Changes in Land Relief in Urbanised Areas Using Laser Scanning and Archival Data on the Example of Łódź (Poland)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
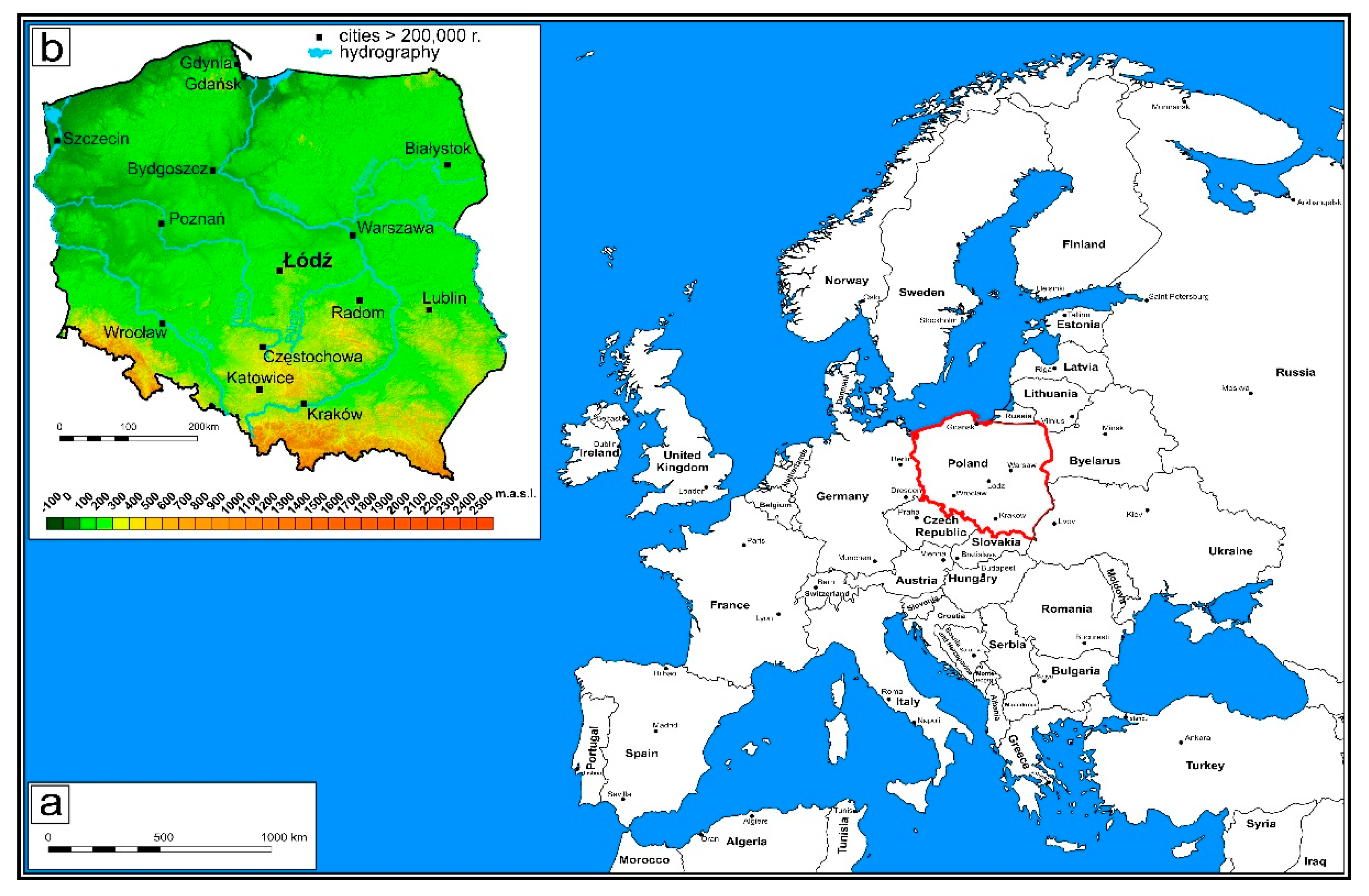
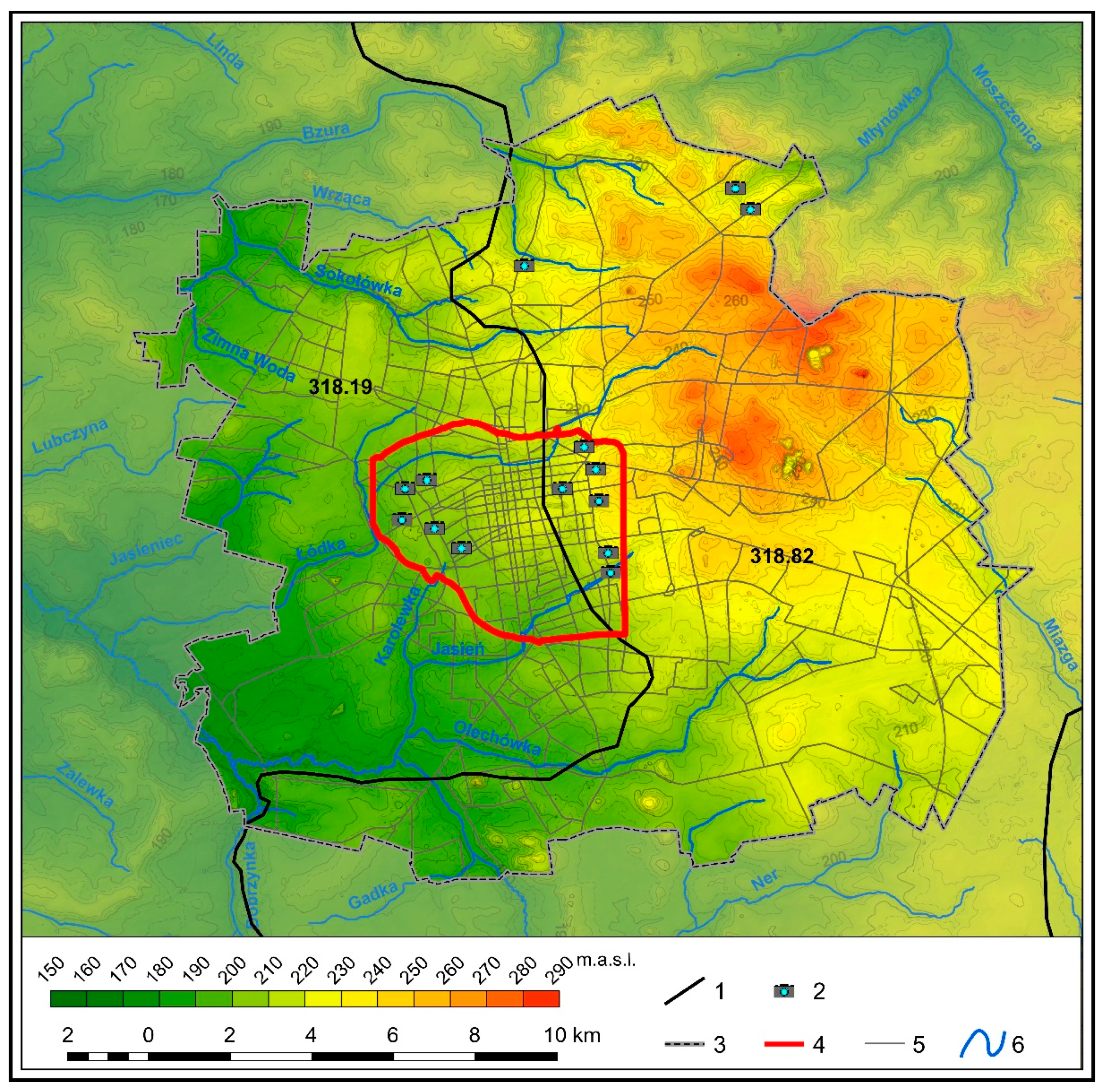
2. Study Area
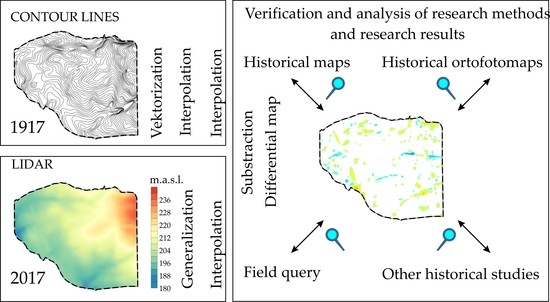
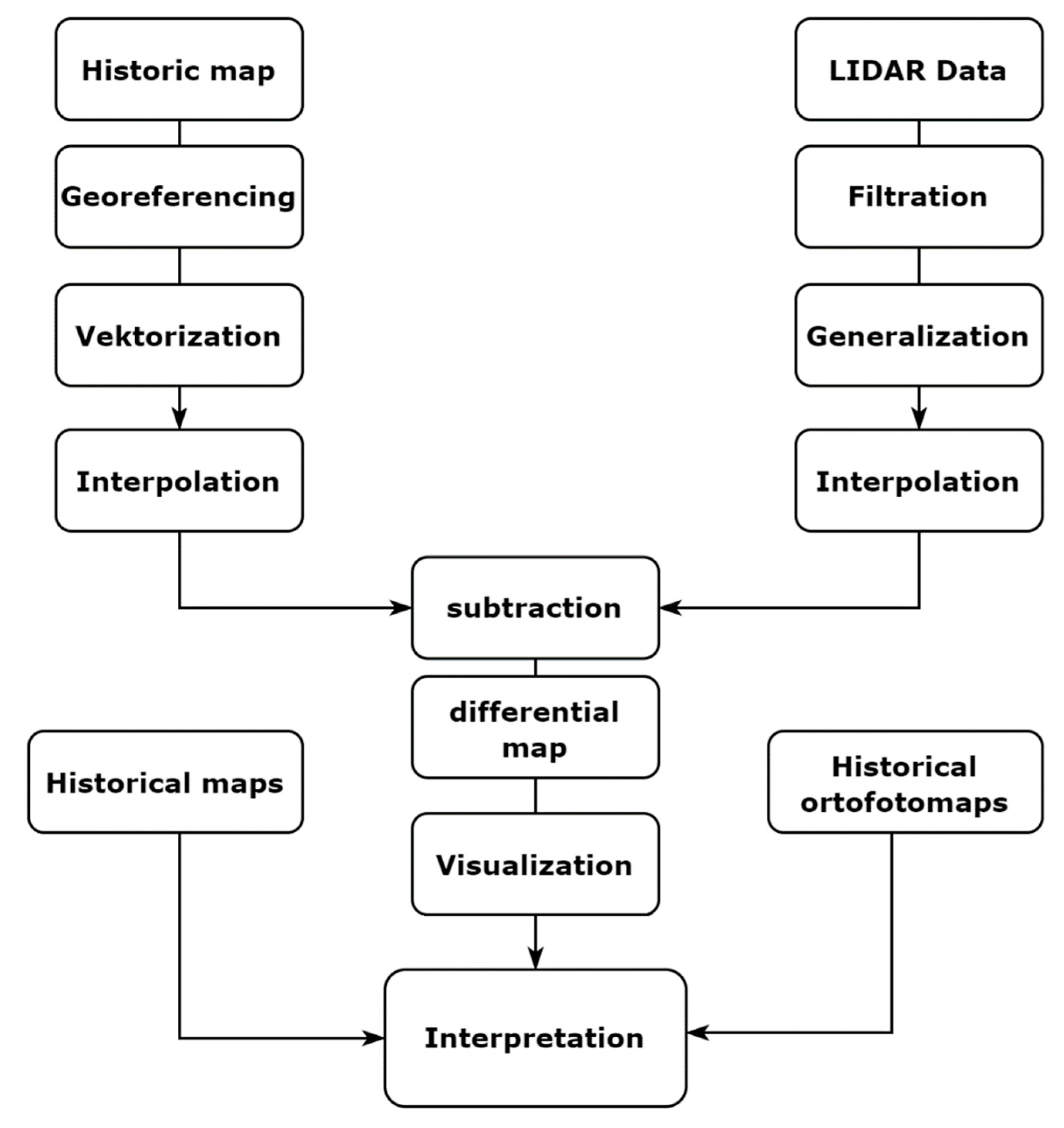
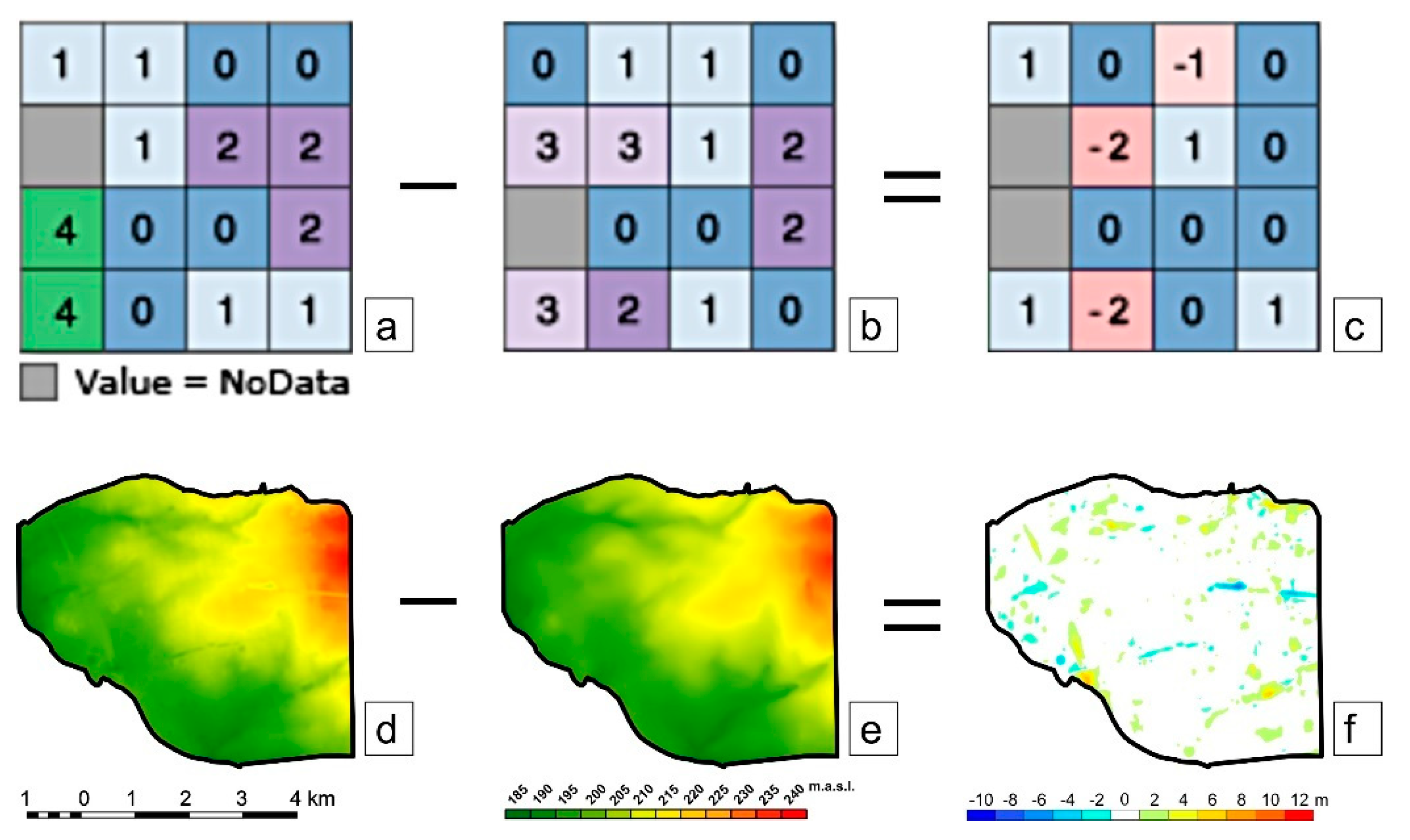
3. Materials and Methods
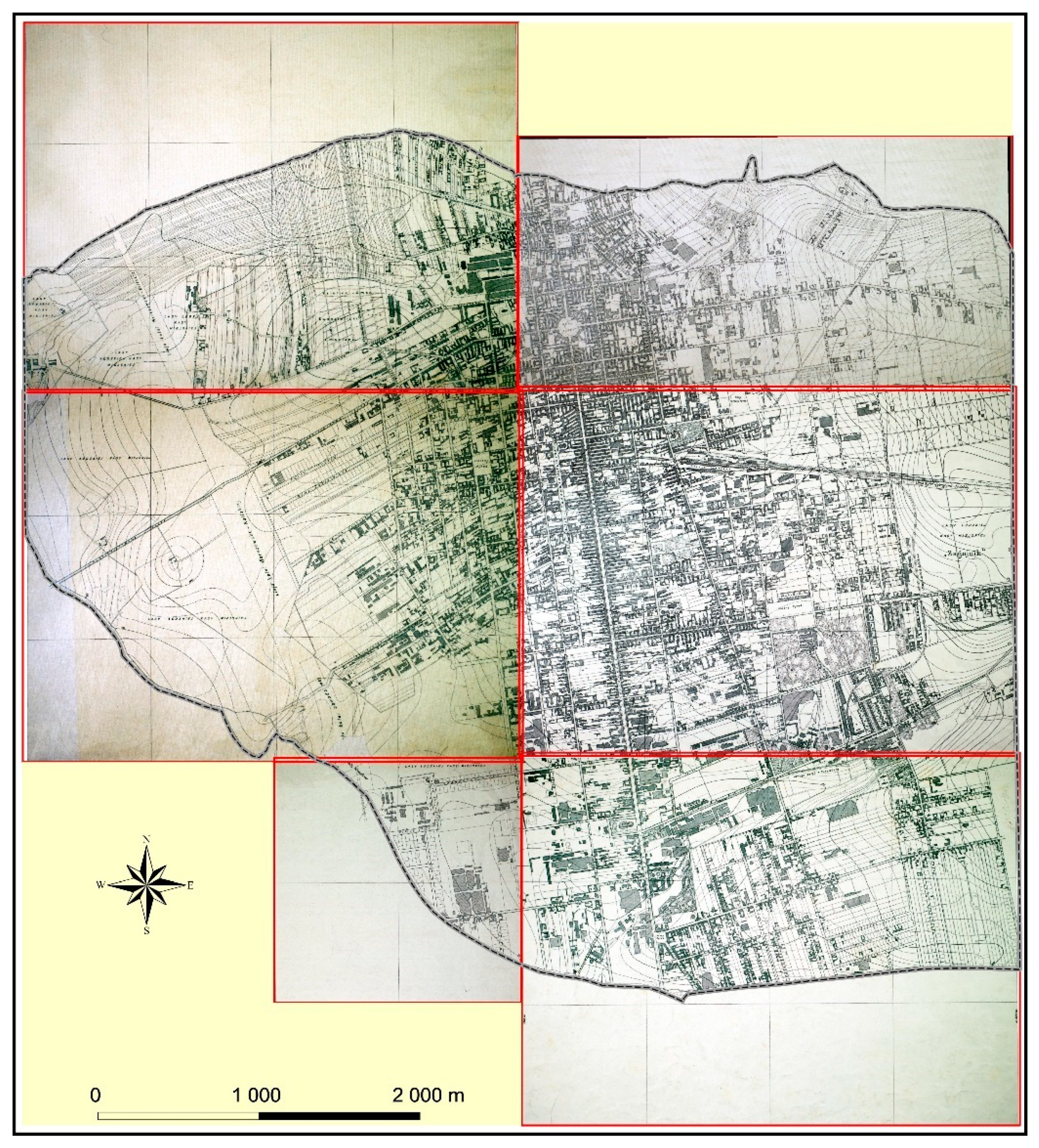
3.1. Historical Model
3.2. The Contemporary Model
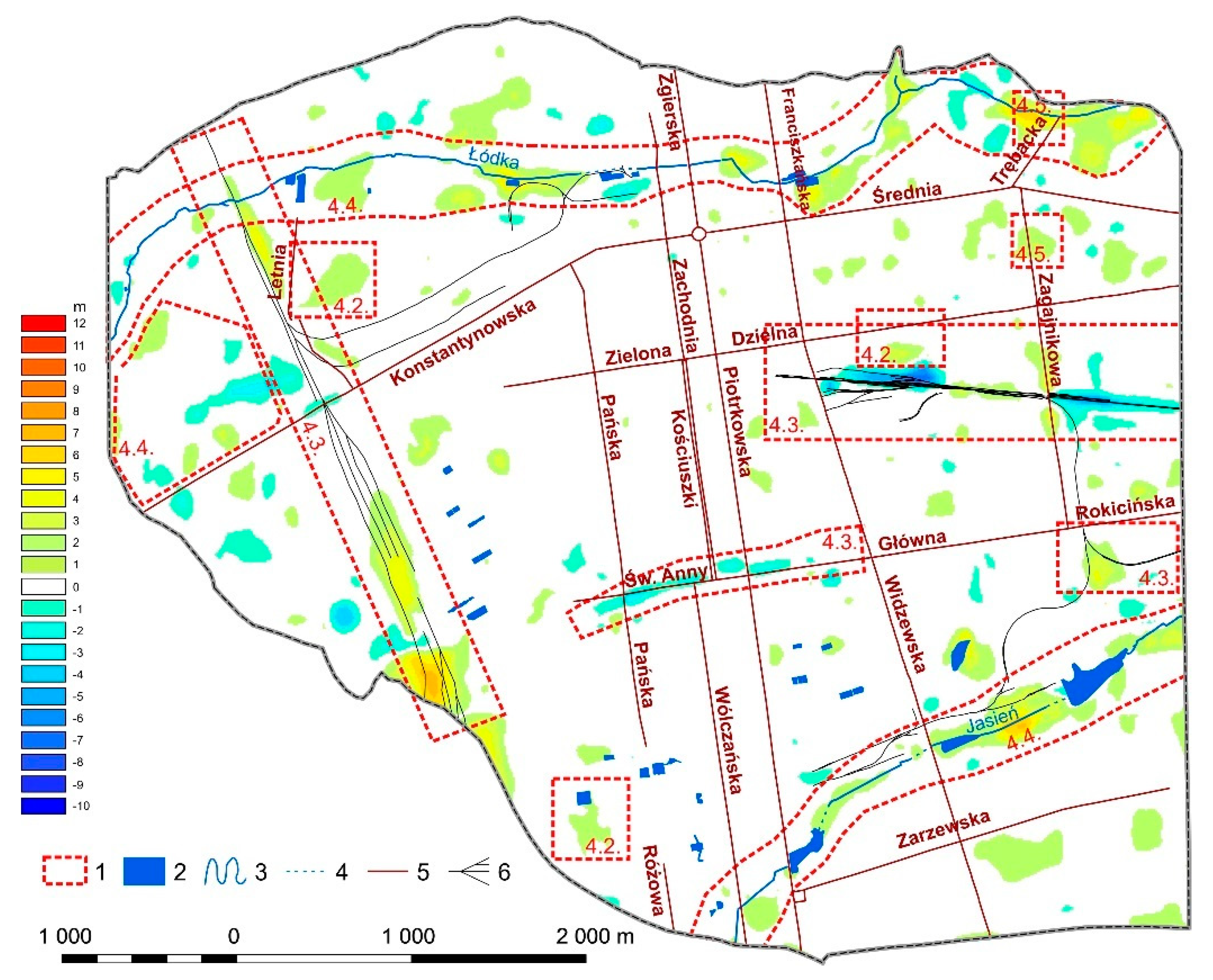
4. Results
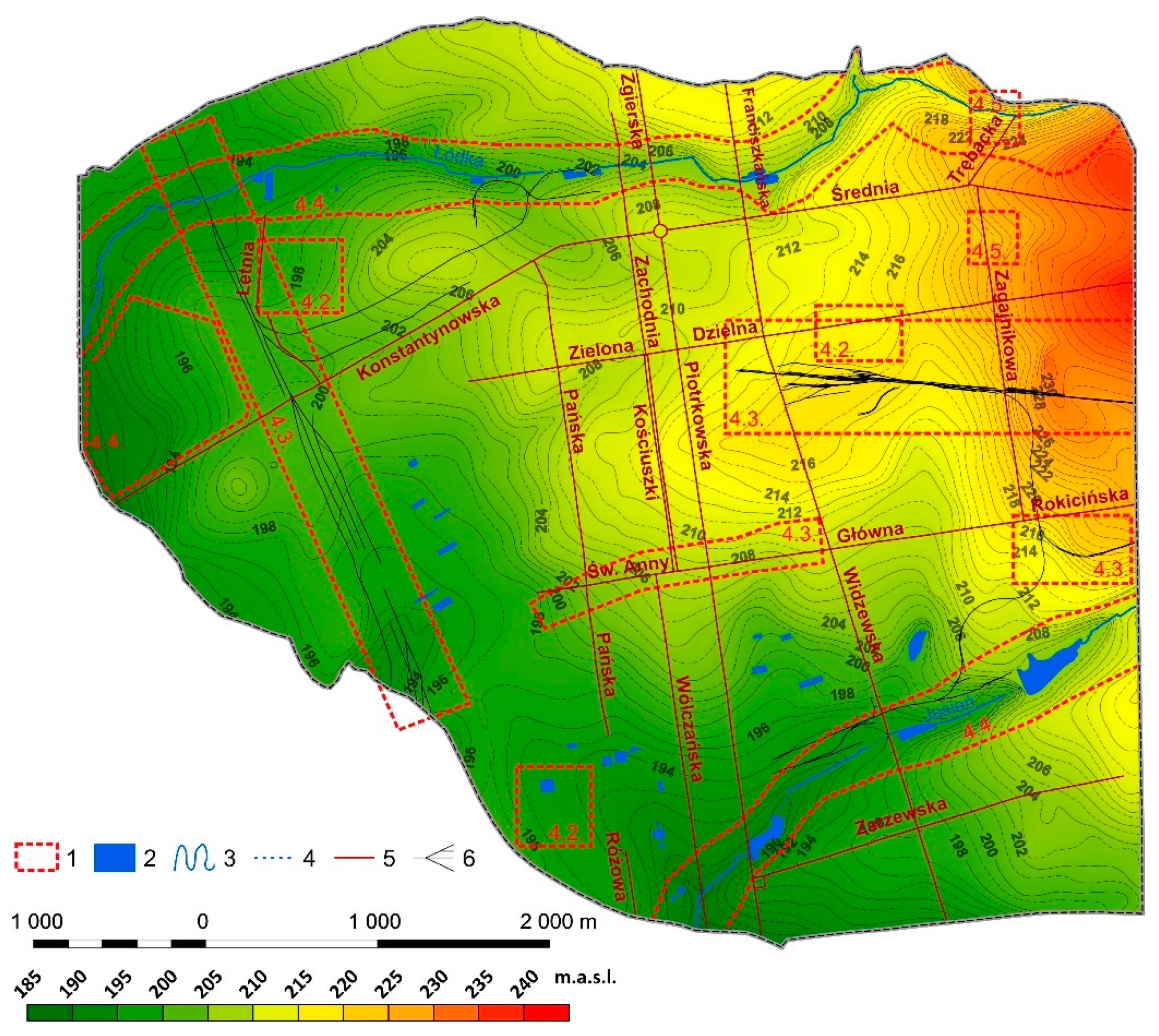
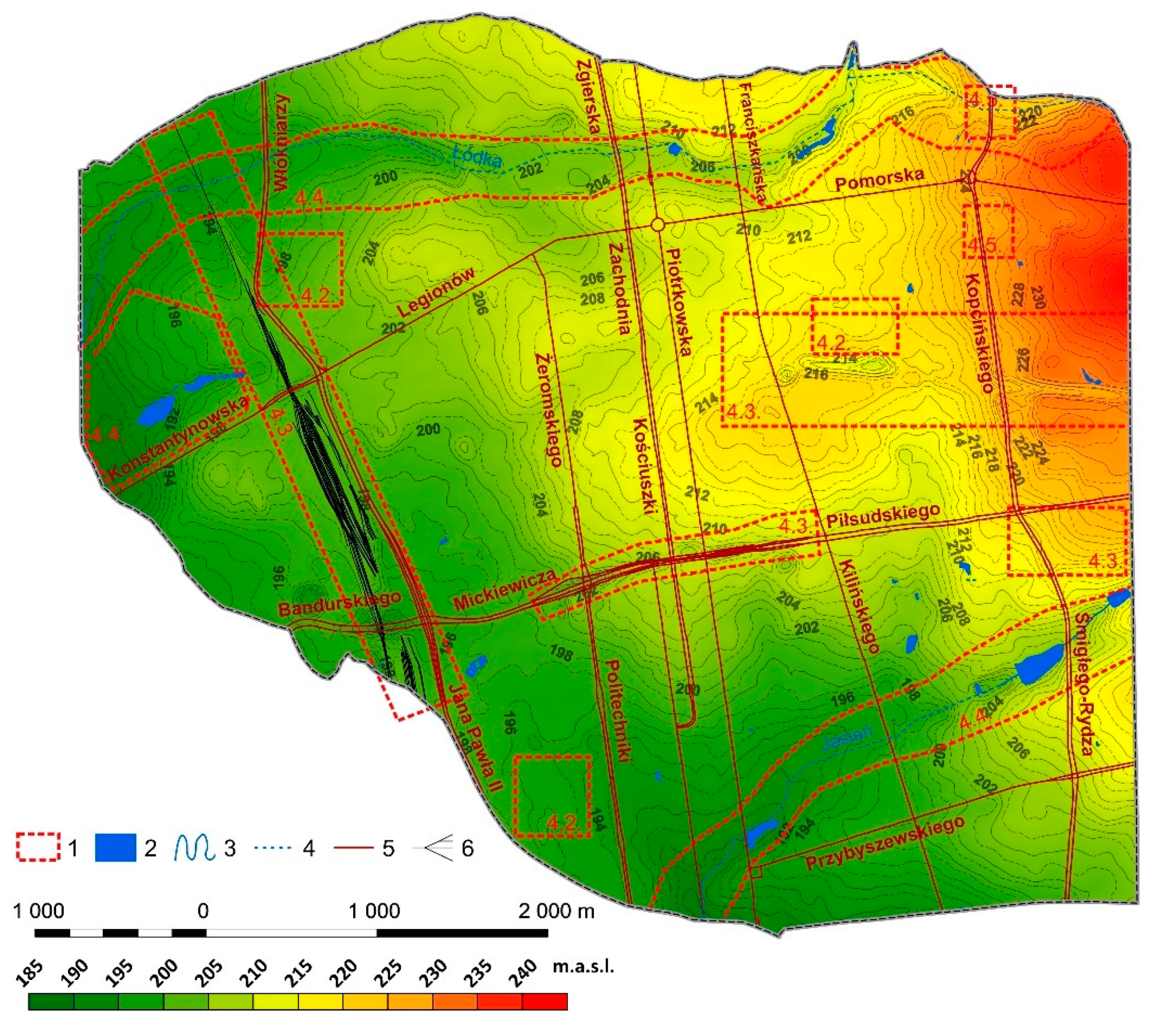
4.1. General Patterns of Relief Changes
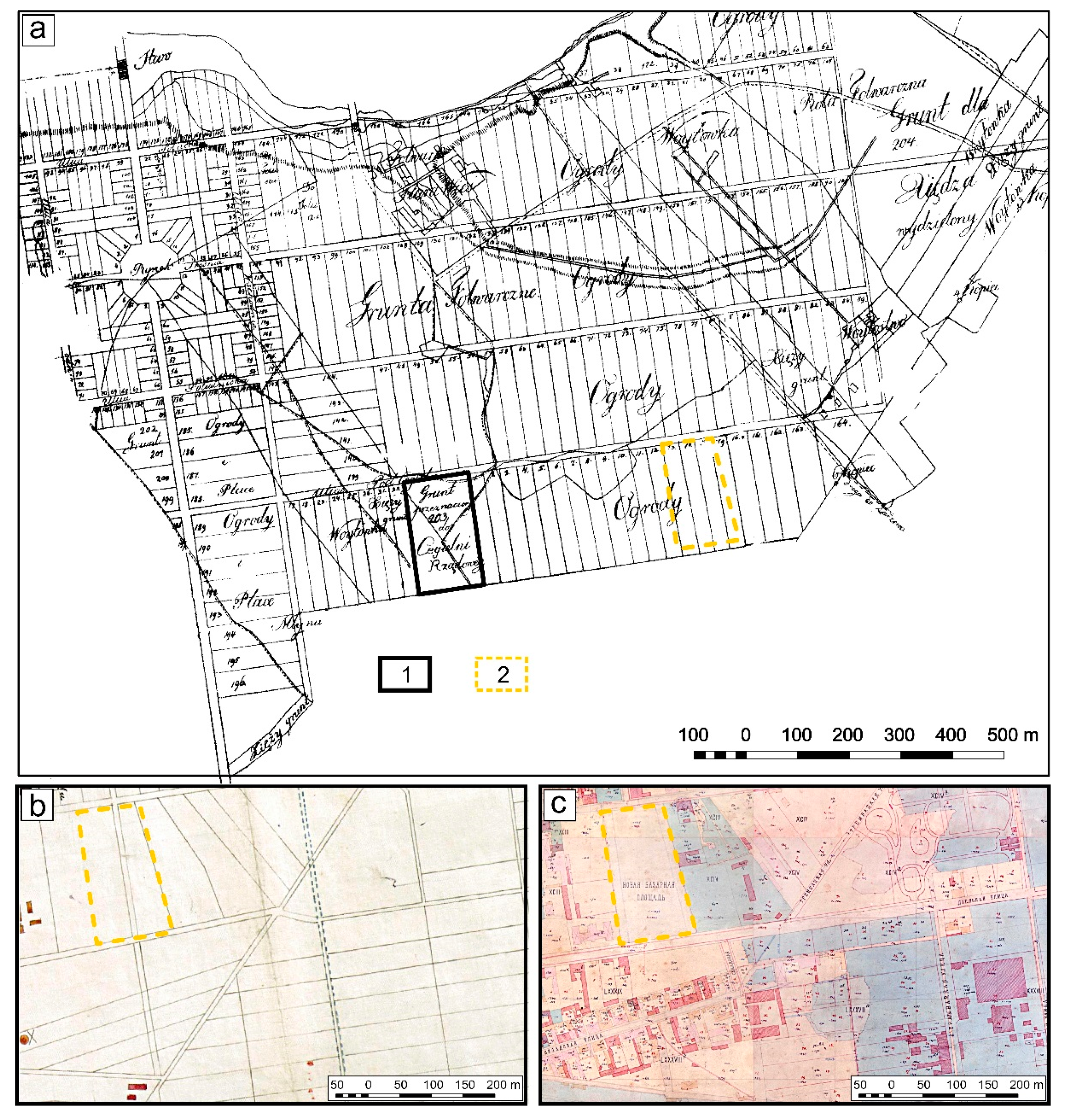
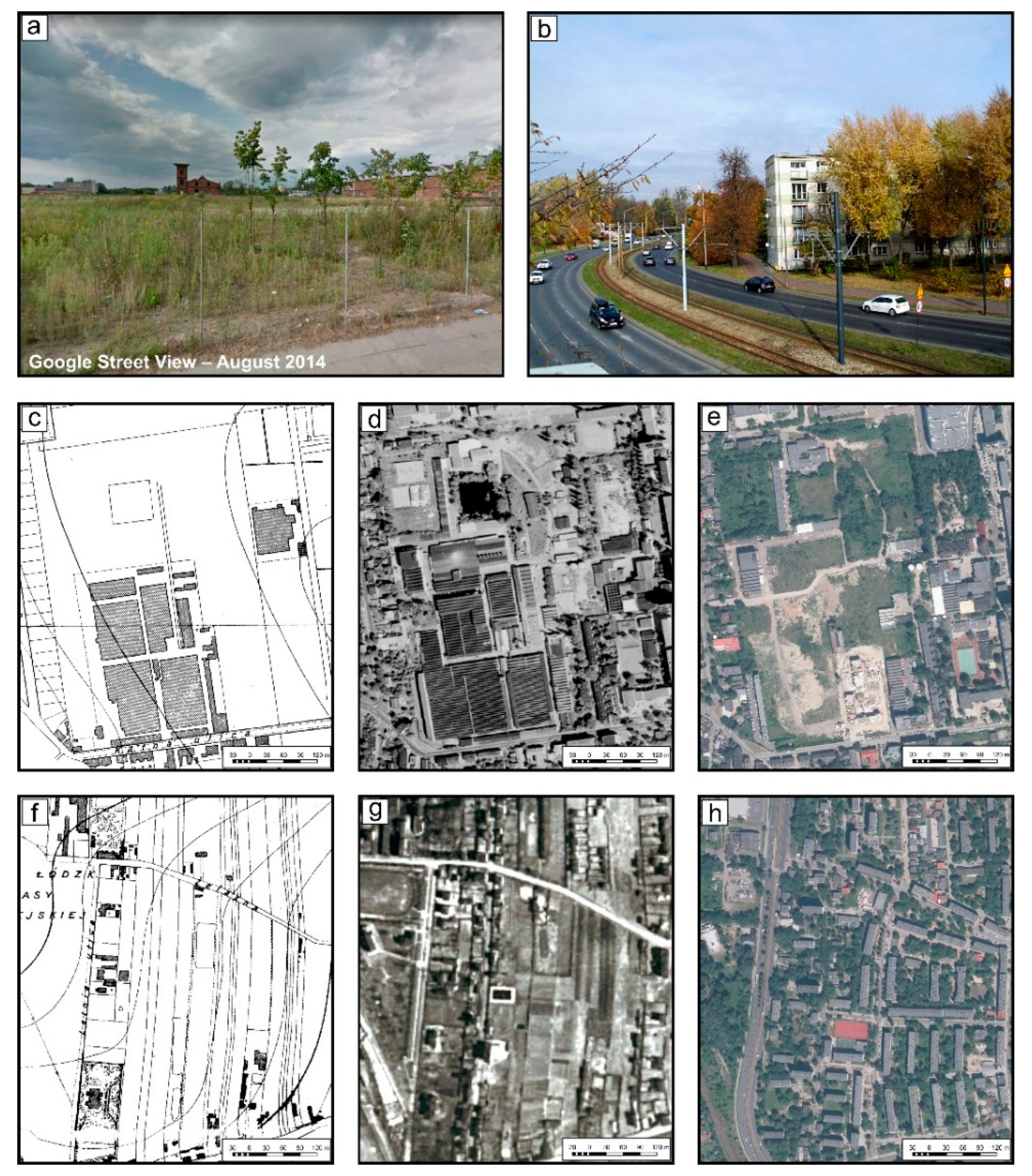
4.2. Elevations Resulting from the Construction or Demolition of Buildings
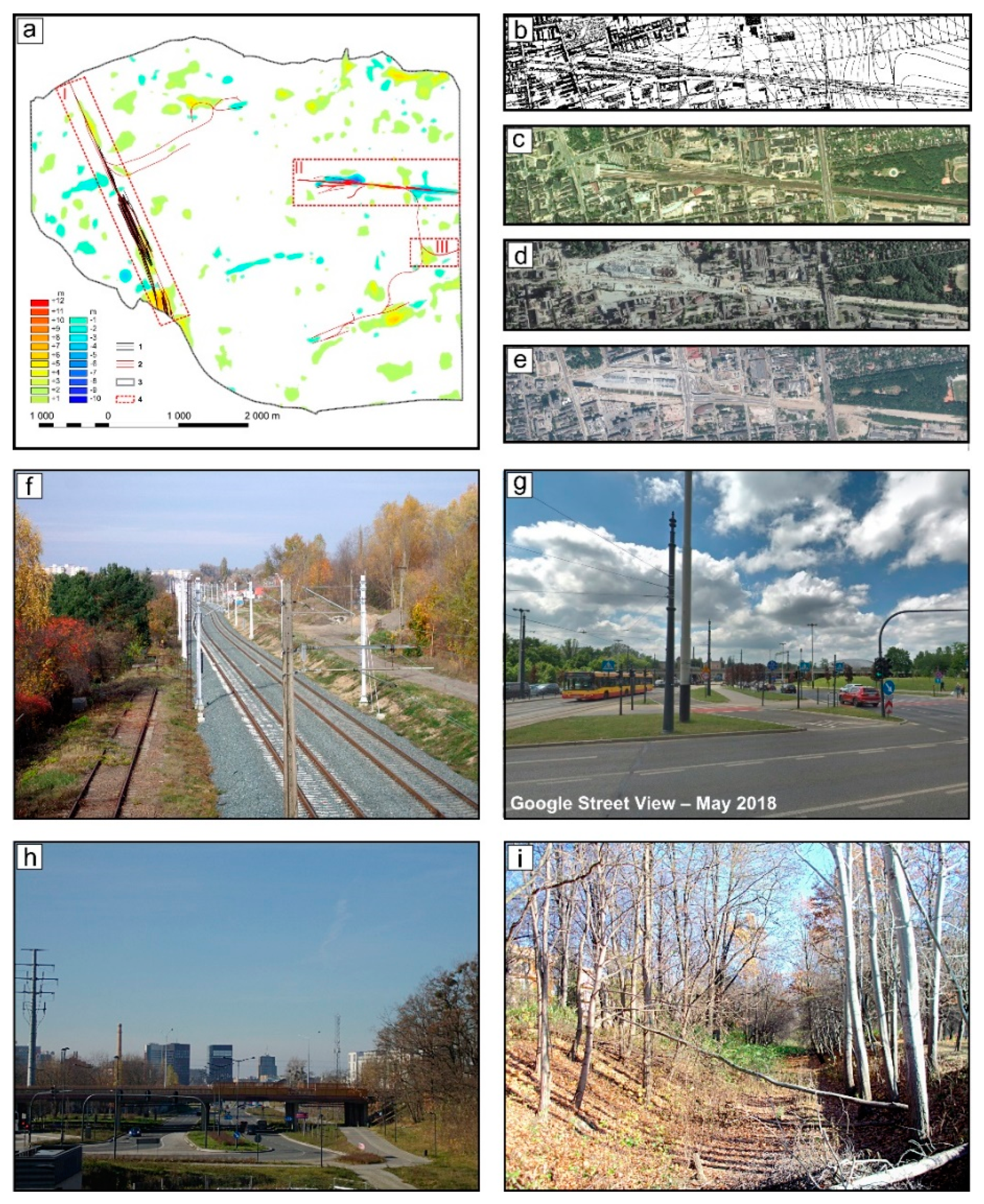
4.3. Changes in Relief Related to the Establishment and Operation of Railways and Roads
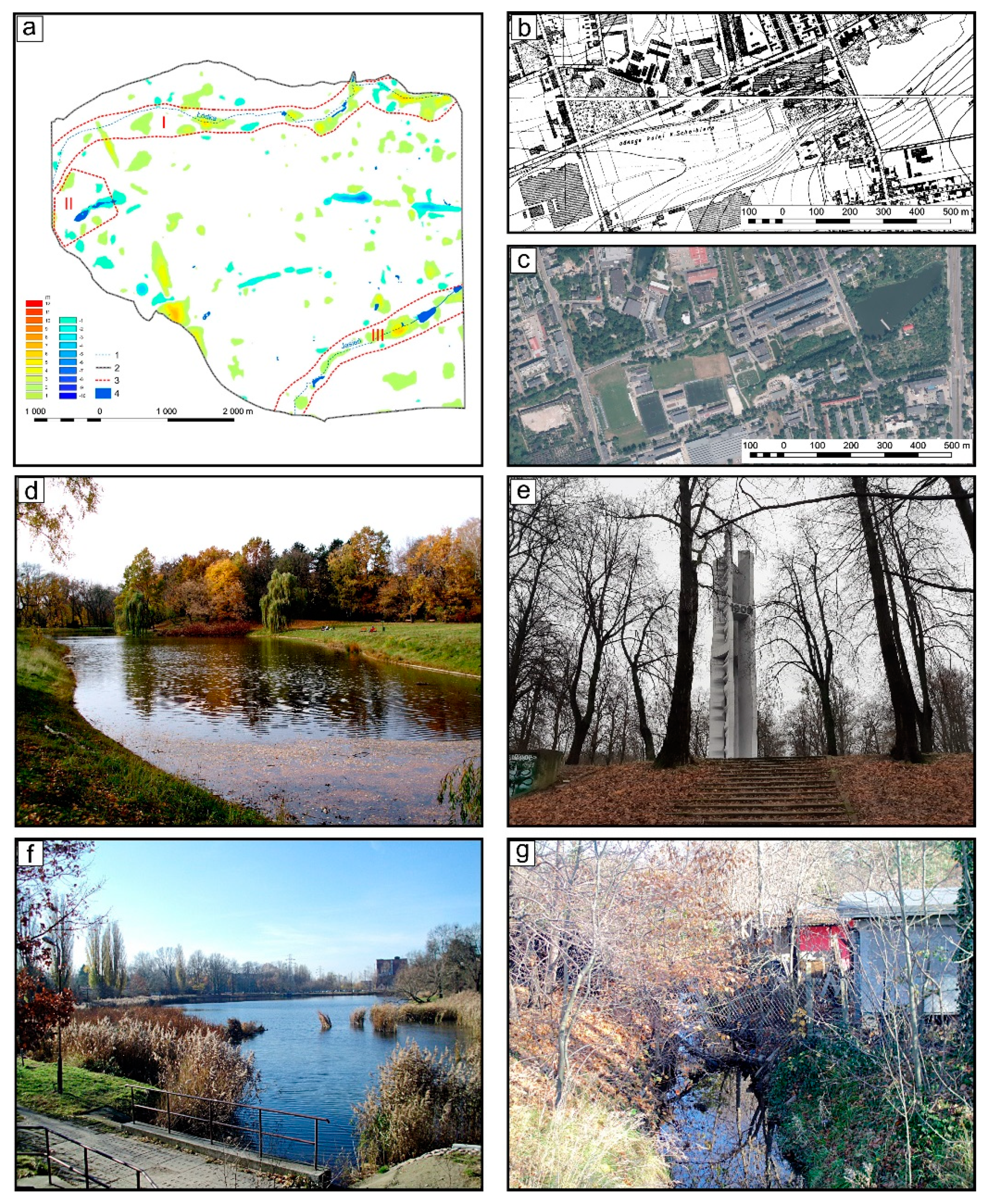
4.4. Changes in Surface Topography in Areas of Former River Valleys
4.5. Changes in Surface Topography on Sites of Former Brickyards, Gravel Pits, Waste Dumps
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- ▪
- In the city centre, the changes in surface relief were minimal. This may be interpreted by the fact that 100 years ago, the downtown area was already in the final stage of urbanisation. Only a few areas—Łódź Fabryczna railway station and Dąbrowskiego square—underwent visible transformations;
- ▪
- Changes in the relief were the result of road and railway investments in the city (viaducts, tunnels, excavations, trenches);
