Abstract
During recent years, several eutrophication processes and subsequent environmental crises have occurred in Mar Menor, the largest hypersaline coastal lagoon in the Western Mediterranean Sea. In this study, the Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites are jointly used to examine the evolution of the main water quality descriptors during the latest ecological crisis in 2021, resulting in an important loss of benthic vegetation and unusual mortality events affecting different aquatic species. Several field campaigns were carried out in March, July, August, and November 2021 to measure water quality variables over 10 control points. The validation of satellite biogeochemical variables against on-site measurements indicates precise results of the water quality algorithms with median errors of 0.41 mg/m3 and 2.04 FNU for chlorophyll-a and turbidity, respectively. The satellite preprocessing scheme shows consistent performance for both satellites; therefore, using them in tandem can improve mapping strategies. The findings demonstrate the suitability of the methodology to capture the spatiotemporal distribution of turbidity and chlorophyll-a concentration at 10–30 m spatial resolution on a systematic basis and in a cost-effective way. The multitemporal products allow the identification of the main critical areas close to the mouth of the Albujon watercourse and the beginning of the eutrophication process with chlorophyll-a concentration above 3 mg/m3. These innovative tools can support decision makers in improving current monitoring strategies as early warning systems for timely assistance during these ecological disasters, thus preventing detrimental conditions in the lagoon.
1. Introduction
Coastal lagoons, as transitional environments between land and sea, occupy 14% of the world’s coastlines [1]. Due to their shallow waters, morphology, trophic status, and physicochemical processes in a semienclosed system, they are considered one of the most productive habitats on Earth [2,3]. These areas play a significant conservational, ecological, and protective role and are home to an important part of global biodiversity [4]. They underpin human livelihoods, well-being, and welfare and provide several ecosystem services, including tourism, fisheries, aquaculture, and industrial, recreational or navigational activities. Coastal lagoons are subject to diverse transformations and uncoordinated management plans by different agencies and stakeholders from the local to national scale, which might, in some cases, degrade their ecological values. A wide range of anthropogenic activities such as urbanization, agriculture, aquaculture or industry use a variety of organic substances and pollutants, which can reach semienclosed bays, inland waters, and lagoons [5]. Considering that these environments are extremely sensitive and vulnerable, they usually show signs of deterioration, pollution, biodiversity loss, alteration of their ecological functioning, and limited ecosystem services [6]. Habitat destruction, water withdrawal, overexploitation, and chemical and biological pollution, such as invasive species, are the main causes of their deterioration, making them one of the most threatened ecosystems in the world [7]. The conservation of coastal lagoons is crucial for their ecological value and the significant number of services they provide [8]. Furthermore, in the context of climate change, coastal lagoons are sentinel systems with an essential role in controlling the fluxes of water, organisms, and nutrients between land, rivers, and oceans, as well as eutrophication and pollution processes [8,9]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to advance monitoring, mapping, and management tools in order to improve the knowledge of these strategic systems, prevent their environmental degradation, and increase their future protection [10].
This is the case of Mar Menor, the largest hypersaline lagoon in the Western Mediterranean Sea (Figure 1) and one of the most iconic and emblematic natural areas in Spain due to its significance in terms of habitats and species, its ecological value, and the uniqueness of its ecosystem. Mar Menor, its surrounding wetlands, and natural areas, are of vital natural importance and a protected landscape as a Wildlife Protection Area, Natura 2000 network, Wetland of International Importance (RAMSAR Convention), and a Regional Park. Moreover, the area is a key component of the regional economy, development, and policy plans due to the variety of uses and human activities developed there. The lagoon, with a maximum depth of 6.5 m and a surface area of 135 km2, presents a long sand bar called “La Manga” acting as a barrier between the Mediterranean Sea and the lagoon, only connected through five shallow inlets called “golas” [11]. The lagoon is close to the Campo de Cartagena region, one of the most intensive agricultural areas in Europe. Several ephemeral wadis drain into the western part of the lagoon, transporting nutrient-enriched waters from agricultural runoff after rainy periods, the Albujon watercourse (Figure 1) being the main collector of the Campo de Cartagena drainage basin and the only permanent wadi flowing into the lagoon [11,12,13,14,15,16]. Therefore, most of the discharges are located in the southern half of the lagoon where the Albujon watercourse maintains a regular flux of water, albeit depending on the torrential and sporadic rainfall regime, as occurred in September 2019 during one of the most extreme storms, known as the “Cold Drop” [13].
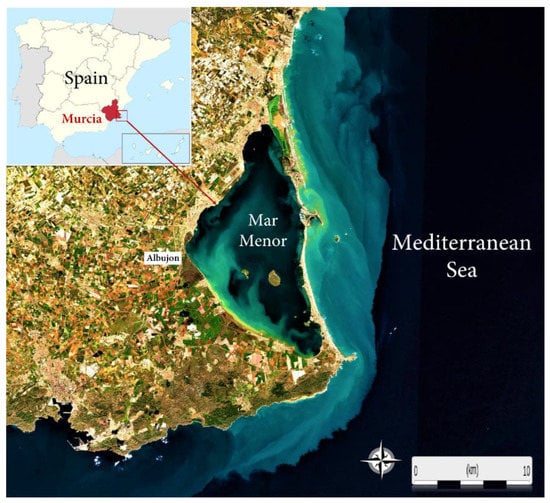
Figure 1.
Location of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon on the southeastern coast of Spain and Sentinel-2 image captured on 21 March 2021 indicating the final transect of the Albujon watercourse flowing into the lagoon.
Nowadays, this ecosystem is a cause for international concern due to the drastic modifications of its natural and physical status caused by anthropogenic activities. The main impacts causing acute degradation of Mar Menor are those from mining, agriculture, tourism, and urban development [11,14]. The land-use modifications that occurred in the watershed during the 1980s and 1990s with relation to agriculture, from dry land to intensively irrigated vegetable crops (Figure 2), have produced a severe excess of nutrients and fertilizers draining into the lagoon from the freshwater discharge [11], which clearly affect the environmental health of the lagoon (Corine Land Cover datasets, https://centrodedescargas.cnig.es/CentroDescargas/; accessed on 1 January 2022). The current problems affecting the lagoon are increased turbidity and chlorophyll-a, resulting in an acute eutrophication process, silting, a general loss of sediment and seawater quality, and the deterioration of submerged seagrass and animal communities. The degradation of the coastal lagoon has also influenced conventional fishing that has been carried out in the lagoon since ancient times [17].
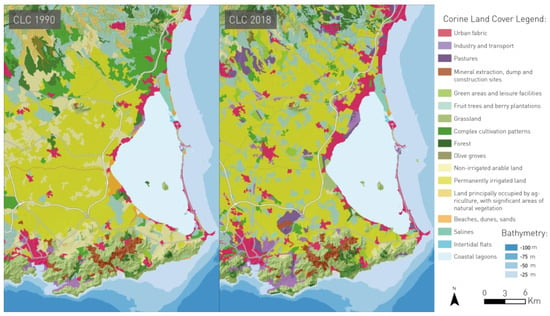
Figure 2.
