Numerical Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for Understanding Scale-Dependent Topographic Effects Governing Anisotropic Reflectance Correction of Satellite Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Simulate the direct irradiance and conduct a sensitivity analysis based upon the inclusion/exclusion of numerous RTP that are assumed to be significant/insignificant. We evaluate solar geometry, atmospheric attenuation, local topography, and cast shadows, where parameterization schemes are compared based upon different assumptions and parameter dependencies.
- Simulate the diffuse-skylight irradiance and conduct a sensitivity analysis based upon the inclusion/exclusion of numerous RTP that are assumed to be significant/insignificant. We evaluate the isotropic versus anisotropic assumption, the influence of secondary ground reflectance, local topography, and meso-scale relief, where parameterization schemes are compared based upon assumptions and parameter dependencies.
2. Background
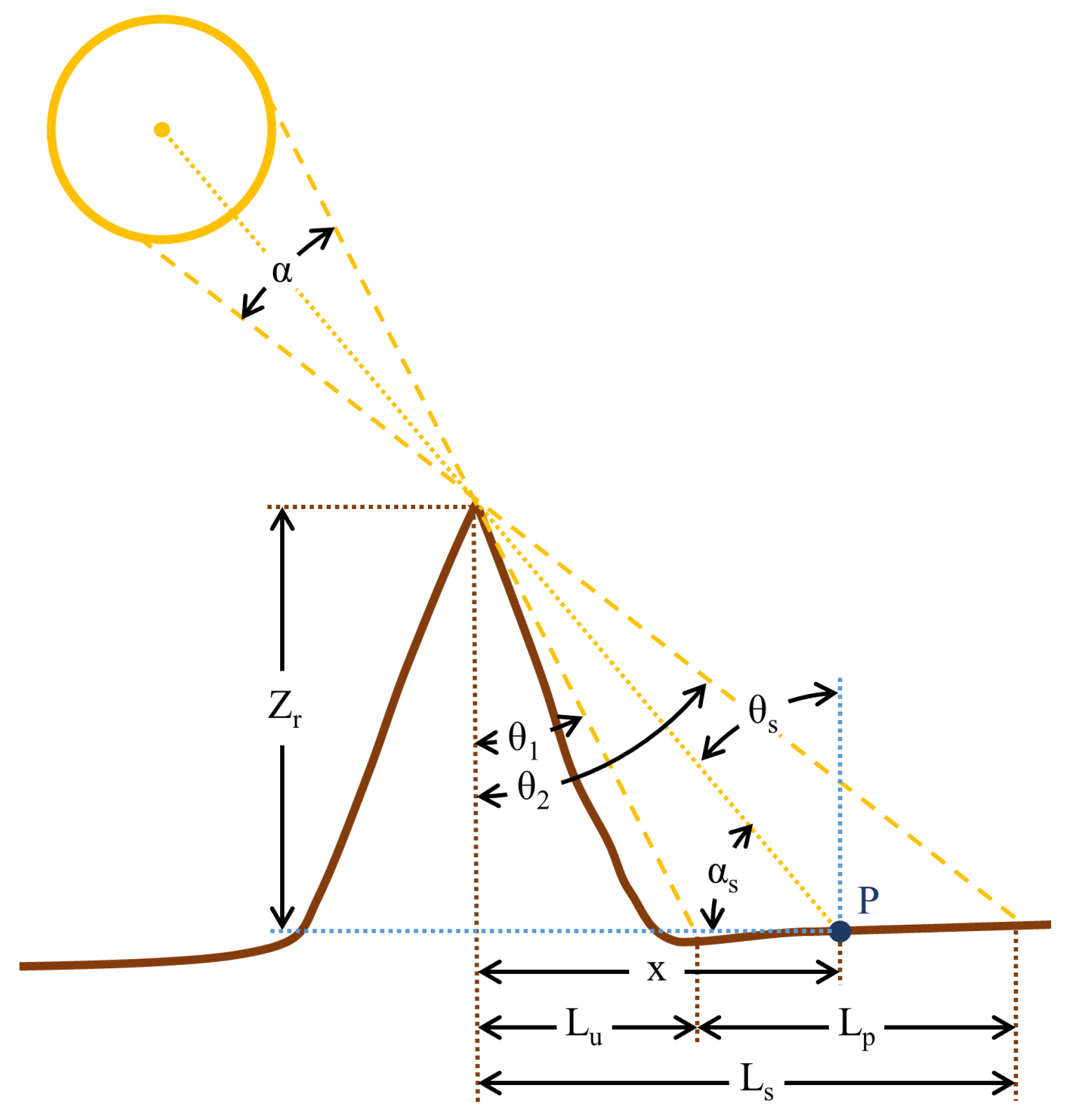
2.1. Direct Irradiance
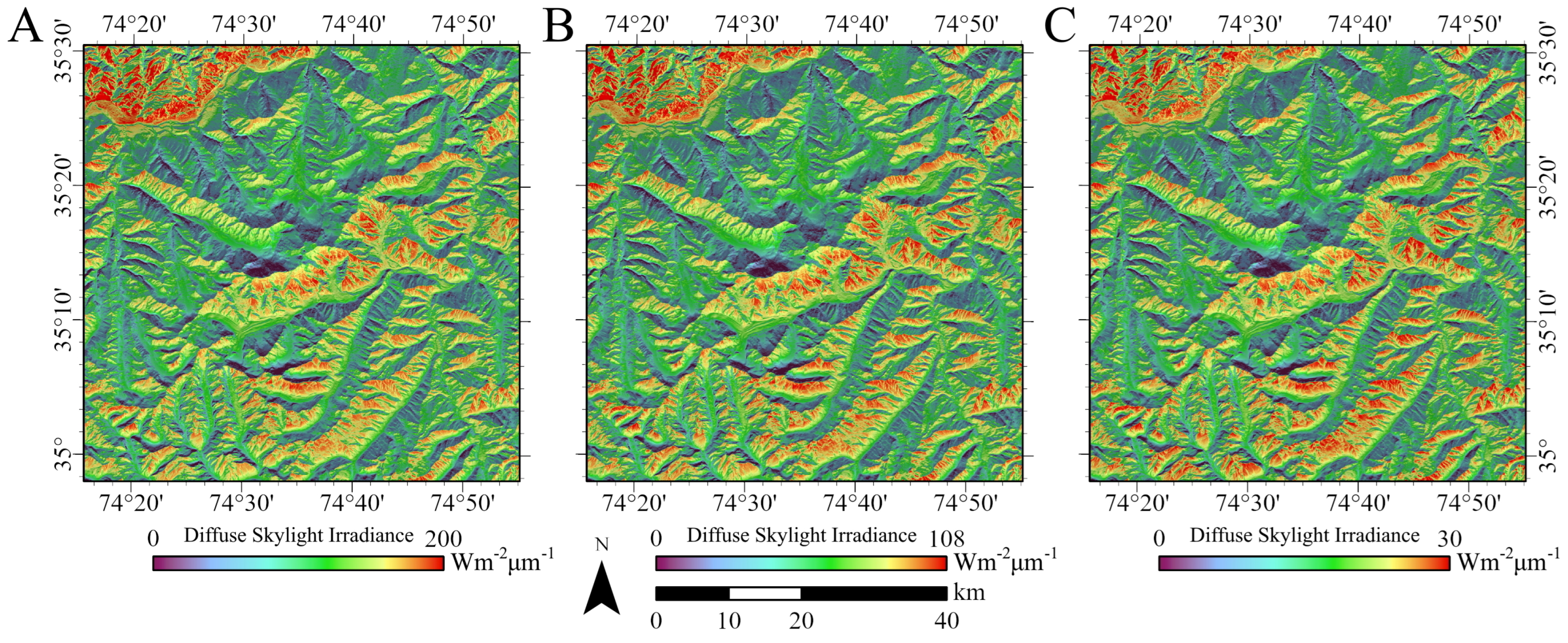
2.2. Diffuse-Skylight Irradiance
2.3. Adjacent-Terrain Irradiance
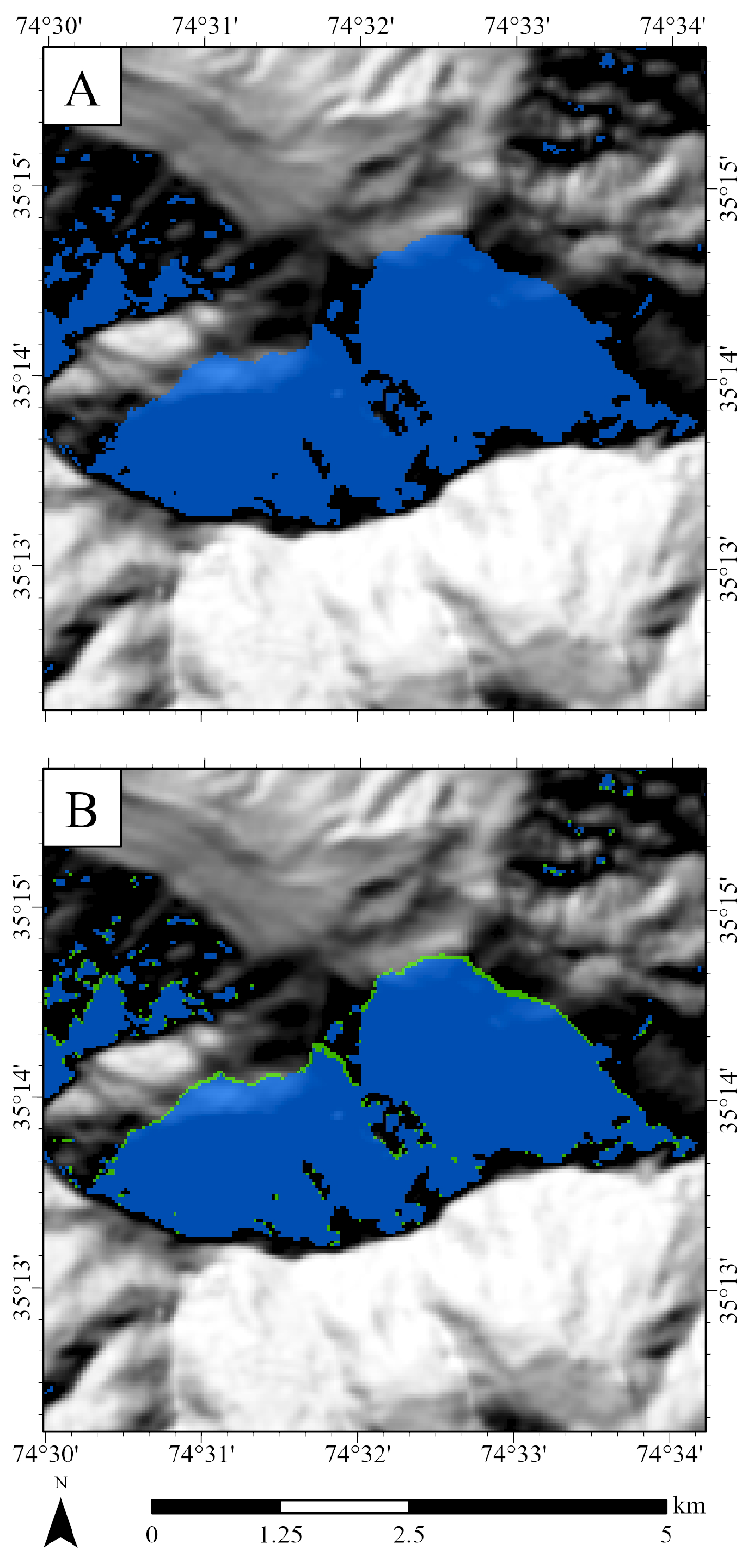
3. Study Area
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data
- Snow, where NDSI and altitude m.
