Micro-Motion Parameter Extraction of Multi-Scattering-Point Target Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
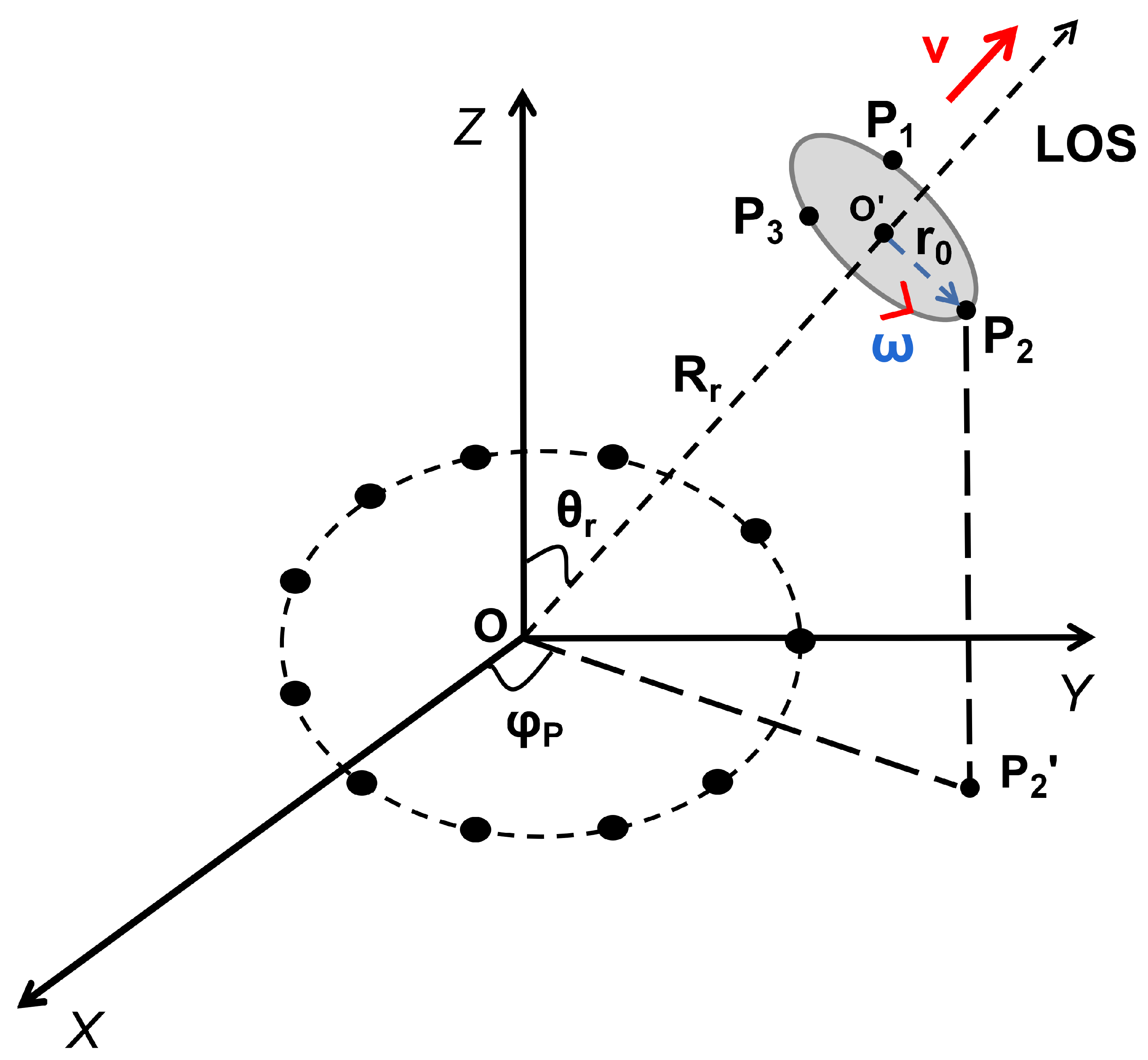
2. Echo Model of Multi-Scattering-Point Target in VEMW Radar
- (1)
- The Doppler shift of the echo signal includes the linear Doppler frequency shift induced by the distance variation of multiple scattering points along the LOS and the angular Doppler frequency shift caused by the translation and rotation motion. For the angular Doppler shift, it is caused by the motion when the two parts are coupled with each other.
- (2)
- The magnitude of the angular Doppler frequency shift is positively related to the transmitted OAM mode l, the rotation radius , and the rotation frequency , which is irrelevant to the signal carrier frequency and the bandwidth B.
- (3)
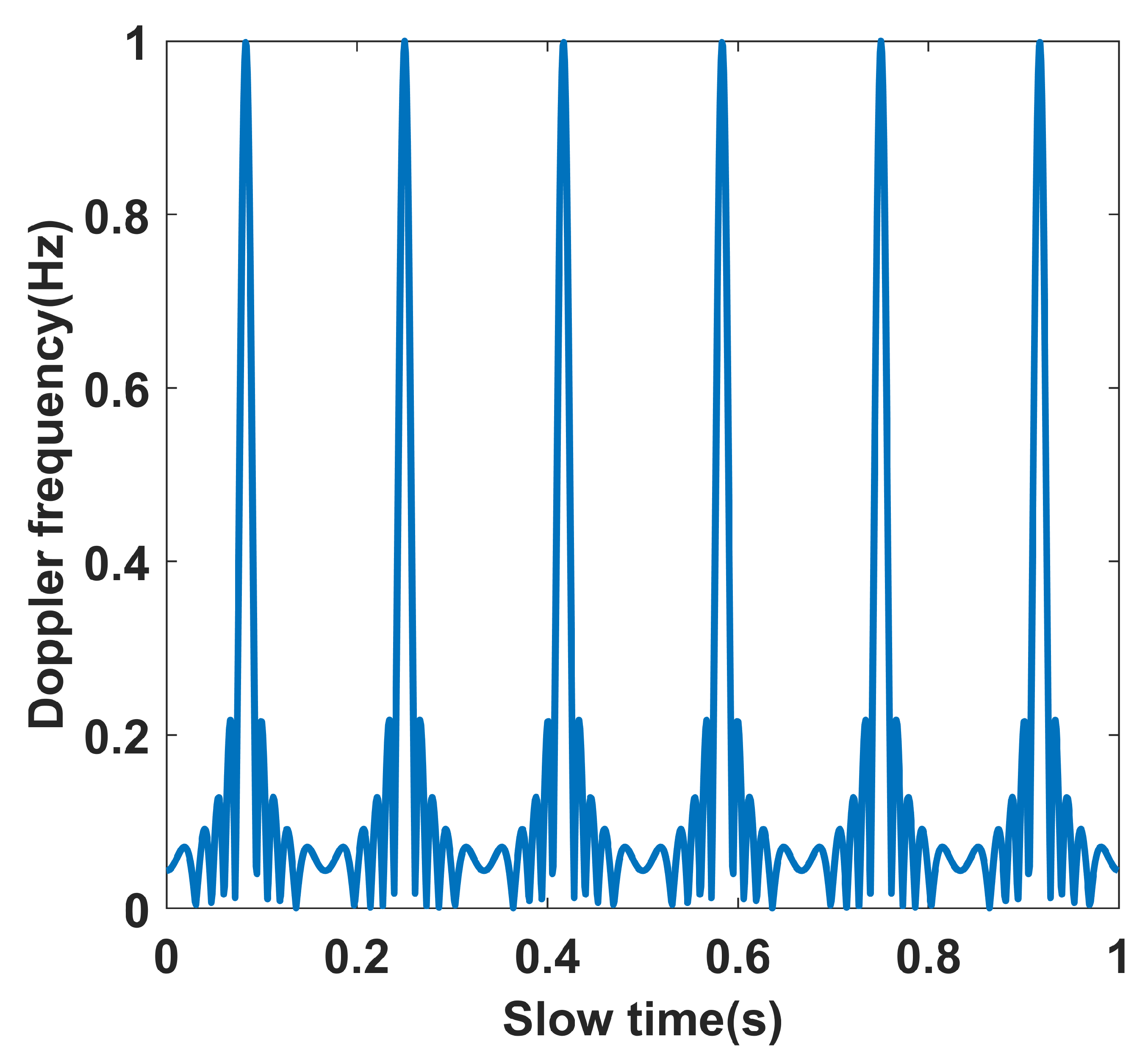
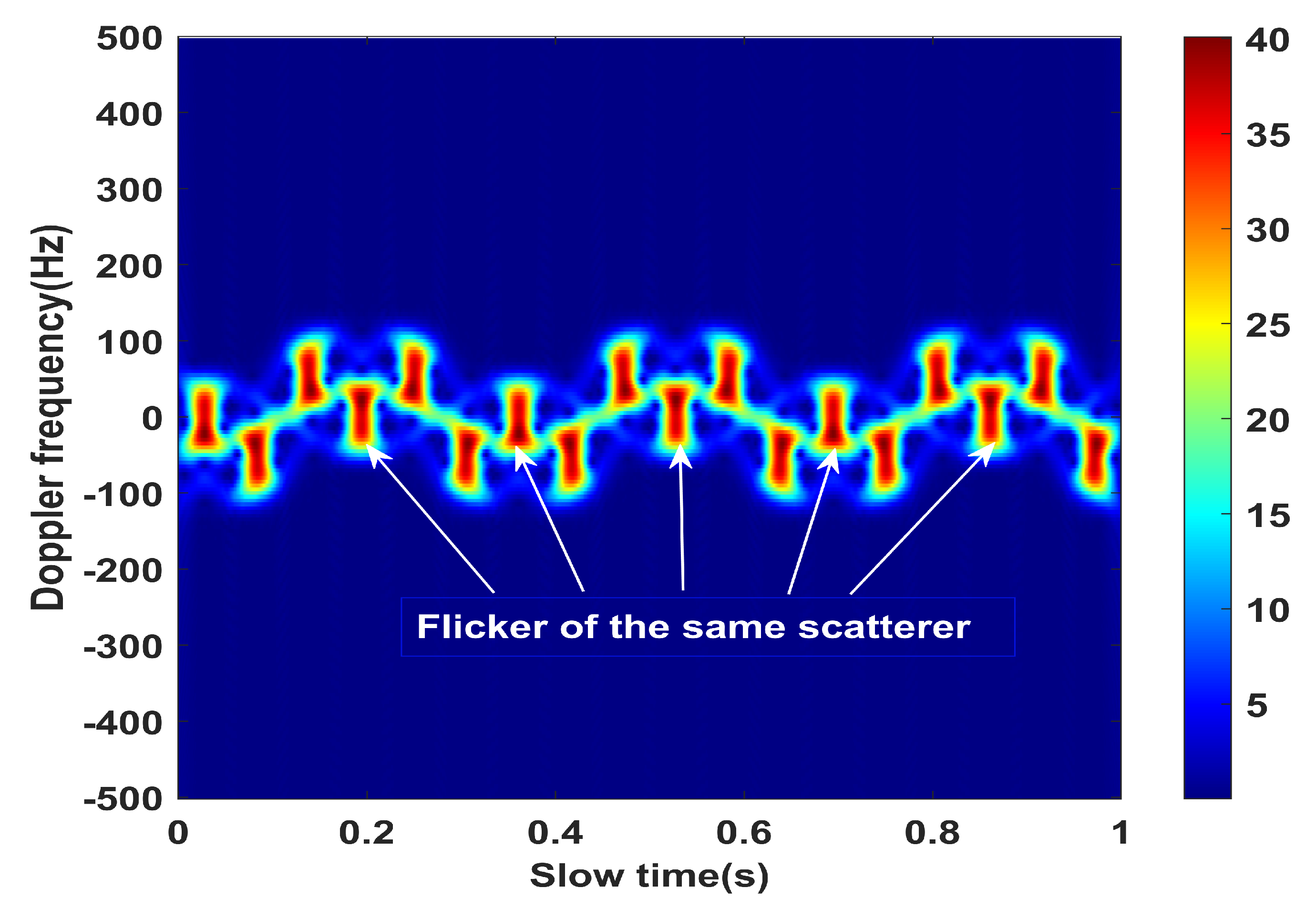
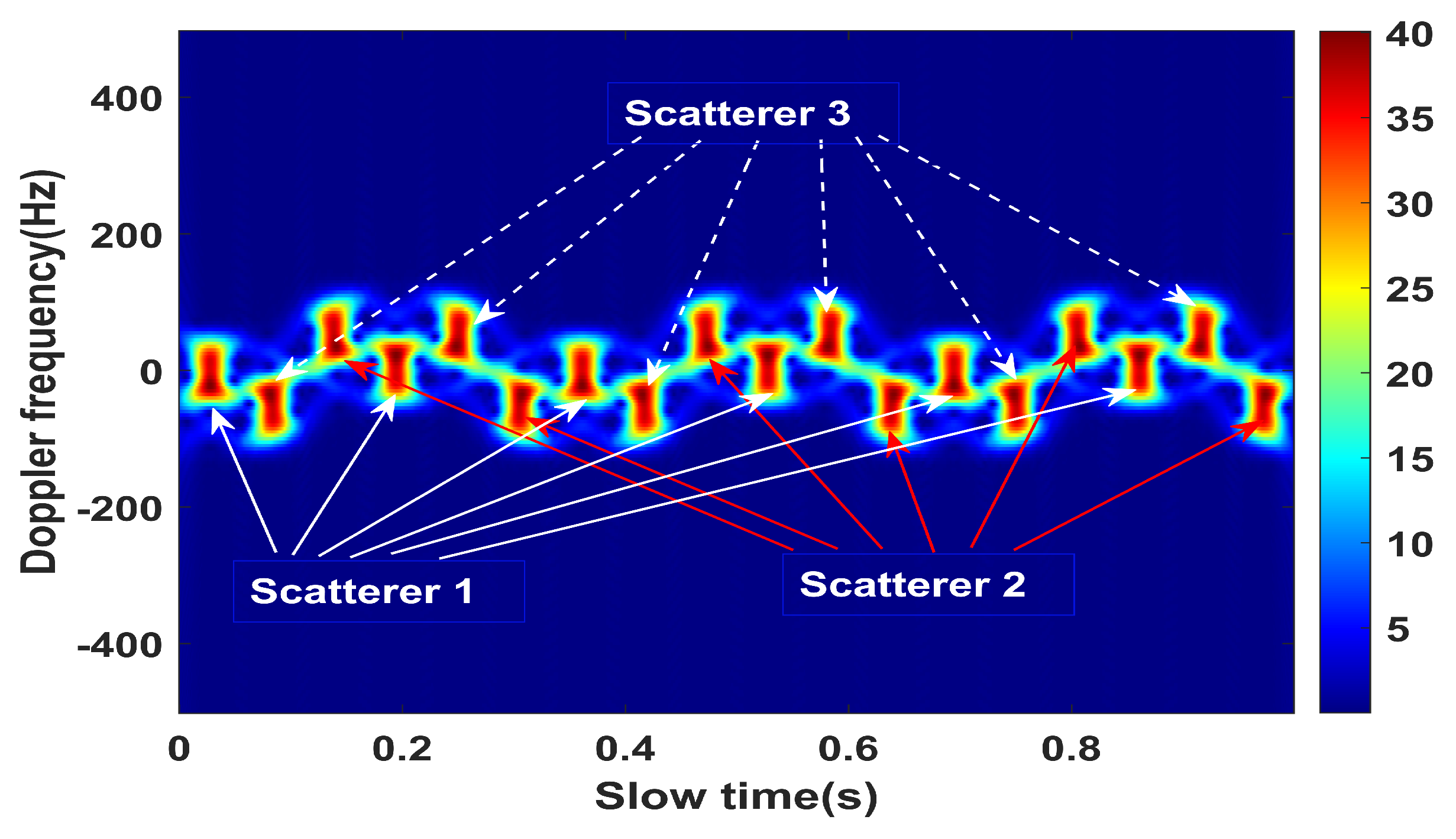
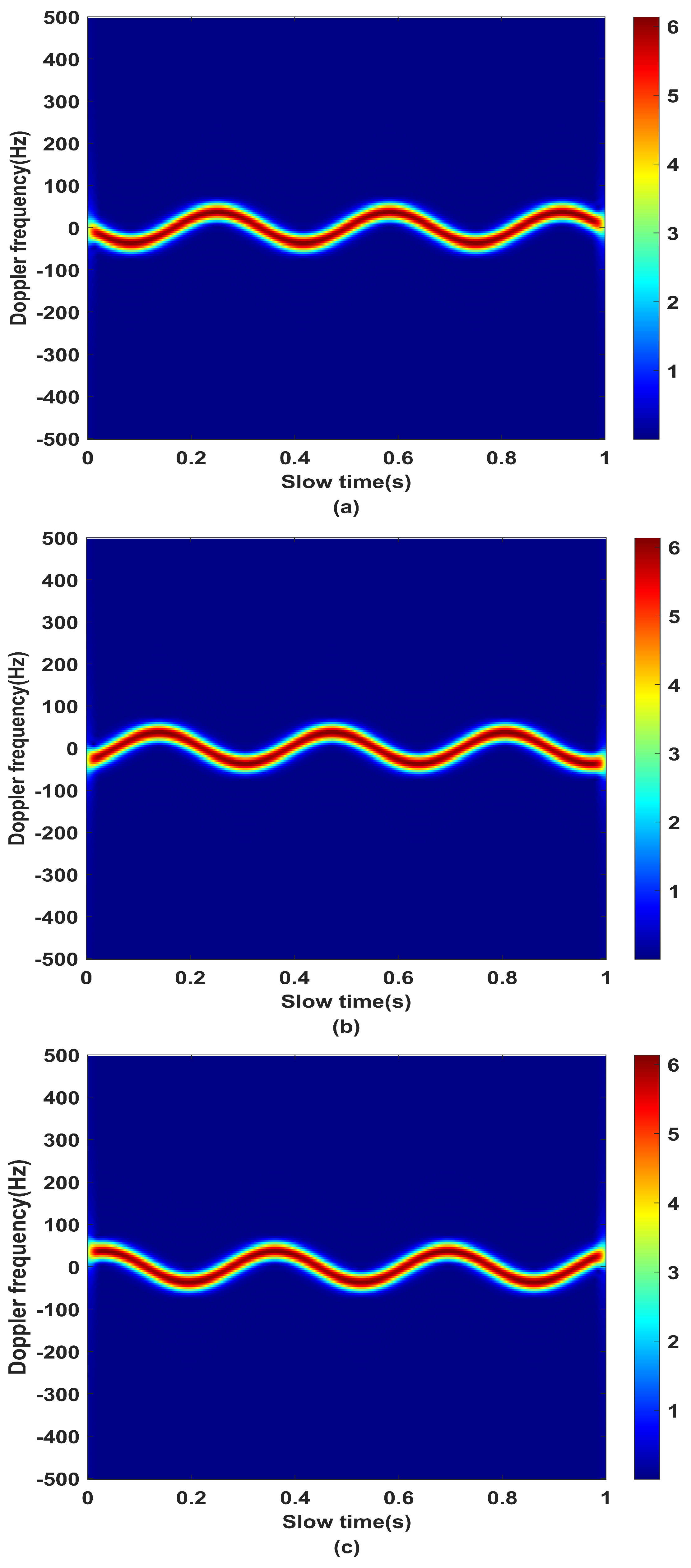
- When the translational component of the target is small or zero, the angular Doppler frequency shift caused by the rotational motion appears as a sinusoidal curve in the TF domain. The angular Doppler shift model at this time can be expressed as
