Abstract
The detachment and mobilization of boulders from rocky shore platforms by waves involves complex geomorphic and hydrodynamic processes. Understanding these processes requires precise information on the rates and patterns of movement of these megaclasts scaled against the wave conditions that generate boulder mobility. Repeat photogrammetry and structure-from-motion (SfM) models commonly used in geomorphic analyses are an interesting option for monitoring boulder dynamics. In this study, we used unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based digital photogrammetry and SfM differential models to identify recent boulder movements over a rocky shore platform in Laghdira, Morocco. Combining these results with data on storm occurrence in the study area allowed us to identify storm waves as the unique driver of the dislodged and mobilized boulders. The identified storm event had a significant wave height of 5.2 m. The UAV models were built from imagery captured in September and December 2019 using a DJI MAVIC PRO PLATINUM, and we used QGIS to produce 2D and 3D model outputs. The exploitation of the 2D model differentials allowed us to appreciate the response of the boulders to the storm waves and to determine platform volumetric changes and, therefore, boulder mobility. The 3D models were valuable in determining the mode of transport of the boulders. Mobility patterns included sliding, overturning with no further mobility, and rotation and saltation, as well as boulder breakup. Storm waves did not have a preferential impact on any particular boulder shape, size category, or position at the outer edge of the platform. These results highlight the utility of combining UAV surveys with identified storm events, which are much more frequent than tsunamis, in determining observed boulder initiation and mobility.
1. Introduction
Coastal boulder deposits (CBDs) are common worldwide on bedrock platforms along high-energy coastlines, and include clasts with a wide variety of dimensions and weights [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. They are frequently found as isolated deposits, or form imbricated boulder ridges that can be several meters high, tens of meters wide, and hundreds of meters long [4,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The presence of large and isolated boulders (~3–8 m dimensions) scattered at high elevations—either at the landward edge of bedrock platforms or on top of bedrock cliffs of varying heights [17,18,19]—is regularly interpreted as evidence of an inland transport and deposition process by storm or tsunami waves [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. At the intertidal zone of bedrock shore platforms, smaller boulders (~1–3 m dimensions) are more commonly found, and their occurrence as isolated clasts or organization into distinctive ridges, mounds, or clusters is indicative of wave transport and sorting [28,29,30,31,32,33,34].
There are numerous studies of storm-driven, bimonthly to century-timescale changes in coastal boulder deposits in intertidal settings [17,32,33,34,35,36,37]. These studies typically report movement of boulders months to years before and after a storm, and reflect poor time-coupling between field observations and actual storm events [34]. An important issue in understanding processes of coastal boulder transport resides in the difficulty of performing in-situ monitoring and observations just before and after storm events. Surveys of boulder movements before, during, and after specific storm events remain rare. However, such surveys are critical in understanding and predicting boulder responses to past, present, or future storms [34,38,39].
In the last few years, photogrammetric surveys to monitor rapid and significant morphological changes (notably in coastal and fluvial environments) have become widely employed [40,41,42,43,44]. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) surveys and structure-from-motion (SfM) photogrammetry using different kinds of software are increasingly employed for high-frequency and high-resolution monitoring of boulder dynamics following storms [31,32]. UAV-derived orthophotographs and comparisons between DEMs can provide excellent datasets and information on coastal boulder patterns and the assessment of potential boulder movements following storm conditions [4,12,15]. The comparison between orthophotographs and 3D model differentials prior to and after storm conditions also enables the identification of boulder detachment processes on rocky platforms [35,37]. These studies demonstrate the reliability of using repeat photogrammetry coupled with the integration of 2D/3D digital terrain models (DTMs) in geographic information systems (GISs) to quantify morphological changes on rocky platforms and, thus, extract accurate measurements of boulders, their movement distances, and their imbrications and/or detachments from bedrock shore platforms.
Here, we investigate the characteristics, the forcing parameters, and the movement of boulders on a rocky shore platform in Laghdira, on the Larache coast of northwest Morocco (Figure 1), following an intense storm in December 2019. Terrestrial and aerial surveys were conducted before and after the storm to analyze the possible geomorphological effects of this high-energy event in the movement of boulders, their disappearance, and the appearance of new ones. By combining UAV-based repeat photogrammetry surveys and quantitative differencing of 2D/3D digital terrain models (DTMs), we (1) detected and quantified potential boulder transport and detachment triggered by the storm, and (2) identified possible boulder transport modes. This study can hopefully provide new insight into boulder dynamics in this area of the Atlantic coast of Morocco, where a previous study has linked the location and potential mobility of boulders to tsunamis [23].
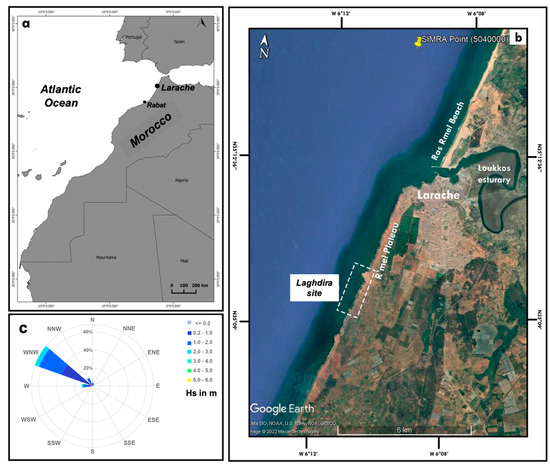
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the study area; (b) Google Earth map of the Laghdira site with wave data source (SIMAR) location; (c) wave rose off the study area based on data from 2000 to 2020 for SIMAR spot 5040000.
2. Study Area
The Laghdira site is part of a dominantly rocky shore south of the Loukkos River estuary and the city of Larache on the northwestern Atlantic coast of Morocco (Figure 1). The coast north of the estuary comprises a sandy beach, Ras Rmel, composed of fine and medium sand, either capped by dunes up to 10 m high or limited inland by a Quaternary sandstone cliff [45]. This sandstone formation also underlies the dunes, and is responsible for the constriction of the Loukkos estuary mouth [46]. The sector south of the estuary, comprising the study site, is composed of actively retreating cliffs that bound the Rmel Plateau, the elevation of which varies between 20 and 30 m asl [23,47]. Older inactive cliffs appear some 1–3 km inland [44]. The active cliffs form an almost rectilinear shoreline with a few promontories, including Punta Nador and Laghdira (the northern limit of our study area). The cliff outcrops consist of an alternation of poorly consolidated Quaternary aeolianites with large foreset beds, thin red sandy levels, continental gastropods, and thin beach deposits. The lowermost part of the cliffs is composed of 2 m thick, horizontally layered, more compacted red Quaternary sandstones with low porosity [23,47]. The retreat of these aeolianite cliffs has led to the cropping out of the sandstones that form the surface of the shore platform (Figure 2). The intertidal width of the platform at Laghdira at mean low tide varies from 20 m at the promontories to 100 m in the widest sectors, with a mean of 60 m. The surface dips gently seawards or landwards (Figure 2). The basal level shows a few wave-cut notches where the shore platform is narrowest. The boulders originate from wave dismantling of this shore platform, and are deposited as single clasts, clusters, or imbricated stacks (Figure 2). Medina et al. [23] and Adil [47] have provided detailed geological descriptions of two sections of the cliff wall and platform: 5.2 km north and 5.4 km south of Laghdira, respectively.

