Insights into Variations and Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
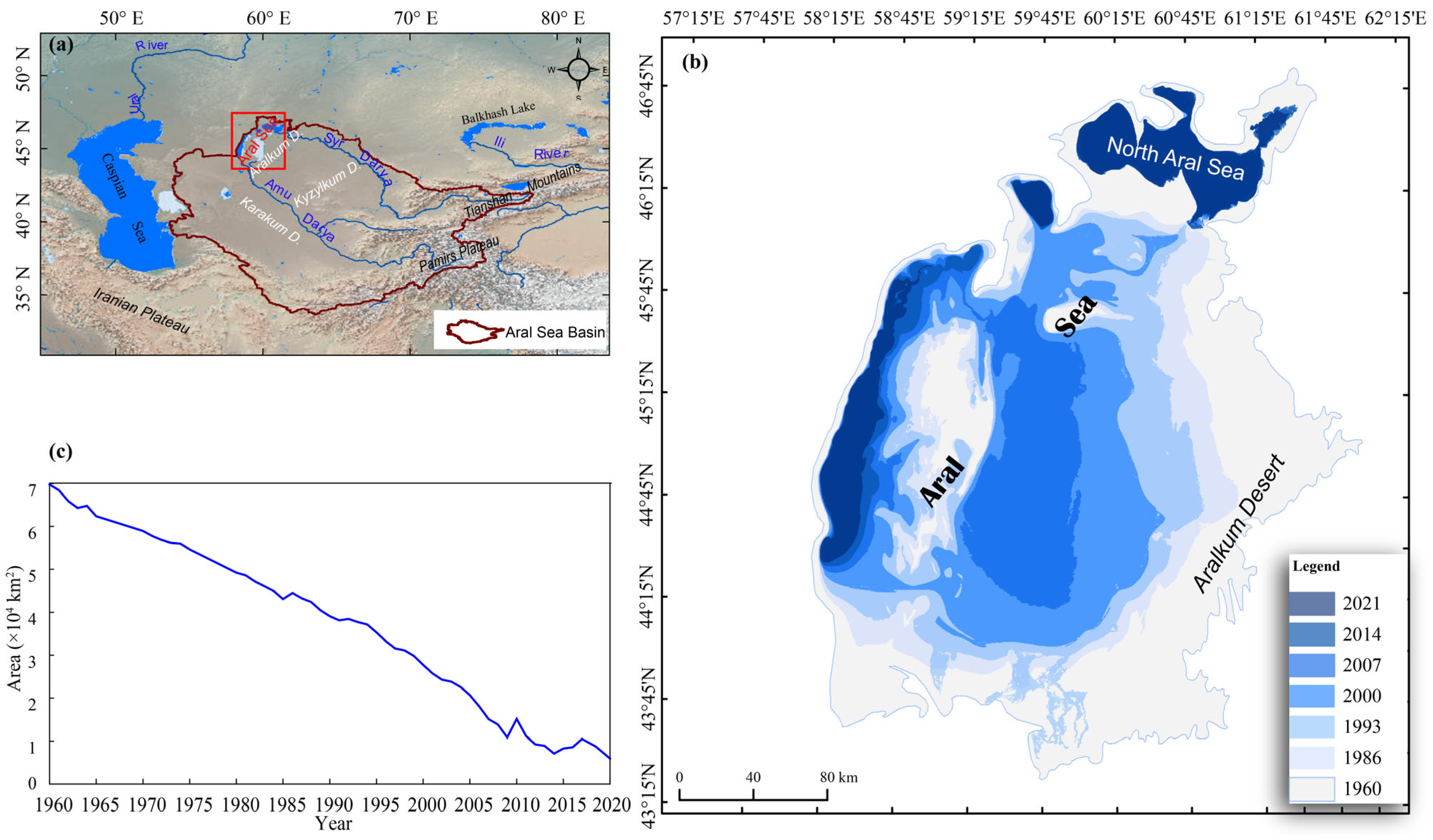
2.1. Regional Environments
2.2. Data and Analytical Methods
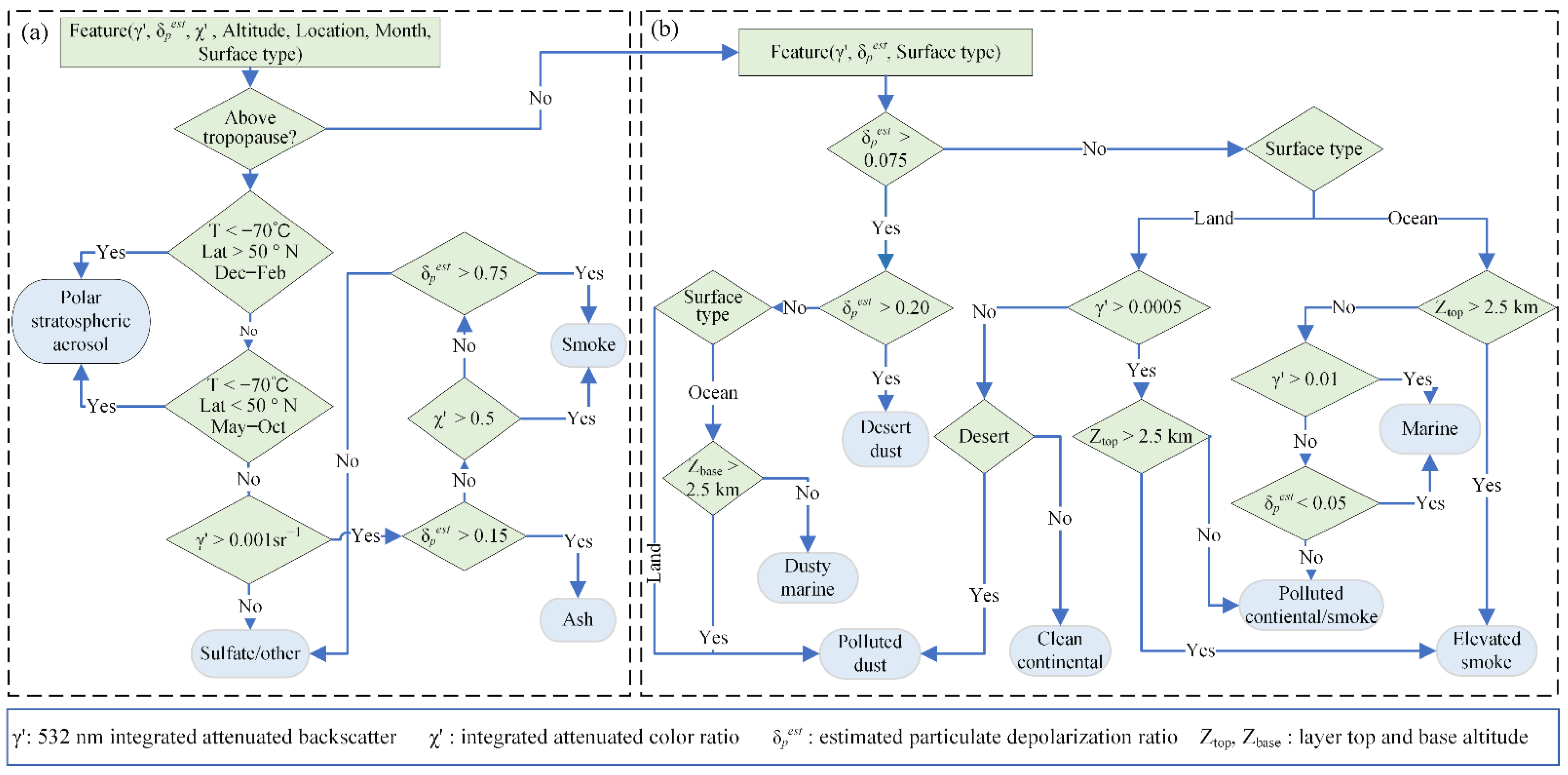
2.2.1. Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Satellite Data
2.2.2. Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) Model
3. Results
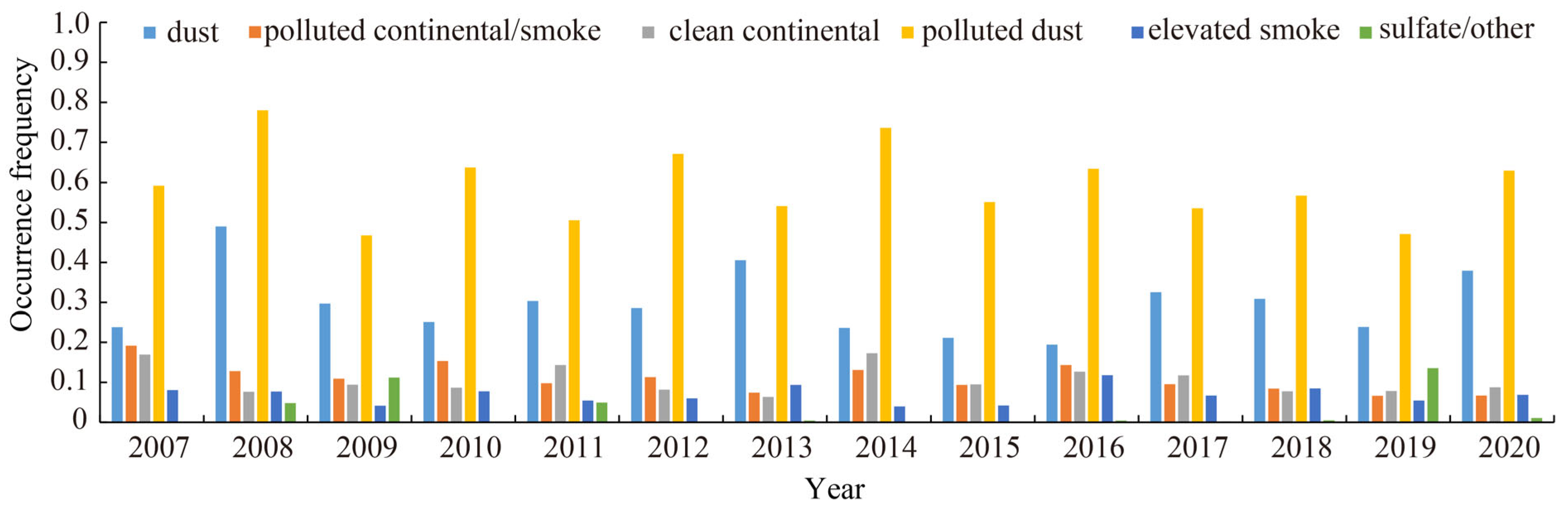
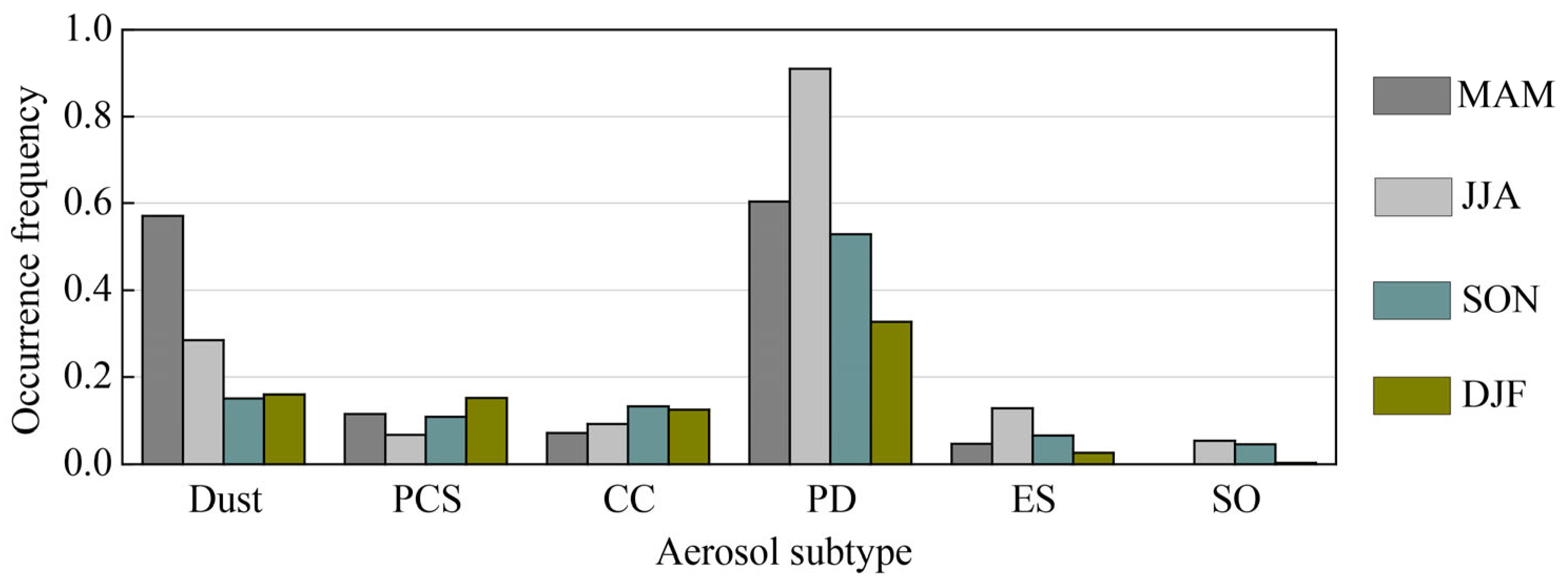
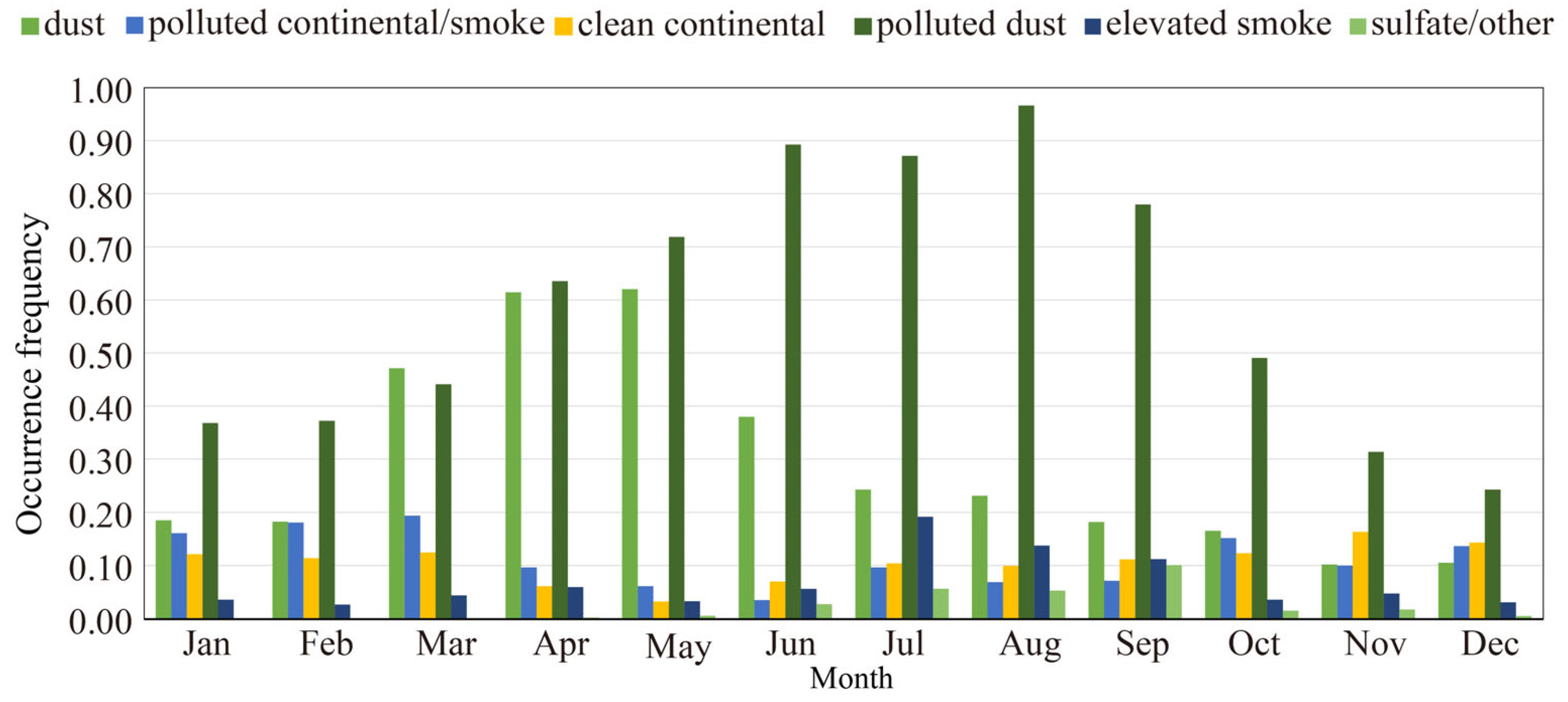
3.1. Aerosol Subtypes in the Atmosphere over the Aral Sea Basin
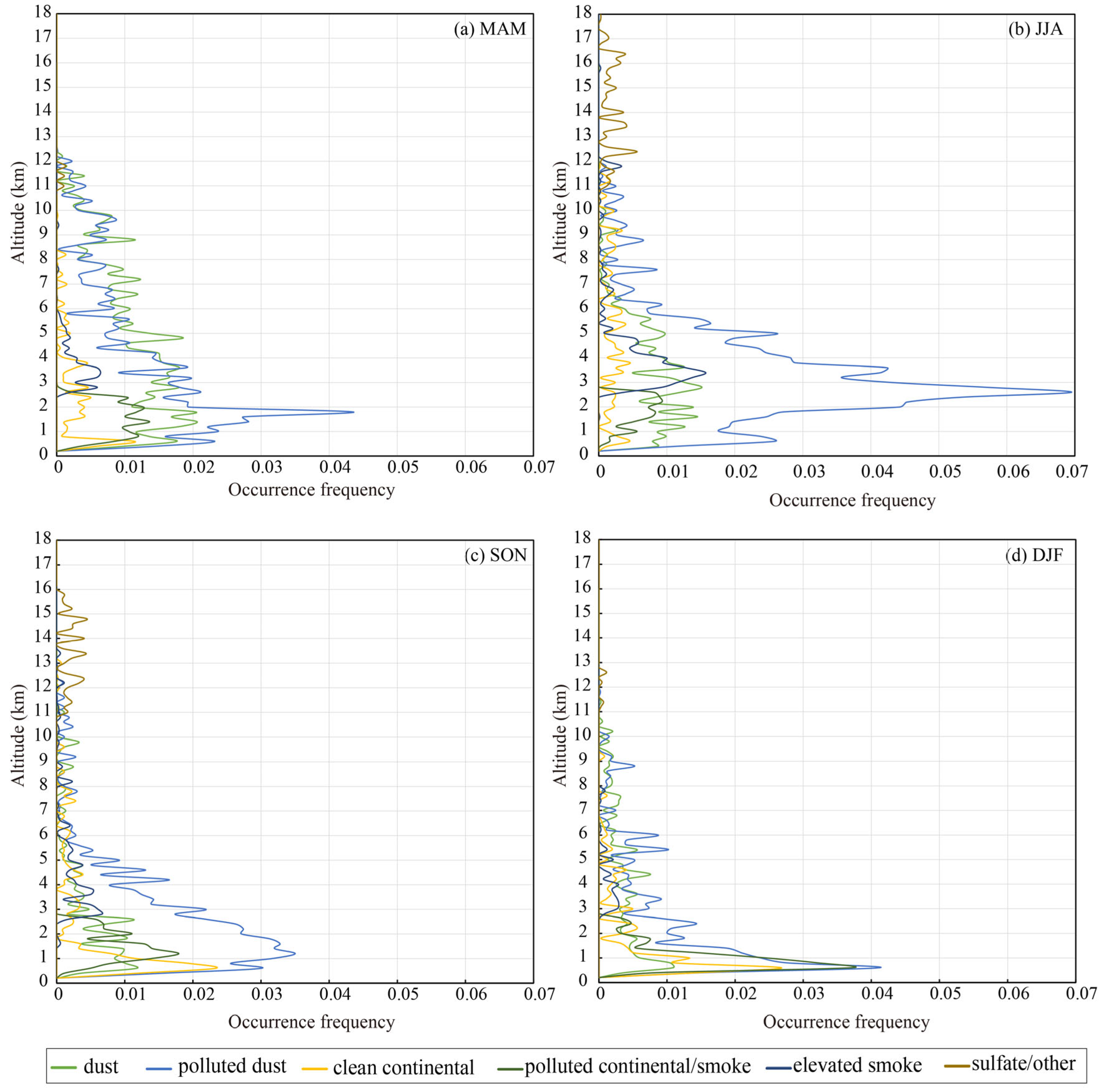
3.2. Features of Atmospheric Aerosol Subtypes over the Aral Sea Basin
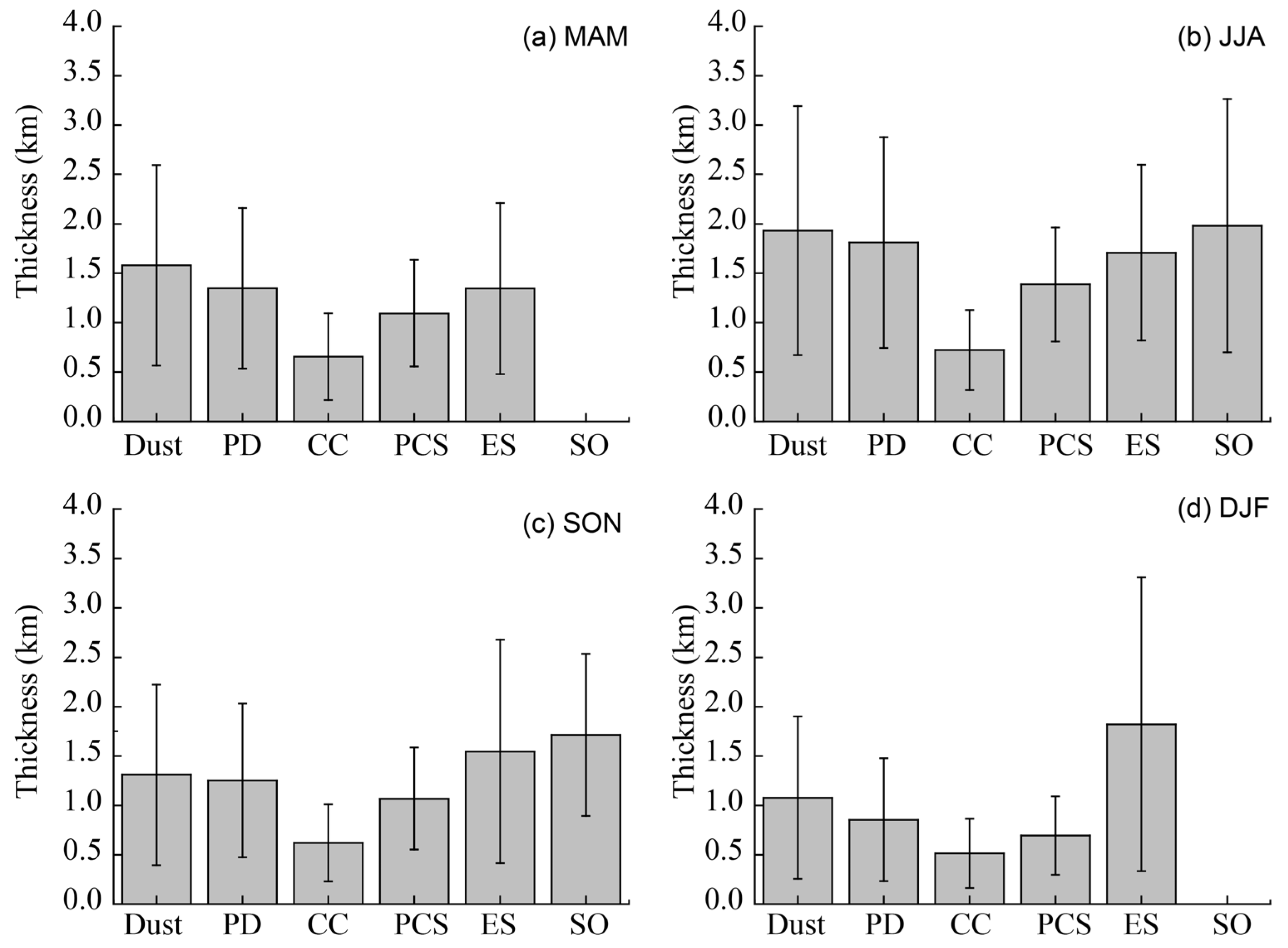
3.3. Altitudes of the Atmospheric Aerosol Layers over the Aral Sea Basin
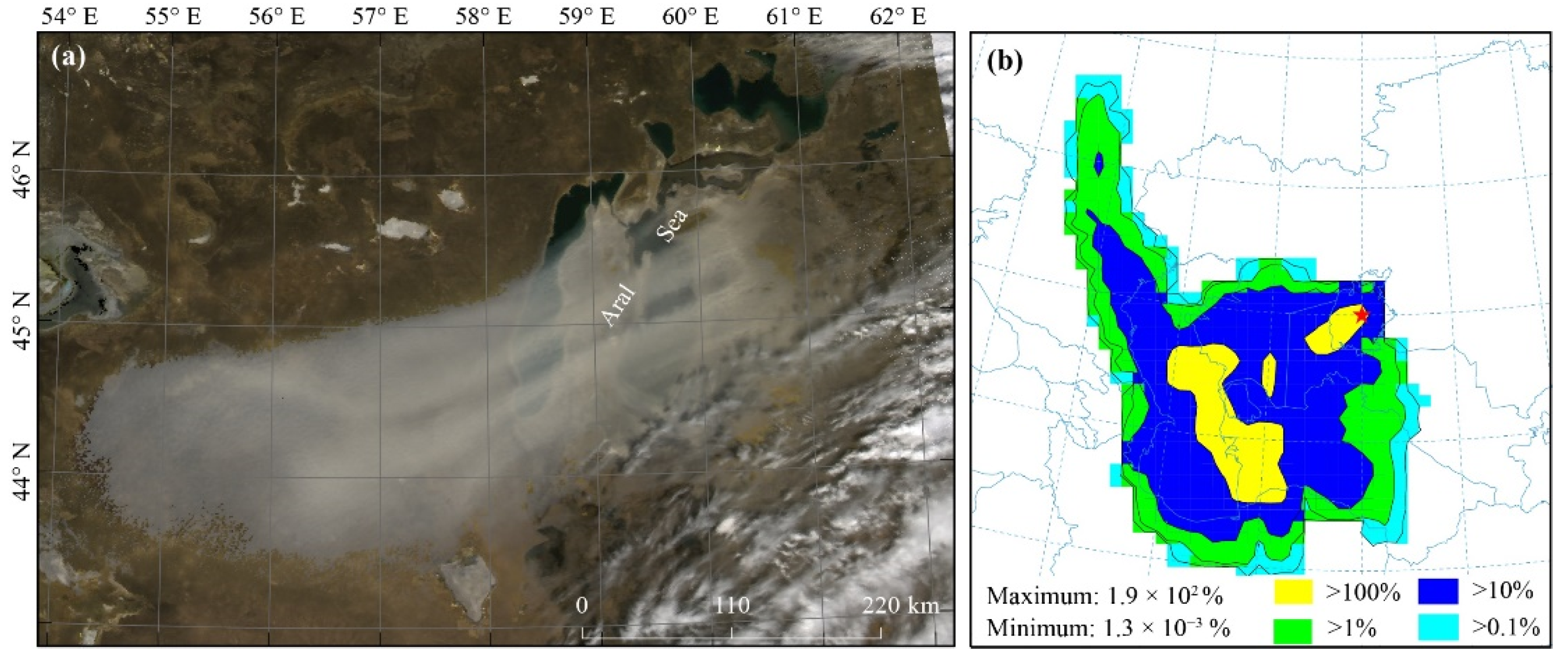
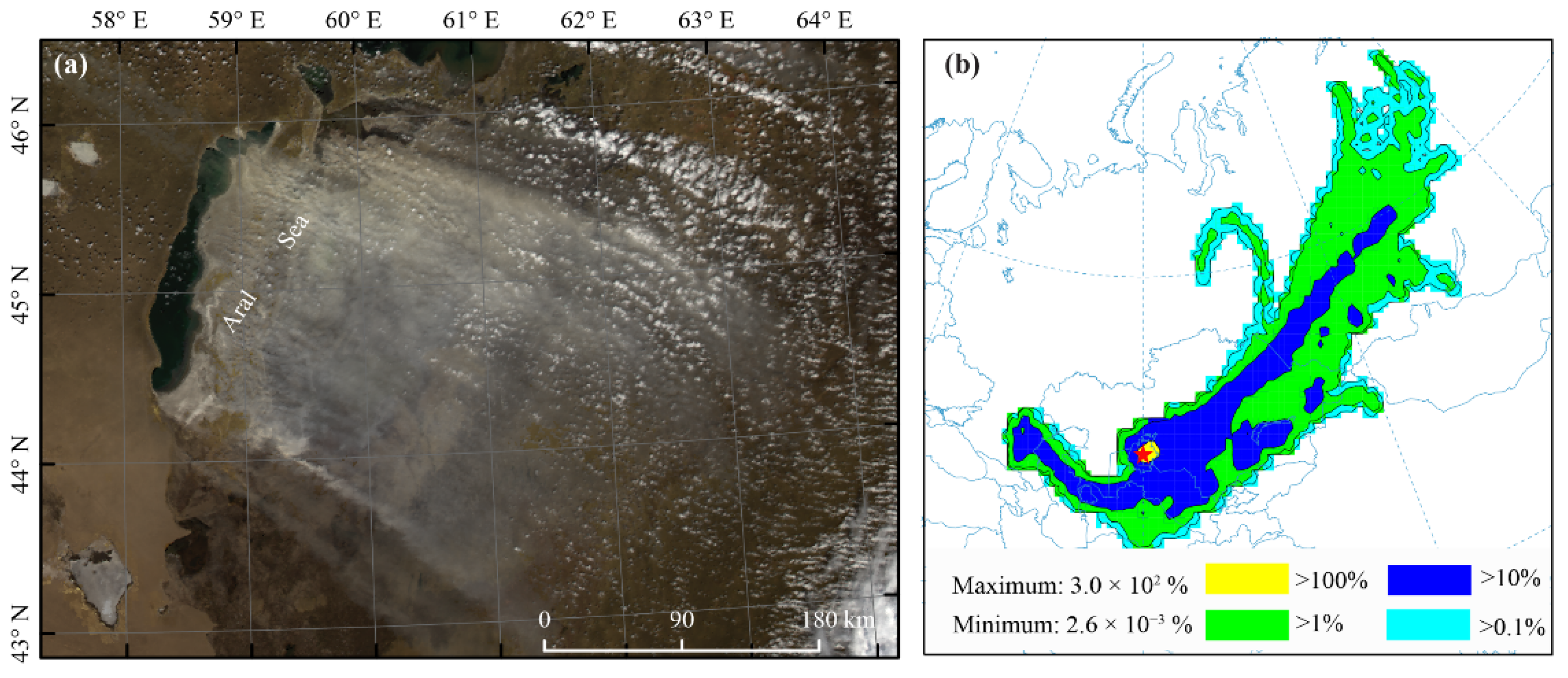
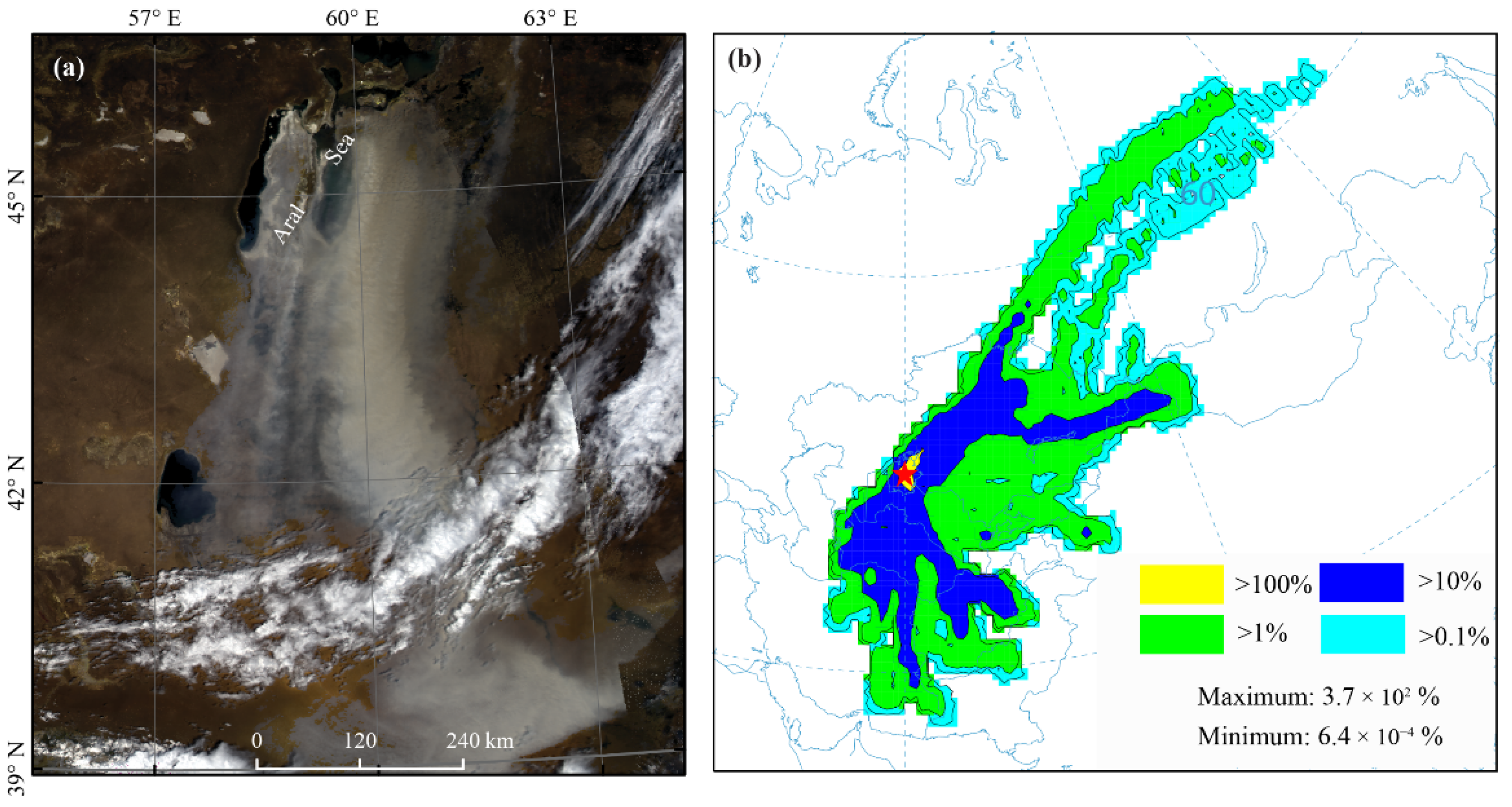
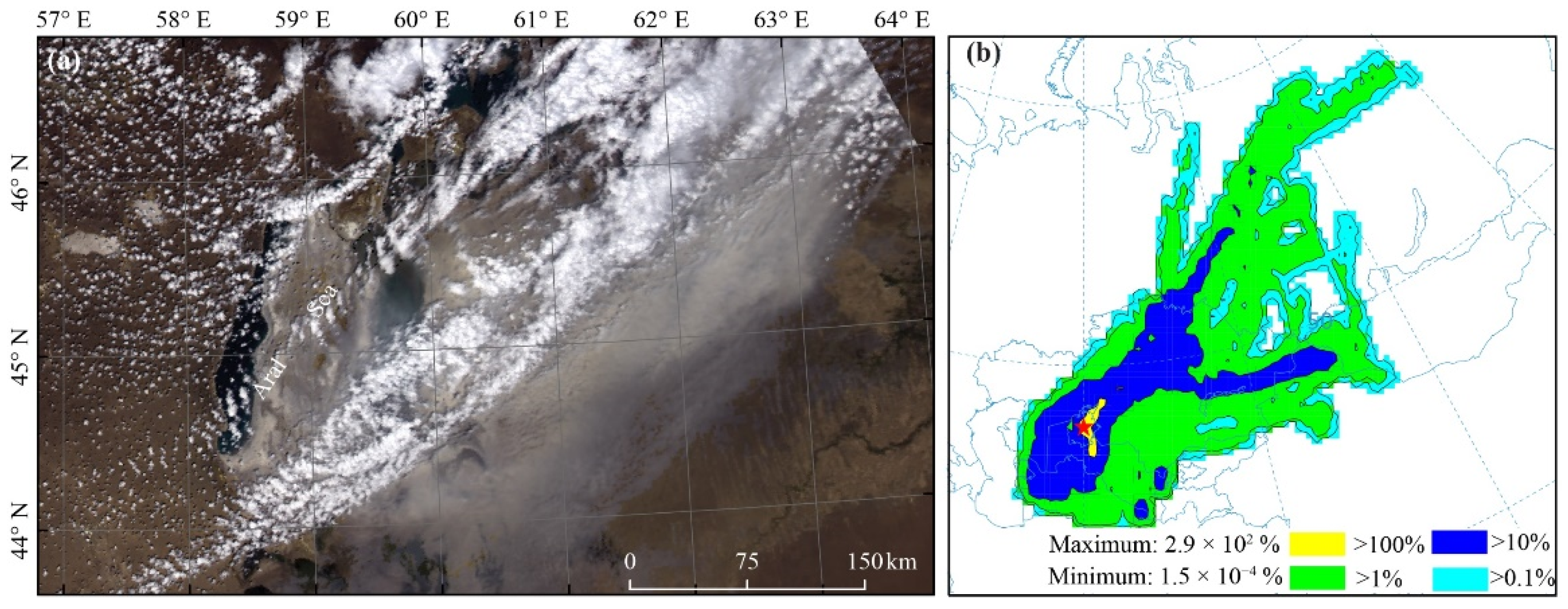
3.4. Case study of the Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin
4. Discussion
4.1. Dominant Atmospheric Aerosol Subtypes over the Aral Sea
4.2. Variations and Long-Range Transport of Aerosols from the Dry Lakebed of the Aral Sea and Their Implications
4.3. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of mineral dust and its impact on climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knippertz, P.; Stuut, J.-B.W. Mineral Dust: A Key Player in the Earth System; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q.; Prospero, J.; Kahn, R.; Remer, L.; Yu, H.; Sayer, A.; Bian, H.; Geogdzhayev, I. Multi-decadal aerosol variations from 1980 to 2009: A perspective from observations and a global model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3657–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Sarah, E.; Null, R.J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, X.