Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth Measured by Sun Photometer at a Rural Site near Beijing during the 2017–2019 Period
Abstract
:1. Introduction
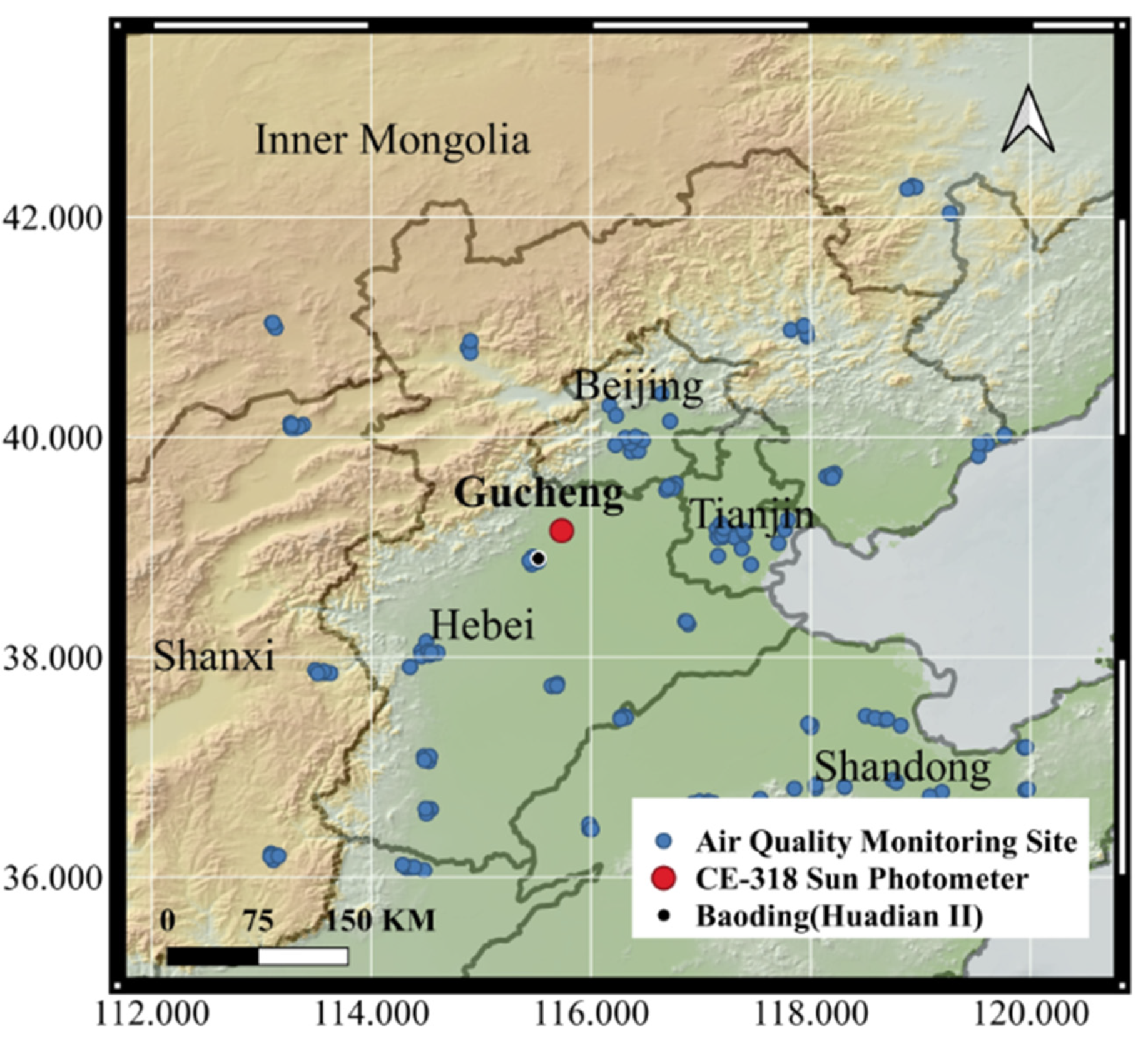
2. Data and Methods
2.1. CE-318 AOD
2.1.1. CE-318 AOD Acquisition Principle
2.1.2. CE-318 AOD Data Description
2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.1. AHI AOD
2.2.2. MODIS AOD
2.3. Other Data
2.4. Temporal Window Selection
3. Results and Discussion
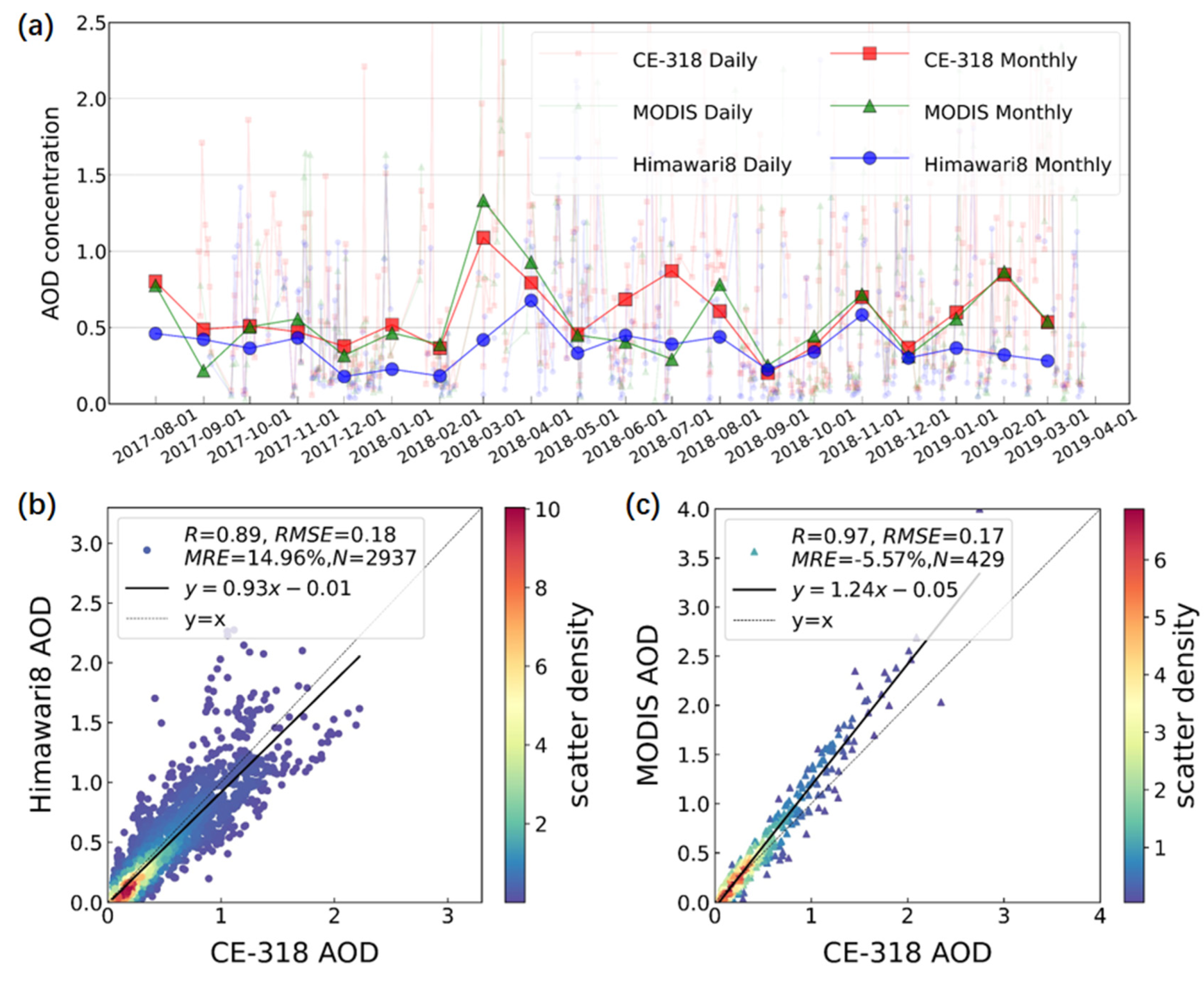
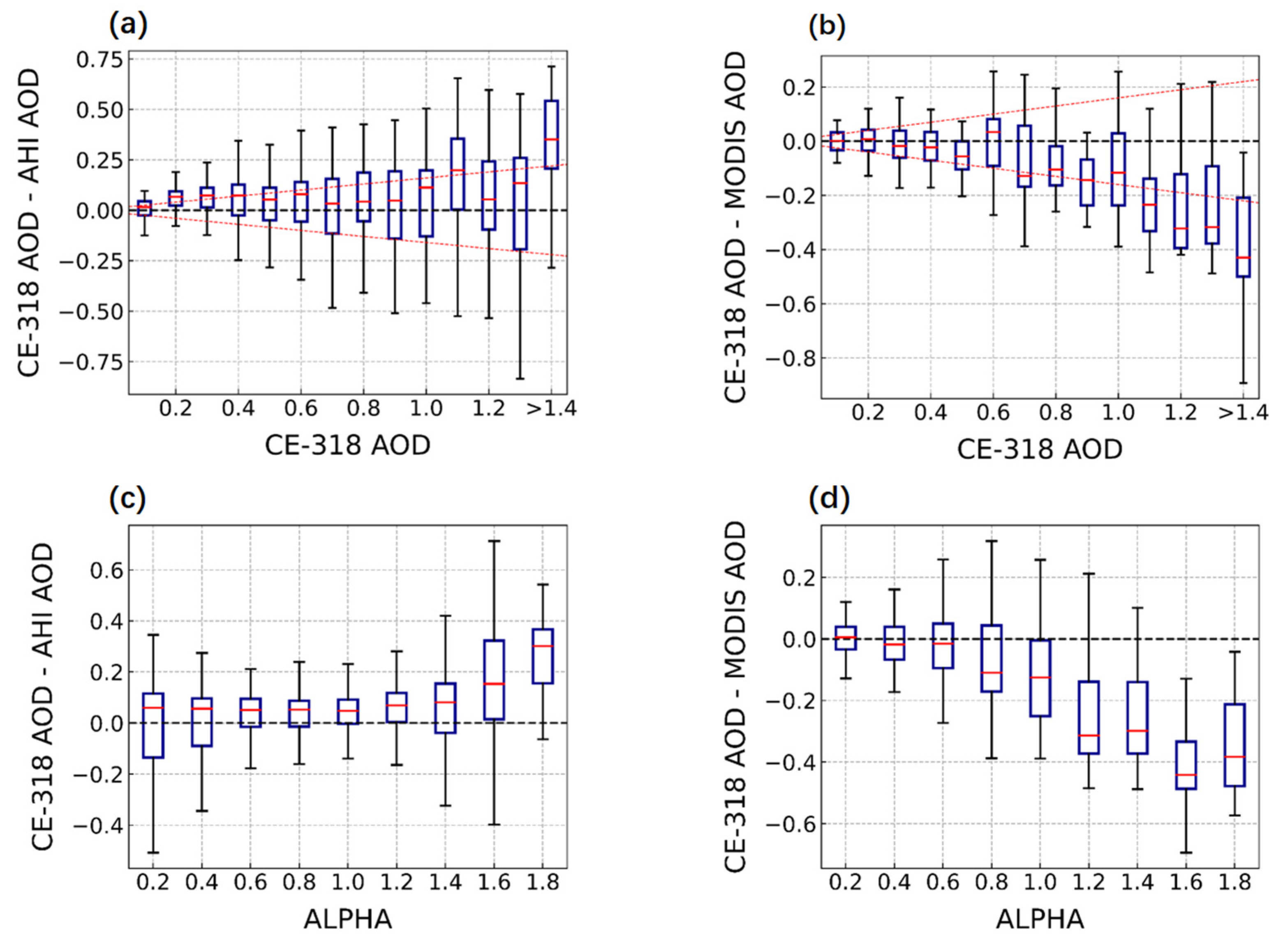
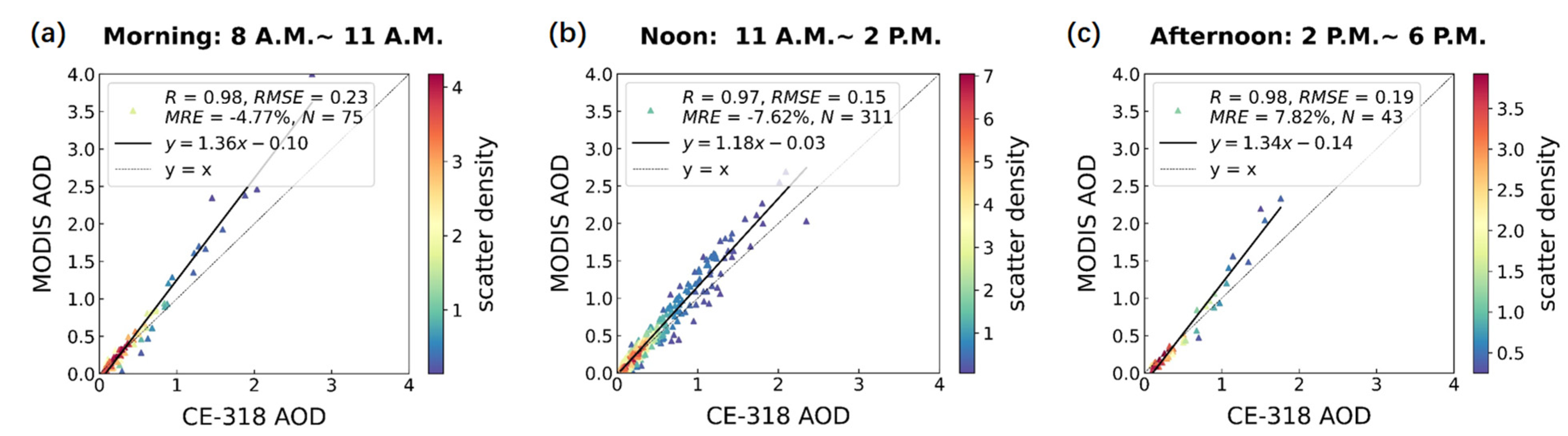
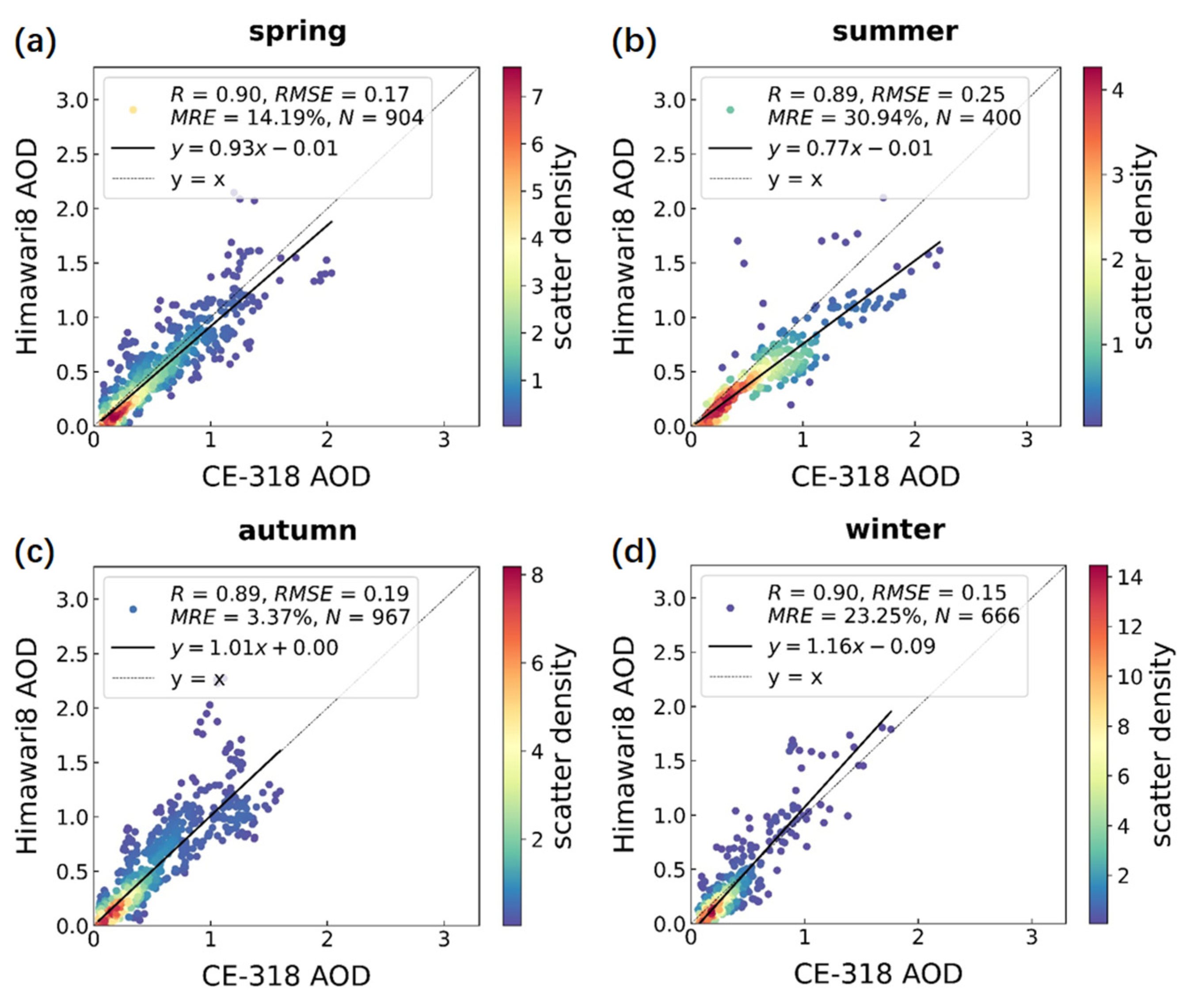
3.1. Comparison and Validation of AHI, MODIS, and CE-318 AOD Inversions
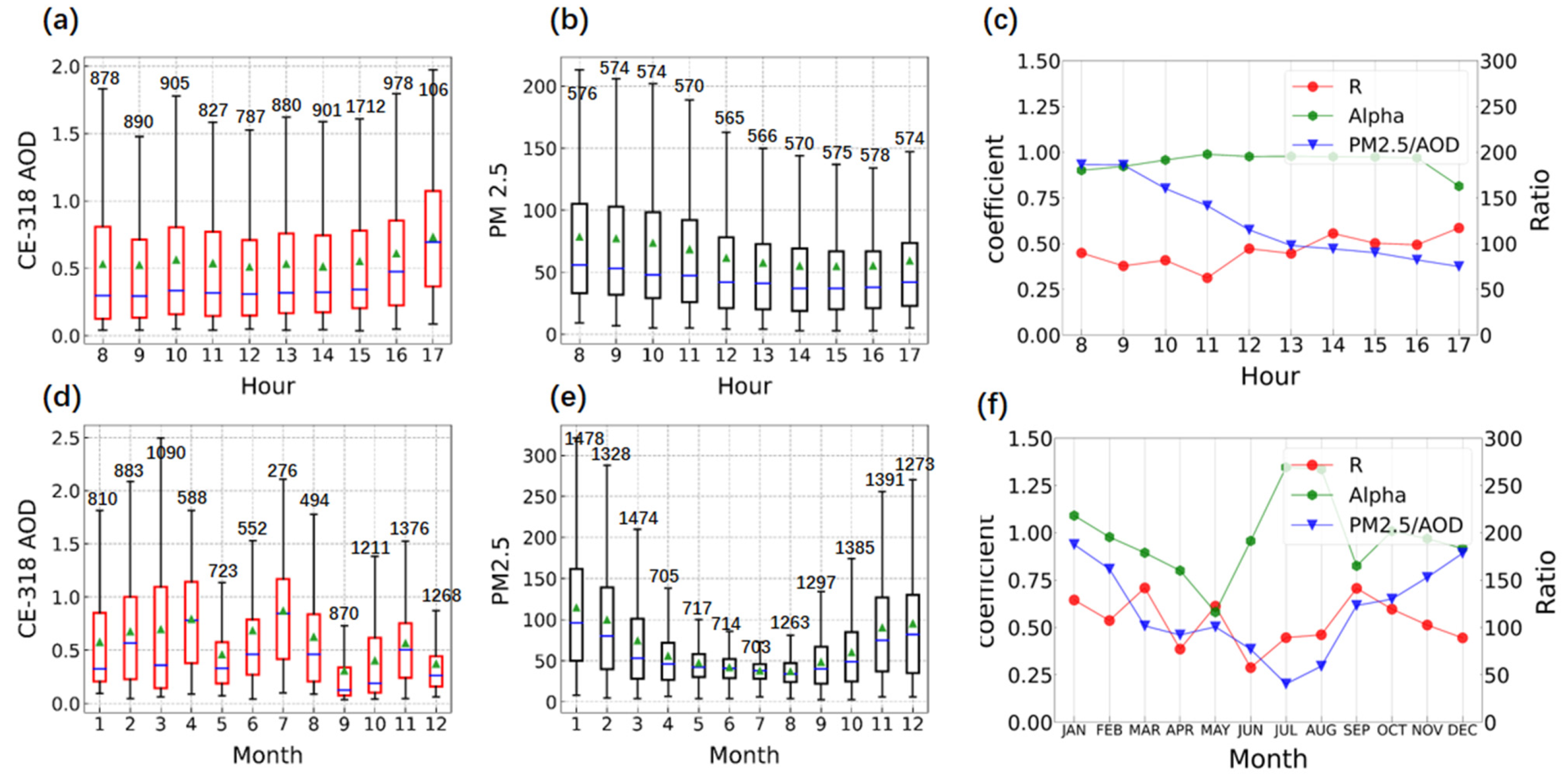
3.2. Comparison of CE-318 AOD and PM2.5 of CNEMC Air Quality Site Validation
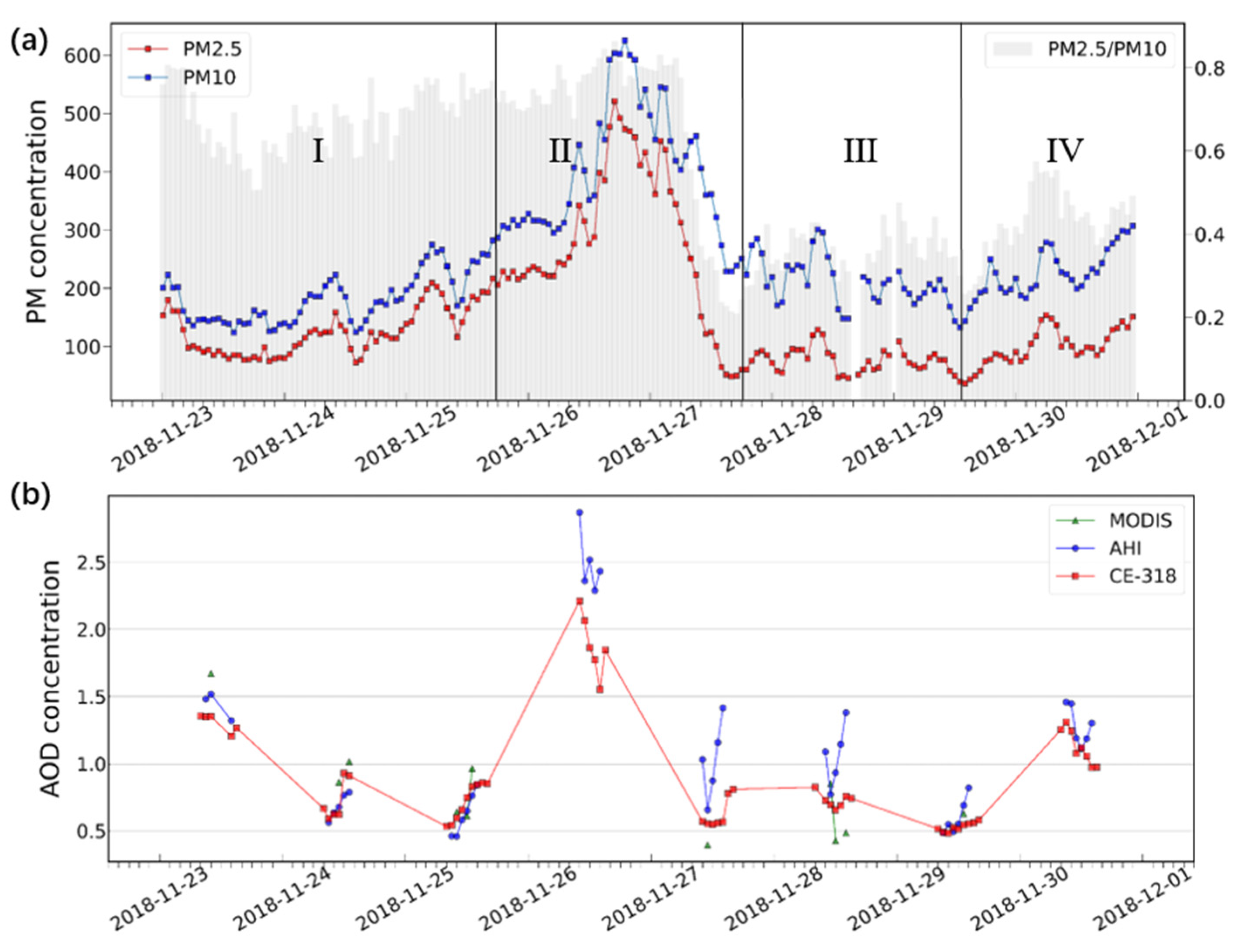
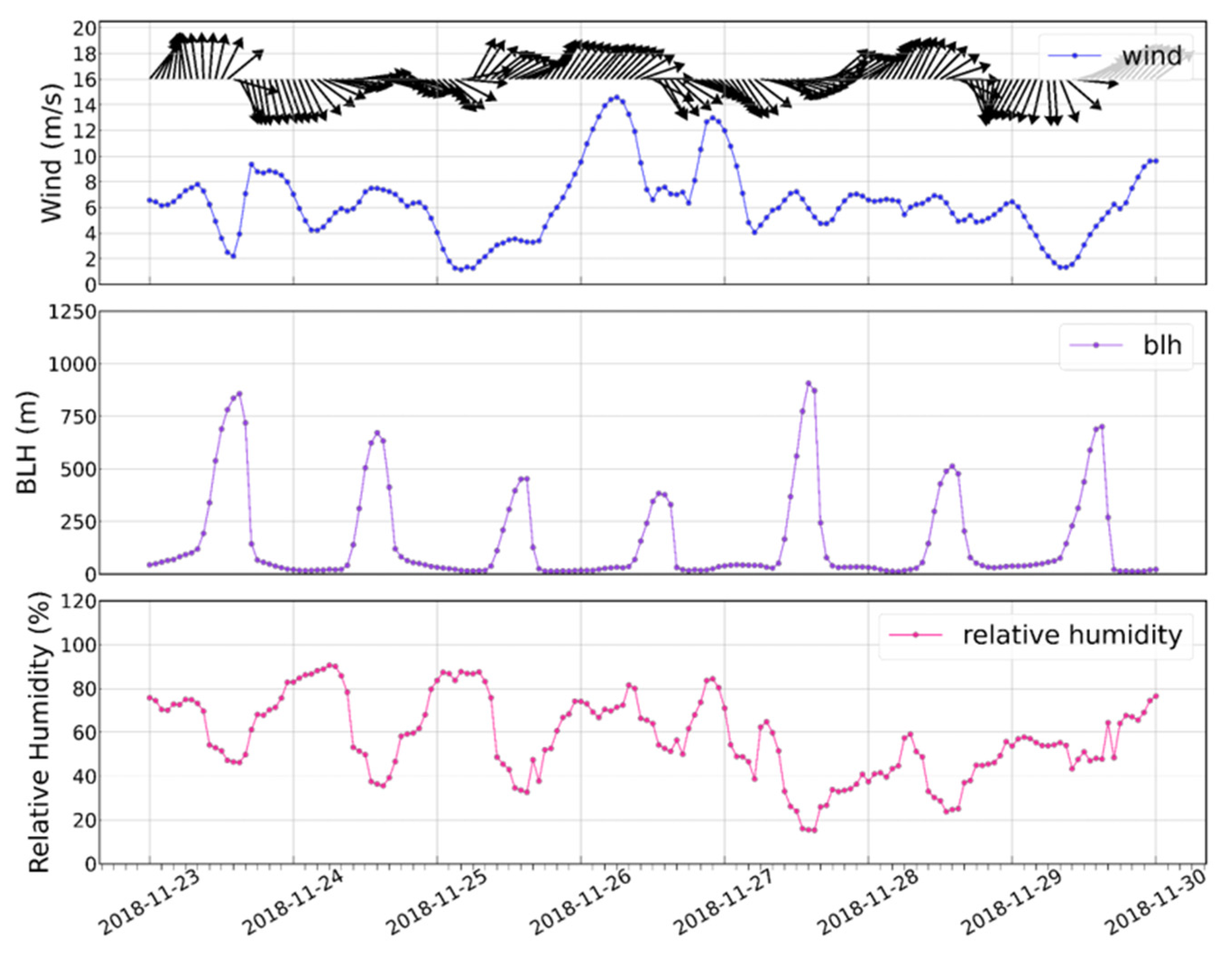
3.3. Analysis of a Pollution Event in Late Autumn in the North China Plain
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, X.; Bing, H.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L. Impacts of atmospheric particulate matter pollution on environmental biogeochemistry of trace metals in soil-plant system: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodny, J.; Tutak, M. Analysis of the diversity in emissions of selected gaseous and particulate pollutants in the European Union countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnick, F.; Pikmann, J.; Fachinger, F.; Moormann, L.; Sprang, F.; Borrmann, S. Aerosol filtration efficiency of household materials for homemade face masks: Influence of material properties, particle size, particle electrical charge, face velocity, and leaks. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cao, L.-M.; Tang, M.-X.; Huang, X.-F.; Saikawa, E.; He, L.-Y. Characterization of organic aerosol at a rural site in the North China Plain region: Sources, volatility and organonitrates. