Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
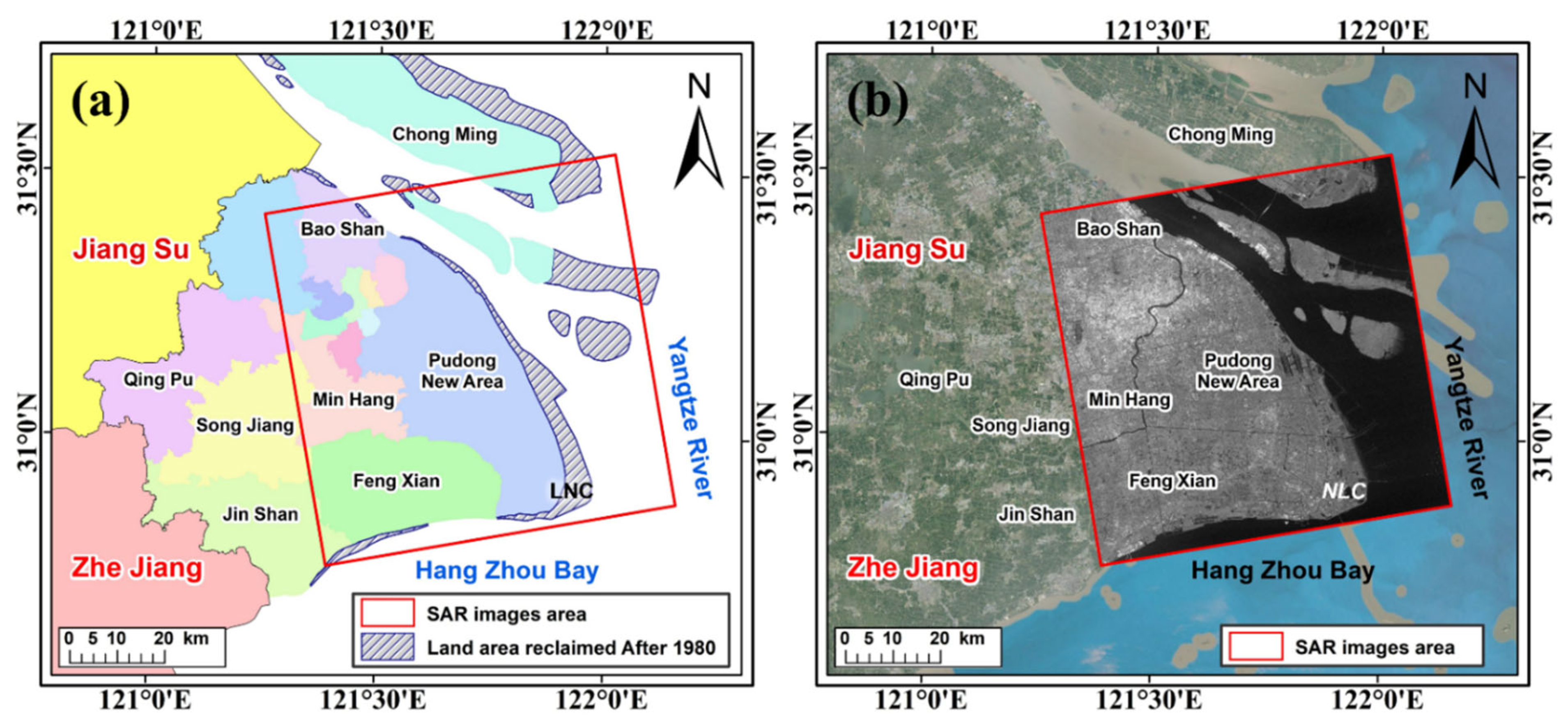
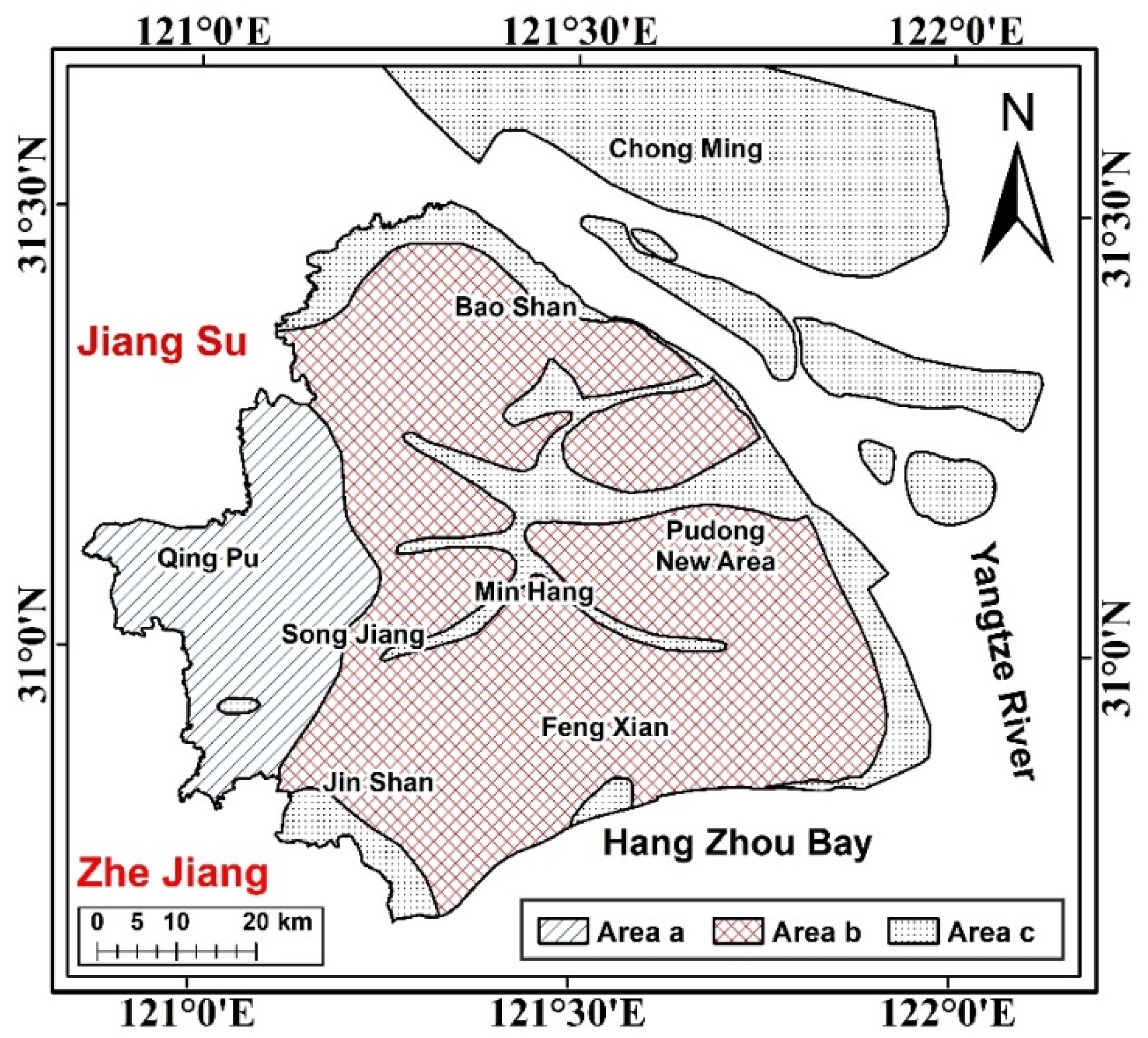
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methods
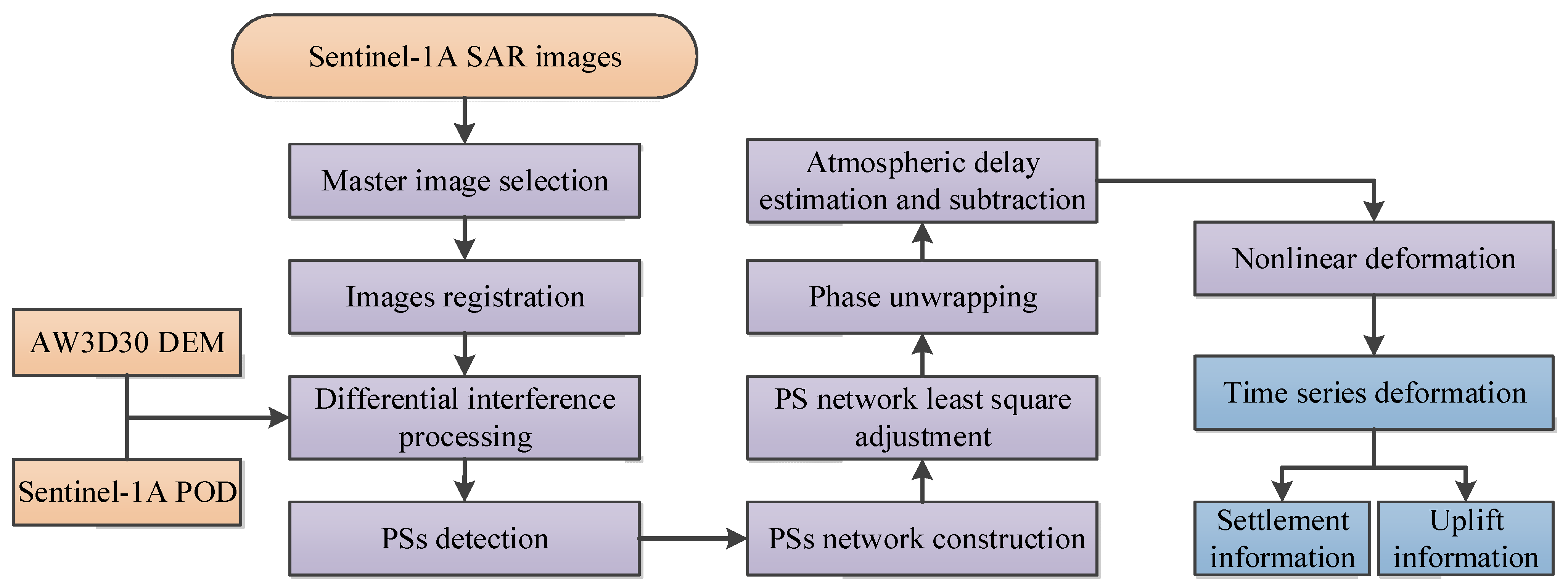
4. Results
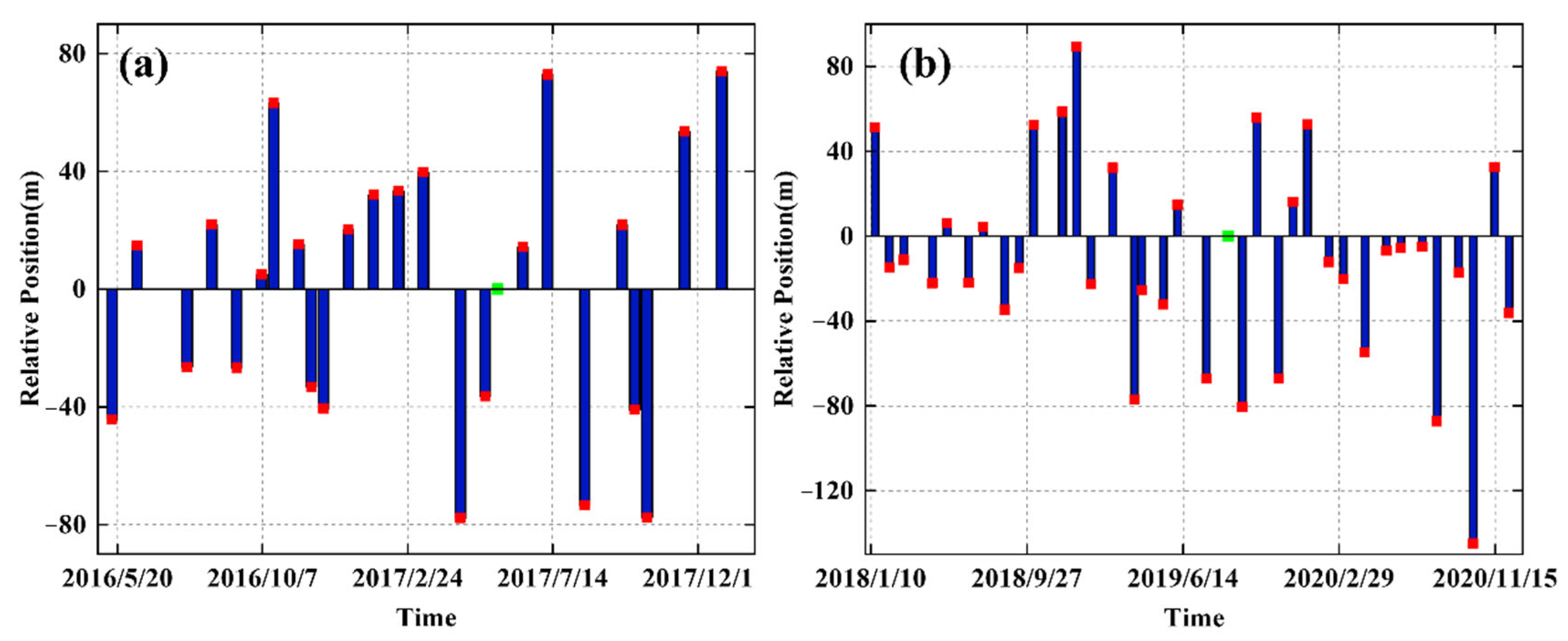
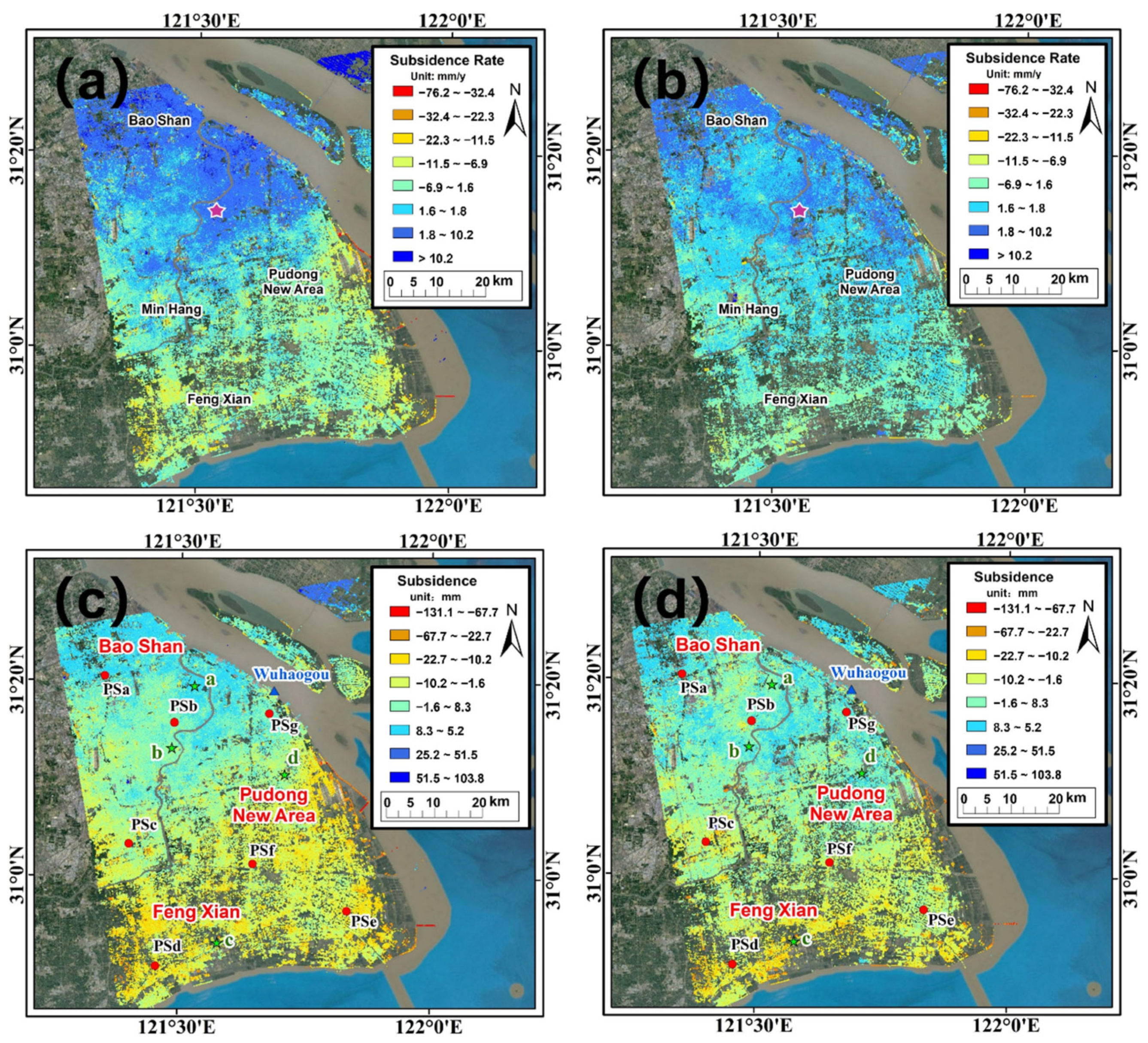
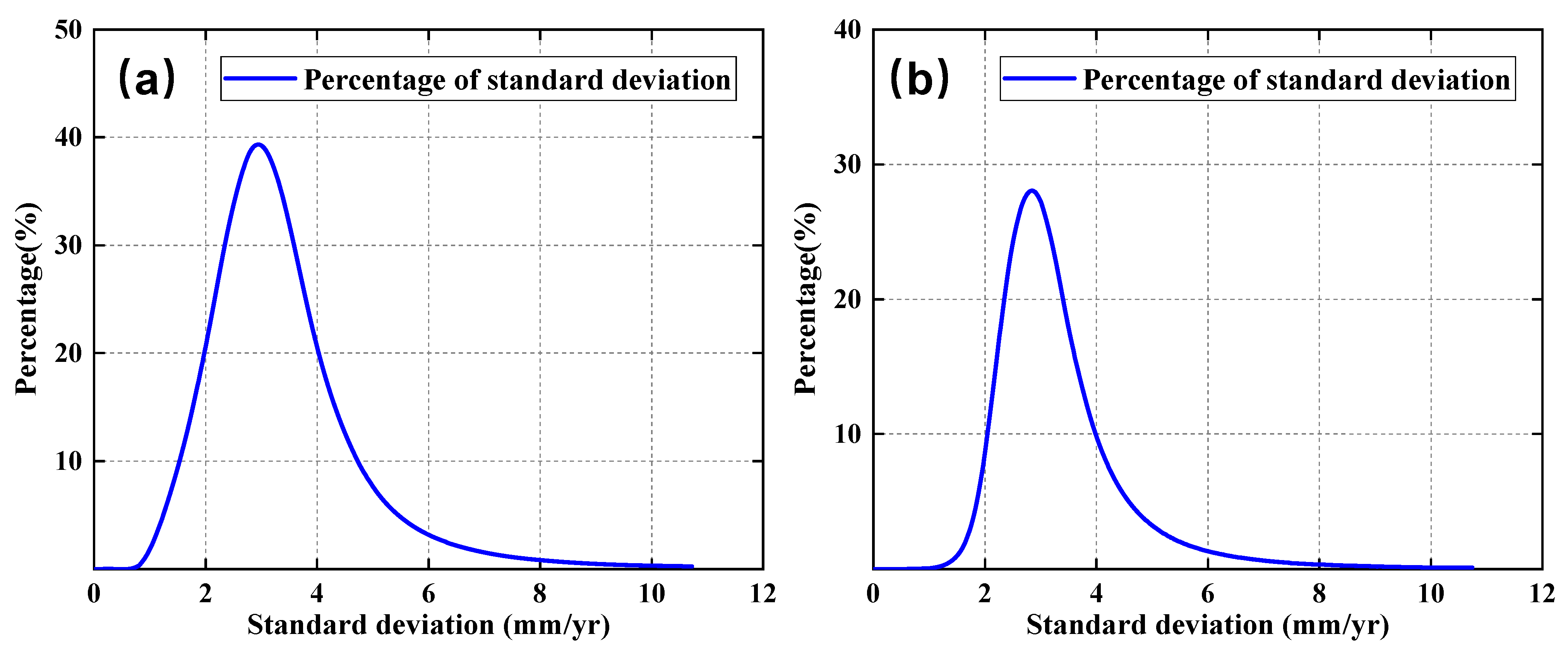
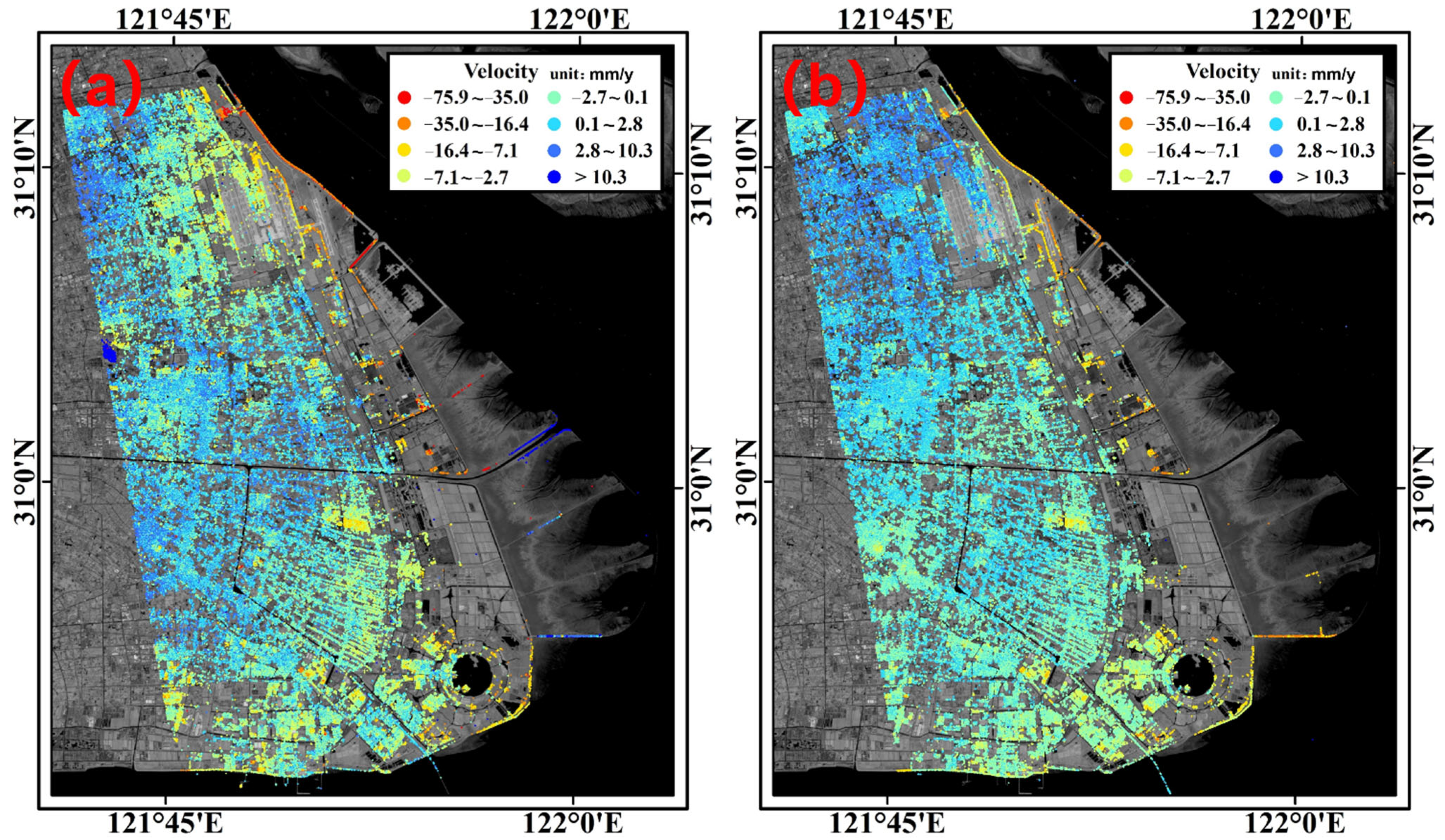
4.1. Internal Precision Analysis of Surface Deformation Results
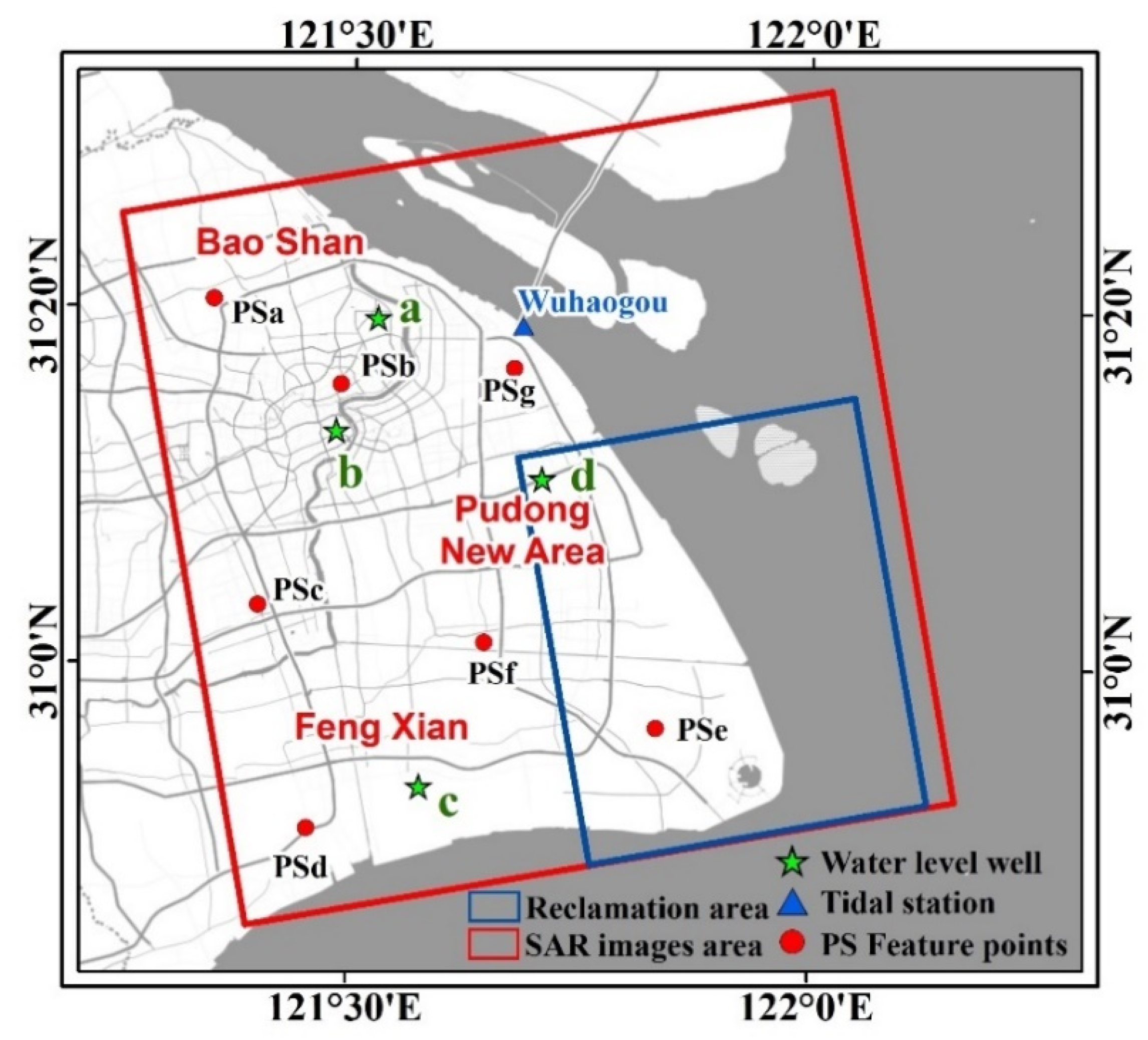
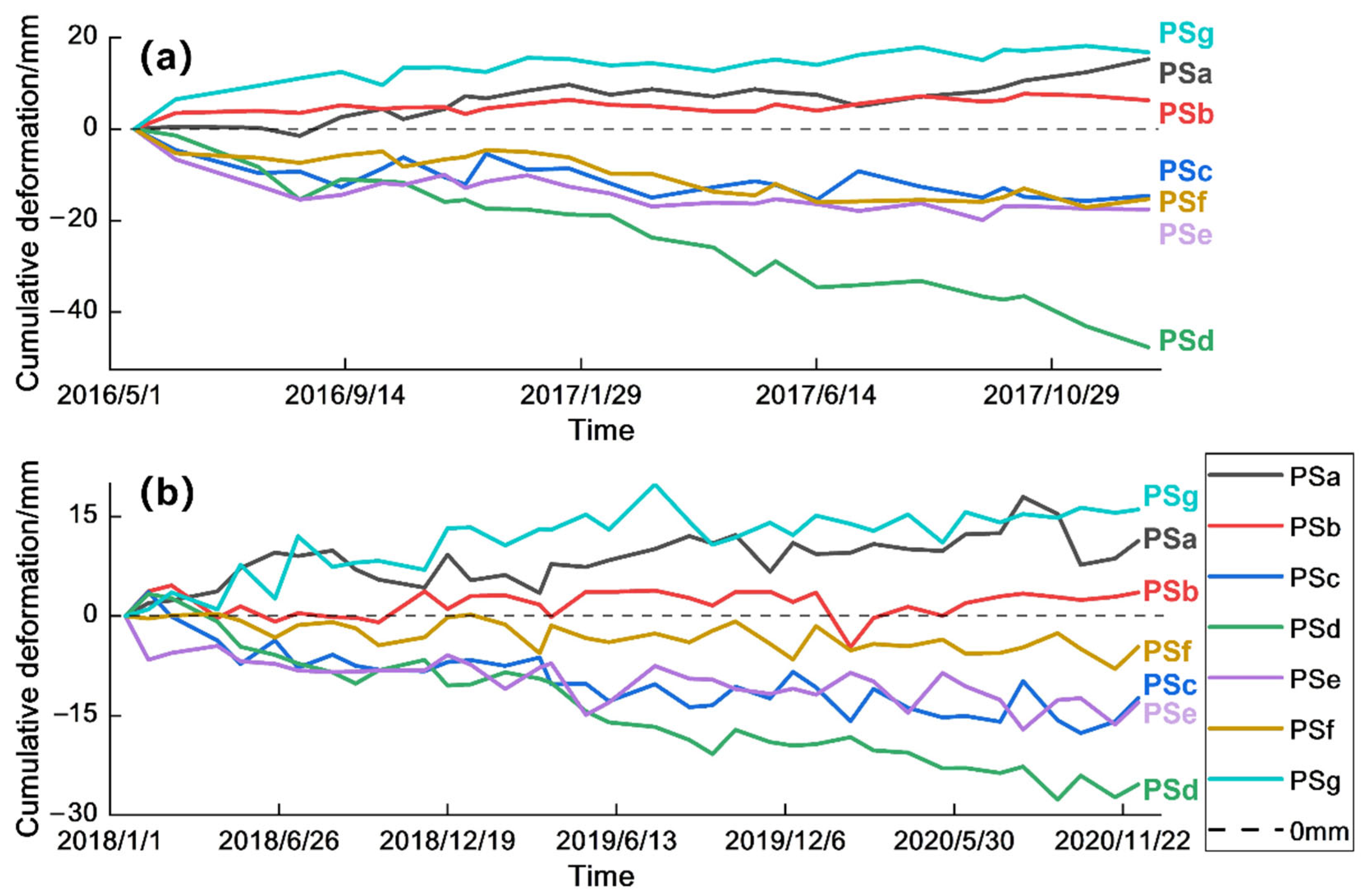
4.2. Analysis of Surface Deformation Feature Points in Shanghai Area
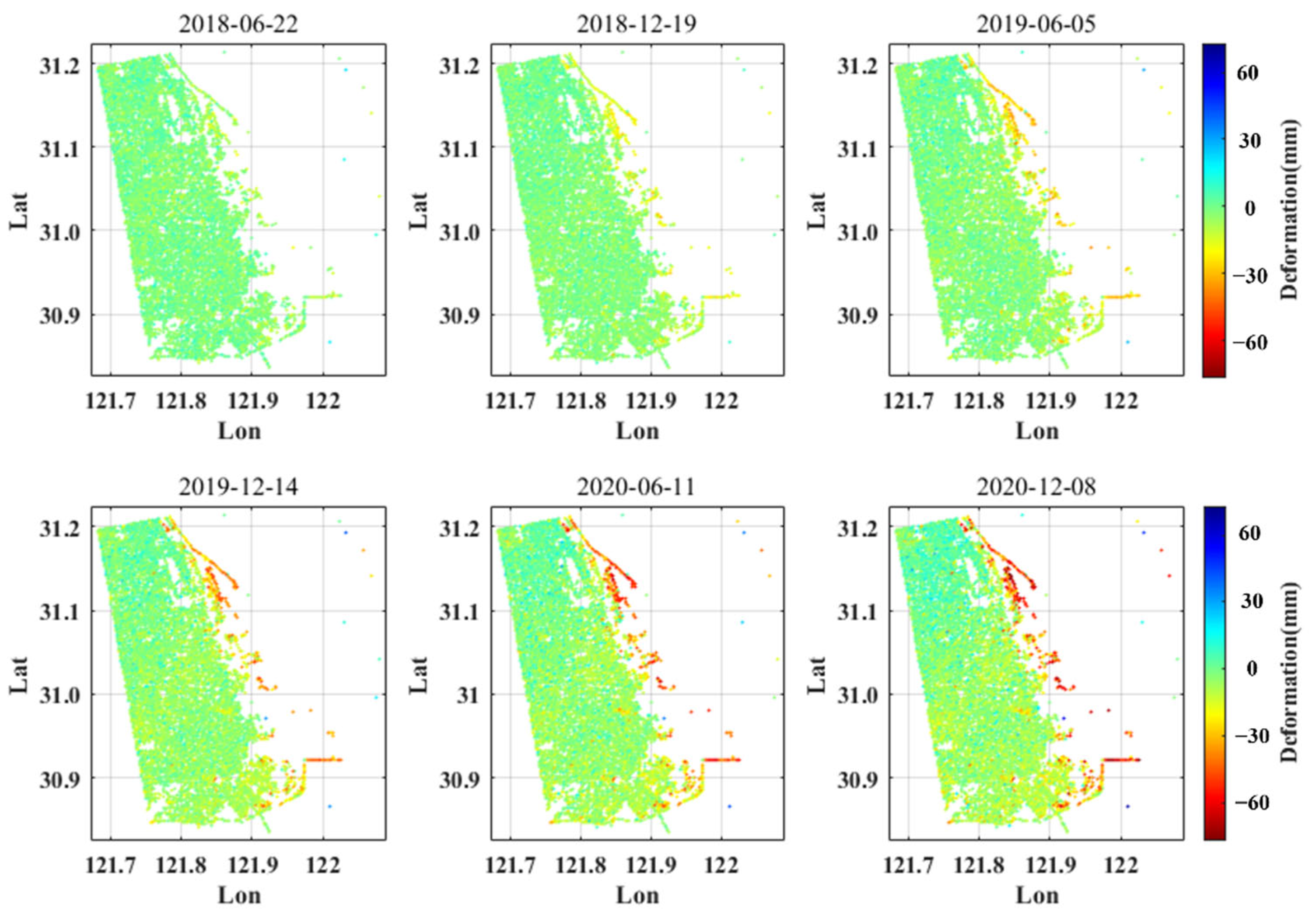
4.3. Time Series Change of Deformation Rate in Shanghai from 2016 to 2020
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of the Causes of Surface Subsidence in Shanghai Area
5.1.1. Influence of Regional Groundwater Levels and Surface Deformation
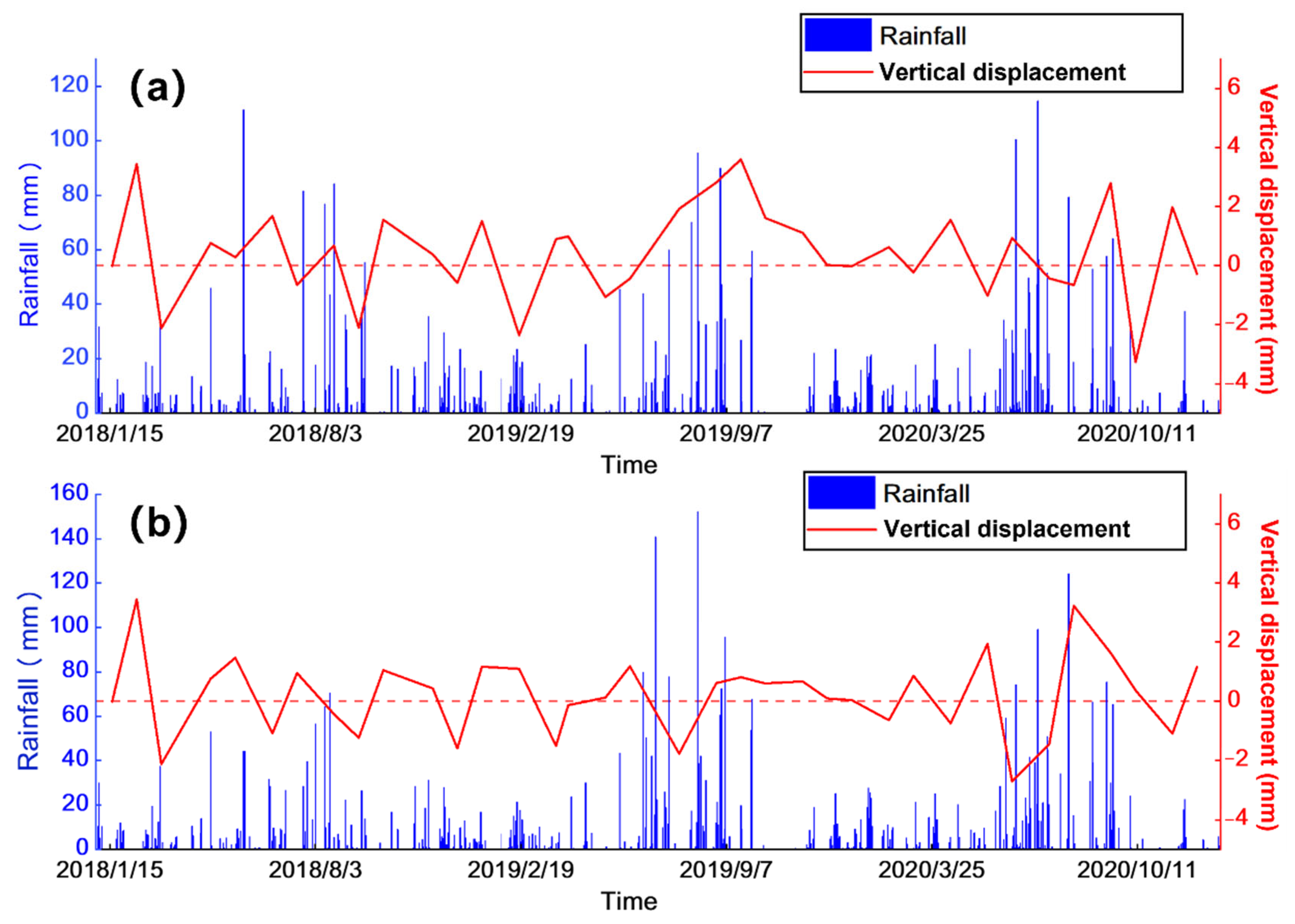
5.1.2. Analysis of Rainfall and Surface Deformation
5.1.3. Correlation between Urban Development and Surface Deformation
5.1.4. Relationship between Shallow Surface Geological Structure and Surface Deformation
5.2. Analysis of Surface Uplift Phenomenon in Shanghai Area
5.2.1. Sediment Accumulation and Surface Uplift
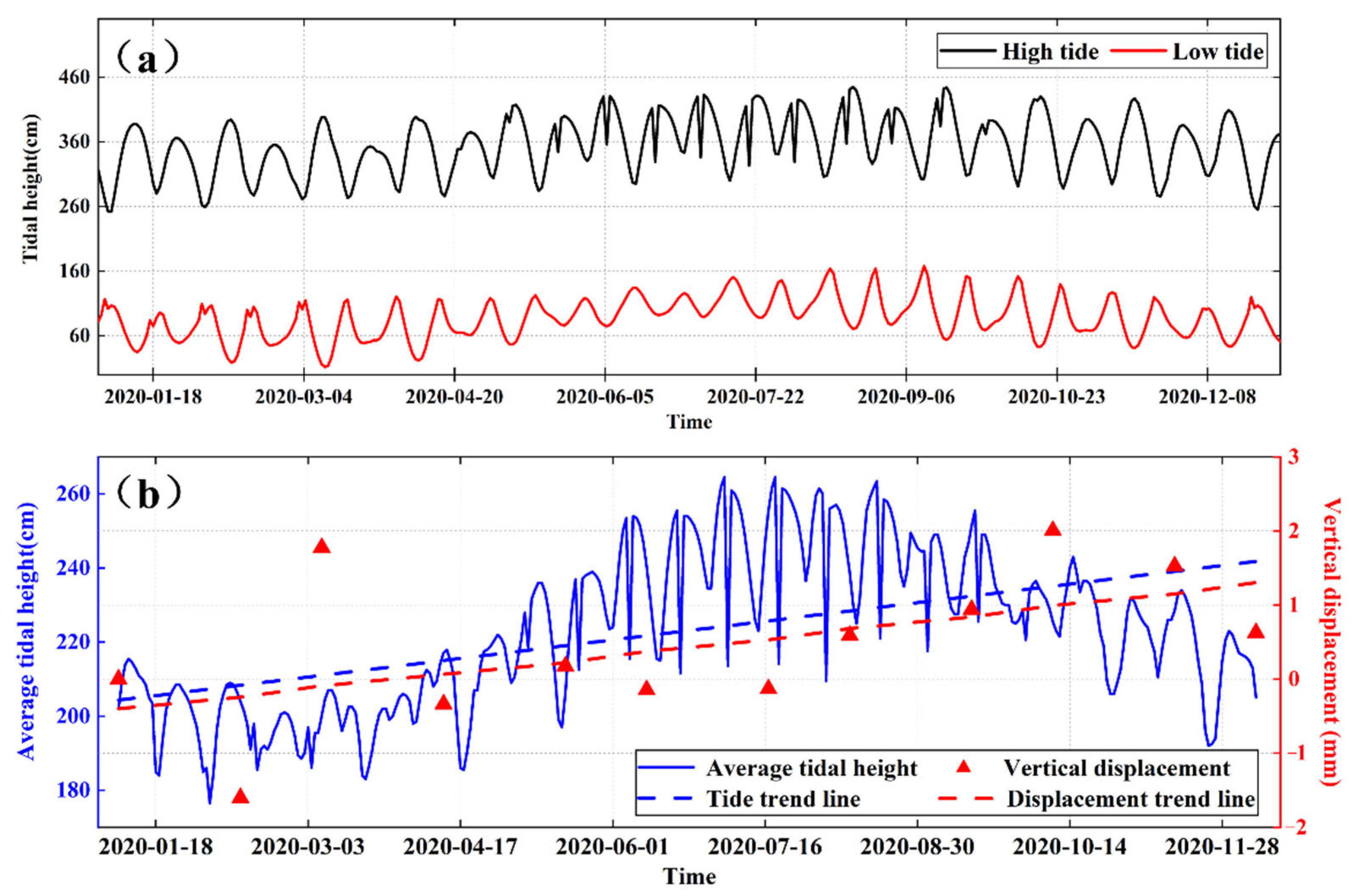
5.2.2. Correlation Analysis between the Seasonal Variation of Tide and Coastal Surface Uplift
5.2.3. Analysis and Study on Surface Deformation and Soil Expansion
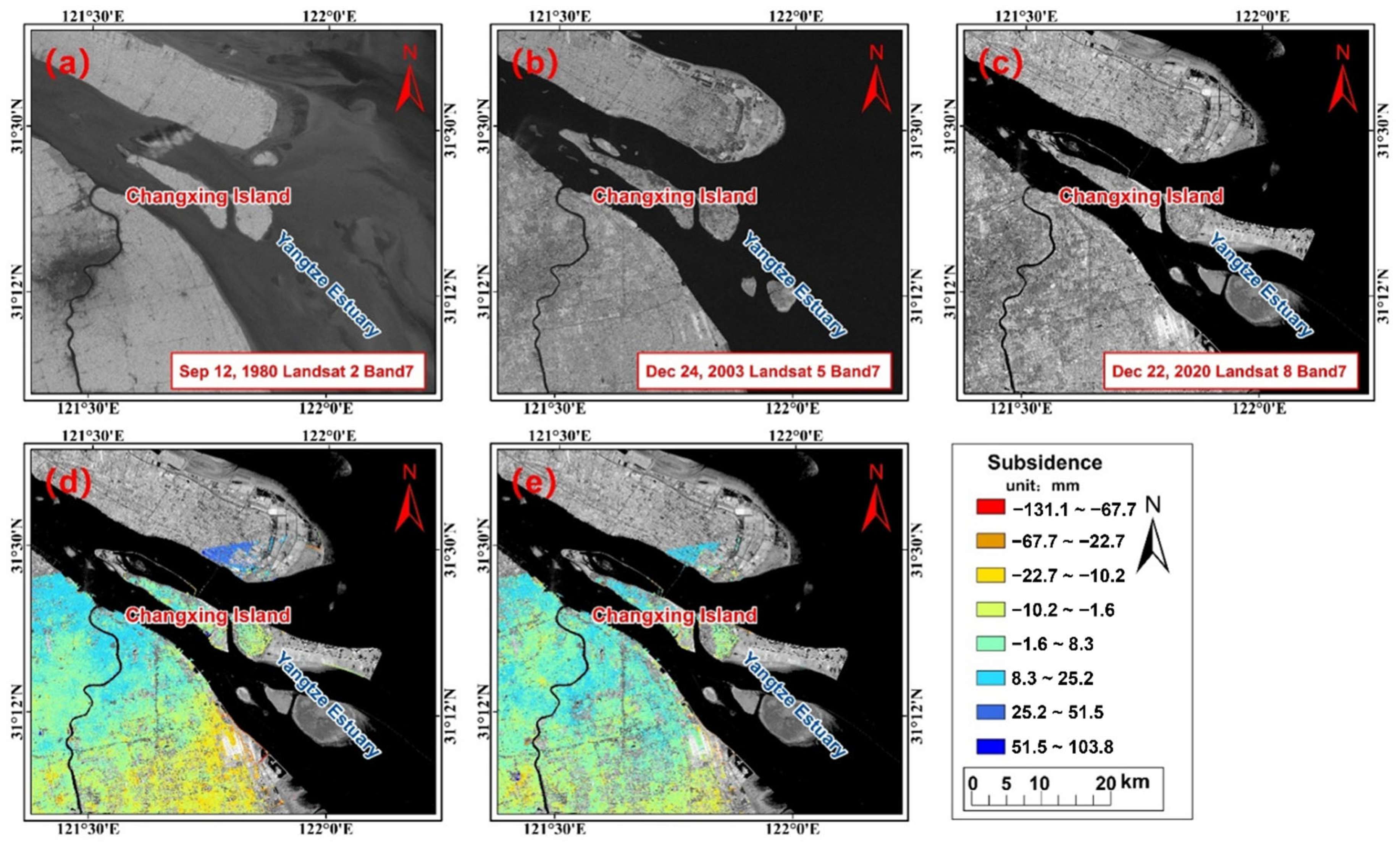
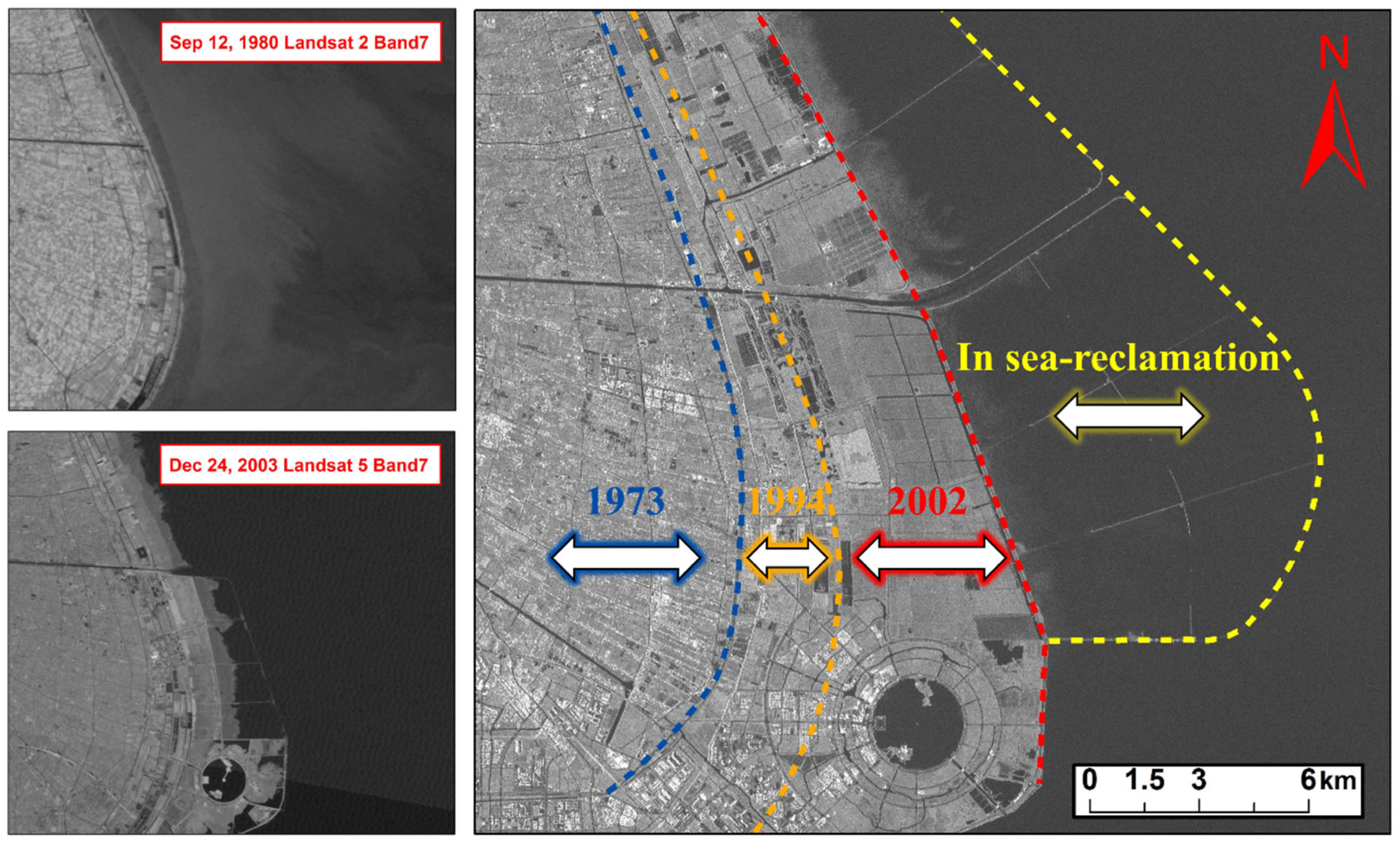
5.3. Surface Deformation in Reclamation Area of Shanghai
