Abstract
Landslides that occur in the littoral zone of a reservoir can directly damage the hydraulic structures and threaten the lives and property around the reservoir. Due to the spatial variability and heterogeneities of rock mass, a limited amount of data obtained from laboratory and in situ tests cannot comprehensively characterize the mechanical properties of rock and soil masses. Therefore, displacement back analysis is often performed to determine the mechanical parameters of rock and soil masses. The spaceborne Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) has proved to be a powerful tool for geodesy in the measurement of landslide movement. However, InSAR can only measure the surface motion of the landslide without the subsurface information. This study uses multi-source monitoring data in the landslide displacement back analysis, including surface InSAR and an internal borehole inclinometer. The identified material parameters and finite element simulation are used to predict the landslide deformation. The case study of the Cheyiping landslide located in the Lancang River basin demonstrates the necessity and feasibility of using multi-source monitoring data in landslide displacement back analysis. The Cheyiping landslide is currently in the creep deformation stage. The decrease in shear strength of rock masses due to the rheological deformation and the change in reservoir water level are the internal and external factors leading to excessive landslide deformation. The numerical modeling can accurately simulate the landslide movement using the identified material parameters. By combing multi-source monitoring data and numerical modeling, the reservoir landslide deformation analysis can help evaluate the landslide deformation state and stability, which is vital for reservoir risk mitigation and the sustainable development of hydropower resources.
1. Introduction
At present, more and more high dams have been built on the mountainous rivers of China. The dam reservoir impoundment could influence the slope stability, reactivate ancient landslides, and even trigger new ones [1,2,3,4]. Due to reservoir water level fluctuations, bank erosion such as landslide and bank collapse has also become a major concern in these areas, threatening the safety of hydraulic structures and the lives and property around the reservoir [5,6,7]. For example, several landslides occurred during the dam construction and the subsequent reservoir storage of the Miaowei Hydropower Station located in Lancang River, causing economic losses of over 110,000,000 CNY ($17,300,000 USD) [8,9]. It has been reported that there are many risks of landslides in the Lancang River basin [10,11]. To avoid landslide disasters, reduce economic losses, and avoid casualties, landslide risk management has been changed from passive management to active prevention and control. One of the most important measures in preventing large-scale landslides is to accurately and timely grasp the development tendency of slope deformation.
For many reasons, accurate landslide displacement measurement and prediction is a challenging task. Since the last decade of the twentieth century, the use of satellite remote sensing techniques for geohazard prevention, mapping, and monitoring has grown significantly, contributing to landslide risk reduction, impact assessments, and disaster responses [12,13]. The Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) time-series technique allows for remote detection and characterization of ground surface displacements with subcentimeter precision and high spatial resolution [14,15,16,17]. Using InSAR for landslide monitoring, deformation information can be acquired in a wide range, long time series, and with high accuracy. Therefore, the InSAR measurement can not only provide spatial information of the landslide deformation but also be used in landslide displacement prediction. Using the monitoring data, many data-driven models have been built to predict landslide displacement, such as artificial neural networks [18,19], random forest [20], extreme learning machine [21], particle swarm optimization support vector machine (PSO-SVM) [22], the Newmark model [23,24,25], the data mining method [26], as well as some hybrid models [27,28,29]. However, these models do not use information other than the deformation monitoring data itself, leading to model overfitting and low landslide deformation prediction accuracy [30]. Thus, in an attempt to overcome this problem, some researchers have used the numerical modeling method to analyze landslide deformation [31,32,33,34].
Due to the spatial variability and heterogeneities of rock and soil masses, only a limited amount of data obtained from laboratory and in situ tests cannot comprehensively characterize the mechanical properties of rock and soil masses [35,36]. Thus, using the material parameters obtained either from laboratory or in situ tests cannot accurately simulate the landslide deformation [37]. In some cases, even the physical and mechanical parameters of rock and soil masses are not available [38,39,40,41]. The displacement back analysis method is therefore commonly employed to identify the material parameters and assess landslide safety [42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. However, previous studies only use either surface or internal deformation monitoring data in the displacement back analysis. For example, Ishii et al. reported a displacement back analysis for estimating the strength parameters of the landslide mass using the displacement data monitored by ground extensometers installed in boreholes [46]. Huang and Li used a displacement back analysis method to determine the mechanical parameters of the rock-soil mixture of the Wujiang landslide using the observed displacement of borehole inclinometers [47]. Ma et al. utilized the displacement back analysis method to determine the mechanical parameters of landslide bodies using the InSAR measurements [48]. As either surface or internal deformation monitoring data alone cannot fully reflect the landslide deformation state, the material parameters identified by the displacement back analysis method may not accurately reflect the mechanical properties of the landslide materials. Furthermore, the realistic three-dimensional (3D) landslide was largely simplified as a two-dimensional (2D) finite element model, which may also undermine the rationality of these studies [49,50].
In this study, we utilize multi-source deformation monitoring data and 3D finite element method (FEM) simulation in landslide displacement back analysis and deformation prediction. The Cheyiping landslide located in the Lancang River basin is used to demonstrate the necessity of this study. The rheological deformation is considered in the finite element simulation to predict the long-term displacement of the Cheyiping landslide. The displacement time series obtained by InSAR measurements and internal borehole inclinometers are used to determine the elasto-viscoplastic parameters of rock and soil masses. Based on the InSAR measurements and numerical modeling, we analyzed the deformation pattern and the deformation stage that the landslide is undergoing. Furthermore, the advantages of landslide displacement back analysis using both surface and internal monitoring data were verified by comparing them with Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and borehole data.
