Prediction of Potential Geothermal Disaster Areas along the Yunnan–Tibet Railway Project
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
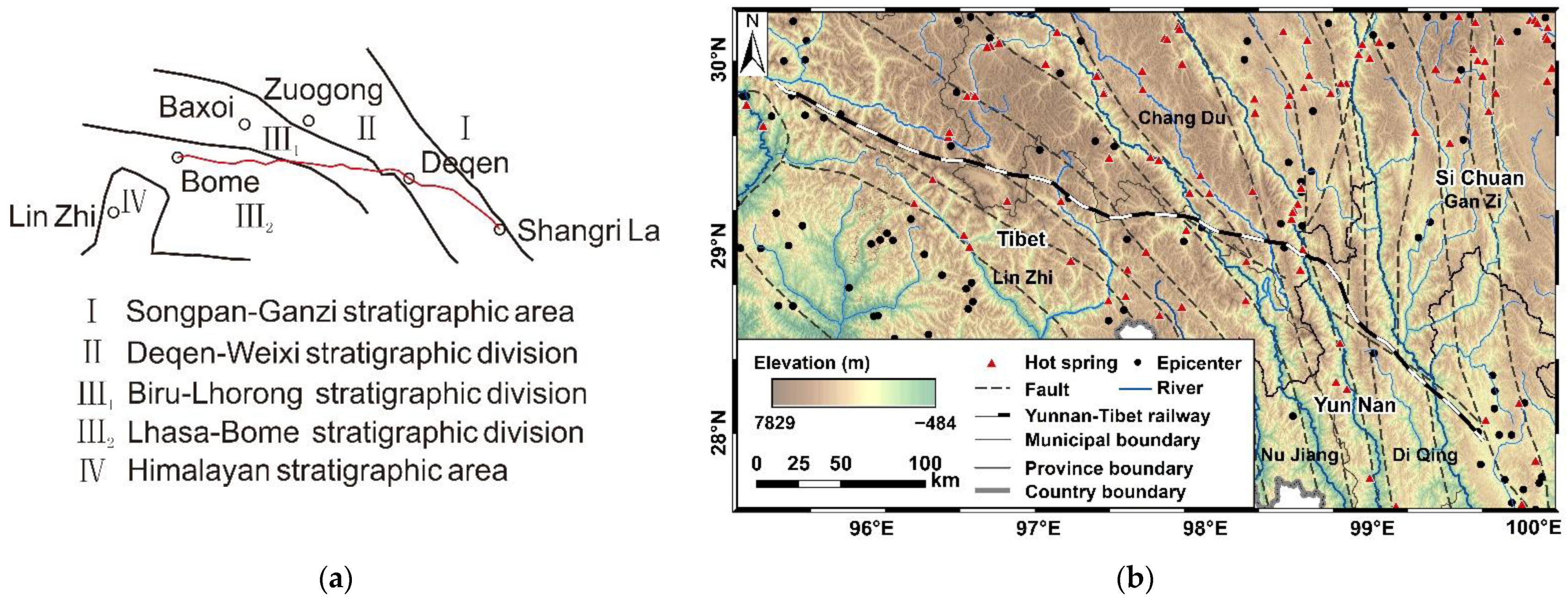
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Geothermal Sample Points
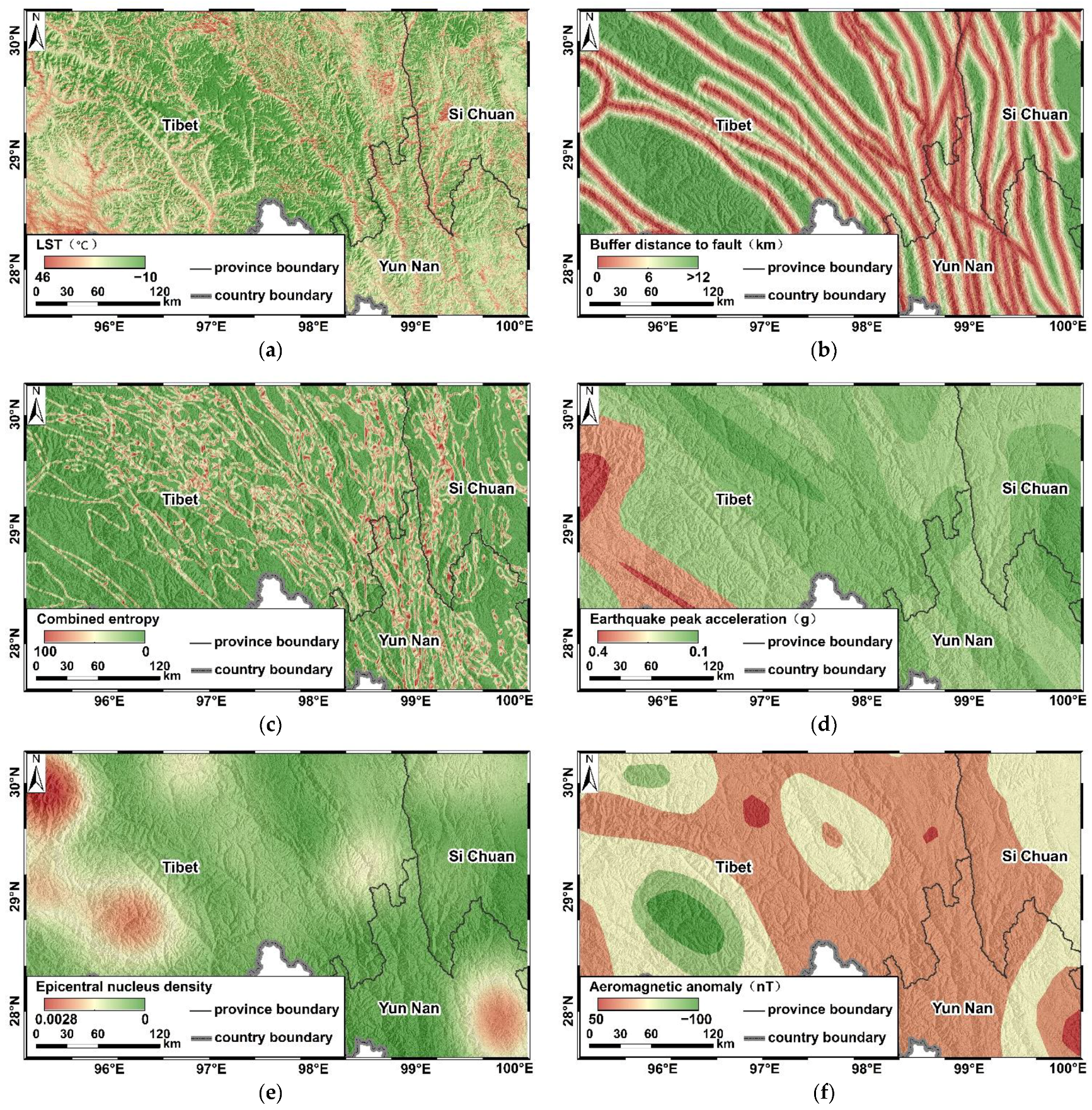
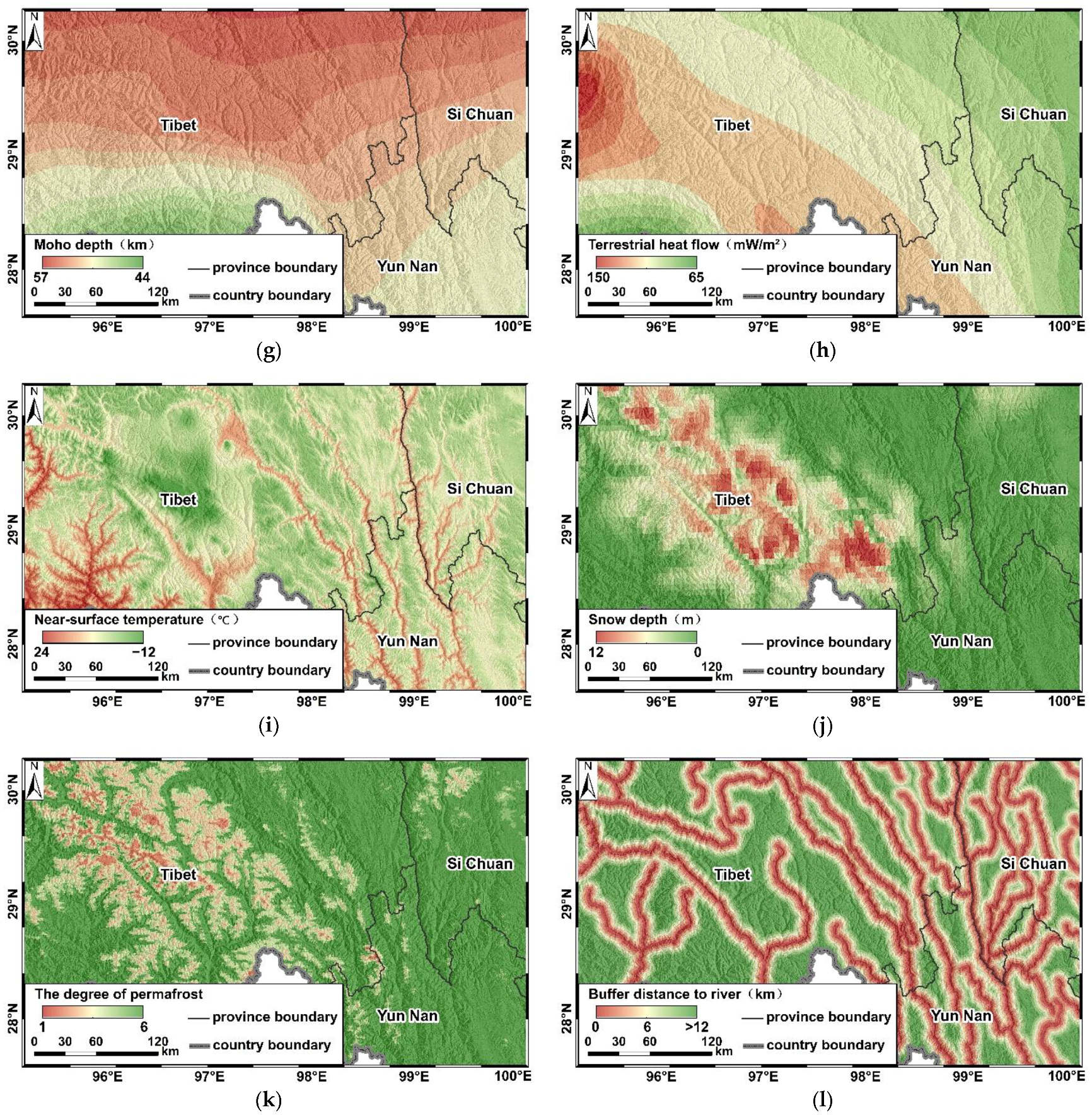
2.2.2. Selection and Processing of Environmental Variables
2.2.3. Collinearity Diagnosis of Environmental Variables
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Prediction Models
2.3.2. Test of Model Prediction Results
3. Result
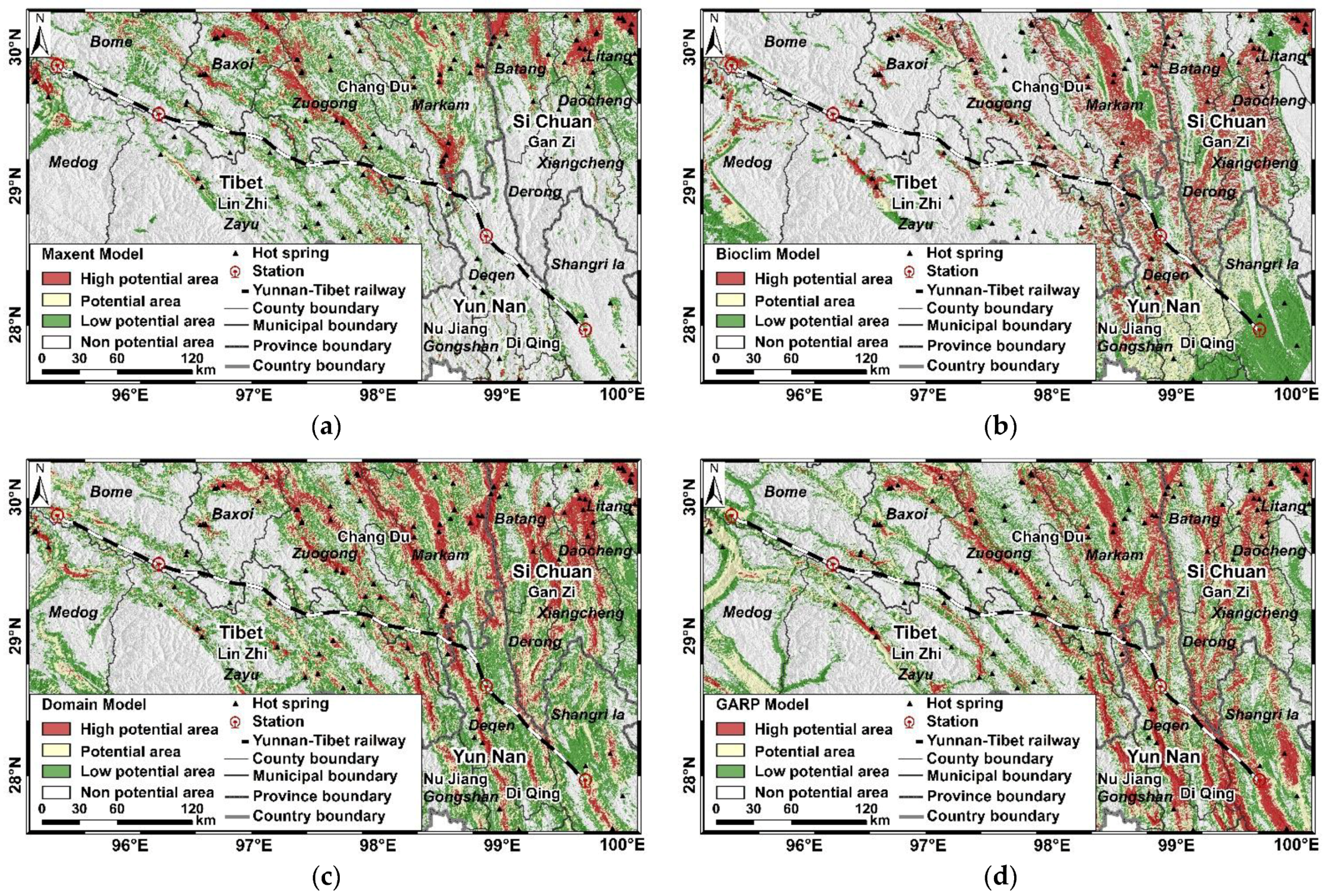
3.1. Predicted Results of Models
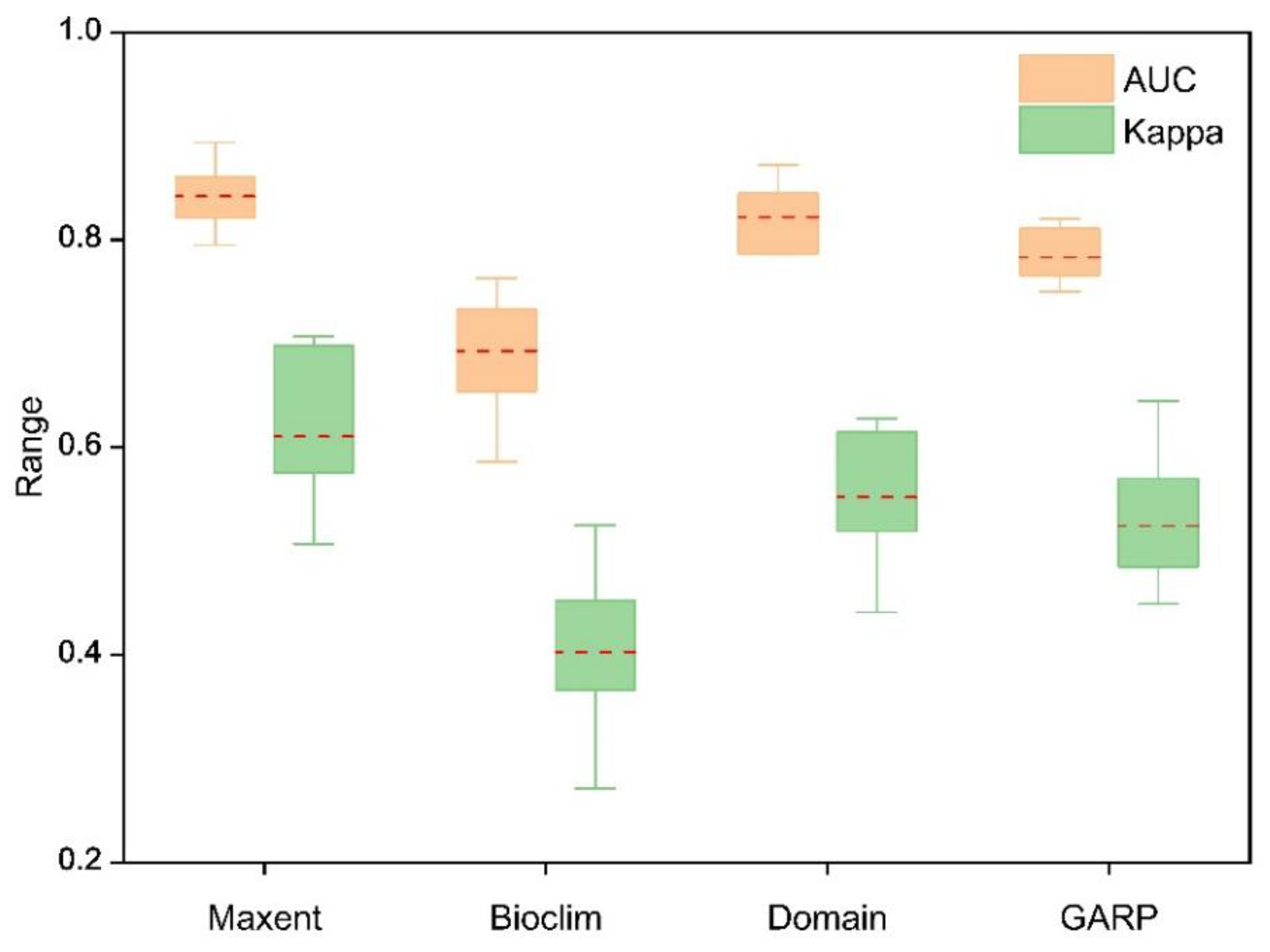
3.2. Evaluation of the Predictive Accuracy of Different Models
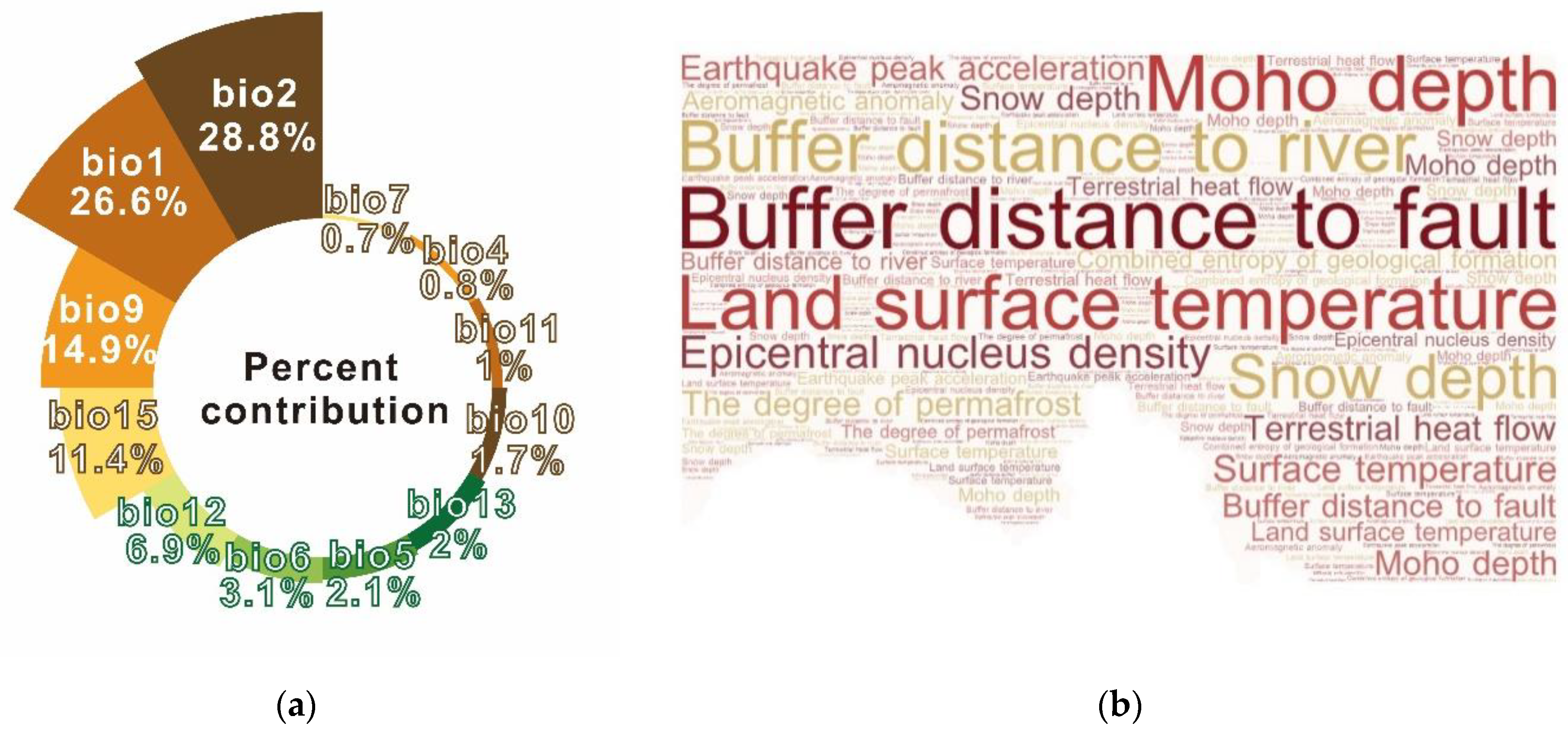
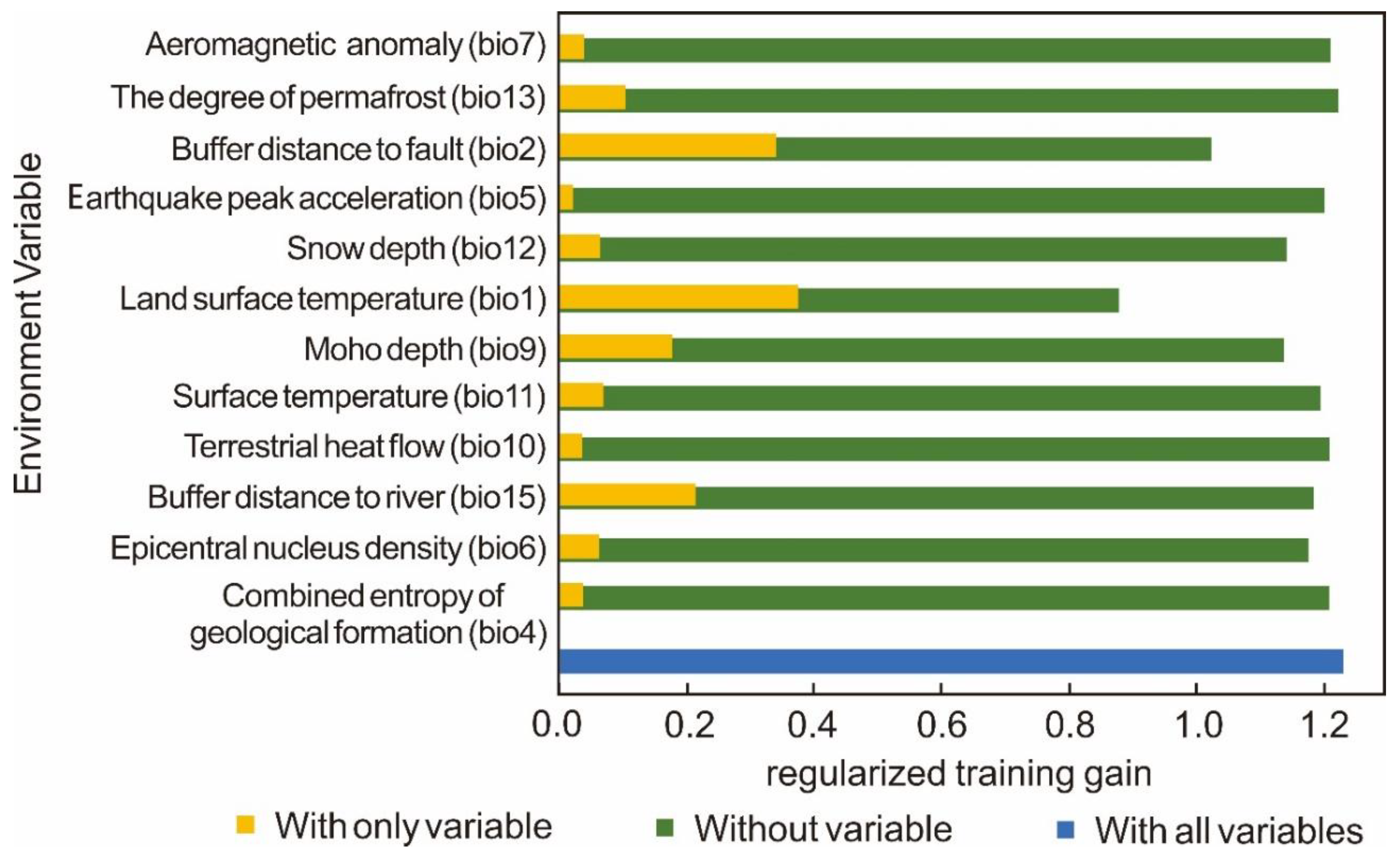
3.3. Analysis of Environmental Variables Affecting the Potential Geothermal Disaster Area
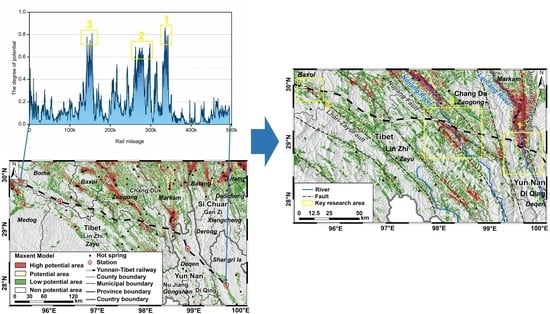
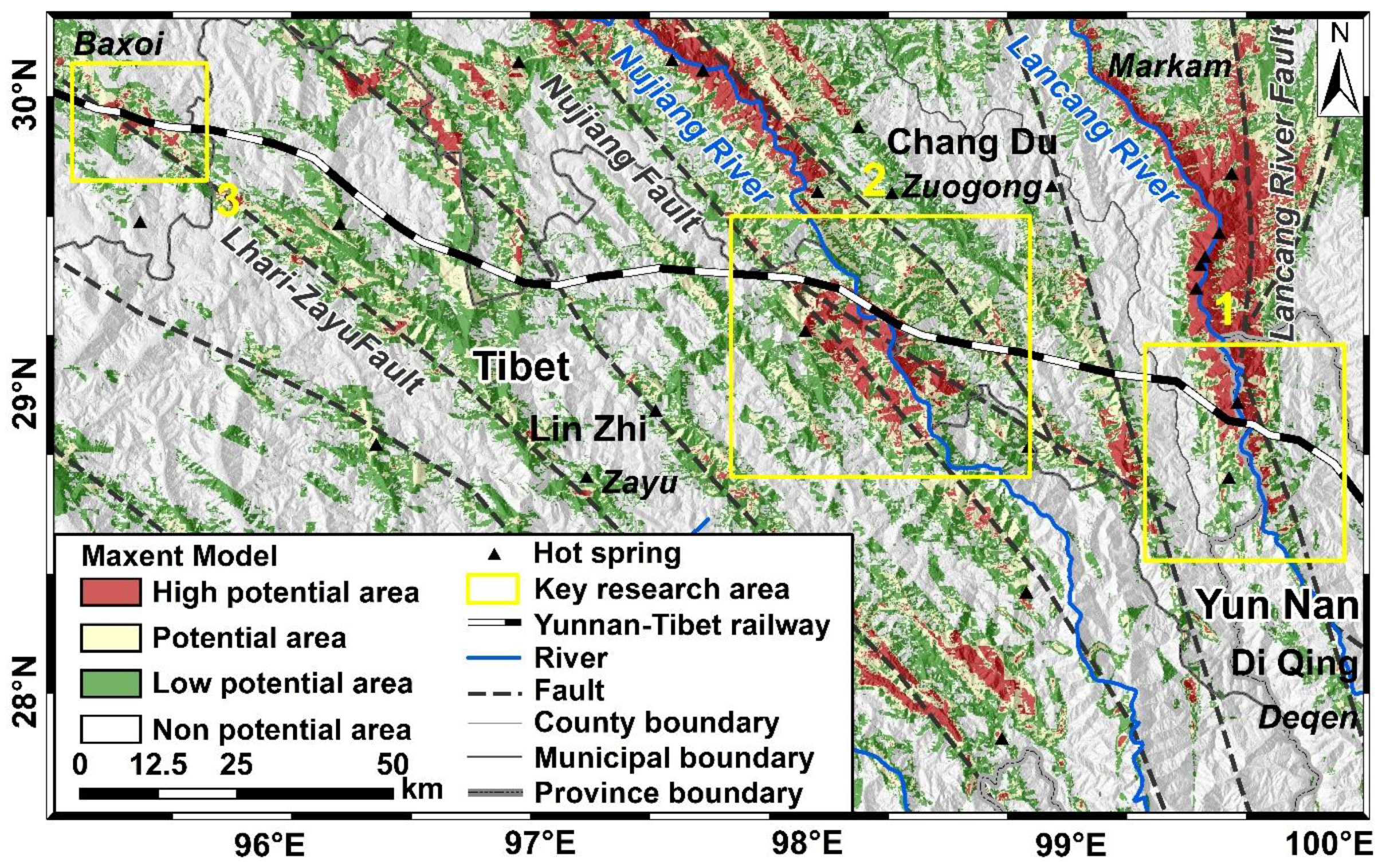
3.4. Analysis of Key Areas of Geothermal Disaster along Yunnan–Tibet Railway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J. Research on Main Engineering Geological Problems and Principles of Geological Route Selection for Yunnan-Tibet Railway. Railw. Stand. Des. 2021, 65, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Analysis and Prediction of Geothermal Characteristics of Sanbaishan Tunnel. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Huang, G. Analysis of Effects of Groundwater Geotemperature Anomaly in Deeply Lying Longon and Big Tunnel. J. Geol. Hazards Environ. Preserv. 1996, 7, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Chen, F.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, D. Big Earth Data: A Practice of Sustainability Science to Achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liang, D.; Chen, F.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J. Big Earth Data Facilitates Sustainable Development Goals. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; He, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Cooling Technology and Effect Analysis for High Geothermal Tunnel on Sichuan-Tibet Railway. China Railw. Sci. 2019, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Du, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q.; Hao, L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Research on the “Space-Aero-Ground” Remote Sensing Geological Survey Technology of Sichuan-Tibet Railway. J. Railw. Eng. Soc. 2021, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, S.; Haeberli, W. Permafrost in Steep Bedrock Slopes and Its Temperature-Related Destabilization Following Climate Change. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaksen, K.; Sollid, J.L.; Holmlund, P.; Harris, C. Recent Warming of Mountain Permafrost in Svalbard and Scandinavia. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, L.; Xie, C.; Pang, Q.; Du, E.; Qiao, Y. Variation Characteristics and Impact Factors of the Depth of Zero Annual Amplitude of Ground Temperature in Permafrost Regions on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2016, 38, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Lan, H. Geothermal Characteristics of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Risk Analysis of Deep Underground Geothermal Hazards for Major Linear Sichuan-Tibet Railway Project. J. Eng. Geol. 2021, 29, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chang, R.; Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Guo, H.; Xiao, K.; Wu, L.; Hou, D.; Zou, L. Quantitative Prediction and Evaluation of Geothermal Resource Areas in the Southwest Section of the Mid-Spine Belt of Beautiful China. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 748–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xiang, J.; Fan, M.; Xu, Y. 3D Mineral Prospectivity Mapping Based on Deep Metallogenic Prediction Theory: A Case Study of the Lala Copper Mine, Sichuan, China. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiang, J.; Hu, Q.; Yang, W.; Lai, Z.; Hu, B.; Wei, W. Quantitative Geoscience and Geological Big Data Development: A Review. Acta Geol. Sin. English Ed. 2016, 90, 1490–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Xiao, K.; Wei, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, N.; Xiang, J. Mineral Prospectivity Mapping Based on Isolation Forest and Random Forest: Implication for the Existence of Spatial Signature of Mineralization in Outliers. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xiao, K.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Yang, F. Maximum Entropy and Random Forest Modeling of Mineral Potential: Analysis of Gold Prospectivity in the Hezuo–Meiwu District, West Qinling Orogen, China. Nat. Resour. Res. 2019, 28, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzied, S.M.; Kaiser, M.F.; Shendi, E.A.H.; Abdel-Fattah, M.I. Multi-Criteria Decision Support for Geothermal Resources Exploration Based on Remote Sensing, GIS and Geophysical Techniques along the Gulf of Suez Coastal Area, Egypt. Geothermics 2020, 88, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.I.; Shendi, E.A.H.; Kaiser, M.F.; Abuzied, S.M. Unveiling Geothermal Potential Sites along Gulf of Suez (Egypt) Using an Integrated Geoscience Approach. Terra Nova 2021, 33, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, Q.; Chen, Z.; Feng, T.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Du, S.; Zhang, X.; Meng, D.; Bian, M.; et al. Weighted Information Models for the Quantitative Prediction and Evaluation of the Geothermal Anomaly Area in the Plateau: A Case Study of the Sichuan–Tibet Railway. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gengping, Z.; Guoqing, L.; Wenjun, B.; Yubao, G. Ecological Niche Modeling and Its Applications in Biodiversity Conservation. Biodivers. Sci. 2013, 21, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.; New, M. Ensemble Forecasting of Species Distributions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Gen, Q.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Predicting Pseudolarix Amabilis Potential Habitat Based on Four Niche Models. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.F.; Wu, M.L.; Guo, J.; Sun, C.Z.; Xie, C.X. Predicting the Global Areas for Potential Distribution of Gastrodia Elata Based on Ecological Niche Models. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q. A Study on The Neotectonic Division & Environment Evolution of Qing-Zang Plateau & Three Parallel Rivers area. Yunnan Geol. 2007, 4, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L. The Particularity of Engineering Geology on Yunnan-Tibet Route in Glacier Snowfield Area. J. Railw. Eng. Soc. 2005, A1, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G. Research on the Engineering Geological Hazards-Reduction Route Selection in Three Parallel Rivers Regions for the Yunnan-Tibet Railway. J. Railw. Eng. Soc. 2019, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Cao, H. In Depth Discussions on The Engineering Geological Problems Along Sanjiang Sector of Yunan-Tibet Railway Line. J. Eng. Geol. 2010, 18, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Du, J.; Li, F. Comparison Study on Resource Evaluation Methods of Shallow Geothermal Energy and Traditional Geothermal Energy. Urban Geol. 2018, 13, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, G. Shallow Geothermal Resources. West. Resour. 2019, 1, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, R. Evaluation and Prediction of Temperature Field in Deep Buried Long Tunnel. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 1996, 23, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Qing, D.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G.; Feng, T.; Wang, D.; Bi, X.; Bian, M.; et al. Research on Quantitative Prediction and Evaluation of Geo- Thermal Anomaly Area in Qamdo-Nyingchi Section of Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2021, 36, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Pezard, P.A. Streaming Electrical Potential Anomaly along Faults in Geothermal Areas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3197–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Pirajno, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Cong, Y.; Fan, J.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, H. Study on the Major Minerals Potential in China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 127, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, Y.; Bayrak, E. Regional Variations and Correlations of Gutenberge-Richter Parameters and Fractal Dimension for the Different Seismogenic Zones in Western Anatolia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 58, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogan, D. Extraction of Lineaments from Gravity Anomaly Maps Using the Gradient Calculation: Application to Central Anatolia. Earth Planets Sp. 2011, 63, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.F. Aeromagnetic Series Maps and Specifications of Qinghai—Tibet Plateau and Adjacent Areas; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, N.; Tang, B.; Zhu, C. Deep Thermal Background of Hot Spring Distribution in the Chinese Continent. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Mao, K.; Xia, X.; Wang, P.; Shi, J.; Bateni, S.M.; Xu, T.; Cao, M.; Heggy, E.; Qin, Z. Dataset of Daily Near-Surface Air Temperature in China from 1979 to 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1413–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Wu, T.; Wu, J.; Xie, C.; Wu, X.; Pang, Q.; et al. A New Map of Permafrost Distribution on the Tibetan Plateau. Cryosph 2017, 11, 2527–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, D.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Development of a Fine-Resolution Snow Depth Product Based on the Snow Cover Probability for the Tibetan Plateau: Validation and Spatial–temporal Analyses. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, H. An Interpolated Temperature and Precipitation Dataset at 1-Km Grid Resolution in China (2000–2012). China Sci. Data 2017, 2, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.H. Confronting Multicollinearity in Ecological Multiple Regression. Ecology 2003, 84, 809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.G.; Slik, J.W.F.; Ma, K.P. Using Species Distribution Modeling to Delineate the Botanical Richness Patterns and Phytogeographical Regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mai, J.; Xian, Y.; Liu, G. Predicting Potential Rainfall-Triggered Landslides Sites in Guangdong Province (China) Using MaxEnt Model under Climate Changes Scenarios. J. Geo Inf. Sci. 2021, 23, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.; Davis, F.W.; Ikegami, M.; Syphard, A.D.; Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L.; Hannah, L. Modeling Plant Species Distributions under Future Climates: How Fine Scale Do Climate Projections Need to Be? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum Entropy Modeling of Species Geographic Distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booth, T.H.; Nix, H.A.; Busby, J.R.; Hutchinson, M.F. Bioclim: The First Species Distribution Modelling Package, Its Early Applications and Relevance to Most Current MaxEnt Studies. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busby, J.R. BIOCLIM—A Bioclimate Analysis and Prediction System. Nat. Conserv. Cost Eff. Biol. Surv. Data Anal. 1991, 6, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive Habitat Distribution Models in Ecology. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunsheng, W. Application of ROC Curve Analysis in Evaluating the Performance of Alien Species’ Potential Distribution Models. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.I.; Richardson, D.M.; Cowling, R.M. Modeling Invasive Plant Spread: The Role of Plant-Environment Interactions and Model Structure. Ecology 1996, 77, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.I.; Richardson, D.M.; Cowling, R.M.; Trinder-Smith, T.H. Predicting the Landscape-Scale Distribution of Alien Plants and Their Threat to Plant Diversity. Conserv. Biol. 1999, 13, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, D.; Peters, D. The GARP Modelling System: Problems and Solutions to Automated Spatial Prediction. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1999, 13, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the Accuracy of Diagnostic Systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Du, Y.; Niu, S.; Zhao, J. Modeling Forest Lightning Fire Occurrence in the Daxinganling Mountains of Northeastern China with MAXENT. Forests 2015, 6, 1422–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Brown, C.S.; Stohlgren, T.J.; Bromberg, J. Field Validation of an Invasive Species Maxent Model. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 36, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.N.; Wang, P.X.; Han, P.; Yan, T.L.; Zhang, S.Y. Application of Kappa Coefficient to Accuracy Assessments of Drought Forecasting Model: A Case Study of Guanzhong Plain. J. Nat. Disasters 2011, 20, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manel, S.; Williams, H.C.; Ormerod, S.J. Evaluating Presence-Absence Models in Ecology: The Need to Account for Prevalence. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, P.; Araújo, M.B. An Evaluation of Methods for Modelling Species Distributions. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, J.; DiTommaso, A.; Wang, R.; Wu, R. Predicting Invasions of Wedelia trilobata (L.) Hitchc. with Maxent and GARP Models. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, P.A.; Graham, C.H.; Master, L.L.; Albert, D.L. The Effect of Sample Size and Species Characteristics on Performance of Different Species Distribution Modeling Methods. Ecography 2006, 29, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A.; Papeş, M.; Eaton, M. Transferability and Model Evaluation in Ecological Niche Modeling: A Comparison of GARP and Maxent. Ecography 2007, 30, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zou, H.F. Optimizing MaxEnt Model in the Prediction of Species Distribution. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Tian, C.M.; Li, T.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.Q. Predicting the Distribution of Dwarf Mistletoe (Arceuthobium Sichuanense) with GARP and MaxEnt Models. Beijing Linye Daxue Xuebao J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 13, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.H.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettmann, F.; Leathwick, J.R.; Lehmann, A.; et al. Novel Methods Improve Prediction of Species’ Distributions from Occurrence Data. Ecography 2006, 29, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M.; Schapire, R.E. A Maximum Entropy Approach to Species Distribution Modeling. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning—ICML ’04, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 83. [Google Scholar]



| Code | Environment Variable | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | Land surface temperature | ℃ |
| Bio2 | Buffer distance to fault | km |
| Bio3 | Fault density | km/km2 |
| Bio4 | Combined entropy of geological formation | - |
| Bio5 | Earthquake peak acceleration | g |
| Bio6 | Epicentral nucleus density | - |
| Bio7 | Aeromagnetic anomaly | nT |
| Bio8 | Bouguer gravity anomaly | mgal |
| Bio9 | Moho depth | km |
| Bio10 | Terrestrial heat flow | mW/m2 |
