Feature Selection for SAR Target Discrimination and Efficient Two-Stage Detection Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
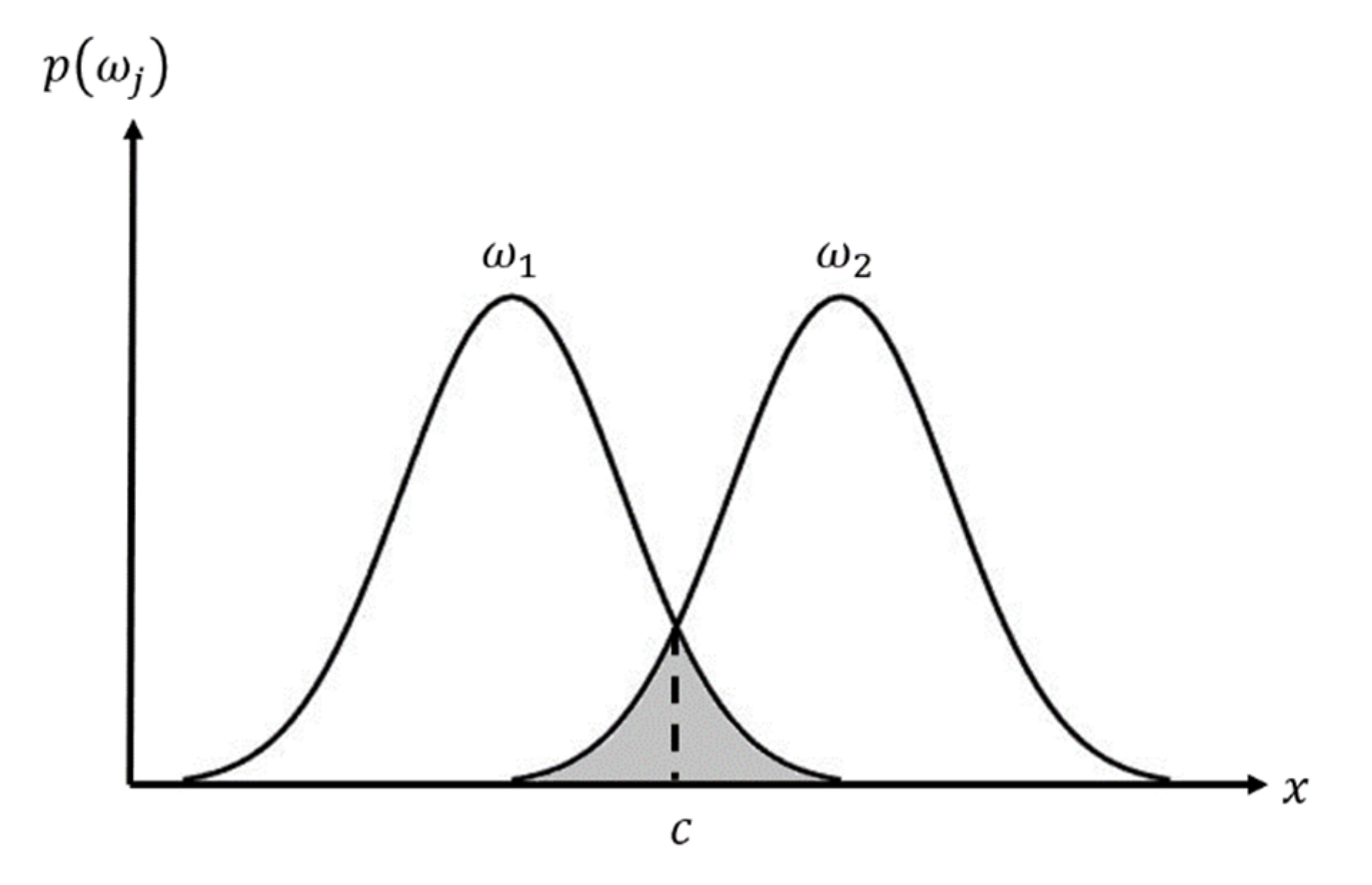
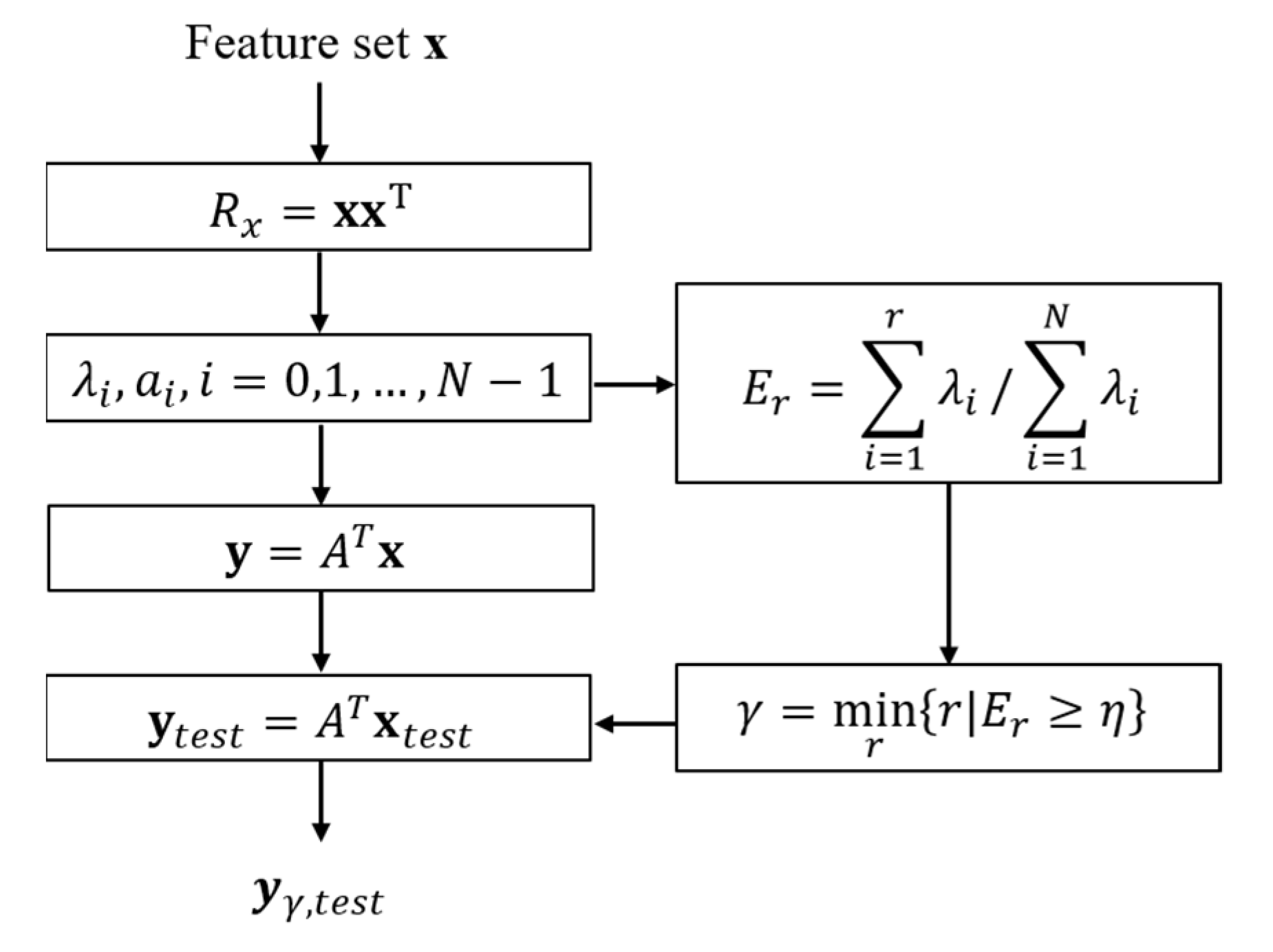
2. Proposed Method
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Settings
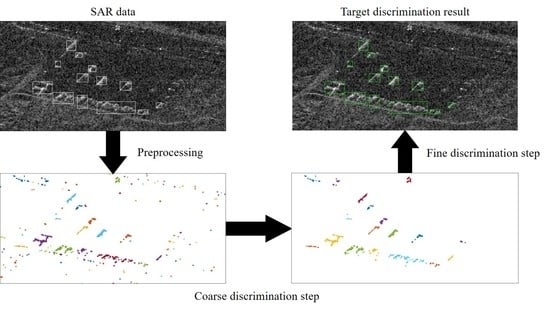
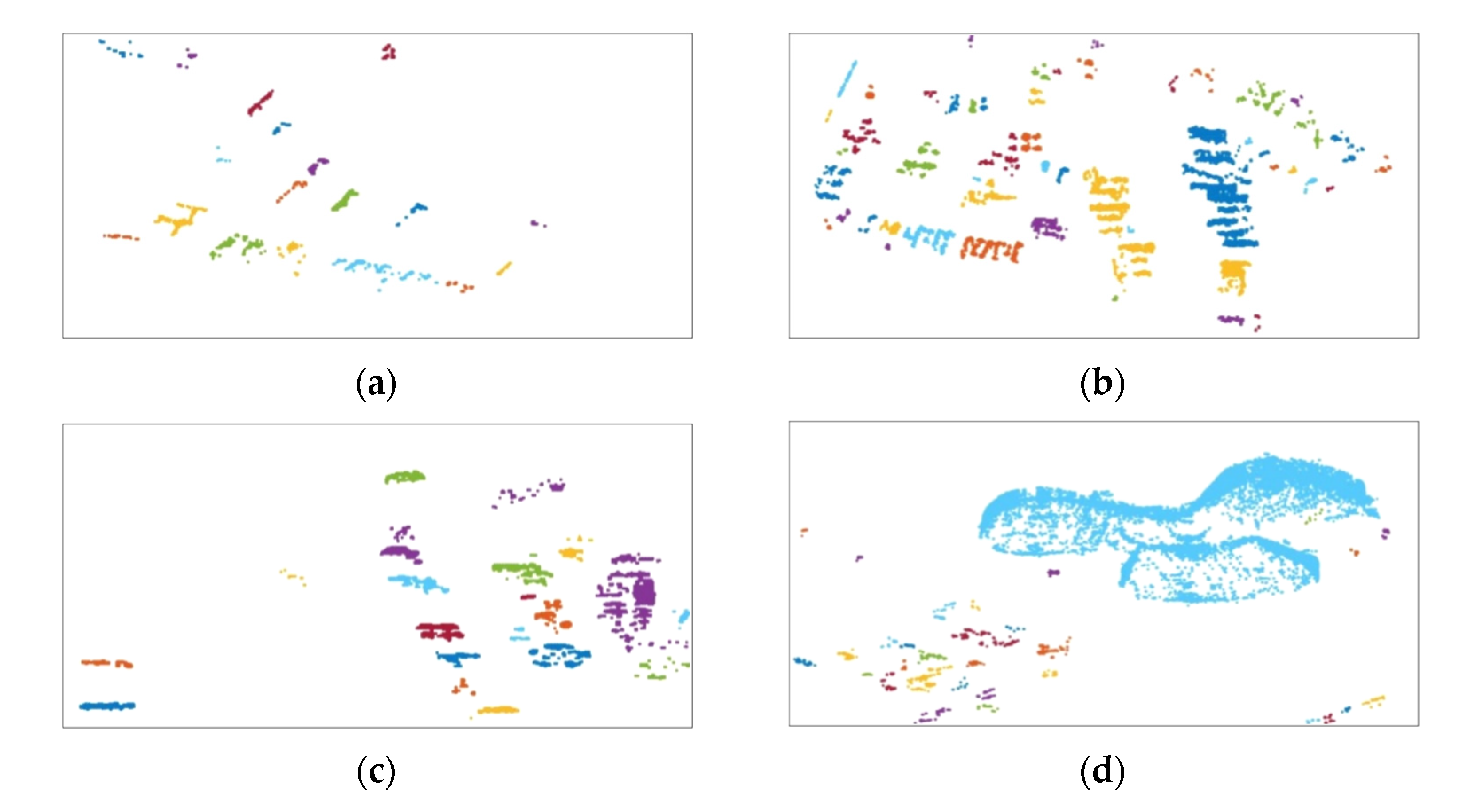
3.2. Preprocessing and Coarse Discrimination Step
3.3. Fine Discrimination Step
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Kreiger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A Tutorial on Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Du, Y.; Du, L.; Li, L. Target Detection Network for SAR Images Based on Semi-Supervised Learning and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, A.; Lapini, A.; Bianchi, T.; Alparone, L. A Tutorial on Speckle Reduction in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. A