Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications for Agriculture and Land Resources Development Using Remote Sensing Datasets in Central Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
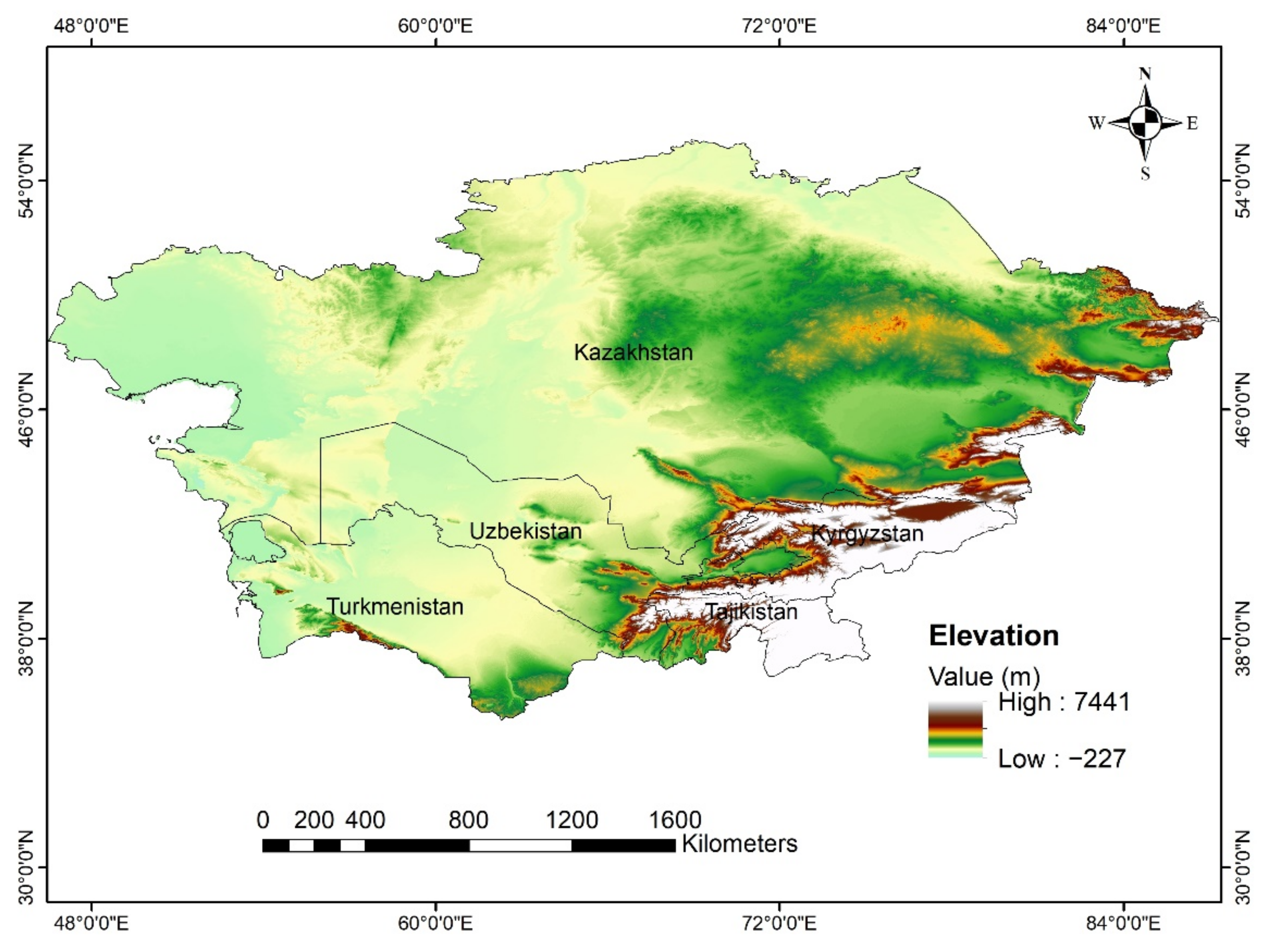
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Soil Salinity across Central Asia
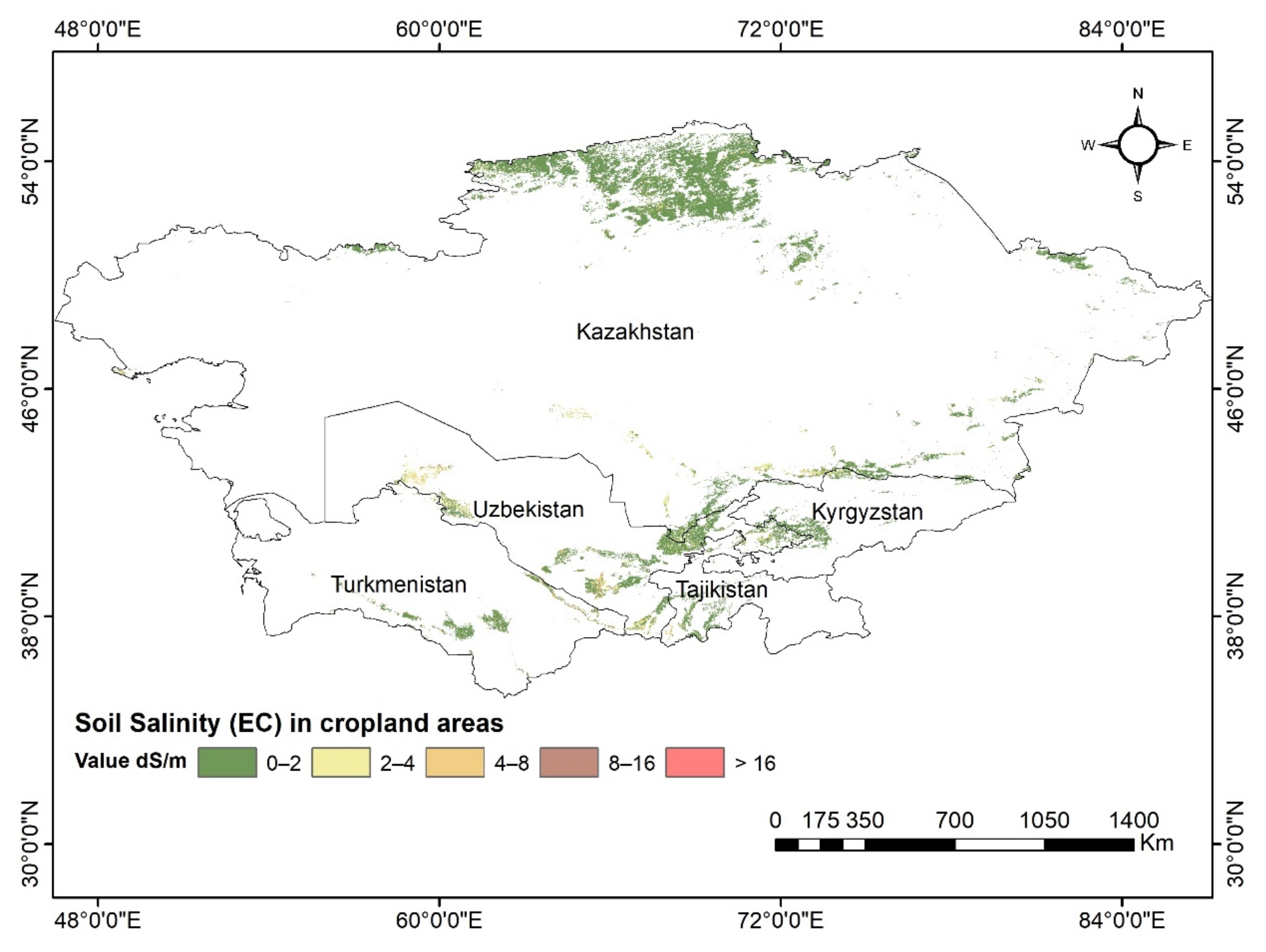
3.2. Soil EC in Cropland Areas
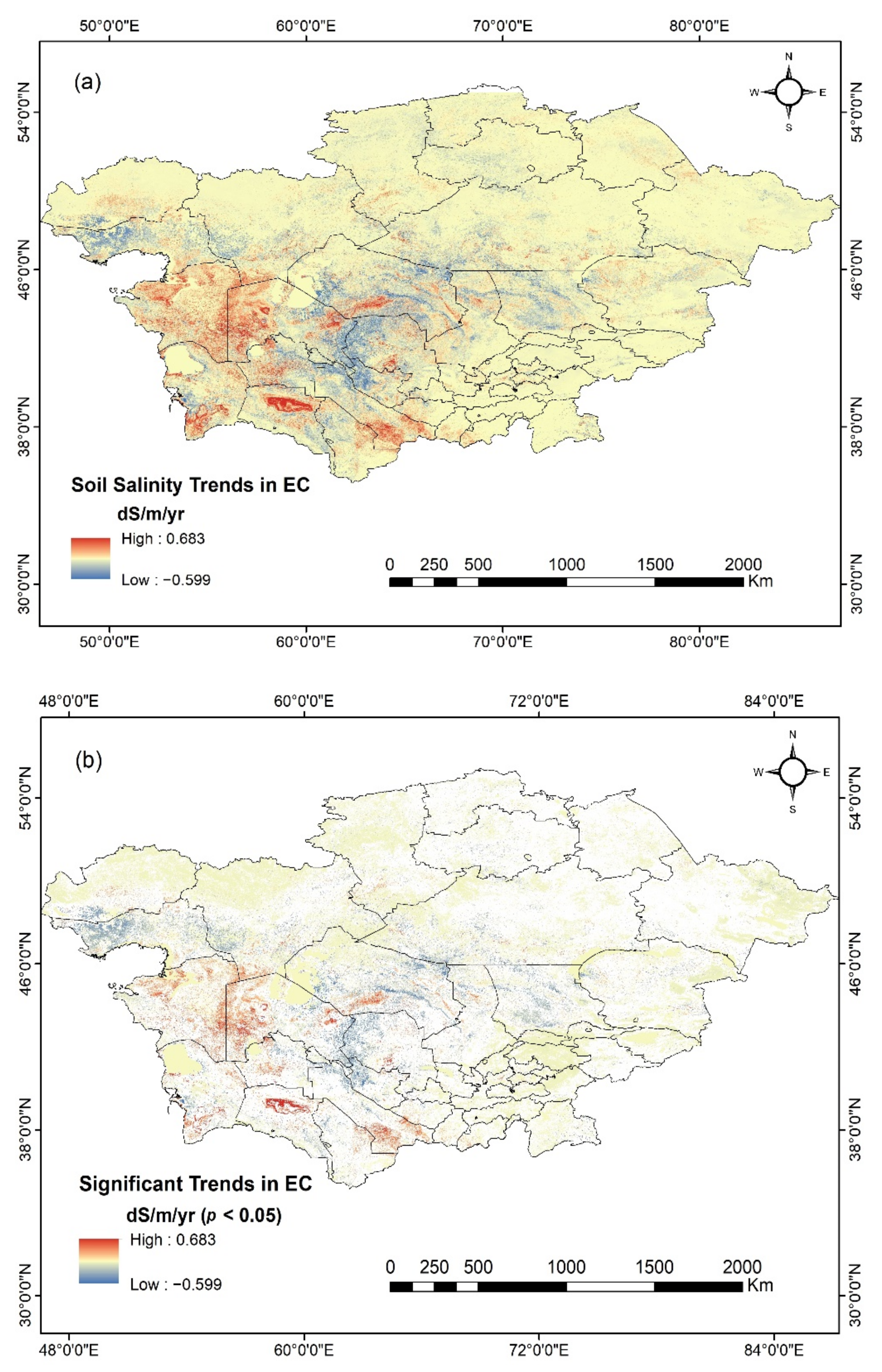
3.3. Soil EC Trends
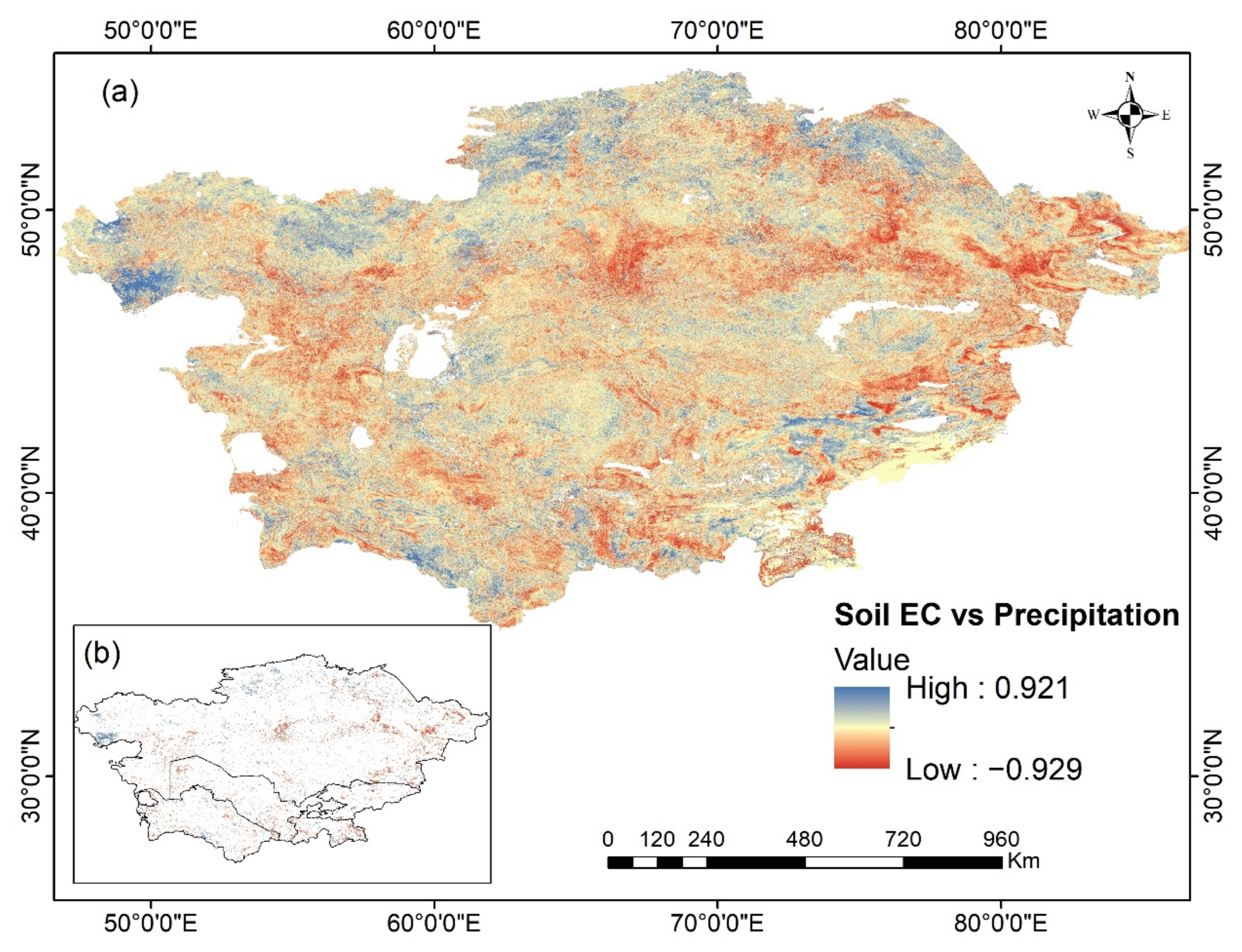
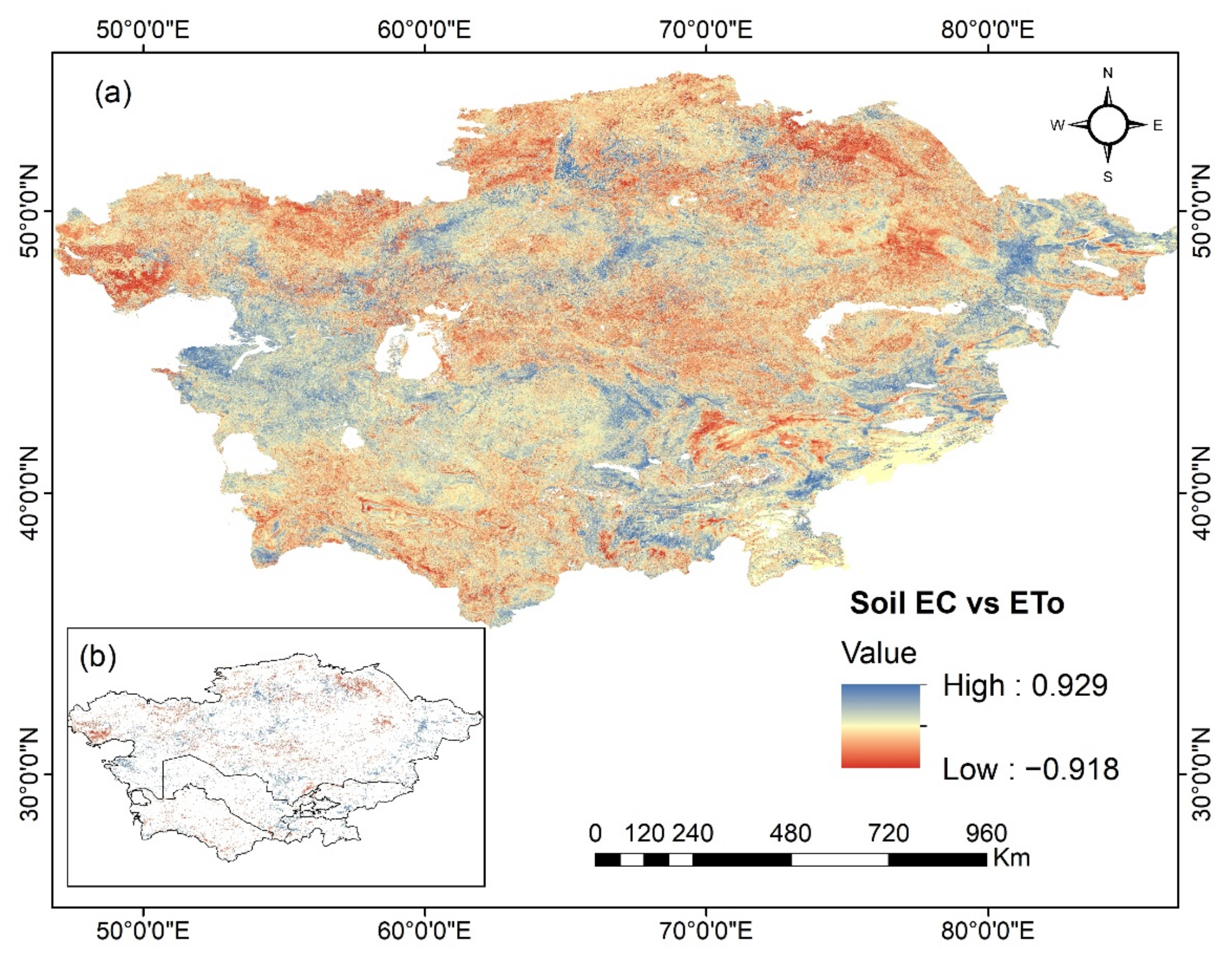
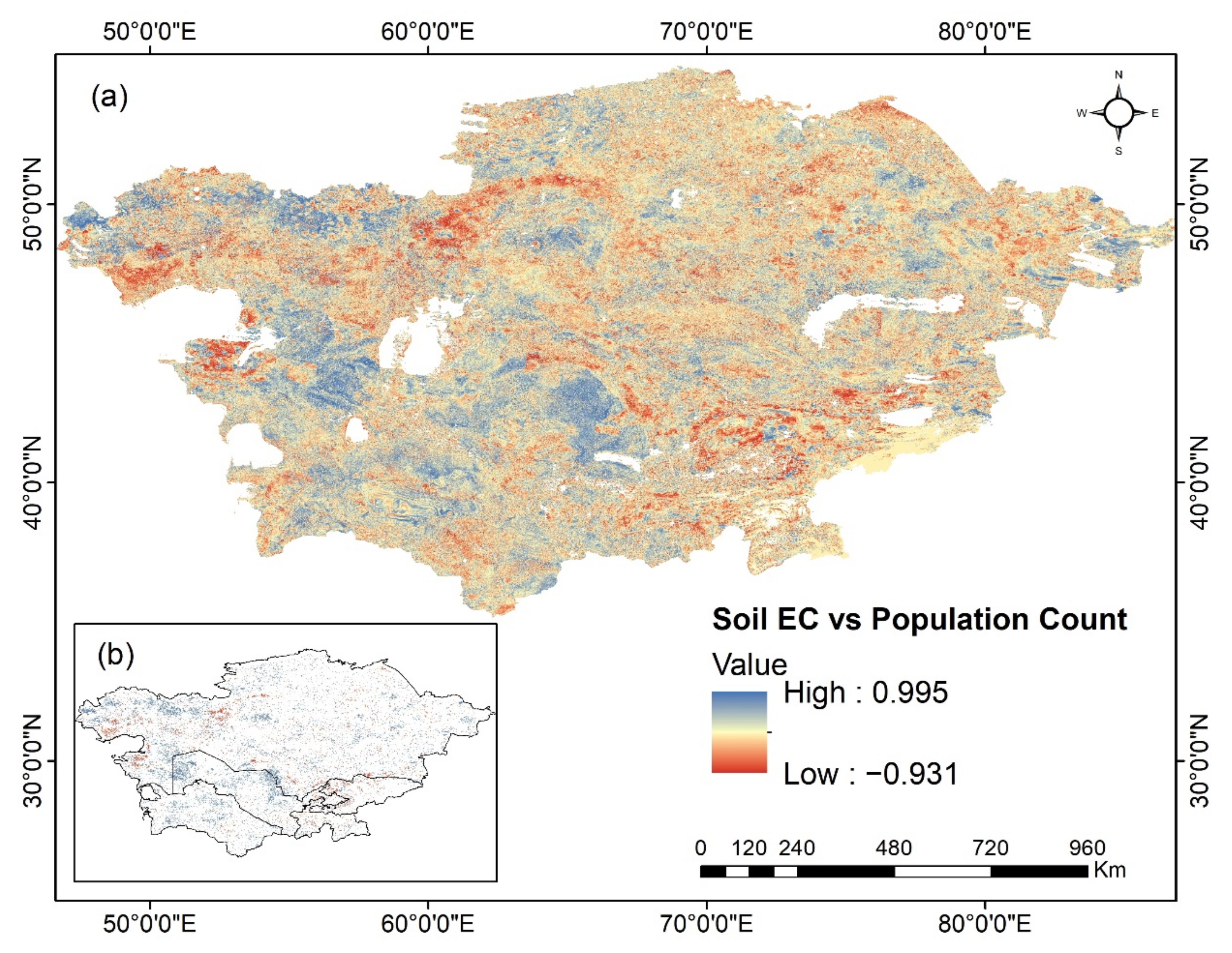
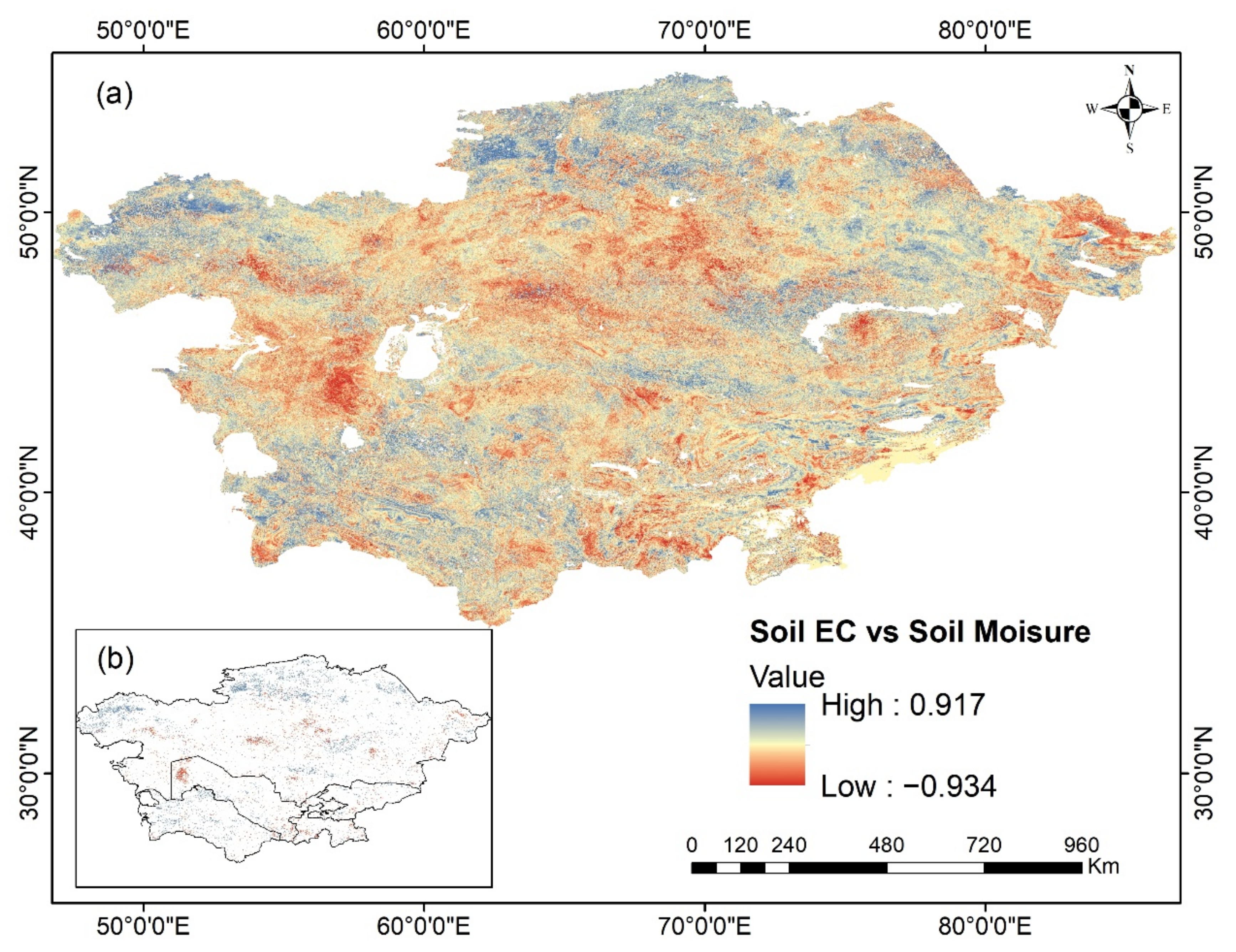
3.4. Factors Affecting Soil EC Variations from 2000 to 2018
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of Salt-Affected Areas
4.2. Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Climate change and soil degradation mitigation by sustainable management of soils and other natural resources. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmatov, R.; Khasanov, S.; Odilov, S.; Li, F. Assessment of the space-time dynamics of soil salinity in irrigated areas under climate change: A case study in sirdarya province, Uzbekistan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasanov, S.; Li, F.; Kulmatov, R.; Zhang, Q. Evaluation of the perennial spatio-temporal changes in the groundwater