An Improved Index for Urban Population Distribution Mapping Based on Nighttime Lights (DMSP-OLS) Data: An Experiment in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Processing
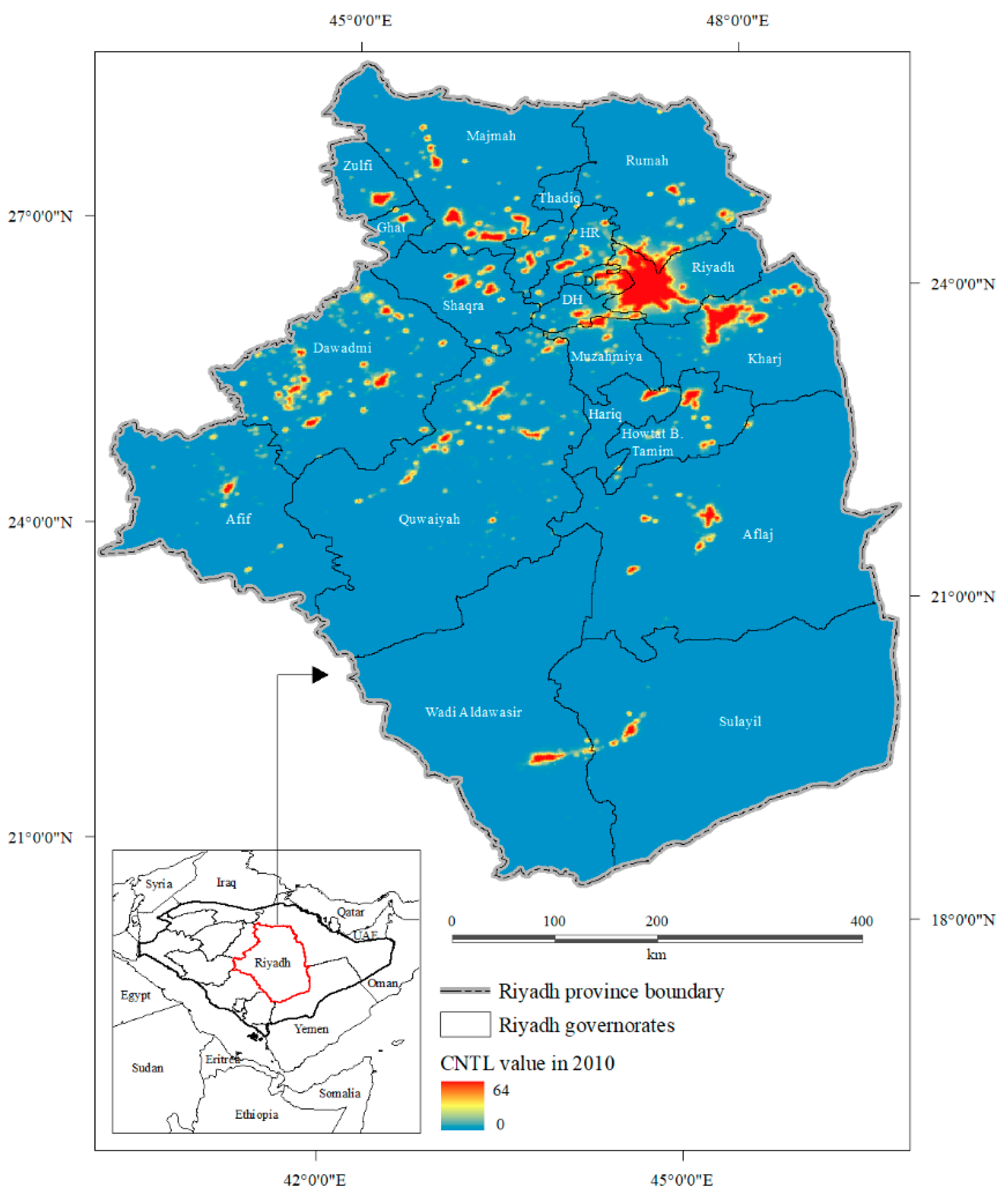
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Population and Administrative Boundaries
2.2.2. Land Use/Cover Data
2.2.3. Satellite Sensor Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Modeling Theories
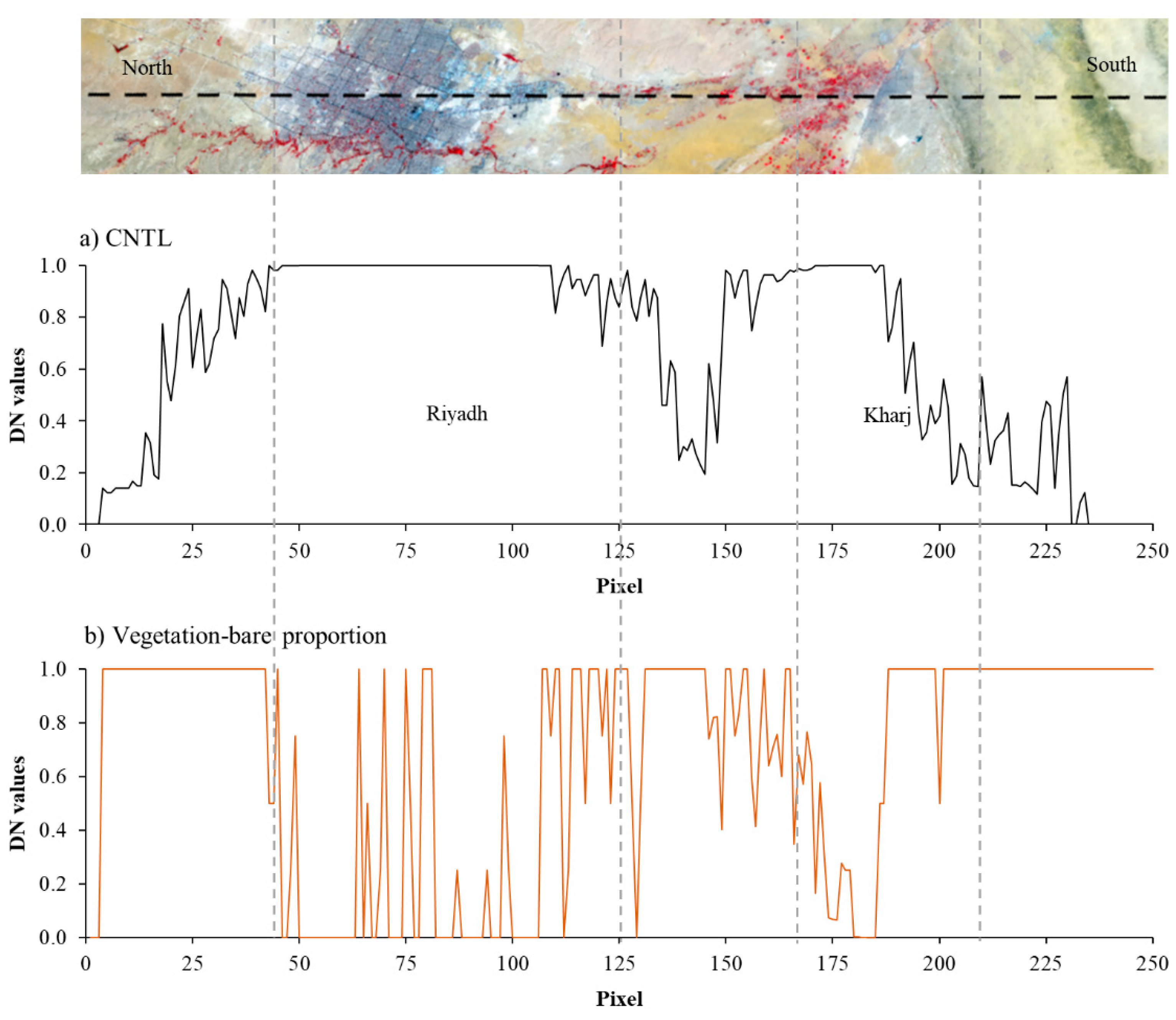
3.2. Land Cover Quality
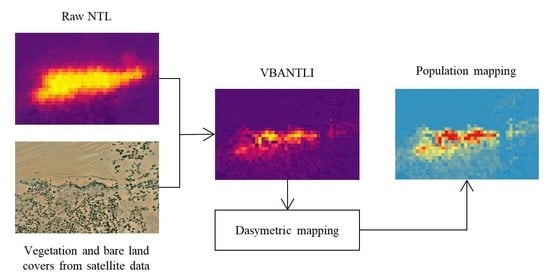
3.3. Vegetation-Bare Adjusted NTL Index (VBANTLI)
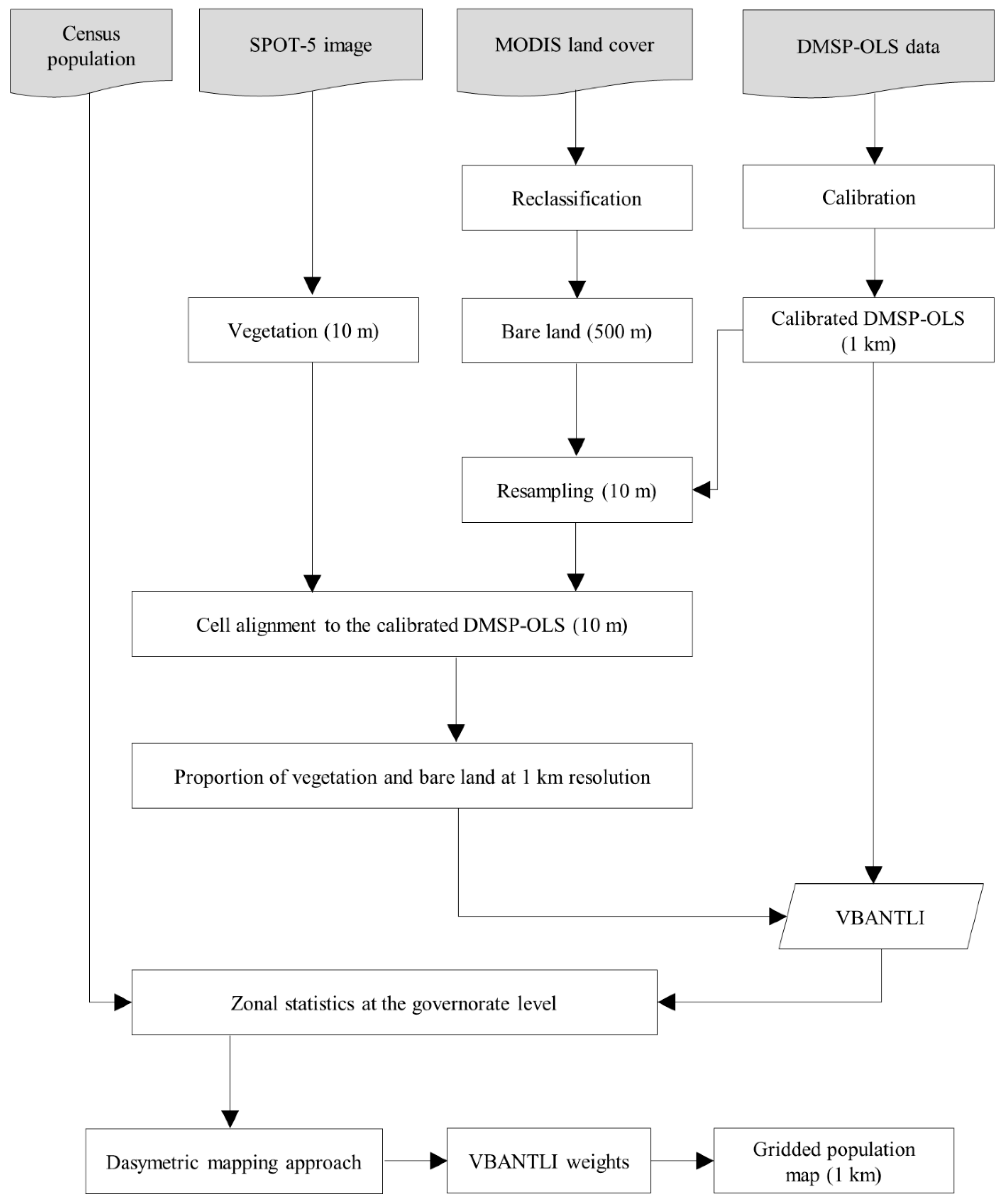
3.4. Implementing VBANTLI