Land cover classification for the Mar Menor lagoon and its surroundings according to Corine Land Cover datasets (https://centrodedescargas.cnig.es/CentroDescargas/; accessed on 1 January 2022) for 1990 and 2018.
The effects of these massive contributions of nutrients in the lagoon ecosystem have been cushioned by its elements that, for decades, have acted as mechanisms of homeostasis and resilience, preventing an excess of nutrients from being available to opportunistic phytoplankton organisms. However, despite the capacity of Mar Menor to resist the effects of elevated nutrient concentration, a succession of catastrophic events have occurred (Figure 3a–c) since 2016 [18,19,20]. In August 2021, the latest environmental crisis caused alarm and considerable concern and was considered worse than previous eutrophication events. The excess of nutrients and organic matter caused anoxia in the deep layer and massive mortality of benthic flora and fauna during several weeks (Figure 3d), causing an impact on public opinion at the local, national, and international level. Images of dying wildlife traumatized citizens and occupied the public agenda, raising questions about the cause of this ecological disaster that keeps getting worse year after year. The Spanish Institute of Oceanography (IEO-CSIC) highlighted the main cause as pollution and the entry of fertilizers and nutrients into the lagoon from intensive agriculture and other human activities, causing the aquatic ecosystem to collapse [21]. This has led to a clear transformation in the regime of the lagoon, from an apparently stable state (with frequent symptoms of eutrophication in recent decades) to an altered and highly unstable state, much more vulnerable to changes in the environment, especially extreme weather events, which are clearly more intense and frequent as a result of global climate change [22]. In fact, in recent years, it has been observed that when the chlorophyll-a values in the lagoon exceed 3 mg/m3, a process of eutrophication occurs immediately [21]. Several administrations and public authorities responsible for managing the lagoon have been developing initiatives in an attempt to solve the problem. The regional government maintains an open-access network with a few constant sampling sites and field-based campaigns for monitoring variables related to water quality, such as water clarity, turbidity or chlorophyll-a, an indicator of phytoplankton biomass in seawater, temperature, salinity, and dissolved oxygen [23]. However, sound management and deterioration control need improved characterization of the spatial variability and distribution of the water quality, in particular in the western area of Mar Menor, where the Albujon watercourse flows into the lagoon. This information remains key not only for long-term monitoring but also for quick emergency response as an early warning system.
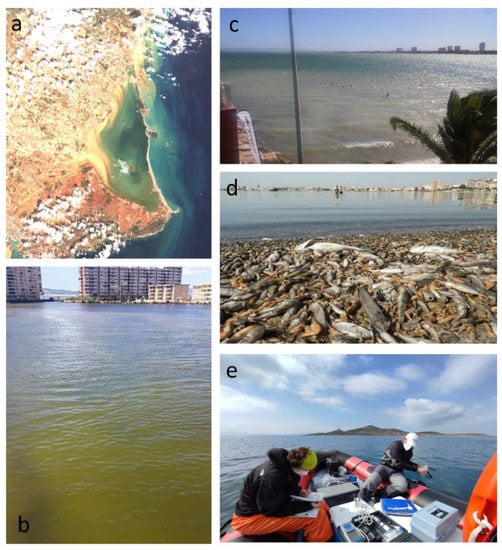

Figure 3.
(a) Sentinel-2 scene in Mar Menor after the extreme weather event known as the “Cold Drop” and the catastrophic flooding on 13 September 2019; (b) surface of the water in the lagoon in July 2016 during the environmental crisis; (c) typical resuspension of sediments and increased turbidity during strong winds; (d) latest environmental catastrophe with massive dead fish and crustacean in August 2021 (authorship: Greenpeace); and (e) field campaign carried out in the lagoon in March 2021.
This study examined the evolution of the main biogeochemical parameters of the seawater quality in the coastal lagoon using the Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellite missions in tandem, both with high spatial resolution. Remote sensing technologies can advance current management and monitoring strategies providing synoptic information of the lagoon, as well as provide insights into past, present, and future eutrophication events, in particular during the severe environmental crisis that occurred in summer 2021. Although ocean color sensors provide a distinct picture of the seawater bio-optical status across several scales not achievable with traditional in situ surveying techniques, application in coastal lagoon biogeochemical monitoring is challenging. In this sense, there are studies that focus on mapping water quality, phytoplankton blooms, and eutrophication events in Mar Menor with traditional ocean color sensors at the moderate spatial resolution of 300–1000 m [24,25,26]. RGB composite images on 3 August 2021 of the Sentinel-3 satellite (300 m spatial resolution), Landsat-8 satellite (30 m spatial resolution), and Sentinel-2 satellite (10 m spatial resolution) are shown in Figure 4. Sentinel-3 is the ocean color mission developed by the European Union’s Copernicus programme to support ocean forecasting systems, environmental and climate monitoring with high accuracy and reliability. However, this example highlights that the moderate spatial resolution of Sentinel-3 might not be adequate in complex coastal areas, such as Mar Menor. In recent years, some studies suggested that in order to appropriately determine the ecological conditions of complex inland or coastal water areas by means of remote sensing tools, improved temporal and spatial capabilities are required [27,28,29,30,31,32], in particular in Mar Menor [13,33,34,35]. Conceived in the first instance to monitor land cover, the notably enhanced spectral and spatial resolution and minor footprint of both Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 platforms provide the opportunity to evaluate terrestrial–aquatic interfaces and their dynamic spatial heterogeneity at local, regional, or global scales [36,37].

Figure 4.
RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image on 3 August 2021 of (a) Sentinel-3 satellite (300 m spatial resolution), (b) Landsat-8 satellite (30 m spatial resolution), and (c) Sentinel-2 satellite (10 m spatial resolution).
The main aims of this study are: (1) to use a consistent atmospheric and sunglint correction strategy with Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 imagery in Mar Menor; (2) to validate the satellite-derived chlorophyll-a and turbidity retrievals with in situ data; (3) to detect the spatiotemporal fluctuations of the biogeochemical parameters during the study period with the multisensor approach; and (4) to evaluate and identify the critical zones in the context of the most recent ecological catastrophe in 2021. This combined information can allow enhanced temporal mapping and predictability of the water mass degradation as an early warning system. Remote sensing technology has large-area and real-time advantages in promoting the monitoring and forecasting of coastal disasters, providing information about when and where the chlorophyll-a values in the lagoon exceed 3 mg/m3 [21]. These tools can be applied in parallel to regular on-site sampling campaigns in order to reduce the detrimental effects of high levels of phytoplankton, algae, and turbidity on the vulnerable lagoon system and to continuously calibrate/validate the different water quality algorithms for more reliable results.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Satellite Imagery
The Sentinel-2A/B twin mission was used for mapping the lagoon thanks to the open data access policy and high spatial resolution (10-20-60 m). The European Commission and the European Space Agency (ESA), in the frame of the Copernicus programme, developed this optical constellation in order to support its operational requirements. Sentinel-2 is a multispectral, wide-swath imaging platform used for monitoring land surfaces, water coverage, soil, and vegetation. In addition, it can also support Copernicus water monitoring over coastal regions and inland waterways. The Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B mission, with a global revisit frequency of five days at the Equator, is based on a constellation of two operationally identical satellites in the same orbit and phased at 180° to each other. The ESA User Handbook describes the temporal, spectral, spatial, and radiometric features of the visible and near-infrared (NIR) bands of both Sentinel-2A and -2B satellites [38]. The stated quality standards for absolute geolocation of the Sentinel-2 scenes (two pixels, 20 m) are within the ESA requirements [39]. The images covering Mar Menor (zone 30 and tile SXG; acquisition time 11:00 UTC) during the study period in 2021 were downloaded from the ONDA DIAS (https://www.onda-dias.eu/cms/es/; accessed on 20 May 2021). These products are the top-of-atmosphere (TOA) datasets at Level-1C (L1C) after the radiometric and geometric corrections.