2. Study Area
The Cheyiping landslide is located in the upper reaches of the Lancang River, Lanping County, the central area of the World Natural Heritage of Three Rivers Parallel. It is a typical recurrence reservoir landslide and is about 39 km away from the Huangdeng Hydropower Station (Figure 1a). It has a width of approximately 600 m and a length of about 1300 m, with a height difference from crown to toe exceeding 700 m, and the left and right sides are bounded by gullies (Figure 1b–e). The borehole data indicate that the landslide thickness is between 20 and 70 m, and the landslide volume is about 20 million m3. The upper and lower parts of the landslide are relatively steep, while the middle part where Cheyiping village is located is relatively gentle. Figure 1f shows the geological cross section along profile 1-1′. According to field investigation, the landslide material mainly consists of quaternary deposits with silty clay and fragmented rubble. The silty mudstone, argillaceous siltstone, and sandstone of the Middle Jurassic Huakaizuo Formation (J2h) constitute the underlying bedrock of the landslide [51]. According to the Varnes classification system [52,53], the Cheyiping landslide can be classified as a translational rockslide. The excessive landslide movement causes damage to the houses and other facilities on the slope (Figure 2).
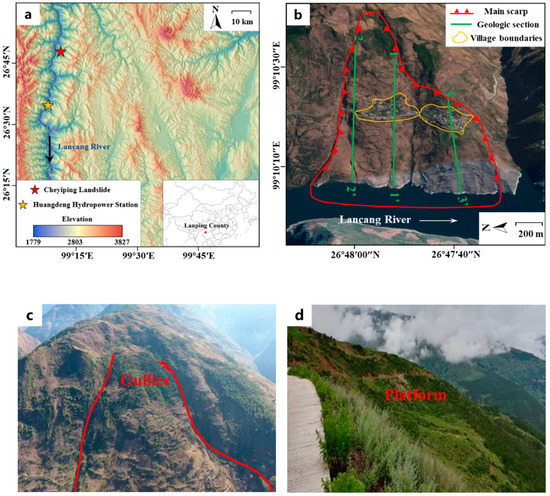
Figure 1.
The Cheyiping landslide in the reservoir area of Huangdeng Hydropower Station: (a) Geographic location of the study area. (b) Aerial view of the Cheyiping landslide and locations of three cross-sections; (c) Gullies; (d) Platform; (e) Engineering geological map of the landslide; (f) Geological cross section alone profile 1-1′.

Figure 2.
Field investigation of the Cheyiping landslide: (a) Damaged house; (b) Cracks in the road pavement; (c) Collapse of the reservoir bank; (d) Tensile cracks.
3. Data and Methods
We combined multi-source deformation monitoring data and finite element simulation to investigate the deformation process of the Cheyiping landslide. A 3D finite element model of the Cheyipong landslide was established considering realistic geological and geomorphological conditions. The surface motion of the Cheyiping landslide was measured using InSAR. By combining the internal deformation monitored by borehole inclinometers and the surface deformation measured by the InSAR technique, the elasto-viscoplastic parameters of rock and soil masses were determined using the displacement back analysis method. The time-dependent deformation of rock and soil masses was considered in the finite element simulation to predict the development of the Cheyiping landslide. The flowchart of this study is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Flowchart of this study.
A total of 73 SAR images acquired by Sentinal-1 were freely accessible through the European Space Agency (ESA) Sentinel science hub to monitor the surface deformation of the Cheyiping landslide using the time-series InSAR technique. Specifically, the datasets were collected from both ascending and descending orbits in order to overcome the limitations of the single track SAR data and SAR imaging geometry [54]. The spatial coverage of the SAR datasets can be found in Figure 4. The basic parameters of SAR data are reported in Table 1. Furthermore, Precise Orbit Data (POD) of ESA was used to correct the orbit error of sentinel-1A data. The 30 m resolution digital elevation model of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission was used to remove topographic phase contribution and geocoding.
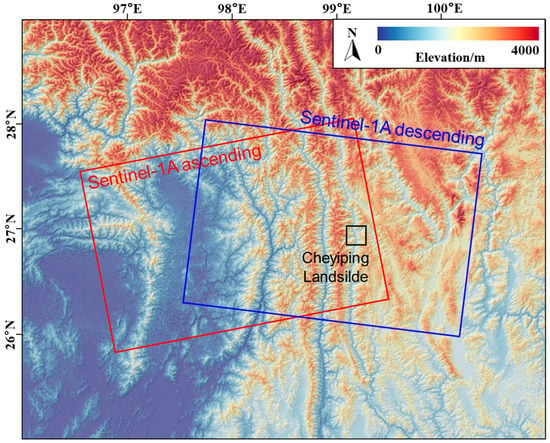
Figure 4.
The spatial coverage of the SAR images.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of SAR images.
These deformation monitoring techniques and the time range of the data are shown in Figure 5. The inclinometer was installed in boreholes to monitor the internal deformation of the landslide. Thirteen boreholes with depths ranging from 51.64 to 80.49 m were drilled into the Cheyiping landslide in 2019. The installed borehole inclinometer has a biaxial probe containing two perpendicular accelerometers. The measurements are made from the bottom of the inclinometer. As the probe is gradually raised to the top of the casing, subsequent readings are taken. Because the rockslide deformation exceeds the measurement range of the inclinometer, the borehole inclinometer monitoring data was only available between September 2019 and May 2020.
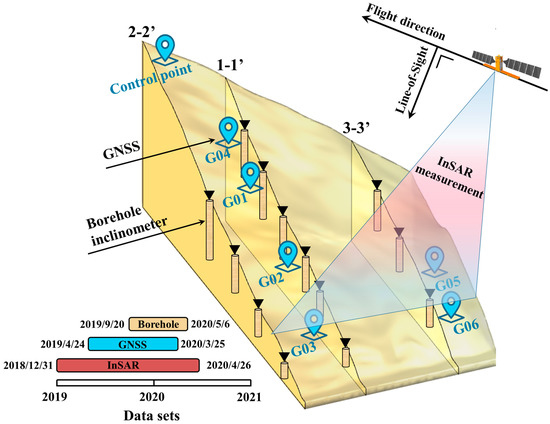
Figure 5.
The distribution of GNSS stations and boreholes and the time ranges of different monitoring data.