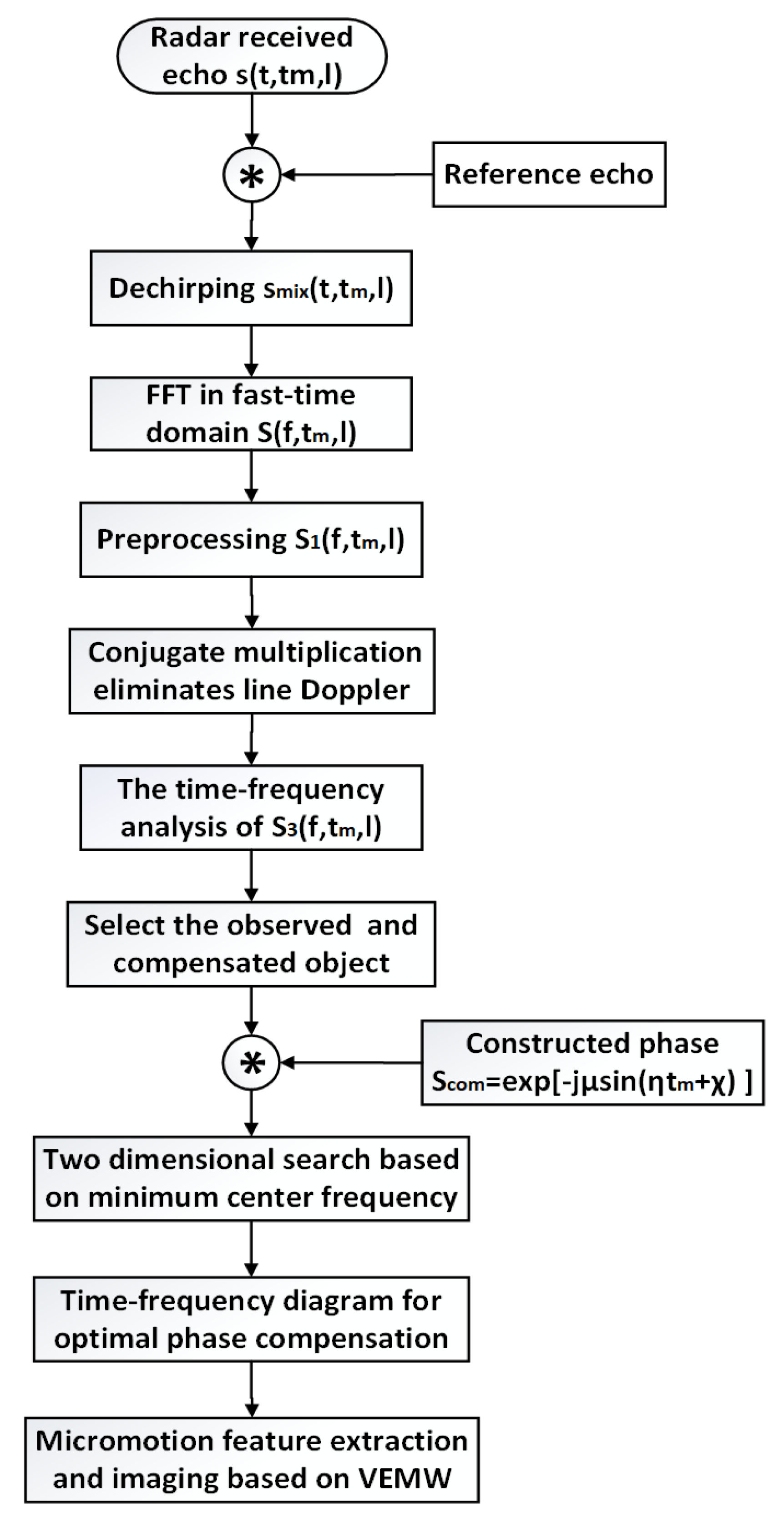
3. Separation of Doppler Effect
3.1. Separation of Line Doppler Effect
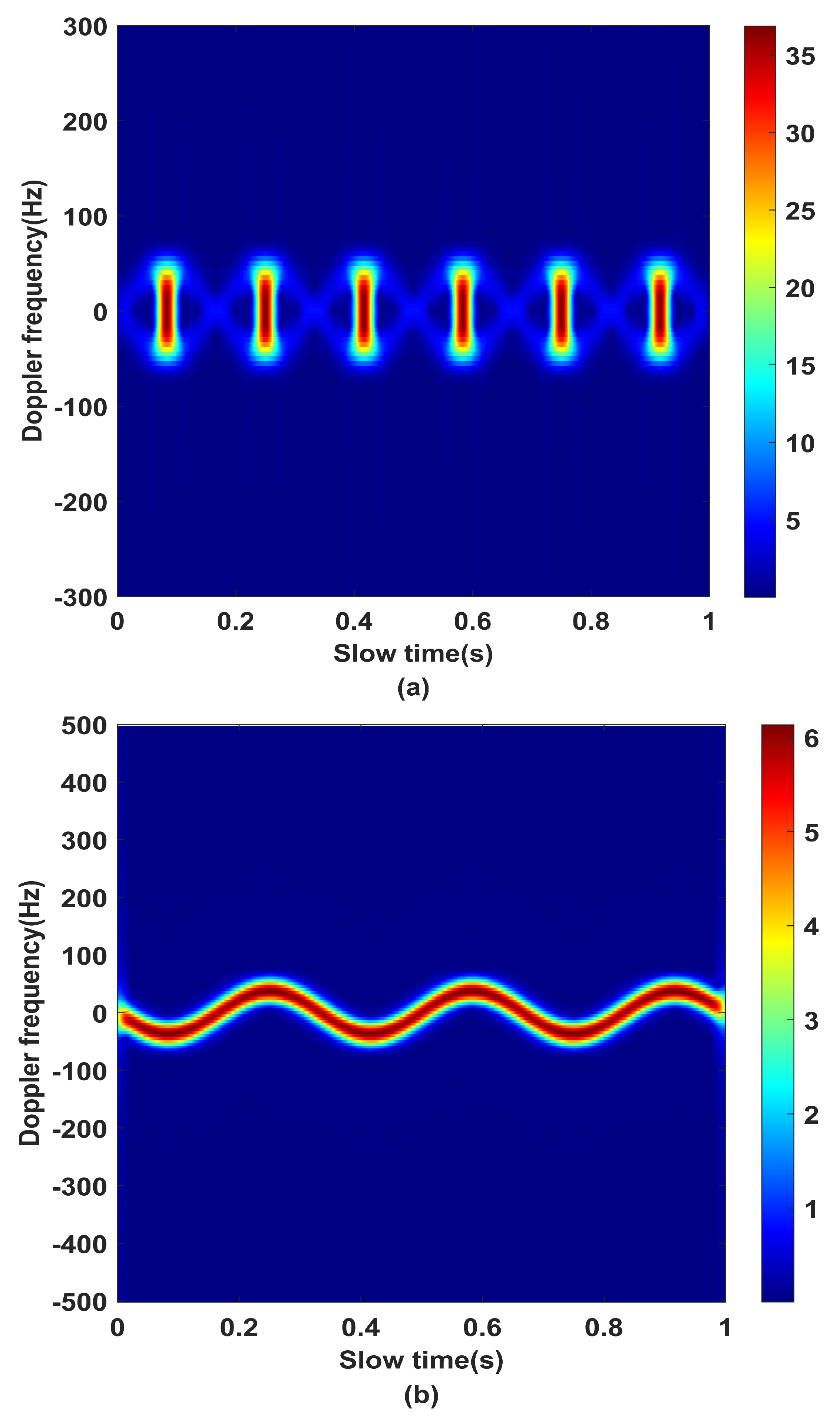
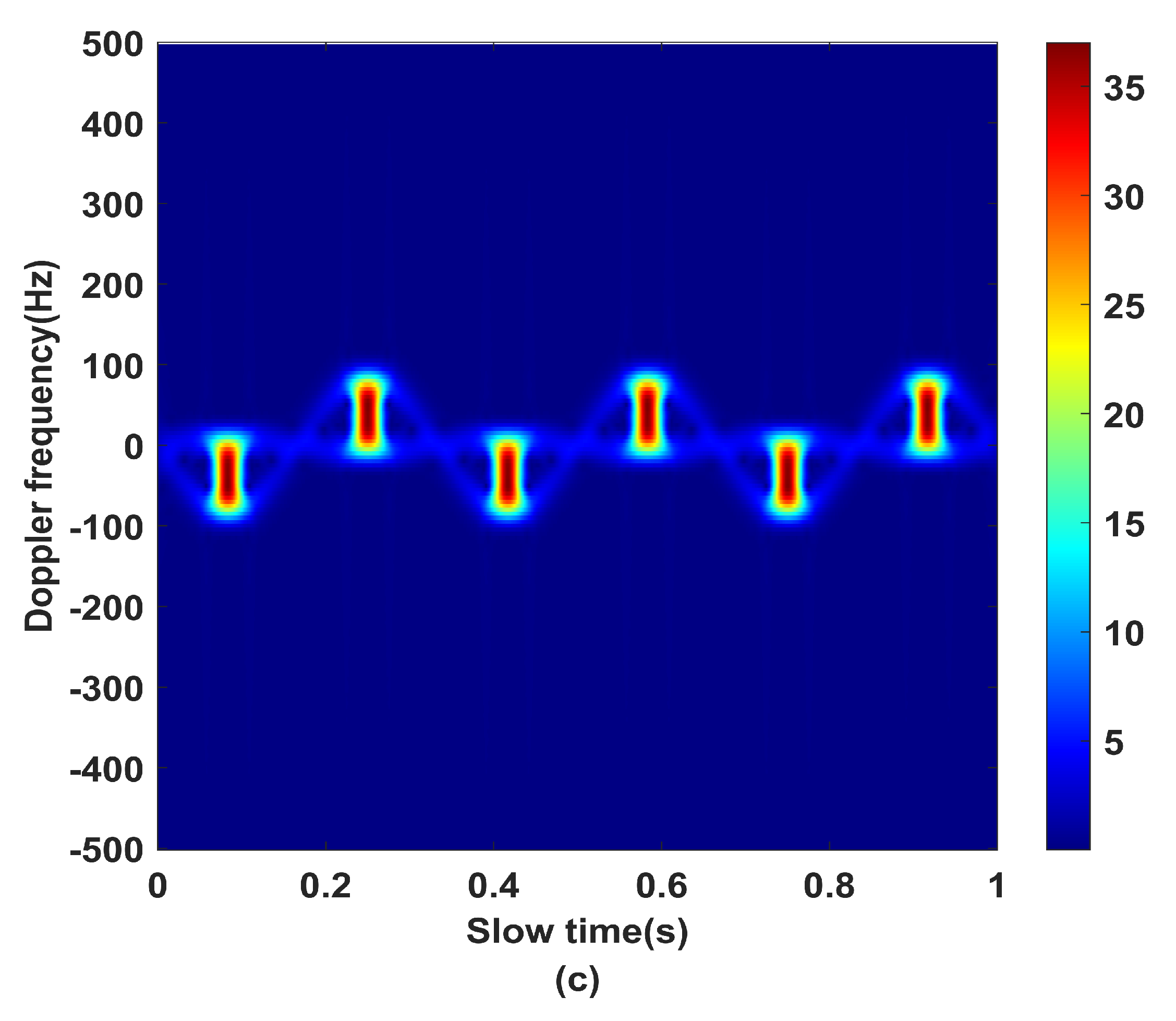
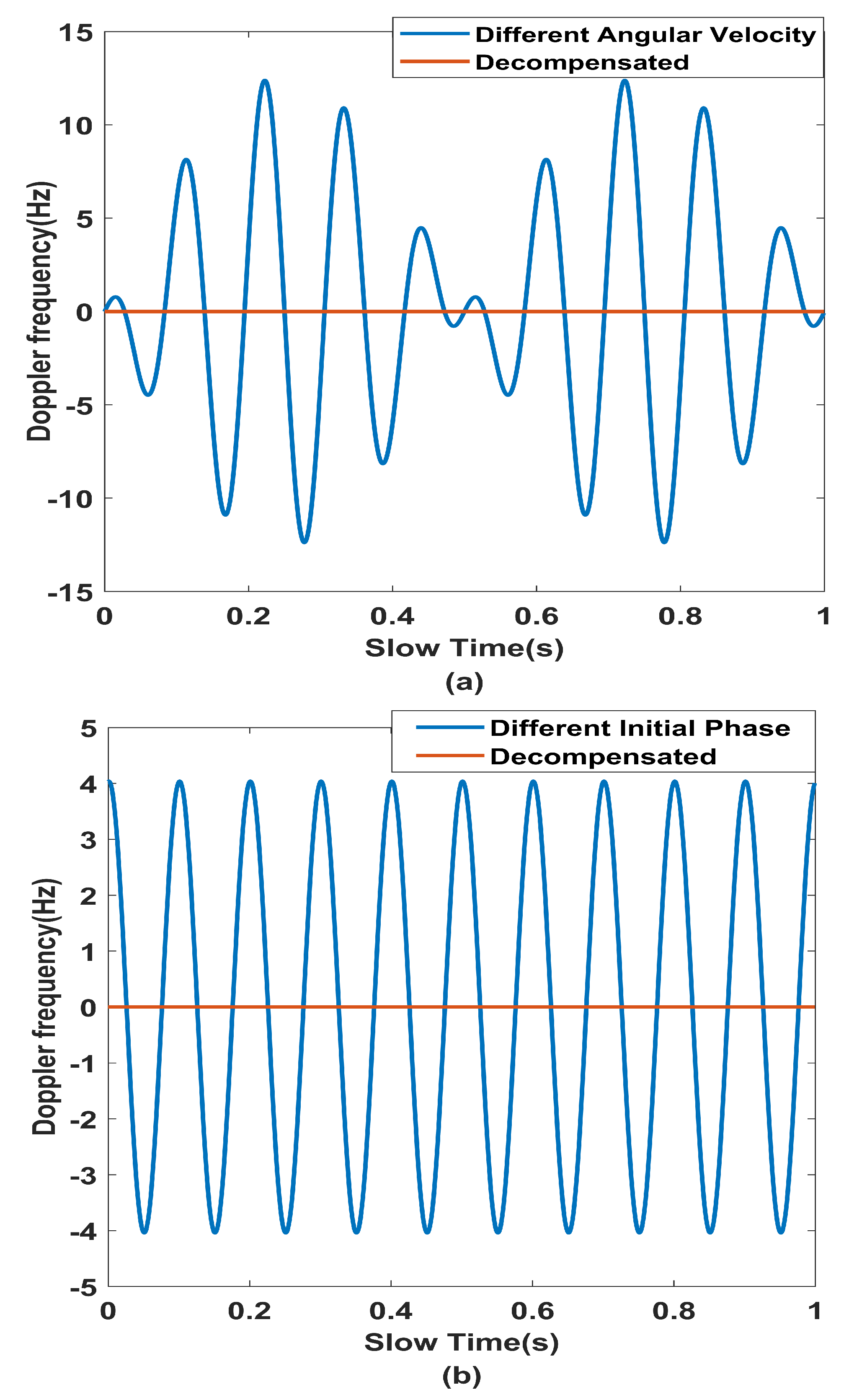
3.2. Separation of Angular Doppler Effect
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
4. Simulation Experiment and Result Analysis
4.1. Simulation Experiment
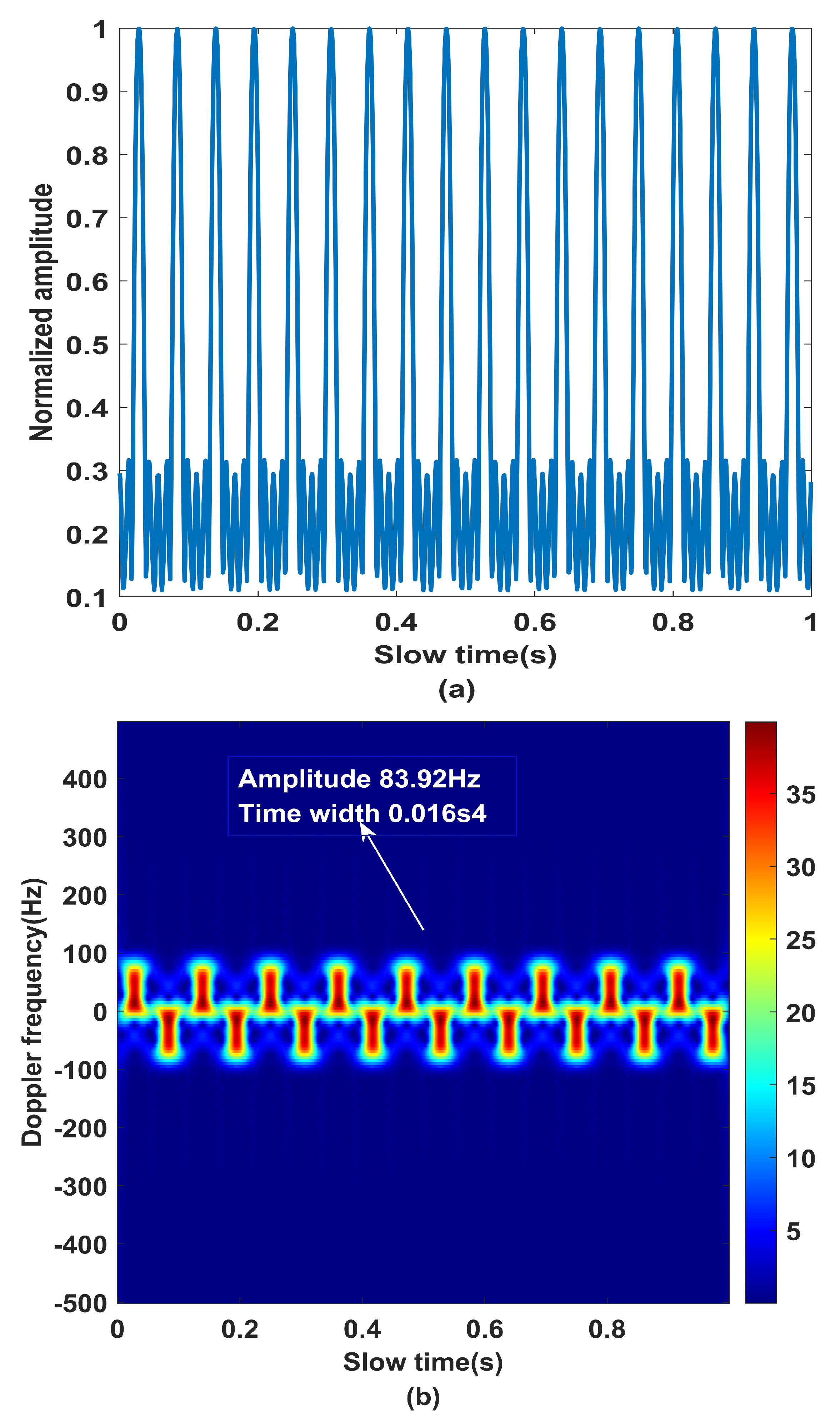
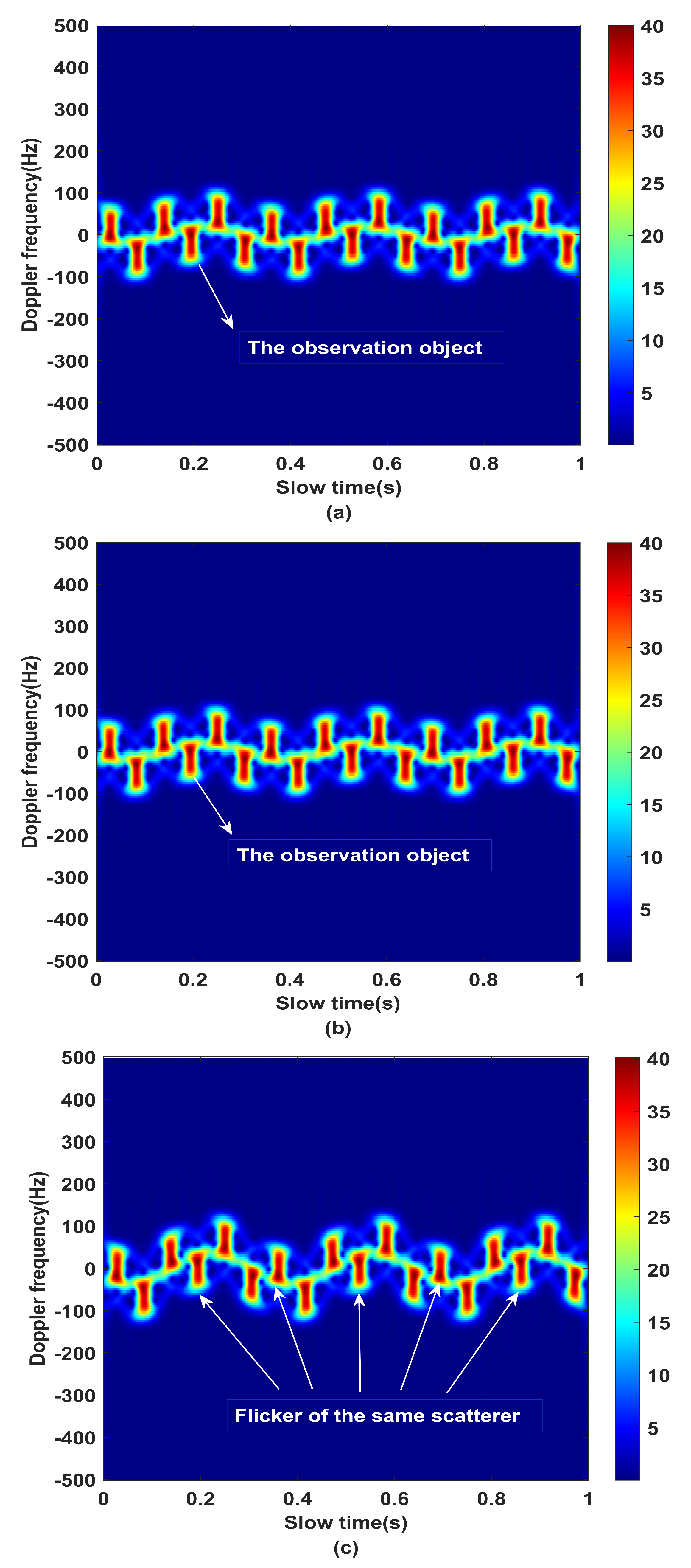
4.2. Effect Analysis of Angular Doppler Separation
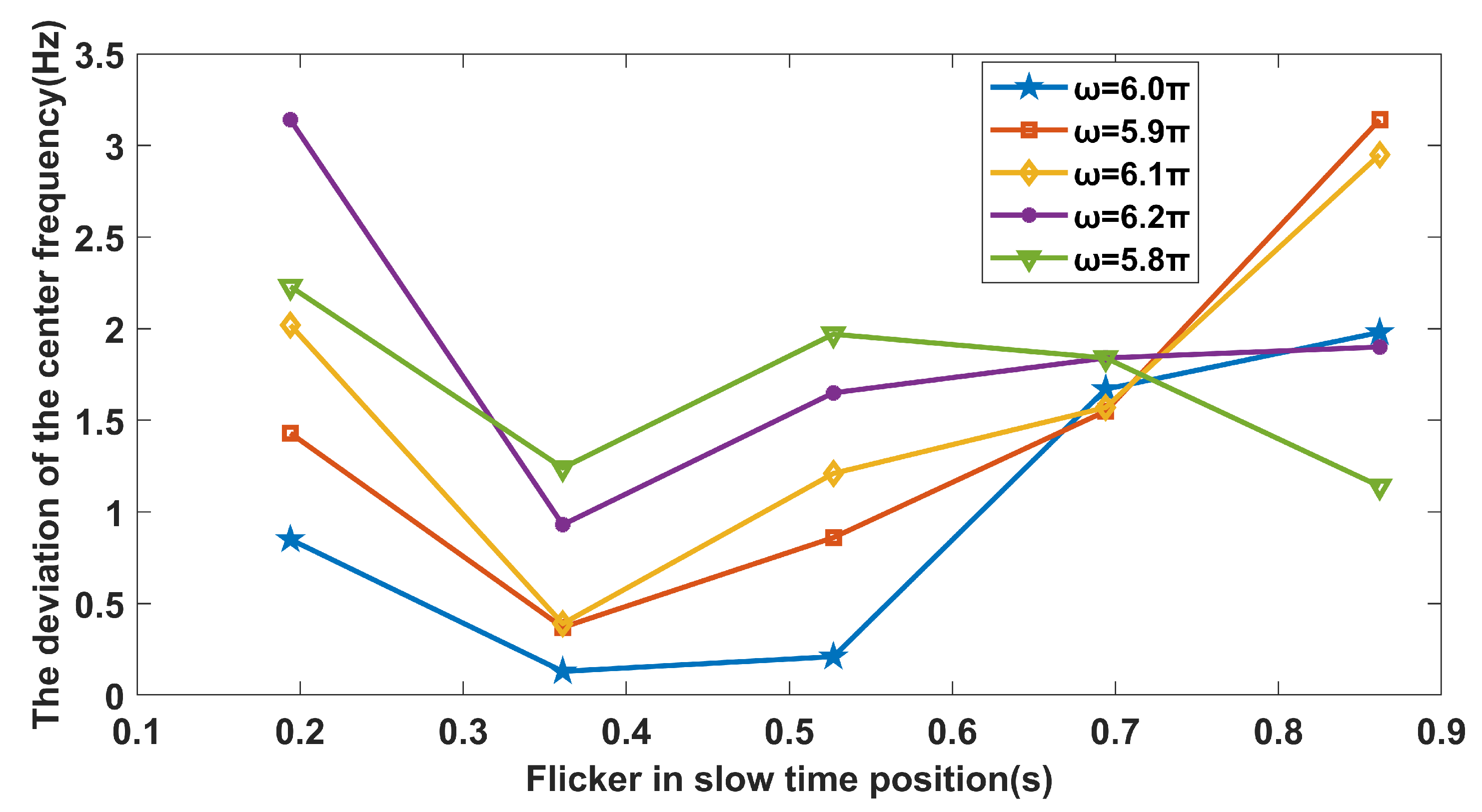
4.3. Parameter Estimation Accuracy Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Li, S.; You, D.; Peng, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z. Targets’ Radial and Tangential Velocities Estimation Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Waves. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, Y. Micro-motion parameter extraction of rotating target based on vortex electromagnetic wave radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, C.; Liang, X.; Zhu, W.; Geng, J.; Jin, R. Multiuser