Figure 2.
Oblique view of the shore platform at Laghdira, showing aspects of the lithology and geomorphology.
The climate of the northwestern Atlantic coast of Morocco is subhumid and characterized by two distinct seasons. Conditions are cool and humid from the months of October to April, which account for 90% of the annual rainfall. From May to September, dry and hot conditions prevail, with virtually no rainfall in July [48,49,50].
The wind regime is closely related to the Azores anticyclone and North Atlantic depressions [48,51]. The dominant winds in the Larache area are from west to west-northwest, with average mean velocities of 5–10 m s−1. During the summer, these winds alternate near the coast with the Chergui wind of continental origin and from the east [52]. The Larache coast is dominantly exposed to moderate- to high-energy swell waves [53] with significant wave heights during normal weather conditions ranging from 1 to 3 m, but which may reach up to 6 m during storms (Table 1) [54]. The archive of wave data for the last 20 years extracted from the SIMAR spot 5040000 (with coordinates 35.25°N and 6.17°W, and run by the Port Authorities of Spain http://www.puertos.es accessed on 1 October 2019) offshore of Larache show that waves from the west-northwest largely dominate in both winter and summer (Figure 1). Tides on the Larache coast are semi-diurnal and mesotidal, with a mean spring range of 3.1 m and a mean neap range of 1.3 m.

Table 1.
Wave characteristics off the study site from 1980 to 2020 (Port Authorities of Spain http://www.puertos.es accessed on 1 October 2019).
3. Materials and Methods
Our investigation of the boulder accumulation combined classical geomorphological and geological investigations with UAV surveys. In order to assess the impacts of the 2019 winter storms and possible boulder movements, two field surveys were conducted in mid-September and at the end of December 2019.
3.1. Field Surveys
In the course of the field surveys, geological and geomorphological observations of the coastal cliffs, shore platform, and boulders were carried out over an area of 980 m × 80 m. In addition to an inventory of the boulders, their locations, sizes, shapes, and lithology were determined. The distribution of these boulders is not homogeneous (Figure 2). We therefore chose to focus on the southern part of the site, which has a wide distribution of boulders with single clasts, clusters, and imbricated stacks (Figure 3).
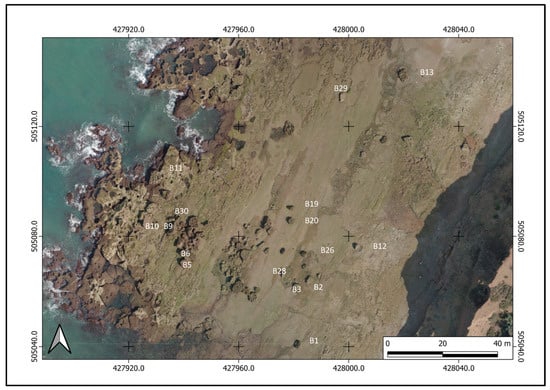
Figure 3.
September 2019 orthophotograph showing the spatial distribution of some of the analyzed boulders.
Thirty-one boulders representing the range of sizes, shapes, and distances from the coastline were measured and analyzed. The dimensions of individual boulders were measured in terms of three perpendicular axes A, B, and C, representing the long, intermediate, and short axes, respectively (Figure 4). The lengths of the A, B, and C axes were used to calculate the B/A and C/B ratios, and to morphologically classify the boulders in our study site according to the Zingg diagram. Boulder locations and distances from the shoreline were measured using a Trimble differential GPS in real-time kinematics mode with an accuracy of +/− 0.15 m (Figure 4), and the X, Y, and Z coordinates were referenced to the World Geodetic System (WGS84).
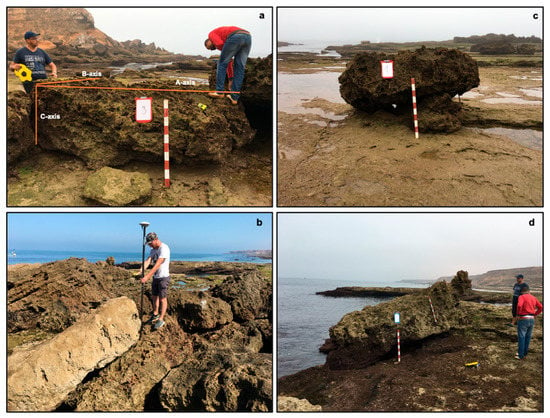

Figure 4.
Examples of boulders at Laghdira: (a) measured boulder axes (A, B, and C); (b) DGPS topographic measurements of boulder positions; (c) imbricated boulders at the upper part of the rocky platform (B1); (d) joint-bounded boulder at the platform edge (B11).
3.2. UAV on-Site Surveys and Image Acquisition
We carried out two UAV flights on 15 September and 26 December 2019 using a DJI MAVIC PRO PLATINUM quadcopter (DJI, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, China) equipped with a 12.35 MP camera. DJI GS Pro Flight Planner softwareTM was used for programming the automatically and autonomously executed flight plans (Figure 5). Images were collected at nadirs along calibrated flight paths parallel to the coast, at an elevation of 70 m (Table 2).
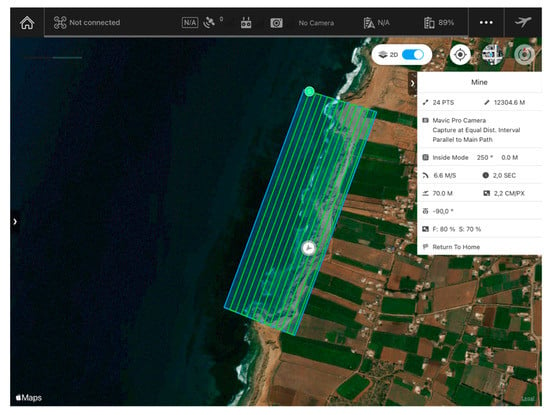
Figure 5.
September 2019 flight path over the study area as seen in the screen capture from the DJI GO 4.

Table 2.
September and December 2019 flight parameters.
High-overlap image sets ensure sufficient target points in adjacent images; as the standard procedure, we planned the flight paths to provide 80% overlap between successive images and 70% sidelap between adjacent paths [35,55,56,57,58,59].
In both surveys, 22 ground control points (GCPs) consisting of black-and-white checkered cardboard, essential for the production of georeferenced aerial images, were deployed—7 on the top of the cliff and 15 at different locations on the rocky platform (Figure 6)—to provide the widest possible coverage. Their positions were recorded using a Trimble differential GPS in real-time kinematics mode. The RMSE values of the September and December 2019 UAV surveys were 14 cm (xy of 13 cm and z of 5.4 cm) and 13 cm (xy of 12 cm and z of 5.2 cm), respectively.

Figure 6.
Ground control points (GCPs) deployed in the study area: (a) photograph of a GCP positioned on the rocky platform; (b) GCP (white arrow) visible on an image; (c) spatial distribution of GCPs in the study area.