A network of six Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) stations was deployed on the Cheyiping landslide for surface deformation measurement. The Trimble GPS receiver continuously collected the GNSS data from 24 April 2019 to 25 March 2020 at a 30 s sampling rate. The GNSS data were downloaded every two weeks from the receiver. In order to prevent data leakage, the GNSS monitoring data were not used in the displacement back analysis. The GNSS data were used to validate the landslide deformation prediction by FEM simulation with identified material parameters.
3.1. InSAR Measurements
The small baseline subset (SBAS) InSAR time-series technique was used to measure the surface deformation of the Cheyiping landslide from space. The SBAS-InSAR technique can improve the temporal sampling rate and deformation monitoring precision by avoiding the decoherence effect caused by long interferometric pairs of spatio-temporal baselines [55,56]. The basic principle of SBAS-InSAR is to form differential interferograms by setting appropriate parameters of spatial and temporal baselines for SAR images, which aims to increase the correlation of the interferograms’ formation. The interferograms are then spatially unwrapped. The whole set of interferograms is inverted using singular value decomposition (SVD) to obtain the least square solution under the minimum norm and the time-series deformation sequence in the study area. Firstly, only interferometric pairs with a temporal baseline of less than 60 days are selected to enhance coherence in the following co-registration and time-series analysis. The Goldstein filtering eliminates the noise in the multi-view differential interferogram to reduce the noise further. Before unwrapping the phase, it is necessary to improve fringe visibility and reduce phase noise. The interferograms were processed using a multi-look operation to suppress the phase noises. Furthermore, the atmospheric artifacts were modeled using high-pass and low-pass filtering of the interferograms. After that, the interferograms were unwrapped using the 3D minimum cost flow (MCF) algorithm dealing with the Delaunay triangulation network. Finally, the standard SBAS inversion steps were executed to obtain the LOS distribution of the annual mean displacement velocity of the Cheyiping landslide.
The spaceborne InSAR observation is insensitive to motion in the north-south direction [54]. If the north-south displacement component can be neglected, we can decompose the displacement measured along ascending () and descending () LOS into horizontal (east-west) component () and vertical components () [57]. For each track, we resampled the mean LOS velocity onto a 20 m × 20 m grid which was used as input for displacement decomposition. The measurement points contained in one grid were combined as a new point. A mean velocity was calculated for the new point by averaging the velocities of all the measurement points in the grid, and its position was in the center of the grid. As described in Equation (1), the horizontal (east-west) component () and vertical component () were computed.
where and are the local incidence angles, and and represent the satellite heading angles in the ascending and descending modes, respectively.
Because the slope direction of the Cheyiping landslide is approximately east-west, the east-west displacement obtained by decomposition can be taken as the horizontal landslide displacement towards the free face. Figure 6 shows the spatial pattern of 2D displacement rates of the Cheyiping landslide. A negative value represents ground motion away from the satellite, while a positive value indicates movement towards the satellite (Figure 6b,c). The low vegetation cover in the study area is beneficial for obtaining spatially intensive InSAR measurements. The deformation regions detected using ascending and descending datasets were generally consistent. However, due to the different sensitivity of the landslide motion direction to the satellite flight direction, the extent of the deformation measured by the ascending dataset is slightly larger than that of the descending dataset. Compared with using ascending or descending data, the landslide movement can be better monitored by combing ascending and descending data.
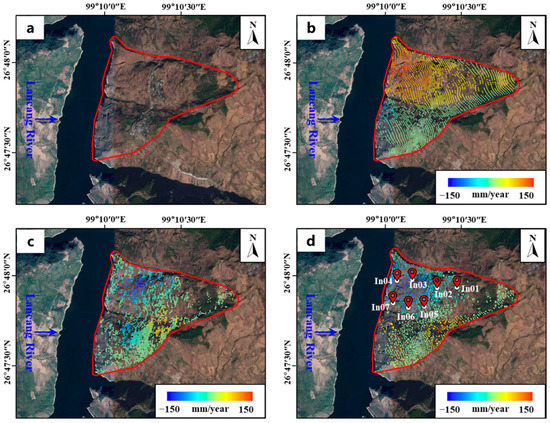
Figure 6.
Mapping and monitoring of the Cheyiping landslide using Sentinel-1 InSAR data stack: (a) Aerial view of the Cheyiping landslide (b) Mean LOS displacement rate map of ascending InSAR measurements; (c) Mean LOS displacement rate map of descending InSAR measurements. (d) East-west displacement rate map.
Figure 6d shows the mean east-west displacement velocity of the Cheyiping landslide. The negative and positive values represent the westward and eastward movement, respectively. The large deformation mainly occurs between two distinct gullies, and the displacement of the lower part of the landslide body is larger than that of the upper area. Figure 7 shows the time series of east-west displacement component of the points depicted in Figure 6d. The displacement time series exhibits a linear trend, and the displacement of the lower part of the landslide body was larger than that of the upper region. Based on field investigation and InSAR measurements, the Cheyiping belongs to a traction landslide with creep deformation [58]. This type of landslide is characterized by a greater degree of deformation in the lower part than in the upper portion of the landslide body, maintaining a certain rate of deformation as a whole and showing creeping deformation [59,60]. Overall, the time-series InSAR technique can identify the landslide hazard zone and monitor the deformation process with high accuracy.
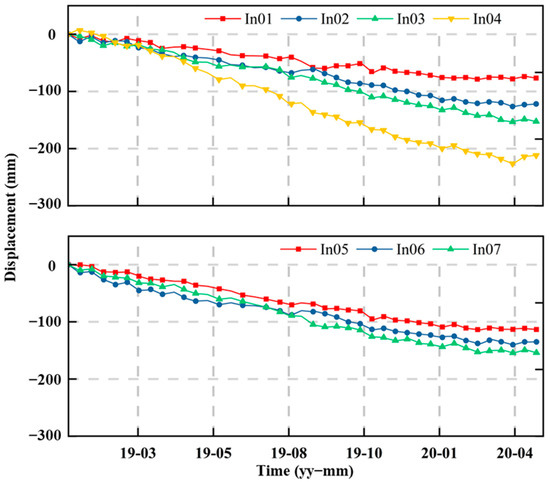
Figure 7.
East-west displacement time series of the indicated points.