In addition, the freely available Landsat-8 visible and NIR spectra imagery from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) were also used for comprehensive monitoring. We downloaded the Level 1 data from the Earth Explorer (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/), orthorectified and terrain corrected at a 30 m spatial resolution, with a 16-day revisit frequency [40,41]. The region of interest was covered by the tiles located in paths 198–199 and row 34 (acquisition time 10:30–10:45 UTC). A low cloud coverage (<40%) filtering was applied over Mar Menor for further analysis of the scenes. When Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 products are combined, the average revisit time in Mar Menor is ~4 days. From the control period before and after the 2021 crisis, 48 images were downloaded and processed (29 and 19 images for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, respectively). However, clouds and severe sunglint contamination diminished the number of usable images, with only 18 final scenes further evaluated (12 and 6 images for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, respectively) to characterize the spatial and temporal distribution of water quality. Table 1 shows the acquisition dates and the quality of the scenes.

Table 1.
List of imagery used in this study during the latest ecological crisis in 2021 corresponding to the Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellites.
Bottom-of-atmosphere (BOA) Level-2A products were generated with one of the most commonly used atmospheric correction softwares (ACOLITE, version 20210114.0), which supports preprocessing of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites. This software incorporates an image-based model, without the need for in situ atmospheric datasets. The Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences (RBINS) developed this free toolbox to correct Level-1 to Level-2 data products over marine, inland, and coastal waters [42]. The Dark Spectrum Fitting (DSF) atmospheric correction algorithm was applied [43,44]. The notably enhanced spectral resolution of Landsat-8 and, in particular, Sentinel-2 satellites, are key to obtain good-quality products by means of the DSF model [44]. Correction of the sunglint over the surface reflectance was performed by means of the additional image-based sunglint correction, since during the study period acute sunglint effects were observed at these latitudes (specific setting parameters: dsf_path_reflectance = tiled, l2w_mask_threshold = 0.05). The remote sensing reflectance (Rrs, sr−1) products along the visible and NIR spectrum were calculated after resampling to 10 m and 30 m pixel size for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, respectively.
The standard products to monitor the biogeochemical conditions in Mar Menor during the ecological crisis with Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellites were seawater turbidity (FNU) and chlorophyll-a (chl-a, mg/m3). We selected both indicators as required by the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD) for the evaluation of the good ecological status of the coastal lagoon. The Nechad et al. semianalytical algorithm (red band, Rrs 665 nm) was applied to estimate turbidity with both satellites [45]. This model has already been validated in different environments [46,47,48] and was previously used in Mar Menor during an extreme weather event in September 2019 [13]. These semianalytical algorithms allow a more global performance since they are based on the inherent optical properties of the seawater. The commonly used OC3 algorithm was applied to calculate the concentration of seawater chl-a [49]. The standard masking procedures were accomplished, eliminating clouds, cloud shadows, land, and the low performance of the sunglint and atmospheric corrections. Turbidity and chl-a maps were at 30 m and 10 m spatial resolution for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2, respectively, with the generation of the final products after 3–4 h following image acquisition for each sensor.
2.2. In Situ Data
Four sampling cruises were carried out during 2021 (March, July, August, and November), where seawater was collected at 10 points homogeneously distributed in the Mar Menor lagoon (Figure 5). The dates of the in situ campaigns during the study period corresponded to 23–24 March, 27 July, 26 August, and 16–17 November 2021. Matchups between in situ and satellite samples were generated when both data acquisitions occurred within 30 h of each other, and the satellite value was calculated as the mean of the 3 × 3 10 m pixel region around the sampling station.
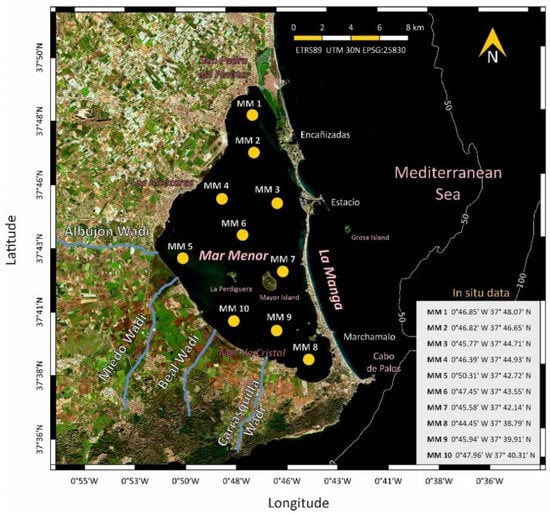
Figure 5.
Control points for data collection during the four in situ campaigns carried out in March, July, August, and November 2021.
In order to determine turbidity, samples were measured just after collection onboard using a portable turbidimeter (2100P, Hach). Prior to calibration, we ensured that the equipment did not suffer anomalies and that the necessary reagents were available. Calibration was performed quarterly, unless the equipment was malfunctioning. The turbidimeter was calibrated at 4 points: 0 NTU, 10 NTU, 200 NTU, and 800 NTU. The standards used in the calibration were certified commercial standards at room temperature in order to avoid misting interferences in the turbidity measurement. The turbidimeter was calibrated according to the equipment manual.
In the case of chl-a, water was collected from a 0.5 m depth in 1 L dark bottles to avoid enhanced photosynthetic activity and kept in a portable fridge until arrival at the laboratory. Three replicates per station were collected. Chl-a concentrations were measured in 700–1000 mL water samples for each replicate, which were filtered through Whatman GF/F 0.2 µm polycarbonate filters. The filters were immediately frozen at −20 °C until pigment extraction in 90% acetone at 4 °C overnight in the dark. Chl-a concentrations were determined with a 10-AU Turner Designs fluorometer calibrated with pure chl-a [50].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Multisensor Approach and Preprocessing
Until now, standard ocean color sensors at the moderate spatial resolution of 300–1000 m were generally used to map water quality, phytoplankton blooms, and eutrophication events in Mar Menor [25,26]. However, features in the lagoon show typical scales of tens of meters that cannot be detected with existing ocean color sensors (Figure 4). In recent years, several studies already demonstrated that, in order to comprehensively evaluate the ecological conditions of heterogeneous coastal areas and land-water inputs using remote sensing technologies, improved spatial resolution should be used with Landsat-8 and/or Sentinel-2 [28,30,31,51]. Undoubtedly, the Sentinel-2 twin mission, although originally not designed for coastal ocean monitoring, is a key tool for the detailed mapping of highly dynamic environments, such as coastal or inland water areas [52].
