Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with MLP Loss Function for Cloud Removal in a Cropland Time Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Investigate whether extending the original pix2pix cGAN objective function with a custom loss function that minimizes the distance between the semantic segmentation of the real and synthetic images, could deliver synthetic pixels that improve crop type mapping with optical remote sensing images covered by clouds and cloud shadows;
- Evaluate the generalization for generative models, meaning, whether models trained in few images selected along the time series could provide suitable synthetic pixels for cloud-covered areas on other images along the same satellite image time series.
2. Background
2.1. Generative Adversarial Network
2.2. Conditional Generative Adversarial Network
2.3. Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network
3. Proposed Method
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Dataset and Satellite Image Pre-Processing
4.2. Experiments Description
4.2.1. MLP Hyper-Parameter Optimization
4.2.2. Evaluation of the MLP Custom Loss Function
4.2.3. Evaluation of the Generative Models Generalization
4.3. Performance Assessment
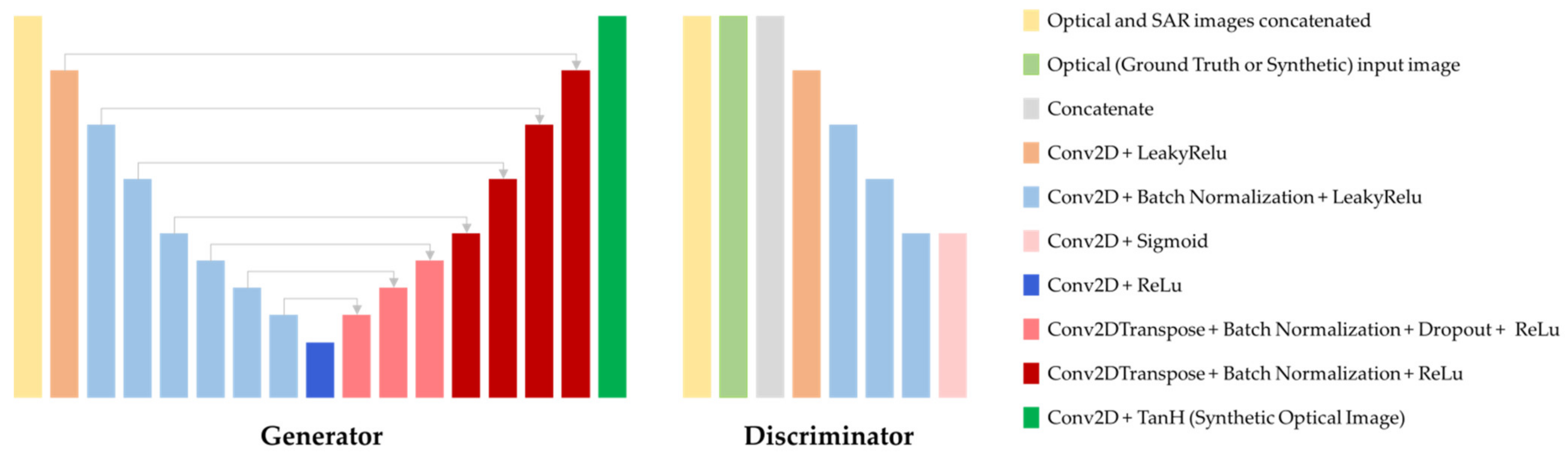
4.4. Pix2pix cGAN Architecture
5. Results
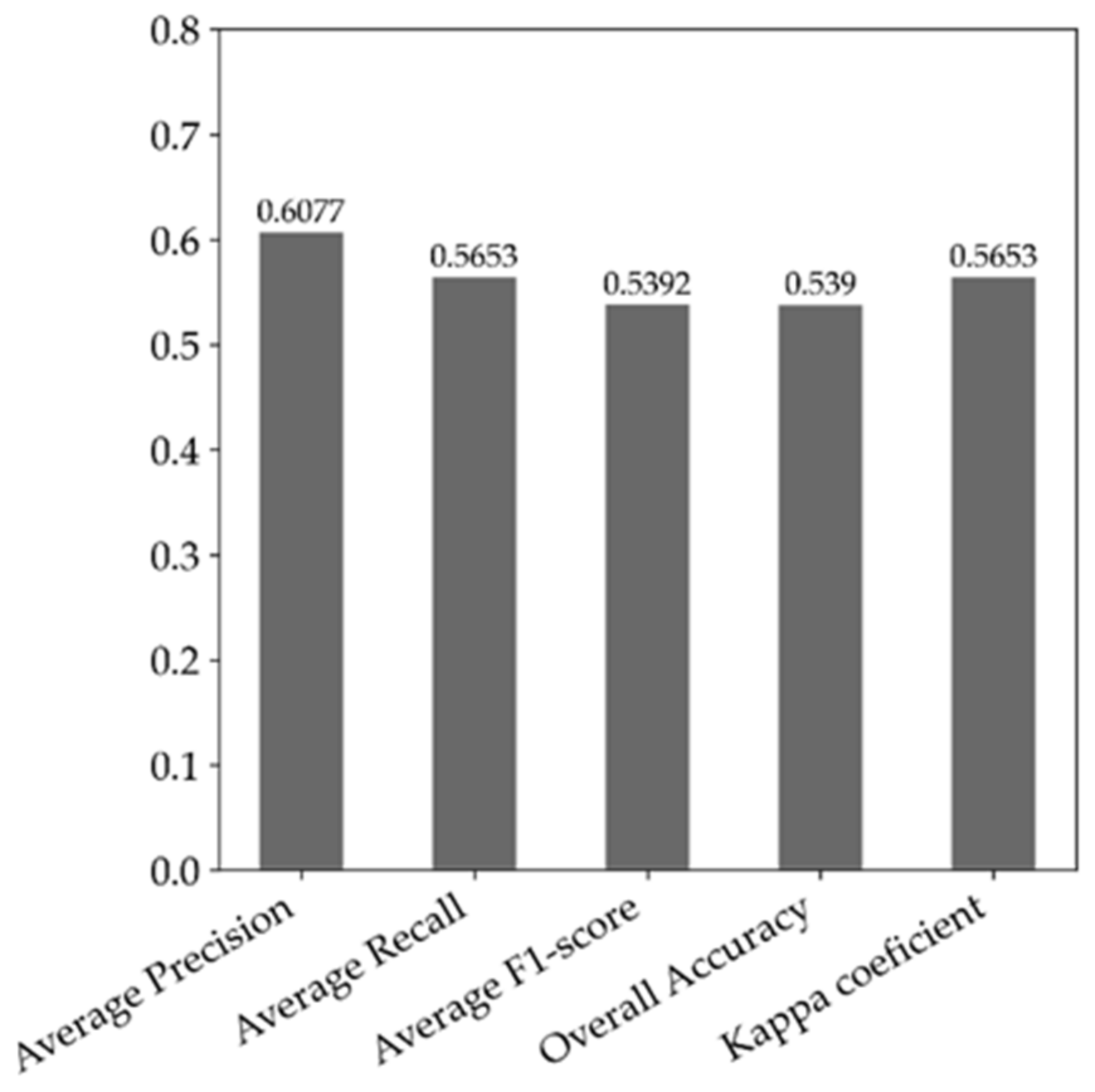
5.1. Performance of the MLP Network Models
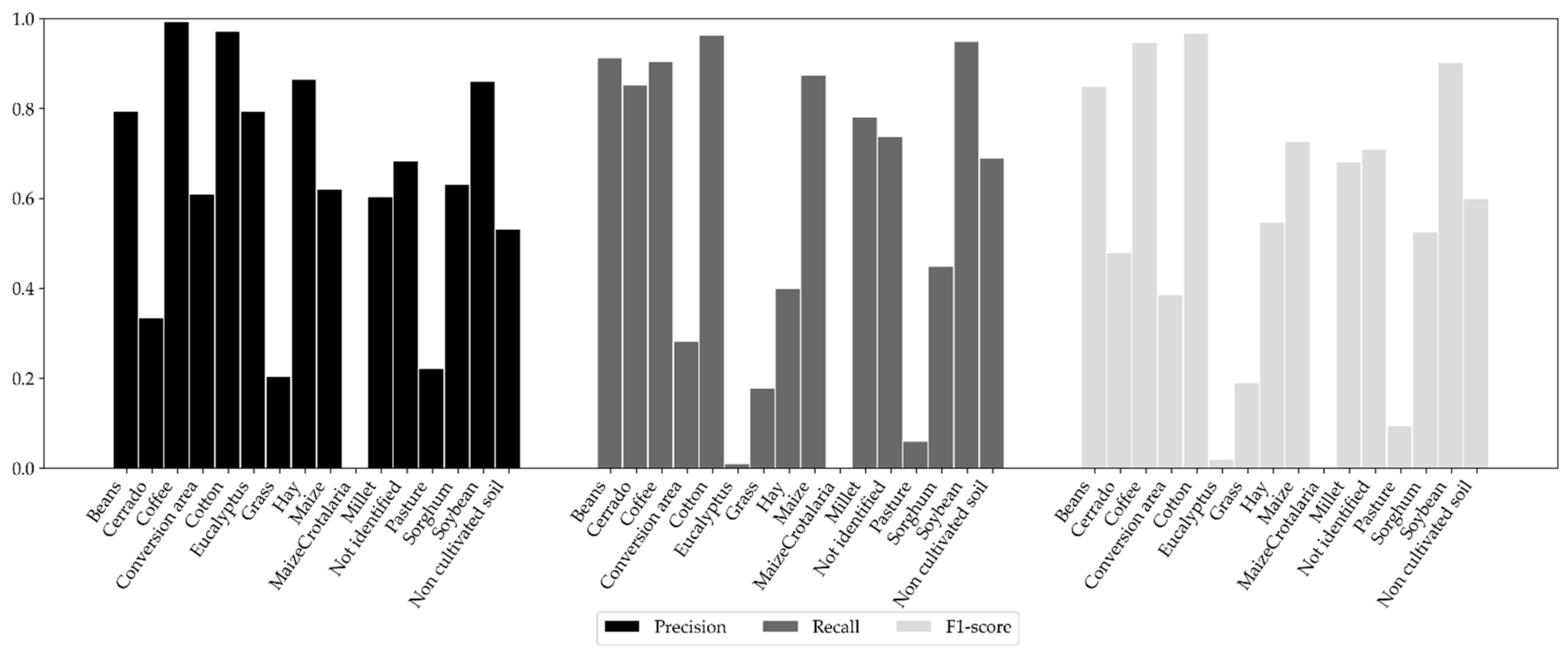
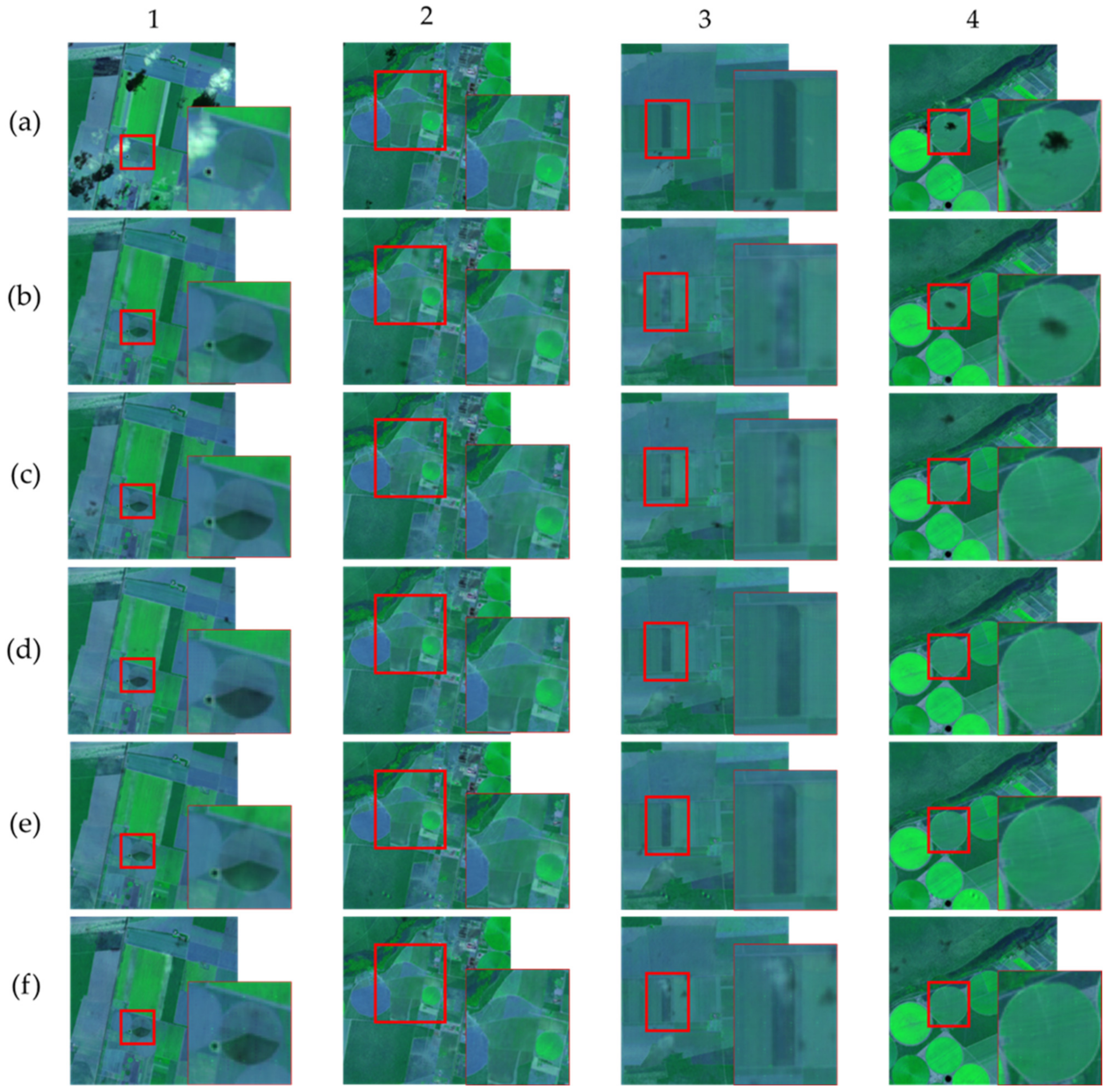
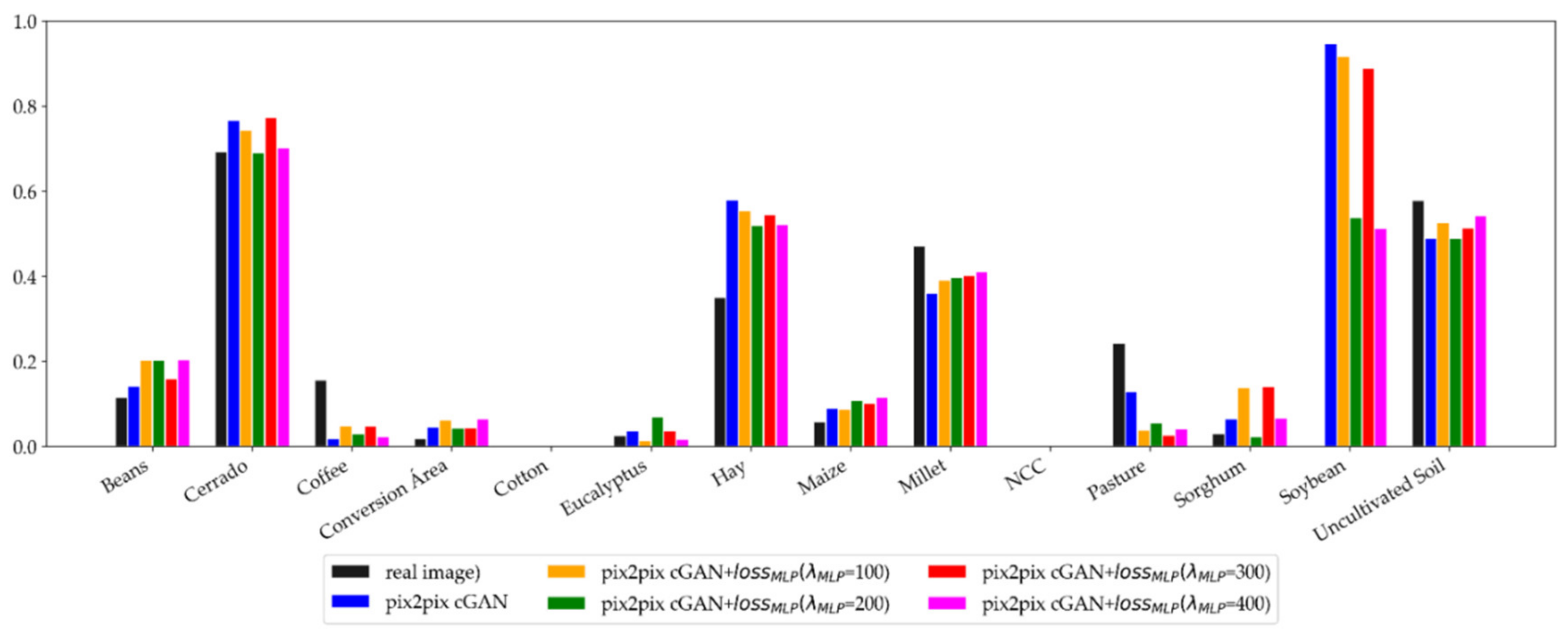
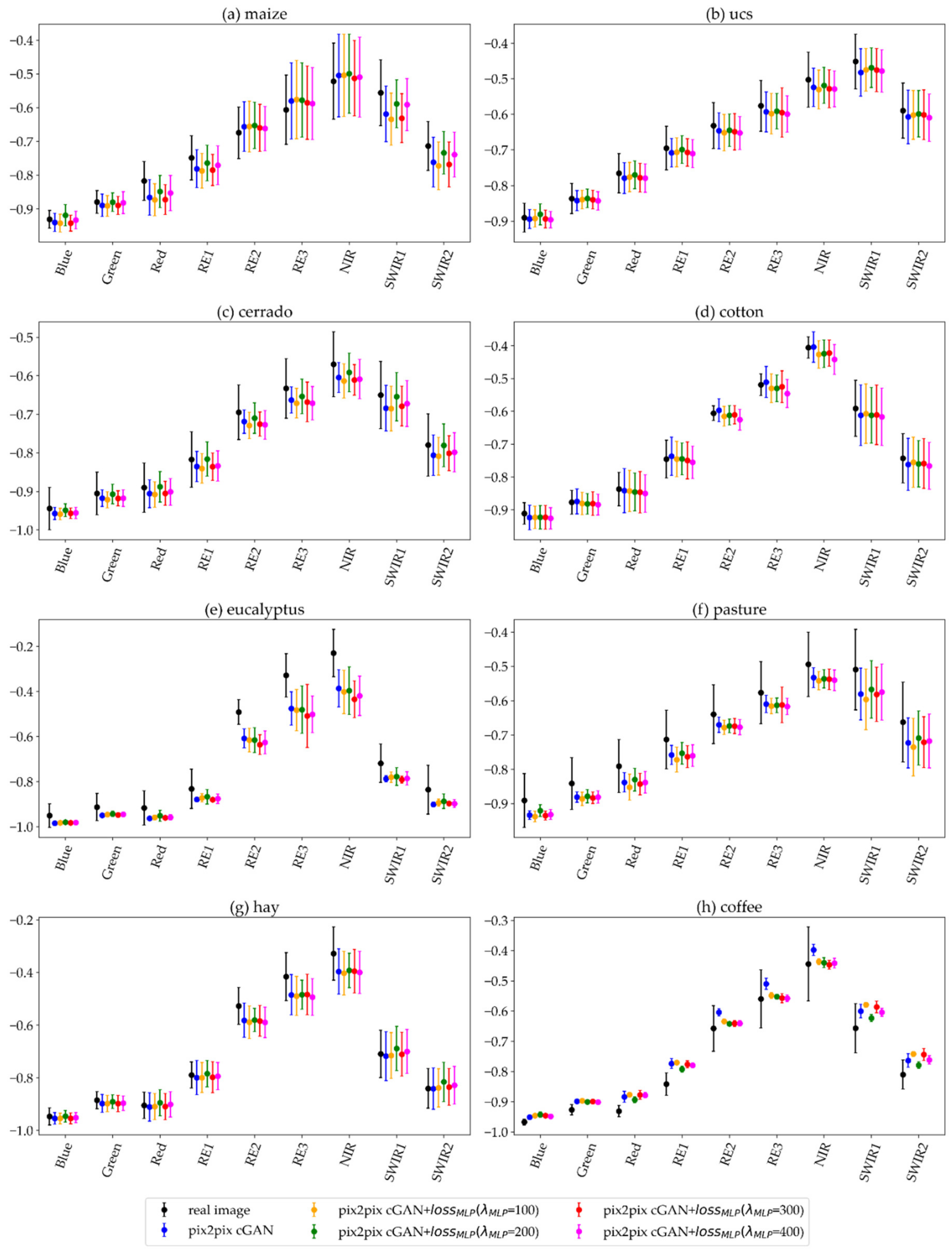
5.2. Synthetic Images Generated with the Pix2pix cGAN with the MLP Loss Function
5.3. Generalization Capability for the Pix2pix cGAN with the MLP Loss Function