level and mineralization, and soil salinity in irrigated lands of arid zone: As an example of Syrdarya Province, Uzbekistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, T.; Sertel, E.; Tanik, A. Monitoring soil salinity via remote sensing technology under data scarce conditions: A case study from Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uri, N. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and sodicity in drylands: A review of causes, effects, monitoring, and restoration measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Kempen, B.; de Sousa, L. Global mapping of soil salinity change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, J.; Klytchnikova, I.; Lampietti, J.; Lundell, M.; Scatasta, M.; Thurman, M. Irrigation in central Asia. social, economic and environmental considerations. In Europe and Central Asia Region Environmentally and Socially Sustainable Development; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K.; Balla, D. Impact of agricultural land use in central Asia: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushiev, H.; Noble, A.D.; Abdullaev, I.; Toshbekov, U. Remediation of abandoned saline soils using glycyrrhiza glabra: A study from the hungry steppes of central Asia. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2005, 3, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmatov, R. Problems of sustainable use and management of water and land resources in Uzbekistan. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Scudiero, E. Review of soil salinity assessment for agriculture across multiple scales using proximal and/or remote sensors. Adv. Agron. 2019, 158, 1–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Predicting long-term dynamics of soil salinity and sodicity on a global scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33017–33027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Tola, E.K.; Madugundu, R.; Fulleros, R.B. Sentinel-2 images for effective mapping of soil salinity in agricultural fields. Curr. Sci. 2021, 121, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghadosi, M.M.; Hasanlou, M. Trend analysis of soil salinity in different land cover types using Landsat time series data (case study Bakhtegan Salt Lake). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.V.; Tran, D.X.; Myint, S.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Pham, H.V.; Luu, T.H.; Vo, T.M.T. Examining spatiotemporal salinity dynamics in the mekong river delta using landsat time series imagery and a spatial regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Potential risk of soil salinization in different regions of central Asia with special