Based on Attention Mechanism for Fast and Accurate Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, X.; Yin, L. Research on image classification method based on improved multi-scale relational network. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Kolouri, S.; Eaton, E.; Kim, K. Deep Transfer Learning for Few-Shot SAR Image Classification. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, Q.; Wang, C.; Gu, H. Monocular 3D vehicle detection with multi-instance depth and geometry reasoning for autonomous driving. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Guo, Q.; Lei, J.; Yu, L.; Hwang, J.-N. IRFR-Net: Interactive Recursive Feature-Reshaping Network for Detecting Salient Objects in RGB-D Images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, Q.; Tang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. DPSNet: Multitask Learning Using Geometry Reasoning for Scene Depth and Semantics. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, M.-W.; Luo, T. Local and Global Feature Learning for Blind Quality Evaluation of Screen Content and Natural Scene Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Fu, H. Multi-dimensional prediction method based on Bi-LSTMC for ship roll. Ocean Eng. 2021, 242, 110106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, P.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Depth Estimation Method for Monocular Camera Defocus Images in Microscopic Scenes. Electronics 2022, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ullah, I.; Liu, X.; Choi, D. A Review of Underwater Localization Techniques, Algorithms, and Challenges. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 6403161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Shao, J. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the BIGSARDATA, Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Tian, R.; Luo, Q.; Jin, J.; Tang, B. Multi-Scale Rotation-Invariant Haar-Like Feature Integrated CNN-Based Ship Detection Algorithm of Multiple-Target Environment in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2019, 57, 10070–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Kuang, G. Squeeze and excitation rank fasterR-CNN for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Jianhua, W.; Mingming, X.; Hui, S.; Zhe, Z.; Shanwei, L.; Colak, A.T.I.; Hossain, S. Ship detection based on deep learning using SAR imagery: A systematic literature review. Soft Comput. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. A Feature Decomposition-based Method for Automatic Ship Detection Crossing Different Satellite SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3201628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ouchi, K. Detection of Ships Cruising in the Azimuth Direction Using Spotlight SAR Images with a Deep Learning Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, M. MetaBoost: A Novel Heterogeneous DCNNs Ensemble Network With Two-Stage Filtration for SAR Ship Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhan, X.; Xu, Y.; Ke, X.; Zeng, T.; Su, H.; et al. SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD): Official Release and Comprehensive Data Analysis. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Diao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kun, F. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR Ship Detection Dataset. J. Radars 2019, 8, 852. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X.; Zhan, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A deep learning dataset dedicated to small ship detection from large-scale sentinel-1 SAR images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Lu, D.; Qiu, X.; Ding, C. SRSDD-v1.0: A High-Resolution SAR Rotation Ship Detection Dataset. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Gong, S.; Xing, M. LASDNet: A Lightweight Anchor-Free Ship Detection Network for SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 2630–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jia, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, F. A Fast Threshold Neural Network for Ship Detection in Large-Scene SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6016–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, T.; Zeng, H.; Yang, W.; Chu, B.; Zou, F.; Ren, W.; Chen, J. An Improved Lightweight RetinaNet for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ji, K.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, L.; Feng, S.; Kuang, G. Light-YOLOv4: An Edge-Device Oriented Target Detection Method for Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10808–10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lei, J.; Xie, W.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Algorithm/Hardware Codesign for Real-Time On-Satellite CNN-Based Ship Detection in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, D. An Efficient and Lightweight CNN Model With Soft Quantification for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, S.; Qin, M. A Fast and Lightweight Detection Network for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection under Complex Backgrounds. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Anagaw, A.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lee, W.-H. Ship Detection Based on YOLOv2 for SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Z. A Lightweight Network Based on One-Level Feature for Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Wan, H.; Xia, R.; Wu, B.; Sun, L.; Xing, M. A Lightweight Position-Enhanced Anchor-Free Algorithm for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, X.; Dong, J. Improved Ship Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOX for SAR Outline Enhancement Image. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T. Lite-YOLOv5: A Lightweight Deep Learning Detector for On-Board Ship Detection in Large-Scene Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A Lightweight YOLO Algorithm for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kong, W.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Yasir, M.; Zhao, L.; Li, J. Multi-Scale Ship Detection Algorithm Based on a Lightweight Neural Network for Spaceborne SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ren, M.; Wu, C. Improved YOLOv4 Based on Attention Mechanism for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 23785–23797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tan, X. Improved YOLOX’s Anchor-Free SAR Image Ship Target Detection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 70001–70015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Qian, W.; Yang, W.; Xu, Y. Multi-Feature Transformation and Fusion-Based Ship Detection with Small Targets and Complex Backgrounds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, L. R-CenterNet+: Anchor-Free Detector for Ship Detection in SAR Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qu, L. Regional Prediction-Aware Network with Cross-Scale Self-Attention for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, Z.; Zou, B. Multi Scale Ship Detection Based on Attention and Weighted Fusion Model for High Resolution SAR Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. SAR Ship Detection Based on YOLOv5 Using CBAM and BiFPN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 2147–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xia, R.; Wu, B.; Sun, L.; Yao, B.; Liu, X.; Xing, M. AFSar: An Anchor-Free SAR Target Detection Algorithm Based on Multiscale Enhancement Representation Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q. A-BFPN: An Attention-Guided Balanced Feature Pyramid Network for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Tan, J. Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Adaptive Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; He, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xing, X. SII-Net: Spatial Information Integration Network for Small Target Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y. Orientation-Aware Feature Fusion Network for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; He, Z.; Lou, A.; Li, X. Center-to-Corner Vector Guided Network for Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Geology, Mapping and Remote Sensing (ICGMRS), Zhoushan, China, 22–24 April 2022; pp. 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Bai, L.; Xue, D.; Lin, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yin, K. GFB-Net: A Global Context-Guided Feature Balance Network for Arbitrary-Oriented SAR Ship Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Xi’an, China, 26–28 July 2022; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Yu, W.; Lv, J. A Single-Stage Arbitrary-Oriented Detector Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Calibration for SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8179–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lang, H. An Oriented SAR Ship Detector with Mixed Convolution Channel Attention Module and Geometric Non-Maximum Suppression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8074–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lang, H. Improving Deep Subdomain Adaptation by Dual-Branch Network Embedding Attention Module for SAR Ship Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8038–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. BiFA-YOLO: A Novel YOLO-Based Method for Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection in High-Resolution SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, M.; He, C. Oriented Ship Detector for Remote Sensing Imagery Based on Pairwise Branch Detection Head and SAR Feature Enhancement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Zeng, T. RBFA-Net: A Rotated Balanced Feature-Aligned Network for Rotated SAR Ship Detection and Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, R.; Huang, K.; Xu, Q. Triangle Distance IoU Loss, Attention-Weighted Feature Pyramid Network, and Rotated-SARShip Dataset for Arbitrary-Oriented SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. European Conference on Computer Vision. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.4729. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J. Oriented R-CNN for Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.05699. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.; Bai, X. Gliding Vertex on the Horizontal Bounding Box for Multi-Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: Fully Convolutional One-Stage Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9626–9635. [Google Scholar]
