Deformation Monitoring of Tailings Reservoir Based on Polarimetric Time Series InSAR: Example of Kafang Tailings Reservoir, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Area and Data
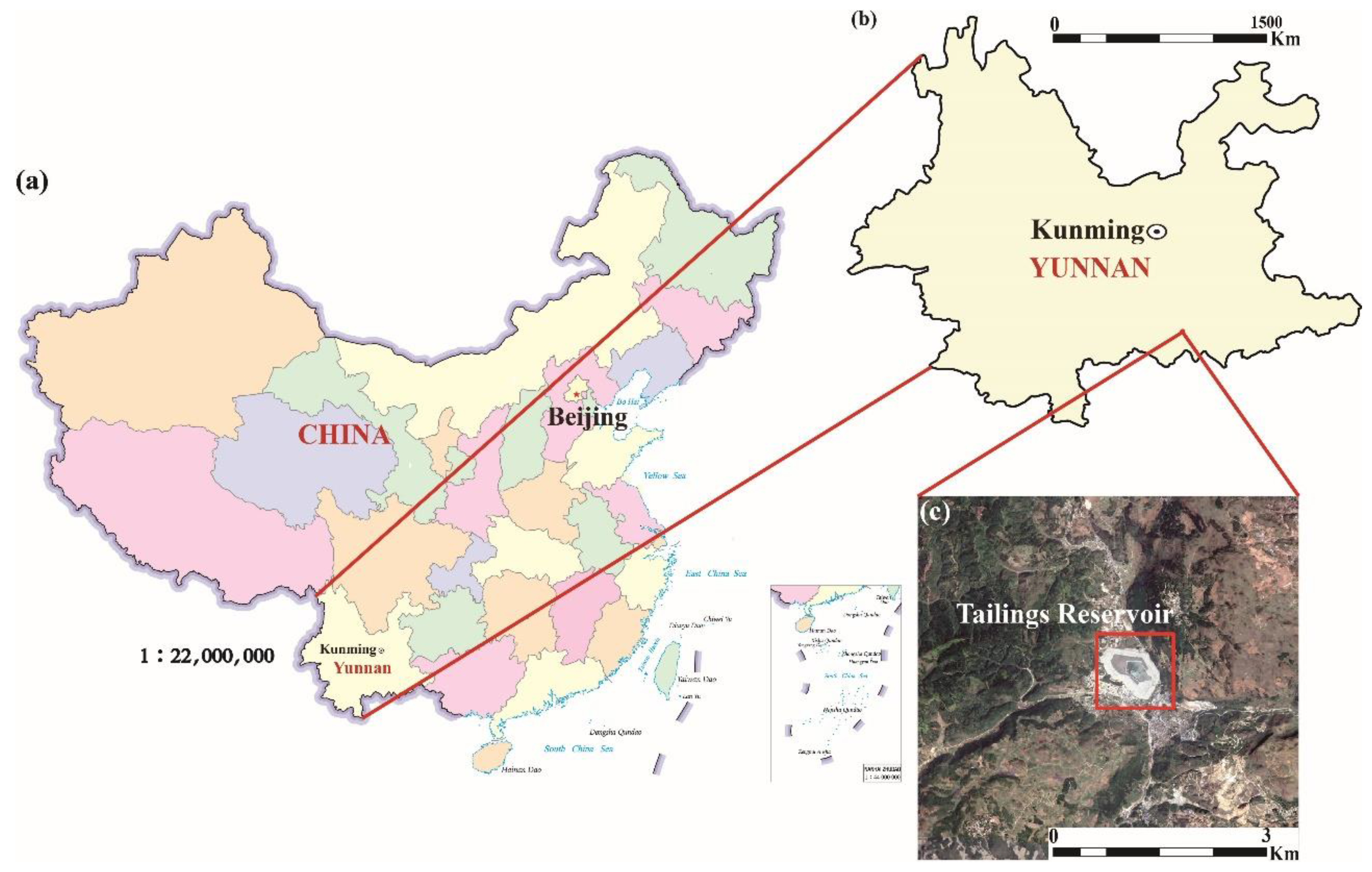
2.1. Experimental Area
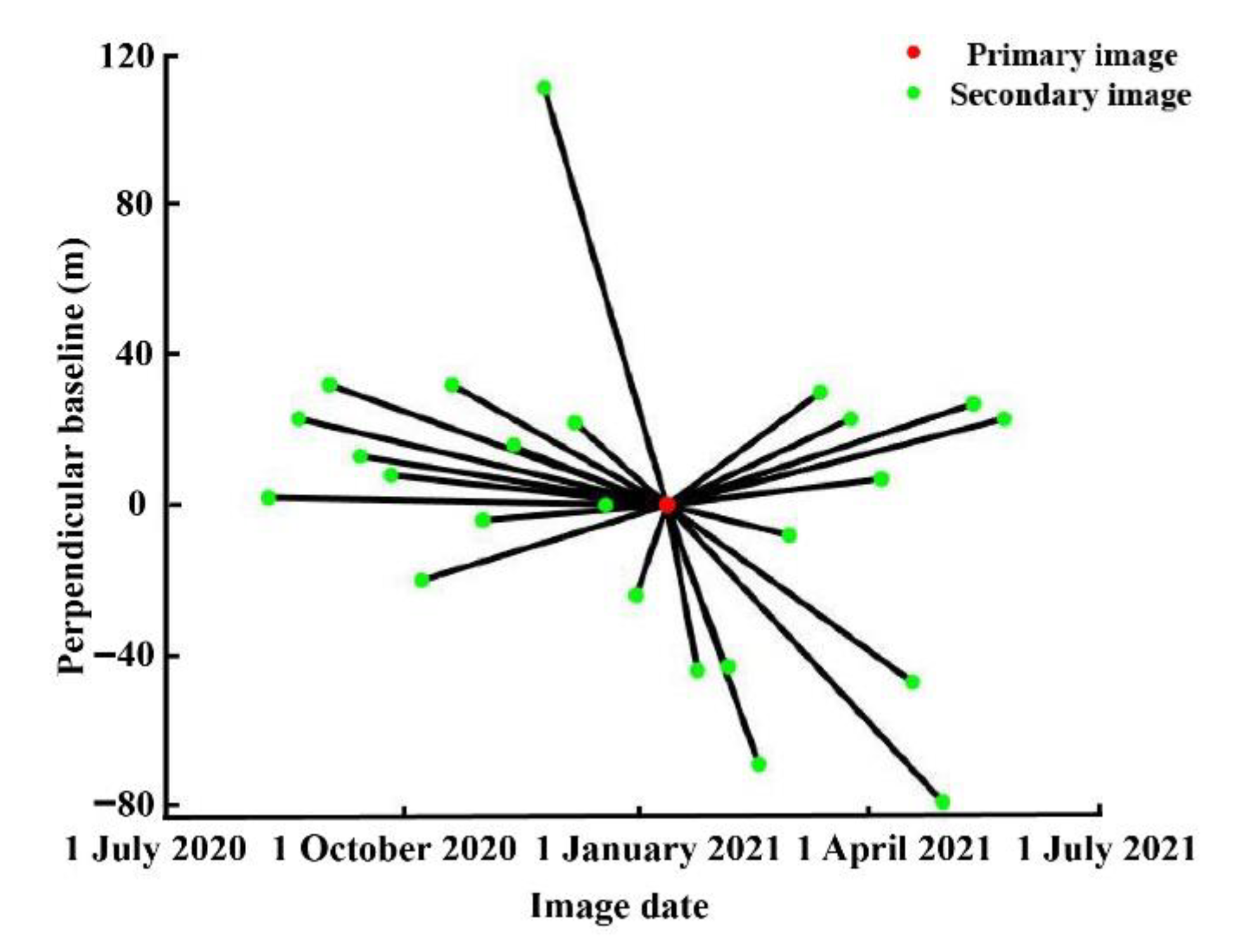
2.2. Experimental Data
