Analysis of Change in Maize Plantation Distribution and Its Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
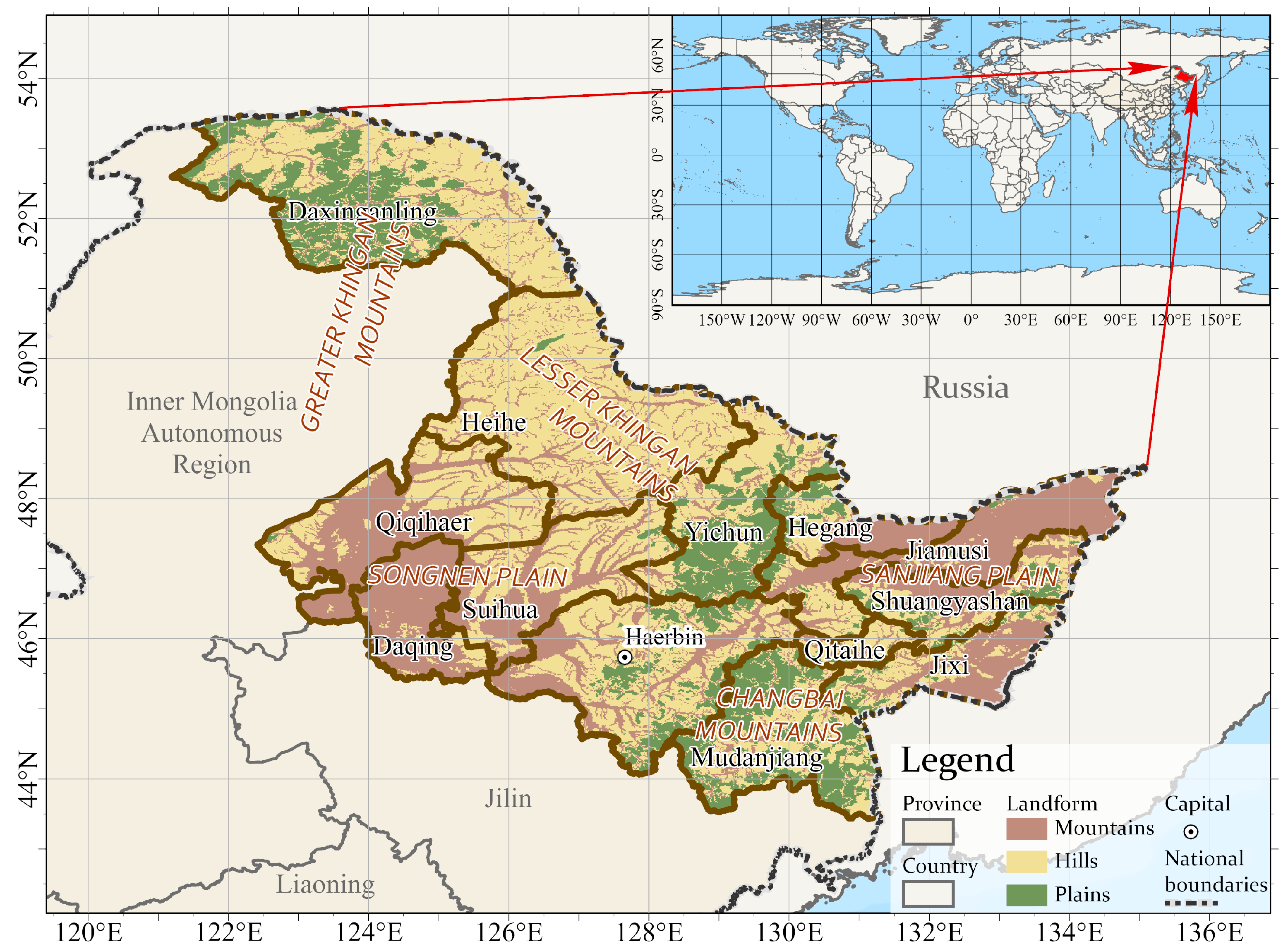
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methodology
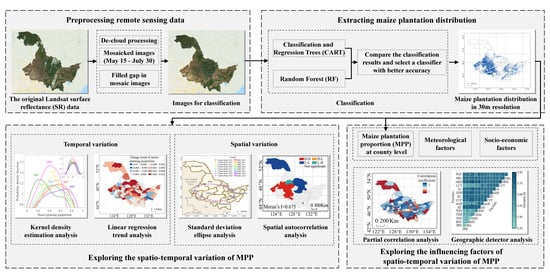
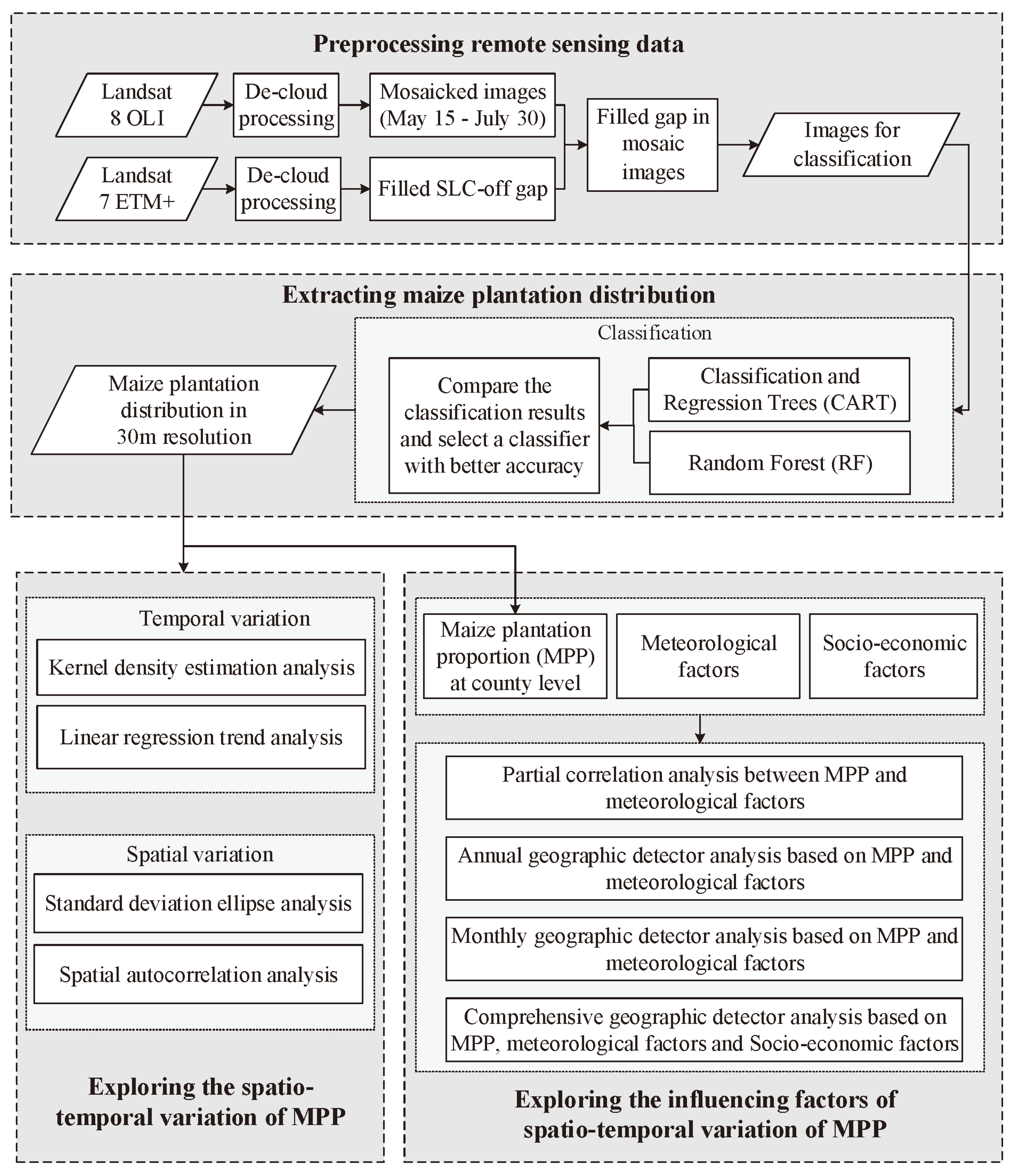
3.1. Preprocessing Remote Sensing Data
3.2. Extracting the Maize Planting Distribution
3.3. Exploring the Spatio-Temporal Variation in Maize Plantation Distribution
3.4. Exploring the Influencing Factors of Maize Plantation Distribution Spatio-Temporal Variation
- Calculate the q statistic values of two factors and : and .
- Overlay the two layers and to obtain the composite layer .
- Calculate the q statistic values of composite layer :
- Compare , and
4. Results
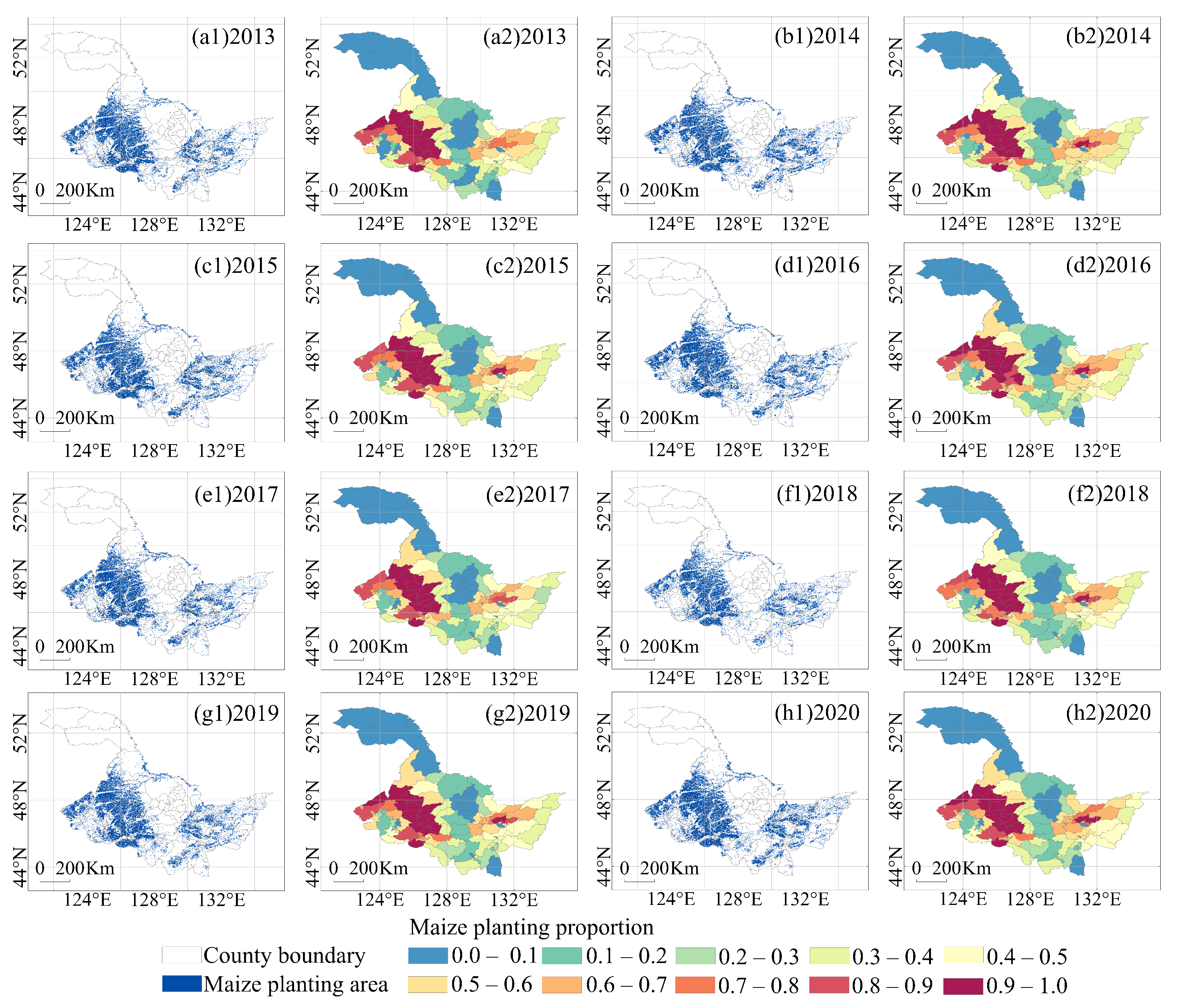
4.1. Maize Plantation Distribution
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Maize Plantation Distribution
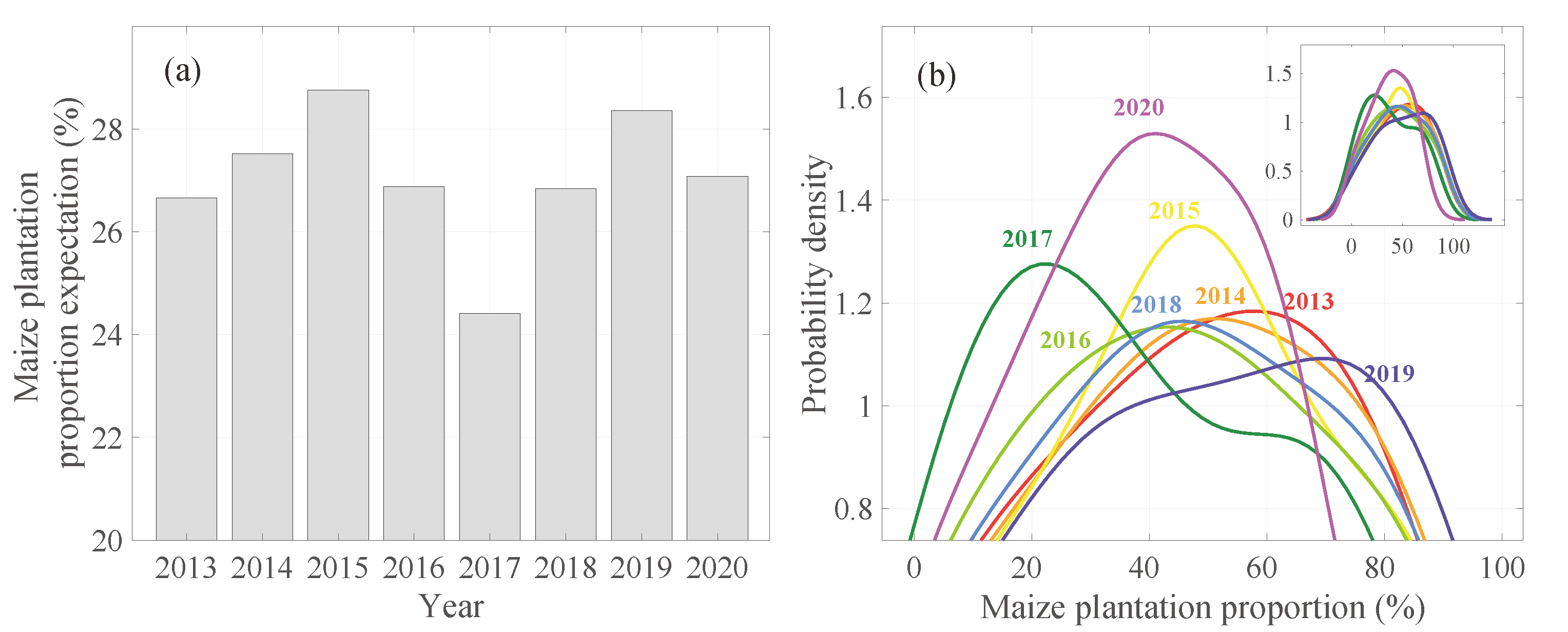
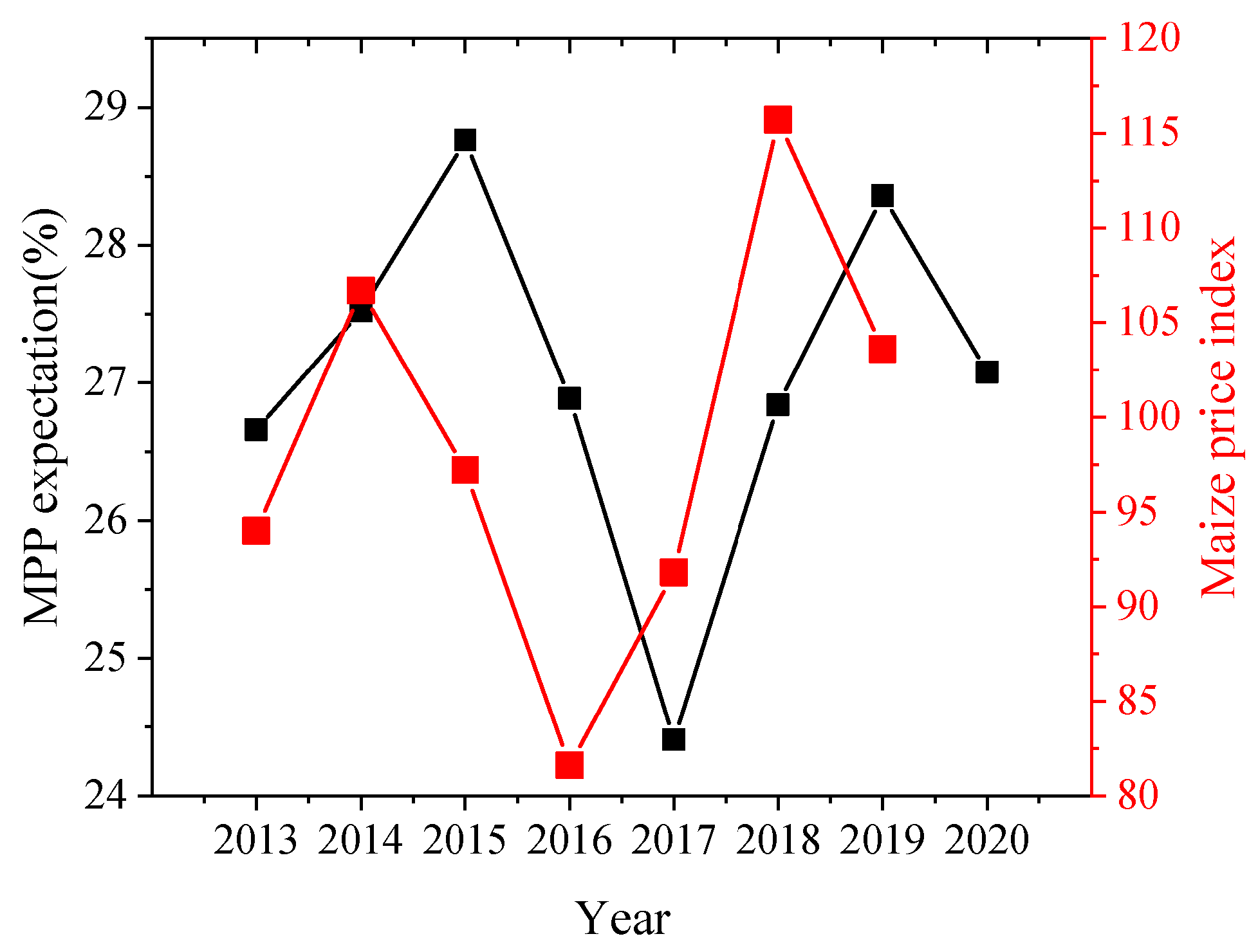
4.2.1. Temporal Variation of Maize Plantation
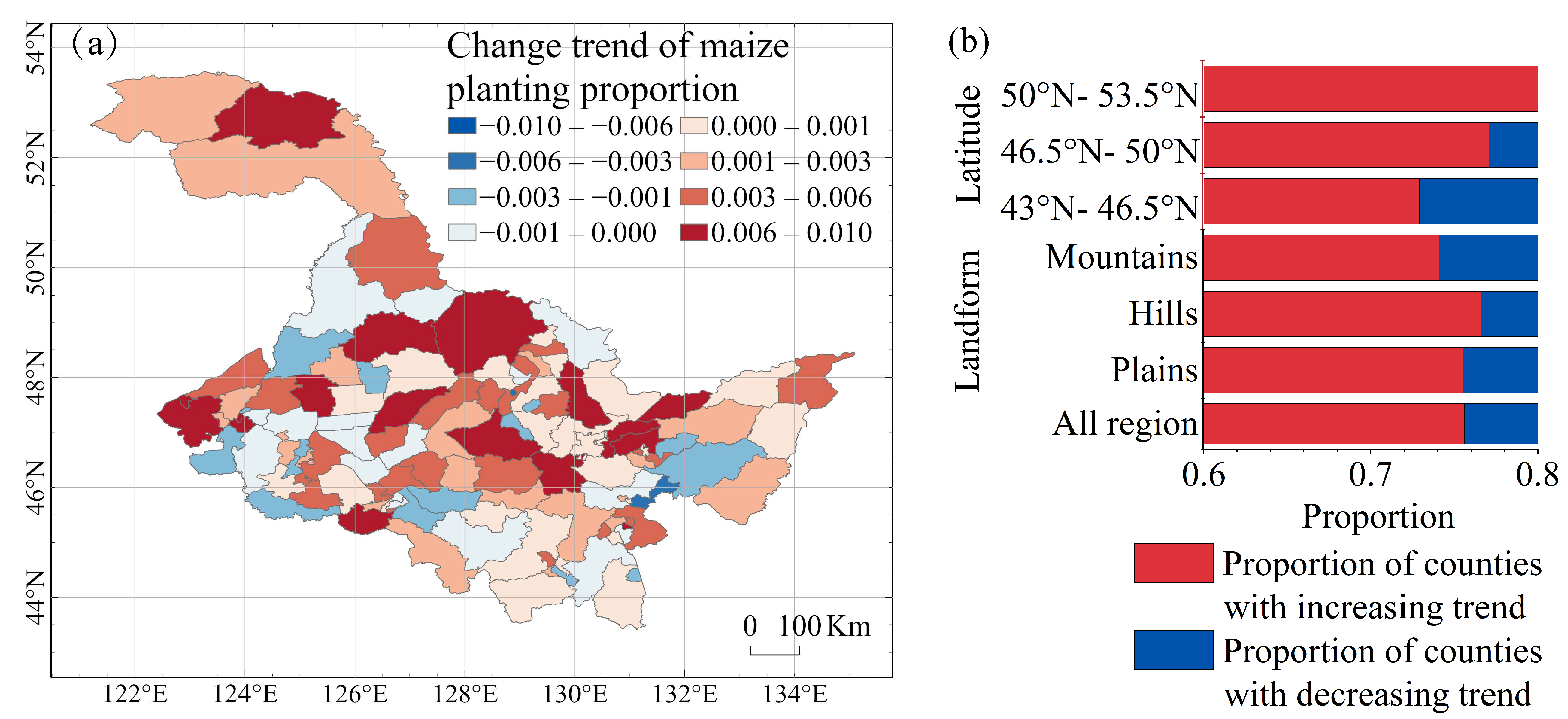
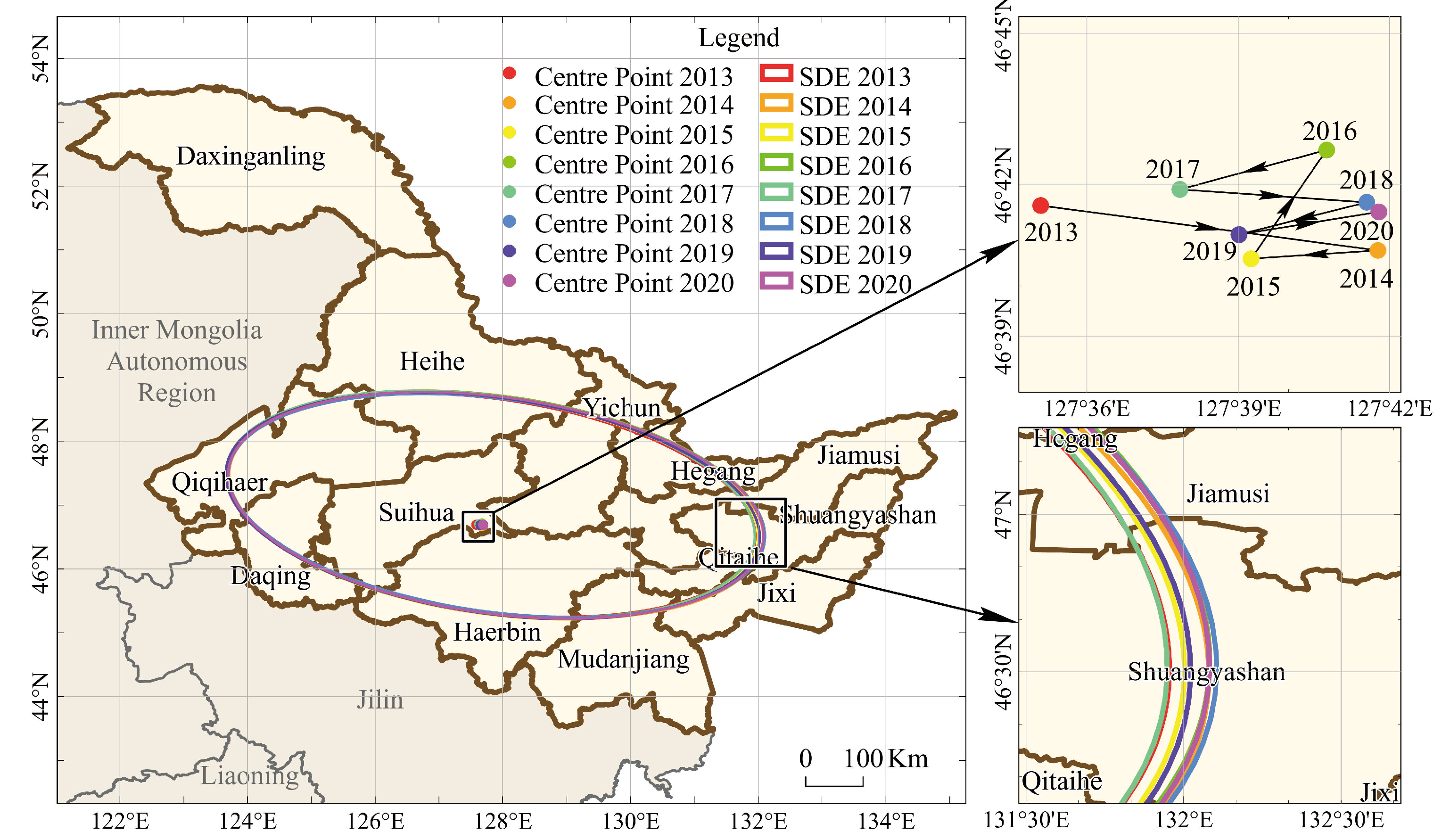
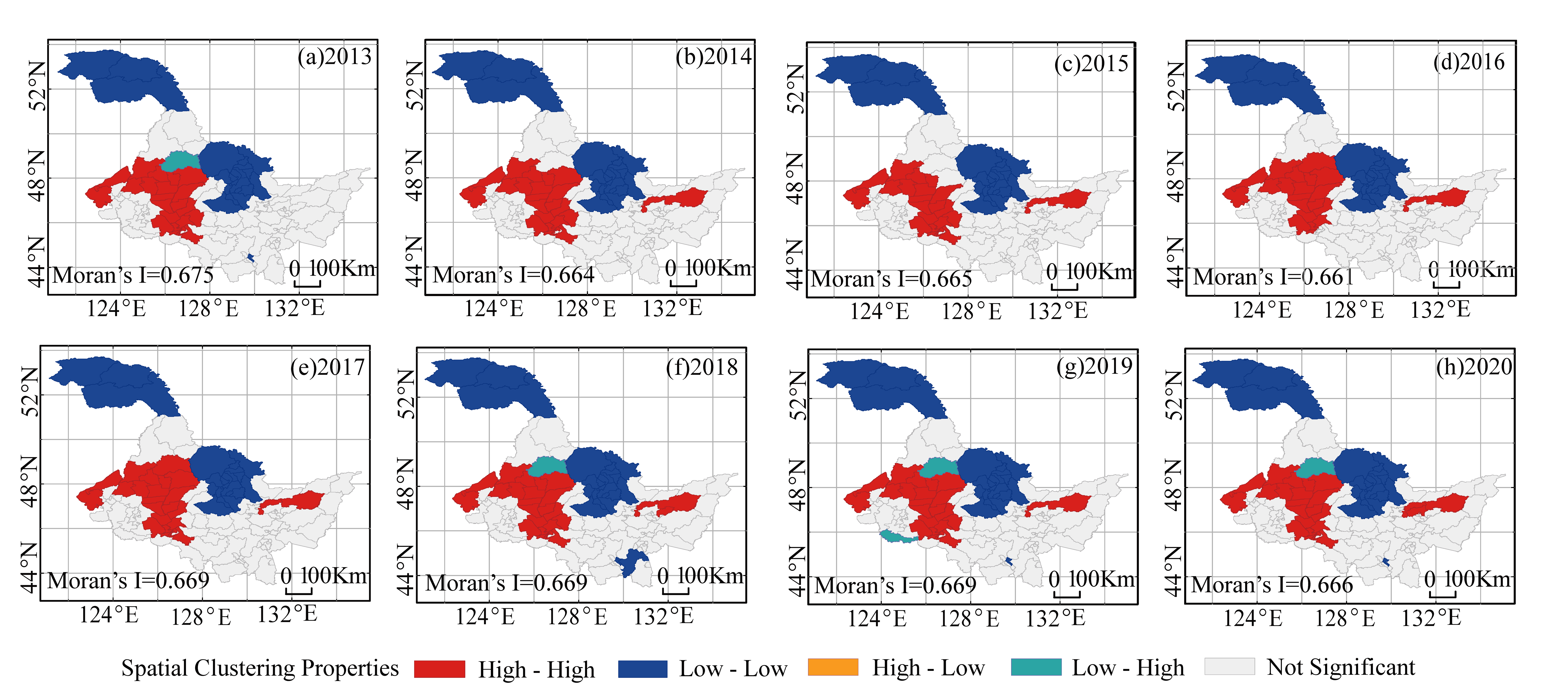
4.2.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Changes in Maize Plantation
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Influencing Factors of Maize Plantation Distribution
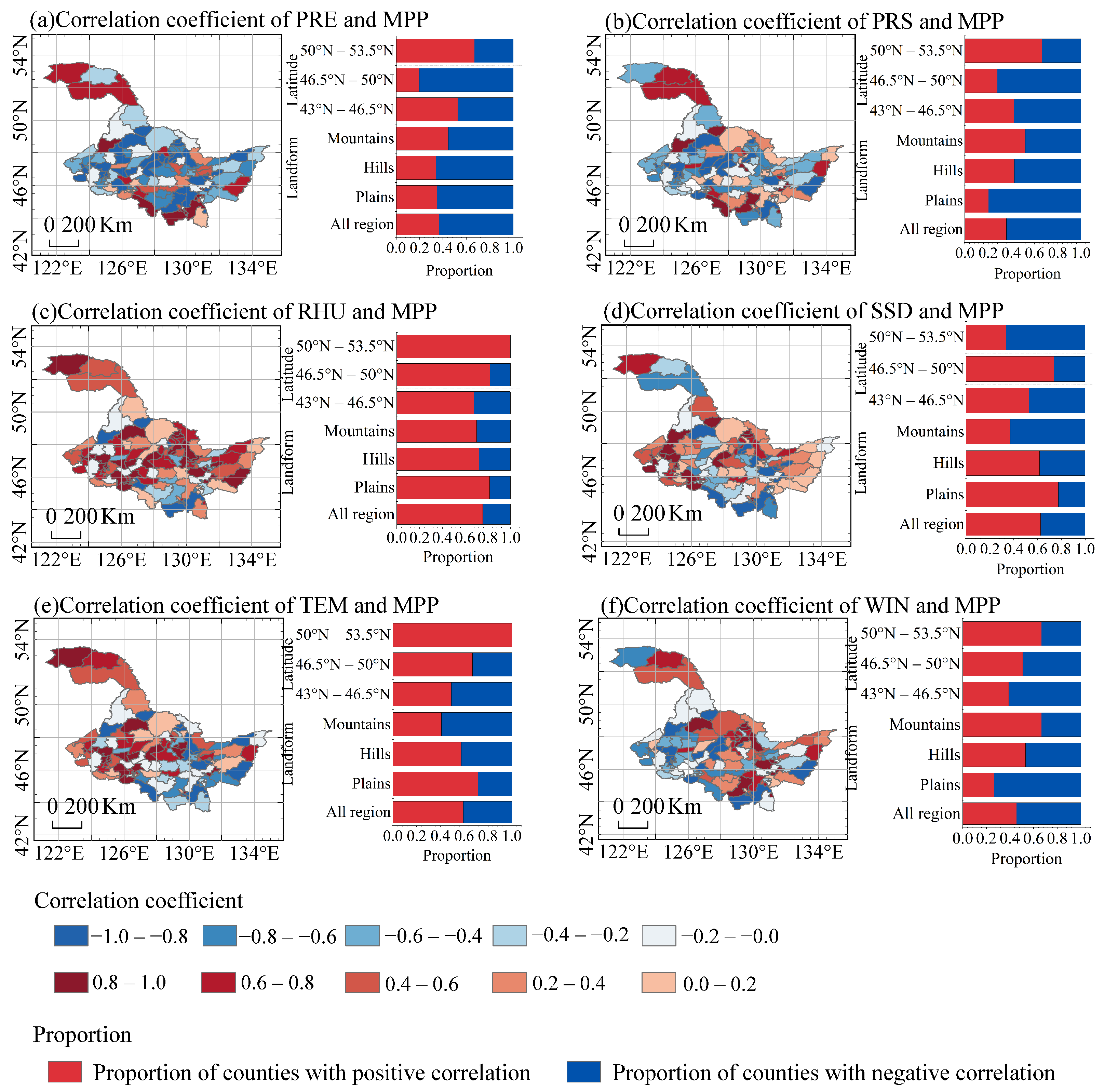
4.3.1. Results of the Partial Correlation Analysis
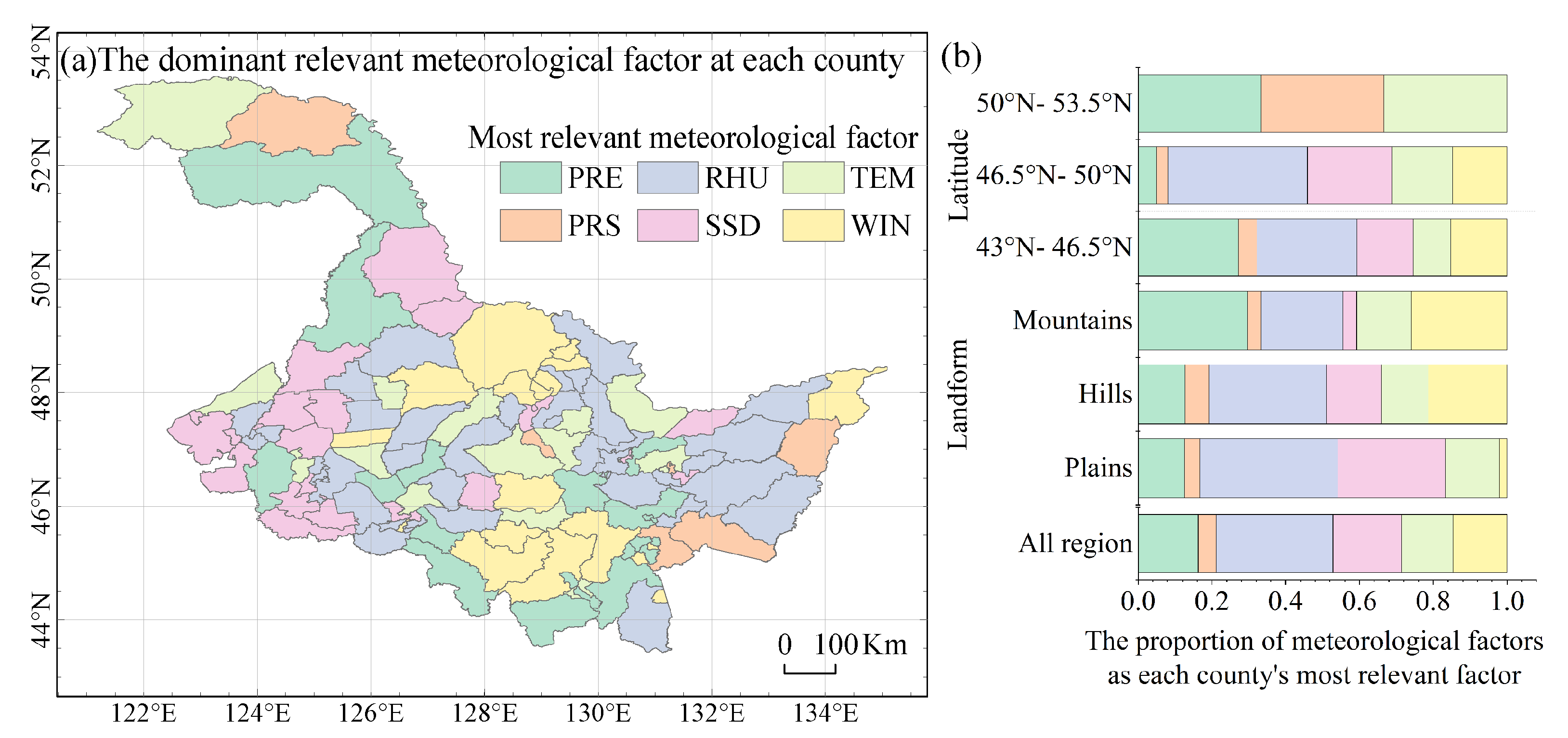
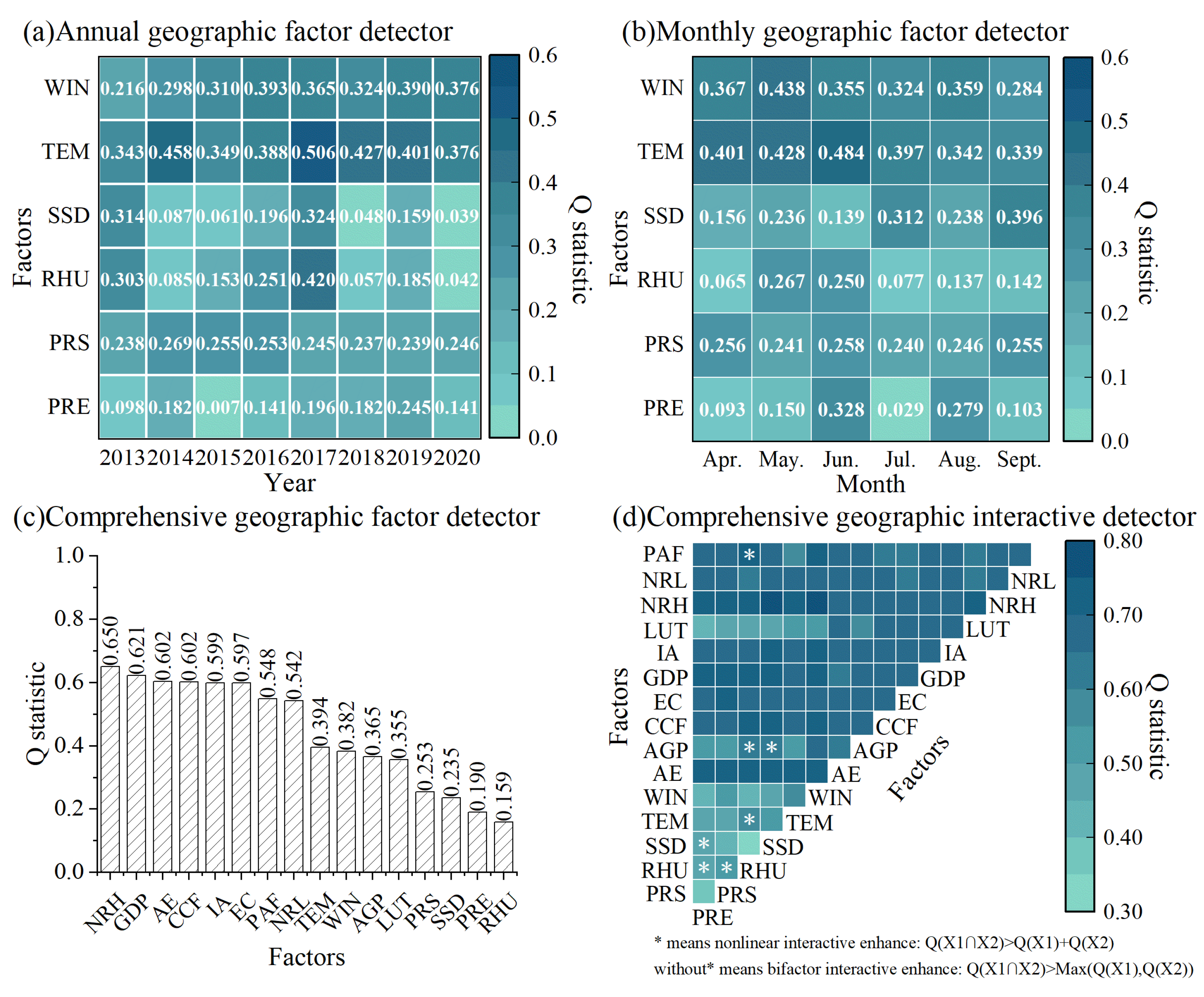