simple speckle smoothing algorithm for synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1983, 13, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Wen, J.-H.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Chen, K.-S.; Chen, A.J. Improved Sigma Filter for Speckle Filtering of SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A Non-local Algorithm for Image Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivathsa, V. Cell Averaging-constant False Alarm Rate Detection in Radar. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Villar, S.A.; Menna, B.V.; Torcida, S.; Acosta, G.G. Efficient Approach for OS-CFAR 2D Technique Using Distributive Histo-grams and Breakdown Point Optimal Concept Applied to Acoustic Images. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, N.S. An Introduction to Kernel and Nearest-neighbor Nonparametric Regression. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Forgy, E.W. Cluster Analysis of Multivariate Data: Efficiency versus Interpretability of Classifications. Biometrics 1965, 21, 768–769. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y. Mean Shift, Mode Seeking, and Clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1995, 17, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD-96), Portland, OR, USA; 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kreithen, D.E.; Halversen, S.D.; Owirka, G.J. Discriminating Targets from Clutter. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-I.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, K.-T. New Discrimination Features for SAR Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y. An Automatic SAR-GMTI Algorithm Based on DPCA. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience Remote Sensing Symposium, Montreal, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumbas, K. Pattern Recognition; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal Component Analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Bae, J.-H.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, K.-T. Efficient ISAR Autofocus Technique Using Eigenimages. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewegmann, C.P.; Kleynhans, W.; Salmon, B.P. Synthetic Aperture Radar Ship Detection Using Haar-Like Features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Tian, R.; Luo, Q.; Jin, J.; Tang, B. Multi-Scale Rotation-Invariant Haar-Like Feature Integrated CNN-Based Ship Detection Algorithm of Multiple-Target Environment in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10070–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



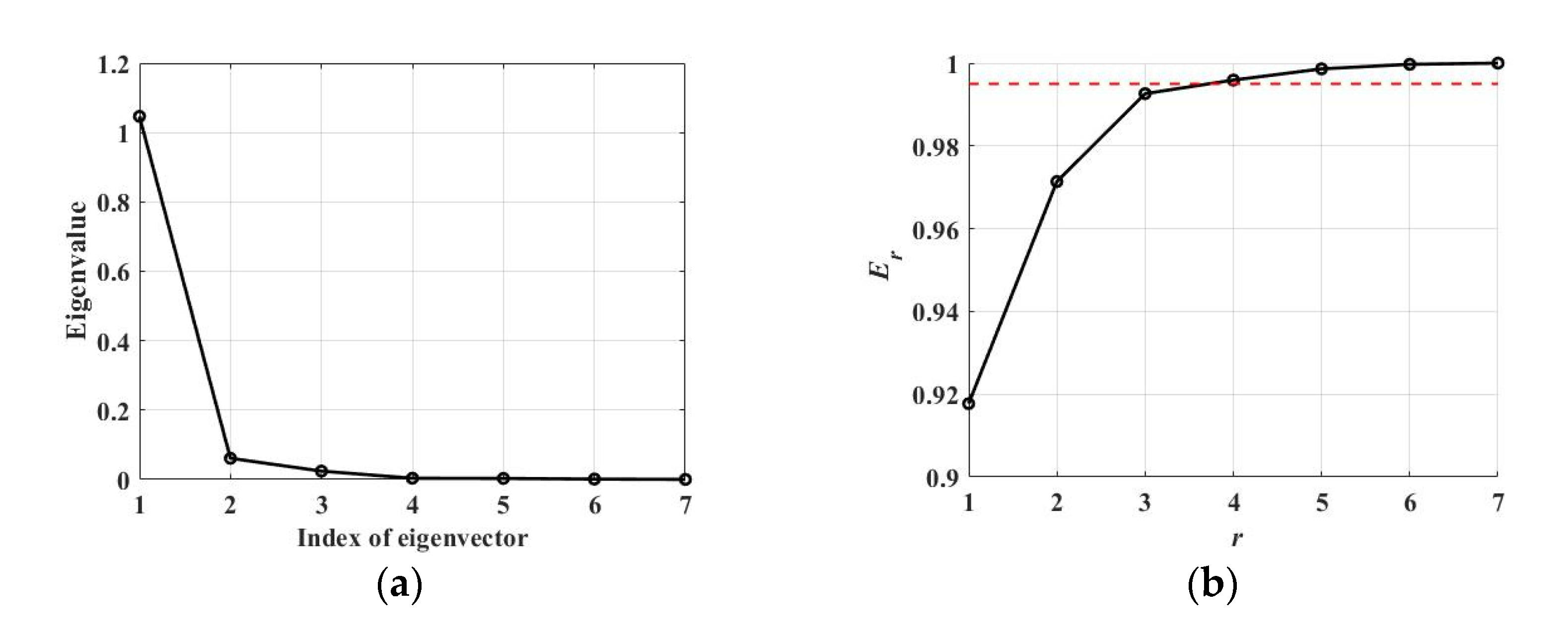
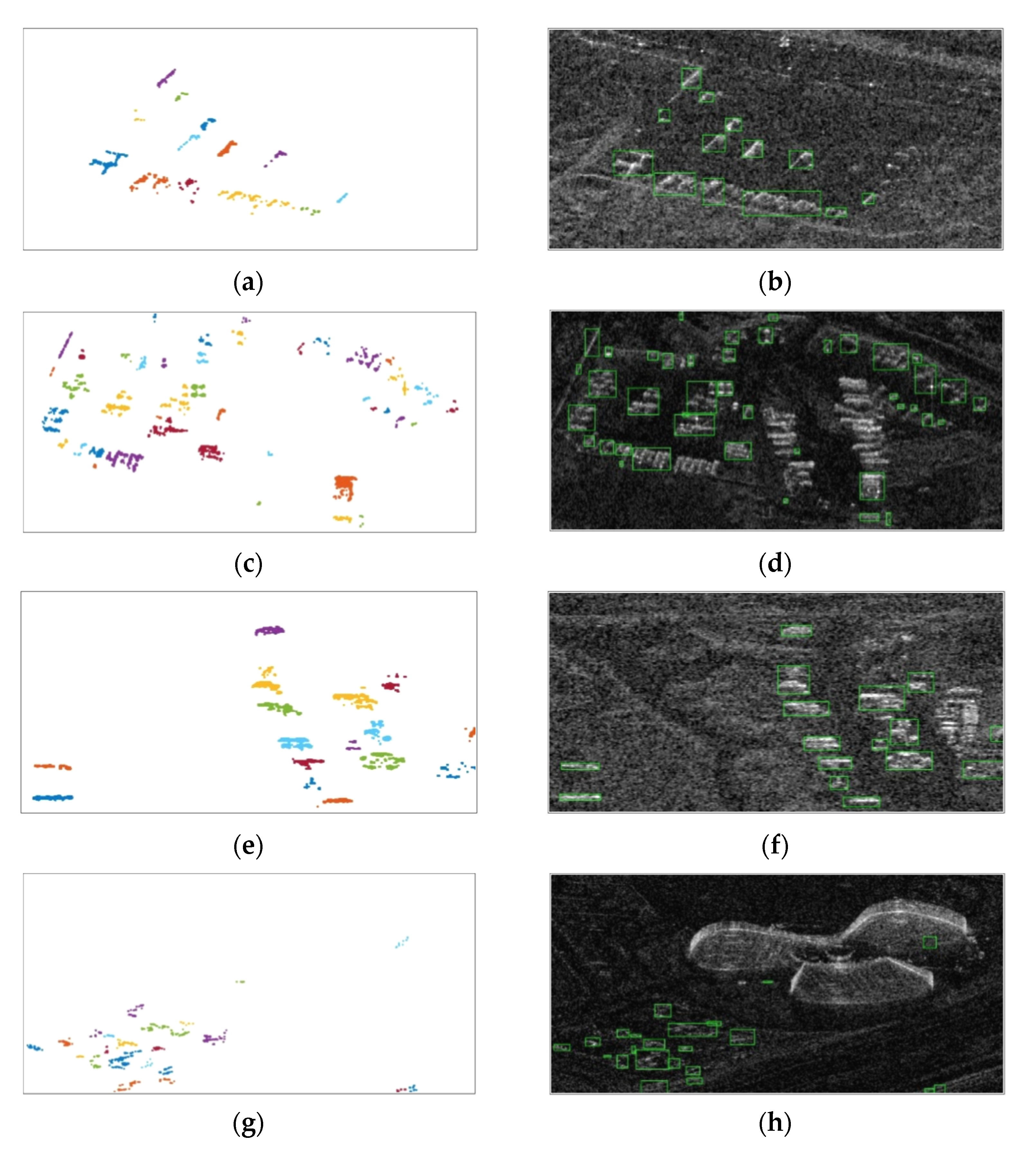
