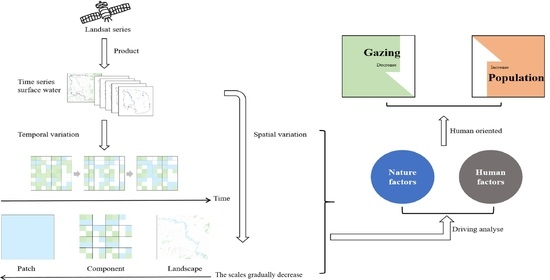
Modelling Dynamic Hydrological Connectivity in the Zoigê Area (China) Based on Multi-Temporal Surface Water Observation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
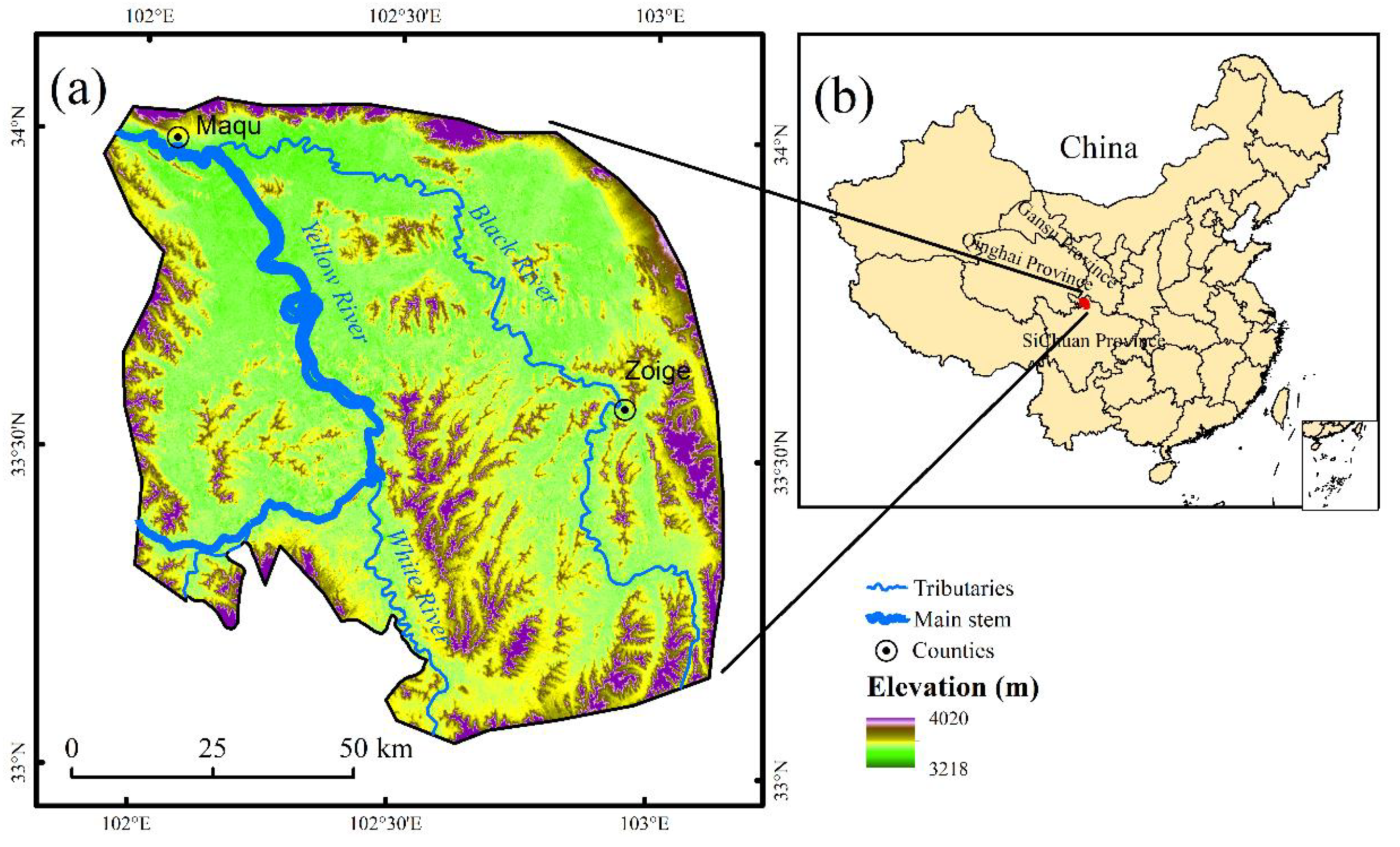
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
- Surface water data were obtained from the global surface water dataset (GSWD) (resolution: 30 m) of the Joint Research Centre using Google Earth Engine (https://code.earthengine.google.com, accessed on 18 November 2021) (dataset: JRC/GSW1_3/YearlyHistory) [27].
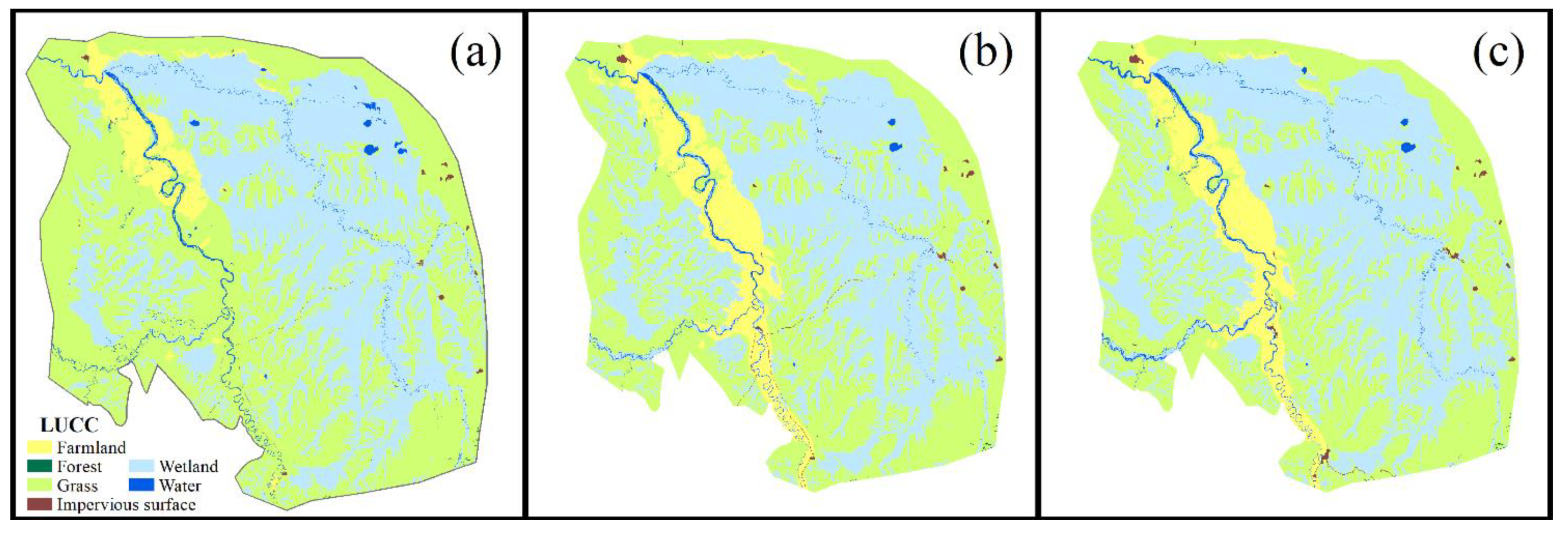
- Land cover (LUCC) data (Figure A5) were obtained from the Global 30 dataset which has a spatial resolution of 30 m (http://www.globallandcover.com/, accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Digital elevation model (DEM) (resolution: 30 m) data were obtained from the Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 18 November 2021).