- The MODIS and SPOT-5 data have different spatial resolutions compared with the NTL data. To allow the harmonization and integration of these data, the NTL and MODIS data were resampled to 10 m. Then, the CNTL data (10 m) were used as a reference raster during the projection of the MODIS and SPOT-5 data so that the cell alignments all match.
- The IGBP scheme of the MODIS land cover data (MCD12Q1) includes 17 classes. The MCD12Q1 product was clipped to the Riyadh province boundary, resulting in five land cover classes: open shrubland, grassland, cropland, urban and built-up land, and bare land. These five classes were reclassified as populated (shrubland, grassland, cropland, and urban and built-up lands) and unpopulated (bare land) areas [22]. The coarse spatial resolution of the MODIS land cover (500 m) is a source of uncertainty, as there may be inhabitants within the vegetated classes [22], especially in rural areas. In the present research, we categorized the MODIS vegetated, urban, and built-up classes as populated. Later, vegetation areas within fine spatial resolution data (SPOT-5) were used to exclude the ground-referenced vegetation as un-populated areas.
- MODIS bare land (0, 1) and SPOT-5 vegetation (0, 1) covers were overlaid at 10 m spatial resolution and pixels scoring 1 in either layer were classed as un-populated. Although the agreement between the two sources is not guaranteed, both contribute to the identification of un-populated areas. Then, the proportion of the un-populated areas was computed at 1 km spatial resolution.