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Lin, C.; Duan, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yan, J.; Xu, W. Primary emissions versus secondary formation of fine particulate matter in the most polluted city (Shijiazhuang) in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2283–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E.; Harrison, M.A.; Olariu, R.-I.; Arsene, C. Photochemical reactions in the tropospheric aqueous phase and on particulate matter. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.; Gryspeerdt, E.; Kinne, S.; Stier, P.; Watson-Parris, D.; Boucher, O.; Carslaw, K.S.; Christensen, M.; Daniau, A.L. Bounding global aerosol radiative forcing of climate change. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Rosenfeld, D.; Liu, X. Review of aerosol–cloud interactions: Mechanisms, significance, and challenges. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 4221–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hu, M.; Zhu, T. Role of secondary aerosols in haze formation in summer in the Megacity Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 31, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, M.; Shang, D.; Wu, Z.; Du, Z.; Tan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, R. Explosive secondary aerosol formation during severe haze in the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2189–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Akimoto, H.; Uno, I. Neutralization of soil aerosol and its impact on the distribution of acid rain over east Asia: Observations and model results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ACH 6-1–ACH 6-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, J.; Ruan, Z.; Yin, P.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Lin, H. Changes in life expectancy of respiratory diseases from attaining daily PM2.5 standard in China: A nationwide observational study. Innovation 2020, 1, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.-Y.; Li, W.-K.; Li, J.-S.; Hong, Q.-H.; Khodahemmati, S.; Gao, J.-F.; Zhou, Z.