- For the dynamic hydrological connectivity driver analysis, surface meteorological data were obtained from the China Meteorological Administration (http://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Socioeconomic data were obtained from the local Sichuan provincial Bureau of Statistics.
2.3. Data Analysis
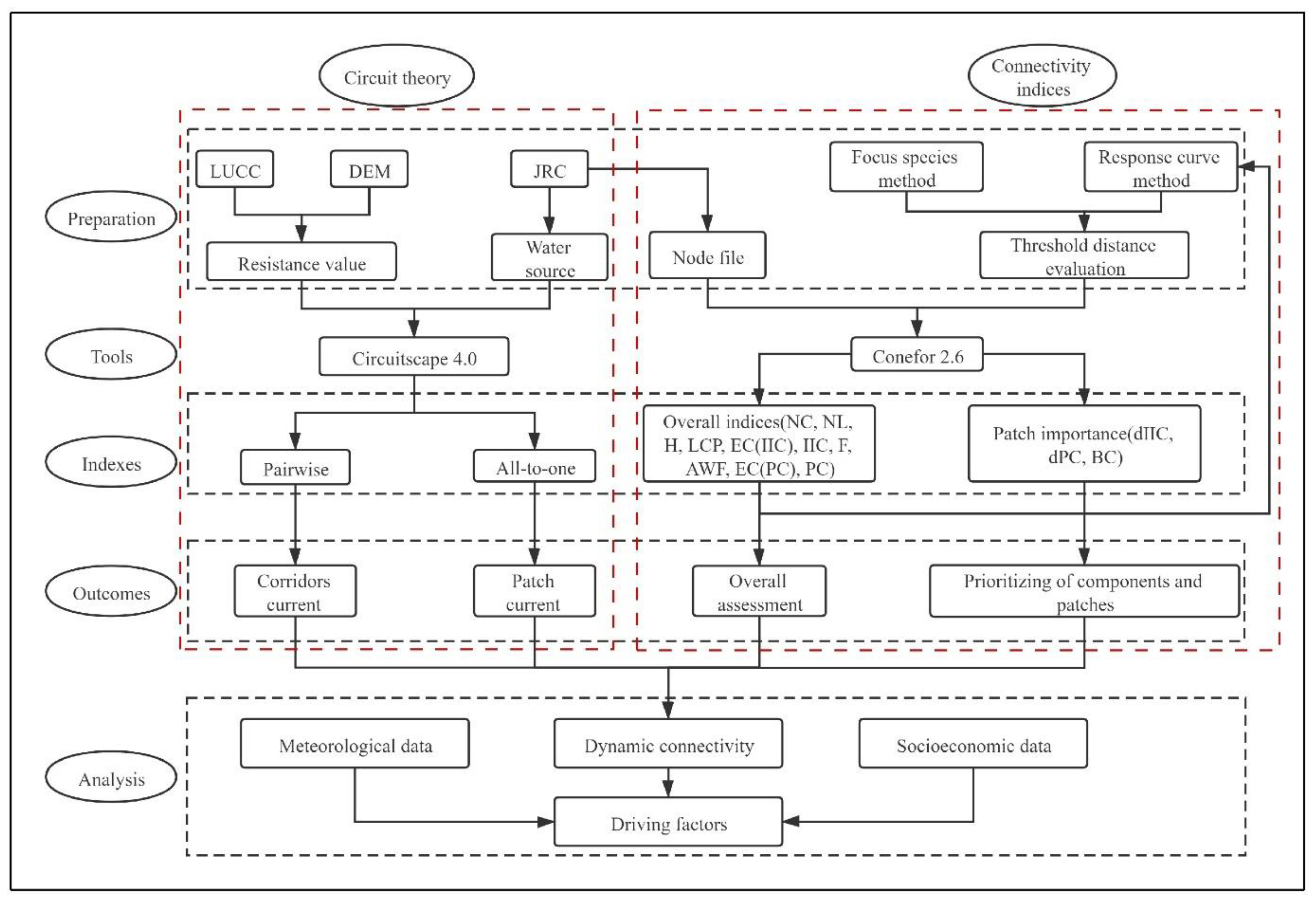
2.3.1. Circuit Theory
2.3.2. Hydrological Connectivity Indices
3. Results
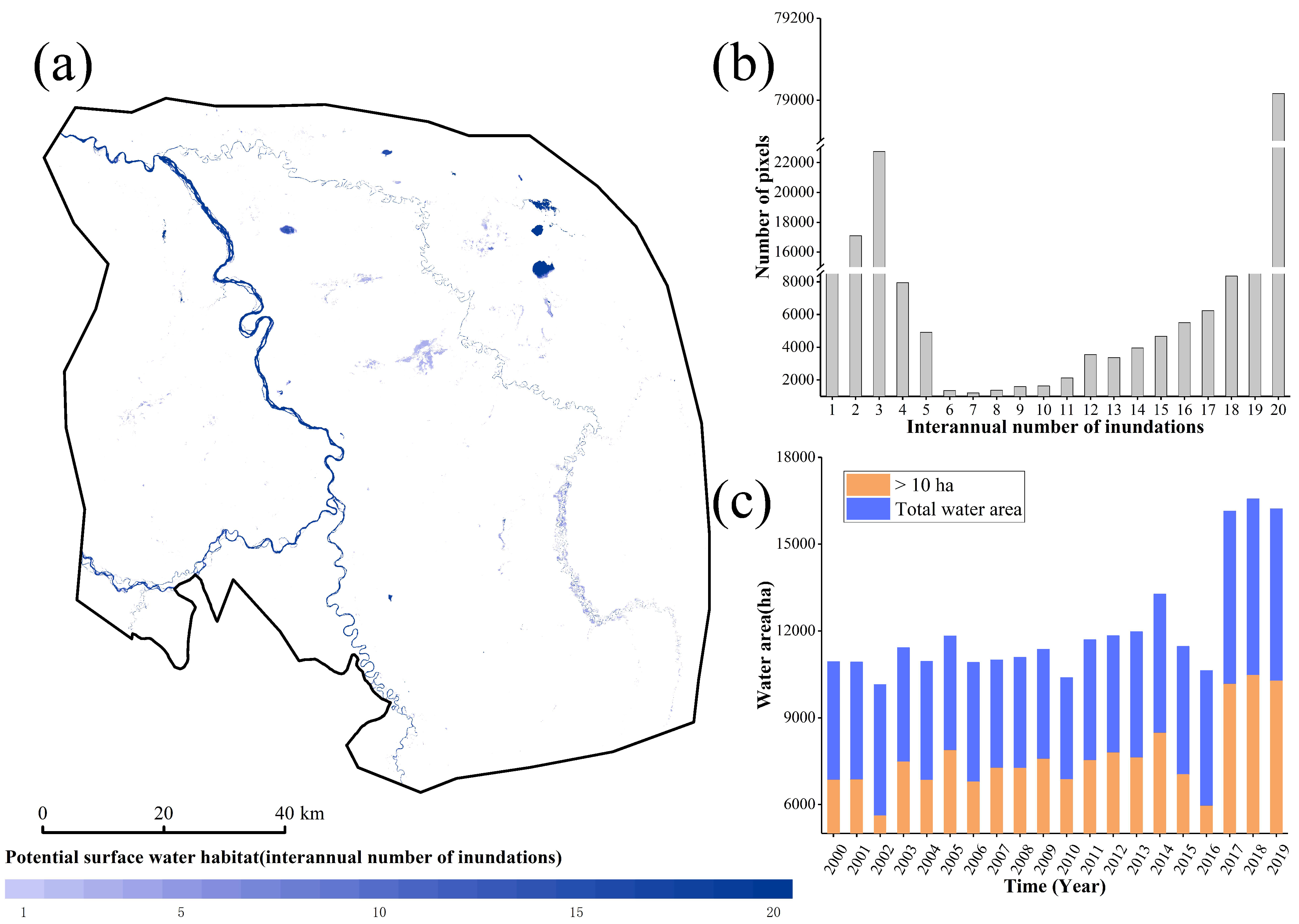
3.1. Surface Water Dynamics
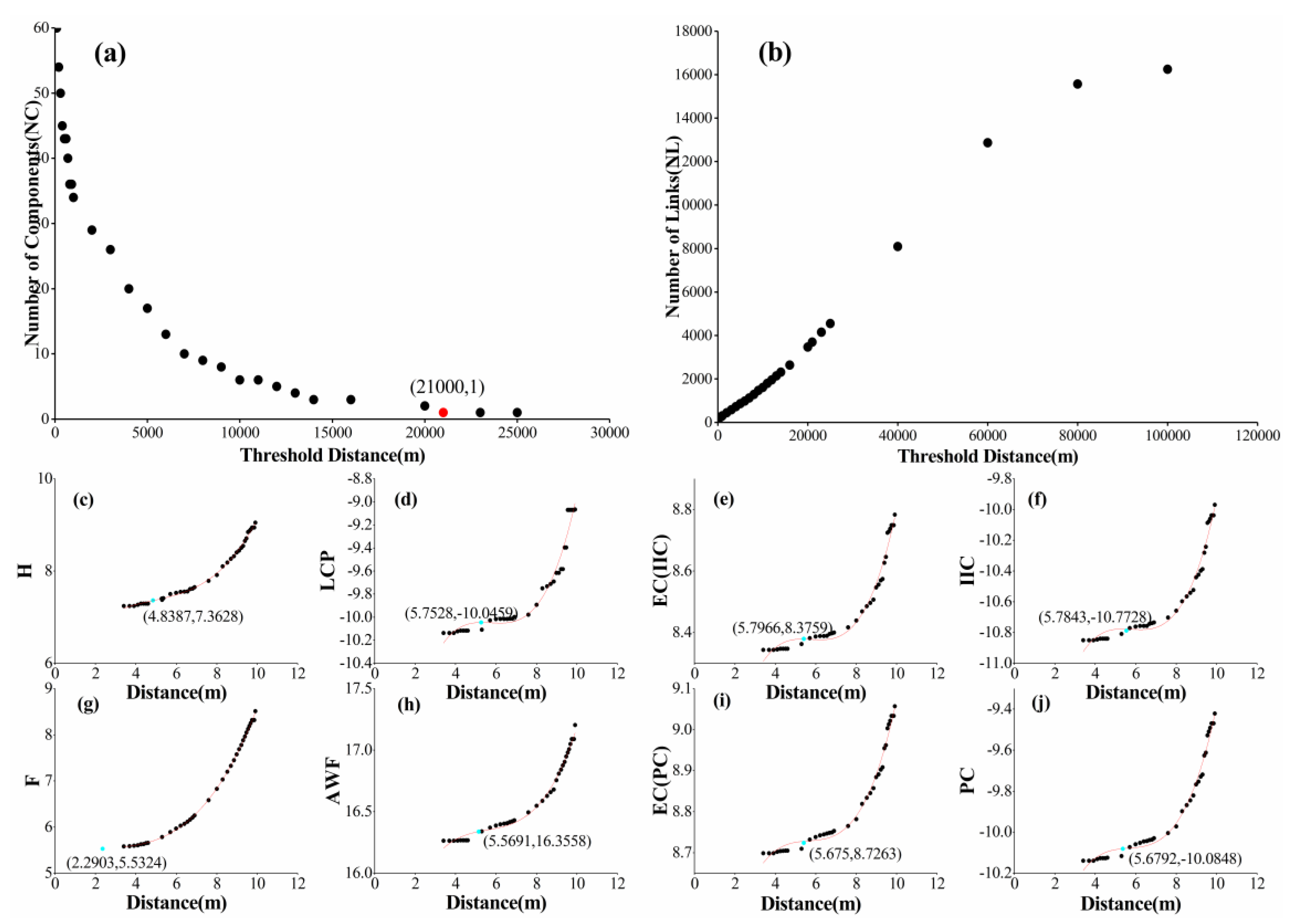
3.2. Optimal Threshold Distance
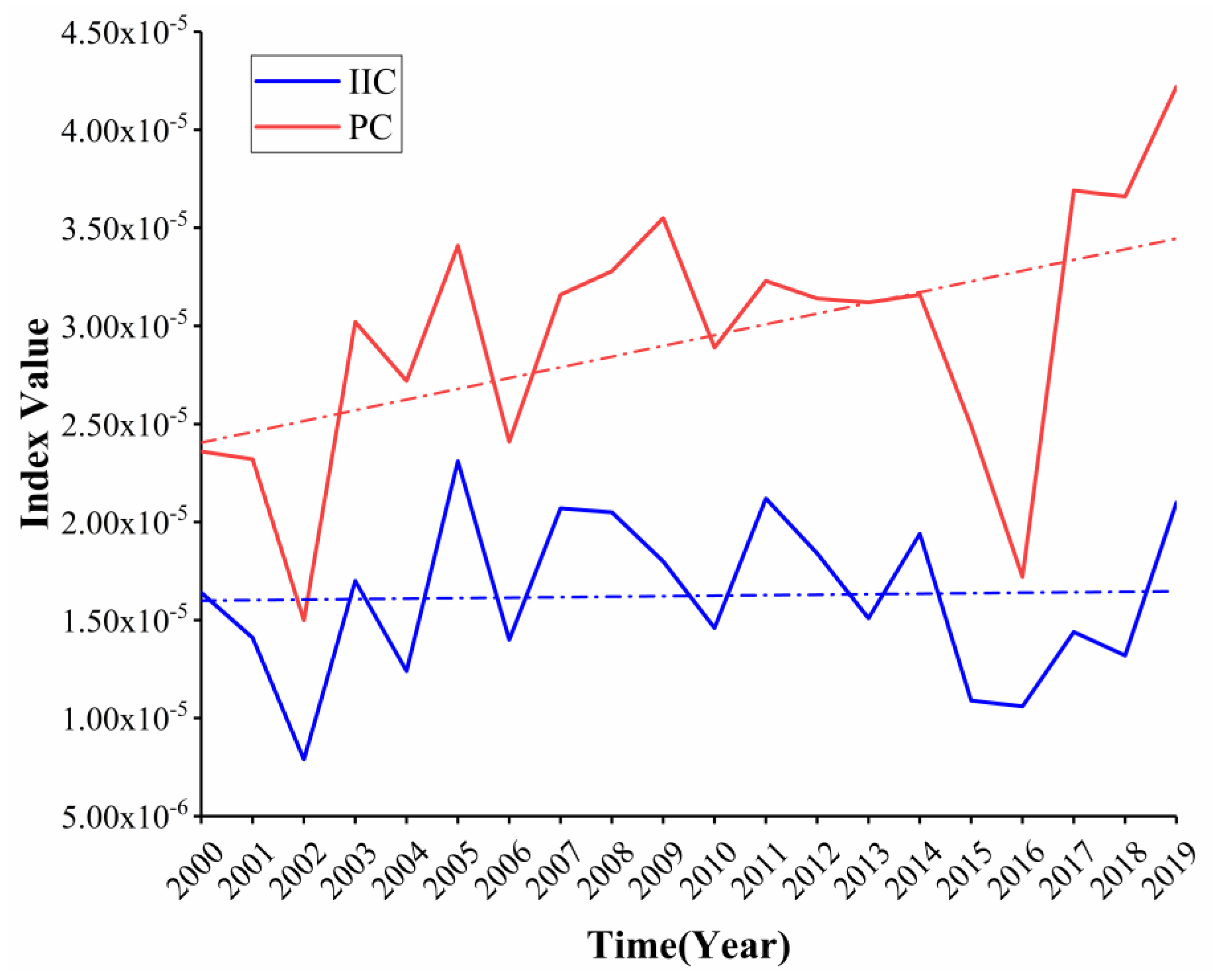
3.3. Annual Pattern of Hydrological Connectivity
3.4. Spatial Pattern of Hydrological Connectivity
3.4.1. Hydrological Connectivity at Landscape Scale
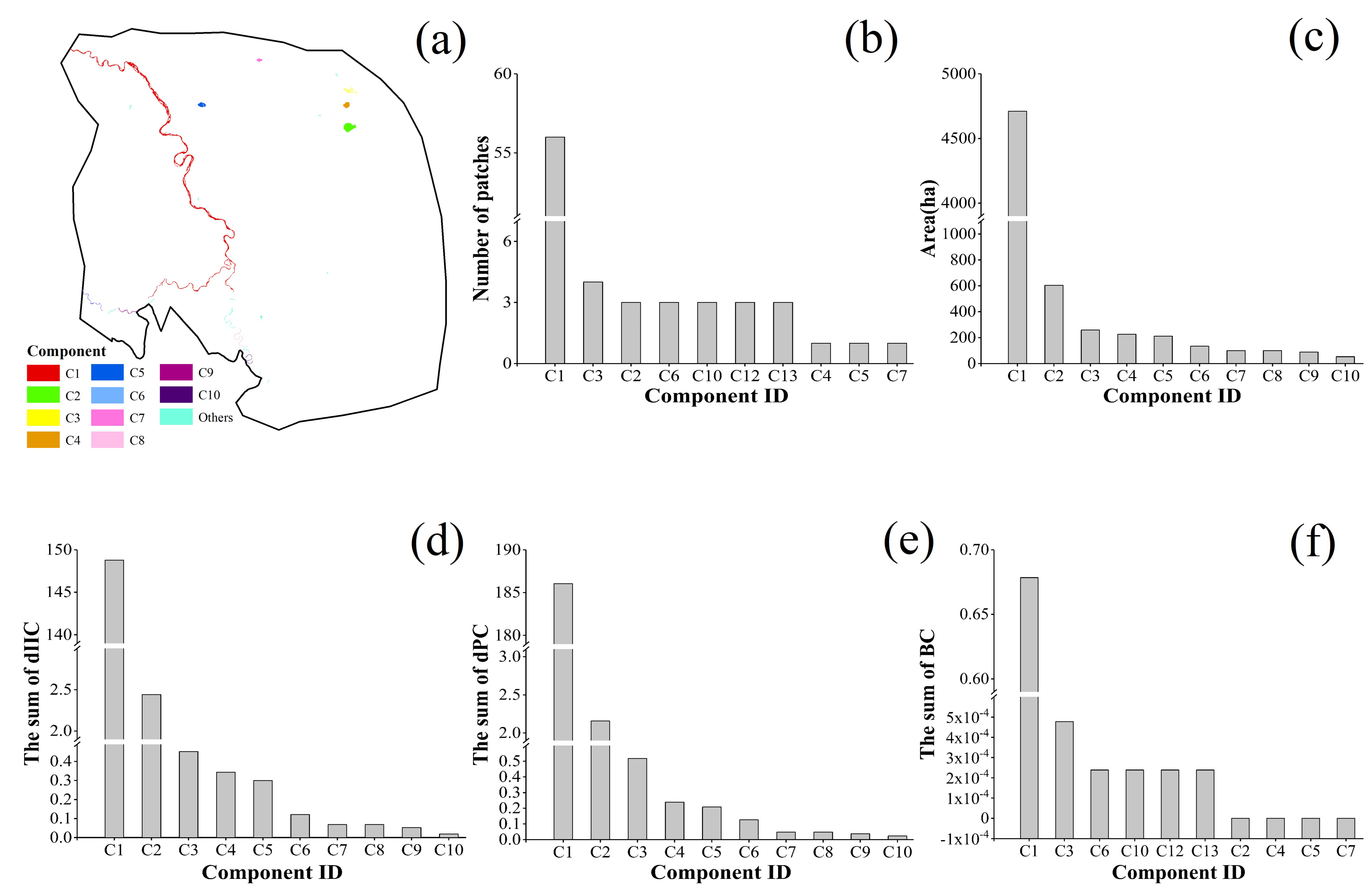
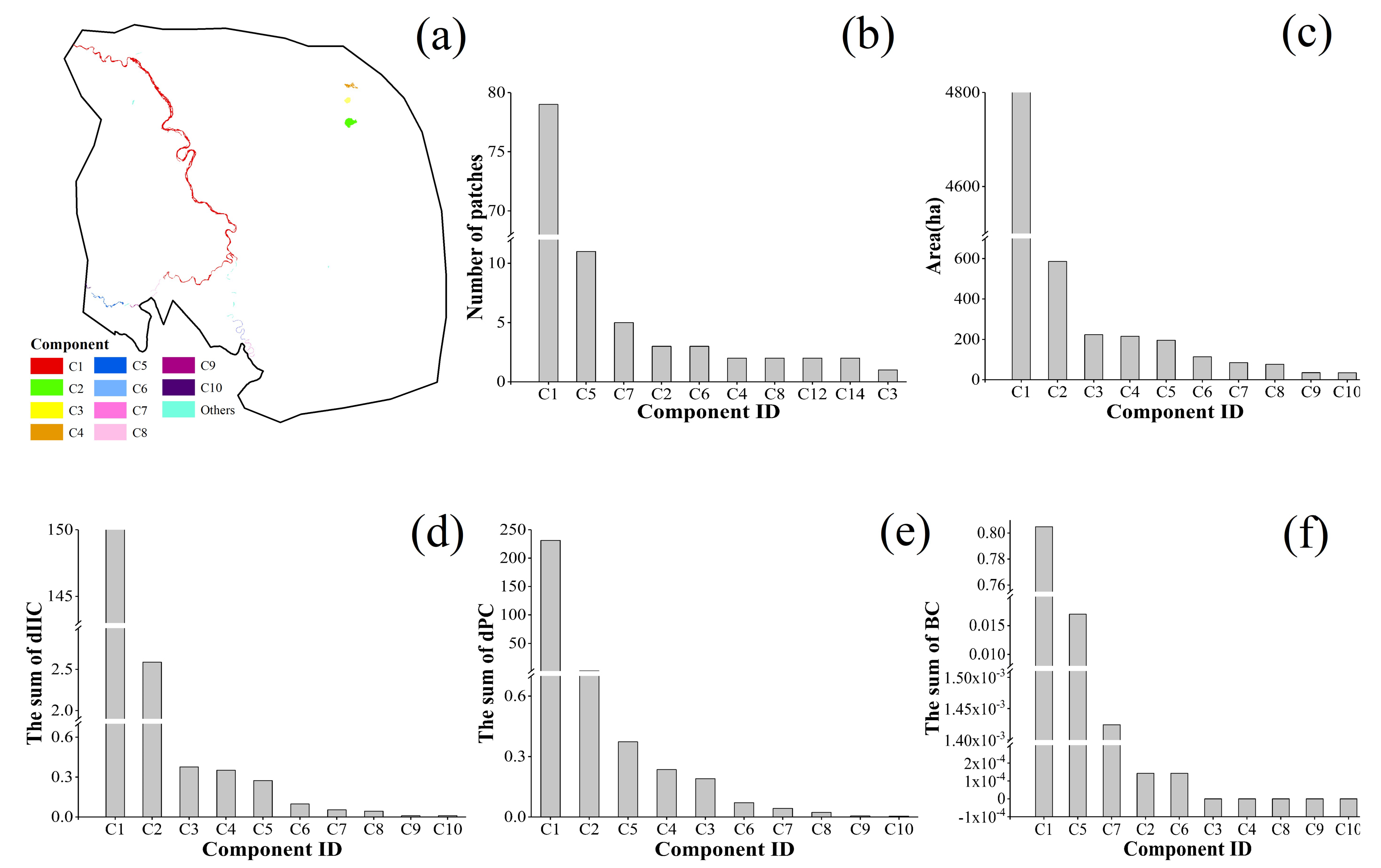
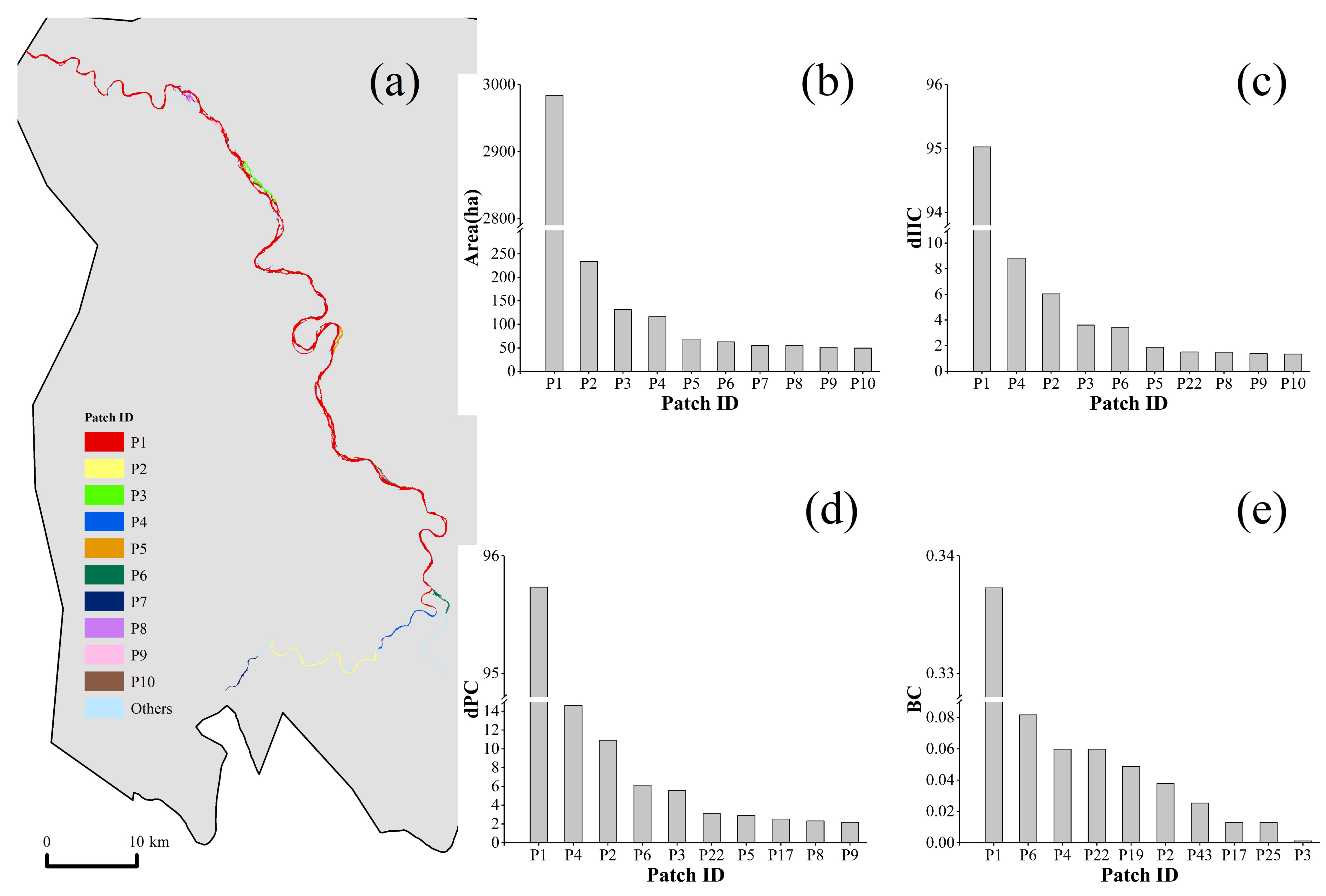
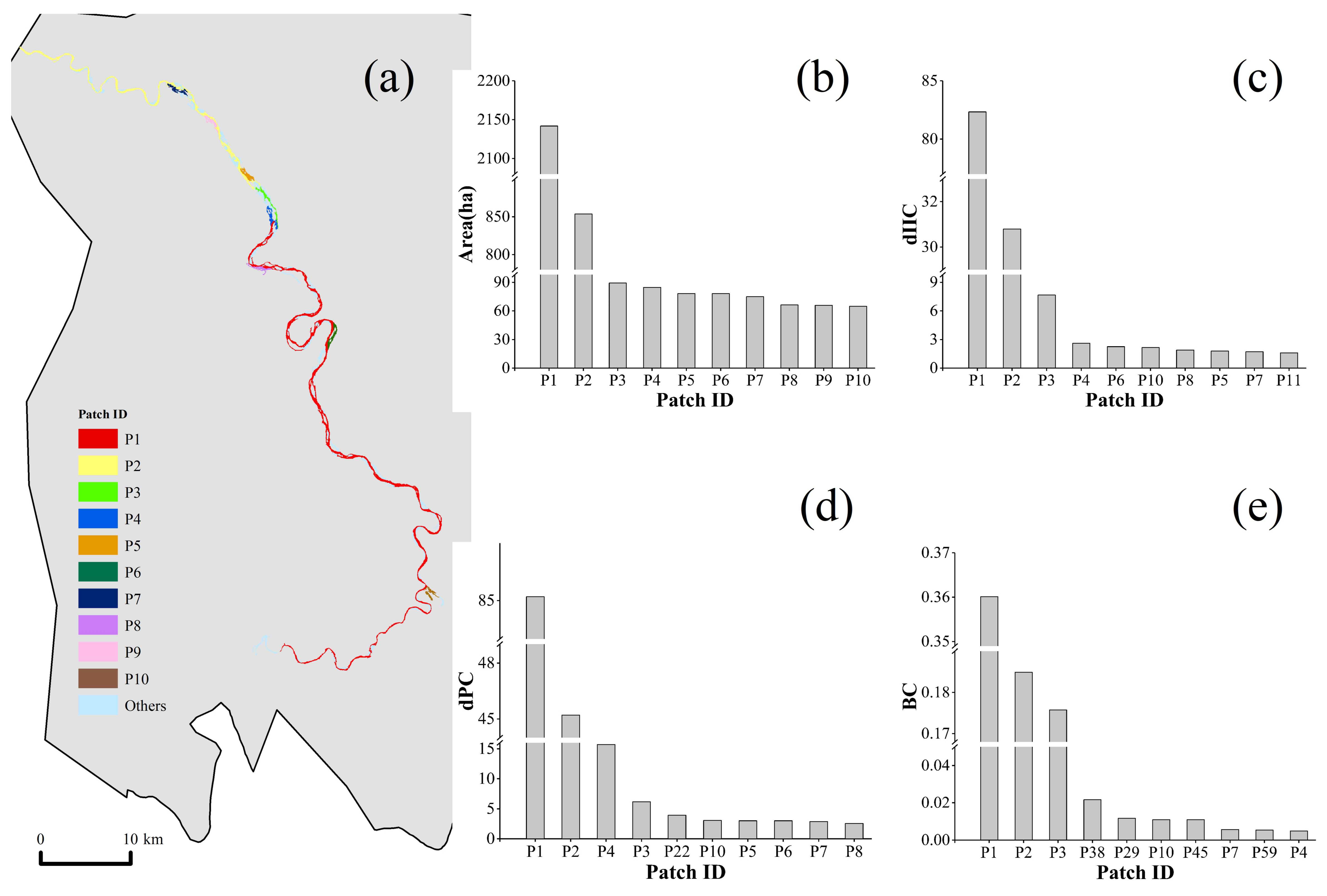
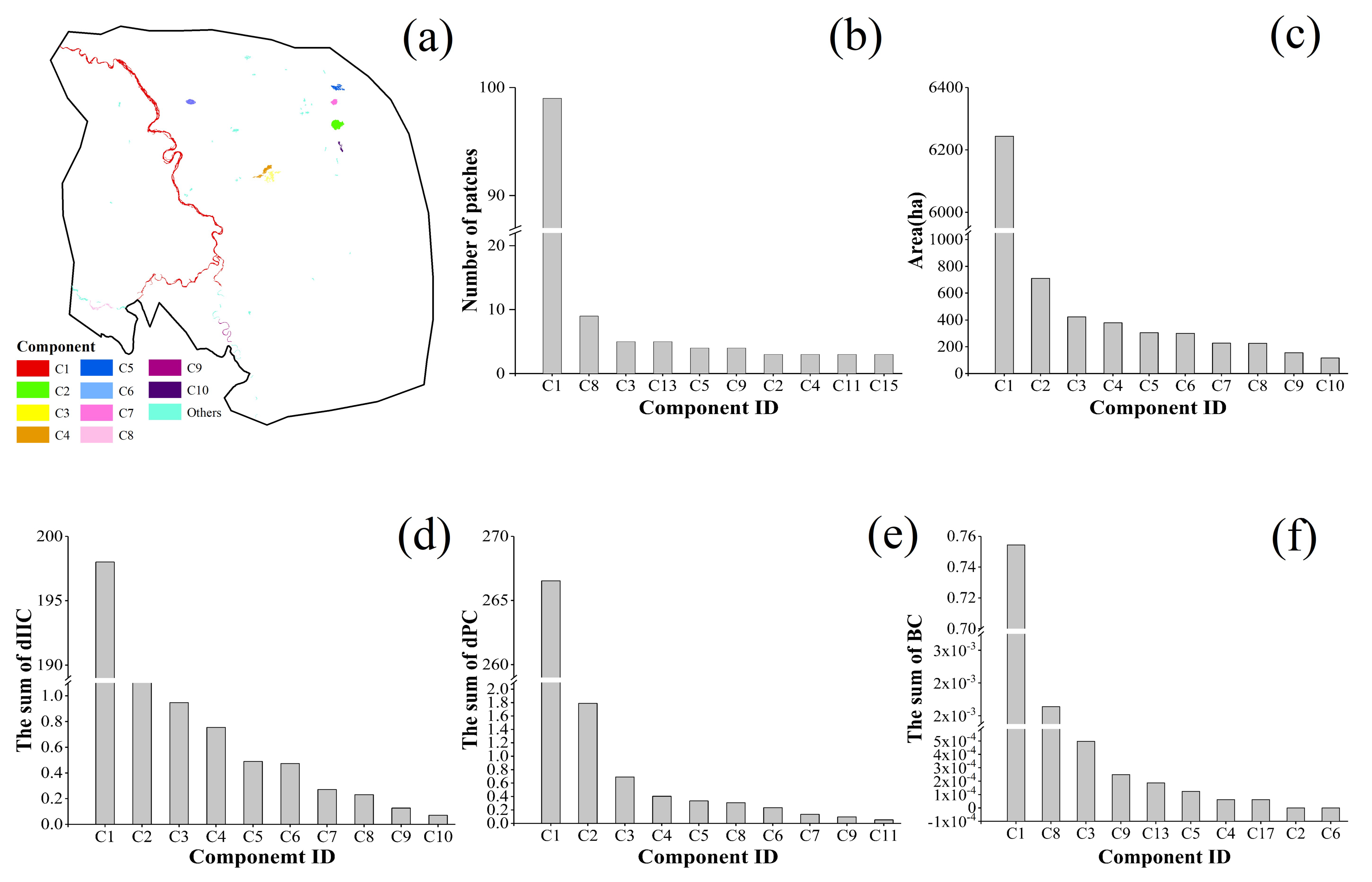
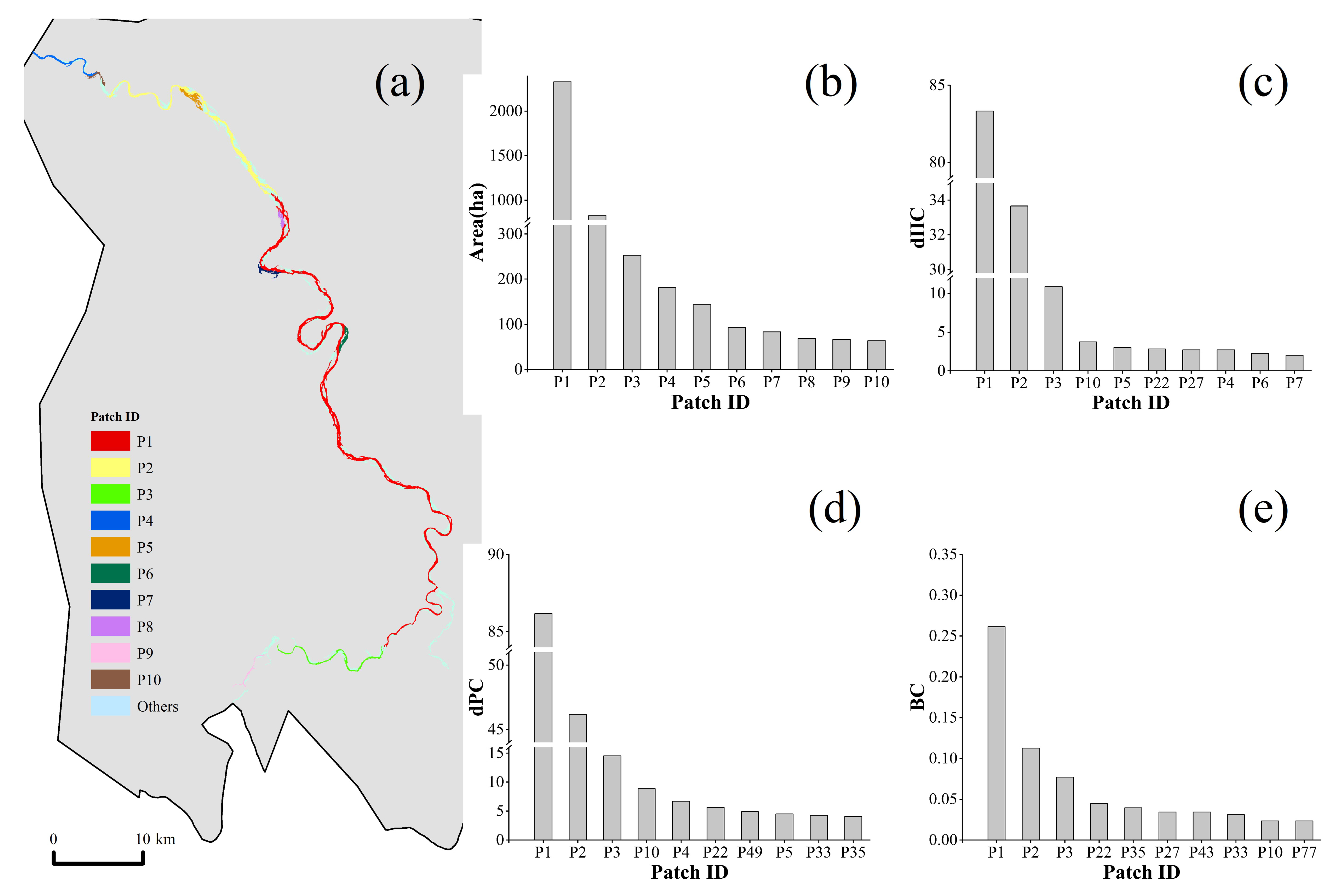
3.4.2. Important Components and Patches
Important Components and Patches
Important Patches
3.5. Determinants of Dynamic Connectivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Year | Annual Precipitation (mm) | Annual Average Temperature (°C) | GDP (104 yuan) | Farmland Area (ha) | Number of Livestock (Count) | Population (Count) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 596.4 | 1.23 | 21,779 | 4725 | 458,945 | 64,075 |
| 2001 | 597.1 | 1.68 | 22,832 | 4743 | 449,315 | 65,444 |
| 2002 | 548.2 | 1.50 | 24,943 | 3664 | 435,723 | 65,923 |
| 2003 | 764.7 | 2.27 | 26,899 | 2775 | 511,199 | 66,551 |
| 2004 | 655.6 | 1.51 | 36,521 | 2934 | 517,224 | 66,504 |
| 2005 | 666.4 | 2.01 | 41,919 | 3075 | 526,379 | 69,882 |
| 2006 | 529.4 | 2.54 | 47,092 | 3086 | 537,553 | 70,283 |
| 2007 | 613.7 | 2.02 | 55,899 | 3089 | 544,189 | 71,850 |
| 2008 | 468.7 | 1.64 | 59,674 | 3714 | 521,041 | 73,353 |
| 2009 | 571.3 | 2.53 | 73,062 | 4006 | 501,997 | 74,602 |