reference to salt reserves in deep layers of soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirokova, Y.; Forkutsa, I.; Sharafutdinova, N. Use of electrical conductivity instead of soluble salts for soil salinity monitoring in central Asia. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2000, 14, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Kulmatov, R.; Wang, G.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhu, N.; et al. Agricultural impacts drive longitudinal variations of riverine water quality of the aral sea basin (amu darya and syr darya rivers), central Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toderich, K.; Ismail, S.; Massino, I.; Wilhelm, M.; Yusupov, S.; Kuliev, T. Extent of Salt-Affected Land in Central Asia: Biosaline Agriculture and Utilization of the Salt-Affected Resources; KIER Working Papers 648; Kyoto University, Institute of Economic Research: Kyoto, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bobojonov, I.; Aw-Hassan, A. Impacts of climate change on farm income security in central Asia: An integrated modeling approach. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulatov, A.; Khamidov, A.; Akhmatov, D.; Pulatov, B.; Vasenev, V. Soil salinity mapping by different interpolation methods in mirzaabad district, syrdarya province. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 883, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Corwin, D.L.; Anderson, R.G.; Skaggs, T.H. Moving forward on remote sensing of soil salinity at regional scale. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latonov, A.P.; Arimov, A.K.; Rathapar, S.P. Using satellite images for multi-annual soil salinity mapping in the irrigated areas of syrdarya province, Uzbekistan. J. Arid Land Stud. 2015, 25, 225–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sidike, A.; Zhao, S.; Wen, Y. Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo County of China using QuickBirddata and soil reflectance spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar]
- Haag, I.; Jones, P.D.; Samimi, C. Central Asia’s changing climate: How temperature and precipitation have changed across time, space, and altitude. Climate 2019, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmatov, R.; Rasulov, A.; Kulmatova, D.; Rozilhodjaev, B.; Groll, M. The modern problems of sustainable use and management of irrigated lands on the example of the bukhara region (Uzbekistan). J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 956–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pankova, E.I.; Konyushkova, M.V. Climate and soil salinity in the deserts of Central Asia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2013, 46, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Friedl, M.A. User Guide to Collection 6 MODIS Land Cover Dynamics (MCD12Q2) Product; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Missoula, MT, USA, 2019; Volume 6, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Parks, S.A.; Hegewisch, K.C. TerraClimate, a high-resolution global dataset of monthly climate and climatic water balance from 1958–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WorldPop. Available online: https://www.worldpop.org/ (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Abrol, I.P.; Yadav, J.S.P.; Massoud, F.I. Salt-Affected Soils and their Management; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1988; ISBN 92-5-102686-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Z.; Walder, F.; Tian, C.; Feng, G. Soil moisture threshold in controlling above- and belowground community stability in a temperate desert of central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
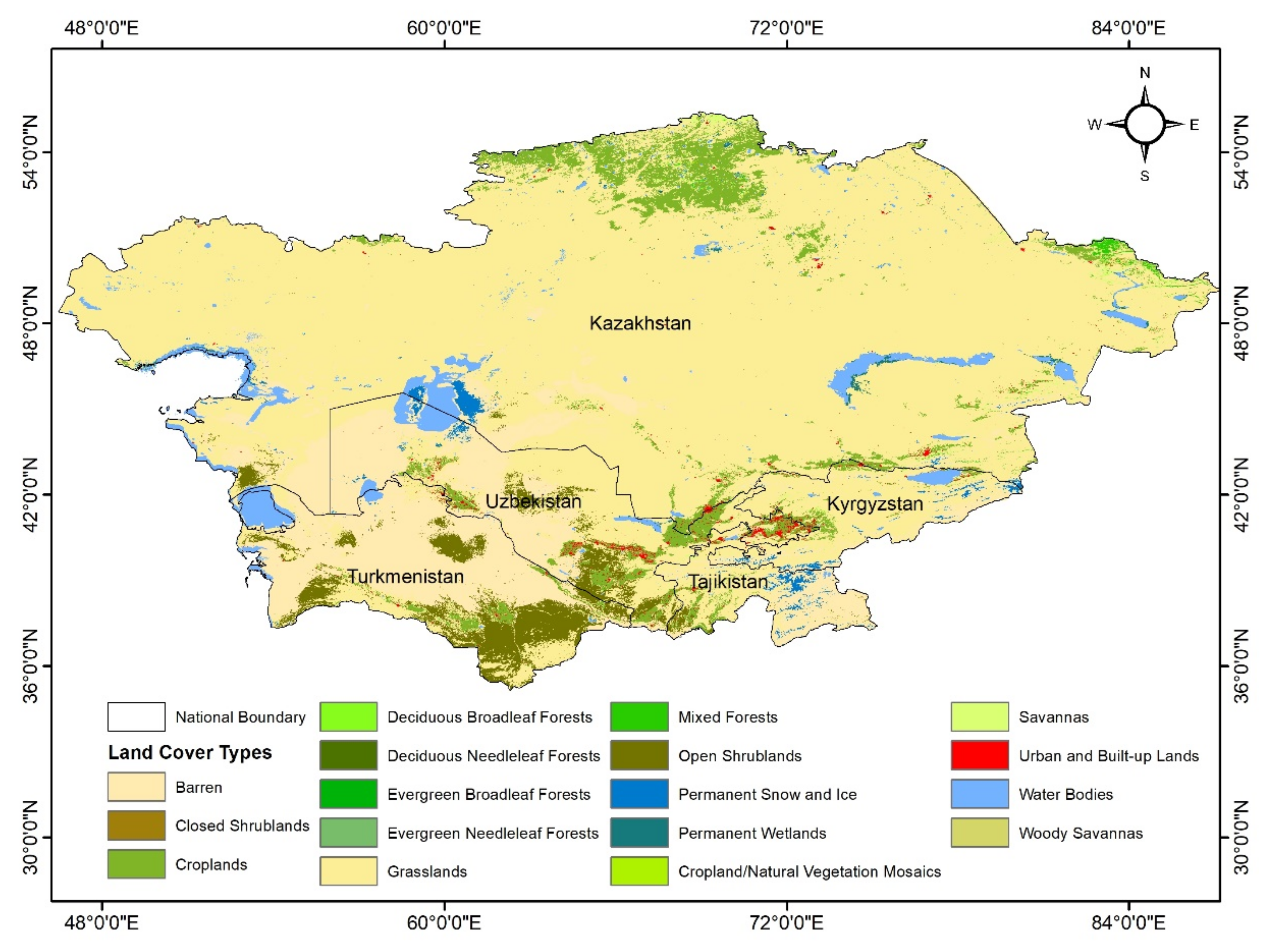

| No. | MODIS Land Cover Types | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Evergreen Needle leaf Forests | 1189 | 0.03 |
| 2 | Evergreen Broadleaf Forests | 4.5 | 0.00 |
| 3 | Deciduous Needle leaf Forests | 144 | 0.00 |
| 4 | Deciduous Broadleaf Forests | 1209 | 0.03 |