During the study period, in particular during summer, acute sunglint contamination also influenced the quality of the imagery over Mar Menor due to the specular reflection of sunlight off the water (see Table 1 for details). Figure 6 shows two images on 9 June 2021 and 4 July 2021 at the top-of-atmosphere (TOA) level, after ACOLITE processing at the bottom-of-atmosphere (BOA) level, and the Rrs of the blue band (492 nm). Accurate performance was accomplished by ACOLITE over low to moderate sunglint conditions, such as on 9 June 2021 (Figure 6a–c), but failed to retrieve Rrs during severe sunglint contamination on 4 July 2021 (Figure 6d–f), thus masking the data. The sunglint is clearly observed at TOA-Level-1C (Figure 6a,d), whereas the residuals are visible at BOA-Level2 (Figure 6e) with intense effects on the eastern area of the Sentinel-2 tile, exactly where Mar Menor is located. This effect is significant during spring and summer, given that minimum information could be retrieved with severe sunglint, restricting the amount of available data when the majority of the blooms occurred. Comparable results were generated in other coastal regions, such as in North Atlantic [53] or Caribbean waters [54]. Irregular residual issues still require further advancements in the sunglint and atmospheric correction approaches to facilitate the extensive combination of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 products during summer. In addition, the typical stripping patterns are clearly observed at both TOA and BOA levels.

Figure 6.
RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image on 9 June 2021 from the Sentinel-2 satellite (10 m spatial resolution) at (a) top-of-atmosphere (TOA) level, (b) bottom-of-atmosphere (BOA) level after ACOLITE, and (c) remote sensing reflectance (Rrs, sr−1) of the blue band (492 nm); (d–f) the same on 4 July 2021. Severe sunglint contamination can be clearly observed in the eastern section of the Sentinel-2 tile affecting Mar Menor.
On 3 August 2021, Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 acquired a scene at 10:45 am and 11:00 am GMT, respectively. Figure 7 shows the spectral signal of both satellites with only a 15 min time difference over three control points distributed across different areas of the lagoon. This exhibits the consistent performance of ACOLITE for both satellite missions, retrieving the spectrum with similar Rrs values for each point and sensor (P1, turbidity of 18.11 and 17.28 FNU; P2, turbidity of 5.5 and 6.1 FNU; and P3, turbidity of 4.08 and 3.93 FNU for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, respectively), thus further corroborating the remarkable value of the combined products. Comparison of Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 Rrs over the visible and NIR bands yielded a bias of −0.00035 sr−1, MAE of 0.00072 sr−1, and MedAE of 0.00049 sr−1. Consistent sunglint and atmospheric correction models are needed to empower the application community to explore these products in order to thoroughly address the ecological conditions of Mar Menor using remote sensing technologies. Recent research already demonstrated the potential of ACOLITE to provide robust information for aquatic and marine applications [30,43,44,54]. A study applied Sentinel-2 data to monitor water quality in Mar Menor using the Sen2Cor atmospheric correction processor (designated for land application with restricted performance in water application) and to generate products at 60 m spatial resolution [35]. However, Pahlevan et al. (2019, 2021) suggested that enhanced information for inland and coastal water quality mapping is required as a critical and urgent task to evaluate spatial and spectral differences under several atmospheric and aquatic conditions [28,55]. This data record is crucial to ensuring a detailed monitoring of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon with both satellite platforms working in tandem.
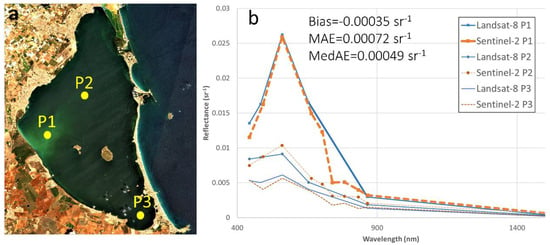
Figure 7.
(a) RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image on 3 August 2021 of the Sentinel-2 satellite at bottom-of-atmosphere (BOA) level, (b) spectral signal of the Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellites over different control points (P1, turbidity of 18.11 and 17.28 FNU; P2, turbidity of 5.5 and 6.1 FNU; and P3, turbidity of 4.08 and 3.93 FNU for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, respectively). Yellow circles in (a) indicate the location of the control pixels.
3.2. Validation of the Water Quality Algorithms
Figure 8 shows the validation matchups for the water quality parameters obtained with Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 during the four in situ campaigns carried out in 2021. We applied the standard OC3 algorithm to calculate chl-a concentration and a regularly used semianalytical algorithm for the determination of turbidity [44,45]. The performance of both algorithms is illustrated in Figure 8a,b, respectively. The chl-a matchups cover the range of 0.5–5 mg/m3 with a bias of 0.37 mg/m3, MAE of 0.43 mg/m3, and MedAE of 0.41 mg/m3 (R2 = 0.903, n = 37), whereas the turbidity ranges from 0.5–6 FNU with a bias of 2.09 FNU, MAE of 2.09 FNU, and MedAE of 2.04 FNU (R2 = 0.54, n = 35). The validation assessment indicated robust statistical analysis, with accurate chl-a retrieval and minimum bias. Predictions of chl-a from both Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 yielded precise results after the ACOLITE atmospheric and sunglint correction. The performance of the ACOLITE and the turbidity model is accurate, but a general satellite overestimation was encountered with biased outcomes, as seen in Figure 8b. Pahlevan et al. (2022) also found overestimation of turbidity retrievals by means of the ACOLITE processor [56]. The turbidity model has already been validated in different regions worldwide with accurate performance [46,47,48,57] and has previously been used in Mar Menor during an extreme weather event [13]. These methodologies are consistent and valid approaches for the assessment of suspended material or turbidity, which contribute towards achieving more precise performance worldwide [45,58].
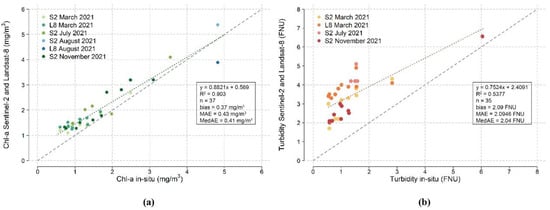
Figure 8.
Validation of water quality parameters obtained with Sentinel-2 (S2) and Landsat-8 (L8) during the four in situ campaigns carried out in March, July, August, and November 2021 for (a) chlorophyll-a concentration (chl-a, mg/m3) and (b) turbidity (FNU).