- Finally, the VBANTLI was computed to downscale the governorate census population to produce 1 km population maps in 2004 and 2010.
3.5. Dasymetric Mapping
3.6. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
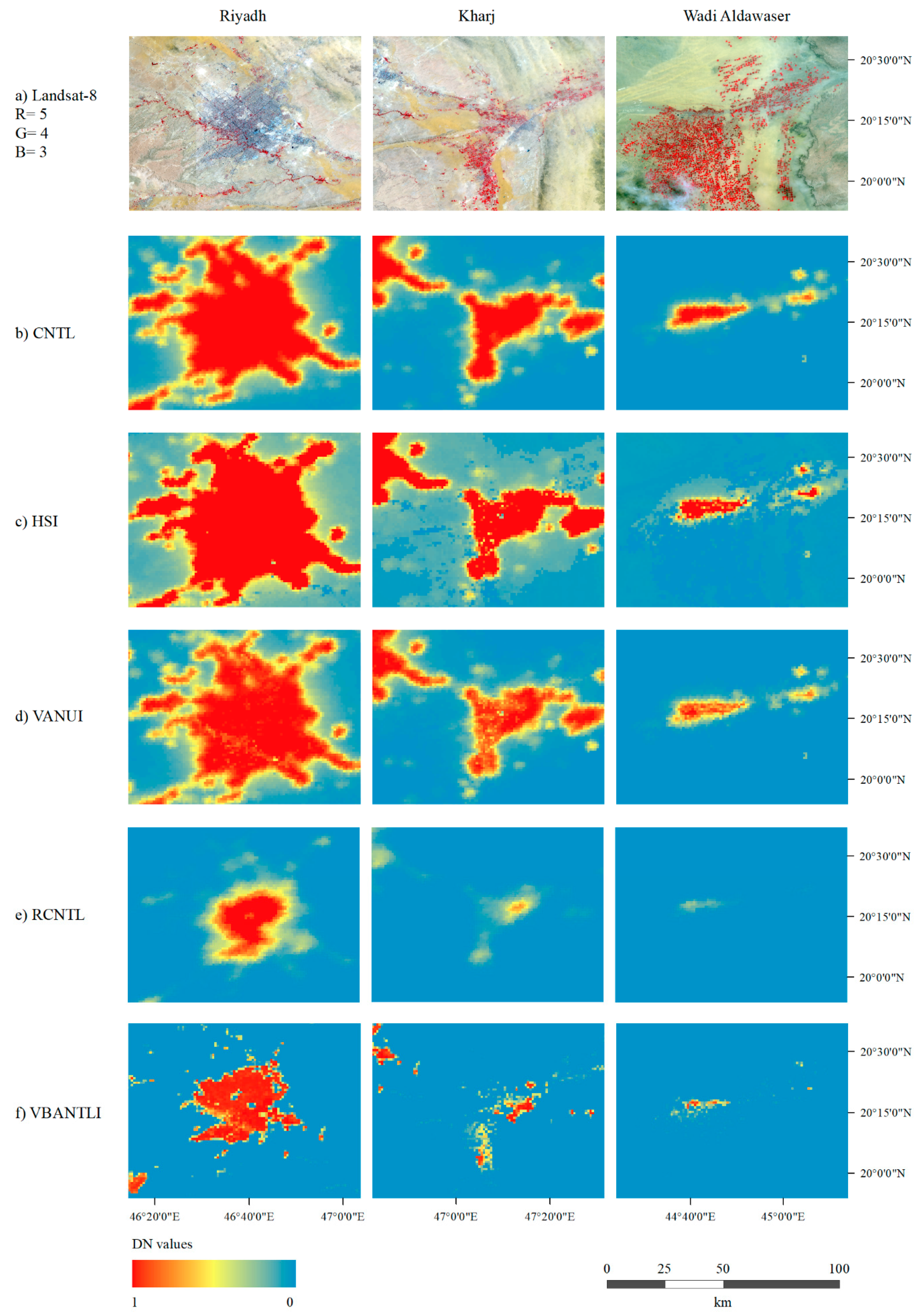
4.1. Evaluation of the Remotely Sensed Products
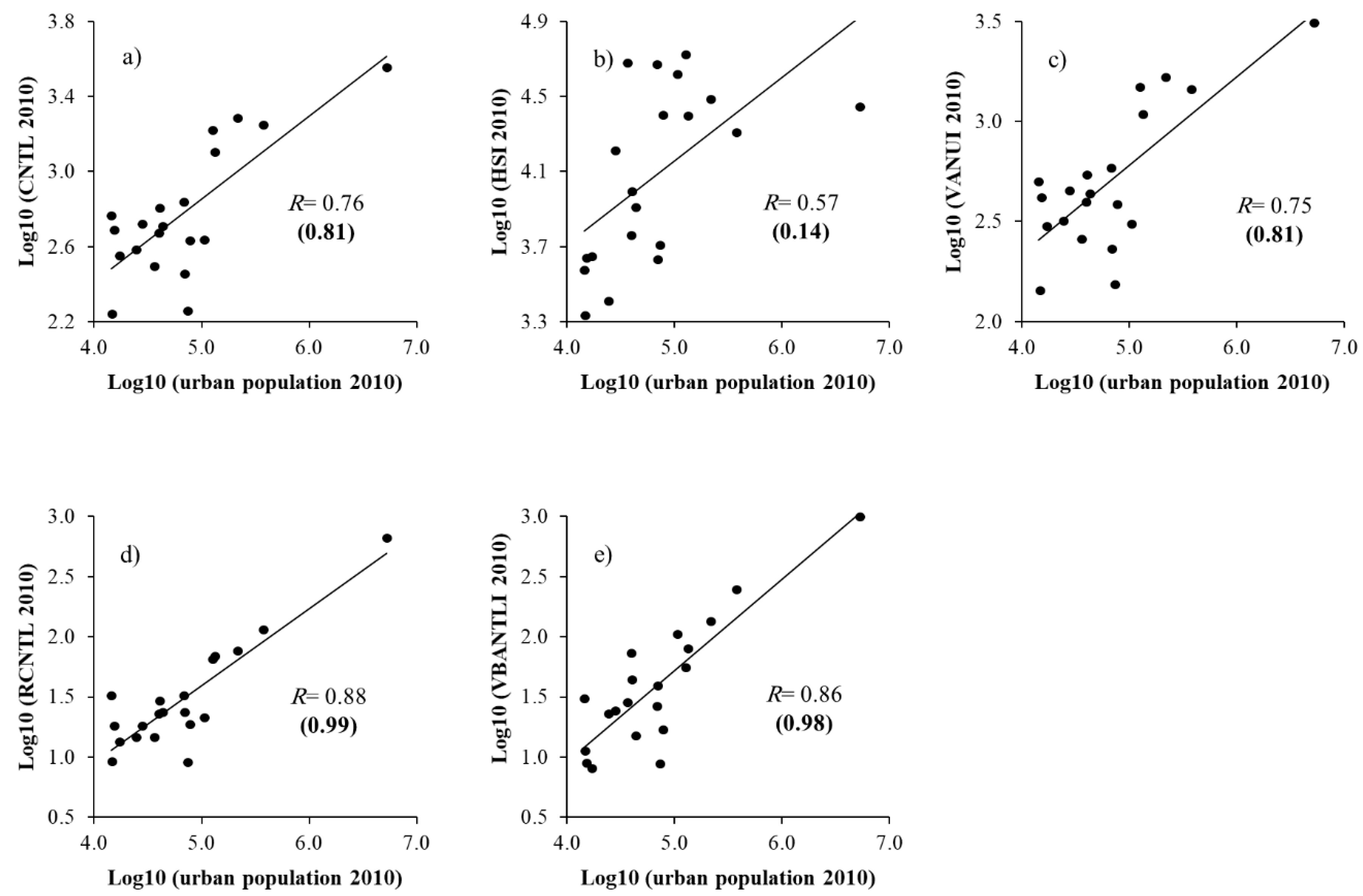
4.2. Relationship between Population Data and the Remotely Sensed Products
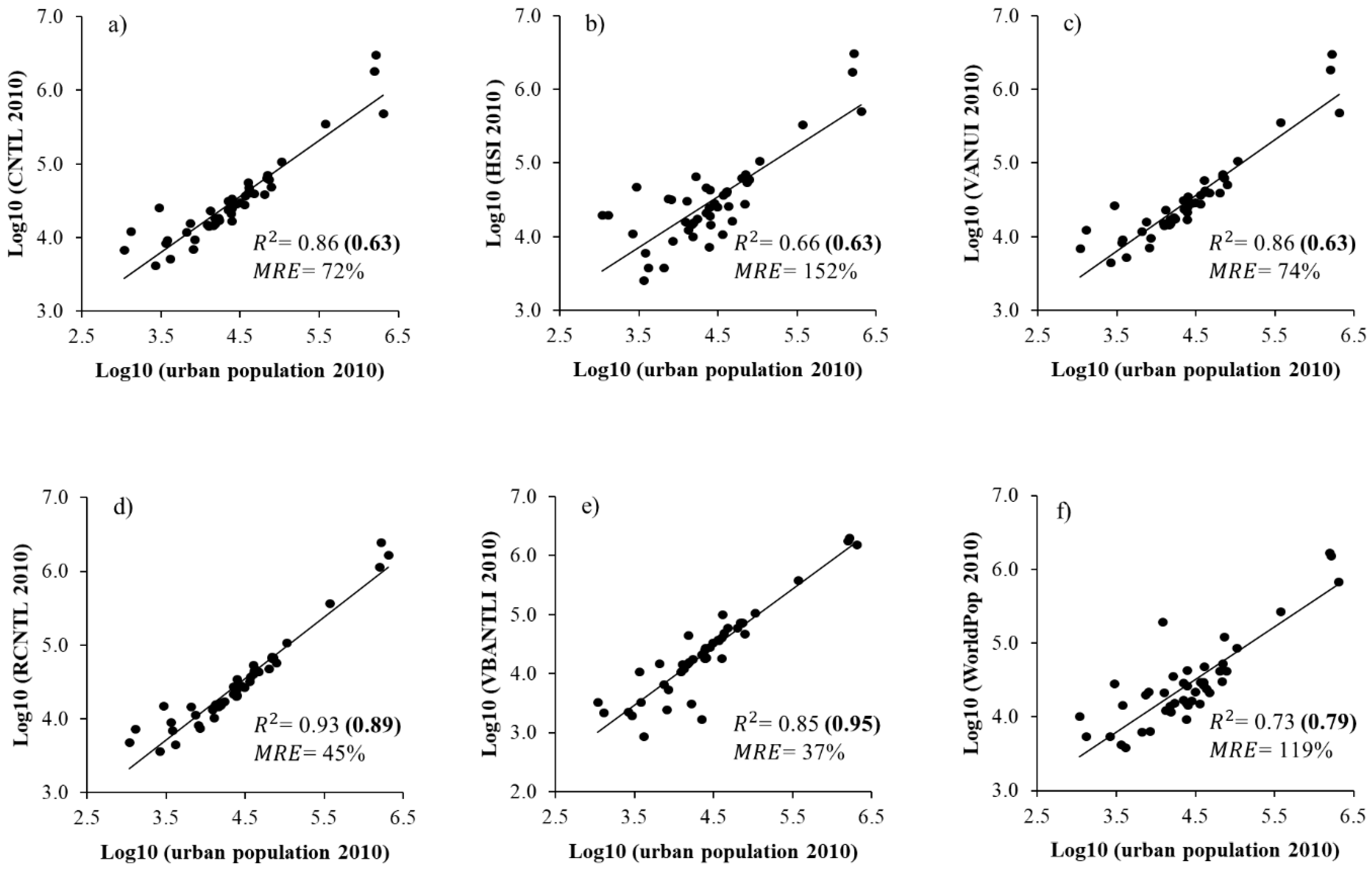
4.3. Validation of the Remotely Sensed Products
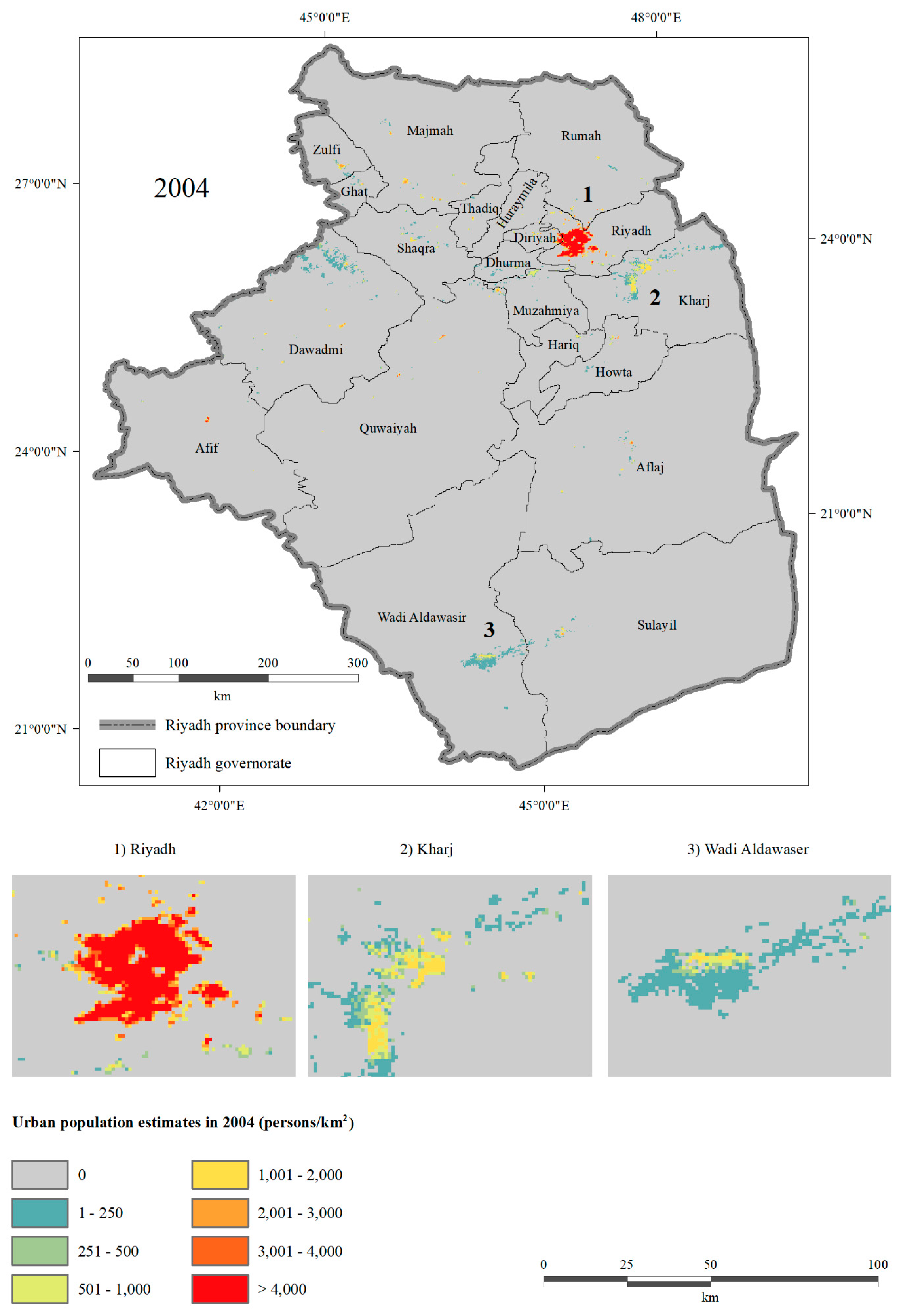
4.4. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Change in Population between 2004 and 2010 in Riyadh Province
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights; Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F. Mapping population density in China between 1990 and 2010 using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yue, W.; Gao, D. Spatial improvement of human population distribution based on multi-sensor remote-sensing data: An input for exposure assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5569–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, M.; Atkinson, P.M. Three-Fold Urban Expansion in Saudi Arabia from 1992 to 2013 Observed Using Calibrated DMSP-OLS Night-Time Lights Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W. Dasymetric mapping of urban population in China based on radiance corrected DMSP-OLS nighttime light and land cover data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Xiang, W. Modeling population density based on nighttime light images and land use