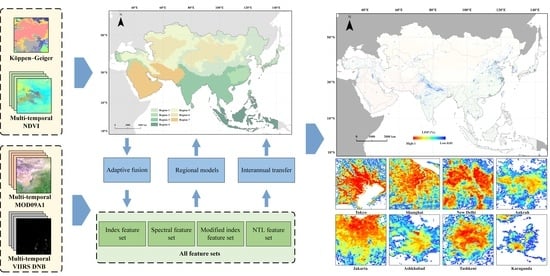
Estimating Large-Scale Interannual Dynamic Impervious Surface Percentages Based on Regional Divisions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Set
2.2. Methods
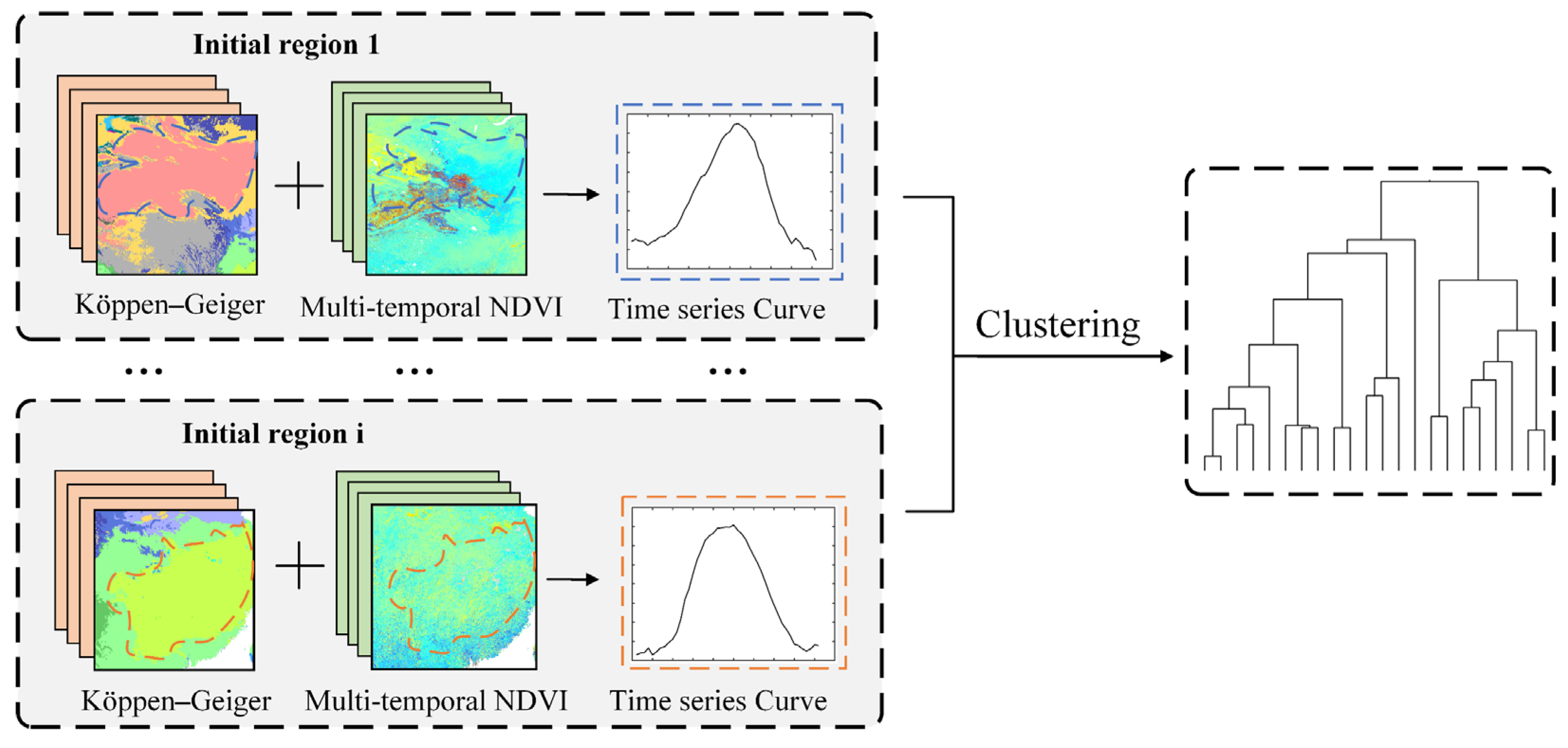
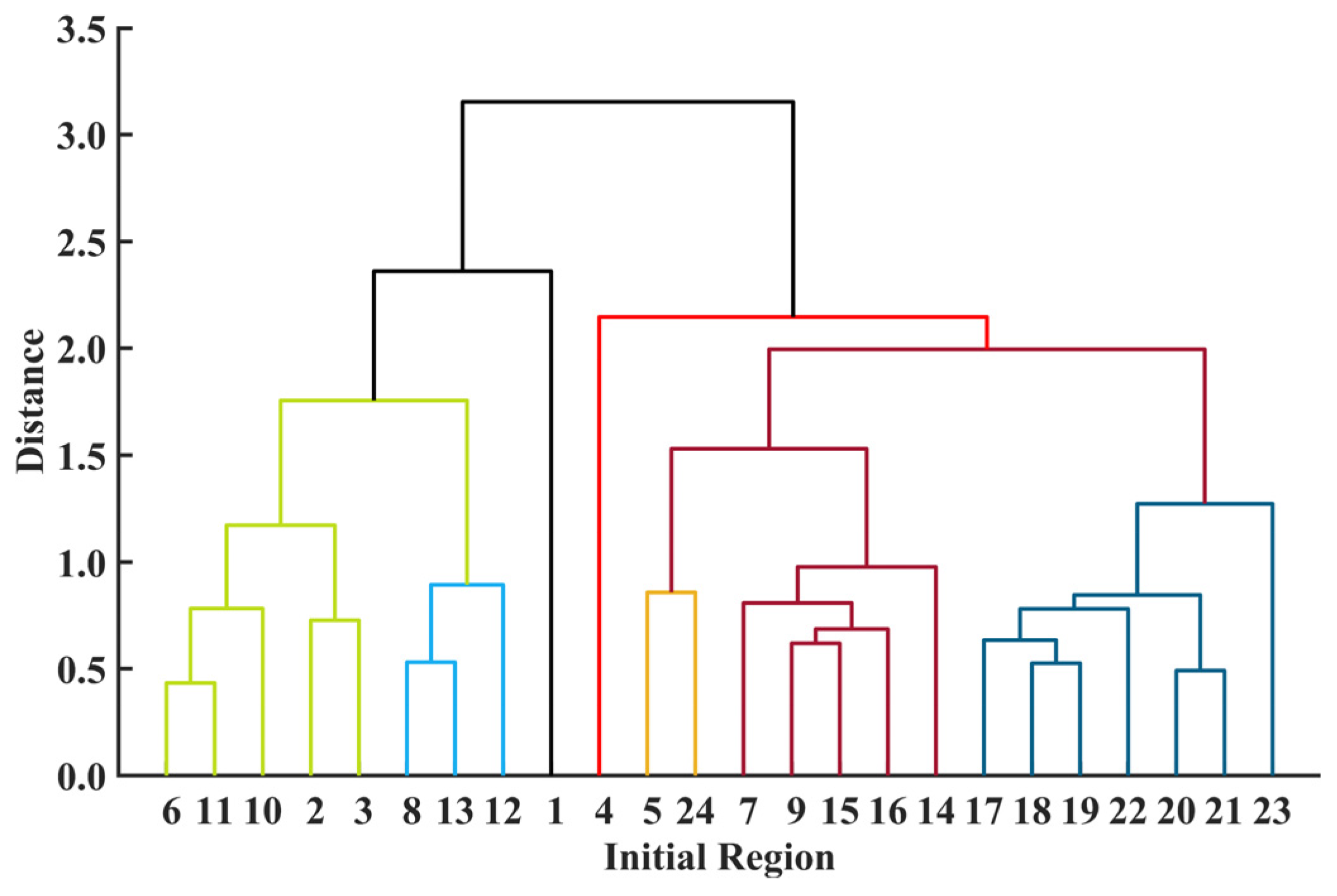
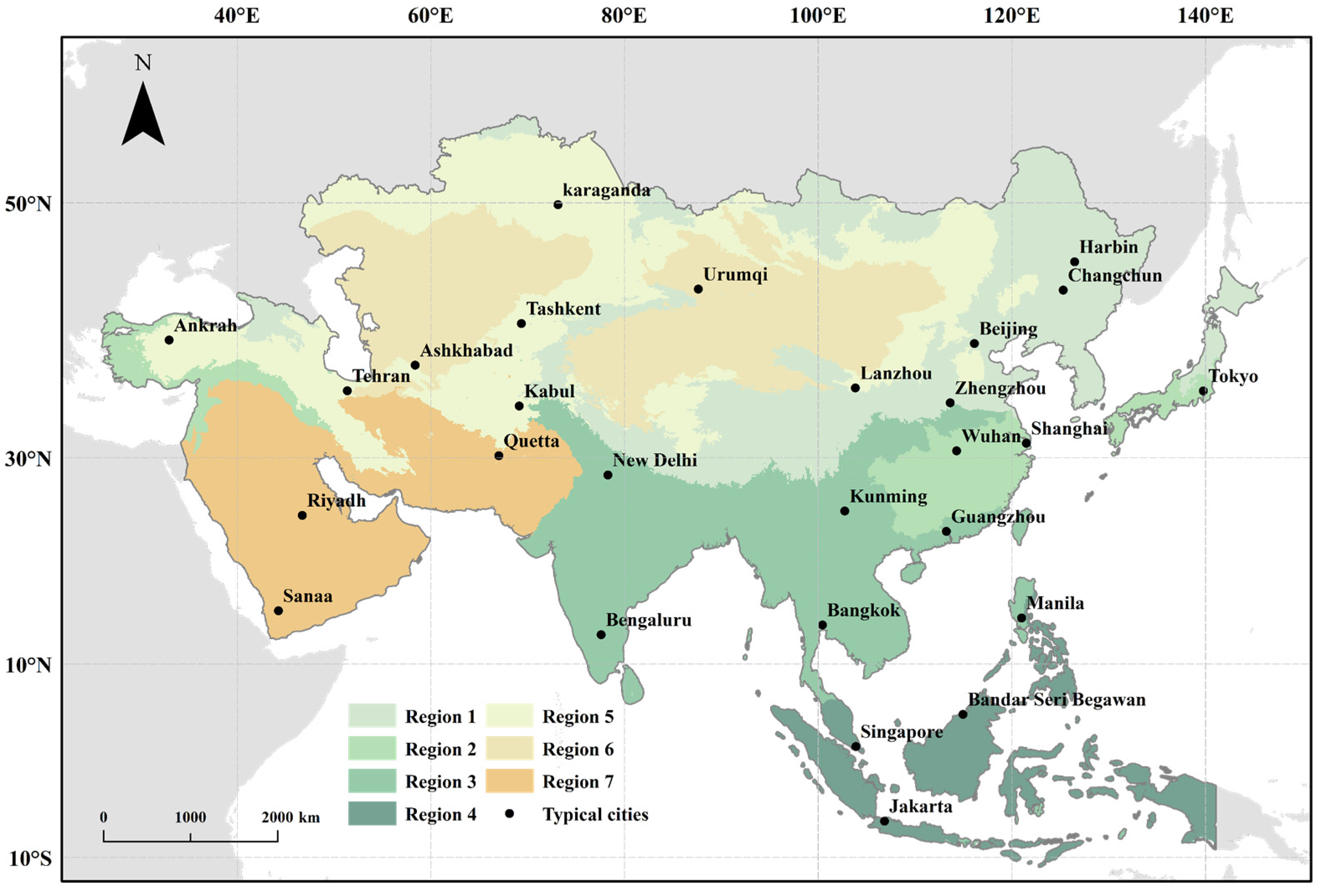
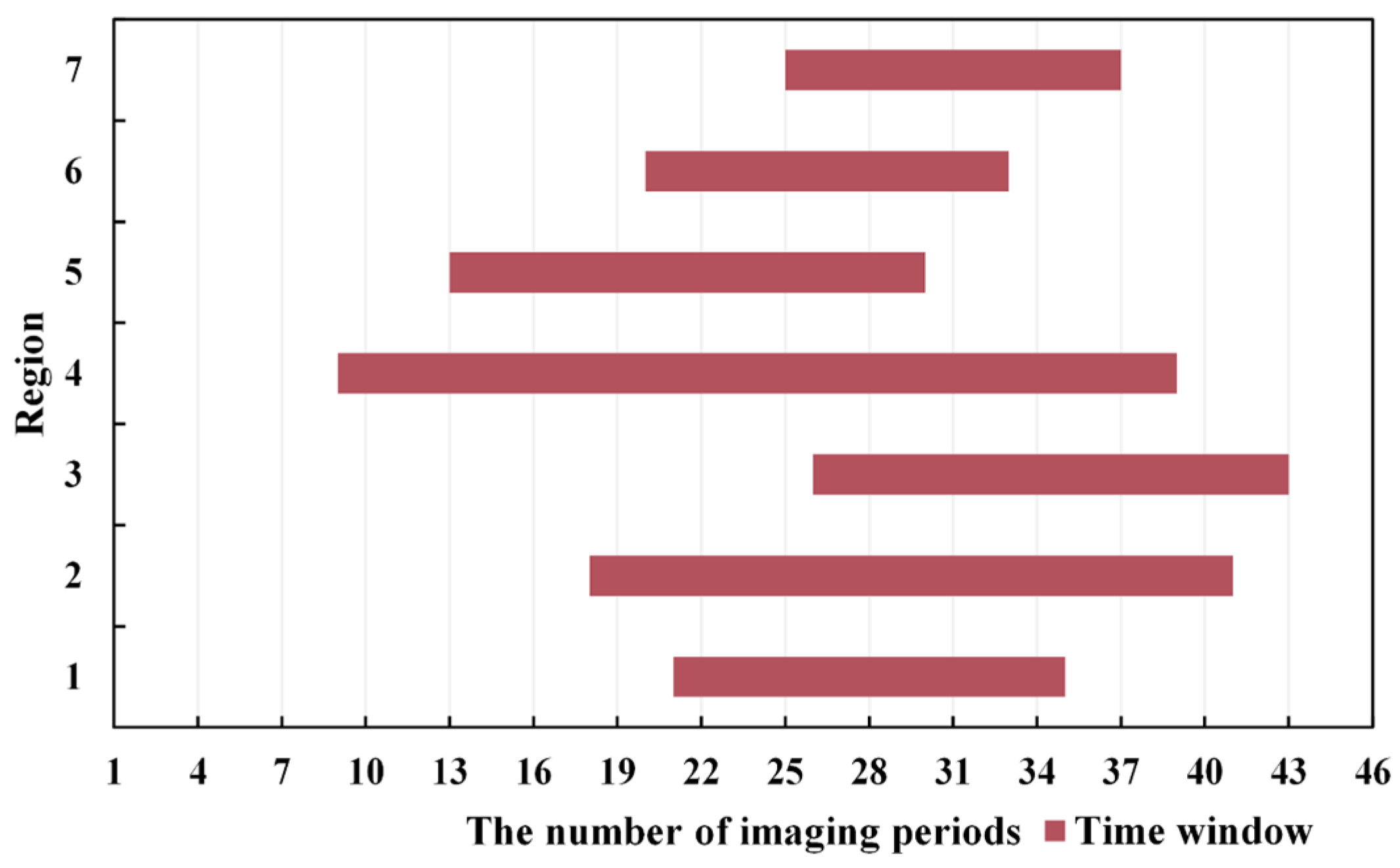
2.2.1. Regional Divisions
2.2.2. Time-Series Data Fusion and Feature Construction
2.2.3. Development of Prediction Models
2.2.4. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Region Division Results
3.2. Comparison of Time-Series Image Synthesis Methods
3.3. Estimation Results of Different Feature Set Combinations
3.4. Comparison of Impervious Surface Percentage Estimation Models
3.5. Evaluation of Interannual Transferability
4. Discussion
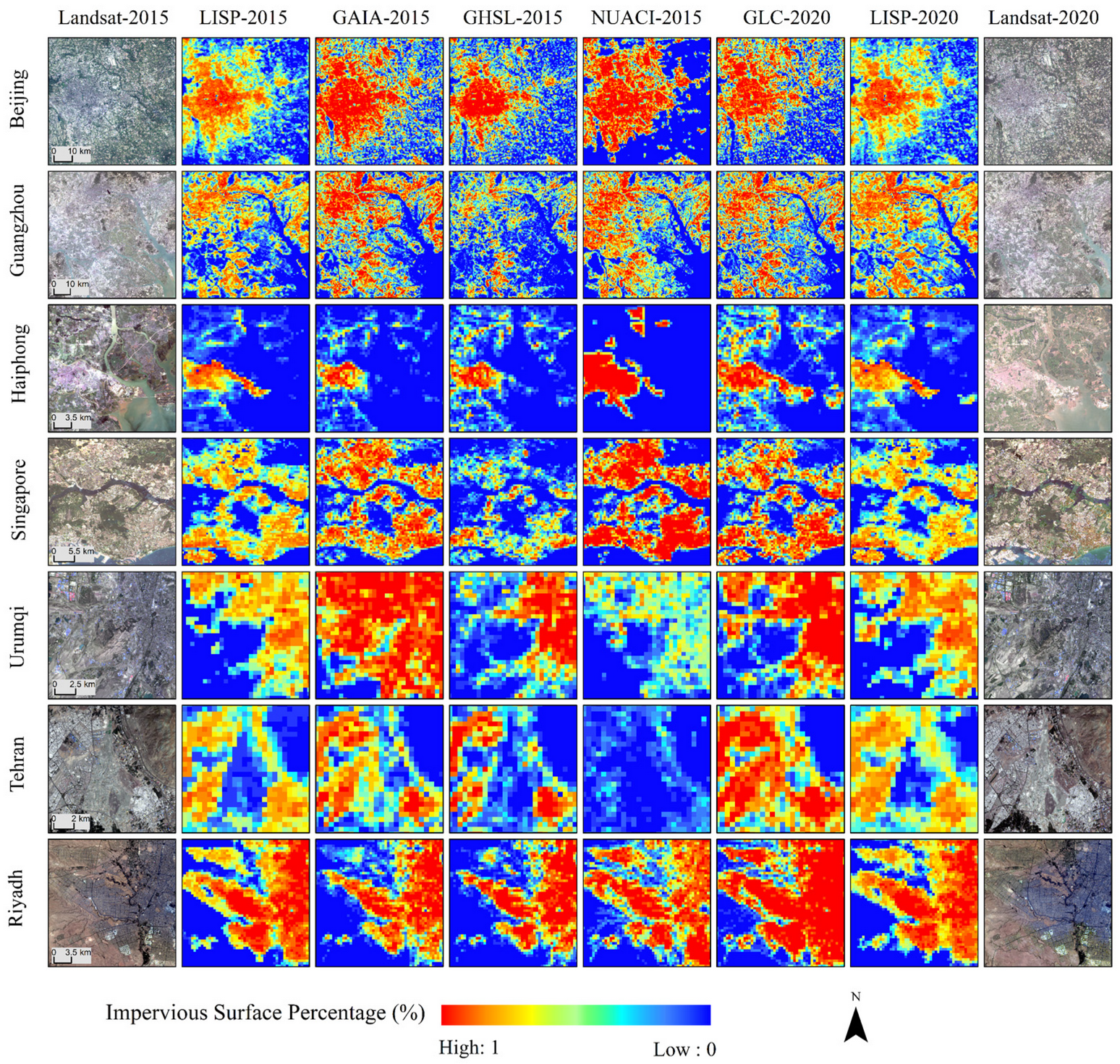
4.1. Comparison with Other Impervious Surface Products
4.2. Advantages and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, C.L., Jr.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithra, S.; Nair, M.H.; Amarnath, A.; Anjana, N. Impacts of impervious surfaces on the environment. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Eom, J.; Yu, S.; Asrar, G.R. Projecting global urban area growth through 2100 based on historical time series data and future Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, A.; Chang, C.; Paulsen, K. The changing spatial form of cities in Western China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 135, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Altan, O.; Cheng, T. Remote sensing monitoring of multi-scale watersheds impermeability for urban hydrological evaluation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Siri, J.G.; Remais, J.V.