3.3. Water Quality Monitoring
Figure 9 shows the RGB composite scenes acquired on 9 and 24 June and 2, 14, 18, and 29 July 2021, whereas Figure 10 and Figure 11 display the image-derived maps for turbidity and chl-a, respectively. The imagery corresponded to the months prior to the ecological crisis in mid-August 2021. Generally, the turbidity levels were low in the lagoon (<5 FNU), except in the western section on 24 June and 14 July 2021, indicating higher levels (~25 FNU). A turbid plume appeared near land where the Albujon watercourse flows into Mar Menor. The most common chl-a condition during this period was <1.5 mg/m3, while higher chl-a concentration (~2.5 mg/m3) was observed close to the turbid plume. Figures S1 and S2 indicate the available (cloud and sunglint-free) Sentinel-2 scenes in August 2021 for further evaluation. On 3 August, a turbid plume was observed in the western section close to the input of the Albujon watercourse with peaked levels ~20 FNU, whereas minimum turbidity was encountered in the rest of the lagoon. The chl-a concentration for this date seemed to increase in the western section, indicating maximum values within the lagoon. The turbidity maps depicted high and constant turbidity values ~20 FNU in August 2021, except a slight decrease on 18 August 2021 on the western side (Figure S2). Moreover, chl-a maps displayed higher concentrations compared with July and the beginning of the bloom during this month, in particular on 13 August 2021 with chl-a ranging from 4 to 9 mg/m3, a strong indicator of algal blooms in Mar Menor. Clear-water lagoon phases are characterized by chl-a concentrations ranging from 1 to 3 mg/m3 [59], as occurred during June and July 2021. However, these typical low chl-a values tipped rapidly towards more eutrophic conditions, with chl-a concentration higher than 3 mg/m3, such as last year’s [18,19,21,60]. We reported that using the multisensor approach during the eutrophication episode in 2021, the beginning of the bloom (chl-a concentration higher than 3 mg/m3) was detected mainly in the western and southern section. This is critical information for early detection of the eutrophication processes, given that the massive mortality of fish and crustaceans occurred during the last weeks of August 2021 [21], as well as an opportunity to enhance emergency management response in early deterioration stages.
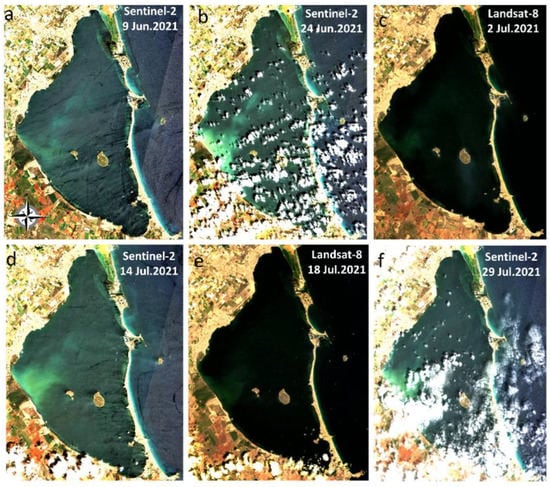

Figure 9.
Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image acquired on (a) 9 June 2021, (b) 24 June 2021, (c) 2 July 2021, (d) 14 July 2021, (e) 18 July 2021, and (f) 29 July 2021.
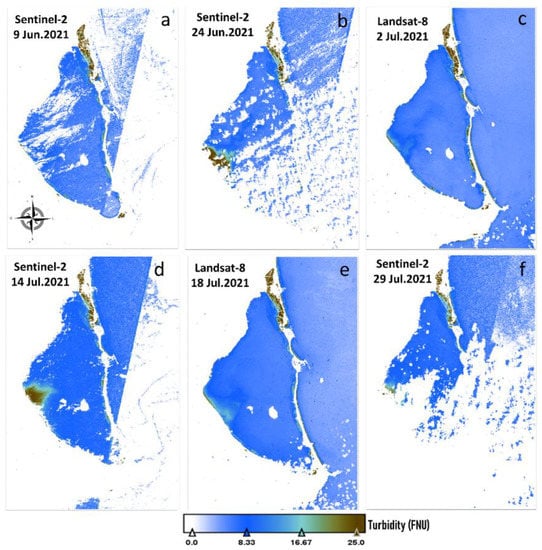
Figure 10.
Turbidity (FNU) from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 9 June 2021, (b) 24 June 2021, (c) 2 July 2021, (d) 14 July 2021, (e) 18 July 2021, and (f) 29 July 2021.
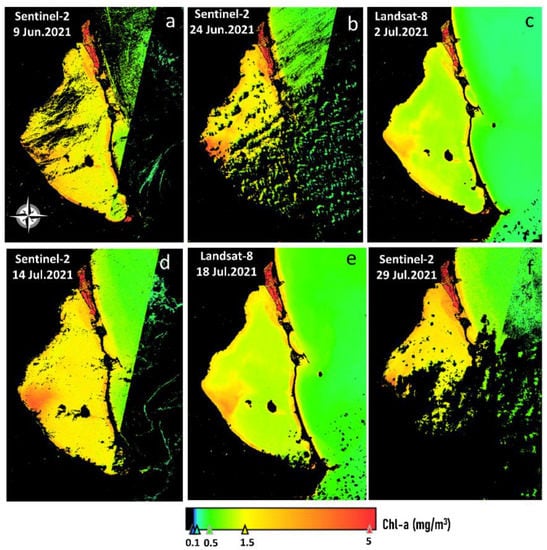
Figure 11.
Chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a, mg/m3) from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 9 June 2021, (b) 24 June 2021, (c) 2 July 2021, (d) 14 July 2021, (e) 18 July 2021, and (f) 29 July 2021.
After this event, the ecosystem equilibrium recovered slightly during September 2021 (Figure S3) as can be observed in the decrease in turbidity retrievals on the western side (Figure S4). However, the Albujon continued to discharge to the western section of the lagoon, indicating increased surface runoff and rising turbidity levels, and a plume was always close to this area. In addition, chl-a concentration gradually reached normal values <3 mg/m3 in some areas in September 2021, although on 7 and 12 September 2021 high chl-a concentrations of ~4–5 mg/m3 persisted not only in the center and south but also in the northern and eastern sections of the lagoon (Figure S5). A minor “Cold Drop” occurred on 20–21 September 2021, but the cloud and haze coverage remained very high during the consecutive days, as can be observed on 22 and 27 September 2021.