data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Peng, J. Exploring factors affecting the relationship between light consumption and GDP based on DMSP/OLS nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sutton, P.C.; Qi, B. Global Mapping of GDP at 1 km2 Using VIIRS Nighttime Satellite Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q. The uncertainty of nighttime light data in estimating carbon dioxide emissions in China: A comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Ebener, S. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagan, H.; Yamagata, Y. Analysis of urban growth and estimating population density using satellite images of nighttime lights and land-use and population data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, W.; Li, W. Expansion analysis of yangtze river delta urban agglomeration using dmsp/ols nighttime light imagery for 1993 to 2012. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Joshi, P.; Seto, K.C. Monitoring urbanization dynamics in India using DMSP/OLS night time lights and SPOT-VGT data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhao, X. Mapping urban areas with integration of DMSP/OLS nighttime light and MODIS data using machine learning techniques. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12419–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Cen, Y. Estimating population density using DMSP-OLS night-time imagery and land cover data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2674–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F. Monitoring population evolution in China using time-series DMSP/OLS nightlight imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Ichinose, T. Restoring urbanization process in China in the 1990s by using non-radiance-calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Xiu, C. Normalization of time series DMSP-OLS nighttime light images for urban growth analysis with pseudo invariant features. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, S. A novel method for urban area extraction from VIIRS DNB and MODIS NDVI data: A case study of Chinese cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6094–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, B.C. Principles and Tools for Remote Sensing of Human Settlements. In Remote Sensing of Human Settlements: Manual of Remote Sensing; Ridd, M.K., Hipple, J.D., Eds.; ASPRS: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 37–147. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Analysis of impervious surface and its impact on urban heat environment using the normalized difference impervious surface index (NDISI). Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Ai, B.; Li, X.; Shi, Q. A normalized urban areas composite index (NUACI) based on combination of DMSP-OLS and MODIS for mapping impervious surface area. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17168–17189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Xu, T.; Huang, L.; Zhou, A. A human settlement composite index (HSCI) derived from nighttime luminosity associated with imperviousness and vegetation indexes. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, A.E.; Stevens, F.R.; Linard, C.; Jia, P.; Tatem, A.J. High resolution population distribution maps for Southeast Asia in 2010 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55882. [Google Scholar]
- WorldPop. Available online: https://www.worldpop.org/doi/10.5258/SOTON/WP00645 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Population Counts. Available online: https://www.worldpop.org/doi/10.5258/SOTON/WP00227 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Liang, D.; Zuo, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Teng, L.; Yang, F. Evaluation of the consistency of MODIS Land Cover Product (MCD12Q1) based on Chinese 30 m GlobeLand30 datasets: A case study in Anhui Province, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 2519–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Response of evapotranspiration to changes in land use and land cover and climate in China during 2001–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Abercrombie, S.P.; Friedl, M.A. Hierarchical mapping of annual global land cover 2001 to present: The MODIS Collection 6 Land Cover product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. A stepwise calibration of global DMSP/OLS stable nighttime light data (1992–2013). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 637. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Elvidge, C.D. DMSP-OLS radiance calibrated nighttime lights time series with intercalibration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1855–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing. White Lands; Ministry of Housing: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2016.
