Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodologies
2.1. PPP-B2b Orbit Recovery
2.2. PPP-B2b Clock Recovery
2.3. Orbit and Clock Evaluation Methods
2.4. Mathematical Model of Real-Time Single-/Dual-Frequency PPP
2.4.1. Dual-Frequency PPP
2.4.2. Single-Frequency Model
2.4.3. Parameter Modeling and Estimation
3. Experiments and Discussions
3.1. Static Data Collection
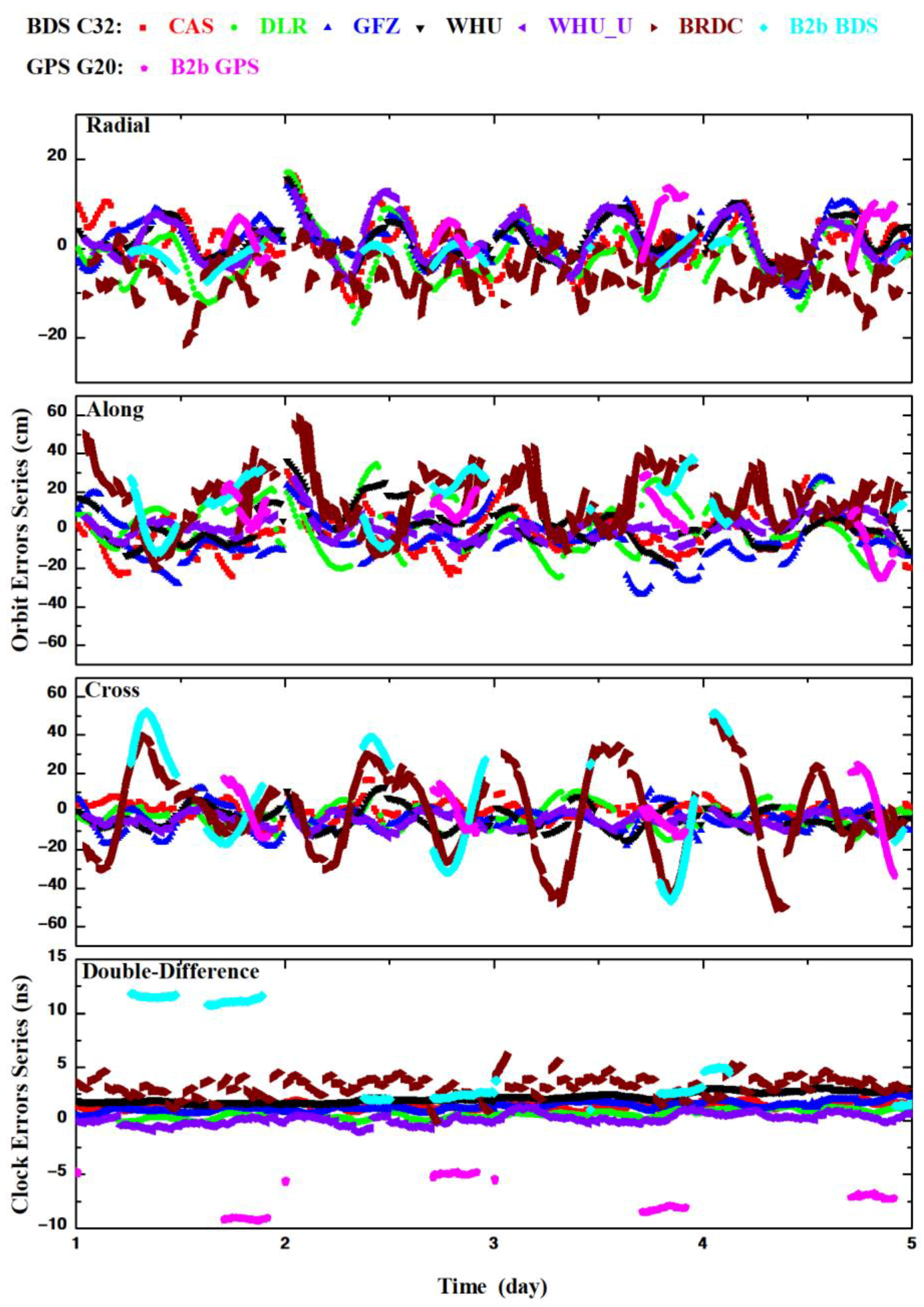
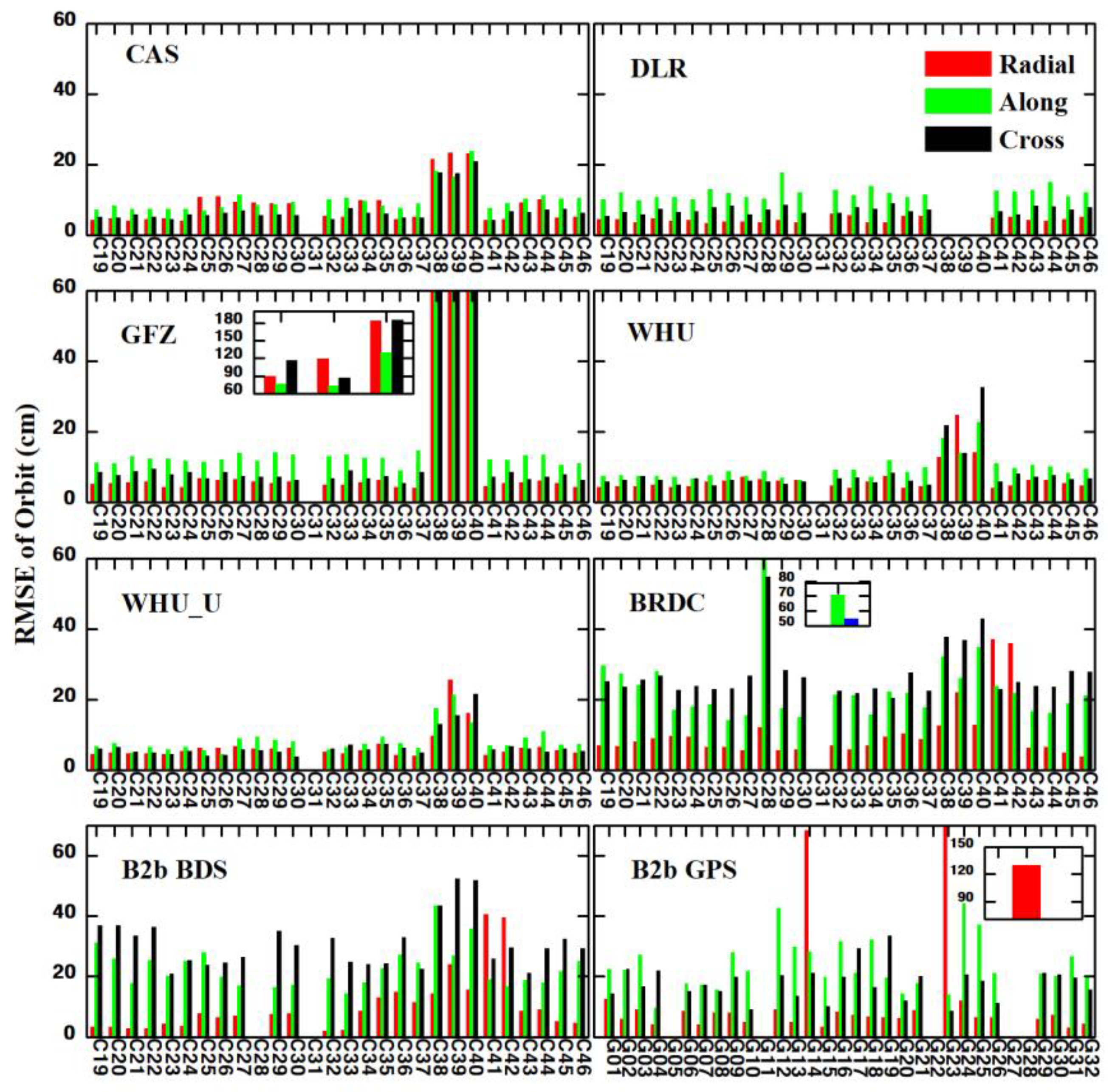