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.L.; Yue, Z.Q.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, S.J. Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng. Geol. 2004, 76, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Ma, R.; Xiao, C.; Liu, Y. Review: Water–rock interactions and related eco-environmental effects in typical land subsidence zones of China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land subsidence: A global challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Statistics Press. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.M.; Li, X.; Hu, J.Y. Monitoring and analyzing on ground subsidence in Beijing area based on SBAS-InSAR. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 36, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Poland, M.; Burgmann, R.; Dzurisin, D.; Lisowski, M.; Masterlark, T.; Owen, S.; Fink, J. Constraints on the mechanism of long-term, steady subsidence at Medicine Lake volcano, northern California, from GPS, leveling, and InSAR. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2006, 150, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Zhou, L.; Ren, C.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Y.J. Spatiotemporal Inversion and Mechanism Analysis of Surface Subsidence in Shanghai Area Based on Time-Series InSAR. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carnlona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, S.; Hunstad, I.; Chini, M.; Salvi, S.; Tolomei, C.; Bignami, C.; Stramondo, S.; Trasatti, E.; Antonioli, A.; Boschi, E. Finite fault inversion of DInSAR coseismic displacement of the 2009 L’Aquila earthquake (central Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.M.; Hu, J.Y.; Li, J.W.; Xu, Y.F.; Pan, Y.J.; Shi, M. Wuhan surface subsidence analysis in 2015–2016 based on sentinel-1A data by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Sanchez, P.