| Bio11 | Near-surface temperature | ℃ |
| Bio12 | Snow depth | m |
| Bio13 | The degree of permafrost | - |
| Bio14 | Amount of precipitation | mm |
| Bio15 | Buffer distance to river | km |
| The Area | The Area under Receiver Operating CharacteristicCurve (AUC) | Consistency Test Statistics (Kappa) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaxEnt | Bioclim | Domain | GARP | MaxEnt | Bioclim | Domain | GARP | |
| 1 | 0.894 | 0.730 | 0.872 | 0.814 | 0.707 | 0.452 | 0.628 | 0.605 |
| 2 | 0.839 | 0.699 | 0.787 | 0.766 | 0.621 | 0.371 | 0.441 | 0.485 |
| 3 | 0.848 | 0.754 | 0.811 | 0.768 | 0.586 | 0.436 | 0.560 | 0.490 |
| 4 | 0.821 | 0.586 | 0.787 | 0.780 | 0.534 | 0.271 | 0.546 | 0.449 |
| 5 | 0.868 | 0.763 | 0.835 | 0.820 | 0.698 | 0.525 | 0.592 | 0.570 |
| 6 | 0.825 | 0.718 | 0.807 | 0.782 | 0.576 | 0.417 | 0.519 | 0.544 |
| 7 | 0.795 | 0.654 | 0.786 | 0.750 | 0.579 | 0.366 | 0.460 | 0.490 |
| 8 | 0.860 | 0.696 | 0.868 | 0.811 | 0.706 | 0.408 | 0.628 | 0.645 |
| 9 | 0.810 | 0.597 | 0.823 | 0.754 | 0.567 | 0.316 | 0.531 | 0.453 |
| 10 | 0.861 | 0.733 | 0.845 | 0.787 | 0.629 | 0.466 | 0.615 | 0.512 |
| Average | 0.842 | 0.693 | 0.822 | 0.783 | 0.620 | 0.403 | 0.552 | 0.524 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Chang, R.; Guo, H.; Pei, X.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Z.; Zou, L. Prediction of Potential Geothermal Disaster Areas along the Yunnan–Tibet Railway Project. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133036
Chen Z, Chang R, Guo H, Pei X, Zhao W, Yu Z, Zou L. Prediction of Potential Geothermal Disaster Areas along the Yunnan–Tibet Railway Project. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133036
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhe, Ruichun Chang, Huadong Guo, Xiangjun Pei, Wenbo Zhao, Zhengbo Yu, and Lu Zou. 2022. "Prediction of Potential Geothermal Disaster Areas along the Yunnan–Tibet Railway Project" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133036
APA StyleChen, Z., Chang, R., Guo, H., Pei, X., Zhao, W., Yu, Z., & Zou, L. (2022). Prediction of Potential Geothermal Disaster Areas along the Yunnan–Tibet Railway Project. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133036