- ▪
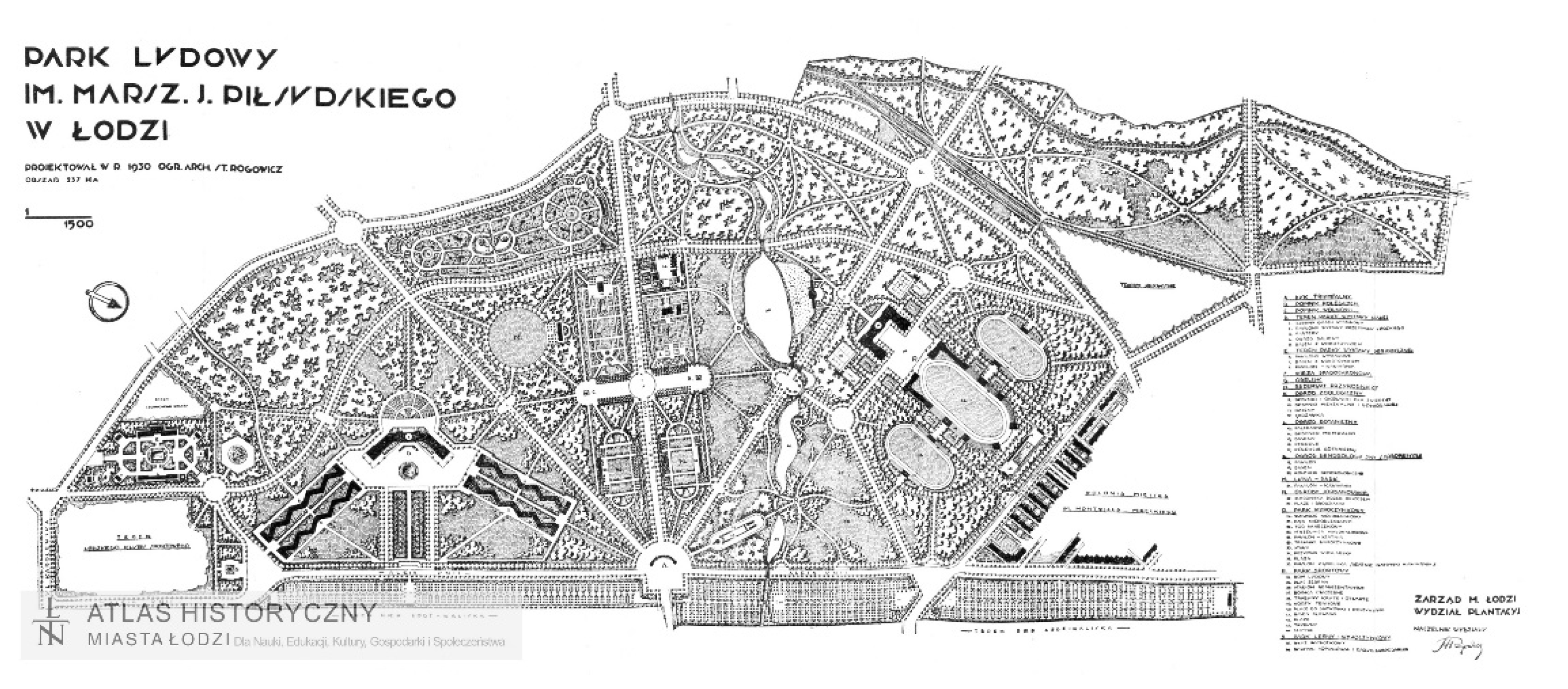
- Changes in surface topography in the former river valley areas resulted from the redirection of water into canals and the creation of ponds for the recreation of the inhabitants in the valley areas;
- ▪
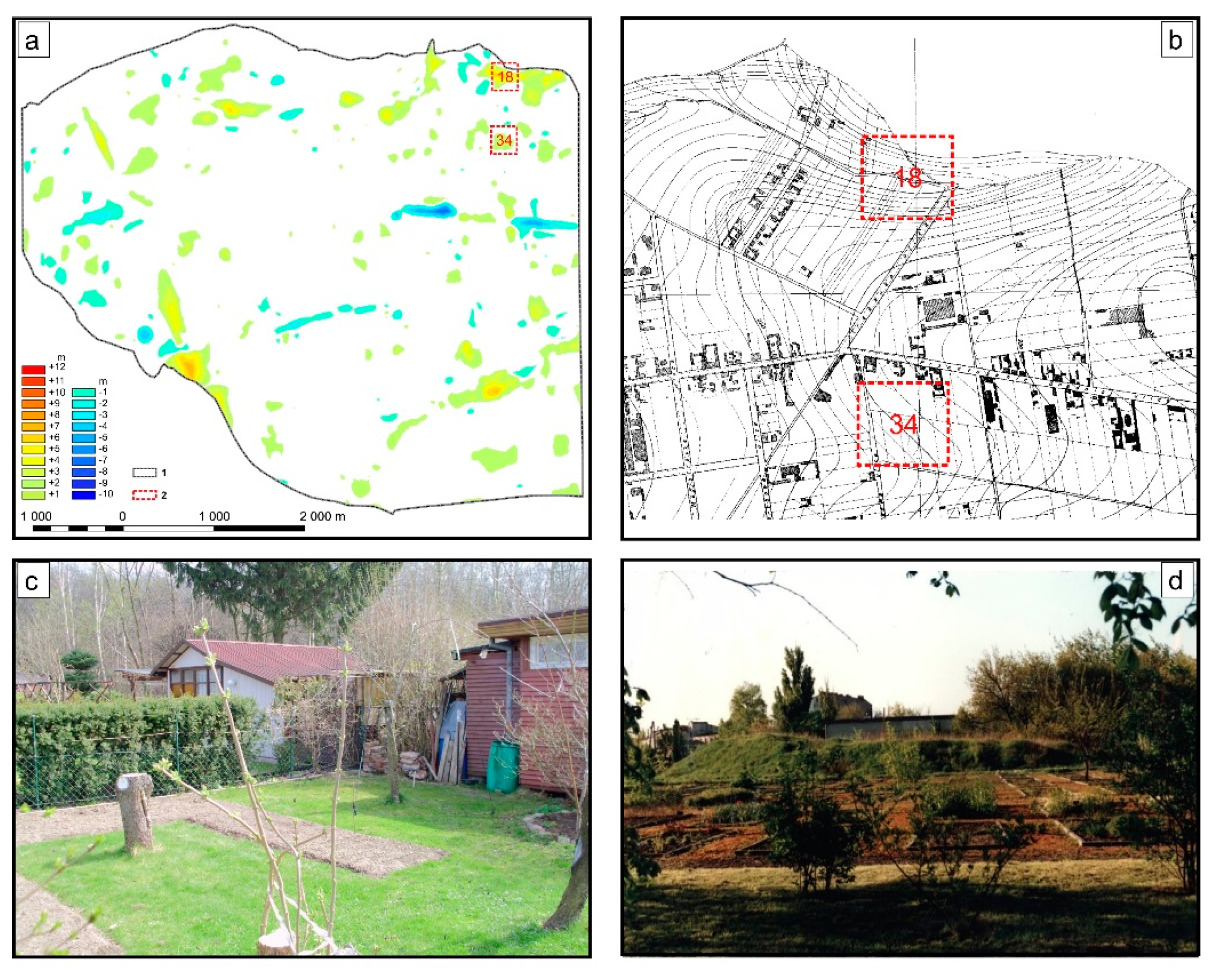
- The changes in surface topography in the areas of former brickyards, gravel pits and waste dumps are a result of land levelling and their use, as for example, allotment gardens;
- ▪
- Changes in the relief resulted from the construction or demolition of buildings (new housing developments, demolition of post-industrial buildings).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wójcik, J. Mining changes on the example of the Wałbrzych Basin relief (The Sudetes, Poland). Zeitschrift Geomorphol. 2013, 57, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowski, J.; Milczarek, W. Analysis of surface changes in the Wałbrzych hard coal mining grounds (SW Poland) between 1886 and 2009. Geol. Q. 2014, 58, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaskulski, M.; Nowak, T. Transformations of landscape topography of the Bełchatów coal mine (Central Poland) and the surrounding area based on DEM analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, C.; Hayakawa, Y.; Obanawa, H. A study of Japanese landscapes using structure from motion derived DSMs and DEMs based on historical aerial photographs: New opportunities for vegetation monitoring and diachronic geomorphology. Geomorphology 2015, 242, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Tien Bui, D.; Sahana, M.; Chen, C.