Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling and Remediation Monitoring in Arid Areas Using Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Oil Spill in 1991
1.2. Related Studies
2. Materials and Methods
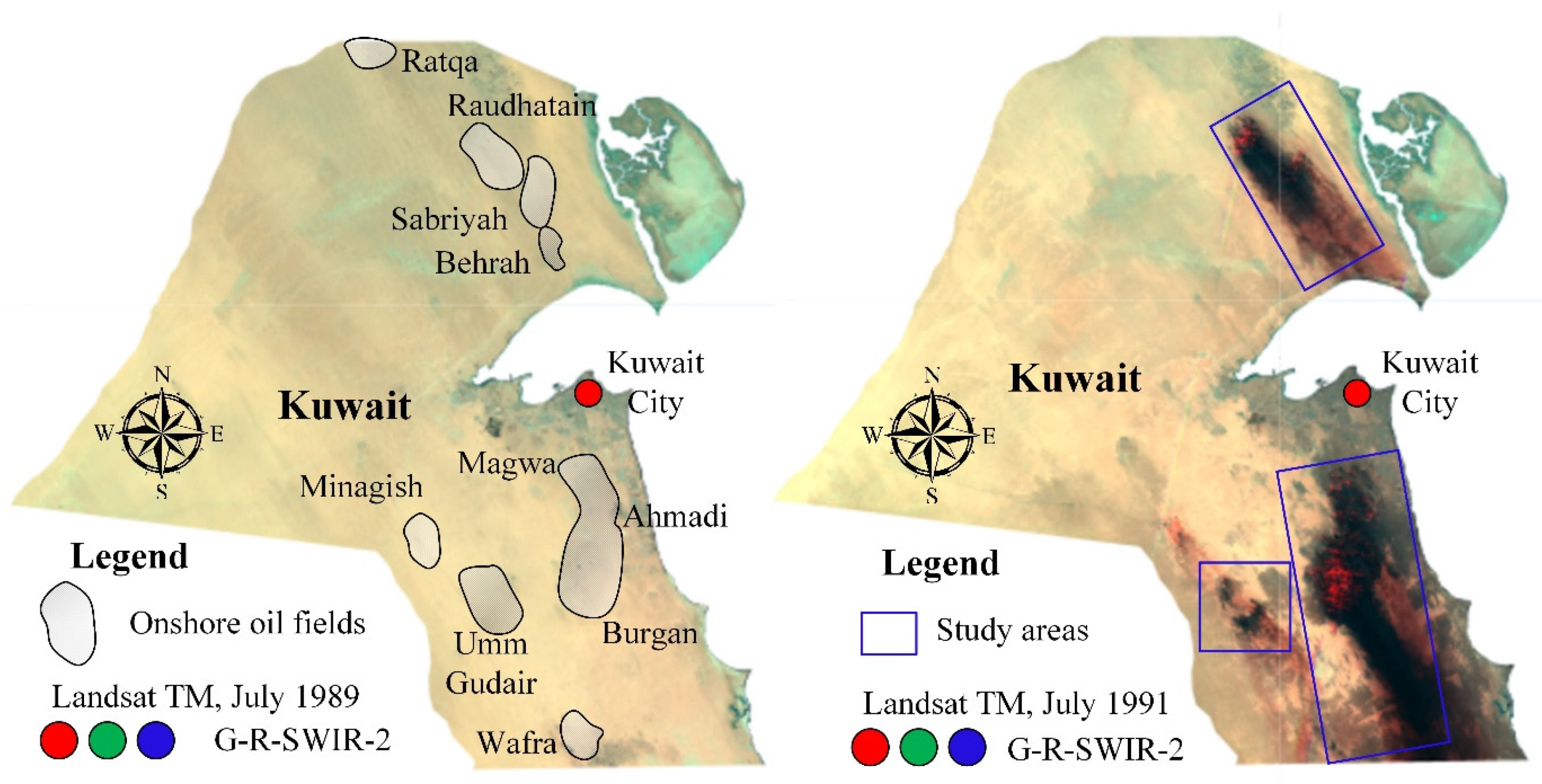
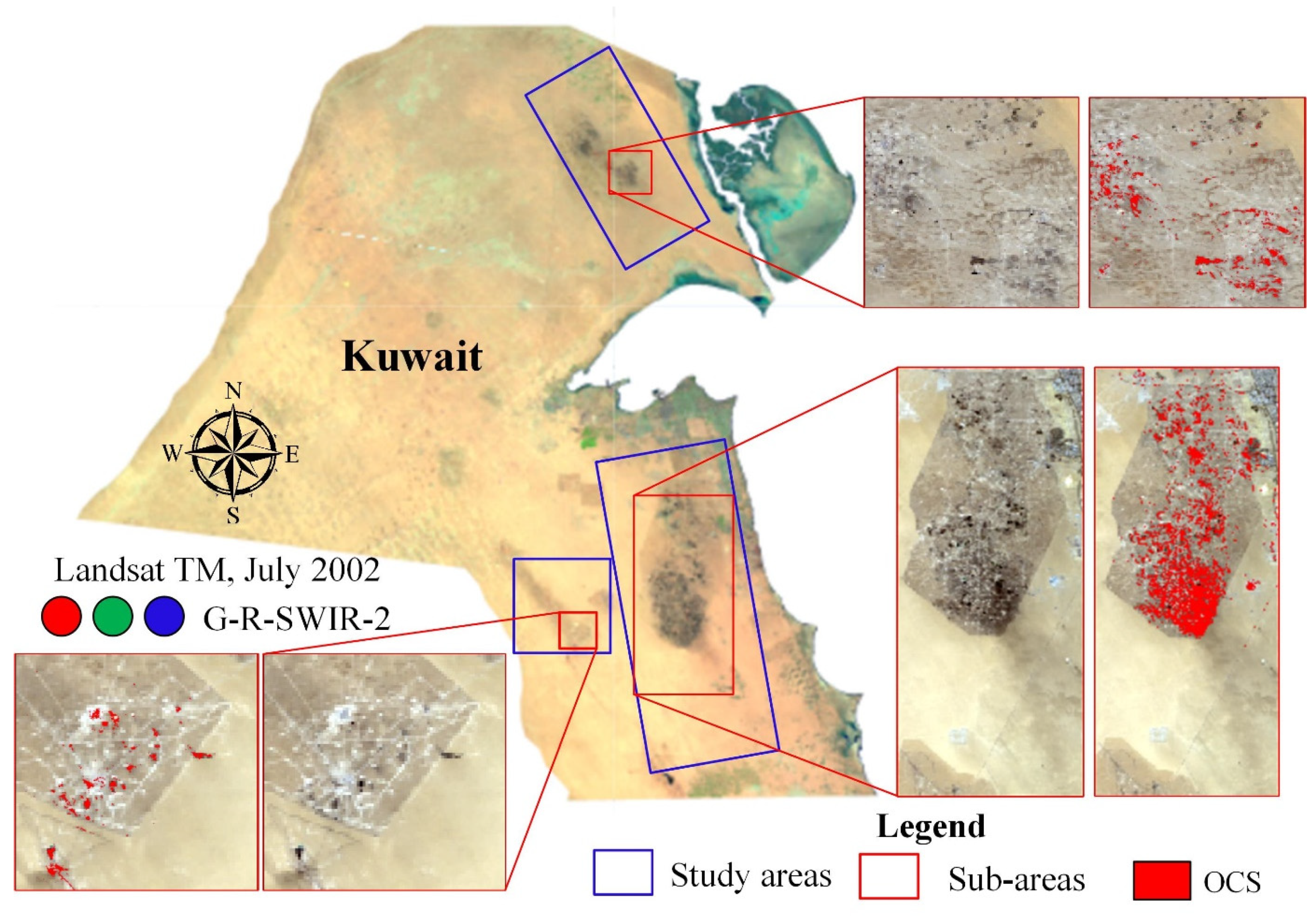
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
Spectral Indices
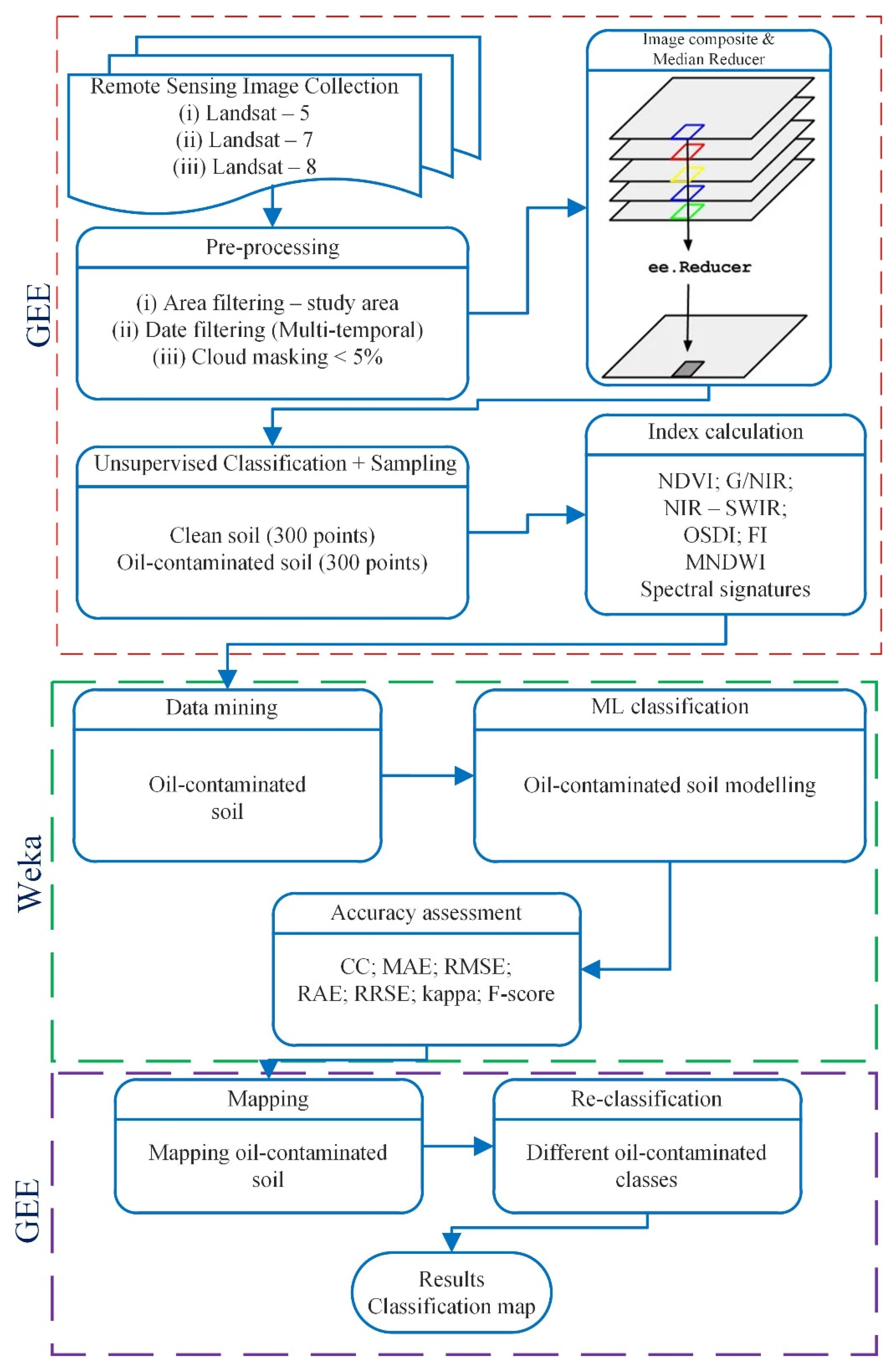
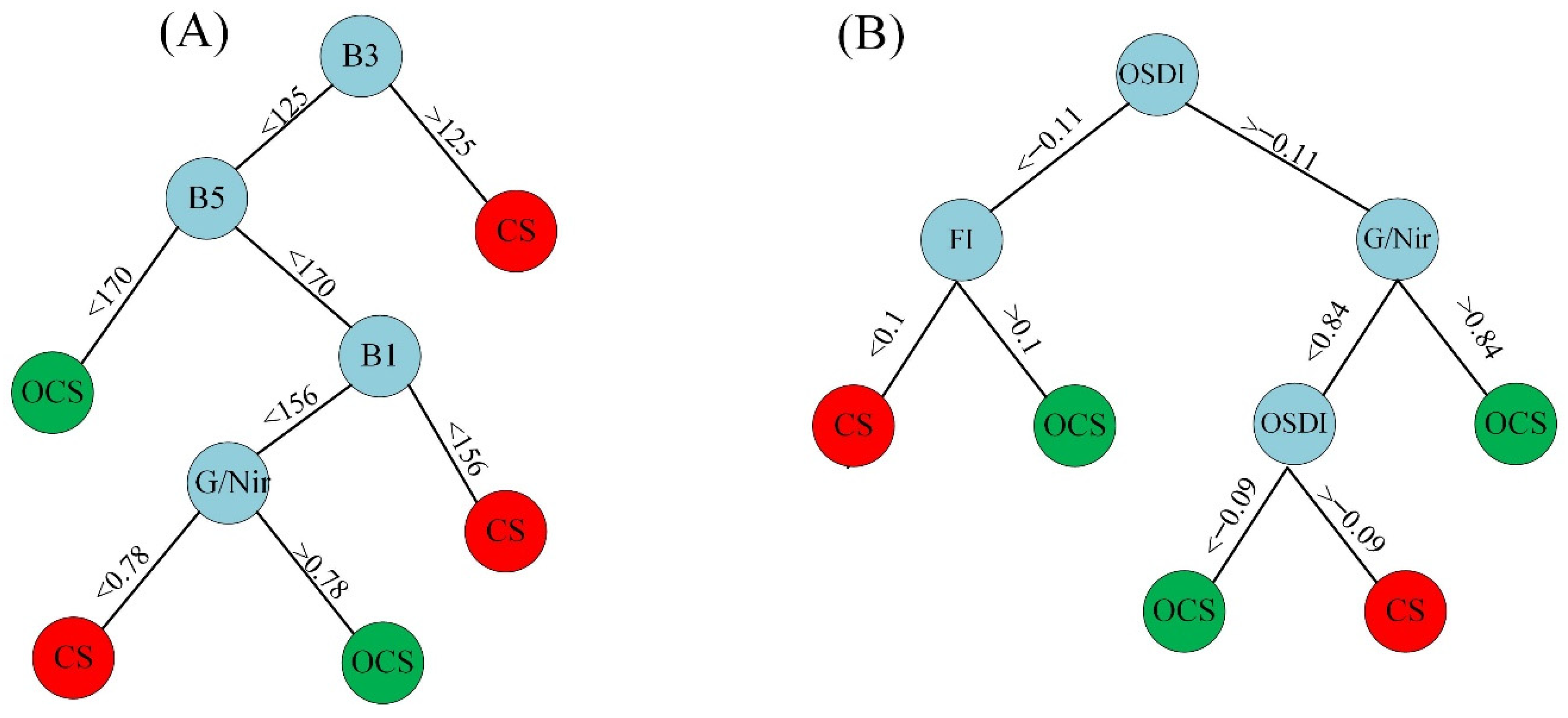
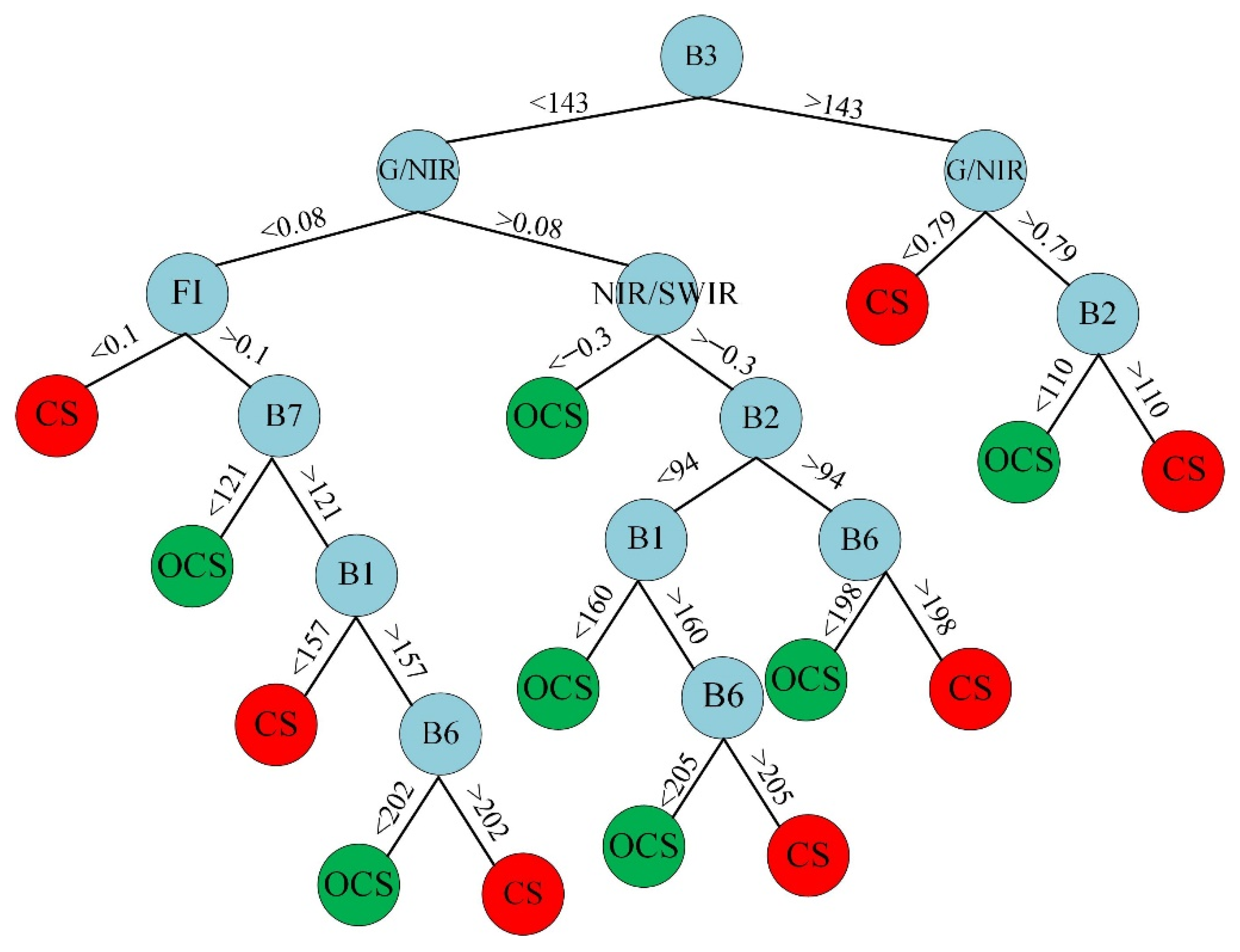
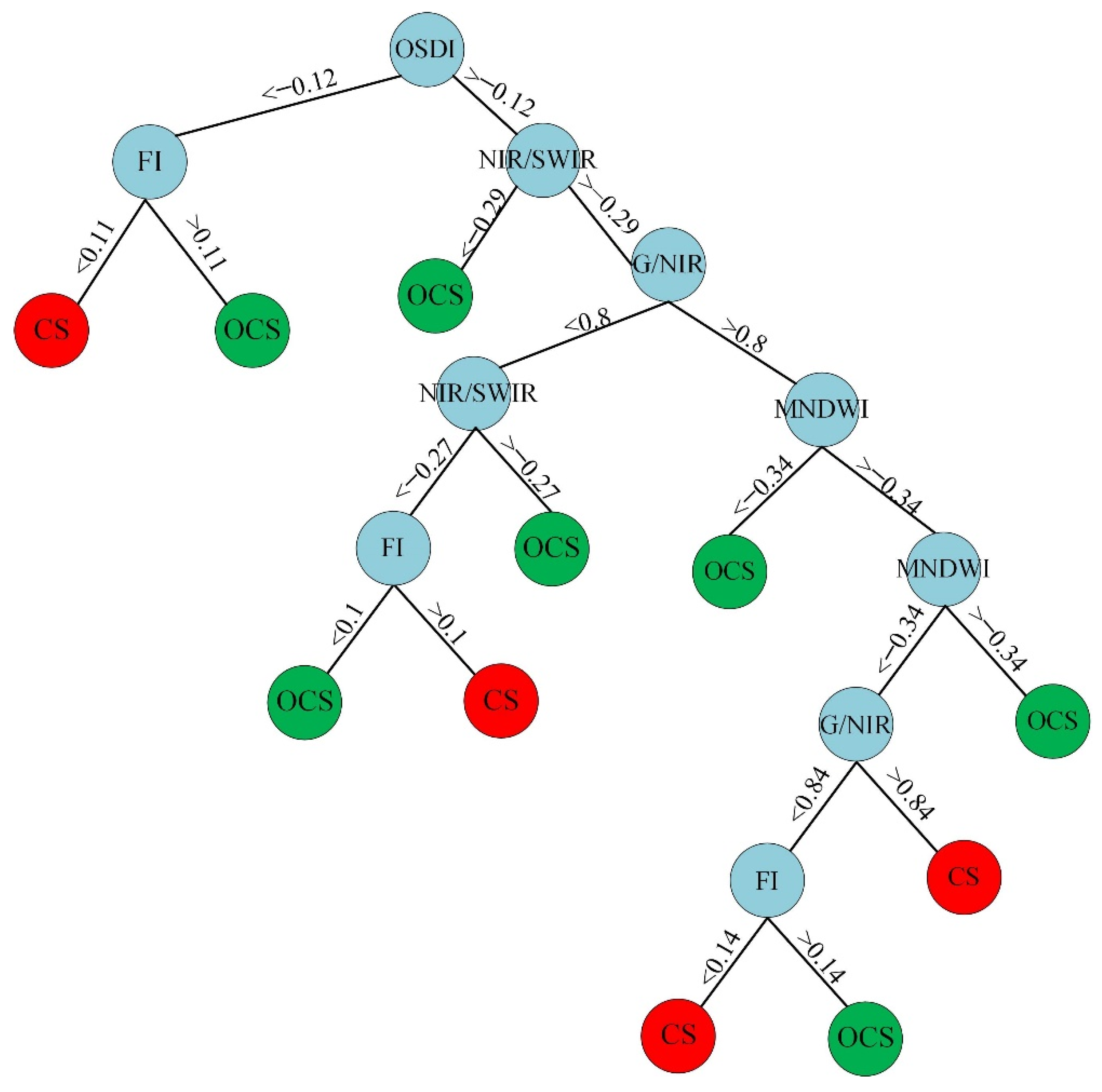
2.3. Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling
3. Results
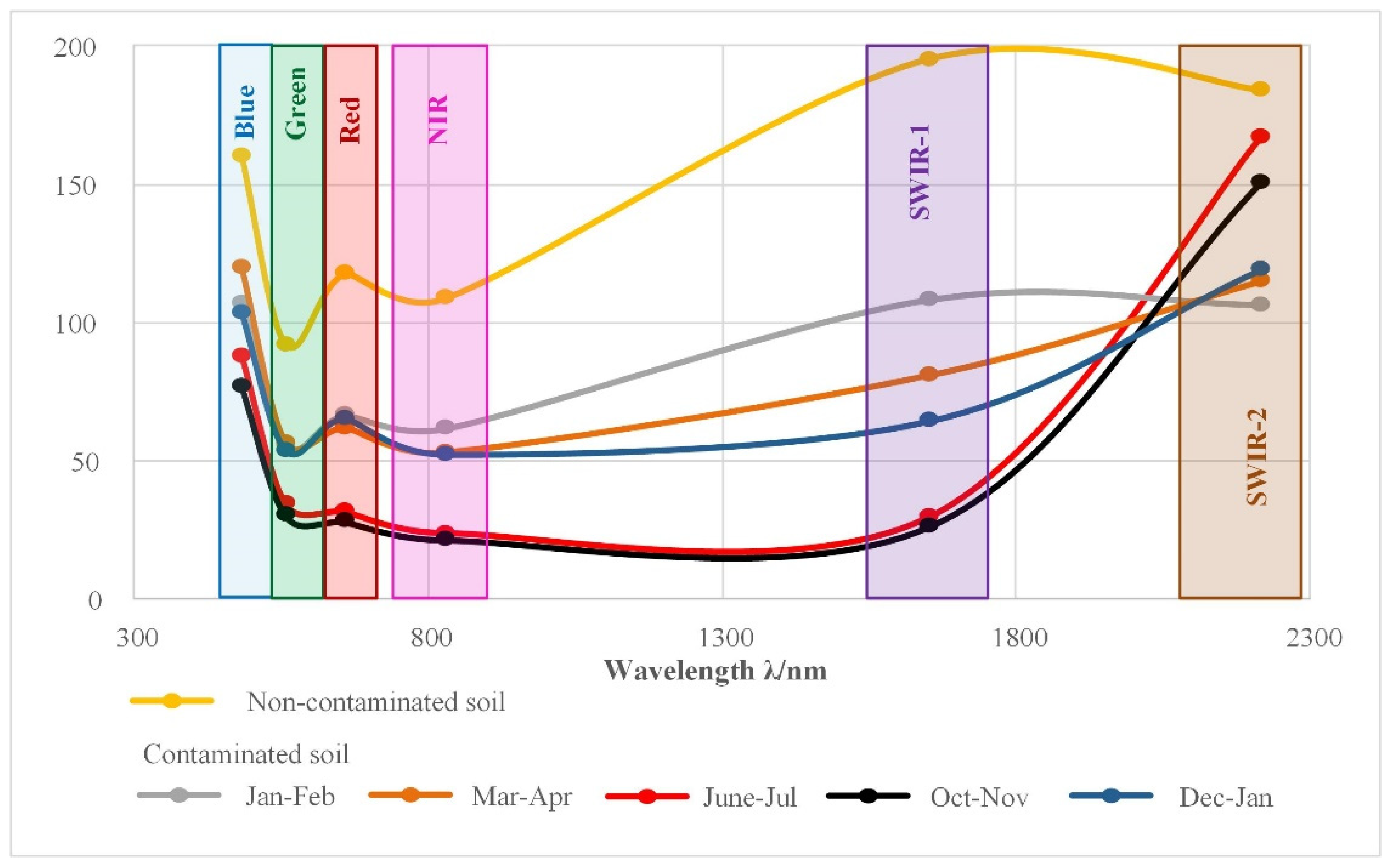
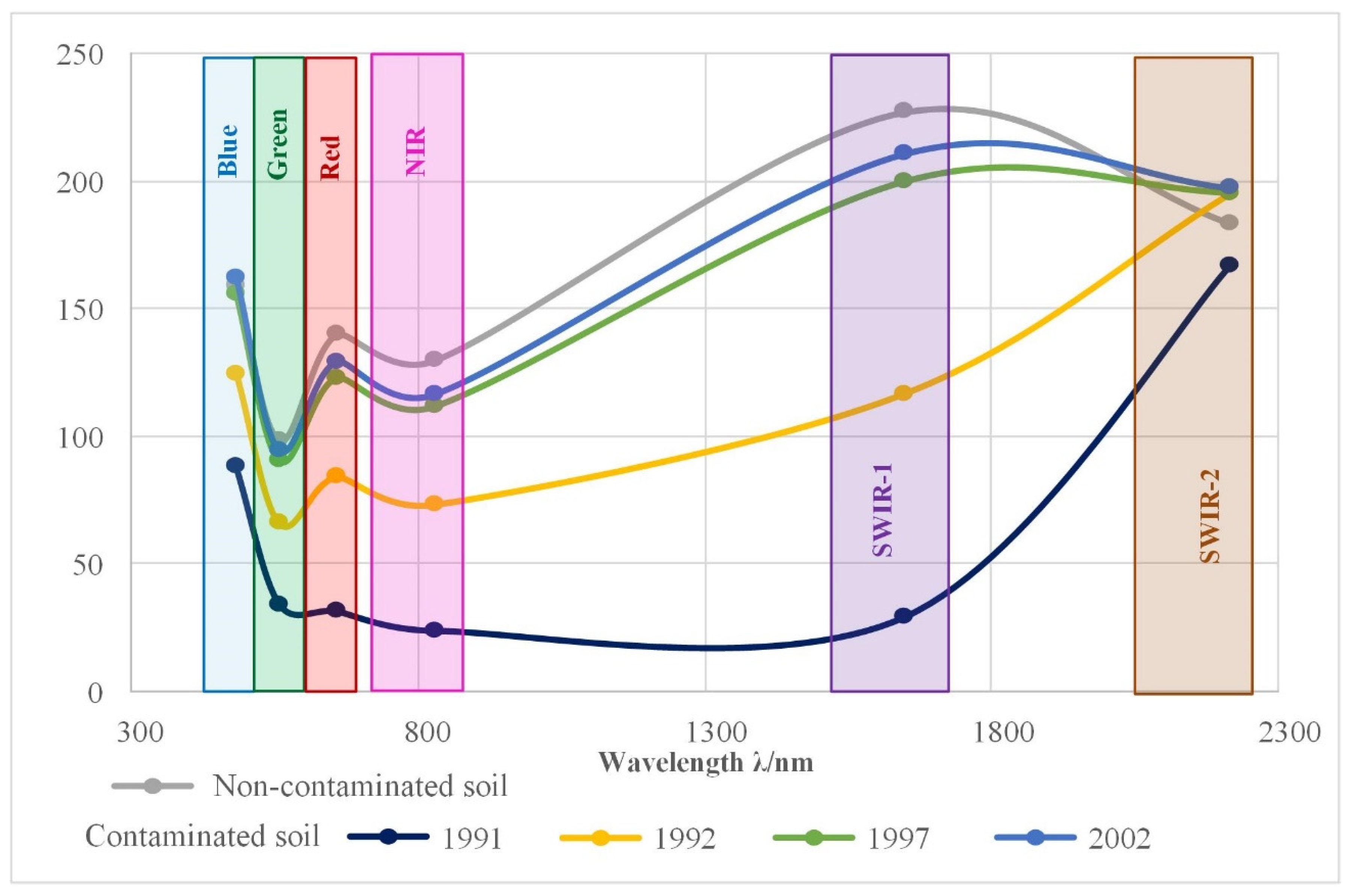
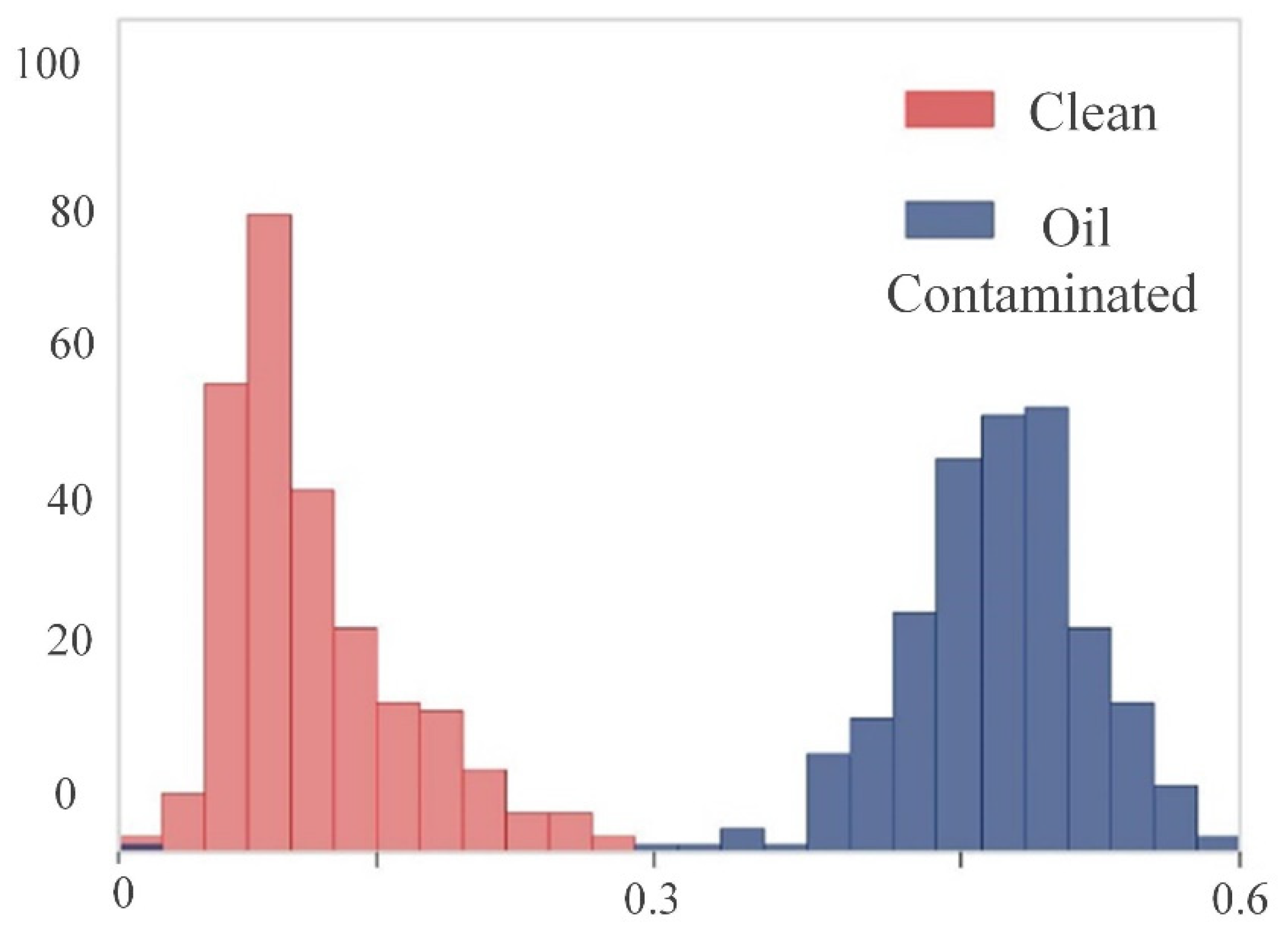
3.1. Unsupervised Classification and Spectral Signature Differences
3.2. Modeling Results
4. Discussion
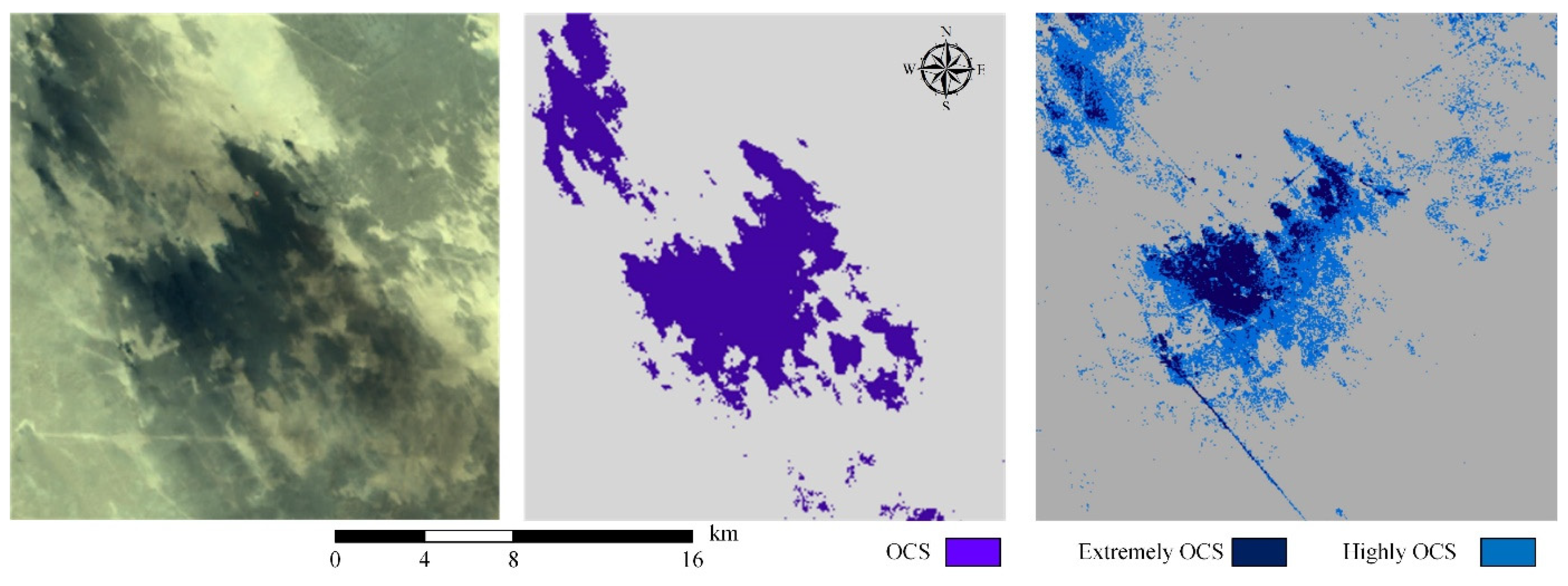
4.1. Oil-Contaminated Soil Classification
4.2. Comparison of Oil-Contaminated Classification Performance
4.3. General Overview of the Proposed Methodology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Baz, F.; Makharita, R.M. The Gulf War and the Environment; Routledge: Bingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pelta, R.; Carmon, N.; Ben-Dor, E. A machine learning approach to detect crude oil contamination in a real scenario using hyperspectral remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinfor. 2019, 82, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarawi, M.; Massoud, M.; Al-Abdali, F. Preliminary assessment of oil contamination levels in soils contaminated with oil lakes in the greater burgan oil fields, kuwait. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 106, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khordagui, H.; Al-Ajmi, D. Environmental impact of the gulf war: An integrated preliminary assessment. Environ. Manag. 