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Duque, S.; Monells, D. The coherent pixels technique (CPT): An advanced DInSAR technique for nonlinear deformation monitoring. In Earth Sciences and Mathematics; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 165, pp. 1167–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Yao, C.L.; Hu, J.Y. Surface Subsidence Analysis by Multi-Temporal InSAR and GRACE: A Case Study in Beijing. Sensors 2016, 16, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yan, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Lu, W.; Yao, M.; Dong, J.; Zhan, J.; Huang, X.; Niu, C.; et al. A spatial-scale evaluation of soil consolidation concerning land subsidence and integrated mechanism analysis at macro-, and micro-scale: A case study in Chongming East Shoal Reclamation Area, Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Deng, K.Z.; Gao, X.X.; Niu, H.P. Monitoring and Analysis of Surface Subsidence in Mining Area Based on SBAS-InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Sheng, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Land Subsidence in Wuhan, China from 2017 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. A Review of Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry Applications in Permafrost Regions: Current Status, Challenges, and Trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 1, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Wu, J.C.; Li, T.; Chen, J. Monitoring Ground Deformation Based on Small Baseline Approach in Shanghai. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 40, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Yang, T.L.; Yang, M.S.; Liao, M.S.; Lin, J.X.; Zhang, L. Attribution Analysis on Deformation Feature of the Shanghai Elevated Highway by Persistent Scatterer SAR Interferometry. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2018, 43, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.S.; Yang, T.L.