Application of a PLS-Augmented ANN Model for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a from Hyperspectral Data in Case 2 Waters of the Western Basin of Lake Erie
Abstract
1. Introduction
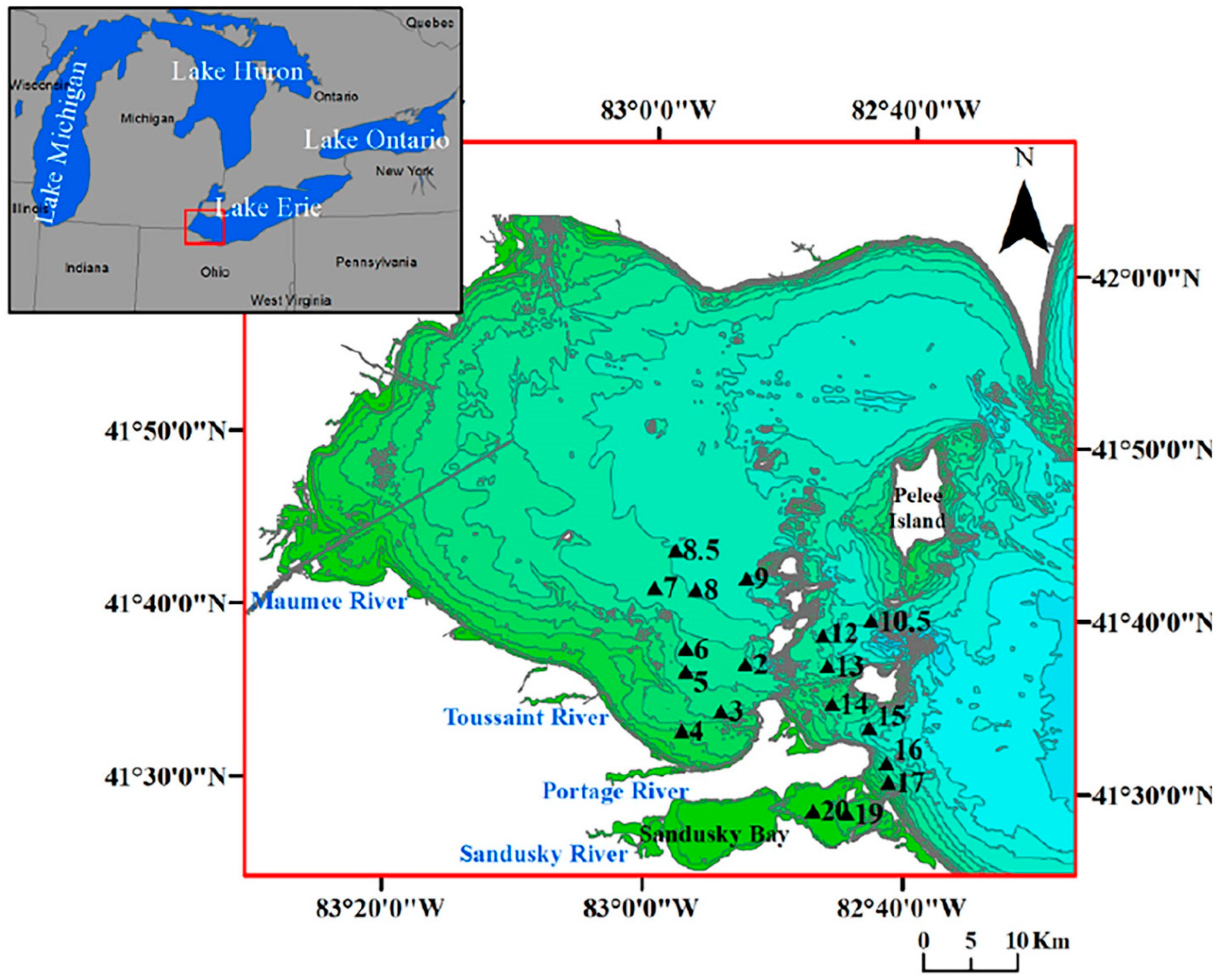
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Reflectance Measurements
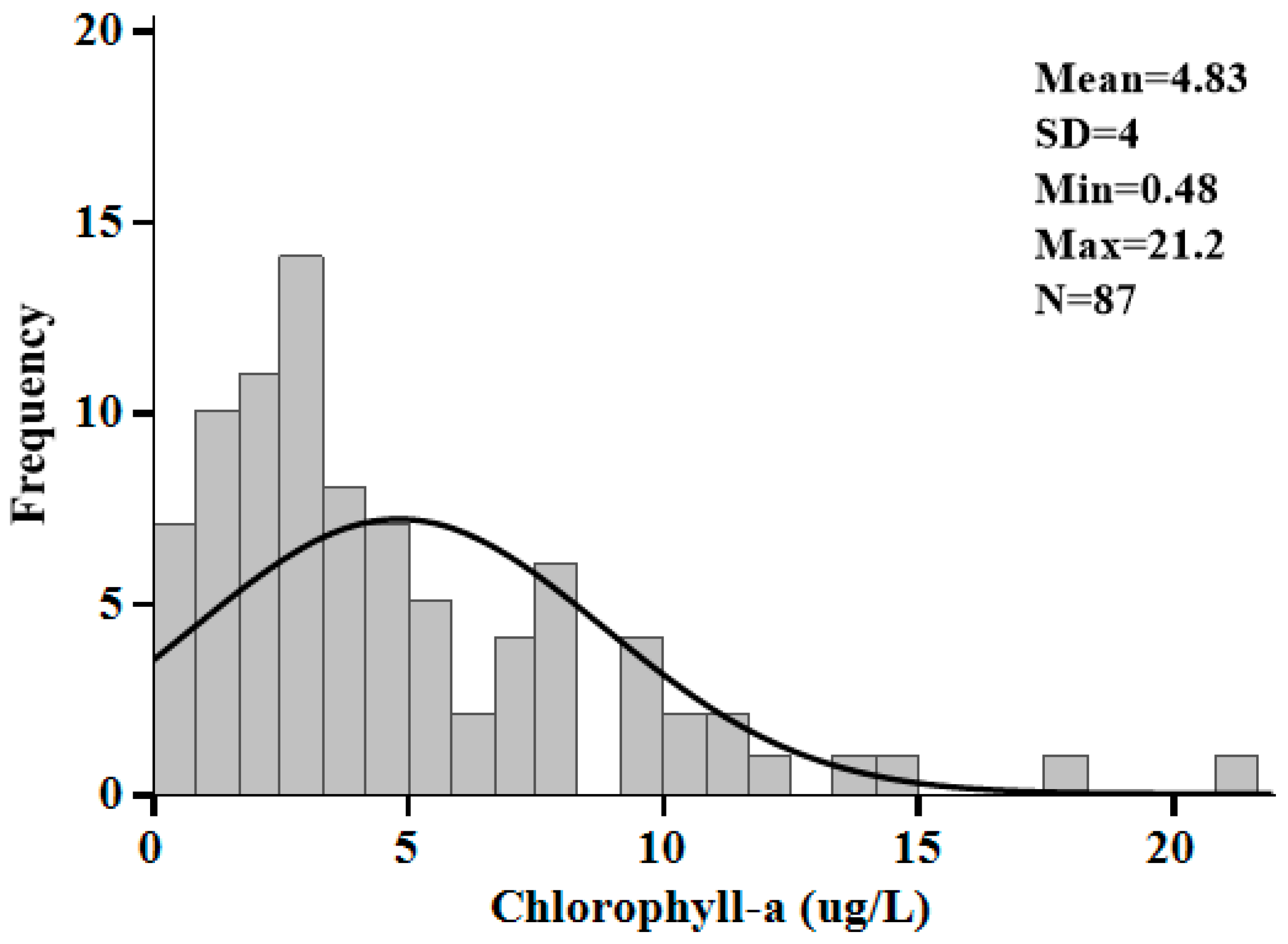
2.1.2. Chl-a Measurements
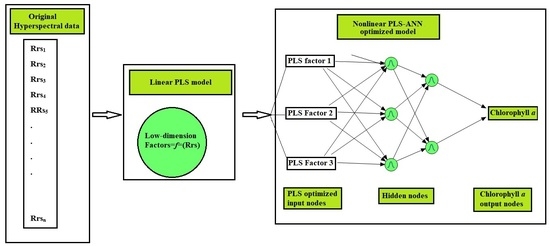
2.2. Methods
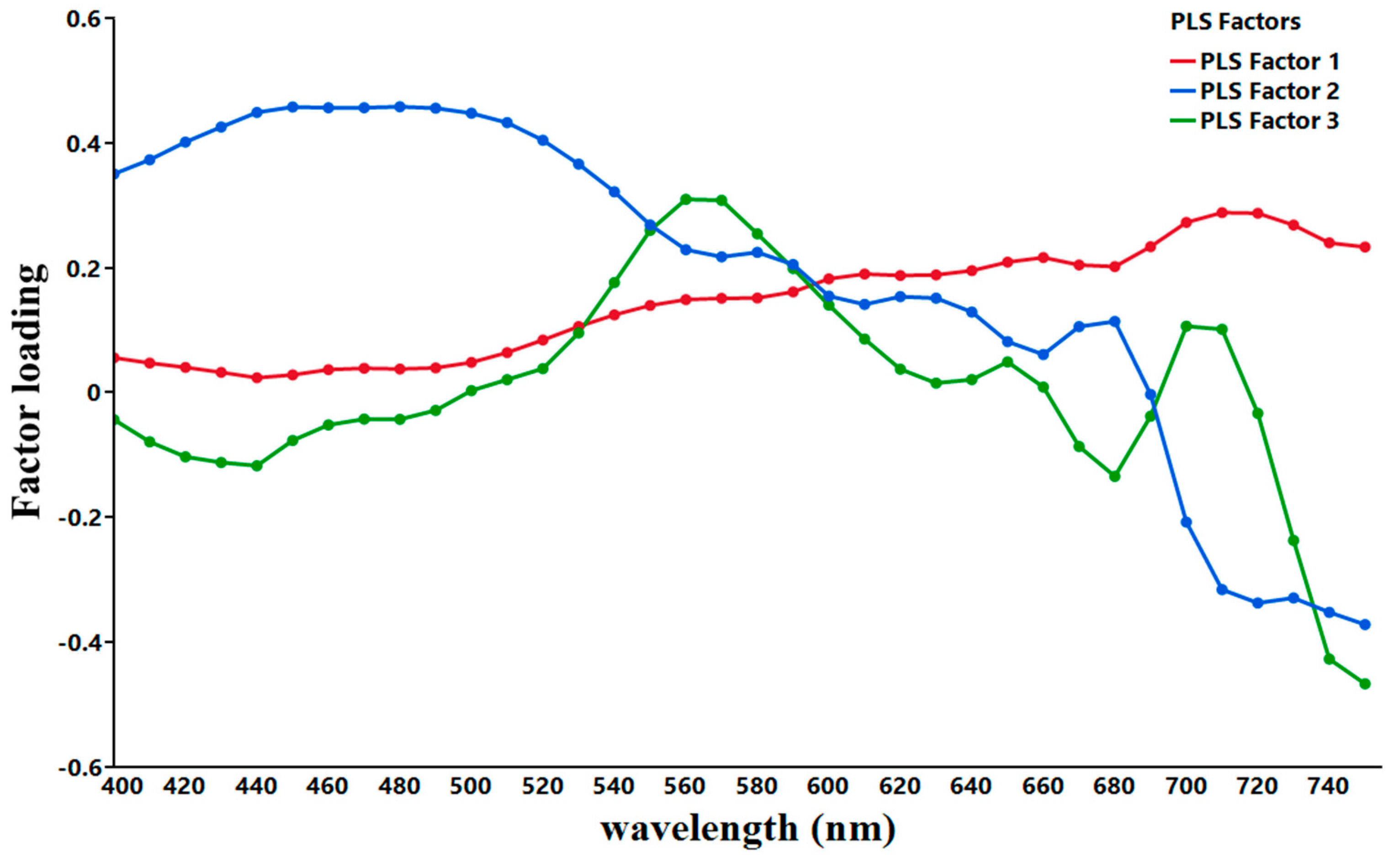
2.2.1. Partial Least Squares (PLS)
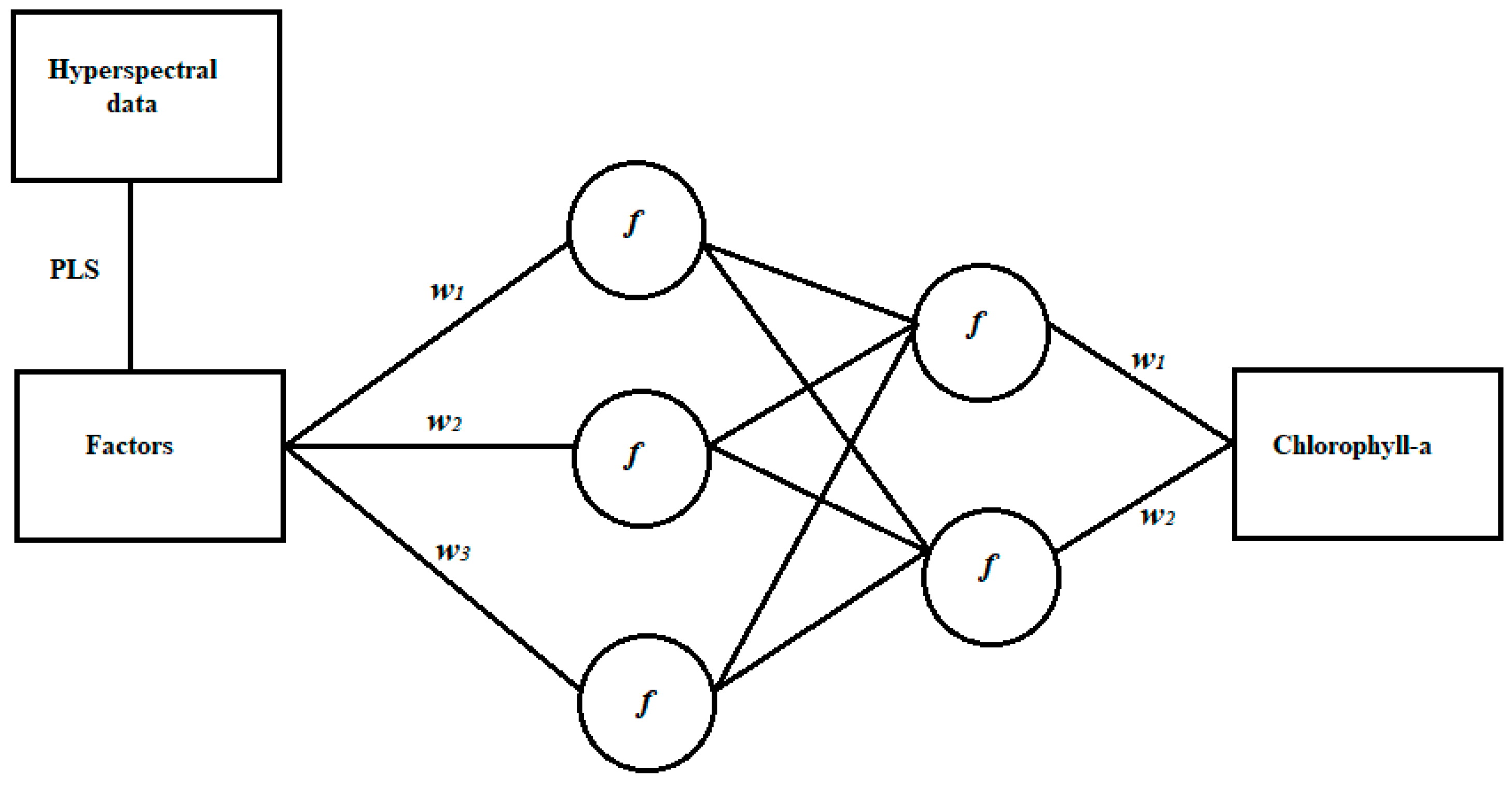
2.2.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
2.2.3. Semi-Empirical Algorithms
Blue-Green Chl-a Algorithm
NIR-Red Chl-a Algorithm
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Error Metrics
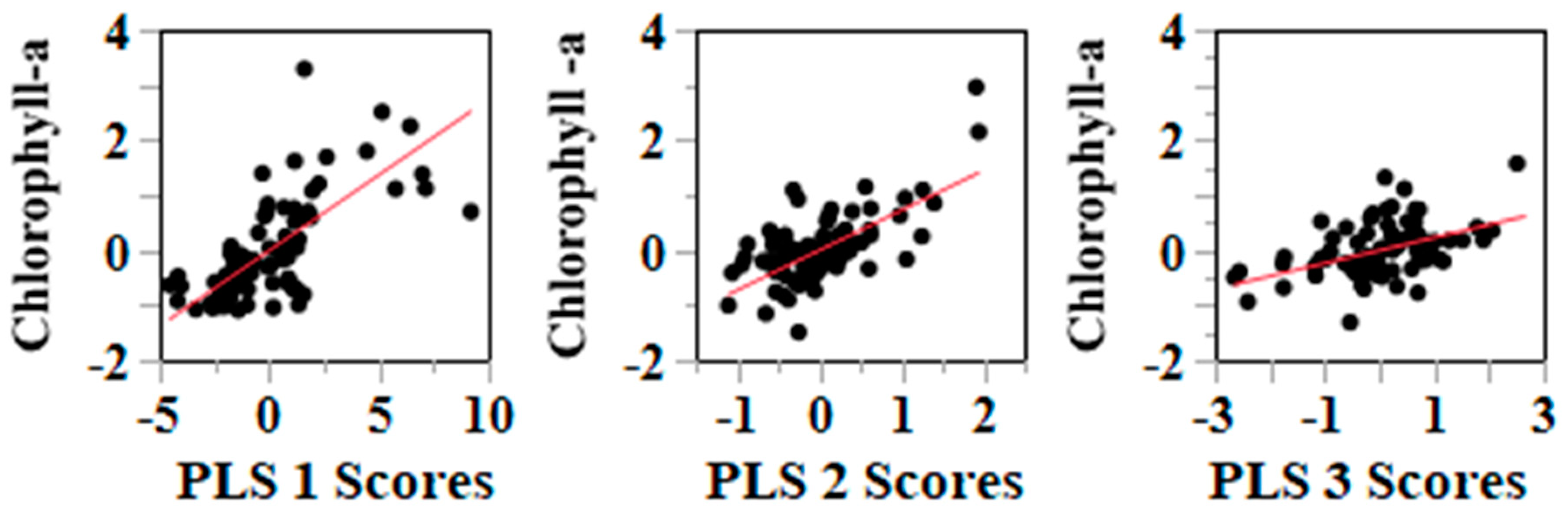
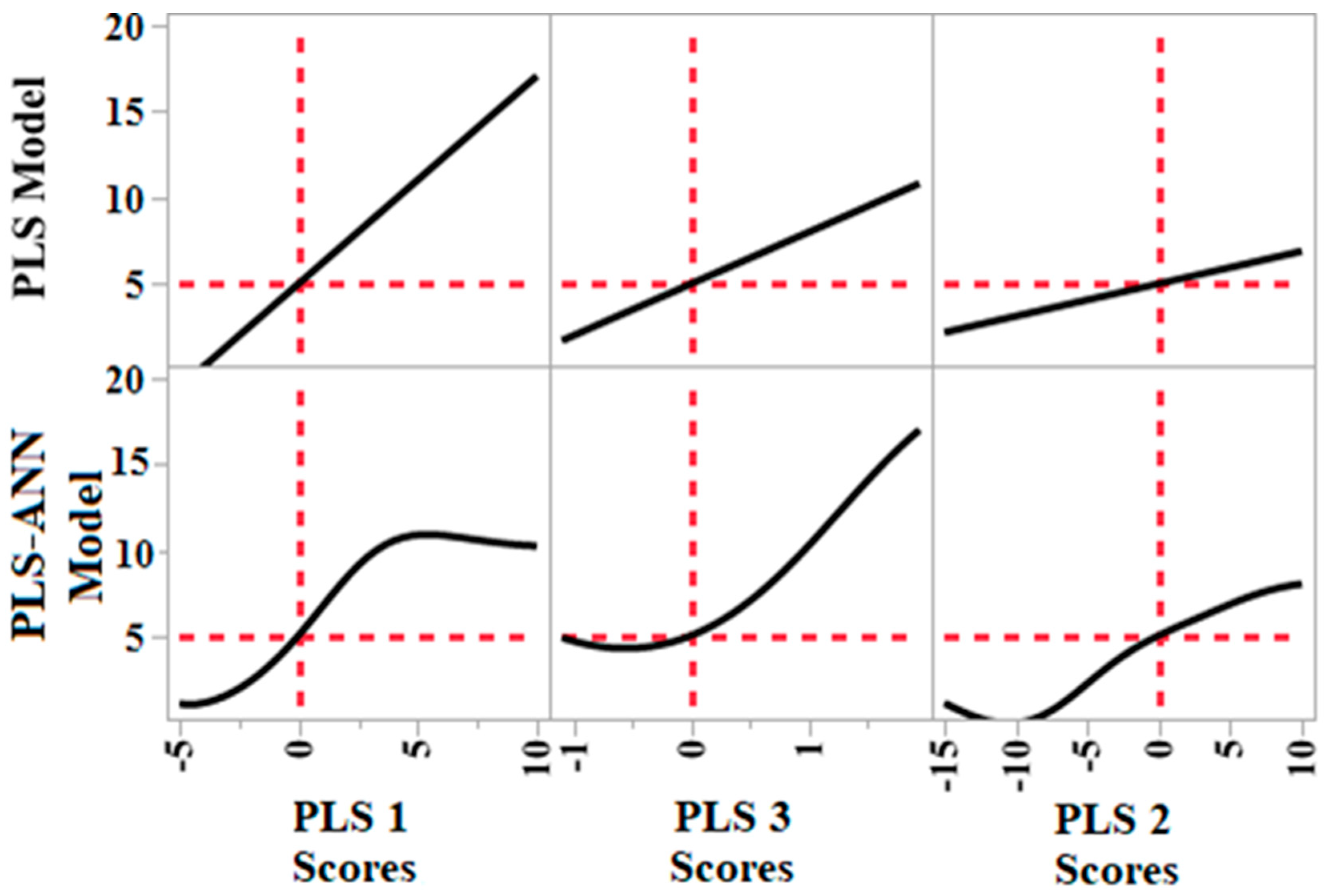
3.2. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration Using the PLS Method
3.3. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration Using the PLS-ANN Method
3.4. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration Using the Blue-Green Algorithm