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. In United Nations General Assembly; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcraft, A.K.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Justice, C.O.; Gifford, L.; Kavvada, A.; Jarvis, I. No pixel left behind: Toward integrating Earth Observations for agriculture into the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Chawla, I.; Mishra, A.K. A review of remote sensing applications in agriculture for food security: Crop growth and yield, irrigation, and crop losses. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C. Advances in remote sensing of agriculture: Context description, existing operational monitoring systems and major information needs. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 949–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, S.; See, L.; Bayas, J.C.L.; Waldner, F.; Jacques, D.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Whitcraft, A.; Baruth, B.; Bonifacio, R.; Crutchfield, J.; et al. A comparison of global agricultural monitoring systems and current gaps. Agric. Syst. 2019, 168, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcraft, A.K.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Killough, B.D.; Justice, C.O. Meeting earth observation requirements for global agricultural monitoring: An evaluation of the revisit capabilities of current and planned moderate resolution optical earth observing missions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1482–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitcraft, A.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Justice, C.O. Cloud cover throughout the agricultural growing season: Impacts on passive optical earth observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Menzel, W.P.; Ackerman, S.; Hubanks, P.A. Spatial and temporal distribution of clouds observed by MODIS onboard the Terra and Aqua satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3826–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudente, V.H.R.; Martins, V.S.; Vieira, D.C.; Silva, N.R.D.F.E.; Adami, M.; Sanches, I.D. Limitations of cloud cover for optical remote sensing of agricultural areas across South America. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarukkai, V.; Jain, A.; Uzkent, B.; Ermon, S. Cloud Removal in Satellite Images Using Spatiotemporal Generative Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1785–1794. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Missing information reconstruction of remote sensing data: A technical review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liew, S.C.; Kwoh, L.K. Automated production of cloud-free and cloud shadow-free image mosaics from cloudy satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the XXth ISPRS Congress, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Melgani, F. Contextual reconstruction of cloud-contaminated multitemporal multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdelkader, S.; Melgani, F.; Boulemden, M. Cloud-contaminated image reconstruction with contextual spatio-spectral information. In Proceeding of the IGARSS 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Benabdelkader, S.; Melgani, F. Contextual spatiospectral postreconstruction of cloud-contaminated images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chova, L.; Amorós-López, J.; Mateo-García, G.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Camps-Valls, G. Cloud masking and removal in remote sensing image time series. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S.; Wheeler, B.; Iiames, J.S.; Campbell, J.B. An evaluation of time-series smoothing algorithms for land-cover classifications using MODIS-NDVI multi-temporal data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christovam, L.; Shimabukuro, M.H.; Galo, M.L.B.T.; Honkavaara, E. Evaluation of SAR to Optical Image Translation Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Cloud Removal in a Crop Dataset. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Arde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Processing Syst. 2014, 2, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, K.; Sakurada, K.; Wang, W.; Kawaguchi, N. Image translation between SAR and optical imagery with generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1752–1755. [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez, J.; Happ, P.N.; Oliveira, D.A.B.; Feitosa, R.Q. SAR to optical image synthesis for cloud removal with generative adversarial networks. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grohnfeldt, C.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X. A Conditional Generative Adversarial Network to Fuse SAR And Multispectral Optical Data For Cloud Removal From Sentinel-2 Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1726–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Komodakis, N. IEEE Cloud-gan: Cloud removal for sentinel-2 imagery using a cyclic consistent generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018–2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1772–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez, J.D.; Happ, P.N.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Oliveira, D.A.B. Synthesis of multispectral optical images from SAR/optical multitemporal data using conditional generative adversarial networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, I.D.A.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Diaz, P.M.A.; Soares, M.D.; Luiz, A.J.B.; Schultz, B.; Maurano, L.E.P. Campo Verde database: Seeking to improve agricultural remote sensing of tropical areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Meng, X.; Jin, W.; Shao, F. A SAR-to-optical image translation method based on conditional generation adversarial network (cGAN). IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 60338–60343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Turnes, J.N.; Castro, J.D.B.; Torres, D.L.; Vega, P.J.S.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Happ, P.N. Atrous cGAN for SAR to Optical Image Translation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 3031199. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, P.R.; Nalepa, J.; Kawulok, M.; Ramos, L.S.; Pastor, J.R. Particle swarm optimization for hyper-parameter selection in deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference, Berlin, Germany, 1 July 2017; pp. 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-de-la-Cruz, J.A.; Acosta-Mesa, H.-G.; Mezura-Montes, E. Evolution of Generative Adversarial Networks Using PSO for Synthesis of COVID-19 Chest X-ray Images, 2021 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC); IEEE: Kraków, Poland, 2021; pp. 2226–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Optimized convolutional neural network by firefly algorithm for magnetic resonance image classification of glioma brain tumor grade. J. Real-Time Image Processing 2021, 18, 1085–1098. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, L. High-quality face image generation using particle swarm optimization-based generative adversarial networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 122, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 26–July 1 2016; pp. 2536–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, I.