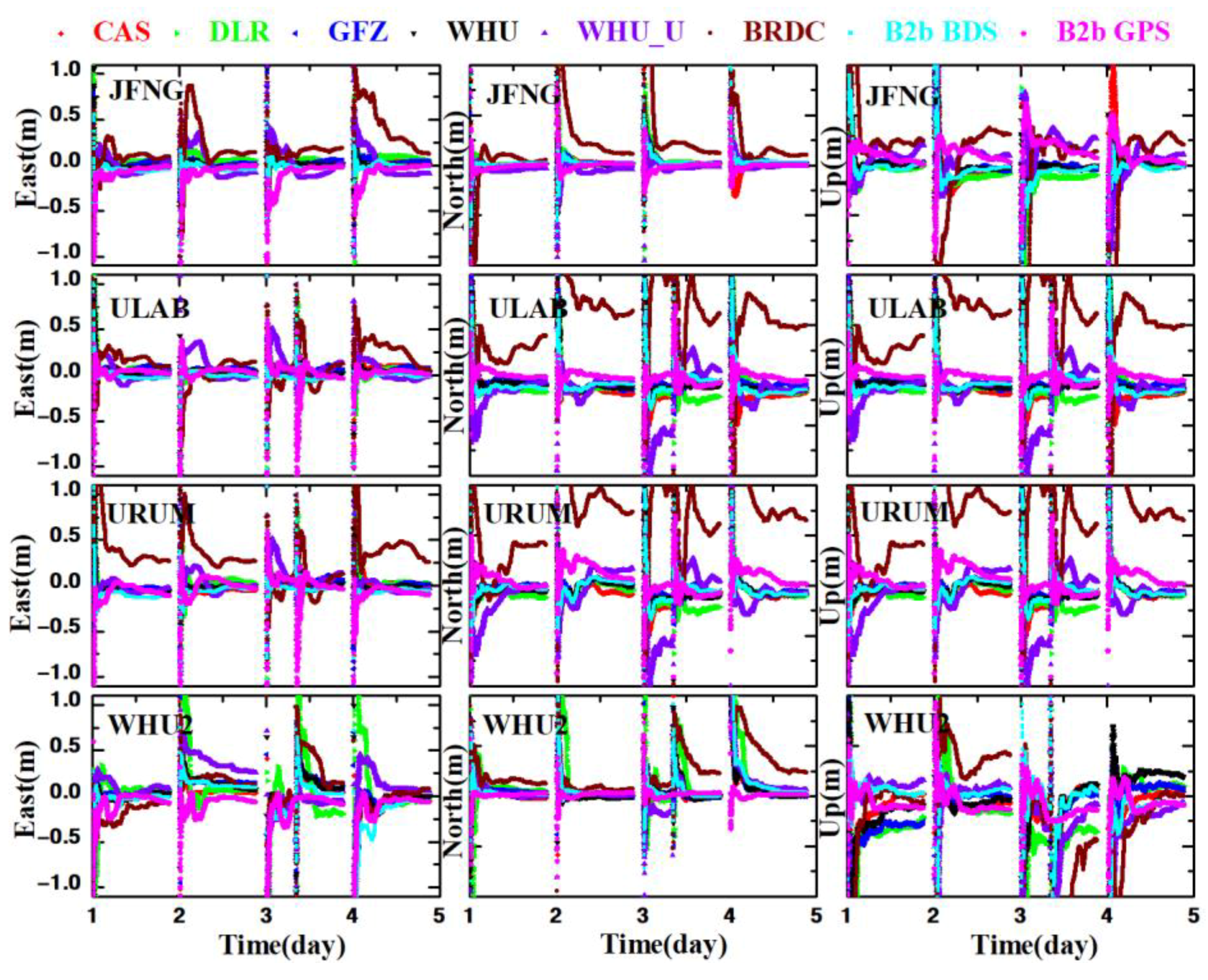
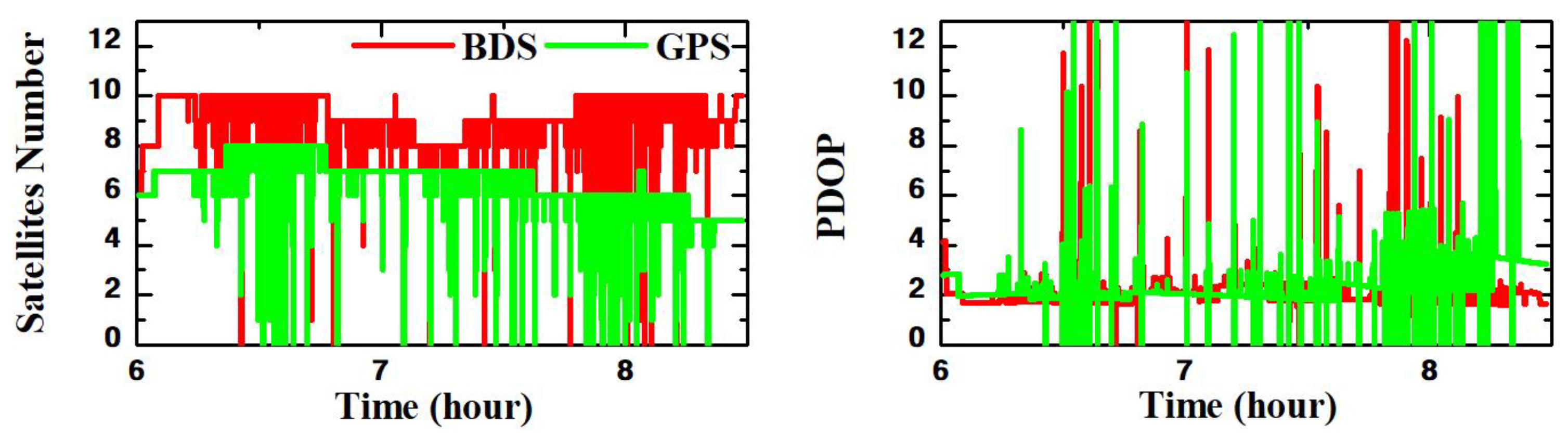
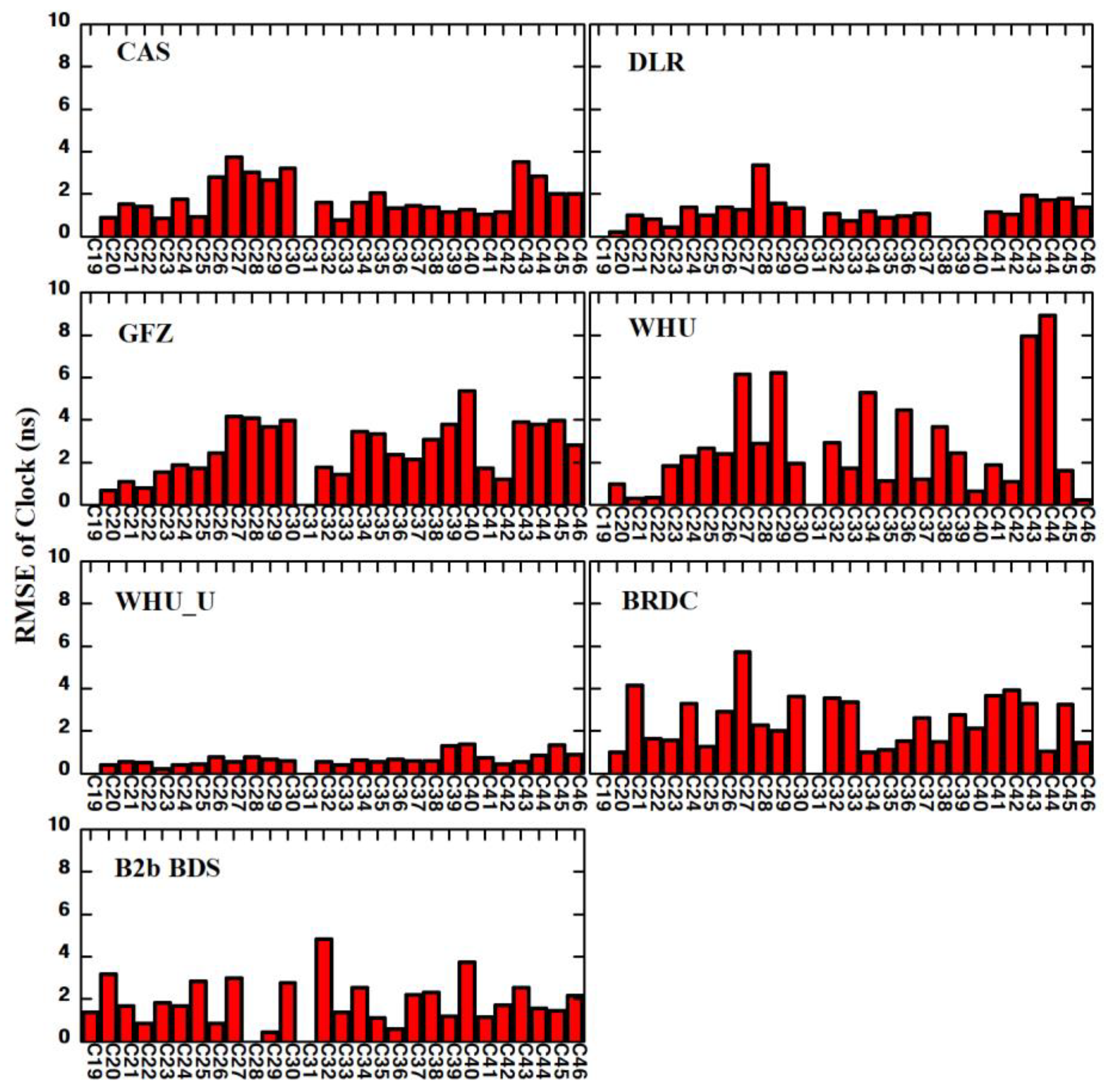
3.2. Assessments of BDS-3 Real-Time Orbits and Clock Products
3.3. Accuracy and Convergence of RT-PPP in MGEX Stations
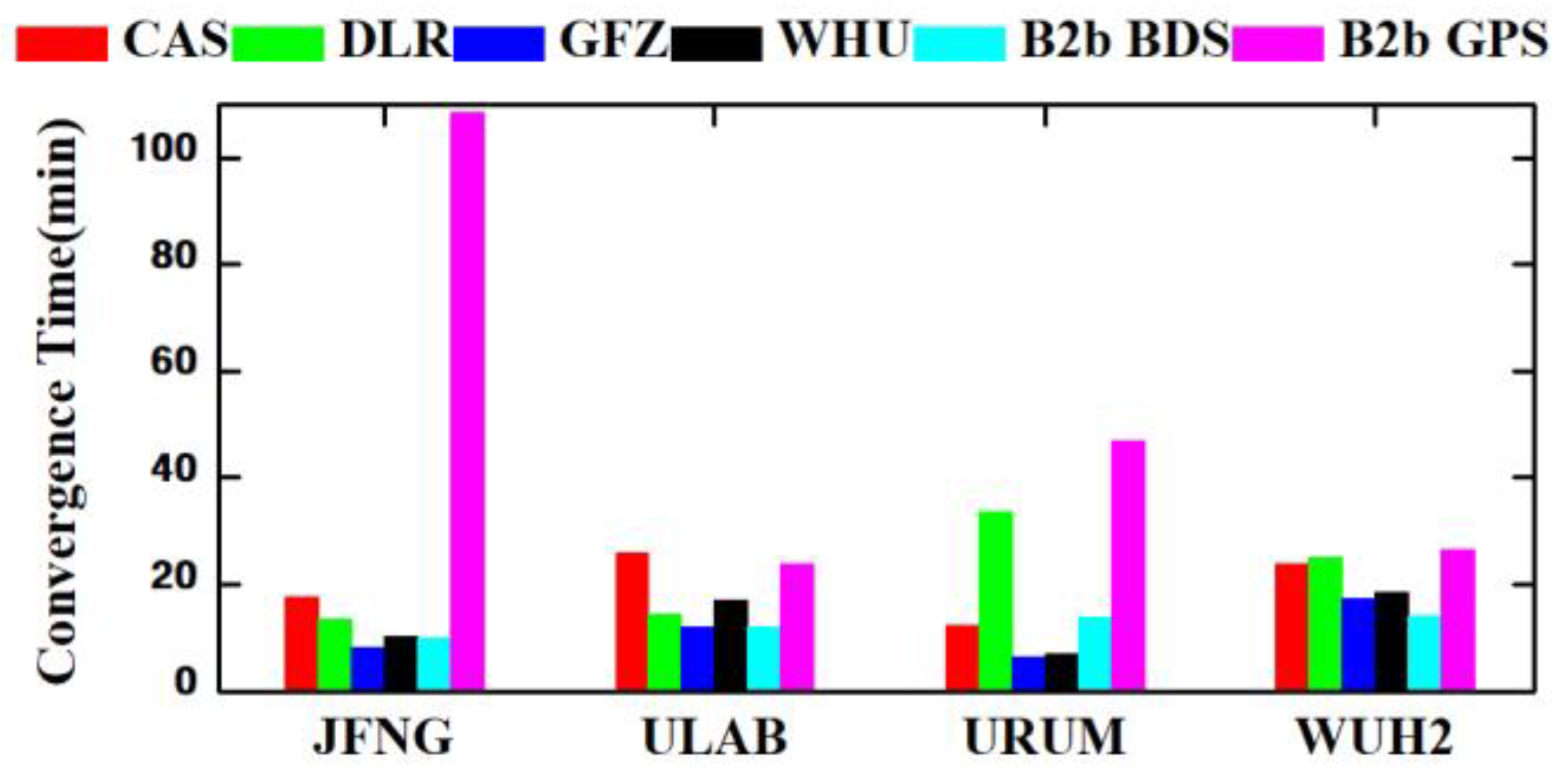
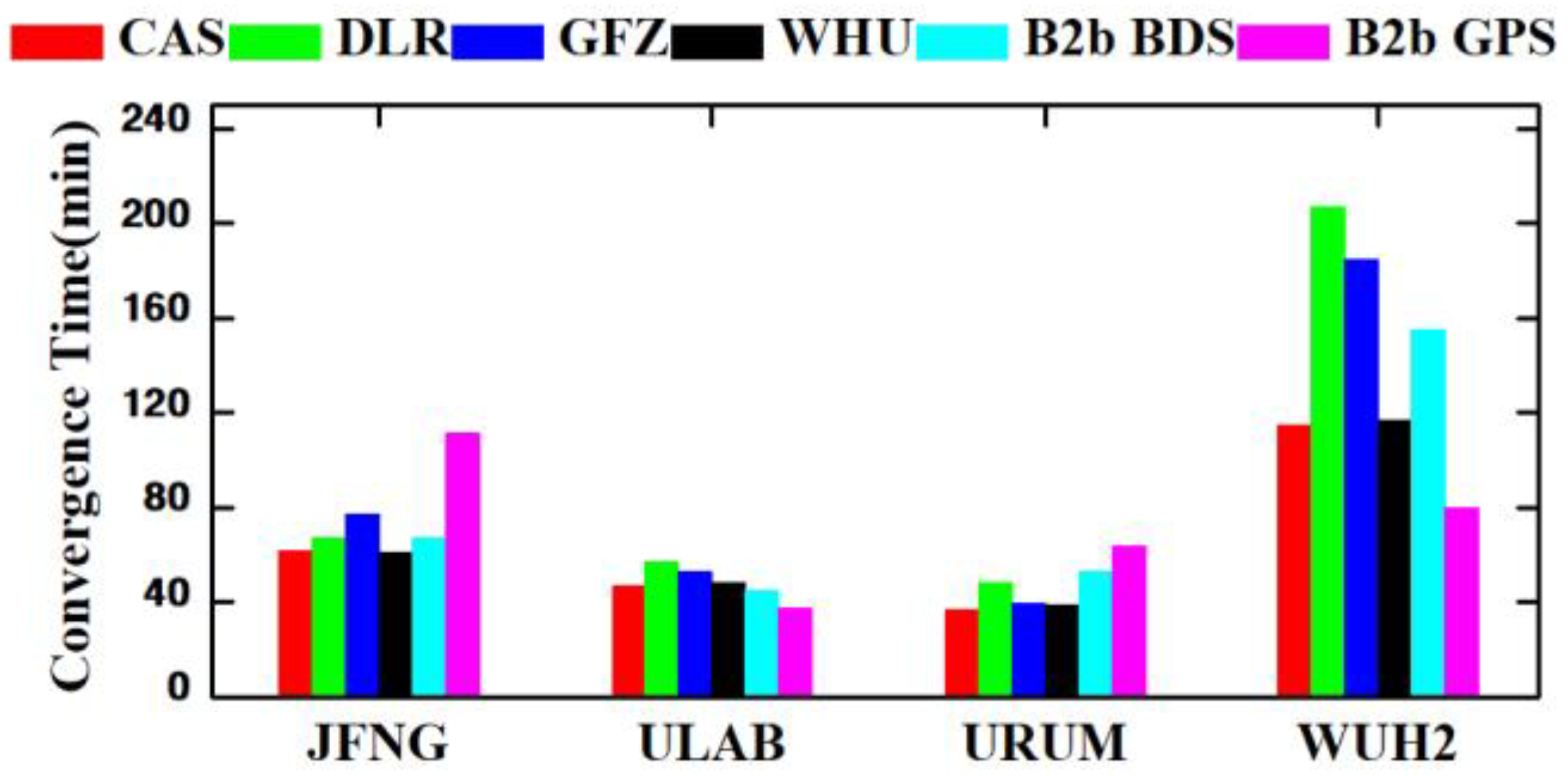
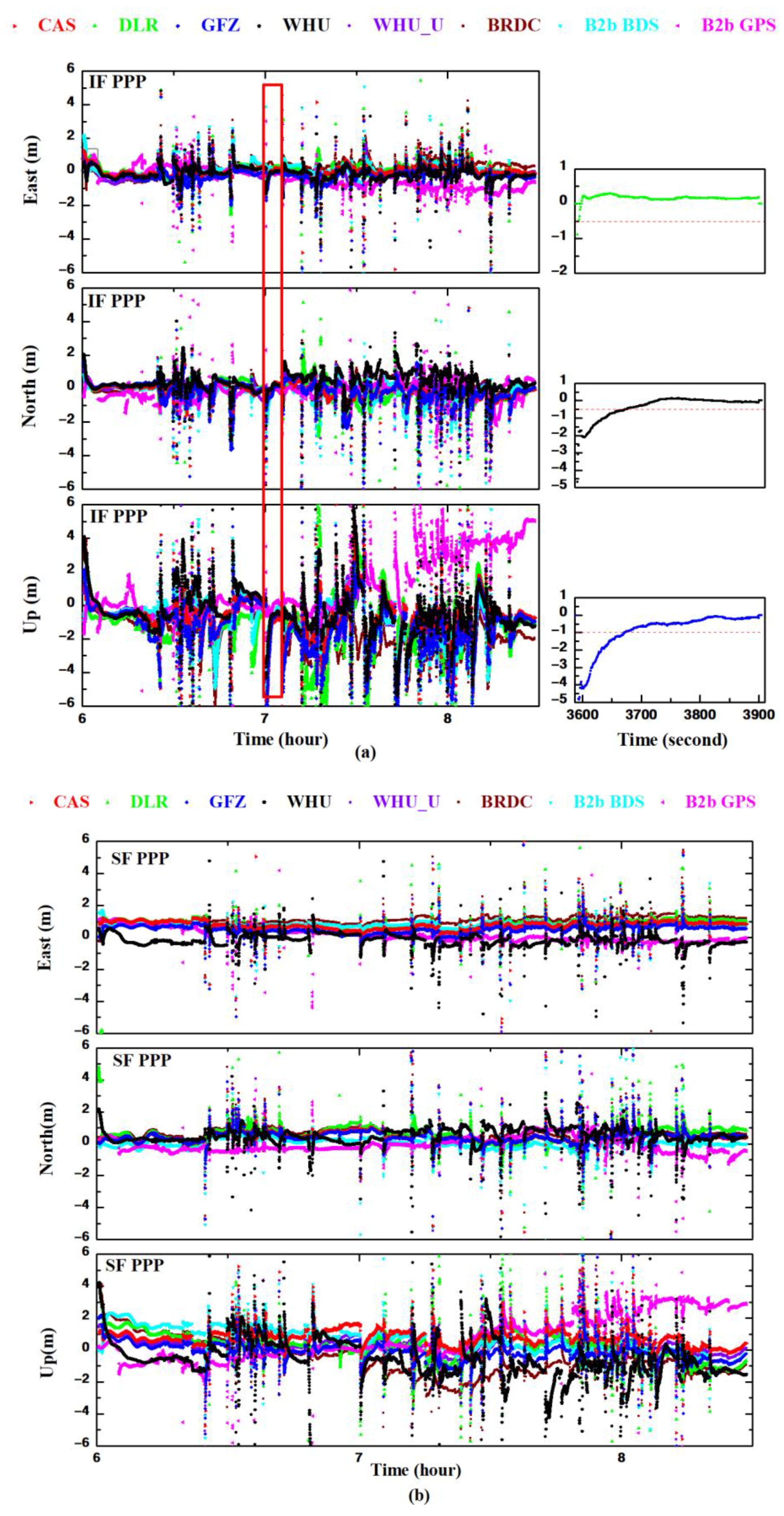
3.3.1. Dual-Frequency PPP
3.3.2. Single-Frequency PPP