3.5. Estimation of Chl-a Concentration Using the NIR-Red Algorithm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albert, A.; Mobley, C. An analytical model for subsurface irradiance and remote sensing reflectance in deep and shallow case-2 waters. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A.; Ortiz, J.; Bonini, N.; Shuman, M.; Sydow, C. Application of Aqua MODIS sensor data for estimating chlorophyll a in the turbid Case 2 waters of Lake Erie using bio-optical models. GISci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 483–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Witter, D.; Ortiz, J. Application of empirical and semi-analytical algorithms to MERIS data for estimating chlorophyll a in Case 2 waters of Lake Erie. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll algorithms for ocean color sensors—OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Bowles, J.H.; Povazhnyi, V.; Saprygin, V.; Wagner, E.J.; Patterson, K.W. HICO-Based NIR–Red Models for Estimating Chlorophyll-α Concentration in Productive Coastal Waters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z. Visible-Infrared Remote Sensing Model and Applications for Ocean Waters; University of South Florida: Tampa, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Roesler, C.S.; Perry, M.J. In situ phytoplankton absorption, fluorescence emission, and particulate backscattering spectra determined from reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1995, 100, 13279–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.M.; Effler, S.W.; Strait, C.M.; Leshkevich, G.A. Optical characterizations and pursuit of optical closure for the western basin of Lake Erie through in situ measurements. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A.; Witter, D.L.; Ortiz, J.D. Multivariate approach to estimate colour producing agents in Case 2 waters using first-derivative spectrophotometer data. Geocarto Int. 2013, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, R.; Fischer, J. Concentrations of chlorophyll, suspended matter, and gelbstoff in case II waters derived from satellite coastal zone color scanner data with inverse modeling methods. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1994, 99, 7457–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.; Ali, K. Application of a partial least-squares regression model to retrieve chlorophyll-a concentrations in coastal waters using hyper-spectral data. Ocean Sci. J. 2016, 51, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, M.; Lin, C.-H.; Chu, H.