Communication by Electromagnetic Vortex Based on Time-Modulated Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, F.; Mari, E.; Sponselli, A.; Thidé, B.; Bianchini, A.; Romanato, F. Encoding many channels on the same frequency through radio vorticity: First experimental test. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, A.; Weihs, G.; Zeilinger, A. Superpositions of the Orbital Angular Momentum for Applications in Quantum Experiments. J. Opt. B 2002, 4, S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thidé, B.; Then, H.; Sjöholm, J.; Palmer, K.; Bergman, J.; Carozzi, T.; Istomin, Y.N.; Ibragimov, N.; Khamitova, R. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 087701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Three-Dimensional Imaging with Bistatic Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q. Real Micro-Doppler Parameters Extraction of Spinning Targets Based on Rotating Interference Antenna. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, C.; Li, S.; Soonyeo, T. Micro-Doppler feature extraction for wideband imaging radar based on complex image orthogonal matching pursuit decomposition. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013, 7, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Nie, X.; Zhou, J. Laser Doppler velocimeter and its calibration system. Measurement 2019, 134, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Daldorff, L.K.S.; Bergman, J.E.S.; Karlsson, R.L.; Thide, B.; Forozesh, K.; Carozzi, T.D.; Isham, B. Orbital Angular Momentum in Radio-A System Study. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtial, J.; Dholakia, K.; Robertson, D.A.; Allen, L.; Padgett, M.J. Measurement of the Rotational Frequency Shift Imparted to a Rotating Light Beam Possessing Orbital Angular Momentum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3217–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, M.; Speirits, F.C.; Barnett, S.M.; Padgett, M.J. Detection of a Spinning Object Using Light’s Orbital Angular Momentum. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2013, 341, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gao, X.; Xie, M.; Zhai, W.; Xu, W.; Huang, S.; Gu, W. Measurement of the rotational Doppler frequency shift of a spinning object using a radio frequency orbital angular momentum beam. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2549–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X. Rotational Doppler effect based on the radio orbital angular momentum wave. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1298–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Brousseau, C.; Mahdjoubi, K.; Emile, O. Measurement of the rotational sense and velocity of an object using OAM wave in the radio-frequency band. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, X. Detection of Rotational Object in Squint Sight Based on Orbital Angular Momentum. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium-China (ACES), Xiamen, China, 17–20 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Doppler effect and micro-Doppler effect of vortex-electromagnetic-wave-based radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, K.; Guo, Z. Detecting targets’ longitudinal and angular accelerations based on vortex electromagnetic waves. Measurement 2022, 187, 110278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Kang, L.; Jianqiu, W.; Hongqiang, W.; Yongqiang, C. Rotational Doppler detection of a cone-shaped target under the illumination of a vortex electromagnetic wave. J. Radars 2021, 10, 740–748. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, J. Mechanical stress induces a scalable circularly polarized LEO satellite antenna with Quadrifilar spiral. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 2120–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Gao, S. Vortex electromagnetic waves generated by using a laddered spiral phase plate and a microstrip antenna. Electromagnetics 2016, 36, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Yan, Z.; Yi, X.; Yang, S.; Fan, F. An efficient method of generating vortex electromagnetic wave based on double-layer transmissive metasurface. Int. J. Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2020, 30, e22325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, R.Y.; Bai, G.D.; Wu, H.T.; Ma, Q.; Chen, X.Q.; Cui, T.J. Transmission-reflection-integrated multifunctional coding metasurface for full-space controls of electromagnetic waves. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, J.; Luo, Y. Micro-motion feature extraction of spinning target based on angular Doppler effect. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2021, 43, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.; Fan, C.; Yang, J.; Huang, X. Imaging and locating multiple ground moving targets based on keystone transform and FrFT for single channel SAR system. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, China, 26–30 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 771–774. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, K.; Horowitz, R. Repetitive and adaptive control of robot manipulators with velocity estimation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1997, 13, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xia, S.; Xu, D.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, X. Feature extraction of rotor blade targets based on phase compensation in a passive bistatic radar. J. Radars 2021, 10, 929–943. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Center frequency | 10 GHz |
| Pulse width | 80 |
| Bandwidth | 2 GHz |
| PRF | 5000 Hz |
| Target rotation velocity | 6 rad/s |
| OAM mode l | 30 |
| Center of rotation | (200 m, 6/30 rad, /3 rad) |
| The radius of UCA | 0.5 m |
| Radius of rotation | 0.5 m |
| Parameters | Real Value | Estimated Value | Evaluated Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scattering points n | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Angular velocity | 6 | 6.12 | 2.17% |
| Initial phase | 1.0472 rad | 1.07 rad | 2.18% |
| Radius of rotation | 0.5 m | 0.5103 m | 2.06% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, Y.; Zang, Y. Micro-Motion Parameter Extraction of Multi-Scattering-Point Target Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235908
Bu L, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Song X, Yang Y, Zang Y. Micro-Motion Parameter Extraction of Multi-Scattering-Point Target Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235908
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Lijun, Yongzhong Zhu, Yijun Chen, Xiaoou Song, Yufei Yang, and Yadan Zang. 2022. "Micro-Motion Parameter Extraction of Multi-Scattering-Point Target Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235908
APA StyleBu, L., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., Song, X., Yang, Y., & Zang, Y. (2022). Micro-Motion Parameter Extraction of Multi-Scattering-Point Target Based on Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14235908