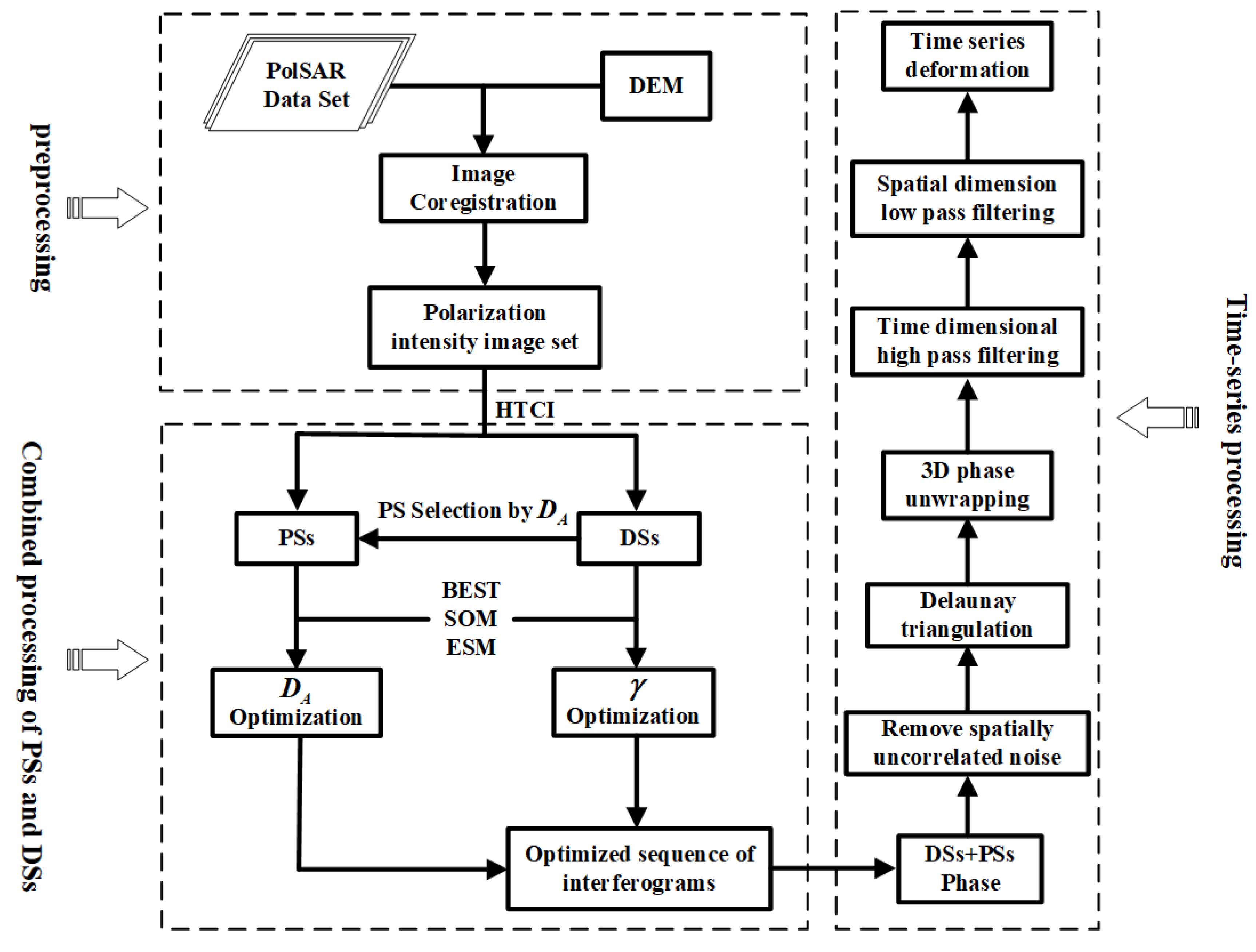
3. Method
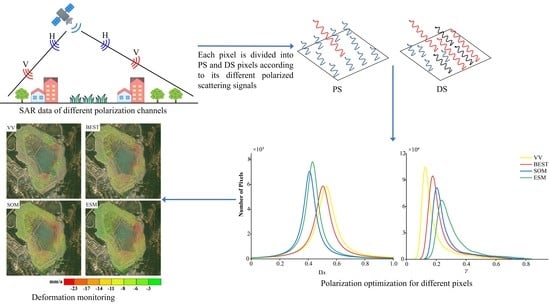
3.1. Statistically Homogeneous Point (SHP) Identification
3.2. Polarimetric Interferometry
3.3. Polarimetric Optimization
3.3.1. BEST
3.3.2. ESM
3.3.3. SOM
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Analysis of Homogenous Point Selection