-J.; Jaelani, L.M.; Syariz, M.A. Spectral Feature Selection Optimization for Water Quality Estimation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, H.; Doerffer, R. Neural network for emulation of an inverse model operational derivation of Case II water properties from MERIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, R.; Schiller, H. The MERIS Case 2 water algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J.; Won, J.; Min, O. Modelling Chlorophyll-a Concentration using Deep Neural Networks considering Extreme Data Imbalance and Skewness. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeongchang-gun, Korea, 17–20 February 2019; pp. 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, I.; Foster, R.; Gilerson, A.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Neural network approach for the derivation of chlorophyll concentration from ocean color. In Proceedings of the SPIE 8724, Ocean Sensing and Monitoring V, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 April–3 May 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Shi, P.; Chen, C. Inversion of oceanic chlorophyll concentrations by neural networks. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas, L.G.; Spyrakos, E.; Palenzuela, J.M.T. Neural network estimation of chlorophyll a from MERIS full resolution data for the coastal waters of Galician rias (NW Spain). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syariz, M.A.; Lin, C.-H.; Van Nguyen, M.; Jaelani, L.M.; Blanco, A.C. WaterNet: A Convolutional Neural Network for Chlorophyll-a Concentration Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiner, L.E.; Yan, X.-H. A Neural Network Model for Estimating Sea Surface Chlorophyll and Sediments from Thematic Mapper Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.M. Neural network emulations for complex multidimensional geophysical mappings: Applications of neural network techniques to atmospheric and oceanic satellite retrievals and numerical modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlik, B.; Křivan, M. Identification of type daily diagrams of electric consumption based on cluster analysis of multi-dimensional data by neural network. Neural Netw. World 2013, 23, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, K.; Shao, T.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Tedesco, L.; Duan, H.; Li, Z.; Shi, K.; Du, J.; Zhao, Y. Using Partial Least Squares-Artificial Neural Network for Inversion of Inland Water Chlorophyll-a. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Lain, L.R.; Bernard, S. An optimized Chlorophyll a switching algorithm for MERIS and OLCI in phytoplankton-dominated waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Ioannou, I.; Ahmed, S.A. Algorithms for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in coastal and inland waters using red and near infrared bands. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24109–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Satellite Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Using the Red and NIR Bands of MERIS—The Azov Sea Case Study. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Moses, W.; Kaganovsky, S.; Sulimani, B.; Leavitt, B.C.; Gitelson, A.A. NIR-red reflectance-based algorithms for chlorophyll-a estimation in mesotrophic inland and coastal waters: Lake Kinneret case study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A. Effect of bio-optical parameter variability on the remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters: Experimental results. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Austin, R.W. Ocean optics protocols for SeaWiFS validation, revision 1. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1995, 42, 805. [Google Scholar]
- Ohde, T.; Siegel, H. Derivation of immersion factors for the hyperspectral TriOS radiance sensor. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 5, L12–L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Schalles, J.F.; Rundquist, D.C.; Han, L.; Stark, R.; Etzion, D. Remote estimation of phytoplankton density in productive waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Issues Advanc. Limnol. 2000, 55, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Schalles, J.F.; Rundquist, D.C.; Schiebe, F.R. The influence of suspended clays on phytoplankton reflectance signatures and the remote estimation of chlorophyll. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 2001, 27, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A. Nature of the peak near 700 nm on the radiance spectra and its application for remote estimation of phytoplankton pigments in inland waters. In Proceedings of the SPIE 1971, 8th Meeting on Optical Engineering in Israel: Optical Engineering and Remote Sensing, Tel Aviv, Israel, 14–16 December 1992; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the MERIS imaging spectrometer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R.; Doerffer, R.; Borstad, G.A. Interpretation of the 685 nm peak in water-leaving radiance spectra in terms of fluorescence, absorption and scattering, and its observation by MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arar, E.J.; Collins, G.B. Method 445.0: Chlorophyll a; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 1–22.