| 2010 | 852 | 2.72 | 85,127 | 4162 | 459,478 | 75,791 |
| 2011 | 705 | 2.28 | 99,942 | 4162 | 455,557 | 76,477 |
| 2012 | 749.6 | 2.53 | 116,062 | 4243 | 446,259 | 70,000 |
| 2013 | 770.5 | 2.77 | 130,460 | 4121 | 408,661 | 77,900 |
| 2014 | 720.6 | 2.73 | 139,128 | 4202 | 364,072 | 78,400 |
| 2015 | 541.4 | 2.65 | 153,687 | 4172 | 304,764 | 78,100 |
| 2016 | 601.3 | 2.86 | 164,280 | 4171 | 306,786 | 77,400 |
| 2017 | 705.1 | 2.88 | 175,912 | 4171 | 358,875 | 78,741 |
| 2018 | 790.8 | 2.83 | 187,545 | 4170 | 393,724 | 78,000 |
| 2019 | 718.5 | 2.79 | 259,044 | 4170 | 430,229 | 77,000 |
Appendix C
Appendix D
References
- Ward, J.V. The Four-Dimensional Nature of Lotic Ecosystems. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1989, 8, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.M. Hydrologic Connectivity and the Management of Biological Reserves: A Global Perspective. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2001, 11, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.J.; Liang, J.S.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.R.; Wang, H.J.; Fu, C.; Sun, J.J. Review on strategies of close-to-natural wetland restoration and a brief case plan for a typical wetland in northern China. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.J.; Gao, X.C.; Peng, J. Summary Comments on Hydrologic Connectivity. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2017, 23, 0586–0594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Fischer, J. Tackling the Habitat Fragmentation Panchreston. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelaria, E.; Renata, P.; Pedro Luis, B.D.R. Forest Loss and the Biodiversity Threshold: An Evaluation Considering Species Habitat Requirements and the Use of Matrix Habitats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The River Continuum Concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischendorf, L.; Fahrig, L. On the Usage and Measurement of Landscape Connectivity. OIKOS 2000, 90, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malard, F.; Tockner, K.; Dole-Olivier, M.J.; Ward, J.V. A Landscape Perspective of Surface–Subsurface Hydrological Exchanges in River Corridors. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C. What is Hydrologic Connectivity and Why is it Ecologically Important? Hydrol. Processes 2003, 17, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, L.; Wainwright, J.; Brazier, R.E. A Conceptual Framework for Understanding Semi-Arid Land Degradation: Ecohydrological Interactions across Multiple-Space and Time Scales. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Western, A.W.; Blöschl, G.; Grayson, R.B. Toward Capturing Hydrologically Significant Connectivity in Spatial Patterns. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Pringle, C.M.; Jackson, C.R. Hydrologic Connectivity and the Contribution of Stream Headwaters to Ecological Integrity at Regional Scales1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M. Evaluating Static and Dynamic Landscape Connectivity Modelling Using a 25-Year Remote Sensing Time Series. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, D.R.; Corstanje, R.; Siriwardena, G.M.; Plummer, K.E.; Harris, J.A. A bird’s eye view: Using circuit theory to study urban landscape connectivity for birds. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1771–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcrae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using Circuit Theory to Model Connectivity in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Liu, D.F.; Zhao, H.Z.; He, J.H.; Liu, Y.L. Exploring the Spatio-Temporal Impacts of Farmland Reforestation on Ecological Connectivity Using Circuit Theory: A Case Study in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of North China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Fan, Z.Q.; Ng, C.N.; Wang, X.R.; Xie, Y.J. Functional Analysis of Landscape Connectivity at the Landscape, Component, and Patch Levels: A Case Study of Minqing County, Fuzhou City, China. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 80, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.H.; Lu, Q.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Ouyang, H.; Deng, W.; Li, A.N. Landscape Pattern Evolution Processes of Alpine Wetlands and Their Driving Factors in the Zoige Plateau of China. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.L.; Chen, Z.K.; Zou, Y.C.; Lu, X.G.; Guo, J.W.; Tang, X.G. Effect of Zoige Alpine Wetland Degradation on the Density and Fractions of Soil Organic Carbon. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Gary, B.; Tami, N.; Pan, B.Z.; Li, Y.F. Shrinkage of the Ruoergai Swamp and Changes to Landscape Connectivity, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2015, 126, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Xue, P.F.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, H.P.; Zhu, G.F.; Cao, Y.P. Monitoring and Landscape Dynamic Analysis of Alpine Wetland Area Based on Multiple Algorithms: A Case Study of Zoige Plateau. Sensors 2020, 20, 7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chen, W.; Cao, C.X.; Tian, H.; Liu, D.; Bao, D.M. Diagnosis of Wetland Ecosystem Health in the Zoige Wetland, Sichuan of China. Wetlands 2018, 38, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, Y.C.; Jin, Y.X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q.B. Remote Sensing and Evaluation of the Wetland Ecological Degradation Process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.H.; Li, A.N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, W.; Lei, G.B.; Xia, H.M.; Tan, J.B. Grassland Fractional Vegetation Cover Monitoring Using the Composited Hj-1a/B Time Series Images and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: A Case Study in Zoige Wetland China. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 7192–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.L.; Wu, N. Rangeland Privatization and Its Impacts on the Zoige Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2005, 2, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Josep, T. Conefor Sensinode 2.2: A Software Package for Quantifying the Importance of Habitat Patches for Landscape Connectivity. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcrae, B.H. Isolation by Resistance. Evolution 2016, 60, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylo, R.; Tulbure, M.R.; Roich, M. Surface- Water Dynamics and Land Use Influence Landscape Connectivity across a Major Dryland Region. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaman, R.; Hall, K.; Shah, V.B.; Edelman, A. Circuitscape in Julia: High Performance Connectivity Modelling to Support Conservation Decisions. Proc. JuliaCon. 2019, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.S.; Cheng, L.; Su, J.; Yin, H.W.; Guo, Y.Q. Developing Regional Econogical Networks along the Grand Canal based on an Integrated Analysis Framework. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Structure Optimization of Green Infrastructure Based on Circuit Theory in Nanjing, China; NanJing University: NanJing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, E.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, D.K. Connectivity Assessment Based on Circuit Theory for Suggestion of Ecological Corridor. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2019, 28, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyi, G.; Saura, S.; Podani, J.; Jordan, F. Contribution of Habitat Patches to Network Connectivity: Redundancy and Uniqueness of Topological Indices. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Estreguil, C.; Mouton, C.; Rodríguez-Freire, M. Network Analysis to Assess Landscape Connectivity Trends: Application to European Forests (1990–2000). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A New Habitat Availability Index to Integrate Connectivity in Landscape Conservation Planning: Comparison with Existing Indices and Application to a Case Study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Miranda, M.; Arellano, E.C.; Saura, S.; Ovalle, C. Landscape Dynamics and Their Effect on the Functional Connectivity of a Mediterranean Landscape in Chile. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Rubio, L. A Common Currency for the Different Ways in Which Patches and Links Can Contribute to Habitat Availability and Connectivity in the Landscape. Ecography 2010, 33, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, M.X.; Wang, C.; Ma, Z.W.; Xiu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.T. Hydrological Connectivity Dynamics and Conservation Priorities for Surface-Water Patches in the Yellow River Delta National Nature Reserve, China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, O.; Saura, S. Ranking Individual Habitat Patches as Connectivity Providers: Integrating Network Analysis and Patch Removal Experiments. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Gao, P.; You, Y.C. Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2018, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tulbure, M.G.; Broich, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Kommareddy, A. Surface Water Extent Dynamics from Three Decades of Seasonally Continuous Landsat Time Series at Subcontinental Scale in a Semi-Arid Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land Use Type | Type Code | Classification | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| entry 1 | data | data | |
| Forest | 20 | - | 20 |
| Shrubland | 40 | - | 25 |
| Grassland | 30 | - | 30 |
| Cropland | 10 | - | 100 |
| Wetland | 50 | >25 ha | 7 |
| 1–25 ha | 9 | ||
| ≤1 ha | 11 | ||
| Waterbody | 60 | >25 ha | 1 |
| 1–25 ha | 3 | ||
| ≤1 ha | 5 | ||
| Artificial surface | 80 | - | 1000 |