- Vegetation, where there was no snow and NDVI .
- Water, where there was neither snow nor vegetation and NDSI .
- Rock and sediment in the remaining space.
4.2. Numerical Modeling
4.2.1. Orbital Dynamics
4.2.2. Atmospheric Transmittance
4.2.3. Direct Irradiance
4.2.4. Diffuse-Skylight Irradiance
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Results
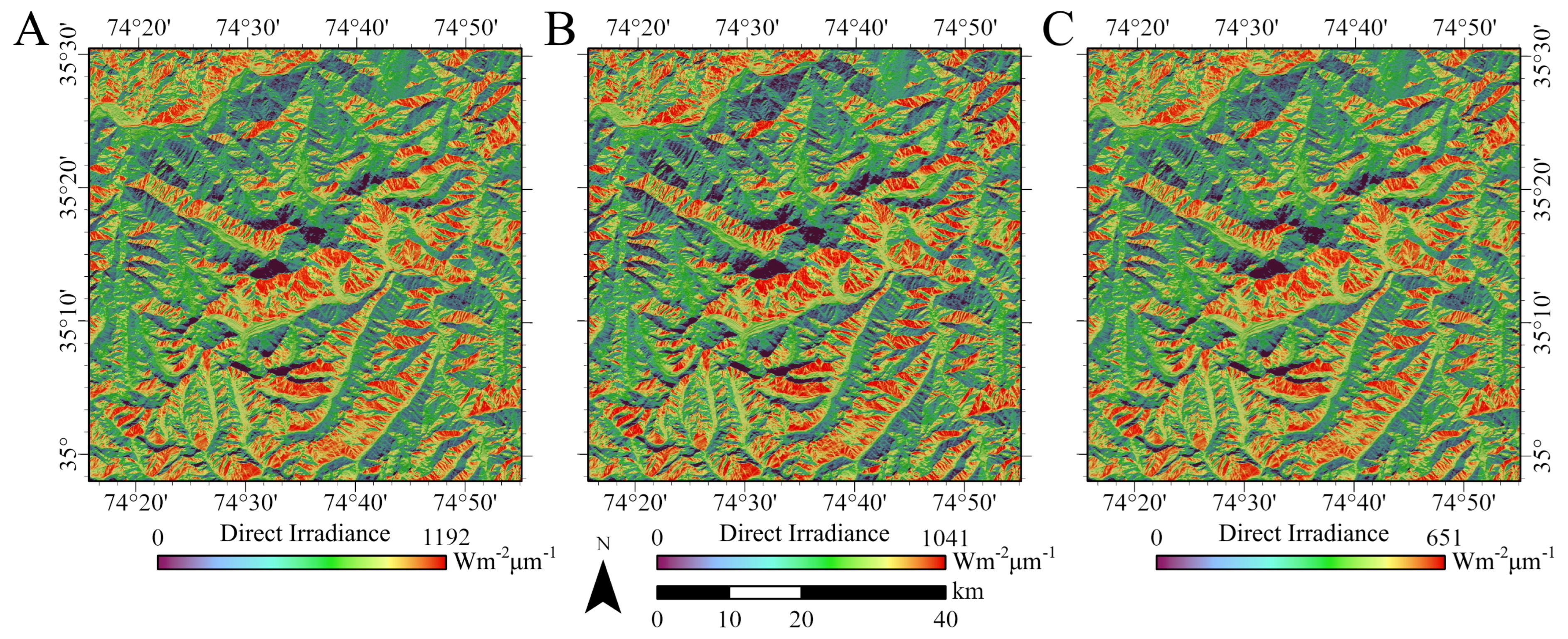
5.1. Direct Irradiance
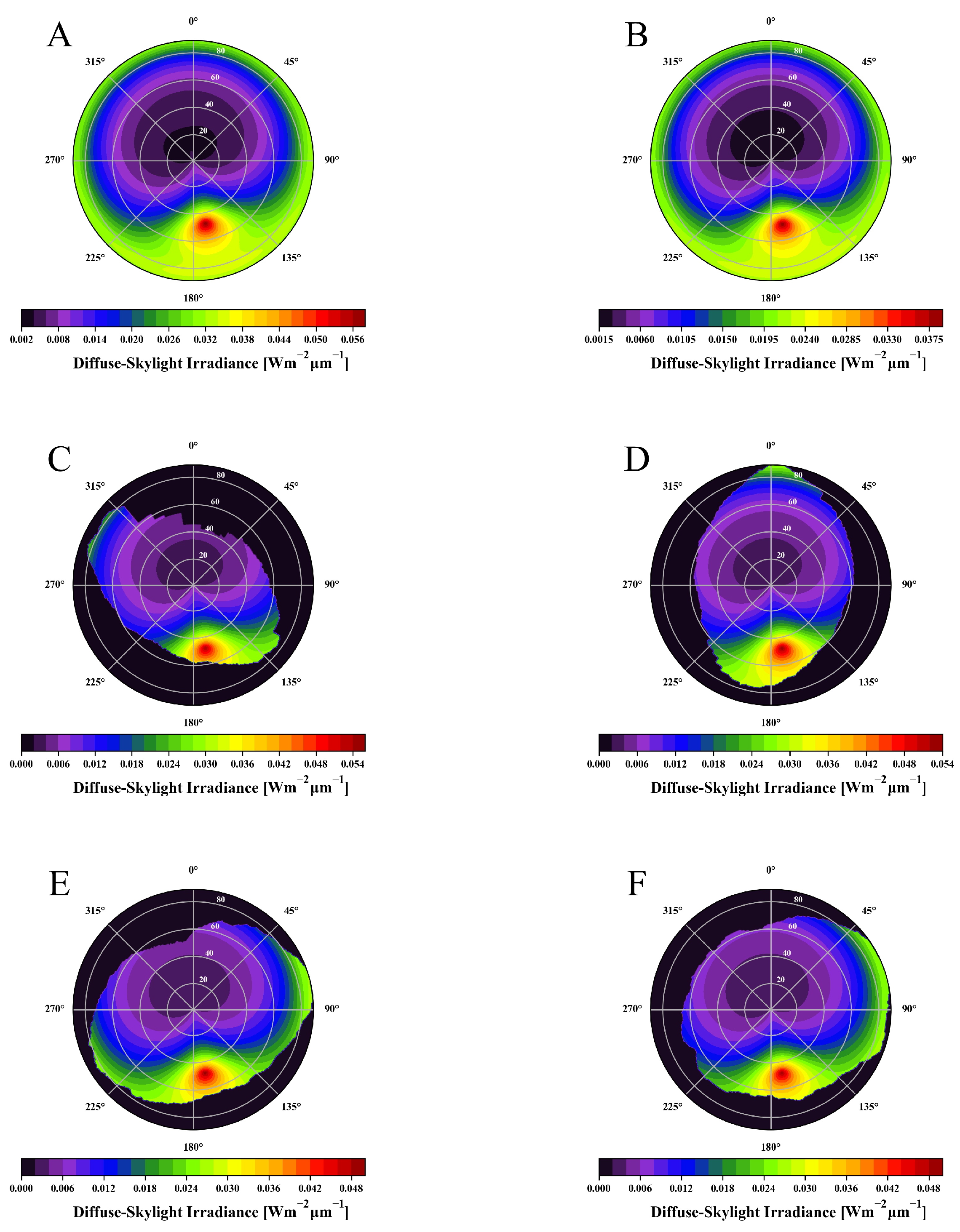
5.2. Diffuse-Skylight Irradiance
6. Discussion
6.1. Direct Irradiance
6.2. Diffuse-Skylight Irradiance
6.3. Anisotropic Reflectance Correction
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mathematical Symbol Notation
| Symbol | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [radians] | Solar angular width. | |
| [radians] | Solar elevation angle. | |
| [radians] | Solar declination. | |
| dimensionless | Obliquity of Earth’s orbit about the Sun. | |
| [m] | Wavelength of light. | |
| [radians] | True longitude of the Earth relative to the vernal equinox. | |
| [radians] | Azimuth angle. | |
| [radians] | Azimuth angle of hemispherical incident energy. | |
| [radians] | Solar azimuth angle. | |
| [radians] | Effective slope-azimuth angle incident energy accounting for topographic correction. | |
| [radians] | Effective slope-azimuth viewing angle accounting for topographic correction. | |
| [kg m] | Density of dry air. | |
| dimensionless | Surface BRDF. | |
| dimensionless | Ground reflectance averaged over a 5 km radius. | |
| dimensionless | Sky reflectance. | |
| [radians] | Maximum relief angle to the horizon. | |
| [radians] | Zenith angle of hemispherical incident energy. | |
| [radians] | Solar zenith angle. | |
| [radians] | Solar zenith angle at scene center. | |
| [radians] | Near-angle of cast-shadow for extent of umbra. | |
| [radians] | Far-angle of cast-shadow for extent of penumbra. | |
| [radians] | Maximum horizon angle. | |
| [radians] | Terrain slope angle. | |
| [radians] | Viewing zenith angle. | |
| [radians] | Effective zenith angle of incident energy accounting for topographic correction. | |
| [radians] | Effective viewing zenith angle accounting for topographic correction. | |
| [radians] | Geocentric solar zenith angle. | |
| [radians] | Latitude. | |
| [sr] | Solid angle for circumsolar region. | |
| d | [km] | Distance. |
| [km] | Earth-Sun distance. | |
| E | [W mm] | Surface irradiance. |
| [W mm] | Exoatmospheric irradiance. | |
| [W mm] | Solar irradiance at 1 AU. | |
| [W mm] | Aerosol scattering irradiance component. | |
| [W mm] | Direct-beam irradiance from the Sun. | |
| [W mm] | Direct normal irradiance. | |
| [W mm] | Diffuse-skylight irradiance. | |
| [W mm] | Diffuse-skylight irradiance for a horizontal surface. | |
| [W mm] | Anisotropic diffuse-skylight irradiance. | |
| [W mm] | Diffuse-skylight irradiance. | |
| [W mm] | Ground/sky backscattering irradiance component. | |
| [W mm] | Irradiance due to Rayleigh scattering. | |
| [W mm] | Adjacent-terrain irradiance. | |
| dimensionless | Earth-Sun distance-correction factor. | |
| dimensionless | Horizontal brightness. | |
| dimensionless | Circumsolar coefficient. | |
| dimensionless | Downward scattered flux. | |
| dimensionless | Downward fraction of scattered radiation. | |
| g | [m s] | Acceleration due to gravity. |
| H | [radians] | Hour angle of the Sun. |
| i | [radians] | Solar-terrain incidence angle. |
| I | [radians] | Hemispherical incidence angle. |
| [radians] | Adjacent terrain incidence angle. | |
| L | [W m srm] | Incident surface-reflected radiance. |
| [W m srm] | Hemispherical downward diffuse radiance. | |
| [m] | Length of the penumbra. | |
| [m] | Length of the umbra. | |
| p | [mb] | Atmospheric pressure. |
| [km] | The nominal solar radius. | |
| dimensionless | Relative humidity. | |
| S | dimensionless | Coefficient for cast shadows, fraction of incident on the landscape. |
| dimensionless | Coefficient for terrain blockage for . | |
| dimensionless | Coefficient for terrain shielding for . | |