-W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Pham, B.T. Evaluating GIS-Based Multiple Statistical Models and Data Mining for Earthquake and Rainfall-Induced Landslide Susceptibility Using the LiDAR DEM. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kavan, J.; Tallentire, G.D.; Demidionov, M.; Dudek, J.; Strzelecki, M.C. Fifty Years of Tidewater Glacier Surface Elevation and Retreat Dynamics along the South-East Coast of Spitsbergen (Svalbard Archipelago). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulski, M.; Szmidt, A. Transformations in morphometry of valley bottom as a result of the creation of a reservoir illustrated with the example of Sulejów Lake. Landf. Anal. 2014, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacina, J.; Lenďáková, Z.; Štojdl, J.; Matys Grygar, T.; Dolejš, M. Dynamics of Sediments in Reservoir Inflows: A Case Study of the Skalka and Nechranice Reservoirs, Czech Republic. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, L.A.; Hodgson, M.E.; Ghoshal, S.; Latiolais, M.M. Geomorphic change detection using historic maps and DEM differencing: The temporal dimension of geospatial analysis. Geomorphology 2012, 137, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luberti, G.M. Computation of modern anthropogenic-deposit thicknesses in urban areas: A case study in Rome, Italy. Anthr. Rev. 2018, 5, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancewicz, K.; Traczyk, A.; Migoń, P. Landform modifications within an intramontane