4.3.2. Results of Geographic Detector Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Agriculture Employees |
| AGP | Agriculture Gross Product |
| CART | Classification And Regression Tree |
| CCF | Consumption of Chemical Fertilizers |
| CFMASK | C Function of Mask |
| CNLULC | Chinese Land Use And Land Cover |
| EC | Electricity Consumed in rural areas |
| IA | Irrigated Area |
| GDP | Gross Regional Product |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation |
| LUT | Land Cover Transformation |
| MPP | Maize Plantation Proportion |
| NRH | Number of Rural Households |
| NRL | Number of Rural Laborers |
| PAF | Percentage of Area with Flood prevention measures |
| Probability Density Function | |
| PRE | Precipitation |
| PRS | Atmospheric Pressure |
| QA | Quality Assessment |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RHU | Relative Humidity |
| SDE | Standard Ellipse analysis |
| SH | Spatial Heterogeneity |
| SR | Surface Reflectance |
| SSD | Sunshine Duration |
| TEM | Temperature |
| WIN | Wind Speed |
Appendix A
| Year | smileCart | smileRandomForest | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | Kappa | Overall Accuracy | Kappa | |
| 2013 | 0.9724 | 0.9436 | 0.9628 | 0.9107 |
| 2014 | 0.9444 | 0.8849 | 0.9328 | 0.9045 |
| 2015 | 0.9882 | 0.9761 | 0.9784 | 0.9478 |
| 2016 | 0.9592 | 0.9183 | 0.9652 | 0.9246 |
| 2017 | 0.9870 | 0.9739 | 0.9723 | 0.9548 |
| 2018 | 0.9783 | 0.9563 | 0.9457 | 0.9369 |
| 2019 | 0.9643 | 0.9245 | 0.9367 | 0.8974 |
| 2020 | 0.9800 | 0.9584 | 0.9124 | 0.8753 |
References
- Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; You, L. Spatio-temporal changes in Chinese crop patterns over the past three decades. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Chen, Y.; Veldkamp, T.A. Spatial explorations of land use change and grain production in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Boote, K.J.; Kimball, B.A.; Ziska, L.H.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Ort, D.; Thomson, A.M.; Wolfe, D. Climate Impacts on Agriculture: Implications for Crop Production. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, D.K.; Gerber, J.S.; MacDonald, G.K.; West, P.C. Climate variation explains a third of global crop yield variability. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, L.; Wood, S.; Wood-Sichra, U. Generating plausible crop distribution maps for Sub-Saharan Africa using a spatially disaggregated data fusion and optimization approach. Agric. Syst. 2009, 99, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Wood, S. Assessing the spatial distribution of crop areas using a cross-entropy method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2005, 7, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, X.; Hou, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K. A Spatialization Method for Grain Yield Statistical Data: A Study on Winter Wheat of Shandong Province, China. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiao, G.; Wen, P.; Zhang, J.; Hou, C. Mapping Tobacco Fields Using UAV RGB Images. Sensors 2019, 19, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ren, T.; Liu, D.; Ma, Z.; Tong, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Identification of Seed Maize Fields With High Spatial Resolution and Multiple Spectral Remote Sensing Using Random Forest Classifier. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, P.; Di, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L. Transfer Learning for Crop classification with Cropland Data Layer data (CDL) as training samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Zurita-Milla, R. An evaluation of Guided Regularized Random Forest for classification and regression tasks in remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 88, 102051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Gumma, M.K.; Teluguntla, P.; Poehnelt, J.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Thau, D. Automated cropland mapping of continental Africa using Google Earth Engine cloud computing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 126, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Dai, S.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Effects of climate change on suitable rice cropping areas, cropping systems and crop water requirements in southern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, E. The effects of past climate change on the northern limits of maize planting in Northeast China. Clim. Chang. 2013, 117, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.; Shah, M.; Tubiello, F.N.; van Velhuizen, H. Socio-economic and climate change impacts on agriculture: An integrated assessment, 1990–2080. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 2067–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanfani, R.; Brasili, C. Regional differences in Chinese agriculture: Results from the 1997 First National Agricultural Census. J. Peasant. Stud. 2003, 30, 18–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Hou, P.; Lobell, D.B.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. The benefits of recent warming for maize production in high latitude China. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, R.; Hou, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Ming, B.; Long, H.; Liang, S. Phenological responses of maize to changes in environment when grown at different latitudes in China. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 144, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Chaoying, H. Climate Change and Its Impact on Water Resources in North China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 718–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Hughes, M.J.; Laue, B. Cloud detection algorithm comparison and validation for operational Landsat data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, P. Bilinear interpolation of digital images. Ultramicroscopy 1981, 6, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Micijevic, E.; Chander, G. SLC-Off Gap-Filled Products Gap-Fill Algorithm Methodology Phase 2 Gap-Fill Algorithm; US Geological Survey Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Gao, F.; Jin, S. A simple and effective method for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Wadsworth