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Achanccaray, P.; Montibeller, B.; Luiz, A.J.B.; Soares, M.D.; Prudente, V.H.R.; Vieira, D.C.; Maurano, L.E.P. LEM benchmark database for tropical agricultural remote sensing application. ISPRS International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science; ISPRS: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2018; Volume 42, pp. 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Shami, A. On hyperparameter optimization of machine learning algorithms: Theory and practice. Neurocomputing 2020, 415, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesen, M.; Simm, J.; Popovic, D.; Moreau, Y.; Moor, B.D. Easy hyperparameter search using optunity. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.1114. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietterich, T.G. Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms. Neural Comput. 1998, 10, 1895–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 9351; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]


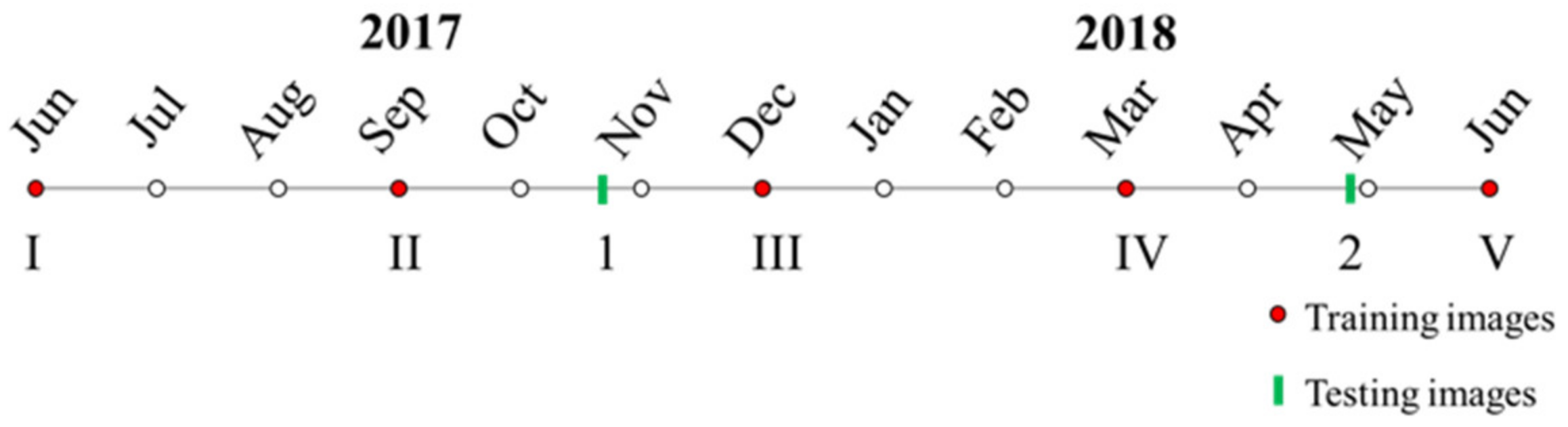



| MSI/Sentinel-2 Images | Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 July 2017 22 October 2017 | hidden layers | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| hidden units | 9–51 | 4–31 | 4–16 | |
| 17 February 2018 10 May 2018 | alpha | 0–0.6 | ||
| dropout | 0–0.6 | |||
| Weigh Sets | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| Image Group | Month | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI Sentinel-2 | C-SAR Sentinel-1 | MSI Sentinel-2 | ||
| Training images | ||||
| I | June | 4 June 2017 | 24 June 2017 | 24 June 2017 |