| Pc | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene 1 | 0.9450 | 0.7222 | 1.0000 | 0.8387 |
| Scene 2 | 0.8776 | 0.8868 | 1.0000 | 0.9400 |
| Scene 3 | 0.9429 | 0.8000 | 1.0000 | 0.8889 |
| Scene 4 | 0.9080 | 0.5588 | 1.0000 | 0.7170 |
| Total | 0.9196 | 0.7600 | 1.0000 | 0.8636 |
| Feature | Overlap | Feature | Overlap |
|---|---|---|---|
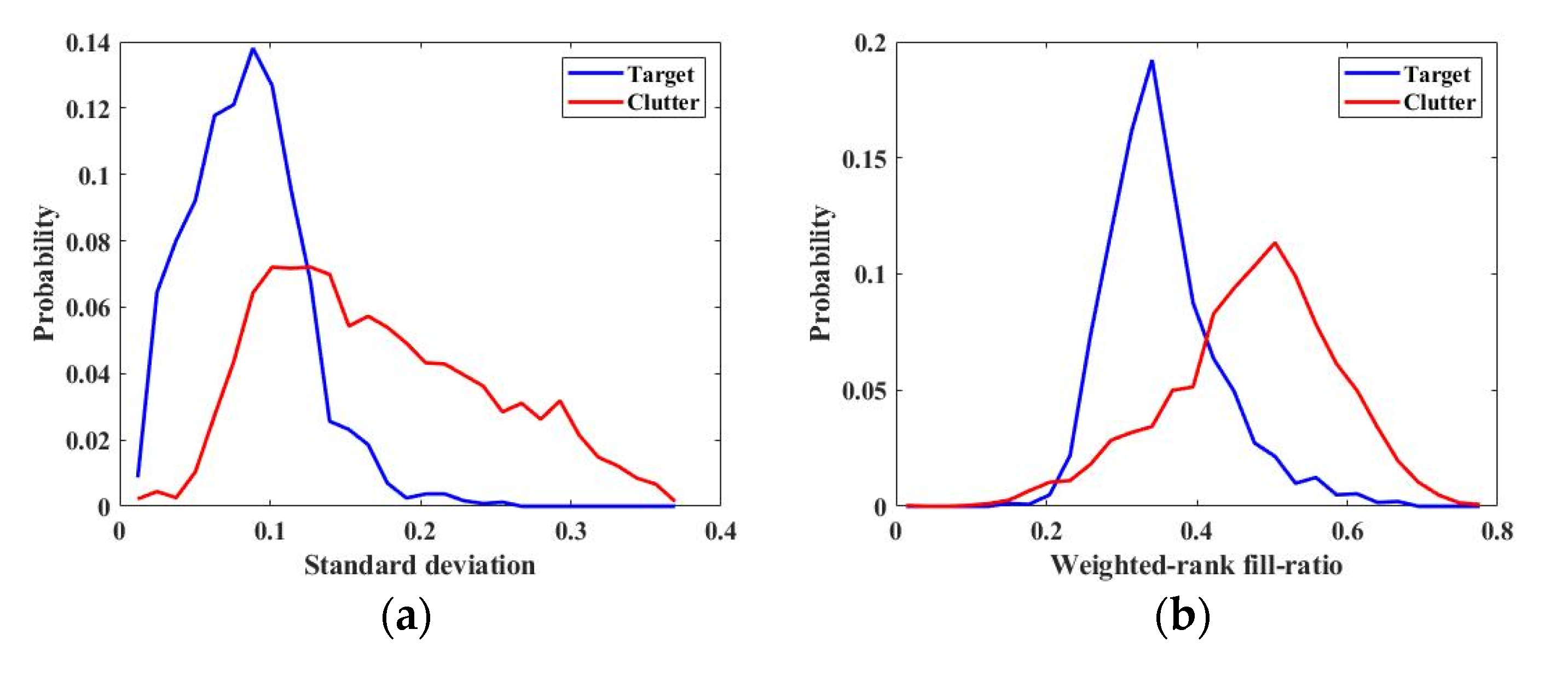
| Standard deviation | 0.4556 | MAXPL | 0.7600 |
| Weighted-rank fill-ratio | 0.4323 | CPL | 0.8812 |
| Fractal dimension | 0.8391 | AMMPL | 0.7406 |
| Mass | 0.7278 | APL | 0.7452 |
| Diameter | 0.7462 | ERPL | 0.8804 |
| Normalized rotational inertia | 0.9550 | SERPL | 0.9446 |
| Max CFAR | 0.4683 | EPLF | 0.8539 |
| Mean CFAR | 0.5785 | SEPLF | 0.8863 |
| Percentage of bright CFAR | 0.9075 | ADP | 0.5785 |
| Count | 0.8083 | SDP | 0.5735 |
| MINPL | 0.7475 | STDDP | 0.2606 |