| T | [K] | Temperature. |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to aerosol scattering. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to aerosol scattering. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to aerosol absorption. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to primary gas absorption. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to ozone absorption. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to Rayleigh scattering. | |
| dimensionless | Transmittance due to water vapor absorption. | |
| dimensionless | Total downward transmittance. | |
| dimensionless | Total atmospheric transmittance due to terrain relief. | |
| dimensionless | Skyview-factor coefficient. | |
| dimensionless | Longitude-component scalar of the solar azimuth angle. | |
| dimensionless | Latitude-component scalar of the solar azimuth angle. |
References
- Thomas, Z.A. Using natural archives to detect climate and environmental tipping points in the Earth System. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Mighall, T.; Stainforth, D.A.; Allen, P.; Macklin, M.; Anderson, E.; Knight, J.; Mauquoy, D.; Passmore, D.; Rea, B.; et al. Uncertainty in geomorphological responses to climate change. Climactic Chang. 2019, 156, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, Y.; Franklin, J.; Seddon, N.; Solan, M.; Turner, M.G.; Field, C.B.; Knowlton, N. Climate change and ecosystems: Threats, opportunities and solutions. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 375, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, J.; Castellana, D.; Ditlevsen, P.D.; Dijkstra, H.A. Abrupt climate change as a rate-dependent cascading tipping point. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 819–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X. Increase in occurrence of large glacier-related landslides in the high mountains of Asia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, M.P.; Dobreva, I.D. Geomorphometry and Mountain Geodynamics: Issues of Scale and Complexity. In Integrating Scale in Remote Sensing and GIS; Remote Sensing Applications; Quattrochi, D., Wentz, E.A., Lam, N.S., Emerson, C.W., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 189–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.B.G.; Bishop, M.P.; Huo, D.; Chi, Z.; Tiwari, U. Issues in Climate Analysis and Modeling for Understanding Mountain Erosion Dynamics. In Technology-Driven Geomorphology: Geospatial Data Science, 2nd ed.; Treatise in Geomorphology; Bishop, M.P., Giardino, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier Publishing Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R. Correction of satellite imagery over mountainous terrain. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 4004–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Yan, K.; Yang, K.; Du, S.; Li, H.; Qi, J.; Wei, Z. Evaualtion of topographic correction models based upon 3-D Radiative Transfer Simulation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 3110907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, A.S.; Kour, R.; Singh, K.K. Effect of Shadow on Atmospheric and Topographic Processed NDSI Values in Chenab Basin, western Himalayas. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 199, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.P.; Young, B.W.; Colby, J.D.; Furfaro, R.; Chi, Z. Theoretical Evaluation of Anisotropic Reflectance Correction Approaches for Addressing Multi-Scale Topographic Effects on the Radiation Transfer Cascade in Mountain Environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, E. A new Approach to Estimating the Diffuse Irradiance on Inclined Surfaces. Renew. Energy 2000, 20, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Pang, Y.; Tortini, R.; Schläpfer, D.; Li, Z.; Roujean, J.L. A Kernel-Driven BRDF Approach to Correct Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery over Forested Areas with Rugged Topography. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Yan, G.; Qi, J.; Mu, X.; Li, L.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, D.; Wild, M. Quantitative Analysis of Terrain Reflected Solar Radiation in Snow-Covered Mountains: A Case Study in Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.P.; Bush, A.B.G.; Copland, L.; Kamp, U.; Owen, L.A.; Seong, Y.B.; Shroder, J.F., Jr. Climate Change and Mountain Topographic Evolution in the Central Karakoram, Pakistan. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2010, 100, 772–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Bishop, M.P.; Young, B.; Chi, Z. Modeling the Feedbacks between Surface Ablation and Morphological Variations on Debris-Covered Baltoro Glacier in the central Karakoram. Geomorphology 2021, 389, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Lin, T.L.; Ranson, K.J. The Lambertian Assumption and LANDSAT Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1980, 46, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Teillet, P.M.; Guindon, B.; Goodenough, D.G. On the Slope-Aspect Correction of Multispectral Scanner Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1982, 8, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Gillespie, A. Topographic Normalization of Landsat TM Images of Forest Based on Subpixel Sun–Canopy–Sensor Geometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.A.; Peddle, D.R.; Coburn, C.A. SCS+C: A modified Sun-canopy-sensor topographic correction in forested terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.; Kumar, L. Diffuse Skylight as a Surrogate for Shadow Detection in High-Resolution Imagery Acquired Under Clear Sky Conditions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Stewart, R.; Arbogast, C.; Seals, R.; Scott, J. An anisotropic hourly diffuse radiation model for sloping surfaces: Description, performance validation, site dependency evaluation. Sol. Energy 1986, 36, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proy, C.; Tanré, D.; Deschamps, P.Y. Evaluation of topographic effects in remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 30, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Ineichen, P.; Seals, R.; Michalsky, J.; Stewart, R. Modeling daylight availability and irradiance components from direct and global irradiance. Sol. Energy 1990, 44, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueymard, C. SMARTS2, a Simple Model of the Atmospheric Radiative Transfer of Sunshine: Algorithms and Performance Assessment; Florida Solar Energy Center: Cocoa, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Liu, Q.; Yan, G. Improved Topographic Normalization for Landsat TM Images by Introducing the MODIS Surface BRDF. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6558–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Frew, J. Rapic Calculation of Terrain Parameters for Radiation from Digital Elevation Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, J.D.; Dymond, J.R. COrrecting Satellite Imagery for the Variance of Reflectance and Illumination with Topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3503–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.; Gong, P.; Clinton, N.; Hui, F. Reduction in Atmospheric and Topographic Effect on Landsat TM Data for Forect CLassification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5623–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; You, D.; Hao, D.; Wu, S.; Lin, X. Characterizing Land Surface Anisotropic Reflectance over Rugged Terrain: A Review of Concepts and Recent Developments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, J.D. Topographic normalization in rugged terrain. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.P.; Colby, J.D. Topographic normalization of multispectral satellite imagery. In Encyclopedia of Snow, Ice and Glaciers; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jupp, D.L.B.; Thankappan, M.; Lymburner, L.; Mueller, N.; Lewis, A.; Held, A. A physics-based atmospheric and BRDF correction for Landsat data over mountainous terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroder, J.F., Jr.; Bishop, M.P. Unroofing of the Nanga Parbat Himalaya. In Tectonics of the Nanga Parbat Syntaxis and the Western Himalaya; Number 170 in Special Publication; Khan, M.A., Treloar, P.J., Searle, M.P., Jan, M.Q., Eds.; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2000; pp. 