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Schultz, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L. Global lake evaporation accelerated by changes in surface energy allocation in a warmer climate. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Abuduwaili, J.; Wang, L. Salt dust storm in the Ebinur Lake region: Its 50-year dynamic changes and response to climate changes and human activities. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, N.; Liu, D. Potential transport pathways of dust emanating from the playa of Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, in arid northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, N.; He, J.; Hua, T.; Qie, Y. Changes in area and water volume of the Aral Sea in the arid Central Asia over the period of 1960–2018 and their causes. Catena 2020, 191, 104566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussenaliyeva, A. Save Kazakhstan′s shrinking Lake Balkhash. Science 2020, 370, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladin, N.V.; Høeg, J.T.; Plotnikov, I. Small Aral Sea brings hope for Lake Balkhash. Science 2020, 370, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroughani, M.; Hashemi, H.; Hosseini, S.H.; Pourhashemi, S.; Berndtsson, R. Desiccating Lake Urmia: A new dust source of regional importance. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boloorani, A.D.; Najafi, M.S.; Soleimani, M.; Papi, R.; Torabi, O. Influence of Hamoun Lakes’ dry conditions on dust emission and radiative forcing over Sistan plain, Iran. Atmos. Res. 2022, 272, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamat, A.-A.A.; Al-Hurban, A.; Saied, N. Change Detection of Lake Chad Water Surface Area Using Remote Sensing and Satellite Imagery. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2021, 13, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policelli, F.; Hubbard, A.; Jung, H.C.; Zaitchik, B.; Ichoku, C. Lake Chad Total Surface Water Area as Derived from Land Surface Temperature and Radar Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strong, C.; Parsons, K.; McTainsh, G.; Sheehan, A. Dust transporting wind systems in the lower Lake Eyre Basin, Australia: A preliminary study. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A. Dust storms and ephemeral lakes. Desert 2018, 23, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, L.G.; Cosentino, N.J.; Iturri, L.A.; García, M.G.; Gaiero, D.M. Is Dust Derived From Shrinking Saline Lakes a Risk to Soil Sodification in Southern South America? J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2021JF006585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, E.H.; Stein, A.F. Large Salt Dust Storms Follow a 30-Year Rainfall Cycle in the Mar Chiquita Lake (Córdoba, Argentina). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Bao, A.; Lei, J.; Xu, W.; Luo, G.; Guan, Q. Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, D.; Wu, G. Saline dust storms and their ecological impacts in arid regions. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarangi, C.; Qian, Y.; Rittger, K.; Ruby Leung, L.; Chand, D.; Bormann, K.J.; Painter, T.H. Dust dominates high-altitude snow darkening and melt over high-mountain Asia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklin, P.; Aladin, N.V.; Plotnikov, I. The Aral Sea: The Devastation and Partial Rehabilitation of a Great Lake; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cretaux, J.F.; Letolle, R.; Bergé-Nguyen, M. History of Aral Sea level variability and current scientific debates. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklin, P. The Aral Sea crisis and its future: An assessment in 2006. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2006, 47, 546–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklin, P. The past, present, and future Aral Sea. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2010, 15, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breckle, S.-W.; Wucherer, W. The Aralkum, a Man-Made Desert on the Desiccated Floor of the Aral Sea (Central Asia): General Introduction and Aims of the Book. In Aralkum—A Man-Made Desert; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, S.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Rashki, A.; Alam, K.; Ranjbar, A. Numerical simulations of dust storms originated from dried lakes in central and southwest Asia: The case of Aral Sea and Sistan Basin. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N. Dust storms in Central Asia: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 85, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Kozhoridze, G.; Batyrbaeva, M.; Vitkovskaya, I.; Orlovsky, N.; Blumberg, D.; Orlovsky, L. Dust emission and environmental changes in the dried bottom of the Aral Sea. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Lei, J. Ecological Restoration and Countmeasures against Desertification Crisis in Aral Sea Region. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, D. Temporal variability and potential diffusion characteristics of dust aerosol originating from the Aral Sea basin, central Asia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Samat, A. Remote sensing-based land surface change identification and prediction in the Aral Sea bed, Central Asia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, F.; Dimov, D.; Kenjabaev, S.; Zaitov, S.; Stulina, G.; Dukhovny, V. Land cover change detection in the Aralkum with multi-source satellite datasets. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Galayeva, O.; Semenov, O.; Bazarbayeva, T. Aeolian transportation of sand and dust in the Aral Sea region. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Aslanov, I.; Lotz, T.; Vereshagina, N. Aeolian dust deposition in the southern Aral Sea region (Uzbekistan): Ground-based monitoring results from the LUCA project. Quat. Int. 2017, 429, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.; Opp, C.; Aslanov, I. Spatial and temporal distribution of the dust deposition in Central Asia–results from a long term monitoring program. Aeolian Res. 2013, 9, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, P.; Hubbard, R.; O’Hara, S.; Wiggs, G.; Wegerdt, J.; Lewis, S.; Small, I.; van der Meer, J.; Upshur, R.; Médecins san Frontières/Aral Sea Respiratory Dust and Disease project team. The impact of airborne dust on respiratory health in children living in the Aral Sea region. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, O.E. Dust Storms and Sandstorms and Aerosol Long-Distance Transport. In Aralkum—A Man-Made Desert: The Desiccated Floor of the Aral Sea (Central Asia); Breckle, S.-W., Wucherer, W., Dimeyeva, L.A., Ogar, N.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklin, P. The Aral sea disaster. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2007, 35, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J. Aeolian Processes as Dust Storms in the Deserts of Central Asia and Kazakhstan; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crighton, E.J.; Barwin, L.; Small, I.; Upshur, R. What have we learned? A review of the literature on children’s health and the environment in the Aral Sea area. Int. J. Public Health 2011, 56, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhupankhan, A.; Khaibullina, Z.; Kabiyev, Y.; Persson, K.M.; Tussupova, K. Health impact of drying aral sea: One health and socio-economical approach. Water 2021, 13, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasmine, M.K.; Aloysius, M.; Jayaprakash, R.; Fathima, C.P.; Prijith, S.S.; Mohan, M. Investigation on the role of aerosols on precipitation enhancement over Kerala during August 2018. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 279, 119101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P. The CALIPSO Automated Aerosol Classification and Lidar Ratio Selection Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.; Kim, J.; Song, C.; Jo, H.-W.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Lim, C.-H.; Lee, W.-K. Applicability Analysis of Vegetation Condition and Dryness for Sand and Dust Storm (SDS) Risk Reduction in SDS Source and Receptor Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time environmental applications and display system: READY. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Xie, L. Distribution and transport characteristics of dust aerosol over Tibetan Plateau and Taklimakan Desert in China using MERRA-2 and CALIPSO data. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hamdi, R.; Luo, G.; Cai, P.; Zhang, M.; Shi, H.; Li, C.; Termonia, P.; De Maeyer, P.; Kurban, A. Numerical study on the climatic effect of the Aral Sea. Atmos. Res. 2022, 268, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wei, J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Lin, P. Irrigation-Induced Environmental Changes around the Aral Sea: An Integrated View from Multiple Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Samat, A.; Ge, Y.; Ma, L.; Tuheti, A.; Zou, S.; Abuduwaili, J. Quantitative Soil Wind Erosion Potential Mapping for Central Asia Using the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Yang, S.; Xia, N.; Ariken, M. Exploring the spatial-temporal characteristics of the aerosol optical depth (AOD) in Central Asia based on the moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Gan, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Assessment of dominating