1993, 17, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.S. An assessment of remediation strategies for kuwaiti oil lakes. Environ. Geotech. 2017, 5, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dousari, A.; Literathy, P. Evidence of hydrocarbon contamination from the burgan oil field, kuwait—Interpretations from thermal remote sensing data. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Kwarteng, A.Y. Multitemporal remote sensing data analysis of kuwait’s oil lakes. Environ. Int. 1998, 24, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, F.; Abuelgasim, A.; Lambin, E.; Al-Doasari, A.; Marr, P.; Ryherd, S.; Morency, R. Detection by satellite images of environmental change due to. In The Gulf War and the Environment; Center for Remote Sensing Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A. Study of characterization of oil contaminated soil in kuwait hera ag ambiental company soil remediation project kuwait. IJISET-Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Besharah, J.; Salman, M.; Al-Matrook, F. Characterization and Quantification of Reclaimable Oil from Oil Lakes Formed in Kuwait Oil Fields; Report No. KISR4081; Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ajmi, D.; Misak, F.; Khalaf, F.; Al-Sudairawi, M.; Al-Dousari, A. Damage Assessment of the Desert and Coastal Environment of Kuwait by Remote Sensing (vt001c); Report No. KISR; Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 1994; Volume 4405. [Google Scholar]
- Salam, A. Process of the Symposium on Restoration and Rehabilitation of the Desert Environment. In The Oil Lakes Environment Disaster; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nertherland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kwarteng, A.Y. Remote sensing assessment of oil lakes and oil-polluted surfaces at the greater burgan oil field, kuwait. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinfor. 1999, 1, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Doasari, A.E. Analysis the Changes in the Tarcrete Layer on the Desert Surface Kuwait Using Satellite Imagery and Cell-Based Modeling; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Zelenay, P.; Thomas, S.; Davey, J.; Gottesfeld, S. Recent advances in direct methanol fuel cells at los alamos national laboratory. J. Power Sources 2000, 86, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Lai, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Ding, J.; Liu, N.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, N. Soil tph concentration estimation using vegetation indices in an oil polluted area of eastern china. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, L.; Salas, E.; Clevers, J.; Wehrens, R.; Leuven, R.; Nienhuis, P.; Buydens, L. Exploring field vegetation reflectance as an indicator of soil contamination in river floodplains. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.M.; Mackey, B.G.; Van Niel, K.P. Estimating forest biomass using satellite radar: An exploratory study in a temperate australian eucalyptus forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 176, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Davenport, I.J.; Neal, J.C.; Schumann, G.J.