3.2. Displacement Back Analysis to Identify Material Parameters
Laboratory tests were conducted to determine the physical and mechanical properties of landslide materials. However, many factors affect the representativeness of the experimental results, which is vital to the deformation and stability analysis. For example, the on-site sampling will inevitably disturb the in situ state of the rocks and soils, and the limited number of test groups and random sampling locations also lead to test data that does not reflect the actual geotechnical conditions [61]. Thus, the multi-source monitoring data and displacement back analysis were employed to identify the mechanical parameters of rock and soil masses. The multi-source monitoring data (i.e., satellite remote sensing and field-installed borehole inclinometers) can reflect the deformation state of the landslide body and provide more comprehensive a posteriori information for displacement back analysis. The displacement back analysis method uses such a posteriori information as the actual deformation monitoring data of a landslide to find an optimal set of parameter combinations so that the simulated values are close to the measured deformation.
Generally, the displacement back analysis for material parameter identification consists of two main ingredients, i.e., the construction of a surrogate model to represent finite element simulation and searching for the optimal material parameters using an optimization algorithm. We build the rockslide deformation surrogate model using a data-driven approach. First, we construct 500 sample points using orthogonal experimental design and random sampling together, each of which represents a set of material parameters of rocks and soils. By combining two sampling methods, the number of sample points and their distribution in the parameter space can guarantee the representativeness and accuracy of the surrogate model. We then perform extensive 3D finite element simulations of the Cheyiping landslide using the 500 parameter sets. The 3D finite element model of the Cheyiping landslide is discretized into 998,686 tetrahedron elements and 177,258 nodes. The finite difference software FLAC3D was used to simulate the landslide deformation. Finally, the surrogate model, an artificial neural network model, is trained using parameter set as input and simulated landslide deformation as model output. The neural-network-based surrogate model can thus replace the 3D finite element simulations.
We use a modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for the parameter inversion analysis, which incorporates a self-organizing topology structure and self-adaptive adjustable parameters. The K-Means clustering method periodically divides the particle swarm into several sub-swarms, providing a new information channel for particles. The information sharing between particles is restricted to the sub-swarm, which helps maintain the diversity of the population and improves the searchability of the particle swarm. The self-adaptive gradient-based parameter adjustment strategy can maintain a dynamic balance between the exploration and exploitation capabilities of each particle. The self-organizing topology and the self-adaptive parameter adjustment strategy can ensure the diversity and search dynamics of the particle swarm. In addition, the Bayesian optimization method is used to optimize the hyperparameters of the modified particle swarm optimization algorithm.
The modified PSO algorithm is used to find the optimal parameter set by minimizing the objective function, which is defined as the 2-norm of the difference between the simulated and observed displacement at the monitoring points.
where is the parameter set of rocks and soils to be identified, is the simulated displacement at the monitoring point, , is the corresponding observed displacement, and is the number of monitoring points used in the displacement back analysis. Seven InSAR measurement points and five monitoring points at different depths of internal borehole inclinometers ZK3-1, ZK-3-5, ZK3-7, ZK3-9, and BZK1-6 were used in the calculation of the objective function (shown in Figure 8).
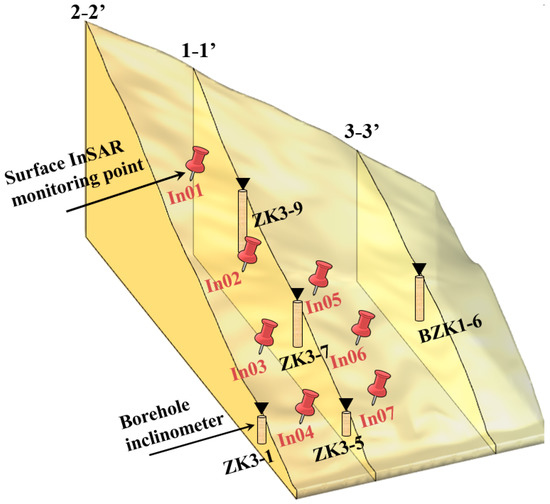
Figure 8.
Displacement monitoring points used in the displacement back analysis, including seven InSAR measurement points and five borehole inclinometers.
The deformation monitoring indicates that the Cheyiping landslide has evident rheological characteristics. Thus, it is necessary to consider the creep deformation of rock and soil masses [62,63]. The viscoplastic constitutive model CPOWER was adopted in the finite element simulation [64]. The viscoplastic model combines the behavior of the viscoelastic two-component Norton power law and the Mohr-Coulomb elastoplastic models. The total strain rate is decomposed into elastic , viscous , and plastic components:
Creep is activated by the von Mises stress in accordance with the Norton power law (, is the second invariant of stress deviator tensor), and the creep rate is
The direction of creep flow is derived from the definition of :
The Norton power law is used to model the creep behavior [65]. The standard form of this law is
where is the creep rate, and are material properties.
According to the geological exploration, the Cheyiping landslide consists of various sediment layers which have been considered in the finite element simulation. The displacement back analysis is thus performed to determine the viscoplastic model parameters for each stratum, including elastic modulus E, cohesion c, internal friction angle φ, and two creep model parameters, and .
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Displacement Back Analysis Using Multi-Source Monitoring Data
Using multi-source monitoring data in the displacement back analysis, we can identify the viscoplastic model parameters of each stratum (as listed in Table 2). The model parameters determined by laboratory tests and engineering analogy are also listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
The identified parameters of each stratum.
To further demonstrate the necessity of using both surface and internal monitoring data in the displacement back analysis, we also performed displacement back analysis using internal and surface deformation data alone. Twelve borehole inclinometer points at different depths of different sites and twelve InSAR measurement points were used in the “Internal ONLY” and “Surface ONLY” displacement back analysis. To verify the numerical simulation results, the beginning time of the FEM simulation was the same as ground data. Figure 9a–c show the deformation contours of the Cheyiping landslide obtained by finite element simulations using the viscoplastic model parameters identified by back analysis with “Surface ONLY”, “Internal ONLY”, and multi-source deformation data, respectively. The landslide simulation results differ significantly in both magnitude and spatial patterns. With “Surface ONLY” displacement back analysis, the maximum deformation and the large deformation region are close to the monitoring results. However, the deformation is not continuous in space, which is not typical of a traction creep deformation landslide (Figure 9a).