urban landscape due to industrial activity, Wałbrzych, SW Poland. J. Maps 2021, 17, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łajczak, A.; Zarychta, R.; Wałek, G. Changes in the topography of Krakow city centre, Poland, during the last millennium. J. Maps 2021, 17, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molewski, P.; Juśkiewicz, W. Próba rekonstrukcji pierwotnej rzeźby obszaru Zespołu Staromiejskiego w Toruniu i jego bliskich przedmieść na podstawie geoinformacji geologicznej i historycznej. Landf. Anal. 2014, 25, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, G.; Ostrowski, P.; Bartold, P.; Bujakowski, F.; Falkowski, T.; Osiński, P. Urban geomorphology of the Vistula River valley in Warsaw. J. Maps 2021, 17, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Del Monte, M.; Faccini, F.; Cattoor, B.; Zwoliński, Z.; Smith, M. Geomorphological mapping in urban areas. J. Maps 2021, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, F.; Giardino, M.; Paliaga, G.; Perotti, L.; Brandolini, P. Urban geomorphology of Genoa old city (Italy). J. Maps 2021, 17, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrone, M.; Piana, P.; Paliaga, G.; D’Orazi, M.; Faccini, F. Coupling Historical Maps and LiDAR Data to Identify Man-Made Landforms in Urban Areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, O. Opis Miasta Łodzi: Pod Względem Historycznym, Statystycznym i Przemysłowym; Drukarnia Gazety Codziennej: Łódź, Poland, 1853. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, R. Central Area Activities in a Post-communist City: Lodz, Poland. Urban Stud. 1997, 34, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewski, S. Urban Tourist Penetration Space—An Industrial City Case Study. Econom. Probl. Tour. 2014, 28, 307–324. [Google Scholar]