| Pc | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scene 1 | 0.9891 | 0.9231 | 1.0000 | 0.9600 |
| Scene 2 | 0.9153 | 0.8810 | 0.9250 | 0.9024 |
| Scene 3 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9412 | 0.9697 |
| Scene 4 | 0.9697 | 0.7727 | 0.8947 | 0.8293 |
| Total | 0.9715 | 0.8817 | 0.9318 | 0.9061 |
| Proposed Method (s) | Single-Step Method (s) | |
|---|---|---|
| Scene 1 | 2.4345 | 13.1425 |
| Scene 2 | 5.9841 | 11.8243 |
| Scene 3 | 2.6811 | 10.3851 |
| Scene 4 | 4.5548 | 19.3136 |
| Average | 3.9136 | 13.6664 |
| Coarse + STD | Coarse + WRFR | Coarse + STDDP | RES | HL Features | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | 0.7500 | 0.7200 | 0.6757 | 0.8936 | 0.7253 | 0.8817 |
| Recall | 0.7841 | 0.4091 | 0.2841 | 0.4884 | 0.7674 | 0.9318 |
| F1-score | 0.7667 | 0.5217 | 0.4000 | 0.6316 | 0.7458 | 0.9061 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, N.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, G.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, K.-T. Feature Selection for SAR Target Discrimination and Efficient Two-Stage Detection Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164044
Jeong N-H, Choi J-H, Lee G, Park J-H, Kim K-T. Feature Selection for SAR Target Discrimination and Efficient Two-Stage Detection Method. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164044
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Nam-Hoon, Jae-Ho Choi, Geon Lee, Ji-Hoon Park, and Kyung-Tae Kim. 2022. "Feature Selection for SAR Target Discrimination and Efficient Two-Stage Detection Method" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164044
APA StyleJeong, N.-H., Choi, J.-H., Lee, G., Park, J.-H., & Kim, K.-T. (2022). Feature Selection for SAR Target Discrimination and Efficient Two-Stage Detection Method. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164044