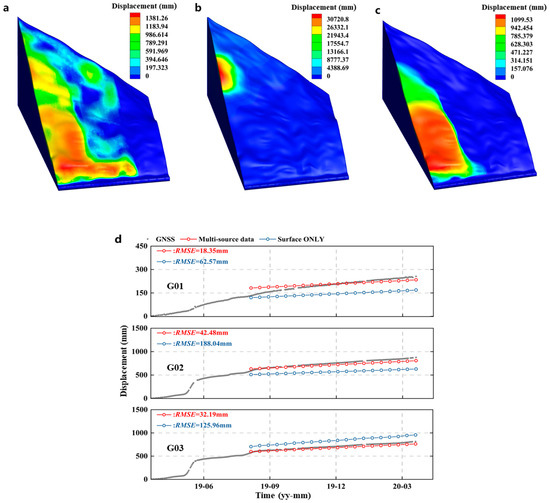
Figure 9.
Comparison of the simulation results: (a–c) Contours of the simulated landslide displacement based on back analysis using “Surface ONLY”, “Internal ONLY”, and multi-source monitoring data, respectively. (d) Comparison of the simulation results at GNSS stations G01, G02, G03 with corresponding GNSS displacement monitoring data.
With “Internal ONLY” displacement back analysis, the landslide simulation result differs significantly from the observed deformation patterns (Figure 9b). The large-scale displacement occurs in the middle and upper part of the Cheyiping landslide, inconsistent with InSAR measurements and field investigation. Besides, the maximum displacement is nearly thirty times larger than the observed value. Due to the limited number of boreholes, the internal monitoring points used in the displacement back analysis cannot capture the spatial details of the landslide deformation.
As shown in Figure 9c, by combing InSAR measurements and borehole inclinometer monitoring data in the displacement back analysis, the identified model parameters and finite element simulation can successfully reproduce the deformation characteristics of the Cheyiping landslide. It is a traction-type circular sliding of the loose surface rock and soil masses within the landslide body. The large deformation region corresponds to the reservoir bank collapse area shown in Figure 2c. We then compared the simulated displacement time series at three GNSS sites with GNSS displacement monitoring data. The locations of these GNSS stations are shown in Figure 5. It should be noted that the GNSS monitoring data was not used in the displacement back analysis to avoid data leakage. As shown in Figure 9d, using “Surface ONLY” and multi-source monitoring data in displacement back analysis, the finite element simulation and identified model parameters can accurately reflect the development trend of these three points. The simulated displacements are in good agreement with the GNSS monitoring data by incorporating both InSAR and borehole inclinometer monitoring data in the displacement back analysis.
Figure 10a,b shows the displacement contours of section 1-1′ for the displacement back analysis using multi-source and “Surface ONLY” monitoring data. In both cases, the simulation results demonstrate a typical shallow landslide involving the movement of a relatively thin layer of the rock and soil masses. As shown in Figure 10c–h, using multi-source monitoring data in displacement back analysis, the simulation results with identified model parameters are much closer to the monitored displacements of boreholes ZK3-5, ZK3-7 and ZK3-9. This verifies that both surface deformation and internal sliding of the landslide can be accurately simulated by displacement back analysis using multi-source monitoring data. The above comparisons demonstrate the necessity of using multi-source monitoring data in displacement back analysis.
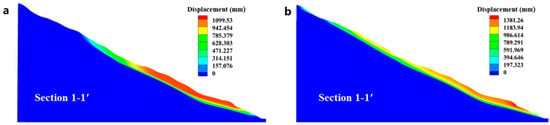
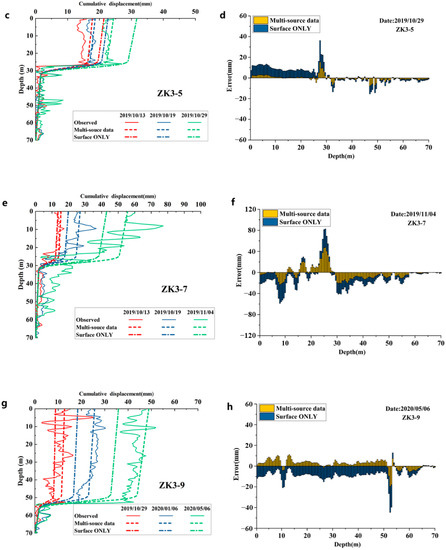
Figure 10.
(a,b) Displacement contours of section 1-1′ for displacement back analysis using multi-source and “Surface ONLY” monitoring data, respectively. (c,e,g) Comparisons of the simulated displacements along the boreholes ZK3-5, ZK3-7, and ZK3-9 with measured data. (d,f,h) Error distributions of the simulated displacements along with the borehole depth.
4.2. Deformation Characterristics and Triggering Factors of the Cheyiping Landslide
The landslide displacement monitoring and finite element simulation indicate that the Cheyiping landslide is typical of the traction landslide with creep deformation. The circular-shaped tension cracks found in the trailing edge and bank collapse observed at the front edge are typical features of this type of landslide. Figure 11 shows the relationship between the GNSS monitoring data at G01, G02, and G03 and the change in reservoir water level. A significant increase in landslide displacement can be observed when the reservoir water level changes. This indicates that the change of reservoir water level is the main external factor causing the deformation of the Cheyiping landslide. The reservoir water level fluctuations significantly change the hydrogeological conditions of reservoir banks and thus affect the steady-state of the bank slope [66]. The rock and soil masses close to the Lancang River are subjected to reservoir water immersion and wave erosion, which change the original stability conditions, causing deformation, collapse, and landslide of the reservoir banks to reach a new equilibrium. The large deformation in the lower part of the deposit then leads to traction in the upper part of the landslide, forming many tension cracks in the trailing edge of the landslide.