- Dzieciuchowicz, J. Ludność Łodzi—Rozwój i Przemiany Strukturalne; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Poland, 2014; ISBN 9788379692637. [Google Scholar]
- Puś, W. Dzieje Łodzi Przemysłowej: Zarys Historii; Muzeum Historii Miasta Łodzi: Łódź, Poland; Centrum Informacji Kulturalnej: Poznań, Poland, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Liszewski, S.; Young, C. A Comparative Study of Łódź and Manchester: Geographies of European Cities in Transition; University of Lodz: Łódź, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kulesza, P. Rozbudowa sieci kolejowej jako czynnik rozwoju aglomeracji łódzkiej do 1914 r. Studia z Historii Społeczno-Gospodarczej XIX i XX Wieku 2009, 6, 137–187. [Google Scholar]
- Affek, A.N.; Wolski, J.; Latocha, A.; Zachwatowicz, M.; Wieczorek, M. The use of LiDAR in reconstructing the pre-World War II landscapes of abandoned mountain villages in southern Poland. Archaeol. Prospect. 2022, 29, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, A. Depopulated localities of former east Prussia as isolated components of the landscape structure in the form of clusters of high vegetation. J. Geogr. Polit. Soc. 2019, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solon, J.; Borzyszkowski, J.; Bidłasik, M.; Richling, A.; Badora, K.; Balon, J.; Brzezińska-Wójcik, T.; Chabudziński, Ł.; Dobrowolski, R.; Grzegorczyk, I.; et