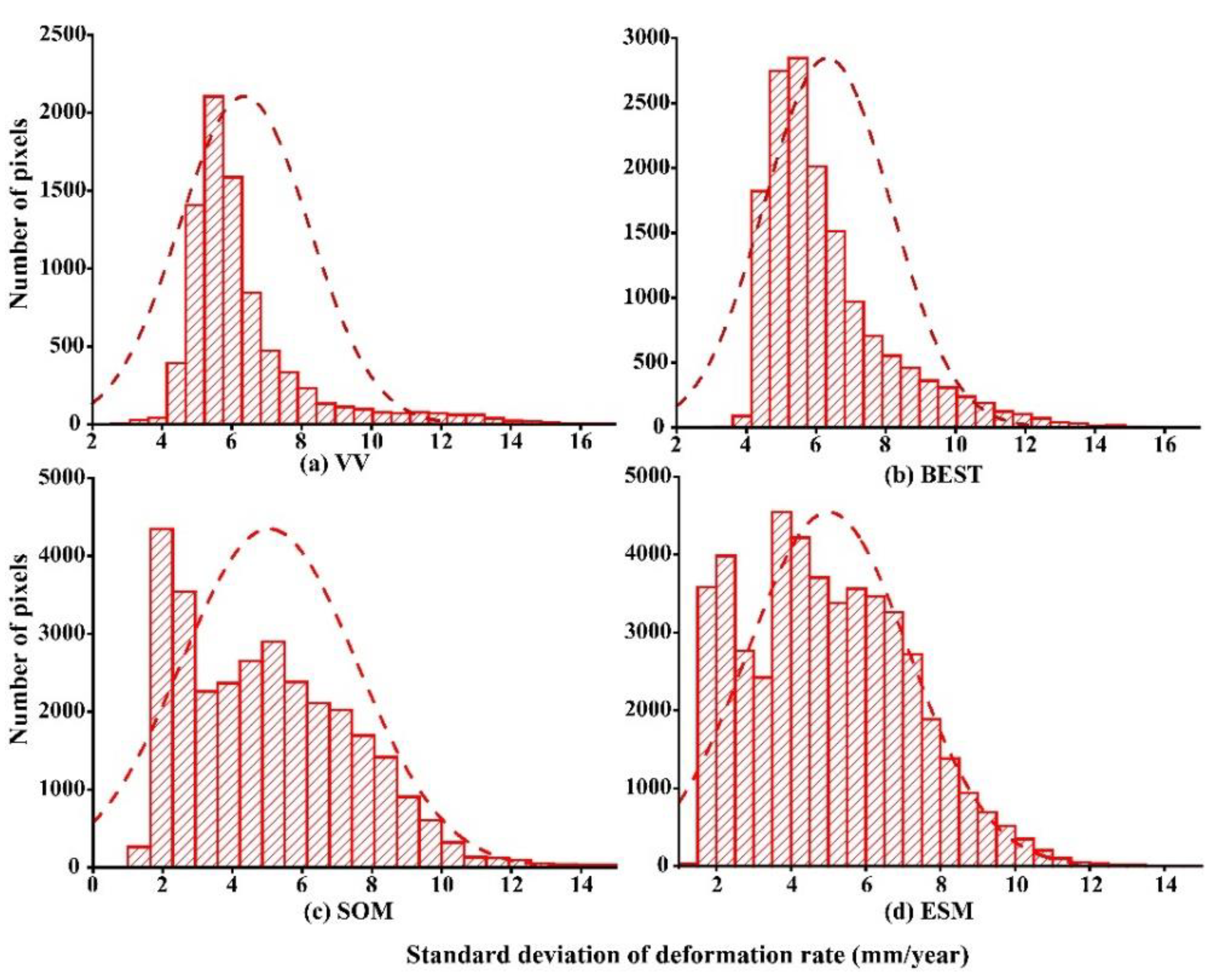
4.2. Polarimetric Optimization
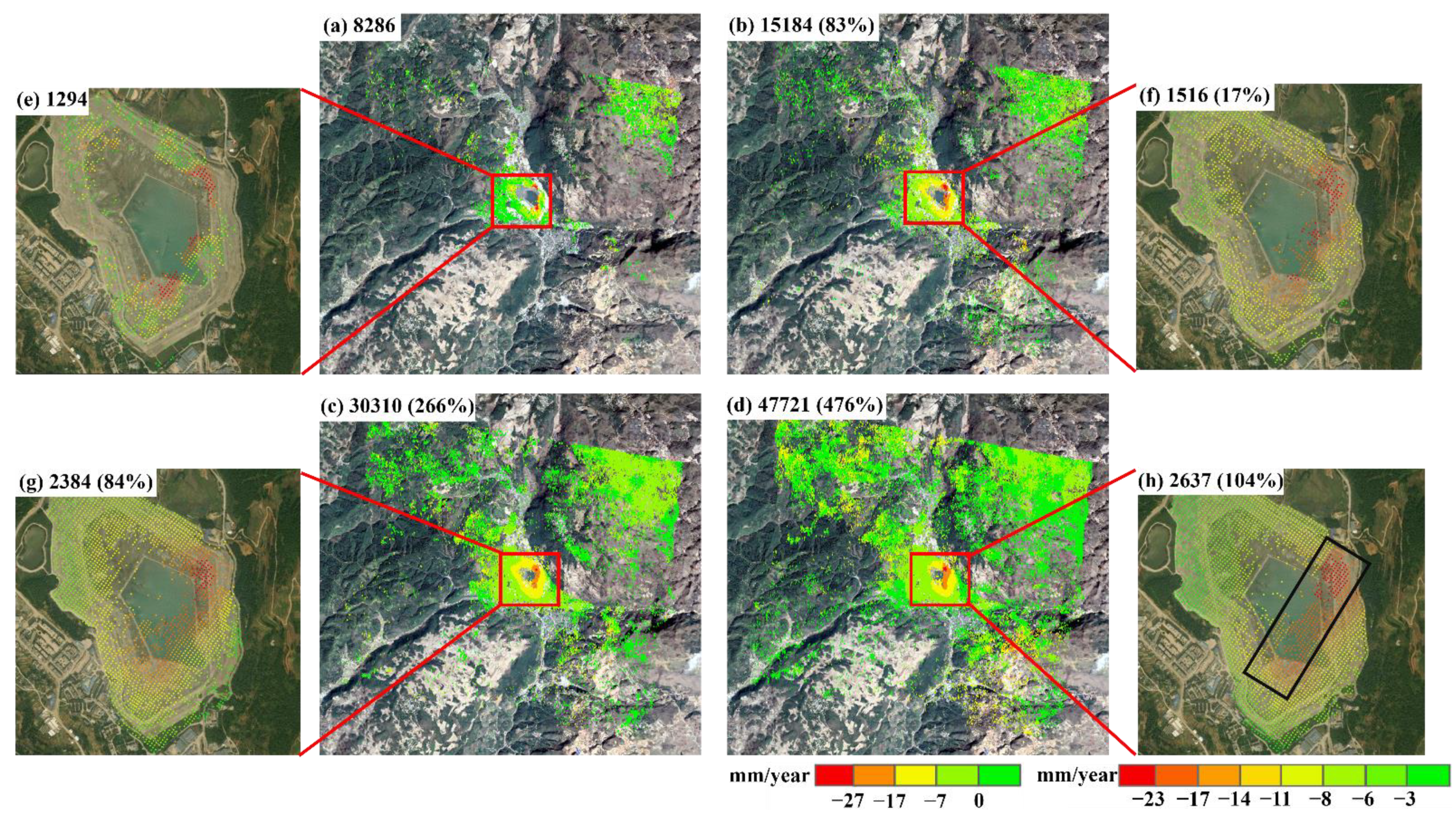
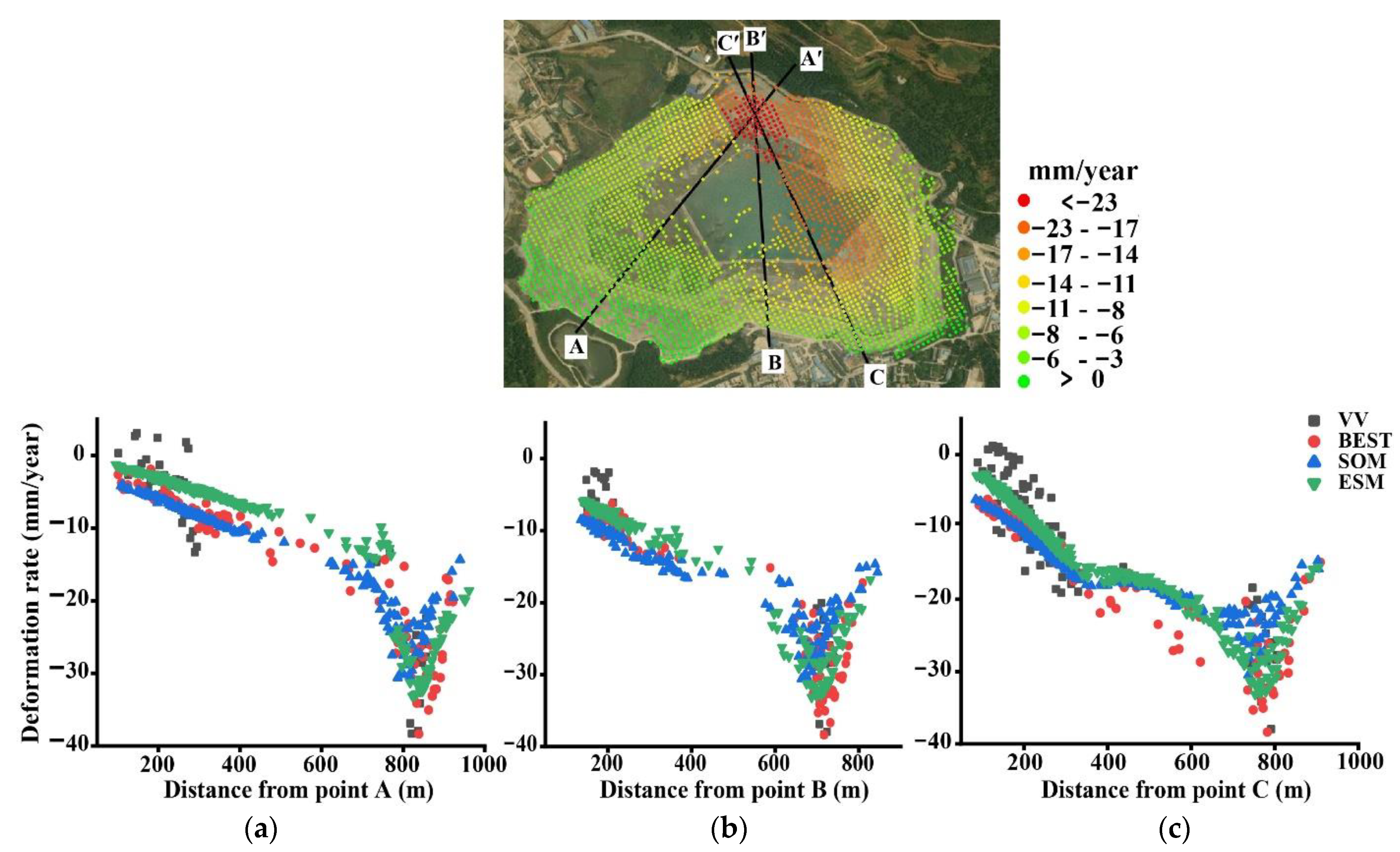
4.3. Deformation Analysis of Tailings Reservoir
5. Discussion
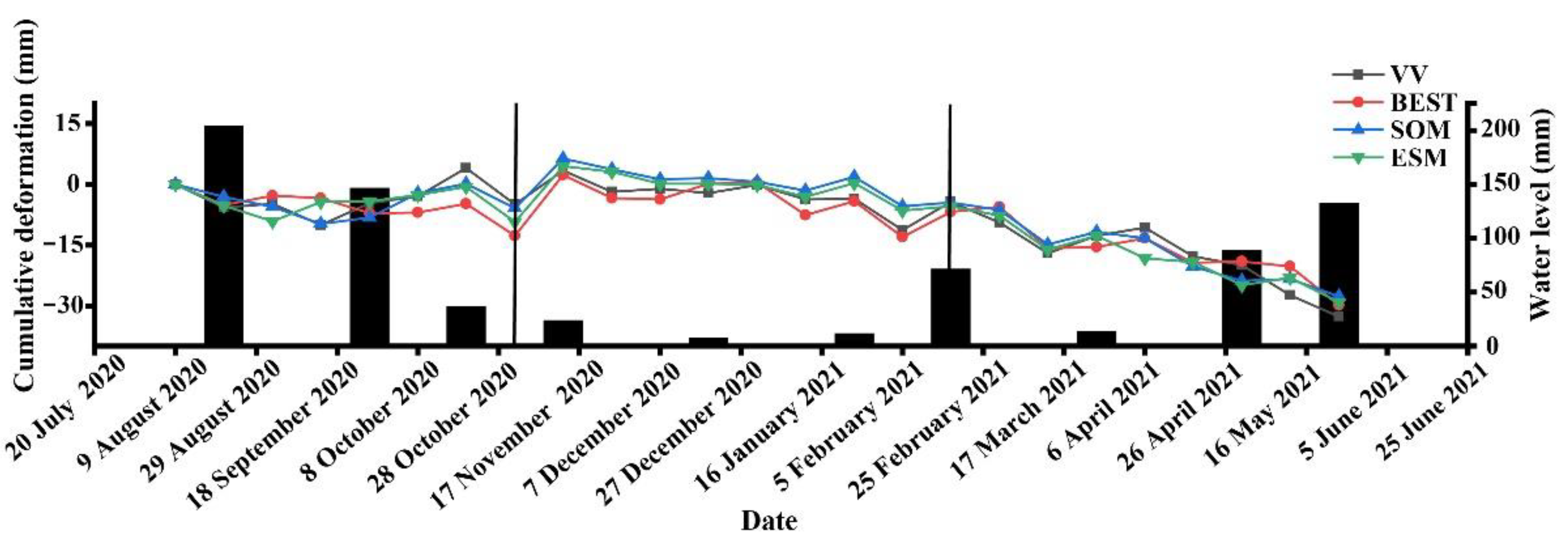
5.1. Analysis of Tailing Pond Deformation Based on Precipitation Data
5.2. Calculation Efficiency Analysis
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Fusing the homogenous points obtained from different polarization channels increased the density of homogenous points, with densities 3.86% and 8.45% higher than that of VH and VV, respectively. The BEST, SOM, and ESM methods were used for polarization optimization. Comparing amplitude dispersion and coherence, the three methods provided significant improvements compared with VV polarization, but the optimization effect was in the order ESM > SOM > BEST.