-X. Effects of DNA damage and oxidative stress in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to PM2.5 from Beijing, China, in winter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mao, C. Spatial effect of industrial energy consumption structure and transportation on haze pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jia, X.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, P.; Su, J. Regional atmospheric pollutant transport mechanisms over the North China Plain driven by topography and planetary boundary layer processes. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 221, 117098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bei, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.; Le, T.; Zuo, M. Insights into particulate matter pollution in the North China Plain during wintertime: Local contribution or regional transport? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2229–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Chang, M.; Guo, P.; Gu, M.; Li, Y. Analysis of air quality characteristics of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei and its surrounding air pollution transport channel cities in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Liao, H. Severe winter haze days in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region from 1985 to 2017 and the roles of anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10801–10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Ning, M.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Defending blue sky in China: Effectiveness of the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” on air quality improvements from 2013 to 2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Tan, X.; Tian, X.; Shi, L. Does the “Blue Sky Defense War Policy” Paint the Sky Blue?—A Case Study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Ge, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, F.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J.; Xie, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W. Characterization of black carbon-containing fine particles in Beijing during wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froyd, K.D.; Murphy, D.M.; Brock, C.A.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Dibb, J.E.; Jimenez, J.-L.; Kupc, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schill, G.P.; Thornhill, K.L. A new method to quantify mineral dust and other aerosol species from aircraft platforms using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6209–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, L.; Bleiweiss, M.P.; Shen, X.; Campbell, J.R.; Lolli, S. Evaluation of Terra-MODIS C6 and C6. 1 aerosol products against Beijing, XiangHe, and Xinglong AERONET sites in China during 2004–2014. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tegen, I.; Hollrig, P.; Chin, M.; Fung, I.; Jacob, D.; Penner, J. Contribution of different aerosol species to the global aerosol extinction optical thickness: Estimates from model results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23895–23915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioris, C.E.; Abboud, I.; Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A. AEROCAN, the Canadian sub-network of AERONET: Aerosol monitoring and air quality applications. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.; Solomon, S.; Barnes, J.; Burlakov, V.; Deshler, T.; Dolgii, S.; Herber, A.B.; Nagai, T.; Neely, R., III; Nevzorov, A. Total volcanic stratospheric aerosol optical depths and implications for global climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7763–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Chen, L. Performance of MODIS high-resolution MAIAC aerosol algorithm in China: Characterization and limitation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, J.C.; Bottino, M.J.; De Souza, J.M. A simplified physical model for assessing solar radiation over Brazil using GOES 8 visible imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D02211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, X. MODIS