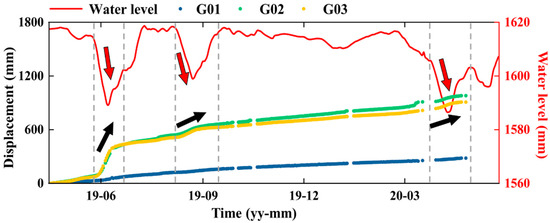
Figure 11.
Time-series of cumulative displacement at G01, G02, and G03 and the change in reservoir water level.
In addition, we can analyze the intrinsic factors responsible for the creep deformation by comparing the identified model parameters with those obtained by experimental tests. Most of the landslides are in the creeping deformation state. The shear strength of landslide material is not a constant value but is closely related to its deformation rate [67,68]. As shown in Table 2, the cohesion (c) and internal friction angle (φ) identified by the displacement back analysis are smaller than the experimental values. This indicates that when the landslide enters the creeping sliding state, the landslide material will gradually decrease its strength due to creep, consistent with the previous studies [69,70,71]. Therefore, for a landslide with considerable creep deformation, it is necessary to consider the reduction of shear strength due to creep effects. In this case, catastrophic failure may occur in a short period of time if the rock and soil masses experience a sudden reduction in the peak shear strength due to external factors.
It is necessary to take some measures to control the landslide deformation. Otherwise, the reservoir water level fluctuations and strength reduction due to creep deformation could cause further deformation and gradual disintegration. First, a row of anti-slip piles should be set up in the lower part of Cheyiping village and along the outer side of the road, with a length of about 400 m, and the axis should be parallel to the road to cut off the traction effect of the landslide upward. For the section near the edge of the two gullies, the potential sliding surface is deeper and the terrain is steeper, which is not conducive to the placement of anti-slip piles and should be supported by anchor cable lattice beams [72]. In addition, we propose to relocate the residents located on the outer side of the road.
4.3. Further Application of Multi-Source Monitoring Data in Deformation Back Analysis
The displacement back analysis method has been widely employed to determine the constitutive model parameters of rock and soil masses and to assess the landslide safety [42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. One of the key issues in the displacement back analysis is the selection of the monitoring data that can reflect the deformation characteristics of the landslide [36]. With the development of new monitoring technology (e.g., LiDAR, ground-based synthetic aperture radar), different landslide monitoring techniques are being applied to the measurements of landslide displacements over time [58]. Satellite and ground-based radar systems have considerably increased the areal coverage and spatial resolution of surface displacement monitoring data. The more functional borehole sensors together with wireless data acquisition and transmission have significantly increased the temporal resolution of subsurface slope deformation monitoring data. These traditional and innovative monitoring techniques provide increased capacity to fully capture the landslide behavior.
A single technique alone only reflects distinct deformation features in different parts of the landslide [54]. A multi-source monitoring dataset can reduce uncertainty and supplement missing information from a single source [73]. For example, the combination of InSAR measurements and a borehole inclinometer enables the simultaneous acquisition of surface and internal landslide displacement data. The multi-source monitoring data assisted in determining the optimal rock and soil masses properties by displacement back analysis. However, the monitoring data obtained from different sources have different monitoring accuracy and spatial and temporal resolutions [74,75]. Systematically combining monitoring data from multiple sensors to take advantage of their complementary characteristics is a complicated task. Particularly with the addition of multiple data sources, it becomes more complex when using a data fusion method. Therefore, a general multi-source data fusion framework is worthy of in-depth study.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the Cheyiping landslide located in the Lancang River basin is used to demonstrate the necessity of using both surface and internal deformation monitoring data in the displacement back analysis. The proposed method can accurately reproduce deformation characteristics and predict the displacement of the landslide. It can be used as an effective tool for landslide deformation analysis, which is of great significance and value for improving landslide risk assessment and landslide prevention.
The InSAR measurements provide surface deformation data with high spatial resolution, which can not only monitor the slow-moving process but also identify the landslide hazard zone. The surface InSAR measurements together with the internal borehole clinometer monitoring data can assist in determining the optimal elasto-viscoplastic parameters of rock and soil masses through the displacement back analysis method to the further numerical simulations. It is clear that the finite element simulation using the identified material parameters can accurately reproduce deformation characteristics of the Cheyiping landslide. The simulated displacement time series are in good agreement with the GNSS data. The multi-source monitoring data and numerical simulation show that the Cheyiping landslide is a traction landslide. The reduction of geotechnical strength parameters due to creep and the change of reservoir water level are internal and external factors leading to deformation.