Time-consuming and costly on-site measurements are regularly carried out to determine the water quality status in the lagoon; nevertheless, these observations are not able to address the heterogeneity and complexity of the spatial distribution within Mar Menor. In fact, in situ data might lack samples from the peak of the bloom or high turbidity levels due to the sparsely distributed single sampling sites. Field campaigns may not have adequately retrieved maximum concentration in chl-a if in situ measurements were not correctly spotted in Mar Menor [35]. The combined satellite data series characterized the dynamic nearshore patterns and fine-scale bio-optical gradients across this complex coastal interface. Satellite maps offered a synoptic perspective of the entire lagoon, detecting higher and lower turbidity and chl-a concentration over the study area. Interestingly, while maximum turbidity levels across the study site were typically located in the western section associated with the drainage of the Albujon, highlighting the impact of hydrological inputs and discharge from this canal, minimum levels were observed on the eastern, northern, and southern sides and along the barrier beach “La Manga”. Our results also present the highest chl-a concentrations along the western coastline, detecting a change due to a proliferation of phytoplankton in early August 2021. The IEO-CSIC suggested that this eutrophication event was due to an excess of nutrient availability flowing from the Albujon [21]. Therefore, the abrupt deterioration of the water quality in Mar Menor reached a stage of severe eutrophication that resulted in an ecological collapse in mid-August, showing a gradual recovery during September 2021 before the minor “Cold Drop” event on 20 September 2021. Among all the wadis transporting materials, water, and nutrients from agricultural run-off, the Albujon is the principal collector of the Campo de Cartagena drainage basin, subjecting the lagoon to nutrient and sediment runoff from the agricultural landscape [11,12,15,16]. These results sustain that in order to remedy the ecological collapse of the lagoon, it is crucial to design and implement environmental strategies and policies [22], in particular those that focus on limiting the suspended material discharged from the Albujon to regulate the massive proliferation of phytoplankton and the eutrophication pressure favored by agricultural dumping [25,61].
3.4. An Early Warning Tool with High Spatial Resolution
The complex distribution and variability of the lagoon can be observed in detail in all the satellite-derived products presented in this study, in particular for the turbid plume located in the western part. These turbid features are usually small in dimension; therefore, detecting them by means of traditional ocean color sensors at lower spatial resolution can be challenging. We recommend using Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 missions in tandem to improve the monitoring and control of Mar Menor. The multisensor methodology might enhance previous studies that attempted to map water quality using coarser spatial resolution imagery at 300–1000 m [24,25,26]. Additional evaluation of previous months in March 2021 also highlighted the importance of our methodology for studying the impact of weather events on the coastal lagoon. Figures S6 and S7 show the RGB composite images and turbidity levels on 11 and 12 March 2021 and on 21 and 28 March 2021, before and after a severe winter storm, respectively. The maps corresponding to 11 and 12 March 2021 presented minimum turbidity levels (<4 FNU) in front of the Albujon. This cycle was occasionally disrupted by the intense winter storm resulting in increased inputs of terrestrial discharges into the entire lagoon. The high resuspension of materials can be observed in both the RGB and turbidity maps after the storm, in particular on 21 March 2021 along the western coastal region with turbidity >50 FNU. A zoom on 21 March 2021 corresponding to the southeastern shore of Mar Menor showed the high variability of the turbidity patterns (Figure S8). Turbidity generally decreases seaward in the lagoon and extreme events, such as storms, can increase turbidity 5-to-10-fold, altering the water quality distribution in the system. In particular, “Cold Drop” events can dramatically alter the ecological status of the lagoon with turbidity levels increasing by more than a factor of five [13]. Previous studies have already indicated that finer spatial resolution is needed to comprehensively determine these complex spatial and temporal features [62].
With three-to-four-day revisits allowed by combined Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 datasets, the managers, end users, and coastal science community will take advantage of these synoptic, improved, consistent, and high-quality products. This information may be critical for operational purposes in the context of the EU WFD [32], from which early warning systems can be implemented. Although work remains to be performed towards improving and developing advanced sunglint, atmospheric, and bio-optical algorithms for both Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8, it is the ideal moment to examine, exploit, and maximize these merged datasets in Mar Menor. Particularly during ecological crises, such as the one explored in this study, this information is crucial to assess appropriate measures to be taken in coastal and inland water ecosystems. However, research must continue to enable retrievals in extremely contaminated sunglint scenes during eutrophic/turbid conditions in summer periods, as demonstrated in this study (Figure 6), as well as the analysis of other biogeochemical variables, such as Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM). In addition, as shown in recent research by Wójcik-Długoborska [63], turbidity measurements in the field may differ from those taken in the laboratory and thus provide different correlations between reflectance and the true value of turbidity. Therefore, we intend to focus additional research on this aspect during the coming field campaigns. Future studies will also be carried out to evaluate the entire Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 series to assess the seasonality of these events and to identify possible common factors, which can be monitored or used as warning systems in the future. The improved resolution afforded by the combined time-series products offers additional insights into processes over weekly or subweekly timescales; nevertheless, these results emphasized the need for enhanced temporal coverage space-based datasets in dynamic coastal environments. With these three satellites now operating, Landsat-9 already in orbit, planned missions launching shortly (e.g., Sentinel-2C/D), and continuously improving atmospheric and sunglint correction techniques, the accessible record of high-to-moderate spatial resolution imagery will provide even more robust water quality monitoring in complex inland and coastal environments.
4. Conclusions
Eutrophication in areas where agricultural and industrial wastewater runoff feeds excessive loads of nutrients into coastal regions can foster algal blooms and undermine the health of these ecosystems. In this study, both Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites were jointly merged as a constellation to estimate indicators of the water quality in the highly unstable and vulnerable Mar Menor coastal lagoon. The validation of satellite biogeochemical parameters, both turbidity and chl-a, retrieved good performance for ranges of 0.5–6 FNU and 0.5–5 mg/m3, respectively. The atmospheric and sunglint correction using the ACOLITE software showed consistent performance for both satellites; therefore, using them in tandem can improve mapping strategies, highlighting the importance of the preprocessing scheme. The results demonstrate the suitability and consistency of the methodology to reliably capture the detailed spatiotemporal distribution of turbidity and chl-a, where satellite imagery was capable of early detection of chl-a levels above 3 mg/m3, which generally triggered the subsequent blooms during recent years. Although neither of the satellite missions have been designed to characterize coastal seawater quality, our approach demonstrated their capacity to provide appropriate information at 10–30 m spatial resolution on a systematic basis and in a cost-effective way. Multitemporal maps were produced, and an analysis of all images showed that the highest turbidity and chl-a levels were always located in the western section. In particular, turbidity and chl-a concentration at the mouth of the draining Albujon watercourse were consistently two times higher than in the northern and eastern sections of the lagoon. The influence of the highly dynamic plume from the Albujon extended over the entire lagoon, yet the strongest gradients typically occur within the first nearshore 1–2 km. Therefore, observing these gradients, their variability, and the impact of land–water exchanges on nearshore dynamics under varying environmental conditions from space requires higher spatial resolution. Imagery from both satellites offered snapshots of water quality patterns that are difficult to map with in situ technologies in such heterogeneous environments. These innovative tools can support decision makers in the implementation of a joint monitoring strategy, better characterization of the water quality distribution, and timely assistance to society during these ecological disasters, thus preventing detrimental conditions in the lagoon. Furthermore, the powerful multisensor system can be used as guidance to complement the ongoing in situ techniques carried out by the local and regional authorities to select relevant areas for data sampling. This information could advance mapping of water quality and bio-optical properties in terrestrial–aquatic environments as an important tool for managers and stakeholders, as well as for the tourism and fishing industry. A new era has begun with the use of the Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 missions as a virtual constellation, with significant opportunities for monitoring the heterogeneous spatiotemporal patterns of inland and nearshore coastal waters at resolutions certainly not observed previously.