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.X.; Qin, X.X.; Liao, M.S. Spatio-Temporal Characterization of a Reclamation Settlement in the Shanghai Coastal Area with Time Series Analyses of X-, C-, and L-Band SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beradino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Li, Z.W.; Hu, J. Research Progress and Methods of InSAR for Deformation Monitoring. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, H. Surface deformation monitoring in Zhengzhou city from 2014 to 2016 using time-series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.R.; Liao, M.S.; Wang, Y. Progress of permanent scatterer interferometry. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2004, 29, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yue, G.S.; Ding, X.B.; Yuan, K.; Feng, G.C.; Xiong, Z.Q. Temporal and spatial characteristics analysis of Deformation along Foshan subway using time series InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 44, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B. Deformation Trend Extraction Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, T.L.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Pepe, A. The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.W.; Wu, J.C.; Ding, X.L.; Wang, M.Z. Elevation Extraction and Deformation Monitoring by Multitemporal InSAR of Lupu Bridge in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.Q.; Yang, T.L.; Yang, M.S.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M.S. Health Diagnosis of Major Transportation Infrastructures in Shanghai Metropolis Using High-Resolution Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Sensors 2017, 17, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Review: Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Motagh, M.; Indu, J.; Karanam, V. Tracking hidden crisis in India’s capital from space: Implications of unsustainable groundwater use. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Water Authority. Shanghai Water Resources Bulletin 2019; Shanghai Water Authority: Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Water Authority. Shanghai Water Resources Bulletin 2020; Shanghai Water Authority: Shanghai, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.H.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.L.; Lu, J.J. Analysis of Time Series InSAR Based Settlement Monitoring along the 2018- 2020 Metro Line in Shanghai Area. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2021, 41, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, F.H.; Yu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Shen, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Luo, Q. Synoptic Analysis of Extreme Meiyu Precipitation over Yangtze River Basin During June–July 2020. Meteorol. Mon. 2020, 46, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Gong, H.L.; Gao, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhou, C.F. Recent ground subsidence in the North China Plain, China, revealed by sentinel-1A datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, A.; Hermas, E. The 2018 long rainy season in Kenya: Hydrological changes and correlated land subsidence. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Pisano, L. Long-term InSAR, borehole inclinometer, and rainfall records provide insight into the mechanism and activity patterns of an extremely slow urbanized landslide. Landslides 2020, 17, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Miguel, A.S.D.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Elvidge, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, C.Y.; Warner, T. Remote sensing of night-time light. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5855–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W.; Li, Q.; Liu, G.B. Characteristics of one-dimensional compressibility of Shanghai clay. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 33, 630–636. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Wang, W.D.; Xu, Z.H. Empirical correlations of compression index and swelling index for Shanghai clay. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 3773–3782. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.Y.; Chen, Q.S.; He, J.F.; Zhang, X.L. Effect of rise of groundwater table on seismic ground response of soft soil in Shanghai. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 33, 989–995. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhao, C.X. One-dimensional consolidation tests of creep deformation and secondary consolidation charhcteristics of soft soils in Shanghai area. J. Eng. Geol. 2008, 16, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.X. Geological Atlas of Shanghai City; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Du, J.; Song, K.S.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, D.F. Land Use Pattern and Its Change in the Mouth of Yangtze River for 5 Periods. Wetland Sci. 2017, 15, 608–612. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.J.; Mei, X.F.; Darby, S.E.; Lou, Y.Y.; Li, W.H. Fluvial sediment transfer in the Changjiang (Yangtze) river-estuary depositional system. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, M.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, X.L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.Q. Influence of ocean tidal loading on InSAR offshore areas deformation monitoring. Geod. Geodyn. 2017, 8, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, H.K. A Reviw on Tidal Triggering of Earthquakes. Earthquake 2011, 31, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bredehoeft, J.D. Response of well-aquifer systems to earth tides. J. Geophys. Res. 1967, 72, 3075–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Camp, M.; Vauterin, P. Tsoft: Graphical and interactive software for the analysis of time series and Earth tides. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 31, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, P. Earth tides. Geophys. Surv. 1974, 1, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talke, S.A.; Jay, D.A. Changing Tides: The Role of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 121–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.L.; Xiao, J.H.; Cai, J.F. Detection of the Urban Surface Deformation and New Strategy for Flood Prevention in Wuhan Central District. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, T.N.; Gillies, R.R.; Schmugge, T.J. An interpretation of methodologies for indirect measurement of soil water content. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 1995, 77, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiles, D.E. Hydrology of swelling soils: A review. Soil Res. 2000, 38, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Guo, J.X.; Chang, J.; Yang, H.P.; Chen, G.Y. Effect of acid rain on swelling property and microstructure of natural expansive soil. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, C.J.; Shi, S.; Gong, J.Y. Tracking of Land Reclamation Activities Using Landsat Observations—An Example in Shanghai and Hangzhou Bay. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Pepe, A.; Devlin, A.T.; Falabella, F.; Yao, C.F.; Li, Z.J. Changes of Chinese Coastal Regions Induced by Land Reclamation as Revealed through TanDEM-X DEM and InSAR Analyses. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M. On the effects of InSAR temporal decorrelation and its implications for land cover classification: The case of the ocean-reclaimed lands of the Shanghai megacity. Sensors 2018, 18, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