al. Physico-geographical mesoregions of poland: Verification and adjustment of boundaries on the basis of contemporary spatial data. Geogr. Pol. 2018, 91, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richling, A.; Solon, J.; Macias, A.; Balon, J.; Borzyszkowski, J.; Kistowski, M. Regionalna Geografia Fizyczna Polski; Bogucki Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Poznań, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Turkowska, K. Geomorfologia Regionu łódzkiego; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego: Łódź, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Klajnert, Z. O glacjalnych uwarunkowaniach vistuliańskich przekształceń rzeźby Wyżyny Łódzkiej. Acta Univ. Lodz. Folia Geogr. Phys. 1997, 1, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Goździk, J.; Wieczorkowska, J. Atlas Miasta Łodzi, Plansza VIIII: Rzeźba Terenu; ŁTN: Łódź, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bartnik, A. Główne cechy środowiska geograficznego Łodzi. Położenie geograficzne Łodzi i główne komponenty jej środowiska. In Atlas Historyczny Miasta Łodzi dla Nauki, Edukacji, Kultury, Gospodarki i Społeczeństwa; ŁTN: Łódź, Poland, 2019; ISBN 78-83-60655-93-1. [Google Scholar]
- Łajczak, A.; Zarychta, R.; Wałek, G. Quantitative Assessment of Changes in Topography of Town Caused by Human Impact, Krakow City Centre, Southern Poland. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnik, A. Mała Rzeka w Dużym Mieście. Wybrane Aspekty Obiegu Wody w Obszarze Zurbanizowanym na Przykładzie Łódzkiej Sokołówki; Uniwersytet Łódzki: Łódź, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak, K. Stanislaw Staszic about Łódź and surrounding towns. The reconstruction of lost report from 1825. Rocz. Łódzki 2018, 68, 197–212. [Google Scholar]