3.3. Aerial Image Analysis and Model Generation
We used Agisoft Metashape Professional software version 1.6.2 to process the images. Image alignment was first performed in order to select the images for the computation of the models and orthophotographs. During each UAV survey, a total of 882 images was recorded; 788 images for the September 2019 survey and 729 for the December 2019 survey were processed to construct the dense clouds. The digital marker coordinates were updated automatically to match the GCP coordinates measured by DGPS in the field. The software measured the differences between GCP coordinates and the estimated coordinates for other points in the model, and refined the projections accordingly. Digital elevation models (DEMs) and orthophotographs of the two surveys were then computed using Agisoft Metashape software, with 2.04 and 3.08 cm/pixel resolutions, respectively.
The next stage consisted in transferring the results to a GIS environment using QGIS version 2.18 (QGIS Development Team, QGIS Geographic Information System, Open-Source Geospatial Foundation Project). The September and December 2019 models aligned well in the QGIS output following examination of areas where we were certain that no morphological changes occurred over the three-month interval.
In order to determine potential boulder displacements, we generated a digital differential model between the September and December 2019 DEMs using QGIS software. Most of the work done on boulder monitoring and dynamics based on UAV and SfM data generally uses only the analysis of the DEM differentials, or accompanies it with complementary field measurements for the verification and characterization of boulder movements (typology and distance) [31,32,33,35]. However, there are other possibilities for generating 3D orthorectified visuals from further processing using Agisoft software (Agisoft, 2019).
Building high-resolution 3D models for the entire study site is computationally demanding. Therefore, we limited ourselves to generating 3D models of the main area of investigation, characterized by isolated boulders and clusters of imbricated boulders (Figure 7). With the dense point clouds created and the whole model correctly georeferenced, it is possible to create a 3D mesh by forming a planar structure “connecting” the points: “processing” tab -> “build a mesh” [51]. It is then possible to specify the “source data” (this involves favoring the dense point cloud, as it is fairly precise and has little space between points), the “surface type” (choose “Arbitrary 3D” for fairly complex geometries), and the “number of faces”. However, the more faces there are, the more computational resources are required, and the finer the resolution of the output model. After this step, the texture can be built and plated on the 3D model. The “mapping mode” determines how the texture will be plated. It is desirable to choose the “generic” or “adjusted orthophoto” modes for arbitrary geometries in order to ensure a better visual quality in the output [51]. The “merge mode” allows one to choose how the pixels of the different images will be combined. At this stage, the “mosaic” mode is preferred, as it allows for selection of the pixels of the center of the image in order to improve the quality of the images, with no luminosity variation during the UAV tracking. Finally, the “size/number of textures” represents the resolution of the image. The greater the size/number, the better the resolution, but at the expense of computation time. The 3D models are generated and can then be processed to search for the evaluation of possible boulder rotation and translation transport.
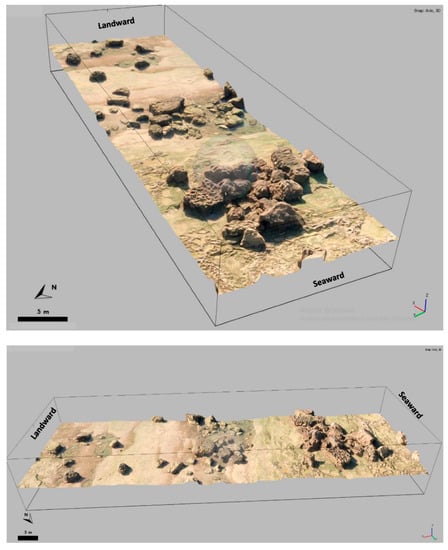
Figure 7.
Plunging axial (top) and lateral oblique (bottom) views of the 3D model generated for the study area from the September 2019 UAV survey.
We shared the two 3D models of the restricted area on the 3D photogrammetric project publication website (Sketchfab.com accessed on 20 January 2020). These models are in low resolution because we opted to share them with the free version of the website, which imposes a reduction in the size of shared files (<40 Mo).
3D model of 15 September 2019: https://skfb.ly/o8LAD.
3D model of 26 December 2019: https://skfb.ly/o8LAD.
Extensive processing of the images also makes it possible to assess the mode of boulder transport following storm events. The change in orientation of the A and B axes provides information on the direction of movement. Analysis of the exposure of the 3 axes A, B, and C of a boulder after one or more storm events could indicate the mode of transport of the boulder. Indeed, with this type of treatment and analysis, Nagle-McNaughton and Cox [35] were able to determine that translation was the dominant transport mode for boulders during storms on the Aran Islands near Galway, Ireland. They were also able to cross-reference the in-situ measurements with UAV image processing to observe rotated or overturned boulders. Biolchi et al. [33] used 3D models to detect and characterize the shifting of boulders (mainly rotation) on the Premantura (Kamenjak) Promontory in Croatia during the October 2018 Storm Vaia.
The areas of erosion and accretion detected in the DEMs of differences between September and December 2019, generated using QGIS, were initially considered to reflect potential boulder movements prior to a comparative re-check between the models, as well as ground-truthing. The field verification provided final validation of boulder mobility.
4. Results
4.1. Boulder Settings and Measurements
The rocky platform of Laghdira consists mainly of a horizontally layered, well-compacted, porous sandstone [23,47]. Along this platform, the longitudinal distribution of boulders is not homogeneous. Some sectors of the platform are completely devoid of megaclasts. Boulders are mainly found on the southern part of the rocky shore platform, where we concentrated our investigations. In this sector, boulders are deposited as single clasts, clusters, or imbricated stacks. In total, 31 boulders of various sizes and shapes were selected and analyzed (Figure 3).
Joint-defined blocks not yet detached from the shore platform and joint-defined sockets were observed at the edge of the shore platform (Figure 4 and Figure 7). The largest boulders, which are also predominantly imbricated, with an onshore orientation (Figure 8), occur closest to the shoreline. The central area of the rocky platform has a wide range of boulder sizes and orientations. Most boulders display a normal polarity, and a few are turned upside-down or laterally (Figure 7). In the same area, small and very small clasts can sometimes be found imbricated below larger clasts. As we approach the top of the intertidal zone near the foot of the cliff, boulders are less present and more dispersed (Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 8). The surface of 90% of the boulders displays biogenic encrustations of vermetids (Figure 4), and several boulders show sharp edges and striae on their surfaces (Figure 4a).
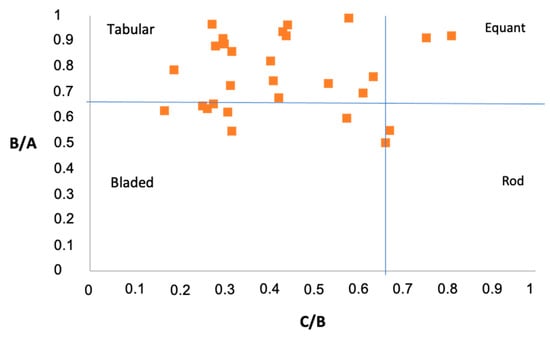
Figure 8.
Zingg shape classification for the 31 selected boulders.
The values of the A, B, and C axes measured on the 31 boulders are shown in Table 2 and Figure 8. The axis values and the volume of the average boulder are 3.38 × 2.51 × 1.01 m and 10.43 m3, respectively. The largest boulder (B11) is 6.27 × 5.53 × 1.56 m, with a resulting volume and mass of 54 m3 and 119 t, respectively.