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs14122744/s1. Figure S1: RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image on (a) 8, (b) 13, and (c) 18 August 2021 of the Sentinel-2 satellite (10 m spatial resolution); Figure S2: Turbidity (FNU) on (a) 3, (b) 8, (c) 13, and (d) 18, August 2021 of the Sentinel-2 satellite (10 m spatial resolution); (e–h) the same for chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a, mg/m3); Figure S3: Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image acquired on (a) 4 September 2021, (b) 7 September 2021, (c) 11 September 2021, (d) 12 September 2021, (e) 17 September 2021, and (f) 22 September 2021; Figure S4: Turbidity (FNU) from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 4 September 2021, (b) 7 September 2021, (c) 11 September 2021, (d) 12 September 2021, (e) 17 September 2021, and (f) 22 September 2021; Figure S5: Chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a, mg/m3) from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 4 September 2021, (b) 7 September 2021, (c) 11 September 2021, (d) 12 September 2021, (e) 17 September 2021, and (f) 22 September 2021; Figure S6: RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 11, (b) 12, (c) 21, and (d) 28 March 2021; Figure S7: Turbidity (FNU) from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 acquired on (a) 11, (b) 12, (c) 21, and (d) 28 March 2021; Figure S8: (a) RGB (Red–Green–Blue) composite image, and (b) Turbidity (FNU) from Sentinel-2 on 21 March 2021 corresponding to the southeastern shore of Mar Menor.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.C.; formal analysis and investigation, I.C.; figures, I.C. and M.R.; original draft preparation, I.C.; writing—review and editing, I.C., M.R., J.S.-E., P.B. and G.N.; fieldwork, J.S.-E. and P.B; supervision, I.C.; project administration, I.C.; funding acquisition, I.C., J.S.-E. and G.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Project RTI2018-098784-J-I00 funded by the MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by “FEDER Una manera de hacer Europa” and the Grant IJC2019-039382-I funded by the MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033. The work was also supported by the Project of the Regional Government “Junta de Andalucía” (PY20-00244), the Project PID2019-109355RA-I00 funded by the MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and the Grant FPU20/01294 funded by the Spanish Ministry of Universities.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the European Commission’s Copernicus programme, the United States Geological Survey (USGS), and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for distributing Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 imagery. This work represents a contribution to the CSIC Thematic Interdisciplinary Platform PTI TELEDETECT. The authors would like to thank Martha B. Dunbar for the English revision and Rocío García for the chlorophyll-a analyses. We also thank the Laboratorio de Medio Ambiente de Galicia for lending us the turbidimeter.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barnes, R.S.K. Coastal Lagoons; CUP Archive; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Coastal Lagoon Research, Present and Future: UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science; UNESCO: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kennish, M.J.; Paerl, H.W. Coastal Lagoons: Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; Kennish, M.J., Paerl, H.W., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, R.; Mostajir, B.; Troussellier, M.; Do Chi, T. Environmental Management and Sustainable Use of Coastal Lagoons Ecosystems. In Lagoons: Biology Management and Environmental Impact; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 333–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hiep, N.H.; Luong, N.D.; Viet Nga, T.T.; Hieu, B.T.; Thuy Ha, U.T.; Du Duong, B.; Long, V.D.; Hossain, F.; Lee, H. Hydrological model using ground- and satellite-based data for river flow simulation towards supporting water resource management in the Red River Basin, Vietnam. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, F.; Castañeda, O. La biodiversidad de las lagunas costeras. Ciencias 2004, 76, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inácio, M.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.B.; Bai, K.; Chen, C.F. Integrating multisensor satellite data merging and image reconstruction in support of machine learning for better water quality management. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 201, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Ecological and Economic Foundations; Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Ruzafa, Á.; Marcos Diego, C.; Gilabert Cervera, F.J. The ecology of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon: A fast changing ecosystem under human pressure. In Coastal Lagoons: Ecosystem Processes and Modeling for Sustainable Use and Development; CRC Press: Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 392–422. ISBN 1-56670-686-6. [Google Scholar]
- García-Pintado, J.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Barberá, G.G.; Albaladejo, J.; Castillo, V.M. Anthropogenic nutrient sources and loads from a Mediterranean catchment into a coastal lagoon: Mar Menor, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Ruiz, J.; Navarro, G. Sentinel-2 Satellites Provide Near-Real Time Evaluation of Catastrophic Floods in the West Mediterranean. Water 2019, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayo, J.; Rojo, D.; Olmos, S. Abundance, morphology and chemical composition of microplastics in sand and sediments from a protected coastal area: The Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cárceles, F.J.; Egea, C.; Rodríguez-Caparrós, A.B.; Barbosa, O.A.; Delgado, M.J.; Ortiz, R.; Álvarez-Rogel, J. Contents of Nitrogen, Ammonium, Phosphorus, Pesticides and Heavy Metals, in a Salt Marsh in the Coast of the Mar Menor Lagoon (SE Spain). FEB Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2006, 15, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-González, R.; Campillo, J.A.; García, V.; León, V.M. Seasonal input of regulated and emerging organic pollutants through surface watercourses to a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, H.M.; Jiménez-Cárceles, F.J. The Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain): A singular natural ecosystem threatened by human activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Campillo, S.; Fernández-Palacios, J.M.; García-Lacunza, A.; García-Oliva, M.; Ibañez, H.; Navarro-Martínez, P.C.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Quispe-Becerra, J.I.; et al. Long-Term Dynamic in Nutrients, Chlorophyll a, and Water Quality Parameters in a Coastal Lagoon During a Process of Eutrophication for Decades, a Sudden Break and a Relatively Rapid Recovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Fernández, J.; León, V.M.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Giménez-Casaduero, F.; Álvarez-Rogel, J.; Esteve-Selma, M.; Gómez, R.; Robledano, F.; Barberá, G.G.; Martínez-Fernández, J. Synthesis Report of the Current State of Mar Menor Lagoon and Its Causes in Relation to the Nutrient Contents; Informe de Asesoramiento Técnico; Instituto Español de Oceanografía (IEO): Madrid, Spain, 2019; 24p. [Google Scholar]