- Imhof, E. Cartographic Relief Presentation; Steward, H.J., Ed.; DE GRUYTER: Berlin, Germany, 1982; ISBN 978-3-11-006711-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski, M.; Nalej, M. Preparing Historical Maps for Presentation in a Geoportal. Acta Univ. Lodz. Folia Geogr. Socio-Oecon. 2015, 22, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M. High-Resolution LiDAR-Derived DEMs in Hydrografic Network Extraction and Short-Time Landscape Changes. In Computational Science and Its Applications—CCSA 2020, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference, Cagliari, Italy, 1–4 July 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 723–737. [Google Scholar]
- Florinsky, I.V. Accuracy of local topographic variables derived from digital elevation models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1998, 12, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Mohanty, K.K.; Kumar, D.; Banerjee, R. Monitoring surface elevation changes in Jharia coalfield, India using synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koter, M. Geneza Układu Przestrzennego Łodzi Przemysłowej; Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Warszawa, Poland, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Jerczyński, M.; Roszak, T. Szlakiem Łódzkiej Kolei; Piątek Trzynastego Wydawnictwo: Łódź, Poland, 2004; ISBN 83-8874-290-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bartnik, D. The Lindley plans of Łódź water supply and sewage system in the collection of Łódź University Library. Z Dziejów Kartogr. 2011, 15, s137–s152. [Google Scholar]
- Kobojek, E. Wpływ terenów poeksploatacyjnych na rozwój przestrzenny i zagospodarowanie miasta na przykładzie Łodzi. Space-Soc.-Econ. 2021, 32, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolaniuk, A. Gardening plots in Łódź as a recreational area for the city’s dwellers. Turyzm/Tourism 1991, 1, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaskulski, M.; Jażdżewska, I.; Szmidt, A. Changes in Land Relief in Urbanised Areas Using Laser Scanning and Archival Data on the Example of Łódź (Poland). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14132961
Jaskulski M, Jażdżewska I, Szmidt A. Changes in Land Relief in Urbanised Areas Using Laser Scanning and Archival Data on the Example of Łódź (Poland). Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14132961
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaskulski, Marcin, Iwona Jażdżewska, and Aleksander Szmidt. 2022. "Changes in Land Relief in Urbanised Areas Using Laser Scanning and Archival Data on the Example of Łódź (Poland)" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14132961
APA StyleJaskulski, M., Jażdżewska, I., & Szmidt, A. (2022). Changes in Land Relief in Urbanised Areas Using Laser Scanning and Archival Data on the Example of Łódź (Poland). Remote Sensing, 14(13), 2961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14132961