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitler, P.K.; Koons, P.O.; Bishop, M.P.; Chamberlain, C.P.; Craw, D.; Edwards, M.A.; Hamidullah, S.; Jan, M.Q.; Khan, M.A.; Khattak, M.U.K.; et al. Crustal Reworking at Nanga Parbat, Pakistan: Metamorphic Consequences of Thermal-Mechanical Coupling Facilitated by Erosion. Tectonics 2001, 20, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.P.; Shroder, J.F., Jr.; Bonk, R.; Olsenholler, J. Geomorphic Change in High Mountains: A Western Himalayan Perspective. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2002, 32, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.A.; Edwards, M.A.; Kidd, W.S.F.; Asif Khan, M.; Seeber, L.; Zeitler, P.K. Tectonics of Nanga Parbat, western Himalaya: Synkinematic plutonism within the doubly vergent shear zones of a crustal-scale pop-up structure. Geology 1999, 27, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, L.A.; Scott, C.H.; Derbyshire, E. The Quaternary glacial history of Nanga Parbat. Quat. Int. 2000, 65–66, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA/METI/AIST/Japan Spacesystems; U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. ASTER GDEM Version 2; Data Set. NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Berger, A. Long-Term Variations of Daily Insolation and Quaternary Climatic Changes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbard, T.; Ikhlef, R.; Morand, F.; Meftah, M.; Renaud, C. On the importance of astronomical refraction for modern solar astrometric measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 483, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Kingdom Hydrographic Office. The Astronomical Almanac for the Year 2013; United Kingdom Hydrographic Office: Taunton, UK; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Bird, R.E.; Riordan, C. Simple Solar Spectral Model for Direct and Diffuse Irradiance on Horizontal and Tilted Planes at the Earth’s Surface for Cloudless Atmospheres. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Bruno, J.; Downey, P. A faster solution to the horizon problem. Comput. Geosci. 1981, 7, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.E.; Dungan, J.L.; Beck, L.R. Kriging in the shadows: Geostatistical interpolation for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, P.T. Remote sensing and cast shadows in mountainous terrain. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 833–839. [Google Scholar]
- Meftah, M.; Corbard, T.; Hauchecorne, A.; Morand, F.; Ikhlef, R.; Chauvineau, B.; Renaud, C.; Sarkissian, A.; Damé, L. Solar radius determined from PICARD/SODISM observations and extremely weak wavelength dependence in the visible and the near-infrared. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, A64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Seals, R.; Ineichen, P.; Stewart, R.; Menicucci, D. A New Simplified Version of the Perez DIffuse Irradiance MOdel for Tilted Surfaces. Sol. Energy 1987, 39, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.A.M.; Hizam, H.; Gomes, C. Estimation of Hourly, Daily and Monthly Global Solar Radiation on Inclined Surfaces: Models Re-Visited. Energies 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Perers, B.; Furbo, S.; Fan, J.; Deng, J.; Dragsted, J. A Comprehensive Approach for Modelling Horizontal Diffuse Radiation, Direct Normal Irradiance and Total Tilted Solar Radiation Based on Global Radiation under Danish Climate Conditions. Energies 2018, 11, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlu, S.; Kittler, R. CIE Gneral sky standard Defining Luminaance Distributions. In Proceedings of the Canadian Conference on Building Energy, Montreal, QC, Canada, 12–13 September 2002; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error measurement to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimple, U.; Sitthi, A.; Simonetti, D.; Pungkul, S.; Leadprathom, K.; Chidthaisong, A. Topographic Correction of Landsat TM-5 and Landsat OLI-8 Imagery to Improve Performance of Forest CLassification in the Mountainous Terrain of Northeast Thailand. Sustainability 2017, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, G.; Li, A.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; et al. Topographic Correction of Forest Image Data Based on the Canopy Reflectance Model for Sloping Terrains in Multiple Forward Mode. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 10 | 8.617 | −0.001 | 8.770 | 0.152 | 8.618 |