| 5 | Mixed Forests | 6886 | 0.17 |
| 6 | Closed Shrub lands | 458 | 0.01 |
| 7 | Open Shrub lands | 154,170 | 3.85 |
| 8 | Woody Savannas | 7898 | 0.20 |
| 9 | Savannas | 10,324 | 0.26 |
| 10 | Grasslands | 2,767,398 | 69.04 |
| 11 | Permanent Wetlands | 10,882 | 0.27 |
| 12 | Croplands | 208,152 | 5.19 |
| 13 | Urban and Built-up Lands | 19,194 | 0.48 |
| 14 | Cropland/Vegetation Mosaics | 643 | 0.02 |
| 15 | Permanent Snow and Ice | 28,515 | 0.71 |
| 16 | Barren | 662,765 | 16.53 |
| 17 | Water Bodies | 128,729 | 3.21 |
| Total | 4,008,561 |
| Soil Salinity Class | EC Class (dS/m) | Effect on Crop Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Non-saline | 0–2 | Insignificant |
| Slightly saline | 2–4 | Limit yield of sensitive crops |
| Moderately saline | 4–8 | Restrict yields of many crops |
| Highly saline | 8–16 | May not only affect resistant crops |
| Extremely saline | >16 | May not affect very few resistant crops |
| EC Class (dS/m) | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–2 | 4,252,440 | 4,392,040 | 4,557,200 | 4,139,280 |
| 2–4 | 281,075 | 242,499 | 192,920 | 254,440 |
| 4–8 | 826,994 | 789,386 | 611,714 | 903,574 |
| 8–16 | 135,661 | 71,038 | 130,989 | 190,928 |