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chan, K.K.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cong, N.; Li, X.; et al. The Tsinghua–Lancet Commission on Healthy Cities in China: Unlocking the power of cities for a healthy China. Lancet 2018, 391, 2140–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Fan, F. Impervious surface extraction based on different methods from multiple spatial resolution images: A comprehensive comparison. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1148–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugg, Z.P.; Finke, T.; Goodrich, D.C.; Moran, M.S.; Yool, S.R. Mapping impervious surfaces using object-oriented classification in a semiarid urban region. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebari, I.; He, D.-C. Automatic fuzzy object-based analysis of VHSR images for urban objects extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, Z.; Deng, J.; Gan, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, K. Mapping impervious surfaces in town–rural transition belts using China’s GF-2 imagery and object-based deep CNNs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, C. Measuring spatio-temporal dynamics of impervious surface in Guangzhou, China, from 1988 to 2015, using time-series Landsat imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Wu, C. A spatially adaptive spectral mixture analysis for mapping subpixel urban impervious surface distribution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 133, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, A.; Jia, X. Stratified spectral mixture analysis of medium resolution imagery for impervious surface mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. A new scheme for urban impervious surface classification from SAR images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Ren, H.; Dong, M.; Feng, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, J. Toward accurate mapping of 30-m time-series global impervious surface area (GISA). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Mi, J. GISD30: Global 30 m impervious-surface dynamic dataset from 1985 to 2020 using time-series Landsat imagery on the Google Earth Engine platform. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1831–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, B. Development of a global 30 m impervious surface map using multisource and multitemporal remote sensing datasets with the Google Earth Engine platform. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.R.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C. Web-enabled Landsat Data (WELD): Landsat ETM+ composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Roy, D.P. The availability of cloud-free Landsat ETM+ data over the conterminous United States and globally. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1196–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Travis, D. Gaps-fill of SLC-off Landsat ETM+ satellite image using a geostatistical approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5103–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, H.; Song, Q.; Zheng, K. A novel index for impervious surface area mapping: Development and validation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; Cai, B. Mapping Impervious Surface Areas Using Time-Series Nighttime Light and MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping impervious surface distribution with integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, G.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, D. Exploring improvement of impervious surface estimation at national scale through integration of nighttime light and proba-v data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; He, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban impervious surfaces in China: An improved assessment using nighttime light data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 130, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, F. Spatialization of electricity consumption of China using saturation-corrected DMSP-OLS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P. A temperature and vegetation adjusted NTL urban index for urban area mapping and analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.K.; Roy, D.P. Using the 500 m MODIS land cover product to derive a consistent continental scale 30 m Landsat land cover classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Spatiotemporally enhancing time-series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, F.; Okujeni, A.; Hauer, J.; Hostert, P.; Nielsen, J.Ø.; van der Linden, S. Mapping patterns of urban development in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, using machine learning regression modeling with bi-seasonal Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, Q.; Shao, Z. An evaluation of monthly impervious surface dynamics by fusing Landsat and MODIS time series in the Pearl River Delta, China, from 2000 to 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Weng, Q. Impervious surface area extraction from IKONOS imagery using an object-based fuzzy method. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radoux, J.; Lamarche, C.; Van Bogaert, E.; Bontemps, S.; Brockmann, C.; Defourny, P. Automated training sample extraction for global land cover mapping. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3965–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, X. 30 m global impervious surface area dynamics and urban expansion pattern observed by Landsat satellites: From 1972 to 2019. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Du, W.; Jiang, H.; Weng, Q.; Guo, H.; Han, Y.; Xing, Q.; Ma, Y. Global 10-m impervious surface area mapping: A big earth data based extraction and updating approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for International Earth Science Information Network-CIESIN-Columbia University. National Aggregates of Geospatial Data Collection: Population, Landscape, And Climate Estimates, Version 3 (PLACE III); NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2012.