About 96% of the boulders exhibit a tabular or bladed shape (Figure 8), and are characterized by slightly smoothed or sharp-cornered edges forming angles in the range between 55 and 80°. No common polarity or prevailing directions of the A and B axes between the different boulders—from the outer edge to the upper rocky platform at the foot of the cliff—could be detected. The lateral distribution of the boulders followed the same pattern. Boulders B1, B12, and B11, which are isolated along the upper rocky platform, have A, B, and C axis values ranging from even to double (Table 3).

Table 3.
A, B, and C axis sizes, volume, and mass of the 31 selected boulders.
4.2. Wave Conditions and Storms between UAV Surveys
A comparison between the UAV surveys of September and December 2019 was carried out in order to identify and quantify any boulder movements related to the December 2019 storms (Figure 9).
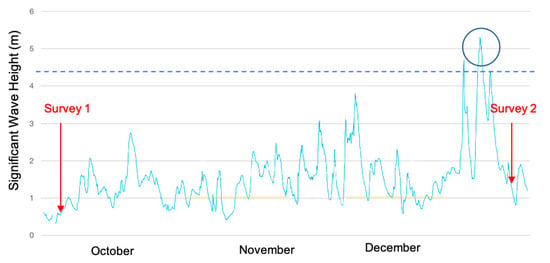
Figure 9.
Significant wave height (m) conditions between the UAV surveys (red arrows), the wave storm threshold adopted for this study (blue dashed line), and the December storm conditions (blue circle). Wave data were obtained from the Port Authorities of Spain (http://www.puertos.es accessed on 1 October 2019).
The storm wave threshold, which corresponds to the minimum wave height under favorable high-tide conditions (especially during spring tides) liable to produce significant morphological changes on beaches and dunes, has been defined in terms of a significant wave height (Hs) value of about 2.5 m at the southwest Spanish Atlantic coast [60], and of 2.5–4.5 m along the Portuguese coast [61], which is relatively similar to the Moroccan Atlantic coast in terms of exposure to Atlantic swells. The storm wave threshold values can vary from one coastline to another depending on initial morphology and the degree to which significant morphological change is considered. Mhammdi et al. [62] have recently attempted to identify the morphological impacts of storms that affect the Moroccan Atlantic coast. In their study, they identified storms—notably those in 2014 and 2017—that caused significant displacement of boulders on the rocky beaches of the coastline between Casablanca and Rabat. Combining historical and recent data, Oliveira et al. [61] defined an Hs of value of 4.5 m as the storm wave threshold, and we also opted for this value in our study.
Between the survey of September 15th and December 26 (Figure 9), wave conditions were generally calm until mid-November, when a few episodes of strong agitation with Hs exceeding 3 m were recorded. This was followed by a relatively calm period until December 19, when wave conditions exceeded the 4.5 m storm wave threshold for a continuous period of 25 h. This storm occurred in a phase of transition from neap to spring tides, which probably significantly reduced its impact on wave propagation over the rocky platform, and, consequently, on boulder mobility.
4.3. UAV Images and SFM Photogrammetry Analysis
Comparison of the September and December models shows no erosion or accretion over much of the rocky platform, and unevenly distributed boulder movements (Figure 10). Areas with orange and green tints at the upper rocky platform are linked to an offset because of the presence of humans or animals (especially donkeys used to transport sand) during the drone flights.
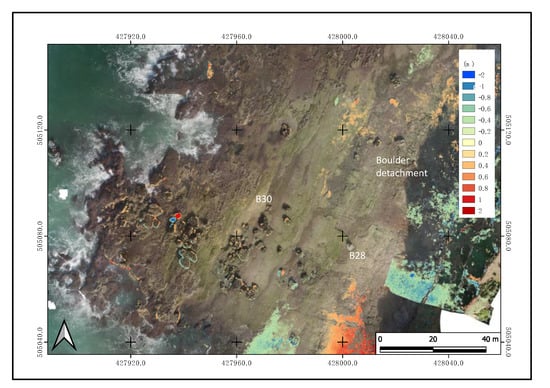
Figure 10.
Orthophoto generated from the December 2019 UAV survey, showing the spatial distribution of three boulders affected by the December storm (B28, B29, and B30). An incipient boulder detachment is also visible in the central sector of the rock platform.
Detailed analysis of the model output differentials indicates detectable boulder movements near the outer edge (B30) and the central areas of the rocky platform (B28 and B29) (Figure 10). A recently initiated detachment process of a new boulder in the central sector of the platform is also visible in the comparison of the UAV surveys (Figure 10).
The quadrangular boulder B29 (≈3.38 m3 and 7.44 t) was oriented with the longer axis parallel to the shoreline and the main axis in the wave direction. Following the December storm, this boulder was found 12 m further inshore and broken into two parts (Figure 10). The alignment of the main axis of the two fragments of this dislocated boulder has now become oriented in the main wave direction.
Boulders B28 and B30 showed lesser mobility following the storm, in the order of 1.2 m for B30 and 1.1 m for B28. This mobility was reflected in the model differential by a sequence of erosion/accretion on similar surfaces, but with non-equivalent variations in boulder-top elevations. The two boulders previously oriented in the direction of wave propagation maintained this sense of their main axis (A) orientation after the storm.
The majority of the boulders have a tabular shape (Figure 8). However, the three boulders that were significantly displaced during this storm belong to three categories of clast shapes: B28 is tabular, B29 is bladed, and B30 is equant in shape. Furthermore, the lightest of the mobile boulders (B28 ≈ 2.82 m3 and 6.21 t) presented a similar displacement distance to the heavier and larger boulder B30 (B30 ≈ 9.91 m3 and 21.79 t). The mobile boulders were located at varying distances from the outer edge of the platform, with B30 being closest and B28 being farthest (Figure 10).
The September and December 2019 differential was of a resolution high enough to identify sliding as the mode of boulder transport for B29. The fresh traces of this boulder’s movement are also detectable in the orthophoto and the model, and were confirmed by the field investigation (Figure 11).
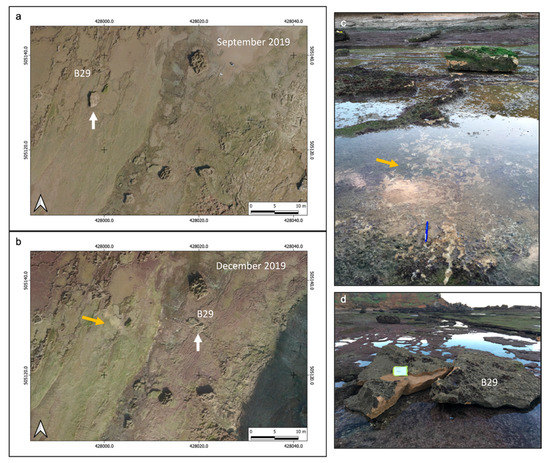

Figure 11.
(a) Initial position and (b) displacement of boulder B29 (white arrows); the orange arrows (b,c) show the initial position and trace of the B29 pedestal; bleu pen in (c) for scale (d) Post-storm position of B29.