| >16 | 4221 | 5431 | 7561 | 12,170 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Measho, S.; Li, F.; Pellikka, P.; Tian, C.; Hirwa, H.; Xu, N.; Qiao, Y.; Khasanov, S.; Kulmatov, R.; Chen, G. Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications for Agriculture and Land Resources Development Using Remote Sensing Datasets in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102501
Measho S, Li F, Pellikka P, Tian C, Hirwa H, Xu N, Qiao Y, Khasanov S, Kulmatov R, Chen G. Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications for Agriculture and Land Resources Development Using Remote Sensing Datasets in Central Asia. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102501
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeasho, Simon, Fadong Li, Petri Pellikka, Chao Tian, Hubert Hirwa, Ning Xu, Yunfeng Qiao, Sayidjakhon Khasanov, Rashid Kulmatov, and Gang Chen. 2022. "Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications for Agriculture and Land Resources Development Using Remote Sensing Datasets in Central Asia" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102501
APA StyleMeasho, S., Li, F., Pellikka, P., Tian, C., Hirwa, H., Xu, N., Qiao, Y., Khasanov, S., Kulmatov, R., & Chen, G. (2022). Soil Salinity Variations and Associated Implications for Agriculture and Land Resources Development Using Remote Sensing Datasets in Central Asia. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102501