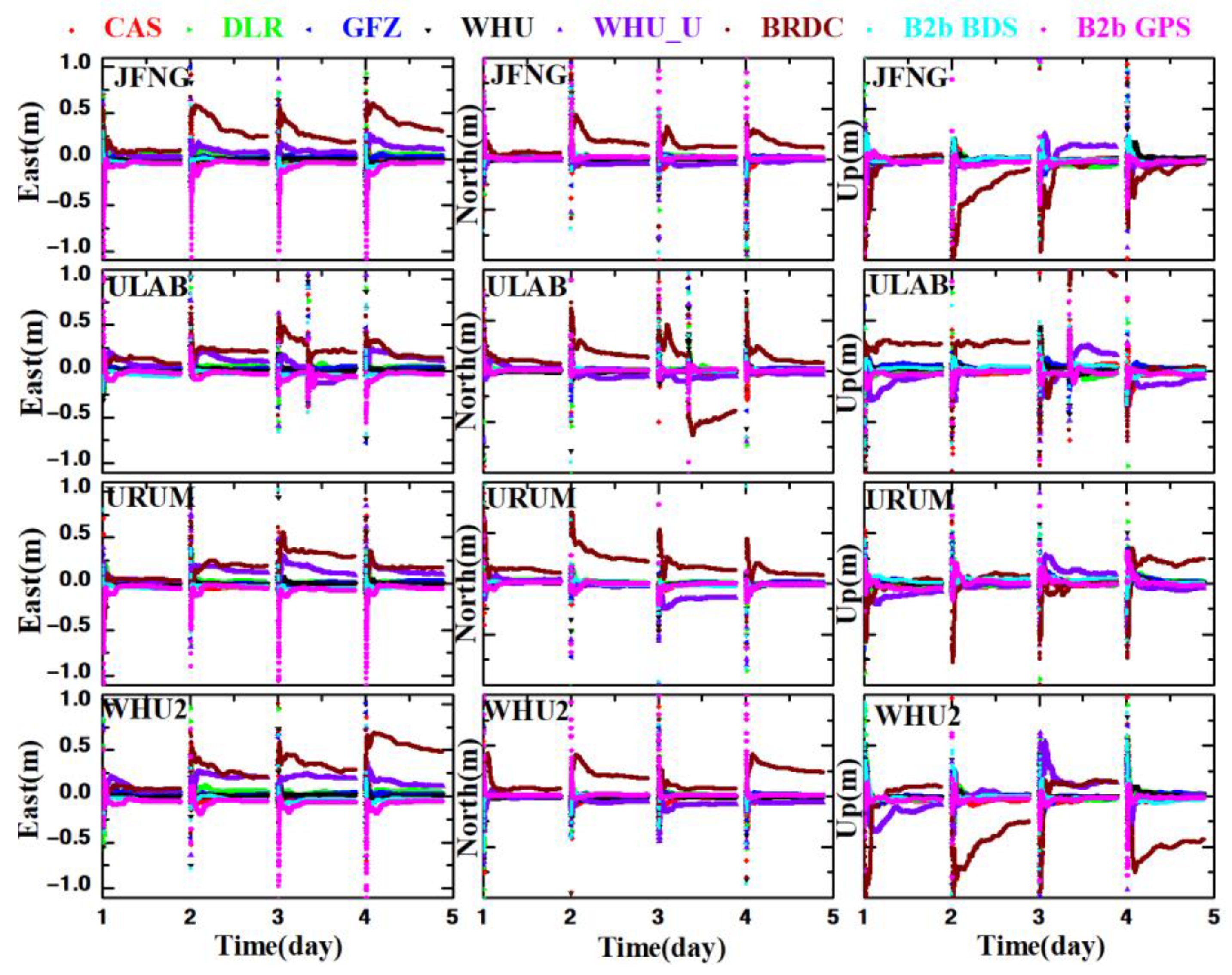
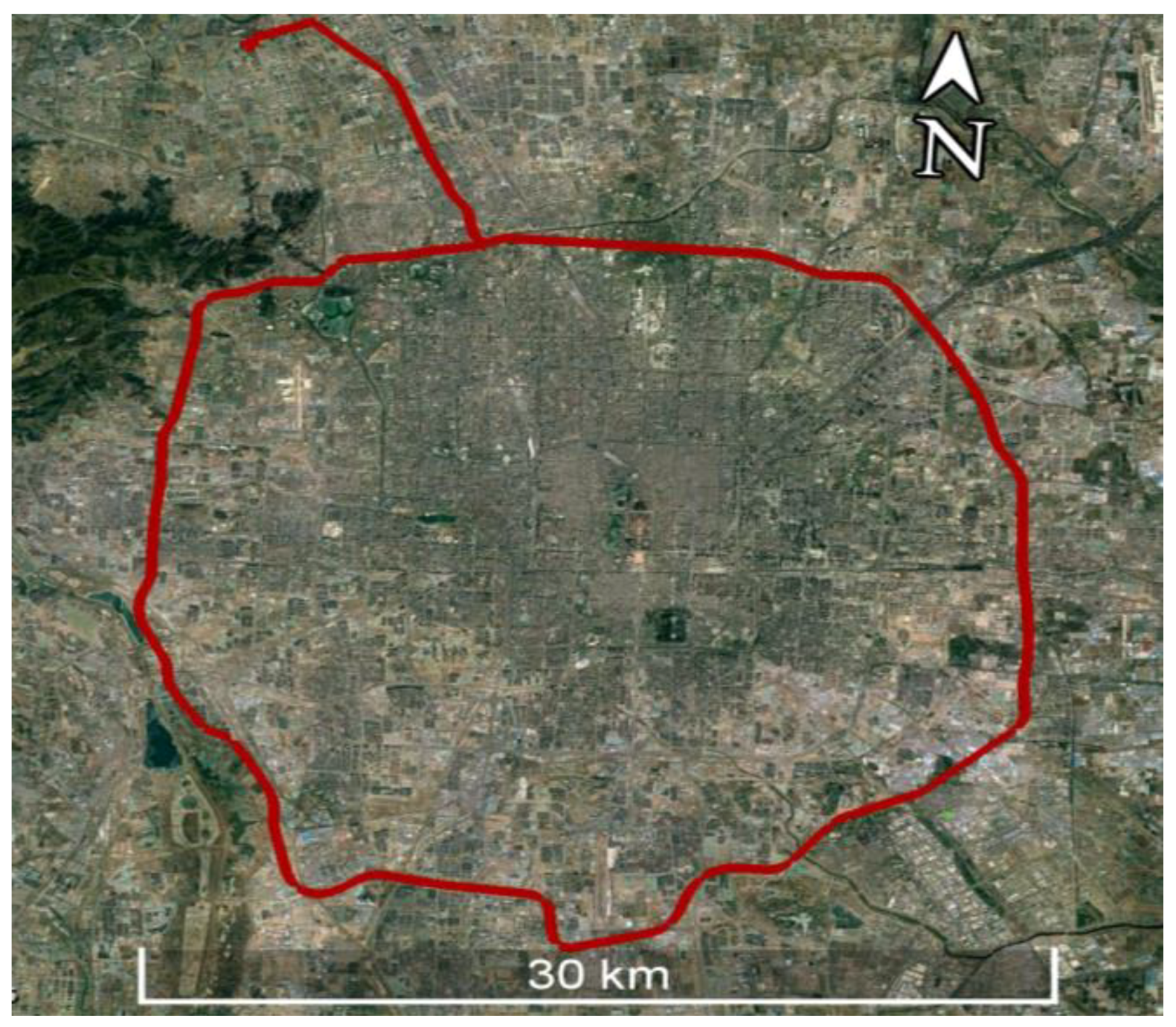
3.4. Accuracy of Real-Time Vehicle-Borne PPP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Resilient PNT concept frame. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shen, X. A New Method for Carrier-Phase-Based Precise Point Positioning. Navigation 2002, 49, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.A.-T. Precise Point Positioning using Un-Differenced Code and Carrier Phase Observations; University of Calgary: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2005; Volume 69, Available online: https://www.collectionscanada.gc.ca/obj/thesescanada/vol2/002/NR37676.PDF?is_thesis=1&oclc_number=302053384 (accessed on 17 October 2022).
- Dow, J.M.; Neilan, R.E.; Rizos, C. The international GNSS service in a changing landscape of global navigation satellite systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogutcu, S. Performance assessment of IGS combined/JPL individual rapid and ultra-rapid products: Consideration of Precise Point Positioning technique. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-W.; Chiang, Y.-T.; Chang, F.-R.; Wang, H.-S. Toward real-time precise point positioning: Differential GPS based on IGS ultra rapid product. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–21 August 2010; pp. 355–358.