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. A new map of global urban extent from MODIS satellite data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEWA. Geodatabase Design for the Agricultural Areas in Saudi Arabia; MEWA: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.F.; Lam, N.S.-N. Areal interpolation: A variant of the traditional spatial problem. Geo-Processing 1980, 1, 297–312. [Google Scholar]
- Eicher, C.L.; Brewer, C.A. Dasymetric mapping and areal interpolation: Implementation and evaluation. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 28, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadh Principality. Governorates of Riyadh Province. 2021. Available online: https://www.riyadh.gov.sa/ar/pages/provinces.aspx (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Kuang, W. Improving fractional impervious surface mapping performance through combination of DMSP-OLS and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, Q.; Bian, Z.; Liu, B.; Wu, Z. A POI and LST Adjusted NTL Urban Index for Urban Built-Up Area Extraction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z. Improved population mapping for China using remotely sensed and points-of-interest data within a random forests model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, N. Population Spatialization in Beijing City Based on Machine Learning and Multisource Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. Improving population mapping using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light image and location-based social media data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Dataset | Format and Date | Resolution or Scale | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMSP-OLS nighttime data | Grid (2004 and 2010) | 1 km | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Geographical Data Center (NOAA/NGDC). |
| DMSP-OLS radiance calibrated nighttime data | Grid (2004 and 2010) | 1 km | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Geographical Data Center (NOAA/NGDC) |
| MODIS land cover data | Grid (2004 and 2010) | 500 m | NASA-LAADS Web |
| Vegetation land cover | Grid (2010–2011) | 10 m | Ministry of Environment Water and Agriculture (MEWA) |
| WorldPop data | Grid (2004 and 2010) | 100 m | WorldPop Web |
| Census population data | Table (2004 and 2010) | Governorate | General Authority for Statistics (GASTAT) |
| Census population data | Shape (2004 and 2010) | Municipality | Royal Commission for Riyadh City (RCRC) |
| 2004 | 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density Type | Group No. | Population Density (Persons/km2) | Built-Up Area (km2) | Population Estimates | Built-Up Areas (km2) | Population Estimates |
| Low-density areas | 1 | 1–250 | 1735 | 165,653 | 2785 | 239,213 |
| 2 | 251–500 | 444 | 157,650 | 620 | 223,847 | |
| Medium-density areas | 3 | 501–1000 | 463 | 334,172 | 608 | 428,116 |
| High-density areas | 4 | 1001–2000 | 411 | 567,281 | 532 | 721,941 |
| 5 | 2001–3000 | 198 | 485,885 | 170 | 428,544 | |
| Very high-density areas | 6 | 3001–4000 | 107 | 389,839 | 118 | 456,811 |
| 7 | >4000 | 677 | 3,357,793 | 815 | 4,278,673 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alahmadi, M.; Mansour, S.; Martin, D.; Atkinson, P.M. An Improved Index for Urban Population Distribution Mapping Based on Nighttime Lights (DMSP-OLS) Data: An Experiment in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061171
Alahmadi M, Mansour S, Martin D, Atkinson PM. An Improved Index for Urban Population Distribution Mapping Based on Nighttime Lights (DMSP-OLS) Data: An Experiment in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061171
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlahmadi, Mohammed, Shawky Mansour, David Martin, and Peter M. Atkinson. 2021. "An Improved Index for Urban Population Distribution Mapping Based on Nighttime Lights (DMSP-OLS) Data: An Experiment in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061171
APA StyleAlahmadi, M., Mansour, S., Martin, D., & Atkinson, P. M. (2021). An Improved Index for Urban Population Distribution Mapping Based on Nighttime Lights (DMSP-OLS) Data: An Experiment in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061171