- Rotated-RetinaNet. Available online: https://github.com/ming71/Rotated-RetinaNet (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Law, H.; Deng, J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 765–781. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Qu, H.; Metaxas, D. Oriented Object Detection in Aerial Images with Box Boundary-Aware Vectors. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 5–9 January 2021; pp. 2149–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Feng, Z.; He, T. R3Det: Refined Single-Stage Detector with Feature Refinement for Rotating Object. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.05612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
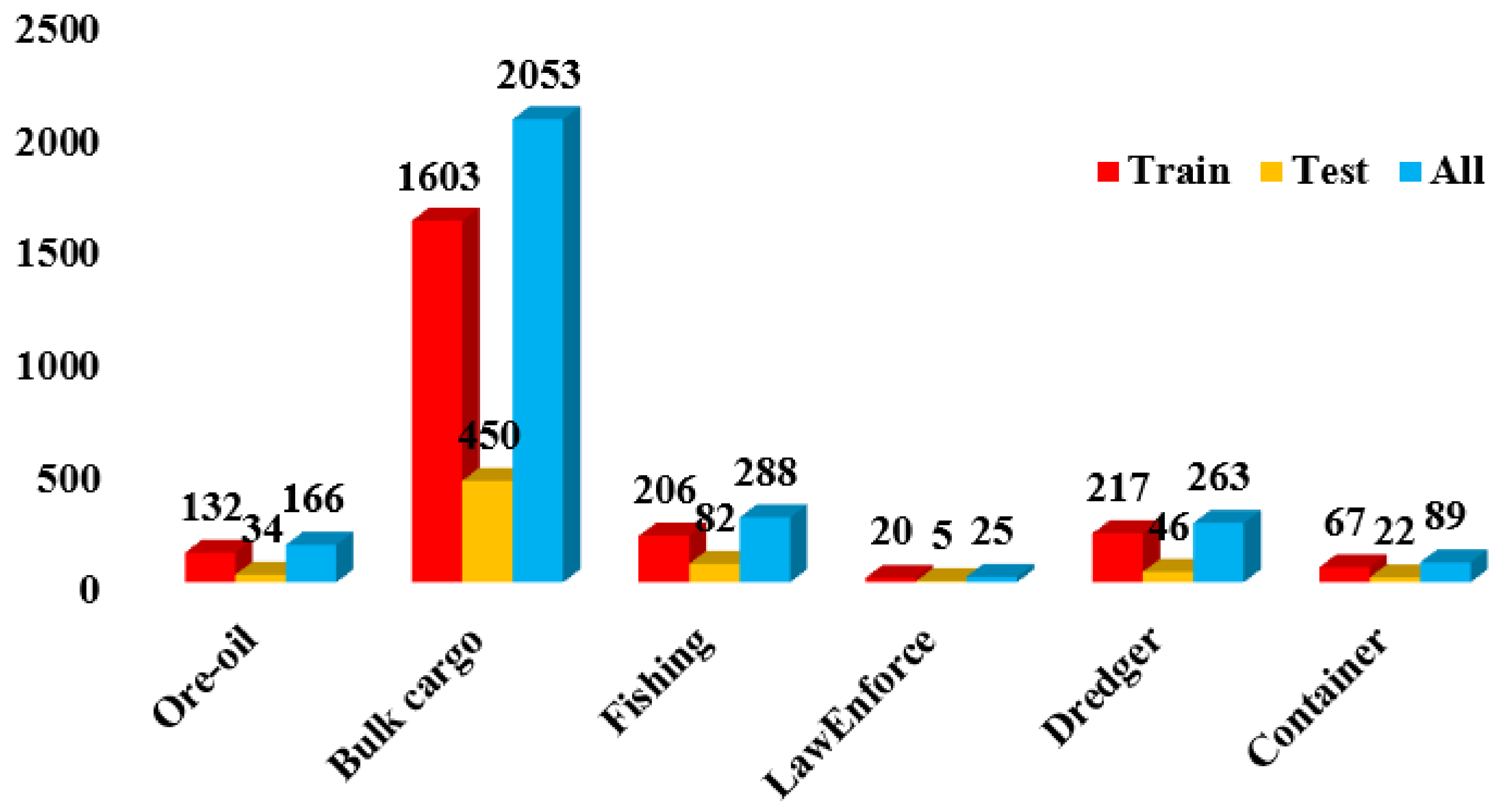


| Dataset | Size (Pixel) | Image (Num) | Ship (Num) | Annotations | Resolution (m) | Categories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSDD | 190–668 | 1160 | 2586 | HBB | 1–15 | 1 |
| SSDD+ | 190–668 | 1160 | 2586 | OBB | 1–15 | 1 |
| Official-SSDD | 190–668 | 1160 | 2586 | Polygon | 1–15 | 1 |
| SAR-Ship-Dataset | 256 × 256 | 43,819 | 59,535 | HBB | 3–25 | 1 |
| Air-SARship-1.0 | 3000 × 3000 | 31 | 461 | HBB | 1, 3 | 1 |
| Air-SARship-2.0 | 1000 × 1000 | 300 | 2040 | HBB | 1, 3 | 1 |
| HRSID | 800 × 800 | 5604 | 16,951 | Polygon | 0.5, 1, 3 | 1 |
| LS-SSDD-v1.0 | 24,000 × 16,000 | 15 | 6015 | HBB | 5 × 20 | 1 |
| RSDD-SAR | 512 × 512 | 7000 | 10,263 | OBB | 2–20 | 1 |
| SRSDD-v1.0 | 1024 × 1024 | 666 | 2884 | OBB | 1 | 6 |
| Project | Model/Parameter |
|---|---|
| System | windows 10 |
| RAM | 32 GB |
| CPU | Intel i7-10875H |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX 2070 |
| Platform | PyTorch |
| Code | python3.8 |
| Framework | CUDA10.1/cudnn7.6.5 |
| Epochs | 200 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Momentum | 0.0005 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 | FPS | Model (MB) | FLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n (Base) | 55.42 | 53.77 | 54.58 | 75.19 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Base + C3SE | 58.11 | 57.54 | 57.82 | 73.00 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Base + C3CBAM | 58.30 | 57.89 | 58.09 | 72.46 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Methods | F1 | FPS | Param (M) | Model (MB) | FLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n (Base) | 54.58. | 75.19 | 1.68 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Base + SimSPPF | 54.58 | 85.47 | 1.68 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 | FPS | Model (MB) | FLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n (Base) | 55.42 | 53.77 | 54.58 | 75.19 | 4.06 | 4.2G |
| Base + OBB | 55.47 | 57.41 | 56.42 | 69.40 | 4.52 | 5.0G |
| Class | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ore-oil | 53.5 | 46.7 | 0.50 |
| Bulk cargo | 52.6 | 59.3 | 0.56 |
| Fishing | 64.3 | 28.0 | 0.39 |
| LawEnforce | 44.2 | 100.0 | 0.61 |
| Dredger | 77.4 | 67.0 | 0.72 |
| Container | 66.4 | 76.2 | 0.71 |
| Ore-Oil | Bulk Cargo | Fishing | LawEnforce | Dredger | Container | Background FN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ore-oil | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Bulk cargo | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.78 |
| Fishing | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| LawEnforce | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| Dredger | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| Container | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.04 |
| Background FN | 0.53 | 0.45 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, B.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Leng, X.; Ji, K. A Lightweight Model for Ship Detection and Recognition in Complex-Scene SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236053
Xiong B, Sun Z, Wang J, Leng X, Ji K. A Lightweight Model for Ship Detection and Recognition in Complex-Scene SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236053
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Boli, Zhongzhen Sun, Jin Wang, Xiangguang Leng, and Kefeng Ji. 2022. "A Lightweight Model for Ship Detection and Recognition in Complex-Scene SAR Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236053
APA StyleXiong, B., Sun, Z., Wang, J., Leng, X., & Ji, K. (2022). A Lightweight Model for Ship Detection and Recognition in Complex-Scene SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6053. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236053