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, C. Performance of real-time precise point positioning. Mar. Geod. 2013, 36, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Hugentobler, U.; Chen, J.; Selmke, I.; Wang, J. Prediction versus real-time orbit determination for GNSS satellites. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W. Performance assessment of real-time multi-GNSS integrated PPP with uncombined and ionospheric-free combined observables. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caissy, M.; Agrotis, L.; Weber, G.; Fisher, S. The IGS real-time service. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2013; p. EGU2013-11168. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, G.; Mervart, L.; Lukes, Z.; Rocken, C.; Dousa, J. Real-time clock and orbit corrections for improved point positioning via NTRIP. In Proceedings of the 20th international technical meeting of the satellite division of the institute of navigation (ION GNSS 2007), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 25–28 September 2007; pp. 1992–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Elsobeiey, M.; Al-Harbi, S. Performance of real-time Precise Point Positioning using IGS real-time service. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; He, X.; Wu, M. Analysis of static and dynamic real-time precise point positioning and precision based on SSR correction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Ningbo, China, 1–3 August 2016; pp. 2022–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. Assessment of multiple GNSS real-time SSR products from different analysis centers. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.; Shi, J.; Huang, Y.; Guo, J.; Xu, C. Evaluation of BDS-2 real-time orbit and clock corrections from four IGS analysis centers. Measurement 2021, 168, 108441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, T.; Fan, C.; Qin, W.; Zhou, F.; Yang, X. An analysis of BDS-3 real-time PPP: Time transfer, positioning, and tropospheric delay retrieval. Measurement 2021, 172, 108871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Shen, N.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, R. Decoding PPP corrections from BDS B2b signals using a software-defined receiver: An initial performance evaluation. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 7871–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial assessment of BDS PPP-B2b service: Precision of orbit and clock corrections, and PPP performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.; Ju, B. Initial Assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gong, H.; Peng, J.; Tang, C.; Huang, X.; Sun, G. Performance assessment of real-time precise point positioning using BDS PPP-B2b service signal. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 3242–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document: Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0). 2020. Available online: http://en.beidou.gov.cn/SYSTEMS/ICD/202008/P020200803538771492778.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Hadas, T.; Bosy, J. IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Chen, J.; Douša, J.; Gendt, G.; Wickert, J. A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ge, M.; Niu, X.; Shen, W.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Tightly coupled integration of multi-GNSS PPP and MEMS inertial measurement unit data. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W. Multi-constellation GNSS precise point positioning with multi-frequency raw observations and dual-frequency observations of ionospheric-free linear combination. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Timing group delay and differential code bias corrections for BeiDou positioning. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ge, M.; Shen, W.; Zhang, H.; Niu, X. Ionospheric and receiver DCB-constrained multi-GNSS single-frequency PPP integrated with MEMS inertial measurements. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, K. PPP models and performances from single-to quad-frequency BDS observations. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, C.; Odolinski, R.; Liu, T. Functional model modification of precise point positioning considering the time-varying code biases of a receiver. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.; Mervart, L.; Stuerze, A.; Rülke, A.; Stöcker, D. BKG Ntrip Client (BNC), Version 2.12; Mitteilungen des Bundesamtes für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierski, K.; Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K. Evolution of orbit and clock quality for real-time multi-GNSS solutions. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, R. Initial assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system signal-in-space range error. GPS Solut. 2019, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Carrier phase ambiguity resolution for the Global Positioning System applied to geodetic baselines up to 2000 km. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 10187–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M. Comprehensive Analyses of PPP-B2b Performance in China and Surrounding Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
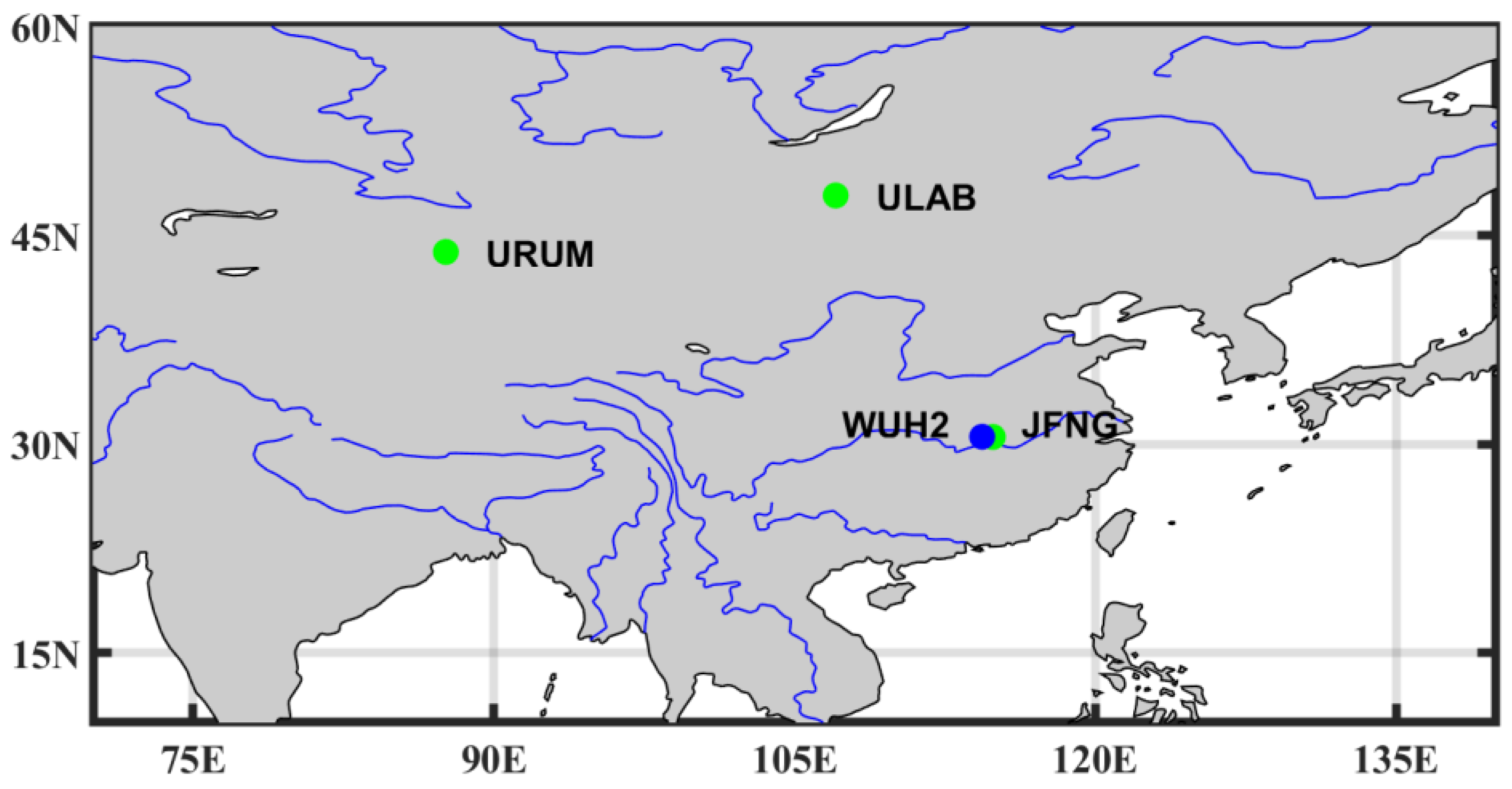


| IGS Center | Orbit | Clock | Code Bias | Phase Bias | VTEC | GNSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKG | 60 s | 5 s | 60 s | 60 s | - | G/R/E |
| CAS | 5 s | 5 s | 10 s | - | 60 s | G/R/E/C |
| CNES | 5 s | 5 s | 5 s | 5 s | 60 s | G/R/E/C |
| DLR | 30 s | 5 s | 30 s | 30 s | - | G/R/E/C/J 1 |
| GFZ | 5 s | 5 s | 5 s | - | - | G/R/E/C |
| WHU | 5 s | 5 s | - | - | - | G/R/E/C |
| Information | Message Type | Sample Rate (s) | Nominal Validity (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite mask | 1 | 48 | - |
| Orbit correction and User range accuracy | 2 | 48 | 96 |
| Differential code bias | 3 | 48 | 86,400 |
| Clock correction | 4 | 6 | 12 |
| Item | Processing Strategies |
|---|---|
| GNSS | BDS-3 and GPS |
| Signal selection of IF PPP | BDS-3: B1I+B3I GPS: L1+L2 |
| Signal selection of SF PPP | BDS-3: B1C GPS: L1 |
| Interval | 30 s |
| Cutoff angle | 10° |
| Weight method | Elevation angle dependent |
| Troposphere | Estimate the wet component |
| Ionospheric | IF PPP: IF combination SF PPP: Estimated |
| PCO/PCV | IGS14.atx |
| Ambiguity | Estimated |
| Adjustment | Sequential least square |
| Satellite DCB | Corrected by DCB products |
| Receiver DCB | IF PPP: IF combination SF PPP: Estimated |
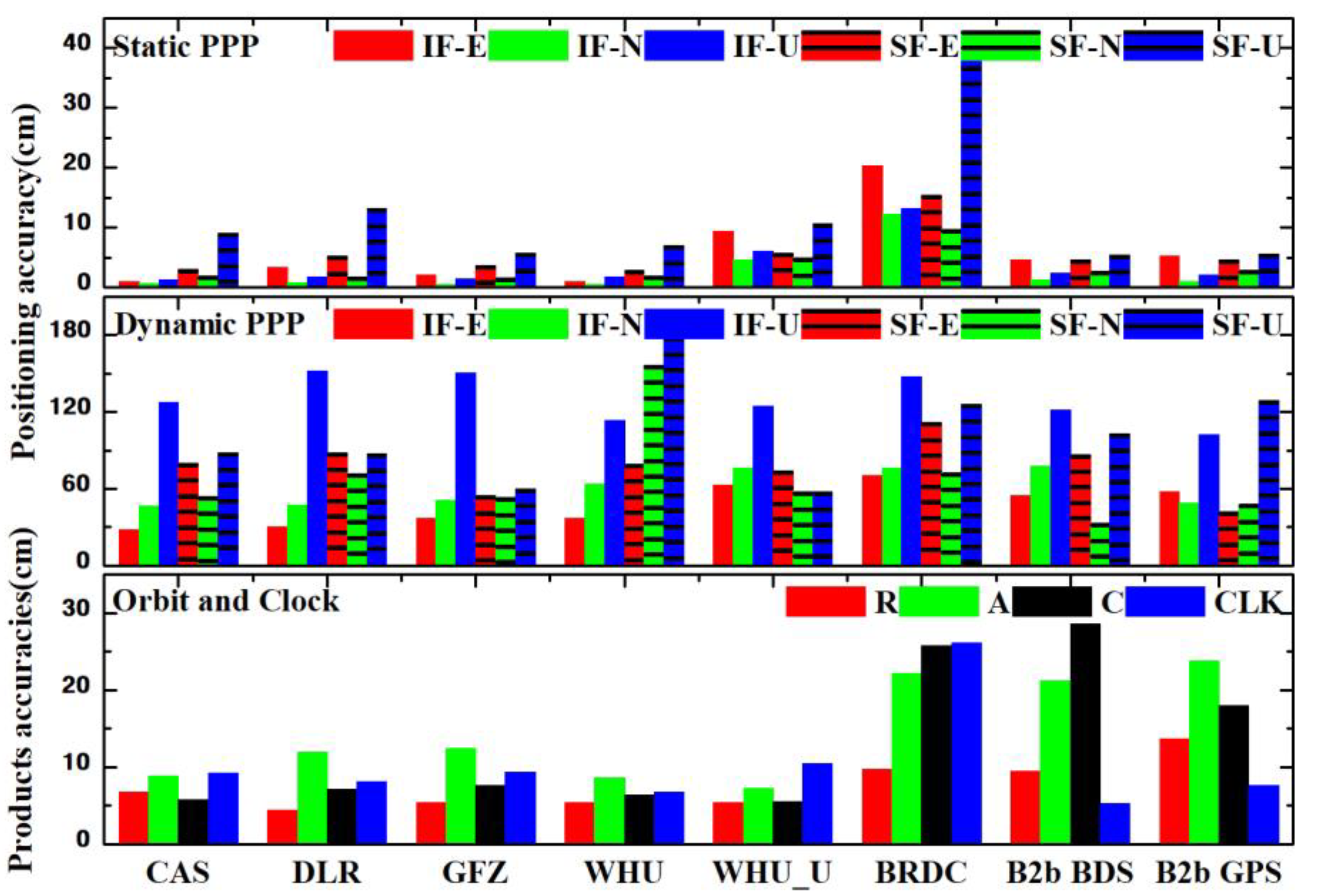
| Products | Orbit (cm) | Clock (ns) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial | Along-Track | Cross-Track | ||
| CAS | 6.73 | 8.82 | 5.79 | 0.31 |
| DLR | 4.37 | 11.95 | 7.08 | 0.27 |
| GFZ | 5.41 | 12.40 | 7.63 | 0.31 |
| WHU | 5.38 | 8.57 | 6.41 | 0.22 |
| WHU_U | 5.39 | 7.25 | 5.54 | 0.35 |