- Torrente, M.D.; Ruiz, J.M.; Muñoz, R.; Segura, A.; Esteller, J.; Casero, J.; Guirao, L.; Moreno, P.; Navarro, I.; Nuez, E.; et al. Collapse of macrophytic communities in a eutrophicated coastal lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. Conf. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, J.; Clemente-Navarro, P.; Mercado, J.M.; Fraile-Nuez, E.; Albentosa, M.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Santos, J. Nuevo Evento de Mortandad Masiva de Organismos Marinos en el Mar Menor: Contexto Y Factores; Informe de Asesoramiento Técnico; Instituto Español de Oceanografía (IEO): Madrid, Spain, 2021; 24p. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, A.M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Martínez-Paz, J.M.; Marcos, C. Ecosystem services and main environmental risks in a coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Murcia, SE Spain): The public perception. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 43, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Data Server (SDC) and Politechnic University of Cartagena (UPCT). 2019. Available online: https://marmenor.upct.es/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Martínez-Alvarez, V.; Gallego-Elvira, B.; Maestre-Valero, J.; Tanguy, M. Simultaneous solution for water, heat and salt balances in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.; Caniego, G.; Hernández-Sáez, N.; Dominguez-Gomez, J.A.; Erena, M. Phytoplankton Distribution in Mar Menor Coastal Lagoon (SE Spain) during 2017. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, J.M.; Cortés, D.; Gómez-Jakobsen, F.; García-Gómez, C.; Ouaissa, S.; Yebra, L.; Ferrera, I.; Valcárcel-Pérez, N.; López, M.; García-Muñoz, R.; et al. Role of small-sized phytoplankton in triggering an ecosystem disruptive algal bloom in a Mediterranean hypersaline coastal lagoon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-H.; Stenstrom, M.K. Using satellite imagery for stormwater pollution management with Bayesian networks. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Chittimalli, S.K.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Vellucci, V. Sentinel-2/Landsat-8 product consistency and implications for monitoring aquatic systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubriot, L.; Zabaleta, B.; Bordet, F.; Sienra, D.; Risso, J.; Achkar, M.; Somma, A. Assessing the origin of a massive cyanobacterial bloom in the Río de la Plata (2019): Towards an early warning system. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Fernández, R.; Escalante, O.M.; Mamán, L.; Navarro, G. New capabilities of Sentinel-2A/B satellites combined with in situ data for monitoring small harmful algal blooms in complex coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Monitoring dissolved organic carbon by combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites: Case study in Saginaw River estuary, Lake Huron. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Tzortziou, M. Capturing dissolved organic carbon dynamics with Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 in tidally influenced wetland–estuarine systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erena, M.; Domínguez, J.A.; Aguado-Giménez, F.; Soria, J.; García-Galiano, S. Monitoring Coastal Lagoon Water Quality through Remote Sensing: The Mar Menor as a Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erena, M.; Domínguez, J.A.; Atenza, J.F.; García-Galiano, S.; Soria, J.; Pérez-Ruzafa, Á. Bathymetry Time Series Using High Spatial Resolution Satellite Images. Water 2020, 12, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, D.; Salvador, P.; Sanz, J.; Casanova, J.L. A new approach to monitor water quality in the Menor sea (Spain) using satellite data and machine learning methods. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, B.P.; Olmanson, L.G.; Mishra, D.R. A harmonized image processing workflow using Sentinel-2/MSI and Landsat-8/OLI for mapping water clarity in optically variable lake systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fichot, C.G.; Baracco, C.; Guo, R.; Neugebauer, S.; Bengtsson, Z.; Ganju, N.; Fagherazzi, S. Determining the drivers of suspended sediment dynamics in tidal marsh-influenced estuaries using high-resolution ocean color remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency (ESA). E. Sentinel-2 User Handbook. ESA Stand. Doc. Date 2015, 1, 1–64. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/685211/Sentinel-2_User_Handbook (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Sentinel-2 MSI Technical Guide 2017. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/web/sentinel/technicalguides/sentinel-2-msi (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Belward, A.; Bindschadler, R.; Cohen, W.; Gao, F.; Goward, S.N.; Helder, D.; Helmer, E.; et al. Free access to Landsat imagery. Science 2008, 320, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.J.; Kvaran, G. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager Design, Characterization and Performance. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10286–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K.G. ACOLITE Processing for Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8: Atmospheric Correction and Aquatic Applications. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of metre-scale optical satellite data for inland and coastal water applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Neukermans, G. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of turbidity in coastal waters. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Berlin, Germany, 9 September 2009; p. 74730H. [Google Scholar]
- Katlane, R.; Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.; Zargouni, F. Optical remote sensing of turbidity and total suspended matter in the Gulf of Gabes. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazirova, K.; Alferyeva, Y.; Lavrova, O.; Shur, Y.; Soloviev, D.; Bocharova, T.; Strochkov, A. Comparison of In Situ and Remote-Sensing Methods to Determine Turbidity and Concentration of Suspended Matter in the Estuary Zone of the Mzymta River, Black Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of Sentinel-3/OLCI data for mapping of suspended particulate matter and chlorophyll-a concentration in Belgian turbid coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll algorithms for ocean color sensors—OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research (SCOR). Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments: Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology; UNESCO: London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Benito, C.V.; Navarro, G.; Caballero, I. Using Copernicus Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 data to monitor harmful algal blooms in Southern Chile during the COVID-19 lockdown. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agengy (ESA). Land Monitoring 2019. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/thematic-areas/land-monitoring (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Caballero, I.; Román, A.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Navarro, G. Water quality monitoring with Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 satellites during the 2021 volcanic eruption in La Palma (Canary Islands). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Stumpf, R.P. Atmospheric correction for satellite-derived bathymetry in the Caribbean waters: From a single image to multi-temporal approaches using Sentinel-2A/B. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 11742–11766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Bélanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A global assessment of atmospheric correction methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over lakes, rivers, and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Anstee, J.; Barbosa, C.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; Cremella, B.; Giardino, C.; Gurlin, D.; et al. Simultaneous retrieval of selected optical water quality indicators from Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-3. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Steinmetz, F.; Navarro, G. Evaluation of the First Year of Operational Sentinel-2A Data for Retrieval of Suspended Solids in Medium- to High-Turbidity Waters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Nim, C.J.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Characterization of turbidity in Florida’s Lake Okeechobee and Caloosahatchee and St. Lucie Estuaries using MODIS-Aqua measurements. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5410–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana, X.; Boix, D.; Gascón, S.; Sala, J.; Comín, F.A. Management and Restoration of Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons in Europe: Reserca i Territori; Càtedra d’Ecosistemes Litorals Mediterranis, Parc Natural del Montgrí, les Illes Medes i el Baix Ter, Museu de la Mediterrània: Girona, Spain, 2018; pp. 1–220. [Google Scholar]
- Faz Cano, A.; Lobera Lössel, J.; Mora Navarro, J.; Simón Andreu, P. Depuración y descontaminación de aguas. In Informe Integral Sobre el Estado Ecológico del Mar Menor; Comité de Asesoramiento Científico del Mar Menor: Madrid, Spain, 2017; pp. 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkaitytė, R.; Razinkovas, A. Factors controlling phytoplankton blooms in a temperate estuary: Nutrient limitation and physical forcing. In Marine Biodiversity: Patterns and Processes, Assessment, Threats, Management and Conservation; Martens, K., Queiroga, H., Cunha, M.R., Cunha, A., Moreira, M.H., Quintino, V., Rodrigues, A.M., Seroôdio, J., Warwick, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Faridatul, M.I.; Wu, B.; Zhu, X. Assessing long-term urban surface water changes using multi-year satellite images: A tale of two cities, Dhaka and Hong Kong. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Długoborska, K.A.; Osińska, M.; Bialik, R.J. The Impact of Glacial Suspension Color on the Relationship Between Its Properties and Marine Water Spectral Reflectance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3258–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).