and Brooks: Belmont, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblatt, M. Remarks on Some Nonparametric Estimates of a Density Function. Ann. Math. Stat. 1956, 27, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On Estimation of a Probability Density Function and Mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Boyle, M.; Hollingsworth, D. A comparison of methods for trend estimation. Appl. Econ. Lett. 1999, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuill, R.S. The Standard Deviational Ellipse; An Updated Tool for Spatial Description. Geogr. Ann. Ser. Hum. Geogr. 1971, 53, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Yi, S.; Liu, J.; Su, X.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y. The Link between Landscape Characteristics and Soil Losses Rates over a Range of Spatiotemporal Scales: Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Li, T.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X. Spatial distribution exploration and driving factor identification for soil salinisation based on geodetector models in coastal area. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 156, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, F. The Possible Effect of Climate Warming on Northern Limits of Cropping System and Crop Yield in China. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Coffel, E.; Winter, J.; Ray, D.; Zscheischler, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Horton, R. Stronger temperature–moisture couplings exacerbate the impact of climate warming on global crop yields. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Ruane, A.C.; Müller, C.; Arneth, A.; Boote, K.J.; Folberth, C.; Glotter, M.; Khabarov, N.; et al. Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3268–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, T.; Du, G.; Dong, J.; Kuang, W.; Maeyer, P.D.; Kurban, A. Divergent changes in cropping patterns and their effects on grain production under different agro-ecosystems over high latitudes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, N.; Liu, W.; Hou, P.; Ming, B.; Xie, R.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Effect of latitude on maize kernel weight and grain yield across China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Gao, X.; Hao, Z.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Hao, F. Farmland shift due to climate warming and impacts on temporal-spatial distributions of water resources in a middle-high latitude agricultural watershed. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Chang, Z. Effects of climate change on agricultural water resource carrying capacity in a high-latitude basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Huang, Y.; Tan, M. Modelling maize phenology, biomass growth and yield under contrasting temperature conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 250–251, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Gitz, D.C.; Sicher, R.C.; Baker, J.T. Temperature dependence of growth, development, and photosynthesis in maize under elevated CO2. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, H.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S. Fighting global food price rises in the developing world: The response of China and its effect on domestic and world markets. Agric. Econ. 2008, 39, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mose, L.O.; Burger, K.; Kuvyenhoven, A. Aggregate supply response to price incentives: The case of smallholder maize production in Kenya. Afr. Crop. Sci. Conf. Proc. 2007, 8, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Lardy, N.R. Prospects and Some Policy Problems of Agricultural Development in China. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1986, 68, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Rural land system reforms in China: History, issues, measures and prospects. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C. Analysis of Change in Maize Plantation Distribution and Its Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153590
Guo R, Zhu X, Zhang C, Cheng C. Analysis of Change in Maize Plantation Distribution and Its Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153590
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Rui, Xiufang Zhu, Ce Zhang, and Changxiu Cheng. 2022. "Analysis of Change in Maize Plantation Distribution and Its Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153590
APA StyleGuo, R., Zhu, X., Zhang, C., & Cheng, C. (2022). Analysis of Change in Maize Plantation Distribution and Its Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province, China. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153590