In the present study, creep parameters are considered within the FEM simulation in order to accurately predict the displacement in the creep deformation stage of the landslide, and its applicability is limited. Therefore, more improved and detailed numerical models should be used to better reconstruct the various phases of the landslide process. These aspects will be investigated in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M., C.G. and W.Z.; methodology, C.G., G.M. and Z.Z.; software, C.G. and Z.Z.; investigation, W.Z., C.G. and H.C.; validation, X.C. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, C.G.; writing—review and editing, G.M., C.G. and W.Z.; supervision, G.M. and W.Z.; funding acquisition, G.M., W.Z. and H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51825905, 52179141, and U1865204), and the Huaneng Group Science and Technology Project (HNKJ18-H24).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the European Space Agency for providing the Copernicus Sentinel-1 images.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, G.; Zheng, H.; Tang, H.; Dai, F. Huangtupo Landslide Stability under Water Level Fluctuations of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Landslides 2016, 13, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.E.; Cui, Y.; Au, K.Y.K.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, H. Case Study: Effects of a Partial-Debris Dam on Riverbank Erosion in the Parlung Tsangpo River, China. Water 2018, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Study on the Deformation Mechanism of Reservoir Landslides Considering Rheological Properties of the Slip Zone Soil: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wu, Y.; Török, Á.; Li, L.; Xue, Y. Centrifugal Model Test on a Riverine Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Induced by Rainfall and Water Level Fluctuation. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, T.; He, J.; Chen, C. Erosion-Based Analysis of Breaching of Baige Landslide Dams on the Jinsha River, China, in 2018. Landslides 2019, 16, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.W.; Stanley, E.H.; Harbor, J.M. Channel Adjustments Following Two Dam Removals in Wisconsin. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick, L.M.; Böhme, M.; Rouyet, L.; Bergh, S.G.; Corner, G.D.; Lauknes, T.R. Structurally Controlled Rock Slope Deformation in Northern Norway. Landslides 2020, 17, 1745–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, G.; Smith, J.V.; Zhang, B.; Shen, P.; Chen, H. A Complex Rockslide Developed from a Deep-Seated Toppling Failure in the Upper Lancang River, Southwest China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 293, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Lv, C.; Zhou, Y.F. Impact of Fluid Turbulent Shear Stress on Failure Surface of Reservoir Bank Landslide. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.K.; Yao, X.; Yao, C.; Li, C.; Gang, C. Mapping of Geomorphic Dynamic Parameters for Analysis of Landslide Hazards: A Case of Yangbi River Basin on the Upper Lancang-Mekong of China. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; De-jie, L.; Kai-hua, C.; Jia-wen, Z. Failure Mechanism and Stability Analysis of the Zhenggang Landslide in Yunnan Province of China Using 3D Particle Flow Code Simulation. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 891–905. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.; Hurni, L.; Gogu, R. Remote Sensing of Landslides: An Analysis of the Potential Contribution to Geo-Spatial Systems for Hazard Assessment in Mountainous Environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, P.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Nuremanguli, T.; Ma, H. Landslide Mapping with Remote Sensing: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1555–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, Y.; Yin, K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Catani, F.; Ahmed, B. Landslide Characterization Applying Sentinel-1 Images and Insar Technique: The Muyubao Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Kim, J.W.; Niu, Y. Diagnosis of Xinmo (China) Landslide Based on Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observation and Modeling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, R. Study on the Creep-Sliding Mechanism of the Giant Xiongba Ancient Landslide Based on the SBAS-InSAR Method, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, N.; Chen, D. Analyzing Landslide-Prone Loess Area of Heifangtai, Gansu, China Using SBAS-InSAR Technique. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4889–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yin, K.; Lacasse, S. Displacement Prediction in Colluvial Landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Niu, R. Displacement Prediction of Baijiabao Landslide Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network in Three Gorges Area, China. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 111, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, W.; Liu, C.; He, C.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H. Landslide Displacement Prediction Using Kinematics-Based Random Forests Method: A Case Study in Jinping Reservoir Area, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 283, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yin, K.; Alexander, D.E.; Zhou, C. Using an Extreme Learning Machine to Predict the Displacement of Step-like Landslides in Relation to Controlling Factors. Landslides 2016, 13, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yin, K.; Cao, Y.; Ahmed, B. Application of Time Series Analysis and PSO-SVM Model in Predicting the Bazimen Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng. Geol. 2016, 204, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingles, J.; Darrozes, J.; Soula, J.C. Effects of the Vertical Component of Ground Shaking on Earthquake-Induced Landslide Displacements Using Generalized Newmark Analysis. Eng. Geol. 2006, 86, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibson, R.W. Regression Models for Estimating Coseismic Landslide Displacement. Eng. Geol. 2007, 91, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, G.; Du, C.; Jin, F.; Feng, K.; Chen, Z. An Integrated SEM-Newmark Model for Physics-Based Regional Coseismic Landslide Assessment. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Liao, K.; Xue, Y. Triggering Factors and Threshold Analysis of Baishuihe Landslide Based on the Data Mining Methods. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 2677–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Tannant, D.D.; Lin, C.; Xia, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J. Combined Forecasting Model with CEEMD-LCSS Reconstruction and the ABC-SVR Method for Landslide Displacement Prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zeng, Z.; Yao, W.; Tang, H. Multiple Neural Networks Switched Prediction for Landslide Displacement. Eng. Geol. 2015, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y. Prediction of Landslide Displacement with Step-like Behavior Based on Multialgorithm Optimization and a Support Vector Regression Model. Landslides 2018, 15, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Huang, B.; Ren, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, B.; Chen, Z. Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion and Sensitivity States. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemenda, A.I.; Bois, T.; Bouissou, S.; Tric, E. Numerical Modelling of the Gravity-Induced Destabilization of a Slope: The Example of the La Clapière Landslide, Southern France. Geomorphology 2009, 109, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Taiebat, H. Finite Element Simulation of an Excavation-Triggered Landslide Using Large Deformation Theory. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, G.; Mantovani, M.; Pasuto, A.; Zabuski, L.; Borgatti, L. Monitoring, Numerical Modelling and Hazard Mitigation of the Moscardo Landslide (Eastern Italian Alps). Eng. Geol. 2012, 128, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Krabbenhoft, K.; Tinti, S. A Case Study and Implication: Particle Finite Element Modelling of the 2010 Saint-Jude Sensitive Clay Landslide. Landslides 2020, 17, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Hwang, J.H.; Luo, Z.; Juang, C.H.; Xiao, J. Probabilistic Back Analysis of Slope Failure—A Case Study in Taiwan. Comput. Geotech. 