AOD sampling rate and its effect on PM2.5 estimation in North China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V. Satellite remote sensing of surface air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7823–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.A.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Estellés, V.; Tomasi, C.; Nakajima, T.; Malvestuto, V.; Martínez-Lozano, J.A. Application of the SKYRAD Improved Langley plot method for the in situ calibration of CIMEL Sun-sky photometers. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 2688–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q. Comprehensive study of optical, physical, chemical, and radiative properties of total columnar atmospheric aerosols over China: An overview of Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET) measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X. Long-term validation of MODIS C6 and C6. 1 Dark Target aerosol products over China using CARSNET and AERONET. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozovsky, I.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Heese, B.; Engelmann, R.; Hofer, J.; Baars, H.; Schechner, Y.; Lyapustin, A.; Chudnovsky, A. Impact of aerosol layering, complex aerosol mixing, and cloud coverage on high-resolution MAIAC aerosol optical depth measurements: Fusion of lidar, AERONET, satellite, and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.M.; Pio, C.; Freitas, M.C.; Reis, M.; Trancoso, M.A. Approaching PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 source apportionment by mass balance analysis, principal component analysis and particle size distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.-H.; Shi, M.-H.; Lian, Y.-X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Fang, D.; Ma, G.; Nie, C.; Krafft, T.; He, L.; Wang, Y. Monitoring history and change trends of ambient air quality in China during the past four decades. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Gupta, P.; Wang, K.; Jena, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Using gap-filled MAIAC AOD and WRF-Chem to estimate daily PM2.5 concentrations at 1 km resolution in the Eastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W. Meteorological parameters and gaseous pollutant concentrations as predictors of daily continuous PM2.5 concentrations using deep neural network in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Sun, Z. Evaluation and improvement of MODIS aerosol optical depth products over China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Q.; Yoo, E.-H. Ground PM2.5 prediction using imputed MAIAC AOD with uncertainty quantification. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Che, H.; Wu, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, M. Mitigating MODIS AOD non-random sampling error on surface PM2.5 estimates by a combined use of Bayesian Maximum Entropy method and linear mixed-effects model. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, M.I.; Kim, G.; Im, J.; Song, C.K. Air Quality Forecasts Improved by Combining Data Assimilation and Machine Learning With Satellite AOD. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, C.; Geng, F.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Pei, Z. Aerosol optical properties retrieved from Sun photometer measurements over Shanghai, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D16204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, N.C.; Herman, J.; Torres, O.; Holben, B.; Tanre, D.; Eck, T.; Smirnov, A.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F. Comparisons of the TOMS aerosol index with Sun-photometer aerosol optical thickness: Results and applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 6269–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, F. Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth validation of the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D03206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, Z.A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.; Kaufmaq, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from aerosol robotic network (aeronet) sun and sky radiance measurments. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-Screening and Quality Control Algorithms for the AERONET Database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Himawari–8/9 Himawari Standard Data User’s Guide (Version 1.3); Japan Meteorological Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2017.
- Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Chan, K.K.Y.; Xu, B. Himawari-8/AHI and MODIS aerosol optical depths in China: Evaluation and comparison. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Assessment of Himawari-8 AHI aerosol optical depth over land. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Che, H.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and possible uncertainty source analysis of JAXA Himawari-8 aerosol optical depth product over China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Nakajima, T.Y. Development of an unbiased cloud detection algorithm for a spaceborne multispectral imager. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D07206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Nagao, T.M.; Murakami, H.; Nomaki, T.; Higurashi, A. Common retrieval of aerosol properties for imaging satellite sensors. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2018, 96B, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, M.; Murakami, H.; Suzuki, K.; Nagao, T.M.; Higurashi, A. Improved hourly estimates of aerosol optical thickness using spatiotemporal variability derived from Himawari-8 geostationary satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3442–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Holben, B. Global monitoring of air pollution over land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y. MODIS Multi-Angle Implementation of Atmospheric Correction (MAIAC) Data User’s Guide; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018.