| 30 | 28.205 | −0.003 | 28.716 | 0.508 | 28.208 |
| 50 | 58.145 | −0.005 | 59.274 | 1.124 | 58.150 |
| 70 | 133.087 | −0.007 | 137.094 | 4.000 | 133.094 |
| 80 | 267.663 | 0.252 | 271.224 | 3.813 | 267.411 |
| 85 | 512.147 | 17.971 | 503.393 | 9.217 | 494.176 |
| Atmosphere Vertical Profiles | Atmospheric Effective Pathlengths | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | T | p | g | O | CO | H | O | ||
| [km] | [K] | [mb] | [kg m] | [m s] | [%] | [km] | [km] | [cm] | [atm-cm] |
| 0 | 288.20 | 1013.25 | 1.2250 | 9.8006 | 55.0 | 4.9292 | 4.8655 | 1.4220 | 0.3434 |
| 1 | 281.71 | 898.84 | 1.1117 | 9.7975 | 50.1 | 3.9490 | 3.7725 | 0.8625 | |
| 2 | 275.23 | 795.15 | 1.0066 | 9.7944 | 46.7 | 3.1476 | 2.9082 | 0.5231 | |
| 3 | 268.77 | 701.41 | 0.9093 | 9.7913 | 44.5 | 2.4956 | 2.2283 | 0.3173 | |
| 4 | 262.31 | 616.85 | 0.8194 | 9.7883 | 43.4 | 1.9676 | 1.6965 | 0.1924 | |
| 5 | 255.85 | 540.78 | 0.7365 | 9.7852 | 43.6 | 1.5422 | 1.2829 | 0.1167 | |
| 6 | 249.39 | 472.51 | 0.6602 | 9.7821 | 45.1 | 1.2014 | 0.9633 | 0.0708 | |
| 7 | 242.93 | 411.42 | 0.5901 | 9.7791 | 48.1 | 0.9299 | 0.7180 | 0.0429 | |
| 8 | 236.48 | 356.92 | 0.5259 | 9.7760 | 53.0 | 0.7149 | 0.5310 | 0.0260 | |
| 9 | 230.07 | 308.43 | 0.4671 | 9.7729 | 60.4 | 0.5456 | 0.3896 | 0.0158 | |
| SS | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| S1S1 | Solar zenith angle only at scene center. | |
| S1S2 | Parallax correction omitted. | |
| S1S3 | Atmospheric refraction correction omitted. | |
| S1S4 | Parallax and refraction corrections omitted. | |
| S1S5 | Total downward Atmospheric transmittance term omitted. | |
| S1S6 | Cosine of the incidence angle omitted. | |
| S1S7 | Cast shadows using solar disk omitted. | |
| S1S8 | Cast shadows using point-source assumption. | |
| S1S9 | Base for comparisons using Equation (2). | |
| S2S1 | Skylight irradiance of Rayleigh component omitted. | |
| S2S2 | Skylight irradiance of aerosol component omitted. | |
| S2S3 | Skylight irradiance of ground scattering component omitted. | |
| S2S4 | Isotropic skylight irradiance computed as on a horizontal surface. | |
| S2S5 | Isotropic skylight irradiance using shielding coefficient. | |
| S2S6 | Perez skylight irradiance model. | |
| S2S7 | Local topographic effects omitted. | |
| S2S8 | Meso-scale topographic shielding omitted. | |
| S2S9 | Base for comparisons using Equation (4). | |
| RMSE | SSI | t | F | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [m] | |||||||||
| S1S1 | 0.00 | 1102.29 | 681.00 | 283.70 | 55.46 | 0.99 | 243.85 | 1.16 | |
| S1S2 | 0.00 | 1109.92 | 680.99 | 283.89 | 55.05 | 0.99 | 243.83 | 1.15 | |
| S1S3 | 0.00 | 1109.85 | 680.72 | 283.97 | 55.27 | 0.99 | 245.09 | 1.15 | |
| S1S4 | 0.00 | 1109.86 | 680.74 | 283.96 | 55.25 | 0.99 | 244.99 | 1.15 | |
| S1S5 | 0.00 | 1363.54 | 837.55 | 349.15 | 114.57 | 0.97 | −456.17 | 0.76 | |
| S1S6 | 0.00 | 1110.23 | 1075.77 | 167.42 | 447.93 | 0.11 | −1976.82 | 3.32 | |
| S1S7 | 0.00 | 1109.92 | 683.35 | 279.22 | 60.08 | 0.98 | 234.30 | 1.19 | |
| S1S8 | 0.00 | 1109.92 | 680.99 | 283.88 | 55.14 | 0.99 | 243.83 | 1.15 | |
| S1S9 | 0.00 | 1192.28 | 731.80 | 305.08 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| [m] | |||||||||
| S1S1 | 0.00 | 993.76 | 613.96 | 255.77 | 28.43 | 0.99 | 139.08 | 1.09 | |
| S1S2 | 0.00 | 1000.20 | 613.94 | 255.93 | 27.86 | 0.99 | 139.11 | 1.09 | |
| S1S3 | 0.00 | 1000.16 | 613.71 | 256.01 | 28.04 | 0.99 | 140.32 | 1.08 | |
| S1S4 | 0.00 | 1000.16 | 613.73 | 256.00 | 28.02 | 0.99 | 140.22 | 1.08 | |
| S1S5 | 0.00 | 1135.56 | 697.52 | 290.78 | 62.69 | 0.99 | −293.35 | 0.84 | |
| S1S6 | 0.00 | 1000.46 | 969.86 | 150.94 | 415.18 | 0.11 | −2155.28 | 3.12 | |
| S1S7 | 0.00 | 1000.19 | 616.07 | 251.73 | 35.31 | 0.99 | 128.62 | 1.12 | |
| S1S8 | 0.00 | 1000.19 | 613.94 | 255.92 | 28.00 | 0.99 | 139.10 | 1.09 | |