- Arino, O.; Ramos Perez, J.J.; Kalogirou, V.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Van Bogaert, E. Global Land Cover Map for 2009 (GlobCover 2009); European Space Agency (ESA): Paris, France; Université catholique de Louvain (UCL): Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using MODIS 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertes, C.M.; Schneider, A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tatem, A.; Tan, B. Detecting change in urban areas at continental scales with MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Schneider, A. The footprint of urban climates on vegetation phenology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Huang, C.; Channan, S.; Baker, M.E.; Townshend, J.R. Urban growth of the Washington, DC–Baltimore, MD metropolitan region from 1984 to 2010 by annual, Landsat-based estimates of impervious cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda, M.; Holtanová, E.; Halenka, T.; Kalvová, J. Climate classification revisited: From Köppen to Trewartha. Clim. Res. 2014, 59, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, B.; Gilabert, M.A. Vegetation dynamics from NDVI time series analysis using the wavelet transform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Mbow, C. Evaluation of earth observation based long term vegetation trends—Intercomparing NDVI time series trend analysis consistency of Sahel from AVHRR GIMMS, Terra MODIS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1886–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Seasonal effects of impervious surface estimation in subtropical monsoon regions. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.K.; Sylvester, K.M. Identification of “ever-cropped” land (1984–2010) using Landsat annual maximum NDVI image composites: Southwestern Kansas case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Mapping global urban areas from 2000 to 2012 using time-series nighttime light data and MODIS products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, E.; Zhang, C.; Samat, A.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Atkinson, P.M. Estimating artificial impervious surface percentage in Asia by fusing multi-temporal MODIS and VIIRS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Liu, C. The integrated use of DMSP-OLS nighttime light and MODIS data for monitoring large-scale impervious surface dynamics: A case study in the Yangtze River Delta. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9359–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Jendryke, M.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Night-time light dynamics during the iraqi civil war. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pok, S.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. An easily implemented method to estimate impervious surface area on a large scale from MODIS time-series and improved DMSP-OLS nighttime light data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T.; Politis, P.; Florczyk, A.J.; Syrris, V.; Melchiorri, M.; Sabo, F.; Soille, P. Automated global delineation of human settlements from 40 years of Landsat satellite data archives. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 140–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florczyk, A.J.; Corbane, C.; Ehrlich, D.; Freire, S.; Kemper, T.; Maffenini, L.; Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Schiavina, M.; et al. GHSL data package 2019. Luxemb. EUR 2019, 29788, 290498. [Google Scholar]
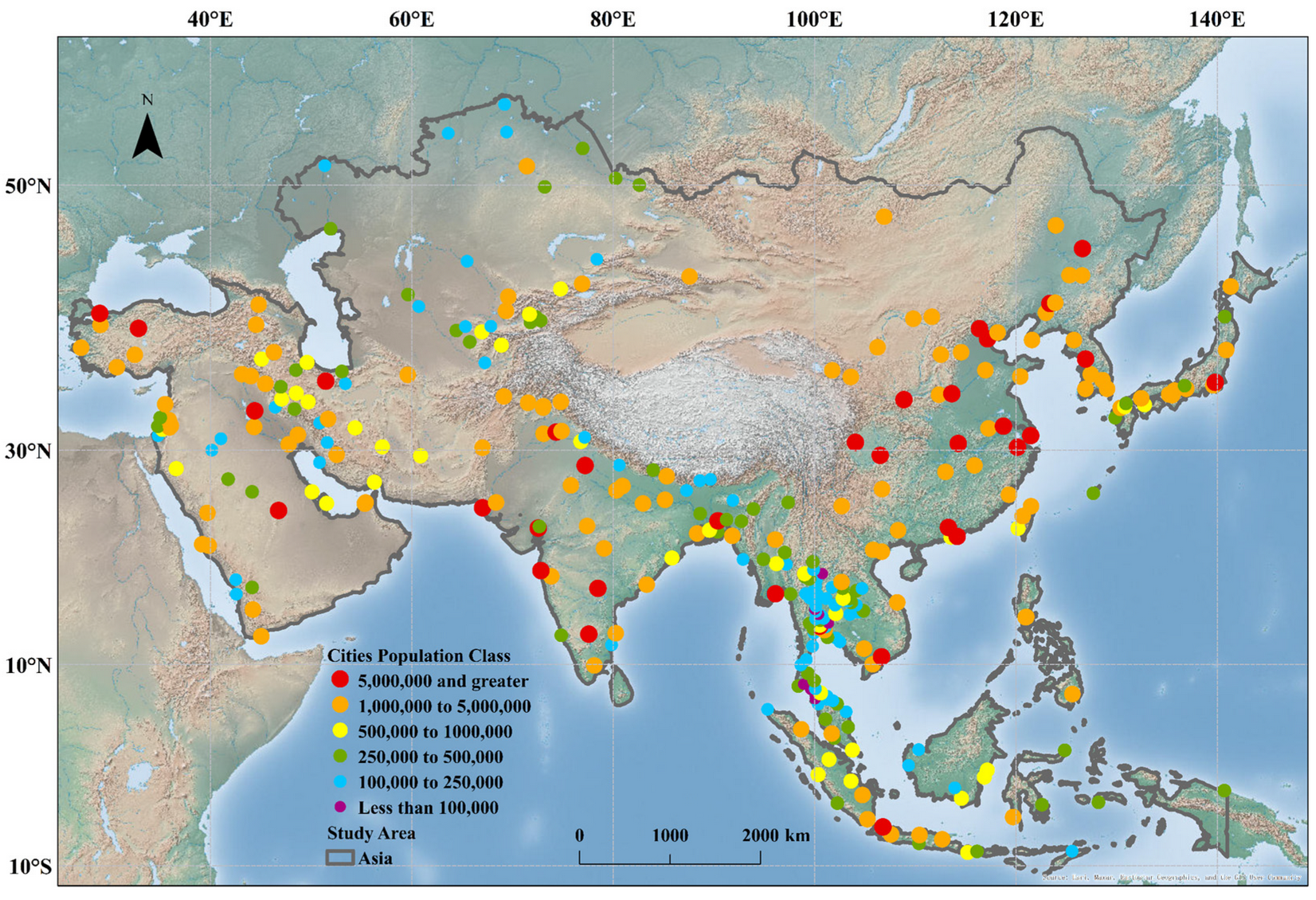





| Type | Name | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Sensing Data | MOD09A1 | MODIS Terra/Aqua Surface Reflectance 8-Day Product, 46 periods in a year, spatial resolution 500 m. | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 10 February 2022) |
| VIIRS DNB | VIIRS DNB Cloud-Free Composites Monthly Product, 12 periods in a year, spatial resolution 500 m. | https://eogdata.mines.edu/products/vnl/ (accessed on 10 February 2022) | |
| Auxiliary Data | Köppen–Geiger climate classification | Köppen–Geiger climate classification global raster data, spatial resolution 1000 m. | http://www.gloh2o.org/koppen/ (accessed on 12 March 2022). |
| Sample Data | GAIA | Global artificial impervious area products from 1985 to 2018, spatial resolution 30 m. | http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn/ (accessed on 5 January 2022) |
| Google Earth historical images | High-resolution historical images. A container collects multi-source data (SPOT5, IKONOS, etc.) | https://earth.google.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2022) |
| Scheme | Feature Set Combination |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ss |
| 2 | Ss + NDSIs |
| 3 | Ss + MNDSIs |
| 4 | Ss + NDSIs + NTL |
| 5 | Ss + MNDSIs + NTL |
| Region | Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 | Scheme 3 | Scheme 4 | Scheme 5 | LISI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8386 | 0.8449 | 0.8440 | 0.8517 | 0.8525 | 0.7014 |
| 2 | 0.8313 | 0.8411 | 0.8405 | 0.8473 | 0.8464 | 0.6548 |
| 3 | 0.8319 | 0.8495 | 0.8487 | 0.8511 | 0.8502 | 0.6170 |
| 4 | 0.8106 | 0.8351 | 0.8321 | 0.8475 | 0.8444 | 0.5275 |
| 5 | 0.8022 | 0.8368 | 0.8404 | 0.8442 | 0.8495 | 0.6146 |
| 6 | 0.7981 | 0.8342 | 0.8406 | 0.8445 | 0.8510 | 0.6017 |
| 7 | 0.7632 | 0.8318 | 0.8402 | 0.8446 | 0.8552 | 0.6512 |
| ALL | 0.7884 | 0.8218 | 0.8205 | 0.8269 | 0.8286 | 0.6231 |
| Region | RFR | SVR | RNN | GPR | MLR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| 1 | 0.8518 | 0.1376 | 0.8516 | 0.1399 | 0.8580 | 0.1393 | 0.8589 | 0.1359 | 0.8046 | 0.1605 |
| 2 | 0.8481 | 0.1323 | 0.8455 | 0.1341 | 0.8427 | 0.1355 | 0.8549 | 0.1294 | 0.7915 | 0.1549 |
| 3 | 0.8505 | 0.1187 | 0.8550 | 0.1176 | 0.8551 | 0.1175 | 0.8617 | 0.1144 | 0.8046 | 0.1598 |
| 4 | 0.8485 | 0.1322 | 0.8440 | 0.1344 | 0.8453 | 0.1337 | 0.8571 | 0.1298 | 0.7916 | 0.1549 |