However, the use of the same differential model did not allow us to identify the transport modes of boulders B28 and B30. We therefore used the 3D models to perform a more in-depth analysis of the transport modes of these two boulders. The 3D models generated from the UAV tracking of the shore platform were exported to the Sketchfab.com (accessed on 20 January 2020) platform in order to visualize them with different exposure angles. This flexibility in the visualization of boulder clusters is advantageous, as it enables the realization of the best comparative angle between the outputs of two consecutive UAV surveys.
Figure 12 displays a view of B28’s position pre- and post-storm, and clearly shows that the boulder was overturned by the storm and not displaced. A view from the sea to the land enables clarification of the mode of movement of boulder B30 following the December 2019 storm (Figure 13). B30 moved laterally (eastwards) while positioning itself on the boulder just ahead (imbrication) and obscuring its sharp eastern edge. It also exposed a new face, but with no biogenic encrustations as yet (Figure 13). This confirms a rotation and saltation of boulder B30 in response to the storm.
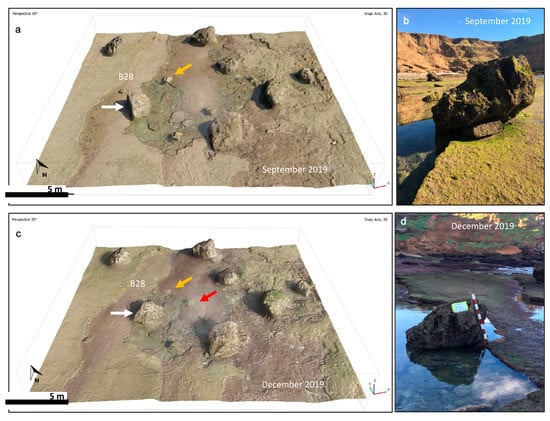

Figure 12.
(a) Initial position of boulder B28 (white arrow); orange arrow shows the position of a small clast near B28; (b) photo of B28 in September 2019; (c) displacement of B28 (white arrow), initial position of small clast (orange arrow) and its new position (red arrow); (d) photo of B28 in December 2019, with bar scale.

Figure 13.
(a) Initial position of boulder B30 in September 2019 (white arrow) and (b) in December 2019; (c) field photo of B30 overturned; orange arrows show striae on the rock platform and adjacent boulder caused by B30’s movement.
5. Discussion
When combined with close monitoring of storms, the employment of the UAV approach at multimonth-to-multiyear time steps allows for distinguishing boulder dynamics of tsunami origin from those of storm origin [63]. At Laghdira, our datasets provide evidence of the detachment and mobilization of three boulders during the December 2019 storm, as well as the emplacement of a new boulder following the storm. Three modes of boulder transport were detected from the analysis of orthophotographs in combination with 3D SfM models. The northern area, mainly characterized by isolated boulders, was subject to the longest boulder displacement (sliding) and the generation of a new boulder. The southern zone, characterized by a broad cross-sectional distribution of imbricated boulders and boulder clusters, showed a combination of saltation and boulder overturn with contrasting sizes and volumes. The presence of some joint-bounded boulders (Figure 4d), of sockets carved at the rocky platform edge, and the correspondence of morphometry between sockets and boulders, could confirm that the production of the blocks at the southern part of the study area occurred because of their detachment from the platform edge. The northern zone, without boulder clusters close to the rocky platform edge, was potentially more affected by the storm, resulting in the longest recorded boulder displacement, but also in the detachment of a new boulder in the central part of the platform. At the southern zone, the imbricated boulder cluster situated near the platform edge may have acted as a wave energy dissipation ramp, thus reducing the potential transport of adjacent boulders (Figure 14).
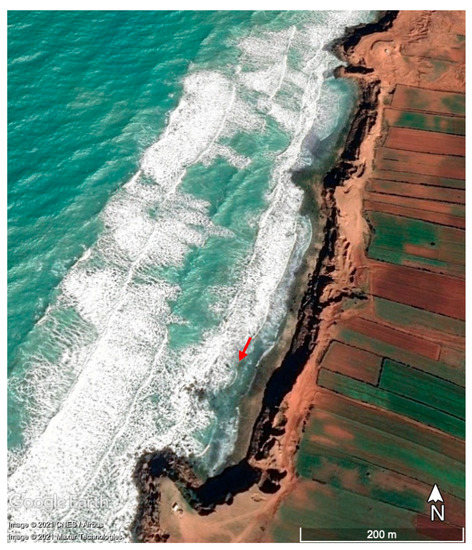

Figure 14.
Satellite image (Google Earth) of Laghdira on 16 February 2016 showing northwesterly storm waves with a significant wave height of 4.5 m (almost the same storm conditions as in December 2019). Wave diffraction and energy damping by the cluster of imbricated boulders (red arrow) can be clearly seen.
Medina et al. [23] assessed the forces and wave heights required to lift, dislodge, and displace the boulders at another rocky site in Larache (situated 5.4 km to the south of Laghdira) by using the equations of Nott (2003) [64] corrected by Pignatelli et al. [65] and Nandasena et al. [66]. The authors estimated that a 17.88 m storm wave height was necessary to move the largest studied boulder (3.9 m × 2.2 m × 1.4 m = 12.01 m3 and 26.42 t).
The storms of 2013–2014 significantly impacted the Atlantic coast of Europe [60,67] but also the Moroccan coast [62]. The recurrence of this type of strong storm over the last 20 years is remarkable, as between 1998 and 2015 there were up to 36 storm events of Hs > 7 m, while only 2 were recorded between 1956 and 1998 [62]. Furthermore, Mhammdi et al. [62] have shown that the storms that hit the Moroccan coast between 2014 (notably Hercules/Christina in 2014) and 2017, with offshore significant wave heights ranging from 3.6 m to 7 m, were able to displace boulders from 8 m3/16 t to 16.5 m3 / 33 t (overturned) on the beaches in the vicinity of Rabat (Figure 1). With the wave conditions recorded during the December 2019 storm, we are approaching the boulder displacement scenario observed on the Rabat coastline in [62], and definitely not the tsunami displacement/deposition scenario (Hs > 17.44) suggested in [23].
Combining short-term monitoring with UAV images and medium-term monitoring based on satellite images available via the Google Earth Engine and/or Bing could enable a better evaluation of the movements of coastal boulders following one or a series of storms [32,35]. Figure 15 depicts a selection of available Google Earth images of Laghdira (2013, 2017, 2018, 2019) at low tide. Comparison of the 2013 and 2014 images shows that boulders B28 and B12 (6.72 m3 and 14.8 tons) moved up on the rock platform by 12 and 14 m, respectively. During this period, the Atlantic coast experienced a series of significant storms (e.g., Hercules/Christina in 2014). A single storm occurred in February 2016. From 2017 to 2018, no detectable changes could be observed, although a high-energy event occurred on 1 March 2018 with a Hs > 5 m during 4 h. Boulder B28 appears onsite between October 2018 and August 2019 (just before our September 2019 fieldwork). This period was marked by two brief high-energy events of >4 m and >5 m, respectively, between October and November 2018. This hasty analysis of low-resolution images to extract possible boulder movements enables the detection of some changes in the locations of these megaclasts at Laghdira. However, it does not allow us to confirm that these movements were caused by the abovementioned high-energy events, even if there is consistency between energy and boulder movement.