| S1S9 | 0.00 | 1041.86 | 639.65 | 266.66 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| [m] | |||||||||
| S1S1 | 0.00 | 639.14 | 394.87 | 164.50 | 6.46 | 0.99 | 42.85 | 1.03 | |
| S1S2 | 0.00 | 642.97 | 394.86 | 164.60 | 5.45 | 0.99 | 42.94 | 1.03 | |
| S1S3 | 0.00 | 642.96 | 394.72 | 164.65 | 5.56 | 0.99 | 44.10 | 1.03 | |
| S1S4 | 0.00 | 642.96 | 394.73 | 164.65 | 5.55 | 0.99 | 44.00 | 1.03 | |
| S1S5 | 0.00 | 671.43 | 412.43 | 171.93 | 13.58 | 0.99 | −104.71 | 0.94 | |
| S1S6 | 0.00 | 643.13 | 623.77 | 97.07 | 273.96 | 0.10 | −2321.12 | 2.95 | |
| S1S7 | 0.00 | 642.97 | 396.23 | 161.89 | 14.99 | 0.99 | 31.51 | 1.06 | |
| S1S8 | 0.00 | 642.97 | 394.86 | 164.59 | 5.73 | 0.99 | 42.92 | 1.03 | |
| S1S9 | 0.00 | 651.13 | 399.89 | 166.70 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| RMSE | SSI | t | F | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | |||||||||
| S2S1 | 19.24 | 144.89 | 99.56 | 19.14 | 37.49 | 0.8414 | 2268.84 | 1.85 | |
| S2S2 | 10.67 | 97.84 | 58.16 | 11.92 | 79.48 | 0.3665 | 5454.76 | 4.77 | |
| S2S3 | 22.07 | 166.54 | 114.67 | 21.95 | 22.04 | 0.9483 | 1264.84 | 1.40 | |
| S2S4 | 142.41 | 190.18 | 165.36 | 7.53 | 39.42 | 0.0031 | −2153.75 | 11.95 | |
| S2S5 | 41.37 | 180.06 | 138.21 | 12.09 | 24.12 | 0.1184 | −140.60 | 4.63 | |
| S2S6 | 100.99 | 245.08 | 172.27 | 26.33 | 38.04 | 0.7567 | −1949.39 | 0.98 | |
| S2S7 | 38.07 | 339.38 | 218.03 | 32.35 | 83.97 | 0.5219 | −3942.42 | 0.65 | |
| S2S8 | 72.39 | 222.37 | 154.96 | 26.16 | 21.70 | 0.8197 | −1017.37 | 0.99 | |
| S2S9 | 25.99 | 199.78 | 136.20 | 26.01 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| m | |||||||||
| S2S1 | 11.08 | 82.46 | 57.33 | 11.00 | 17.38 | 0.8902 | 1894.18 | 1.66 | |
| S2S2 | 4.99 | 46.17 | 27.34 | 5.63 | 47.85 | 0.2769 | 6162.25 | 6.33 | |
| S2S3 | 12.36 | 92.02 | 63.96 | 12.22 | 10.59 | 0.9628 | 1106.97 | 1.34 | |
| S2S4 | 79.03 | 101.58 | 90.21 | 3.53 | 21.49 | 0.0010 | −2177.18 | 16.09 | |
| S2S5 | 22.71 | 96.32 | 75.41 | 6.42 | 13.16 | 0.1179 | −140.34 | 4.86 | |
| S2S6 | 57.46 | 135.22 | 95.81 | 14.49 | 22.57 | 0.7335 | −2121.24 | 0.96 | |
| S2S7 | 20.82 | 185.75 | 118.99 | 17.71 | 45.85 | 0.5206 | −3939.70 | 0.64 | |
| S2S8 | 39.63 | 118.81 | 84.54 | 14.12 | 11.80 | 0.8200 | −1022.00 | 1.01 | |
| S2S9 | 14.21 | 108.19 | 74.32 | 14.17 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| m | |||||||||
| 2S1 | 3.38 | 24.52 | 17.33 | 3.32 | 3.50 | 0.9524 | 1322.80 | 1.42 | |
| S2S2 | 1.04 | 9.52 | 5.61 | 1.18 | 15.41 | 0.1915 | 7329.21 | 11.31 | |
| S2S3 | 3.60 | 26.52 | 18.55 | 3.54 | 2.24 | 0.9839 | 827.40 | 1.25 | |
| S2S4 | 22.57 | 27.64 | 25.17 | 0.80 | 5.99 | 0.0001 | −2194.15 | 24.30 | |
| S2S5 | 6.38 | 26.36 | 21.05 | 1.76 | 3.68 | 0.1378 | −139.41 | 5.05 | |
| S2S6 | 16.80 | 38.03 | 27.25 | 4.09 | 6.81 | 0.7103 | −2285.81 | 0.94 | |
| S2S7 | 5.88 | 51.87 | 33.22 | 4.99 | 12.81 | 0.5261 | −3919.38 | 0.63 | |
| S2S8 | 11.05 | 32.32 | 23.59 | 3.90 | 3.28 | 0.8214 | −1024.32 | 1.03 | |
| S2S9 | 4.01 | 29.75 | 20.74 | 3.96 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bishop, M.P.; Young, B.W.; Colby, J.D. Numerical Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for Understanding Scale-Dependent Topographic Effects Governing Anisotropic Reflectance Correction of Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215339
Bishop MP, Young BW, Colby JD. Numerical Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for Understanding Scale-Dependent Topographic Effects Governing Anisotropic Reflectance Correction of Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215339
Chicago/Turabian StyleBishop, Michael P., Brennan W. Young, and Jeffrey D. Colby. 2022. "Numerical Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for Understanding Scale-Dependent Topographic Effects Governing Anisotropic Reflectance Correction of Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215339
APA StyleBishop, M. P., Young, B. W., & Colby, J. D. (2022). Numerical Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis for Understanding Scale-Dependent Topographic Effects Governing Anisotropic Reflectance Correction of Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215339