- Uppala, S.M.; Kållberg, P.; Simmons, A.J.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.C.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Luo, N.; Zhao, W.; Shi, W.; Yan, X. Evaluation and Comparison of Himawari-8 L2 V1. 0, V2. 1 and MODIS C6. 1 aerosol products over Asia and the oceania regions. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Fan, M.; Tao, M.; Wei, J.; Jin, J.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q. Validation of Himawari-8 aerosol optical depth retrievals over China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Evaluation of the multi-angle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC) aerosol algorithm for Himawari-8 data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Li, R.-B.; Tian, X.-P.; Wei, J. Analysis of the temporal and spatial variation of aerosols in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region with a 1 km AOD product. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Cai, K.; Si, Y.; Yu, C.; Zheng, H.; Li, S. Evaluation of Himawari-8 version 2.0 aerosol products against AERONET ground-based measurements over central and northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D03211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Qin, W.; Bilal, M. A high-precision aerosol retrieval algorithm (HiPARA) for advanced himawari imager (AHI) data: Development and verification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Fan, M.; Wei, J.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of MAIAC aerosol retrievals over China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Combined use of satellite and surface observations to study aerosol optical depth in different regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gong, W.; Chen, S.; Jin, S.; Wang, J. Controlling factors analysis for the Himawari-8 aerosol optical depth accuracy from the standpoint of size distribution, solar zenith angles and scattering angles. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 233, 117501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Duan, M.; Pu, W.; Ma, Z.; Quan, W.; Zhou, H.; Che, H. Similarities and Differences in the Temporal Variability of PM2.5 and AOD between Urban and Rural Stations in Beijing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lennartson, E.M.; Wang, J.; Gu, J.; Castro Garcia, L.; Ge, C.; Gao, M.; Choi, M.; Saide, P.E.; Carmichael, G.R.; Kim, J. Diurnal variation of aerosol optical depth and PM 2.5 in South Korea: A synthesis from AERONET, satellite (GOCI), KORUS-AQ observation, and the WRF-Chem model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15125–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Han, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xiaohui, D.; Wei, P. On the opposite seasonality of MODIS AOD and surface PM2.5 over the Northern China plain. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, L.; Wang, W. Opposite seasonality of the aerosol optical depth and the surface particulate matter concentration over the north China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Cheng, M.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Meng, F. The contribution of residential coal combustion to PM2.5 pollution over China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in winter. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, M.; Yim, S.H.L. The spatiotemporal relationship between PM 2.5 and aerosol optical depth in China: Influencing factors and implications for satellite PM 2.5 estimations using MAIAC aerosol optical depth. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 18375–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, R. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on sun photometer measurements at a semi-arid rural site in Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekinwala, N.L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Raman, R.S.; Bhushan, M.; Bali, K.; Dey, S. A framework for setting up a country-wide network of regional surface PM2.5 sampling sites utilising a satellite-derived proxy–The COALESCE project, India. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Pio, C.A. Size-differentiated composition of inorganic atmospheric aerosols of both marine and polluted continental origin. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimette, J.R.; Flagan, R.C. The extinction coefficient of multicomponent aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, S.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, J. Analysis of a Severe Regional Haze-fog-dust Episode over North China in Autumn by Using Multiple Observation Data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Tong, Q.; Xiu, A.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S. Simulating performance of CHIMERE on a late autumnal dust storm over Northern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Uno, I.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Fu, P.; Yang, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Shimizu, A. Significant impacts of heterogeneous reactions on the chemical composition and mixing state of dust particles: A case study during dust events over northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Time ≤ 2 Min | Time ≤ 5 Min | Time ≤ 7 Min | Time ≤ 10 Min | Time ≤ 20 Min | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | |
| d = 1 pixel | 426 | 0.865 | 0.145 | 919 | 0.840 | 0.164 | 1078 | 0.840 | 0.161 | 1215 | 0.840 | 0.161 | 1759 | 0.833 | 0.163 |
| d ≤ 3 pixels | 1002 | 0.808 | 0.174 | 2533 | 0.790 | 0.183 | 2937 | 0.787 | 0.183 | 3267 | 0.780 | 0.185 | 4183 | 0.782 | 0.184 |
| d ≤ 6 pixels | 1304 | 0.805 | 0.175 | 3425 | 0.786 | 0.185 | 3955 | 0.781 | 0.187 | 4334 | 0.782 | 0.188 | 5256 | 0.782 | 0.188 |
| d ≤ 12 pixels | 1483 | 0.793 | 0.182 | 3959 | 0.774 | 0.194 | 4558 | 0.769 | 0.195 | 4907 | 0.766 | 0.199 | 5776 | 0.769 | 0.198 |
| Time ≤ 2 Min | Time ≤ 5 Min | Time ≤ 7 Min | Time ≤ 10 Min | Time ≤ 20 Min | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | N | R2 | RMSE | |
| d = 1 pixel | 89 | 0.953 | 0.170 | 245 | 0.957 | 0.177 | 342 | 0.956 | 0.180 | 392 | 0.949 | 0.177 | 456 | 0.942 | 0.179 |
| d ≤ 3 pixels | 100 | 0.954 | 0.156 | 270 | 0.955 | 0.170 | 376 | 0.955 | 0.177 | 429 | 0.949 | 0.173 | 497 | 0.939 | 0.185 |
| d ≤ 6 pixels | 107 | 0.955 | 0.153 | 287 | 0.953 | 0.170 | 397 | 0.923 | 0.187 | 451 | 0.924 | 0.182 | 525 | 0.918 | 0.192 |
| d ≤ 12 pixels | 108 | 0.956 | 0.153 | 293 | 0.953 | 0.169 | 407 | 0.924 | 0.190 | 463 | 0.925 | 0.184 | 539 | 0.918 | 0.194 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Yuan, J.; Wei, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Xia, H. Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth Measured by Sun Photometer at a Rural Site near Beijing during the 2017–2019 Period. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122908
Wu X, Yuan J, Wei T, Zhang Y, Wu K, Xia H. Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth Measured by Sun Photometer at a Rural Site near Beijing during the 2017–2019 Period. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122908
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiu, Jinlong Yuan, Tianwen Wei, Yunpeng Zhang, Kenan Wu, and Haiyun Xia. 2022. "Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth Measured by Sun Photometer at a Rural Site near Beijing during the 2017–2019 Period" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122908
APA StyleWu, X., Yuan, J., Wei, T., Zhang, Y., Wu, K., & Xia, H. (2022). Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth Measured by Sun Photometer at a Rural Site near Beijing during the 2017–2019 Period. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122908