| II | September | 12 September 2017 | 4 September 2017 | 7 September 2017 |
| III | December | 1 December 2017 | 9 December 2017 | 6 December 2017 |
| 22 October 2017 | ||||
| IV | March | 1 March 2018 | 3 March 2018 | 6 March 2018 |
| 14 February 2018 | ||||
| V | June | 14 June 2018 | 19 June 2018 | 19 June 2018 |
| Generalization testing images | ||||
| 1 | October | 17 October 2017 | 10 October 2017 | 22 October 2017 |
| 2 | April | 10 May 2018 | 2 May 2018 | 30 April 2018 |
| Generative Models | Synthetic Images Labels | |
|---|---|---|
| two images | I-II | - |
| II-III | 1/II-III | |
| III-IV | - | |
| IV-V | 2/IV-V | |
| three images | I-II-III | 1/I-II-III |
| III-IV-V | 2/III-IV-V | |
| five images | I-II-III-IV-V | 1/I-II-III-IV-V |
| 2/I-II-III-IV-V | ||
| transfer learning | I-II-III-IV-V + TL 1 | 1/I-II-III-IV-V + TL 1 |
| I-II-III-IV-V + TL 2 | 2/I-II-III-IV-V + TL 2 | |
| same image | 1 | 1/1 |
| 2 | 2/2 |
| OA | Kappa | F1-Score | PSNR | SSIM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real image | 0.431 | - | 0.308 | - | 0.447 | - | - | - |
| I-A (pix2pix cGAN) | 0.414 | −1.7% | 0.292 | −1.6% | 0.425 | −2.1% | 22.89 | 0.765 |
| =100) | 0.428 | −0.3% | 0.303 | −0.5% | 0.438 | −0.9% | 22.90 | 0.767 |
| =200) | 0.400 | −3.1% | 0.269 | −3.9% | 0.411 | −3.5% | 23.16 | 0.777 |
| =300) | 0.437 | 0.6% | 0.313 | 0.6% | 0.442 | −0.5% | 22.87 | 0.765 |
| = 400) | 0.427 | −0.4% | 0.298 | −1.0% | 0.436 | −1.0% | 23.00 | 0.771 |
| p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Image | A | B | C | D | |
| Real image | - | - | - | - | - |
| A | - | - | - | - | |
| B | - | - | - | ||
| C | - | - | |||
| D | - | ||||
| E | |||||
| Article | Method | Artifacts (Training/Results) | Geometry Differences | Pixel Values Differences | Semantic Segmentation (OA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bermudez et al. [21] | pix2pix cGAN | no/no | some | yes | Real: ~65%~85% |