- (2)
- Deformation monitoring of a tailings reservoir showed that compared with VV polarization, the three optimization methods significantly improved the point selection density. In the image coverage area, the three optimization methods increased the density by 1.83 (BEST), 3.66 (SOM), and 5.76 (ESM) times compared with that with VV polarization, whereas in the tailings reservoir area, density increased by 1.17 (BEST), 1.84 (SOM), and 2.04 (ESM) times.
- (3)
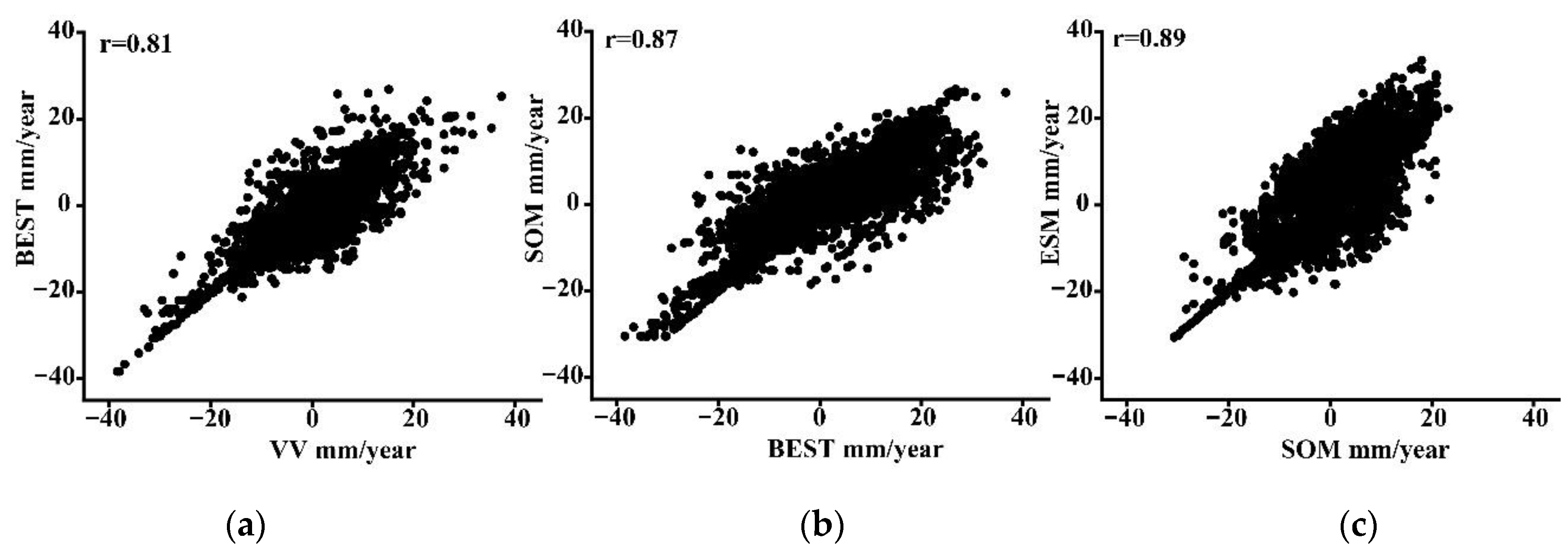
- Correlation coefficients between VV and BEST, BEST and SOM, and SOM and ESM were 0.81, 0.87, and 0.89, respectively, indicating that the calculated deformation rates of the tailings reservoir had a certain reliability. In addition, with the increase in point selection density, SOM and ESM methods effectively reduced the standard deviation of deformation rate, which improved the accuracy of subsequent phase unwrapping.
- (4)
- Although the BEST method increased the point selection density, it only selected the optimal phase on the basis of existing polarization channel data and did not fully use the polarization information. By contrast, the SOM and ESM methods more fully used polarization information to improve the phase quality of pixels by searching the polarization space. However, those two methods needed to use an exhaustive method to search the polarization space, and as a result, the computational efficiency was low. By increasing the step length of the ESPO method, the search times of the whole polarization space will be reduced, and the computational efficiency will be effectively improved, but this means that the monitoring density will decrease. In addition, using parallel computing, calling GPU, or using more efficient CMD methods will effectively solve the problem of low computational efficiency. Therefore, how to improve the computational efficiency of SOM and ESM will be the focus of future research.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adiansyah, J.S.; Rosano, M.; Vink, S.; Keir, G. A framework for a sustainable approach to mine tailings management: Disposal strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naeini, M.; Akhtarpour, A. A numerical investigation on hydro-mechanical behaviour of a high centreline tailings dam. S. Afr. Inst. Civil Eng. 2018, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, C.C.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhong, K.B.; Shi, G.L. Review and summary of handling process of Xiangfen ‘9.8′ extremely major tailings dam break. China Emerg. Manag. 2011, 10, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.G. Study on Overtopping Dam Failure Mechanism and Protection Measures of Tailings Reservoir. Master’s Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.Y.; Ge, L.L.; Ng, A.H.M.; Zhu, Q.G.Z.; Horgan, F.G.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment for tailings dams in Brumadinho of Brazil using InSAR time series approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.D.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Du, S. Using temporarily coherent point interferometric synthetic aperture radar for land subsidence monitoring in a mining region of western China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacone, J.P.; Lato, M.; Troncoso, J.; Perissin, D. InSAR monitoring of active, inactive and abandoned tailings facilities. In Proceedings of the 5th International Seminar on Tailings Management, Santiago, Chile, 11 July 2018; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gamaf, F.; Mura, J.C.; Paradella, W.R.; De Oliveira, C.G. Deformations prior to the Brumadinho dam collapse revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR data using SBAS and PSI techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, P.; Antonielli, B.; Sciortino, A.; Scancella, S.; Bozzano, F. Tracking deformation processes at the Legnica Glogow Copper district (Poland) by Satellite InSAR—II: Żelazny Most Tailings Dam. Land 2021, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.D.