| Index Type | Curve Fitting Equations | R2 | Inflection Points (x) | Corresponding Distance (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | y = 0.0093x3 − 0.135x2 + 0.7539x + 5.8221 | 0.9973 | 4.8387 | 126.3050 |
| LCP | y = 0.0151x3 − 0.2606x2 + 1.4914x − 12.876 | 0.9663 | 5.7528 | 315.0716 |
| EC(IIC) | y = 0.0059x3 − 0.1026x2 + 0.5901x + 7.2536 | 0.9804 | 5.7966 | 329.1784 |
| IIC | y = 0.0119x3 − 0.2065x2 + 1.19x − 13.05 | 0.9803 | 5.7843 | 325.1544 |
| F | y = 0.0062x3 − 0.0426x2 + 0.1219x + 5.4022 | 0.9995 | 2.2903 | 9.877901 |
| AWF | y = 0.0082x3 − 0.137x2 + 0.7943x + 14.765 | 0.9925 | 5.5691 | 262.1980 |
| EC (PC) | y = 0.004x3 − 0.0681x2 + 0.3887x + 7.9826 | 0.9890 | 5.6750 | 291.4883 |
| PC | y = 0.008x3 − 0.1363x2 + 0.7781x − 11.573 | 0.9890 | 5.6792 | 292.7152 |
| Influencing Factor | Large Livestock Population | Population | Annual Precipitation | Farmland Area | Mean Annual Temperature | GDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of Correlation | 0.829 | 0.774 | 0.77 | 0.753 | 0.743 | 0.578 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Modelling Dynamic Hydrological Connectivity in the Zoigê Area (China) Based on Multi-Temporal Surface Water Observation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010145
Gao C, Huang C, Wang J, Li Z. Modelling Dynamic Hydrological Connectivity in the Zoigê Area (China) Based on Multi-Temporal Surface Water Observation. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010145
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chao, Chang Huang, Jianbang Wang, and Zhi Li. 2022. "Modelling Dynamic Hydrological Connectivity in the Zoigê Area (China) Based on Multi-Temporal Surface Water Observation" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010145
APA StyleGao, C., Huang, C., Wang, J., & Li, Z. (2022). Modelling Dynamic Hydrological Connectivity in the Zoigê Area (China) Based on Multi-Temporal Surface Water Observation. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010145