| Synthetic: ~55%~75% | |||||
| Bermudez et al. [24] | pix2pix cGAN * | no/no | small | some | Real: 84.6% |
| Synthetic: 74.6% | |||||
| Enomoto et al. [20] | cGAN | - | blurred | some | - |
| Li et al. [26] | - | very similar | very similar ** | - | |
| Turner et al. [28] | atrous-cGAN | no/no | very similar | small | Real: ~63%~81% |
| Synthetic: 62%~80% | |||||
| Ours | original pix2pix cGAN | yes/yes | very similar | small | Real: 43.1% |
| Synthetic: 41.4% | |||||
| Ours | * | yes/yes * | very similar | very similar | Real: 43.1% |
| Synthetic: 40%~43.7% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christovam, L.E.; Shimabukuro, M.H.; Galo, M.d.L.B.T.; Honkavaara, E. Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with MLP Loss Function for Cloud Removal in a Cropland Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010144
Christovam LE, Shimabukuro MH, Galo MdLBT, Honkavaara E. Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with MLP Loss Function for Cloud Removal in a Cropland Time Series. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010144
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristovam, Luiz E., Milton H. Shimabukuro, Maria de Lourdes B. T. Galo, and Eija Honkavaara. 2022. "Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with MLP Loss Function for Cloud Removal in a Cropland Time Series" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010144
APA StyleChristovam, L. E., Shimabukuro, M. H., Galo, M. d. L. B. T., & Honkavaara, E. (2022). Pix2pix Conditional Generative Adversarial Network with MLP Loss Function for Cloud Removal in a Cropland Time Series. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010144