| BRDC | 9.70 | 22.21 | 25.74 | 0.87 |
| B2b BDS | 9.42 | 21.26 | 28.65 | 0.18 |
| B2b GPS | 13.73 | 23.83 | 17.96 | 0.25 |
| Direction | CAS | DLR | GFZ | WHU | WHU_U | BRDC | B2b BDS | B2b GPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
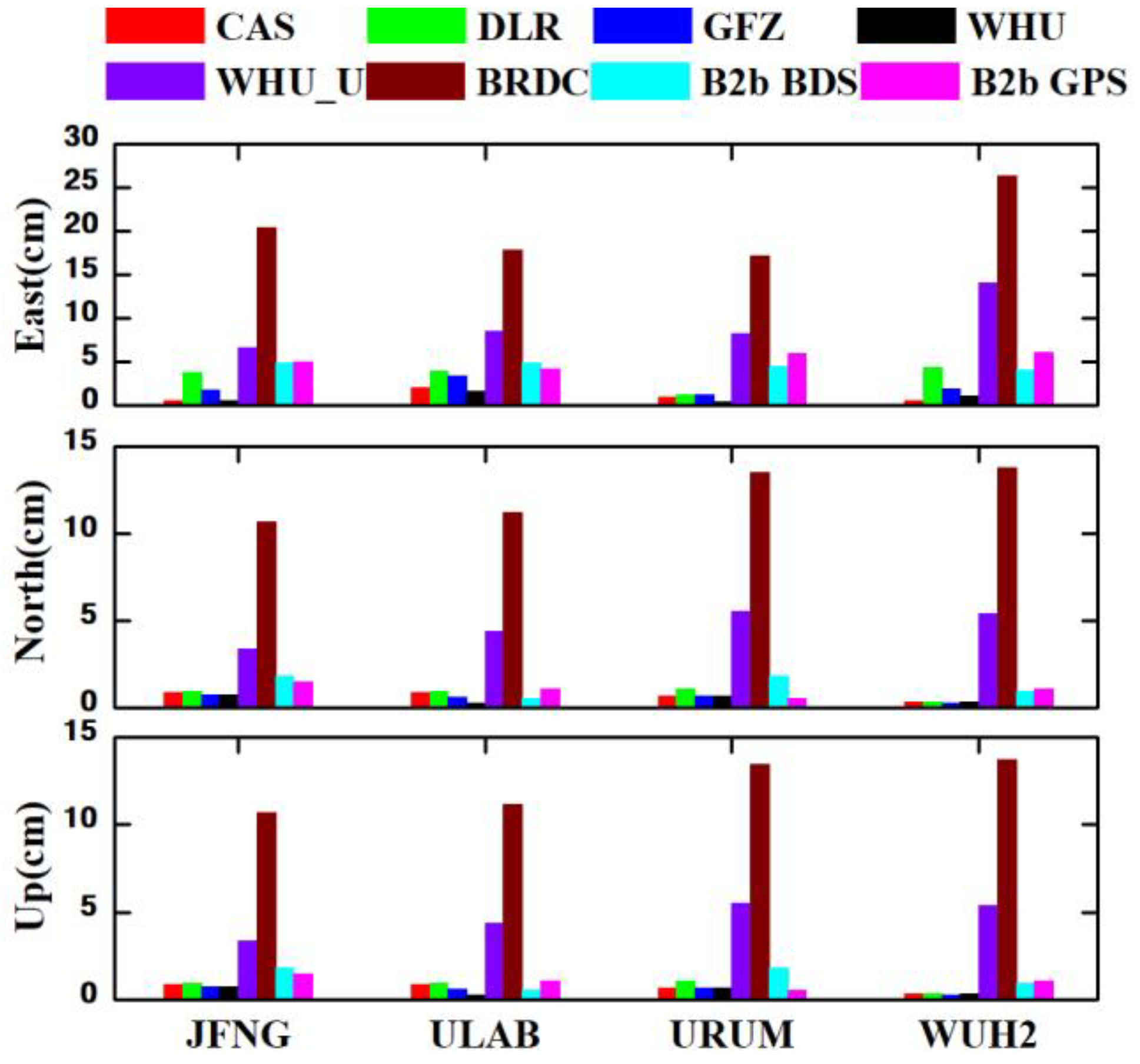
| E | 1.1 | 3.3 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 9.4 | 20.4 | 4.6 | 5.3 |
| N | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 4.7 | 12.3 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| U | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 6.0 | 13.2 | 2.4 | 2.2 |
| 2D | 1.3 | 3.5 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 10.5 | 23.9 | 4.8 | 5.4 |
| 3D | 1.9 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 12.1 | 27.7 | 5.4 | 5.9 |
| Direction | CAS | DLR | GFZ | WHU | WHU_U | BRDC | B2b BDS | B2b GPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 3.0 | 5.2 | 3.7 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 15.5 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| N | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 4.9 | 9.7 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| U | 9.1 | 13.2 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 10.7 | 39.5 | 5.5 | 5.6 |
| 2D | 3.6 | 5.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 7.6 | 18.3 | 5.4 | 5.4 |
| 3D | 9.8 | 14.3 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 13.1 | 43.5 | 7.7 | 7.8 |
| Item | Processing Strategies |
|---|---|
| GNSS | BDS-3 and GPS |
| Signal selection of IF PPP | B1I+B2b GPS: L1+L2 |
| Signal selection of SF PPP | BDS-3: B2b GPS: L1 |
| Interval | 1 s |
| Cutoff angle | 10° |
| Weight method | Elevation angle dependent |
| Troposphere | Estimate the wet component |
| Ionospheric | IF PPP: IF combination SF PPP: Estimated |
| PCO/PCV | IGS14.atx |
| Ambiguity | Estimated |
| Adjustment | Sequential least square |
| Satellite DCB | Corrected by DCB products |
| Receiver DCB | IF PPP: IF combination SF PPP: Estimated |
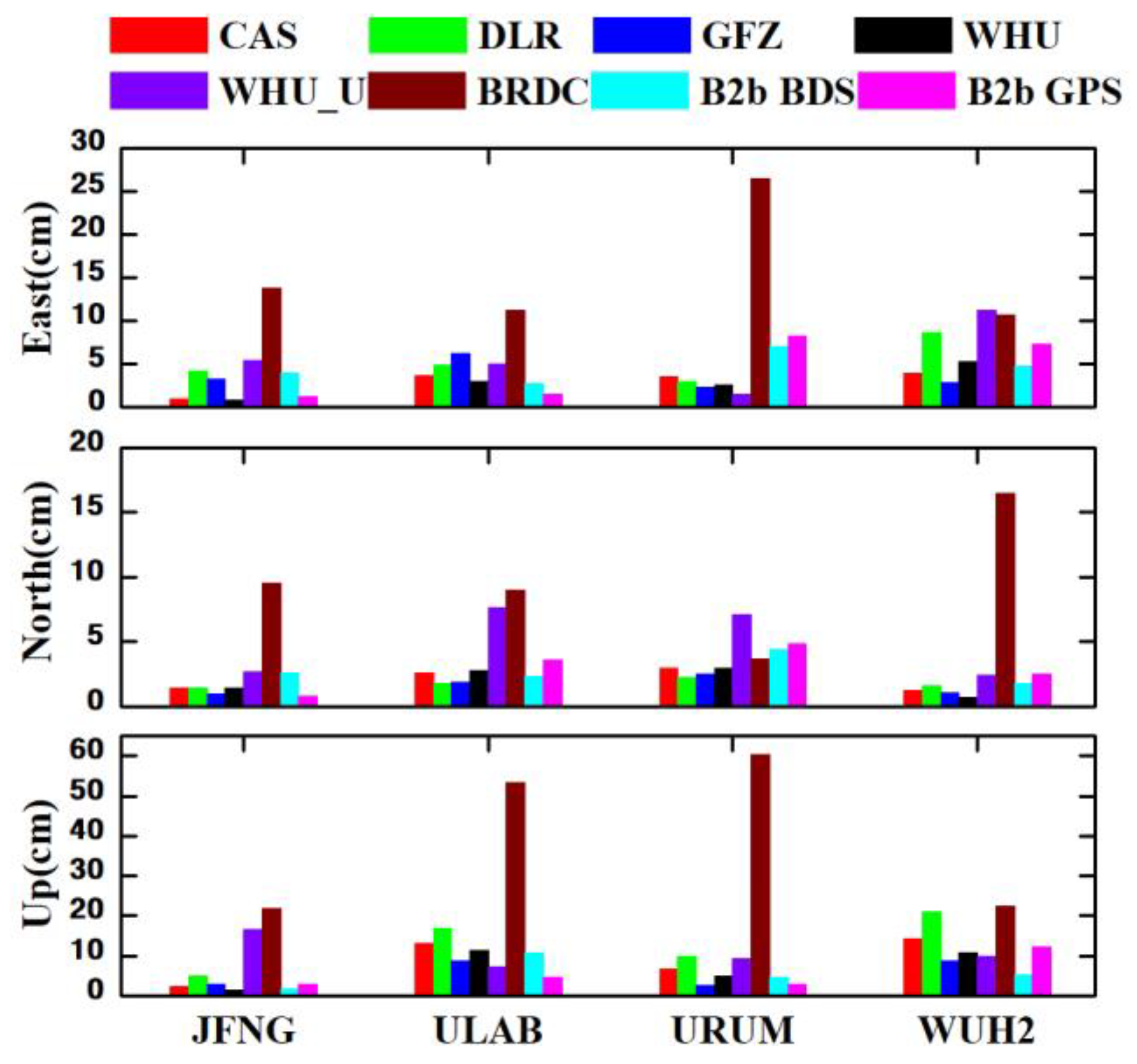
| Direction | CAS | DLR | GFZ | WHU | WHU_U | BRDC | B2b BDS | B2b GPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 27.8 | 33.0 | 35.4 | 34.9 | 35.5 | 49.2 | 35.8 | 57.0 |
| N | 61.9 | 51.8 | 53.9 | 62.1 | 49.7 | 46.1 | 55.0 | 47.9 |
| U | 115.7 | 139.4 | 138.2 | 108.4 | 125.5 | 169.4 | 121.3 | 101.4 |
| 2D | 58.9 | 61.4 | 64.5 | 71.2 | 61.1 | 67.5 | 65.7 | 74.5 |
| 3D | 129.9 | 152.3 | 152.5 | 129.7 | 139.5 | 182.4 | 137.9 | 126.0 |
| Direction | CAS | DLR | GFZ | WHU | WHU_U | BRDC | B2b BDS | B2b GPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 80.0 | 88.6 | 54.3 | 79.4 | 73.9 | 111.8 | 87.1 | 42.3 |
| N | 53.9 | 72.0 | 53.1 | 156.7 | 57.3 | 72.7 | 32.9 | 47.8 |
| U | 88.6 | 87.8 | 60.0 | 178.6 | 57.3 | 126.3 | 103.5 | 129.2 |
| 2D | 96.5 | 114.2 | 75.9 | 175.7 | 93.5 | 133.4 | 93.1 | 63.9 |
| 3D | 131.0 | 144.0 | 96.8 | 250.5 | 109.6 | 183.7 | 139.2 | 144.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, R.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Lv, J.; Gao, Z. Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225835
Lan R, Yang C, Zheng Y, Xu Q, Lv J, Gao Z. Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Ruohua, Cheng Yang, Yanli Zheng, Qiaozhuang Xu, Jie Lv, and Zhouzheng Gao. 2022. "Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225835
APA StyleLan, R., Yang, C., Zheng, Y., Xu, Q., Lv, J., & Gao, Z. (2022). Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225835