2013, 51, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ering, P.; Babu, G.L.S. Probabilistic Back Analysis of Rainfall Induced Landslide- A Case Study of Malin Landslide, India. Eng. Geol. 2016, 208, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, M.; Bertello, L.; Bernardi, A.R.; Caputo, G. Back Analysis of a Large Landslide in a Flysch Rock Mass. Landslides 2017, 14, 2041–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Zuo, S.; Lin, Y.L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Reliability Back Analysis of Shear Strength Parameters of Landslide with Three-Dimensional Upper Bound Limit Analysis Theory. Landslides 2016, 13, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q. Stability Analysis of Earthquake-Induced Rock Slope Based on Back Analysis of Shear Strength Parameters of Rock Mass. Eng. Geol. 2017, 228, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, X. InSAR Observation and Numerical Modeling of the Earth-Dam Displacement of Shuibuya Dam (China). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinoda, M.; Miyata, Y.; Kurokawa, U.; Kondo, K. Regional Landslide Susceptibility Following the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake Using Back-Calculated Geomaterial Strength Parameters. Landslides 2019, 16, 1497–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okui, Y.; Tokunaga, A.; Shinji, M.; Mori, S. New Back Analysis Method of Slope Stability by Using Field Measurements. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1997, 34, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Ru, Z.; Sun, Q. Probabilistic Back Analysis Based on Bayesian and Multi-Output Support Vector Machine for a High Cut Rock Slope. Eng. Geol. 2016, 203, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yin, T.; Zhou, C. A Back-Analysis Method Using an Intelligent Multi-Objective Optimization for Predicting Slope Deformation Induced by Excavation. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yao, D. Comprehensive Monitoring of Talus Slope Deformation and Displacement Back Analysis of Mechanical Parameters Based on Back-Propagation Neural Network. Landslides 2021, 18, 1889–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Ota, K.; Kuraoka, S.; Tsunaki, R. Evaluation of Slope Stability by Finite Element Method Using Observed Displacement of Landslide. Landslides 2012, 9, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Li, C. Back-Analysis for the Elasto-Viscoplastic Parameters of Landslides Based on the Observed Displacements: A Case Study of the Wujiang Landslide, China. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 4639–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y. Coupling InSAR and Numerical Modeling for Characterizing Landslide Movements under Complex Loads in Urbanized Hillslopes. Landslides 2021, 18, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y. A Three-Dimensional Large-Deformation Random Finite-Element Study of Landslide Runout Considering Spatially Varying Soil. Landslides 2021, 18, 3149–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, A.; Conte, E.; Donato, A. Two and Three-Dimensional Numerical Analysis of the Progressive Failure That Occurred in an Excavation-Induced Landslide. Eng. Geol. 2014, 183, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Deng, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G. Behavior of Major and Trace Elements during Weathering of Sericite-Quartz Schist. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnes, D. Slope Movement Types and Processes. Spec. Rep. 1978, 176, 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hungr, O.; Leroueil, S.; Picarelli, L. The Varnes Classification of Landslide Types, an Update. Landslides 2014, 11, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Samsonov, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, M.; Tomás, R. Three-Dimensional and Long-Term Landslide Displacement Estimation by Fusing C- and L-Band SAR Observations: A Case Study in Gongjue County, Tibet, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Schmidt, D. Active Movement of the Cascade Landslide Complex in Washington from a Coherence-Based InSAR Time Series Method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, X. Remote Sensing of Deformation of a High Concrete-Faced Rockfill Dam Using InSAR: A Study of the Shuibuya Dam, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, D.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R. InSAR Study of Landslides: Early Detection, Three-Dimensional, and Long-Term Surface Displacement Estimation—A Case of Xiaojiang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, S.; Han, S.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, Q.; Xin, P. Rainfall-Induced Landslide in Loess Area, Northwest China: A Case Study of the Changhe Landslide on September 14, 2019, in Gansu Province. Landslides 2020, 17, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Cui, Z.Q.; Wang, X.P. Mass Rock Creep and Landsliding on the Huangtupo Slope in the Reservoir Area of the Three Gorges Project, Yangtze River, China. Eng. Geol. 2000, 58, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Criss, R.; Su, A.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, C. Deformation Response of the Huangtupo Landslide to Rainfall and the Changing Levels of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yuan, W.; Ma, G.; Chang, X. Combined Finite-Discrete Element Method Modeling of Rockslides. Eletronic Libr. 2018, 34, 1530–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, H.; Mizuno, T.; Ishii, T. Prediction of a Landslide and Analysis of Slide Motion with Reference to the 2004 Ohto Slide in Nara, Japan. Geomorphology 2010, 124, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, A.; Charlier, J.B.; Fabbri, O.; Bertrand, C.; Carry, N.; Mudry, J. Functioning and Precipitation-Displacement Modelling of Rainfall-Induced Deep-Seated Landslides Subject to Creep Deformation. Landslides 2016, 13, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yang, C.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, N.; Ge, X.; Li, H.; Han, Y. Stability Evaluation of Underground Gas Storage Salt Caverns with Micro-Leakage Interlayer in Bedded Rock Salt of Jintan, China. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Ma, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Cai, R. Damage Evolution and Deformation of Rock Salt Under Creep-Fatigue Loading. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maihemuti, B.; Wang, E.; Hudan, T.; Xu, Q. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Reservoir Bank Fractured Rock-Slope Deformation and Failure Processes. Int. J. Geomech. 2016, 16, 4015058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Chen, C.H. Application of DDA to Simulate Characteristics of the Tsaoling Landslide. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Huo, Z.T.; Matsumoto, T.; Huang, B.L. The July 14, 2003 Qianjiangping Landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 2004, 1, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Cui, D.; Su, A.; Xiang, W. Creep Properties of Clastic Soil in a Reactivated Slow-Moving Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 267, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, R.; Wen, Z. Improved Nonlinear Burgers Shear Creep Model Based on the Time-Dependent Shear Strength for Rock. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Hu, C.; Zhou, W.; Ma, G.; Zhang, C. A Combined Continuous-Discontinuous Approach for Failure Process of Quasi-Brittle Materials. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2014, 57, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, K.B.; Yu, H.; Tao, Z.Y. Field Investigation and Numerical Study of a Siltstone Slope Instability Induced by Excavation and Rainfall. Landslides 2020, 17, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Long, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Feng, P.; Li, B.; Xian, J. Mechanism Analysis and Partition Characteristics of a Recent Highway Landslide in Southwest China Based on a 3D Multi-Point Deformation Monitoring System. Landslides 2021, 18, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Garthwaite, M.C. Resolving Three-Dimensional Surface Motion with InSAR: Constraints from Multi-Geometry Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Jia, C.; Chen, S.; Li, H. SBAS-InSAR Based Deformation Detection of Urban Land, Created from Mega-Scale Mountain Excavating and Valley Filling in the Loess Plateau: The Case Study of Yan’an City. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).