Figure 15.
Satellite images (Google Earth Engine) of Laghdira in 2013, 2017, 2018, and 2019: (a) positions of boulders B12, B19, B20, and B28 in 2013; (b) displacement of boulders B12 and B28 between 2013 and 2017; (c) no significant and detectable changes in boulder locations in 2018; (d) appearance of boulder B29 on the rock platform of the study site in 2019.
Recently, boulder studies have become more oriented towards the observation of movements and re-assemblages after exceptional storms [31,62,63]. Naylor et al. [34] highlighted the difficulty of obtaining repeat photographic analysis of pre-, mid-, and post-storm data in order to demonstrate how a storm influences boulder dynamics in key morphodynamic zones. Combining hydrodynamic measurements and/or hydrodynamic modeling with high-resolution boulder site monitoring could enable verification of the reliability and applicability of various empirical models [64,65,66,67] commonly used for the characterization of the energy and wave heights necessary for boulder mobility, and which can regularly over- or underestimate the forcing conditions.
UAV surveys and SfM model analysis captured the start and end points of boulders within a single storm event with measured waves at Laghdira, Morocco. This dataset could provide an excellent opportunity to apply empirical models of the energy flux and wave heights required for boulder mobility [64,65,66], and to test their effectiveness and adaptability, and even eventually calibrate them for the geomorphological specificities of Laghdira in order to project future boulder dynamics at this site. This study shows that with pre- and post-storm UAV surveys, we can confirm that wave erosion and wave-induced morphological changes are active at Laghdira. The appearance of a new detached boulder in the central zone of the rock platform attests to the continuity of landform change in this coastal setting. However, the location of mobile boulders at varying distances from the outer edge of the platform, as during the December storm (Figure 10), also shows that incident wave energy did not have a preferential impact on any particular boulder’s shape, size category, or position within the outer edge of the Laghdira platform.
Where boulder accumulations are close to populated areas or socioeconomic activities such as ports, urban centers, and tourist facilities [68,69,70], understanding the dynamics of these megaclasts becomes paramount to preventing risks related to their mobility during storm conditions and, in particular, the potential hazard to coastal infrastructure that they may pose. People, vehicles, and other property have been known to be impacted by waves and boulder projections on islands such as Malta and Jamaica [10,12,71], but also in Morocco during storms [62]. Coastal hazard maps and warnings of expected high waves exist in many countries, but are mainly intended for marine submersion. However, maps of the potential mobility of megaclasts under extreme or high-energy storm conditions unfortunately do not exist. Understanding the dynamics of boulders under the impacts of storm conditions and, thus, being able to produce risk maps of boulder movements, cannot be achieved through modelling and the use of hydrodynamic formulae that systematically underestimate or overestimate the wave conditions necessary for megaclast mobility [71,72], or through monitoring by satellite or aerial imagery spaced out over time, which will simply show an accumulation of boulder movements generated by several wave events—not an individual one [35]. It is therefore necessary to be able to carry out regular and rapid pre- and post-storm monitoring in order to better detect the different types and distances of possible boulder movements, and then combine them with modelling and in situ hydrodynamic monitoring. This possibility to conduct reliable, rapid, and inexpensive monitoring of pre- and post-storm boulder dynamics is exemplified by our study.
6. Conclusions
The analysis of drone-derived SfM models before and after a storm in December 2019 enabled the identification of three large boulders that were moved or rotated, along with the placement of a new boulder at the rocky platform of Laghdira on the storm-exposed Atlantic coast of Morocco. The SfM data and resulting models were of very high resolution (1–10 cm/pixel) owing to the use of a high overlap between successive photos and the deployment of GCPs that allowed for the improvement of quantitative differencing capabilities.
This study also illustrates how the combination of 2D model differentials with 3D model visuals enable us to go beyond the simple quantification of transport and distances travelled by megaclasts, and even specify the travel mode. The three boulders that were displaced during the December 2019 storm had different locations on the platform, as well as different shapes, volumes, and mass; this demonstrates that the movement of the boulders in time and space on this rocky shore platform is not a simple match between incoming wave energy and size/weight.
We also demonstrated that a tsunamigenic origin for coastal boulder movements at Laghdira, as initially inferred by other authors, is not valid, and various other boulder movements that occurred between 2013 and 2019 were shown to have occurred under the impact of storms.
The boulder-tracking technique used in this study, does not require extensive field logistics, and is a promising methodology that could allow scientists to perform the high-resolution monitoring and comparisons needed to better substantiate the connections between storm waves and boulder movements. Such monitoring techniques may also be useful to monitor the impacts of sea-level rise on boulder mobility. Sea-level rise associated with climate change and more energetic storms on the coast of Morocco [73] could enable waves to rework these megaclasts more frequently, but also to reach higher levels on rocky platforms and, thus, access cliffs from which new boulders can be detached.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; methodology, M.S. and J.A.M.; field geomorphological and geological surveys, M.S., J.A.M., G.B., A.E.M. and A.T.; UAV surveys operations preparation, G.B.; validation, G.B. and R.L.G.; data curation, R.L.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and E.J.A.; visualization, M.S. and E.J.A.; supervision, M.S.; project administration, M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is part of the project Gof-Boulders “Geomorphological control on offshore boulders transport along a wave-dominated coast” funded by ISblue—the Interdisciplinary graduate school for the blue planet (ANR-17-EURE-0015)—and co-funded by a grant from the French government under the program “Investissements d’Avenir”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study did not report any data.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Iliass Sedrati for his untiring help and logistical preparation of the survey missions, Anass Sedrati and Haj Abdallah Sedrati for their support during the field surveys, and Reda Hawat for operating the drone. We also thank the Provincial Directorate in Larache of the Ministry of Equipment, Transport, Logistics, and Water, as well as the Royal Armed Forces, for authorizations and support in the field.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Trenhaile, A.S. Rock coasts, with particular emphasis on shore platforms. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Chao, R.; Pérez-Alberti, A.; Trenhaile, A.S.; Coasta-Casais, M.; Valcàrcel-Diaz, M. Shore platform abrasion in a para-periglacial environment, Galicia, northwestern Spain. Geomorphology 2007, 83, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Hansom, J.D.; Jarvis, J. Patterns and rates of erosion produced by high energy wave processes on hard rock headlands: The Grind of the Navir, Shetland, Scotland. Mar. Geol. 2008, 248, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.; Jahn, K.L.; Watkins, O.G.; Cox, P. Extraordinary boulder transport by storm waves (west of Ireland, winter 2013–2014), and criteria for analysing coastal boulder deposits. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, J. Extremely high-energy wave deposits inside the Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Determining the cause—Tsunami or tropical cyclone. Mar. Geol. 1997, 141, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.B.; Mori, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Chen, S.-E.; Tajima, Y.; Pecor, W.; Toride, K. Observations and modeling of coastal boulder transport and loading during Super Typhoon Haiyan. Coast. Eng. J. 2016, 58, 1640004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.B.; Mori, N.; Yasuda, T.; Shimozono, T.; Tomiczek, T.; Donahue, A.; Shimura, T.; Imai, Y. Extreme block and boulder transport along a cliffed coastline (Calicoan Island, Philippines) during Super Typhoon Haiyan. Mar. Geol. 2017, 383, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Hansom, J.D.; Williams, D.M.; Jarvis, J. Distribution, geomorphology and lithofacies of cliff-top storm deposits: Examples from the high-energy coasts of Scotland and Ireland. Mar. Geol. 2006, 232, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.M.; Hall, A.M. Cliff-top megaclast deposits of Ireland, a record of extreme waves in the North Atlantic—Storms or tsunamis? Mar. Geol. 2004, 206, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Rowe, D.-A.; Brown, L.; Mandal, A. Wave-emplaced boulders: Implications for development of prime real estate seafront, North Coast Jamaica. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2014, 73, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, M.S.; Pirrotta, C.; Gerardi, F. Large boulders along the south-eastern Ionian coast of Sicily: Storm or tsunami deposits? Mar. Geol. 2010, 275, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Furlani, S.; Antonioli, F.; Baldassini, N.; Deguara, J.C.; Devoto, S.; Stefano, A.D.; Evans, J.; Gambin, T.; Gauci, R. Boulder accumulations related to extreme wave events on the eastern coast of Malta. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2016, 16, 737–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronuzzi, G.; Sansò, P. Boulders transport by catastrophic waves along the Ionian coast of Apulia (southern Italy). Mar. Geol. 2000, 170, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronuzzi, G.; Pignatelli, C.; Sansò, P.; Selleri, G. Boulder accumulations produced by the 20th of February, 1743 tsunami along the coast of southeastern Salento (Apulia region, Italy). Mar. Geol. 2007, 242, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.; Zentner, D.B.; Kirchner, B.J.; Cook, M.S. Boulder ridges on the Aran Islands (Ireland): Recent movements caused by storm waves, not tsunamis. J. Geol. 2012, 120, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autret, R.; Dodet, G.; Fichaut, B.; Suanez, S.; David, L.; Leckler, F.; Ardhuin, F.; Ammann, J.; Grandjean, P.; Allemand, P. A comprehensive hydro-geomorphic study of cliff-top storm deposits on Banneg Island during winter 2013–2014. Mar. Geol. 2016, 382, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.; Burningham, H. Boulder dynamics on an Atlantic-facing rock coastline, northwest Ireland. Mar. Geol. 2011, 283, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansom, J.D.; Barltrop, N.D.P.; Hall, A.M. Modelling the processes of cliff-top erosion and deposition under extreme storm waves. Mar. Geol. 2008, 253, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansom, J.D.; Hall, A.M. Magnitude and frequency of extra-tropical North Atlantic cyclones: A chronology from cliff-top storm deposits. Quat. Int. 2009, 195, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.J.; Dawson, S.; Ramalho, R.S.; Engel, M.; Dourado, F.; Bosnic, I.; Andrade, C. A review on onshore tsunami deposits along the Atlantic coasts. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, C.; Scheffers, A.; Scheffers, S.; Mastronuzzi, G. Assessment of extreme wave flooding from geomorphologic evidence in Bonaire (Netherlands Antilles). Z. Geomorphol. 2010, 54 (Suppl. 3), 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanez, S.; Fichaut, B.; Magne, R. Cliff-top storm deposits on Banneg Island, Brittany, France: Effects of giant waves in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean. Sediment. Geol. 2009, 220, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, F.; Mhammdi, N.; Chiguer, A.; Akil, M.; Jaaidi, E.B. The Rabat and Larache boulder fields; new examples of high-energy deposits related to extreme waves in north-western Morocco. Nat. Hazards. 2011, 59, 725–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig-Munar, F.X.; Rodríguez-Perea, A.; Martín-Prieto, J.A.; Gelabert, B.; Vilaplana, J.M. Tsunami Boulders on the Rocky Coasts of Ibiza and Formentera (Balearic Islands). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamatsu, A.; Goto, K.; Rojas-Consuegra, R.; Acosta, E.; Rodríguez, A.; Mori, N.; Imamura, F. Potential Risk of extreme wave in Trinidad of Cuba inferred from coastal Boulders. II Simposio Sobre Riesgos de Desastres y Riesgos Climáticos. XI Convención Internacional Sobre Medio Ambiente y Desarrollo, La Habana, Cuba. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Reinaldo-Consuegra/publication/318350648_POTENTIAL_RISK_OF_EXTREME_WAVE_IN_TRINIDAD_OF_CUBA_INFFERED_FROM_COASTAL_BOULDERS/links/59650fb1a6fdcc69f148b90d/POTENTIAL-RISK-OF-EXTREME-WAVE-IN-TRINIDAD-OF-CUBA-INFFERED-FROM-COASTAL-BOULDERS.pdf (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Whelan, F.; Kelletat, D. Boulder deposits on the southern Spanish Atlantic coast: Possible evidence for the 1755 AD Lisbon tsunami. Sci. Tsunami Hazards 2005, 23, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Consuegra, R.; Isaac-Mengana, J.; Pupo, F.M.; Peros, M.C. Coarse Detrital Deposits from Hurricane Wilma on the Western Coast of Cojimar, Havana, Cuba. In Proceedings of the International Conference on BioGeoSciences; Varadero, Cuba, 23–27 October 2017, Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Etienne, S.; Paris, R. Boulder accumulations related to storms on the south coast of the Reykjanes Peninsula (Iceland). Geomorphology 2010, 114, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Okada, K.; Imamura, F. Characteristics and hydrodynamics of boulders transported by storm waves at Kudaka Island, Japan. Mar. Geol. 2009, 262, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R. Megagravel deposits on the west coast of Ireland show the impacts of severe storms. Weather 2020, 75, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R. Very large boulders were moved by storm waves on the west coast of Ireland in winter 2013–2014. Mar. Geol. 2019, 412, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Furlani, S.; Devoto, S.; Scicchitano, G.; Korbar, T.; Vilibic, I.; Sepic, J. The origin and dynamics of coastal boulders in a semi-enclosed shallow basin: A northern Adriatic case study. Mar. Geol. 2019, 411, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolchi, S.; Denamiel, C.; Devoto, S.; Korbar, T.; Macovaz, V.; Scicchitano, G.; Vilibic, I.; Furlani, S. Impact of the October 2018 storm Vaia on coastal boulders in the northern Adriatic Sea. Water 2019, 11, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, L.A.; Stephenson, W.J.; Smith, H.C.; Way, O.; Mendelssohn, J.; Cowley, A. Geomorphological control on boulder transport and coastal erosion before, during and after an extreme extra-tropical cyclone. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle-McNaughton, T.; Cox, R. Measuring Change Using Quantitative Differencing of Repeat Structure-From-Motion Photogrammetry: The Effect of Storms on Coastal Boulder Deposits. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, Z.; Stephenson, W.; Finlayson, B. Morphodynamics of a boulder beach, Putuo Island, SE China coast: The role of storms and typhoon. Mar. Geol. 2011, 283, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peréz-Alberti, A.; Trenhaile, A.S. An initial evaluation of drone-based monitoring of boulder beaches in Galicia, north-western Spain. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormets, R.; Crook, K.W.; Felton, E.A. Sedimentology of rocky shorelines: 3. Hydrodynamics of megaclast emplacement and transport on a shore platform, Oahu, Hawaii. Sediment. Geol. 2004, 172, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, F.; Goto, K.; Ohkubo, S. A numerical model for the transport of a boulder by tsunami. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2008, 113, C01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunier, G.; Fleury, J.; Anthony, E.J.; Gardel, A.; Dussouillez, P. Close-range airborne Structure-from-Motion Photogrammetry for high-resolution beach morphometric surveys: Examples from an embayed rotating beach. Geomorphology 2016, 261, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, E.; Rovere, A.; Pedroncini, A.; Stark, C.P.; Casella, M.; Ferrari, M.; Firpo, M. Drones as tools for monitoring beach topography changes in the Ligurian Sea (NW Mediterranean). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteau, B.; Vericat, D.; Gibbins, C.; Batalla, R.J.; Green, D.R. Application of Structure-from-Motion photogrammetry to river restoration. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodget, A.S.; Austrums, R.; Maddock, I.P.; Habit, E. Drones and digital photogrammetry: From classifications to continuums for monitoring river habitat and hydromorphology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2017, 4, e1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminga, A.D.; Eaton, B.C.; Hugenholtz, C.H. UAS-based remote sensing of fluvial change following an extreme flood event. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanás, R. Notas Para el Conocimiento de la Geografía Física y Urbana de Alcazarquivir. Consejo Superior de Insvestigaciones Científicas; Instituto de Estudios Africanos: Madrid, Spain, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Fillali, L.; Garzon, G.; Arribas, J. Petrografía de los depósitos arenosos fluviales y costeros en la península de Tanger: Implicaciones sobre la dinámica fluvial y litoral. Rev. De La Soc. Geológica De España. 2005, 18, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Adil, S. Les Formations Quaternaires de Larache: Sédimentologie, Paléoenvironnement, Datation Radiochimique et Problème D’aménagement. 3rd. Cycle Thesis, Université Mohammed V Faculté des Sciences, Rabat, Morocco, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- El Gharbaoui, A. La Terre et l’homme Dans la péninsule Tingitaine; étude sur l’homme et le Milieu Naturel Dans le Rif Occidental; Institut Scientifique: Rabat, Morocco, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhmadi, B.; Benavente, J.; Cruz-Sanjulián, J. Geometría, piezometría y parámetros hidráulicos de los acuíferosde la cuenca baja del río Loukkos (Marruecos). Geogaceta 1994, 16, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhmadi, B.; Benavente, J.; Cruz-Sanjulián, J.; Sanromá, A. Caracterización hidrodinámica e hidroquímica de los acuíferos de la Cuenca Baja del río Loukkos (Marruecos). Bol. Geoologico. Y Min. 1995, 106, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- El Moutchou, B.; Benali, H.; Mamouni, A. Evolution diachronique de la ligne du rivage le long des littoraux méditerranéens occidentaux marocains: Cas des sites côtiers de Ksar Esghir. Bou Ahmed et Jebha (Maroc). J. Natl. Génie Côtier-Génie Civil 2014, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mekadem, N.; El Moutchou, B. Study of the structural continuity from hinterlands to continental shelf in Larache area (NW Morocco): Morphostructural approach. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Taaouati, M.; Nachite, D.; Benavente, J.; Elmrini, A. Seasonal Changes and Morphodynamic Behavior of a High-Energy Mesotidal Beach: Case Study of Charf el Akab Beach on the North Atlantic Coast of Morocco. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaidi, E.B.; Cirac, P. La Couverture Sédimentaire Meuble du Plateau Continental Atlantique Marocain Entre Larache et Agadir. Bull Inst Géol Bassin D’aquitaine Bordx. 1987, 42, 3–51. [Google Scholar]
- Agisoft Metashape User Manual: Professional Edition. 2019. Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/pdf/metashape-pro_1_5_en.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Grenzdörffer, G.J.; Engel, A.; Teichert, B. The photogrammetric potential of low-cost UAVs in forestry and agriculture. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 31, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J.; Malet, J.; Maquaire, O.; Grussenmeyer, P. The use of small-format and low-altitude aerial photos for the realization of high-resolution DEMs in mountainous areas: Application to the Super-Sauze earthflow (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Gr. 2002, 27, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sánchez, J.; López-Granados, F.; Borra-Serrano, I.; Peña, J.M. Assessing UAV-collected image overlap influence on computation time and digital surface model accuracy in olive orchards. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesas-Carrascosa, F.-J.; Notario García, M.; Meroño de Larriva, J.; García-Ferrer, A. An analysis of the influence of flight parameters in the generation of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) orthomosaicks to survey archaeological areas. Sensors 2016, 16, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Anfuso, G. Winter wave climate, storms and regional cycles: The SW Spanish Atlantic coast. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 2142–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.C.A.; Graça Neves, M.; Fidalgo, R.; Esteves, R. Variability of wave parameters and Hmax/Hs relationship under storm conditions offshore the Portuguese continental coast. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 153, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhammdi, N.; Medina, F.; Belkhayat, Z.; El Aoula, R.; Geawahri, M.A.; Chiguer, A. Marine storms along the Moroccan Atlantic coast: An underrated natural hazard? J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 163, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesl, F.; Engel, M.; Eco, R.C.; Galang, J.B.; Gonzalo, L.A.; Llanes, F.; Quix, E.; Brückner, H. Digital mapping of coastal boulders—High-resolution data acquisition to infer past and recent transport dynamics. Sedimentology 2019, 67, 1393–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, J. Tsunami or storm waves? determining the origin of a spectacular field of wave emplaced boulders using numerical storm surge and wave models and hydrodynamic transport equations. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli, C.; Sansò, P.; Mastronuzzi, G. Evaluation of tsunami flooding using geomorphologic evidence. Mar. Geol. 2009, 260, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandasena, N.A.K.; Paris, R.; Tanaka, N. Reassessment of hydrodynamic equations: Minimum flow velocity to initiate boulder transport by high energy events (storms, tsunamis). Mar. Geol. 2011, 281, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.B.; Cox, R.; Dias, F. Storm waves may be the source of some “tsunami” coastal boulder deposits. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor-Blanco, G.; Alcántara-Carrió, J.; Jackson, D.W.T.; Flor, G.; Flores-Soriano, C. Coastal erosion in NW Spain: Recent patterns under extreme storm wave events. Geomorphology 2021, 387, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, D.A. Finding Coastal Megaclast Deposits: A Virtual Perspective. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah Hosseini, M.; Morhange, C.; De Marco, A.; Wante, J.; Anthony, E.J.; Sabatier, F.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Pignatelli, C.; Piscitelli, A. Coastal boulders in Mar-tigues, French Mediterranean: Evidence for extreme storm waves during the Little Ice Age. Z. Geomorphol. 2013, 57 (Suppl. 4), 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causon Deguara, J.; Gauci, R. Evidence of extreme wave events from boulder deposits on the south-east coast of Malta (Central Mediterranean). Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandasena, N.A.K.; Tanaka, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Osada, M. Boulder transport by the 2011 great East Japan tsunami: Comprehensive field observations and whither model predictions? Mar. Geol. 2013, 346, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmi, S.; Snoussi, M.; Khalfaoui, O.; Aitali, R.; Flayou, L. Increasing pressures, eroding beaches and climate change in Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 164, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).