| 5 | 0.8494 | 0.1189 | 0.8507 | 0.1174 | 0.8481 | 0.1186 | 0.8587 | 0.1156 | 0.7955 | 0.1585 |
| 6 | 0.8505 | 0.1295 | 0.8502 | 0.1283 | 0.8492 | 0.1279 | 0.8592 | 0.1205 | 0.8155 | 0.1588 |
| 7 | 0.8554 | 0.1401 | 0.8555 | 0.1401 | 0.8578 | 0.1399 | 0.8618 | 0.1329 | 0.8015 | 0.1596 |
| ALL | 0.8202 | 0.1452 | 0.8190 | 0.1481 | 0.8163 | 0.1498 | 0.8326 | 0.1415 | 0.7212 | 0.1853 |
| Region | unCorr (2015) | Corr (2015) | unCorr (2020) | Corr (2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| 1 | 0.8279 | 0.1463 | 0.8398 | 0.1415 | 0.8296 | 0.1479 | 0.8405 | 0.1427 |
| 2 | 0.8205 | 0.1426 | 0.8332 | 0.1350 | 0.8215 | 0.1450 | 0.8354 | 0.1373 |
| 3 | 0.8120 | 0.1352 | 0.8275 | 0.1305 | 0.8127 | 0.1342 | 0.8286 | 0.1311 |
| 4 | 0.8234 | 0.1410 | 0.8354 | 0.1331 | 0.8254 | 0.1395 | 0.8376 | 0.1311 |
| 5 | 0.8239 | 0.1405 | 0.8327 | 0.1344 | 0.8248 | 0.1409 | 0.8335 | 0.1357 |
| 6 | 0.8276 | 0.1492 | 0.8321 | 0.1432 | 0.8261 | 0.1487 | 0.8343 | 0.1439 |
| 7 | 0.8165 | 0.1534 | 0.8247 | 0.1468 | 0.8197 | 0.1528 | 0.8279 | 0.1479 |
| Region | LISP-2015 | GAIA-2015 | GHSL-2015 | NUACI-2015 | LISP-2020 | GLC-2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| 1 | 0.8402 | 0.1406 | 0.7498 | 0.2009 | 0.8111 | 0.1473 | 0.5845 | 0.2495 | 0.8380 | 0.1413 | 0.8329 | 0.1382 |
| 2 | 0.8336 | 0.1323 | 0.7684 | 0.1992 | 0.8272 | 0.1350 | 0.7433 | 0.1860 | 0.8348 | 0.1355 | 0.8349 | 0.1388 |
| 3 | 0.8249 | 0.1329 | 0.8095 | 0.1413 | 0.7912 | 0.1518 | 0.6367 | 0.1920 | 0.8216 | 0.1315 | 0.7681 | 0.1681 |
| 4 | 0.8314 | 0.1372 | 0.8282 | 0.1422 | 0.8071 | 0.1455 | 0.5784 | 0.2292 | 0.8336 | 0.1397 | 0.7846 | 0.1436 |
| 5 | 0.8326 | 0.1389 | 0.7889 | 0.1488 | 0.7867 | 0.1695 | 0.4835 | 0.2164 | 0.8343 | 0.1386 | 0.8081 | 0.1474 |
| 6 | 0.8335 | 0.1415 | 0.8016 | 0.1486 | 0.7925 | 0.1625 | 0.5047 | 0.2059 | 0.8352 | 0.1394 | 0.8023 | 0.1518 |
| 7 | 0.8269 | 0.1431 | 0.8185 | 0.1457 | 0.7842 | 0.1552 | 0.3134 | 0.4449 | 0.8293 | 0.1459 | 0.7784 | 0.1543 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Li, E.; Samat, A.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L. Estimating Large-Scale Interannual Dynamic Impervious Surface Percentages Based on Regional Divisions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153786
Xu T, Li E, Samat A, Li Z, Liu W, Zhang L. Estimating Large-Scale Interannual Dynamic Impervious Surface Percentages Based on Regional Divisions. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153786
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tianyu, Erzhu Li, Alim Samat, Zhiqing Li, Wei Liu, and Lianpeng Zhang. 2022. "Estimating Large-Scale Interannual Dynamic Impervious Surface Percentages Based on Regional Divisions" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153786
APA StyleXu, T., Li, E., Samat, A., Li, Z., Liu, W., & Zhang, L. (2022). Estimating Large-Scale Interannual Dynamic Impervious Surface Percentages Based on Regional Divisions. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153786