aerosol properties and their long-term trend in the Pan-Third Pole region: A study with 10-year multi-sensor measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Qiao, H.; Sun, M.; Huang, Z. Comparative Analysis of Aerosol Optical Properties in Typical Regions of Mineral Dust and Salt Dust. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Claiborn, C.; Lei, J.; Vaughan, J.; Wu, S.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Aeolian dust in Central Asia: Spatial distribution and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Abuduwaili, J.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X. A Cluster Analysis of Forward Trajectory to Identify the Transport Pathway of Salt-Dust Particles from Dried Bottom of Aral Sea, Central Asia. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hamdi, R.; Cai, P.; Luo, G.; Ochege, F.U.; Zhang, M.; Termonia, P.; De Maeyer, P.; Li, C. Impacts of Historical Land Use/Cover Change (1980–2015) on Summer Climate in the Aral Sea Region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD032638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, T.; Tan, R.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J. CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklin, P.; Aladin, N.V.; Chida, T.; Boroffka, N.; Plotnikov, I.S.; Krivonogov, S.; White, K. The Aral Sea: A story of devastation and partial recovery of a large Lake. In Large Asian Lakes in a Changing World; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 109–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Ravi, S.; Van Pelt, R.S.; Costa, P.J.; Dukes, D. Tracer techniques in aeolian research: Approaches, applications, and challenges. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Aerosol Subtypes | Season | Spring (20,173) a | Summer (21,535) | Autumn (14,753) | Winter (10,515) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOD | <0.25 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–0.75 | 0.75–1 | >1 | <0.25 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–0.75 | 0.75–1 | >1 | <0.25 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–0.75 | 0.75–1 | >1 | <0.25 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–0.75 | 0.75–1 | >1 | |
| Tropospheric aerosol | Dust | 37% | 2% | 1% | 0 | 1% | 16% | 2% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 14% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 1% |
| Polluted continental/smoke | 8% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Clean continental | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Polluted dust | 41% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 1% | 56% | 2% | 0 | 0 | 1% | 50% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 1% | |
| Elevated smoke | 3% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 1% | 5% | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1% | |
| Stratospheric aerosol | Sulfate/other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, N.; Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Issanova, G.; Saparov, G. Insights into Variations and Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133201
Wu N, Ge Y, Abuduwaili J, Issanova G, Saparov G. Insights into Variations and Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133201
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Na, Yongxiao Ge, Jilili Abuduwaili, Gulnura Issanova, and Galymzhan Saparov. 2022. "Insights into Variations and Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133201
APA StyleWu, N., Ge, Y., Abuduwaili, J., Issanova, G., & Saparov, G. (2022). Insights into Variations and Potential Long-Range Transport of Atmospheric Aerosols from the Aral Sea Basin in Central Asia. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133201