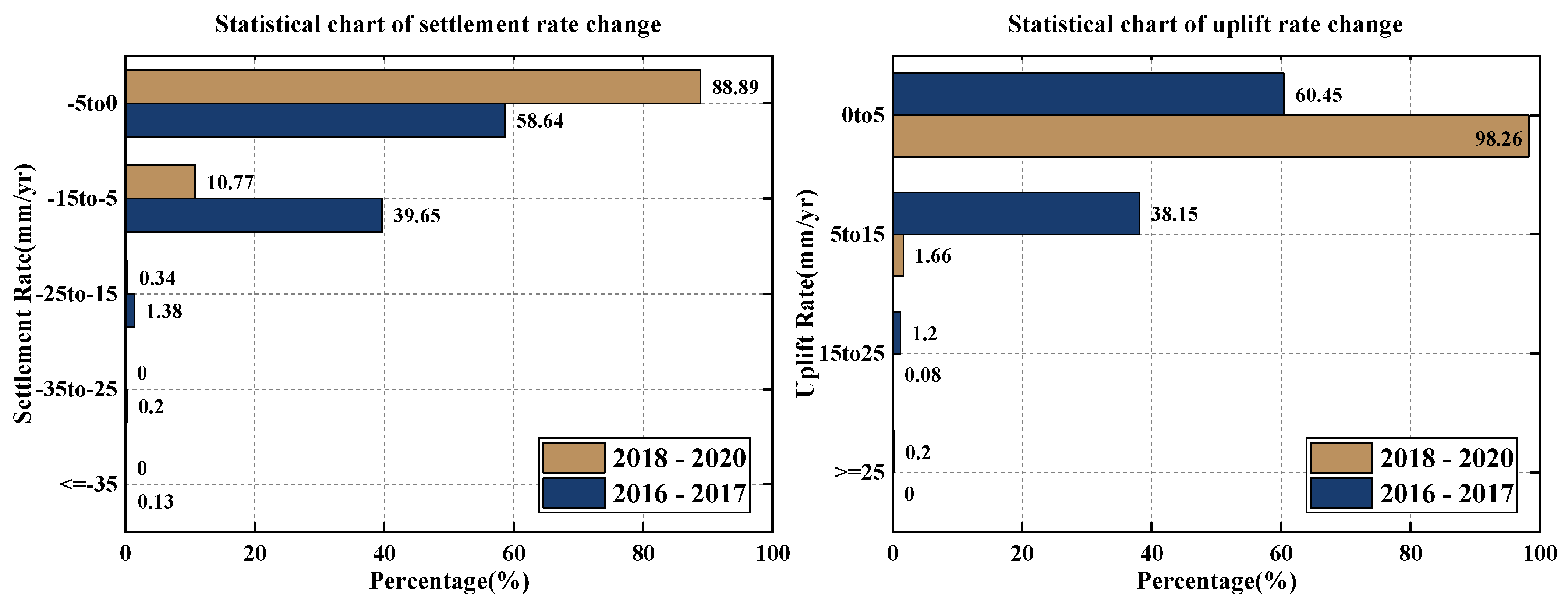


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Band (wavelength in cm) | C (5.6 cm) |
| Imaging mode | Sentinel-1A IW |
| Number of images | 61 |
| Pass direction | Ascending |
| Time span | From 15 May 2016 to 8 December 2020 |
| Study | Band | Method | Period | Research Object | Deformation RATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perissin, et al. (2012) [17] | X | PS-InSAR | 2008–2010 | Major subways and highways | −40 mm/y~40 mm/y |
| Chen, et al. (2013) [27] | X | MT-InSAR | 2007–2010 | Main urban surface | −21.6 mm/y~12.8 mm/y |
| Yu, et al. (2017) [28] | X/C | D-InSAR | 2015–2016 | Coastal areas | −30 mm/y~30 mm/y |
| Zhao, et al. (2017) [29] | X | PS-InSAR | 2008–2010 | Lupu Bridge | −10 mm/y~10 mm/y |
| Qin, et al. (2017) [30] | X | PS-InSAR | 2013–2016 | Major transportation lines | −22 mm/y~6 mm/y |
| Yang, et al. (2018) [20] | X/C/L | TS-InSAR | 2007–2010 | New Lingang City | −35 mm/y~10 mm/y |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, J.; Xian, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, L. Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174368
Li J, Zhou L, Zhu Z, Qin J, Xian L, Zhang D, Huang L. Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(17):4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiahao, Lv Zhou, Zilin Zhu, Jie Qin, Lingxiao Xian, Di Zhang, and Ling Huang. 2022. "Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology" Remote Sensing 14, no. 17: 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174368
APA StyleLi, J., Zhou, L., Zhu, Z., Qin, J., Xian, L., Zhang, D., & Huang, L. (2022). Surface Deformation Mechanism Analysis in Shanghai Areas Based on TS-InSAR Technology. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174368