-P.; Bates, P.D. Near real-time flood detection in urban and rural areas using high-resolution synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans. GeoSci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; El-Baz, F. Identifying the effects of the gulf war on the geomorphic features of kuwait by remote sensing and gis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- Abdunaser, K. Spatio-temporal analysis of oil lake and oil-polluted surfaces from remote sensing data in one of the libyan oil fields. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozigis, M.S.; Kaduk, J.D.; Jarvis, C.H. Mapping terrestrial oil spill impact using machine learning random forest and landsat 8 oli imagery: A case site within the niger delta region of nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3621–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghais, N.; Pullar, D. Modelling the impacts current patterns urban form expansion in kuwait with the use abm and gis. In Proceedings of the 21st International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Broadbeach, QLD, Australia, 29 November–4 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Algharib, S.M. Spatial Patterns of Urban Expansion in Kuwait City between 1989 and 2001; Kent State University: Kent, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.-S.; Wahba, S. Oil lakes and contamination of soil in kuwait. In Assessments And Remediation of Oil Contaminated Soils; New Age International (P) Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1999; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, B.; Al-Duwaisan, D.; Al-Naseem, A. Characterization oil contaminated soil. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology IPCBEE, Singapore, 26–28 February 2011; pp. 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Brovelli, M.A.; Sun, Y.; Yordanov, V. Monitoring forest change in the amazon using multi-temporal remote sensing data and machine learning classification on google earth engine. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, A.; Tokareva, O.S. Using modis ndvi products for vegetation state monitoring on the oil production territory in western siberia. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences. Space Engineering—Les Ulis, 2016, Tomsk, Russia, 12–14 April 2016; p. 5003. [Google Scholar]
- Adamu, B.; Tansey, K.; Ogutu, B. Using vegetation spectral indices to detect oil pollution in the niger delta. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.-L.; Yekeen, S.T.; Pradhan, B.; Althuwaynee, O.F. Spatio-temporal analysis of oil spill impact and recovery pattern of coastal vegetation and wetland using multispectral satellite landsat 8-oli imagery and machine learning models. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. An oil slick detection index based on landsat 8 remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Workshop on Big Geospatial Data and Data Science (BGDDS), Wuhan, China, 22–23 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, E.; Brown, L.; Borstad, G.; Mudge, T.; Álvarez, M. Characterization oil slicks at sea using remote sensing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2012 Oceans, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 14–19 October 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Niu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of the ability of spectral indices of hydrocarbons and seawater for identifying oil slicks utilizing hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, G.; Donkin, A.; Witten, I.H. Weka: A machine learning workbench. In Proceedings of the ANZIIS’94-Australian New Zealnd Intelligent Information Systems Conference, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 9 November–2 December 1994; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha Kiranmai, S.; Jaya Laxmi, A. Data mining for classification of power quality problems using weka and the effect of attributes on classification accuracy. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2018, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Jaafari, A.; Nguyen-Thoi, T.; Van Phong, T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Satyam, N.; Masroor, M.; Rehman, S.; Sajjad, H.; Sahana, M. Ensemble machine learning models based on reduced error pruning tree for prediction of rainfall-induced landslides. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 575–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Jamali, A.; Gibril, M.B.A.; Kok Foong, L.; Bahiraei, M. Evaluation of tree-base data mining algorithms in land used/land cover mapping in a semi-arid environment through landsat 8 oli image; shiraz, iran. Geom. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, O.; Kaplan, G. Response spectra-based post-earthquake rapid structural damage estimation approach aided with remote sensing data: 2020 samos earthquake. Buildings 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, W.; Asem, S. Application of gis for mapping oil-contaminated soil in kuwait. In AMCIS 2007 Proceedings; Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 2007; p. 484. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, W.-K.; Jung, H.-S. Performance comparison of oil spill and ship classification from x-band dual-and single-polarized sar image using support vector machine, random forest, and deep neural network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.; Grealish, G.; Roy, W. Types and extent of soil contamination in greater al-burqan oil field, kuwait. Kuwait J. Sci. Eng. 2006, 33, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Mostagab, H.; Senosy, M.; Al Rashed, A.; Salem, M.E. The impact of hydrocarbon pollution on soil degradation using gis techniques and soil characterization in burgan oil field, south kuwait. J. Environ. Prot. 2018, 9, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


| Index | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | NIR − RED/NIR + RED | [28] |
| G/NIR | G/NIR | [29] |
| NDMI | NIR − SWIR/NIR + SWIR | [30] |
| OSDI | GREEN − NIR/GREEN + NIR | [31] |
| FI | BLUE − RED/BLUE + RED | [32,33] |
| MNDWI | GREEN − SWIR/GREEN + SWIR | [22] |
| ML Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | MAE | RAE (%) | Kappa | TP | FP | Precision | Recall | F-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-I | 100% | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RT-II | 100% | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SVM-I | 96% | 0.04 | 8.8 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| SVM-II | 100% | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RF-I | 100% | 0 | 0.1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RF-II | 99% | 0 | 0.6 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| ML Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | MAE | RAE (%) | Kappa | TP | FP | Precision | Recall | F-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-I | 100% | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RT-II | 99% | 0 | 1.1 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| SVM-I | 97% | 0.03 | 5.5 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| SVM-II | 97% | 0.03 | 6.6 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| RF-I | 100% | 0 | 0.1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RF-II | 99% | 0 | 1.2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| ML Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | MAE | RAE (%) | Kappa | TP | FP | Precision | Recall | F-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-I | 99% | 0 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| RT-II | 97% | 0.03 | 6.6 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.03 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| SVM-I | 97% | 0.03 | 5.5 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| SVM-II | 78% | 0.2 | 44.4 | 0.56 | 0.78 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.77 |
| RF-I | 98% | 0.03 | 6.0 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| RF-II | 97% | 0.03 | 6.9 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaplan, G.; Aydinli, H.O.; Pietrelli, A.; Mieyeville, F.; Ferrara, V. Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling and Remediation Monitoring in Arid Areas Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102500
Kaplan G, Aydinli HO, Pietrelli A, Mieyeville F, Ferrara V. Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling and Remediation Monitoring in Arid Areas Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102500
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaplan, Gordana, Hakan Oktay Aydinli, Andrea Pietrelli, Fabien Mieyeville, and Vincenzo Ferrara. 2022. "Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling and Remediation Monitoring in Arid Areas Using Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102500
APA StyleKaplan, G., Aydinli, H. O., Pietrelli, A., Mieyeville, F., & Ferrara, V. (2022). Oil-Contaminated Soil Modeling and Remediation Monitoring in Arid Areas Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102500