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, Y.Z.; Yang, H.L. Surface subsidence monitoring with an improved distributed scatterer interferometric SAR time series method in a filling mining area. Geocarto Int. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.D.; Lopez, J.M.; Vicente, F. A contribution of polarimetry to satellite differential SAR interferometry: Increasing the number of pixel candidates. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglésias, R.; Monells, D.; Fàbregas, X.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Aguasca, A.; Lopez-Martinez, C. Phase quality optimization in polarimetric differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Zoej, M.J.V.; Hooper, A.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. A new polarimetric persistent scatterer interferometry method using temporal coherence optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6547–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullissa, A.; Perissin, D.; Tolpekin, V.; Stein, A. Polarimetry-based distributed scatterer processing method for PSI applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3371–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.X.; Feng, H.; Yan, S.Y.; Fan, H.D.; Xu, D.B.; Wang, Y.J. Polarimetric persistent scatterer interferometry for ground deformation monitoring with VV-VH Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.J.; Cheng, Z.Z.; Yang, R.; Zhou, G.H. Geochemical survery and assessment of tailings of the Gejiu tin-polymetallic mining area, Yunnan Province. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. 2015, 42, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Zhou, Z.H.; Feng, C.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, C.G.; Peng, H.J.; Yu, M. A preliminary study of the Triassic large-scale mineralization in China and its geodynamic setting. Geol. China 2012, 39, 1437–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Li, S.M.; Guo, R.; Yuan, L.W. Study on deformation evolution of sand-covered tailings dam based on time series InSAR. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 16, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Ou, M.X.; Dai, Z.F.; Wang, X.F. Experimental analysis of leaching consolidation on tailings sand. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. 2020, 31, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, P.Y.; Wang, W.H. Effect of heavy metal compounds on the micro-aggregate stability in Kafang tailing pond. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2020, 38, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F. Sedimentary Consoildation Characteristices of Tailings in Kafang Tailings Reservoir and Stability of Tailings Dam. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.L.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast statistically homogeneous pixel selection for covariance matrix estimation for multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yong, B.; Tian, X.; Malhotra, R.; Hu, R.; Li, Z.W.; Yu, Z.B.; Zhang, X.X. The potential of more accurate InSAR covariance matrix estimation for land cover mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Andrea, M.G. Distributed scatterer interferometry with the refinement of spatiotemporal coherence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostinski, A.; Boerner, W. On foundations of radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–398. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing; Oxford University: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Wideband radar inversion studies using the entropy-alpha decomposition. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1997, 37, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Sato, M. PolInSAR complex coherence estimation based on covariance matrix similarity test. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 4699–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipia, L.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Duque, S.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Marturia, J. Polarimetric differential SAR interferometry: First results with ground-based measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 16, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Multibaseline polarimetric SAR interferometry coherence optimization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azadnejad, S.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Perissin, D. Evaluation of polarimetric capabilities of dual polarized Sentinel-1 and TerraSAR-X data to improve the PSInSAR algorithm using amplitude dispersion index optimization. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 2, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagues, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.; Fortuny, J.; Fabregas, X.; Broquetas, A.; Sieber, A.J. Indoor experiments on polarimetric SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processinginterferometric data-stacks SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap methods: Another look at the jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jordi, J.J. Coherency matrix decomposition-based polarimetric persistent scatterer interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7819–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
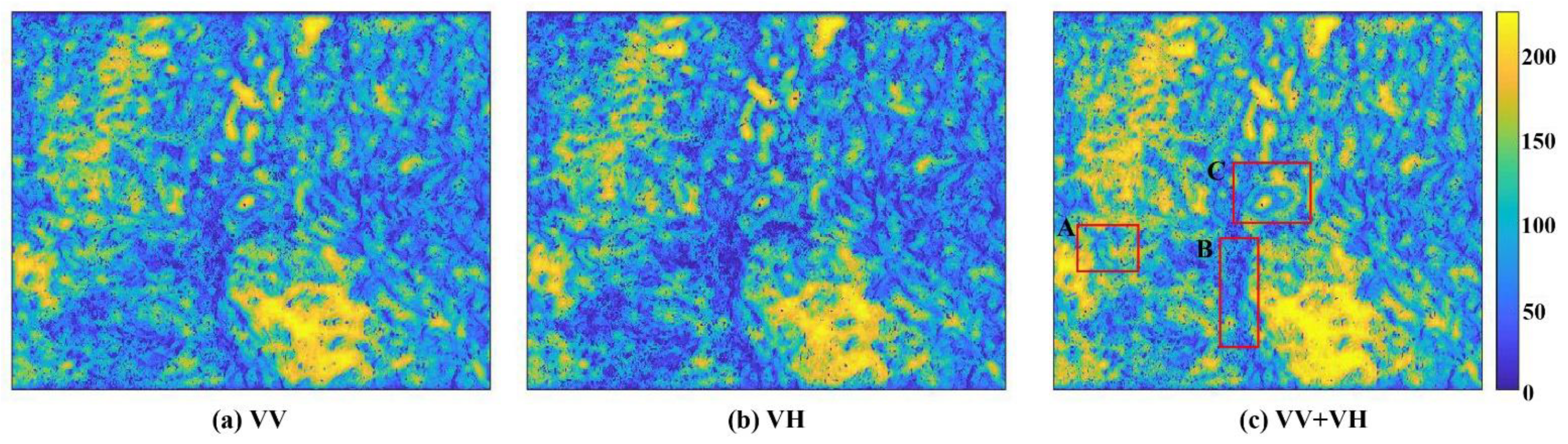

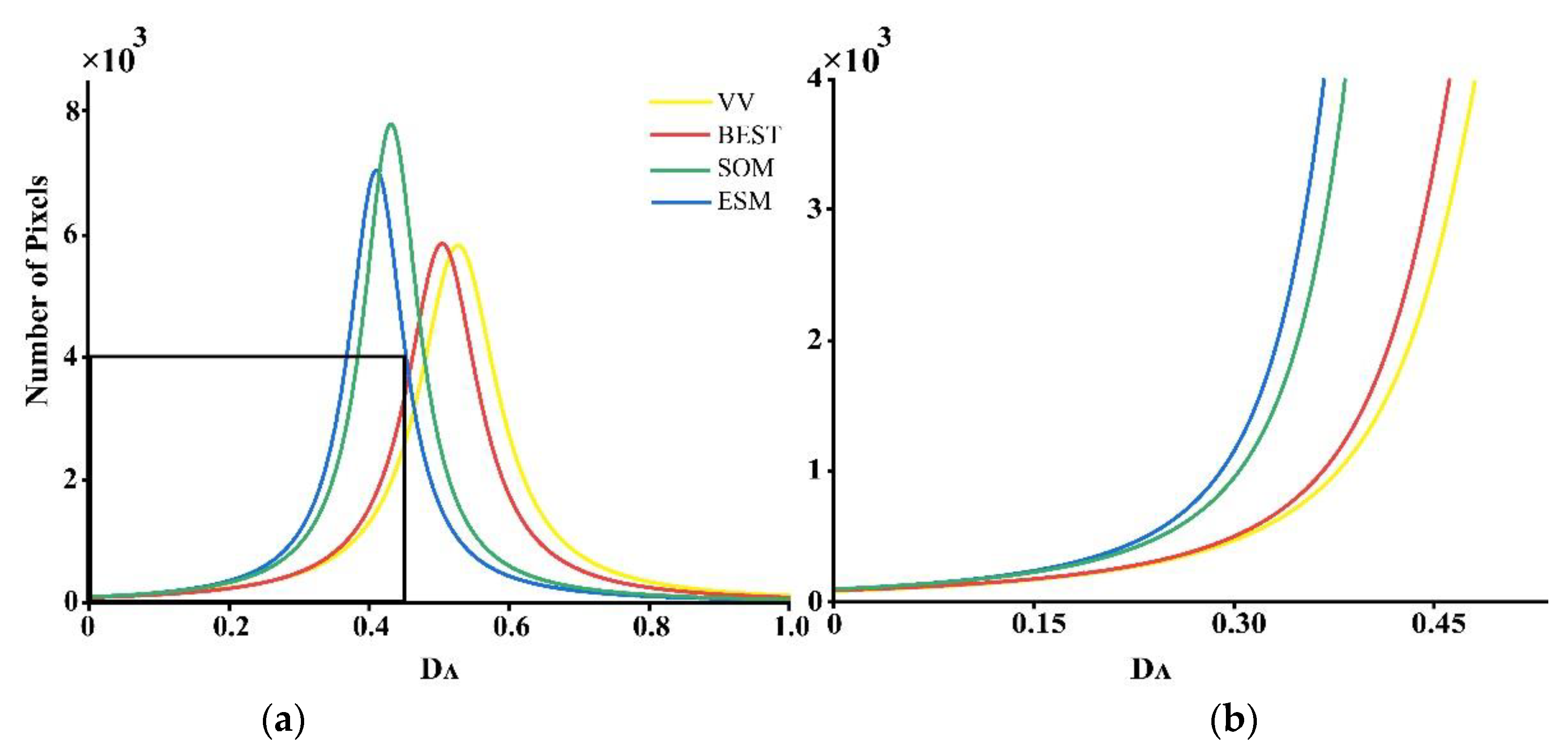

| Polarization | Mean Value | SHP > 20 | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VH | 74 | 225,142 | 3.86 |
| VV | 68 | 215,618 | 8.45 |
| VH + VV | 89 | 233,831 |
| Method | Time (h) | Improvement | Test Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| BEST | 1.5 | 83% (17%) | Kafang (500 × 2500) |
| SOM | 28 | 266% (84%) | |
| ESM | 37 | 476% (104%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Zheng, X.; Fan, H.; Tian, Z. Deformation Monitoring of Tailings Reservoir Based on Polarimetric Time Series InSAR: Example of Kafang Tailings Reservoir, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153655
Wu H, Zheng X, Fan H, Tian Z. Deformation Monitoring of Tailings Reservoir Based on Polarimetric Time Series InSAR: Example of Kafang Tailings Reservoir, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153655
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hao, Xiangyuan Zheng, Hongdong Fan, and Zeming Tian. 2022. "Deformation Monitoring of Tailings Reservoir Based on Polarimetric Time Series InSAR: Example of Kafang Tailings Reservoir, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153655
APA StyleWu, H., Zheng, X., Fan, H., & Tian, Z. (2022). Deformation Monitoring of Tailings Reservoir Based on Polarimetric Time Series InSAR: Example of Kafang Tailings Reservoir, China. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153655