- Esbensen, K.H.; Guyot, D.; Westad, F.; Houmoller, L.P. Multivariate Data Analysis-In Pactice. An Introduction to multivariate data analysis and experimental design (4th edn), Kim H. Esbensen, CAMO, OSLO, 2000, ISBN 82-9933302-4, xviii + 600pp, US$230.00. J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Mu, G. Simultaneous dimensionality reduction and human age estimation via kernel partial least squares regression. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, A.; Williams, L.J.; McIntosh, A.R.; Abdi, H. Partial Least Squares (PLS) methods for neuroimaging: A tutorial and review. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cao, X.; Tian, L. Partial Least Squares Regression Performs Well in MRI-Based Individualized Estimations. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Lek, S. Artificial Neural Networks: Multilayer Perceptron for Ecological Modeling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Linz, J.E.; Harte, B.R. Electronic sensor array coupled with artificial neural network for detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 119, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Building Neural Network for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kangas, L.J.; Rasco, B.A. Applications of Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) in Food Science. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, F.M.; Kostanic, I. Principles of Neurocomputing for Science and Engineering; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-based NIR-red algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a concentrations in coastal waters—The Azov Sea case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.; Barrow, T.; Holz, J.C. Assessing the potential of SeaWiFS and MODIS for estimating chlorophyll concentration in turbid productive waters using red and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case II waters using MODIS and MERIS data—successes and challenges. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, B.N.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J. Performance metrics for the assessment of satellite data products: An ocean color case study. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.E.; Mix, A.C. Pleistocene Precipitation Balance in the Amazon Basin Recorded in Deep Sea Sediments. Quat. Res. 1999, 51, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, B.C.; Balsam, W.L. Visible spectroscopy; a rapid method for determining hematite and goethite concentration in geological materials. J. Sediment. Res. 1991, 61, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.D.; Witter, D.L.; Ali, K.A.; Fela, N.; Duff, M.; Mills, L. Evaluating multiple colour-producing agents in Case II waters from Lake Erie. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8854–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Algorithm | n | Bias | MAE | Percent Wins (%) | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLS | 87 | 1.16 | 1.41 | 16.28 | 0.76 | 1.95 |
| PLS-ANN | 87 | 1.1 | 1.31 | 58.14 | 0.92 | 1.22 |
| Blue-green Model | 87 | 1.21 | 1.73 | 12.79 | 0.61 | 1.75 |
| NIR-red Model | 87 | 1.19 | 1.74 | 12.79 | 0.56 | 1.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, K.A.; Moses, W.J. Application of a PLS-Augmented ANN Model for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a from Hyperspectral Data in Case 2 Waters of the Western Basin of Lake Erie. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153729
Ali KA, Moses WJ. Application of a PLS-Augmented ANN Model for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a from Hyperspectral Data in Case 2 Waters of the Western Basin of Lake Erie. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153729
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Khalid A., and Wesley J. Moses. 2022. "Application of a PLS-Augmented ANN Model for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a from Hyperspectral Data in Case 2 Waters of the Western Basin of Lake Erie" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153729
APA StyleAli, K. A., & Moses, W. J. (2022). Application of a PLS-Augmented ANN Model for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a from Hyperspectral Data in Case 2 Waters of the Western Basin of Lake Erie. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153729