Assimilation of Multi-Source Precipitation Data over Southeast China Using a Nonparametric Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
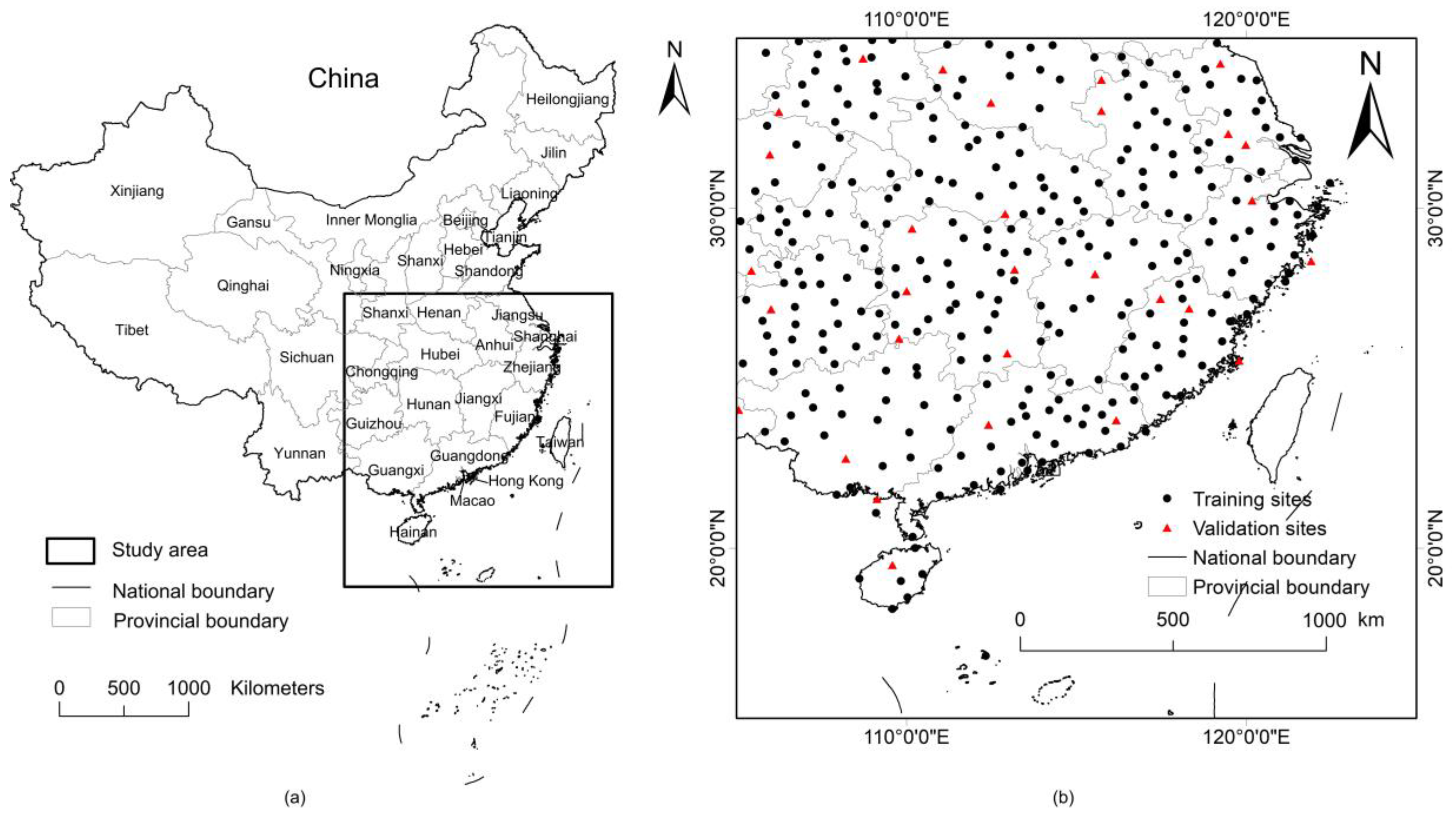
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The Framework Based on Nonparametric General Regression
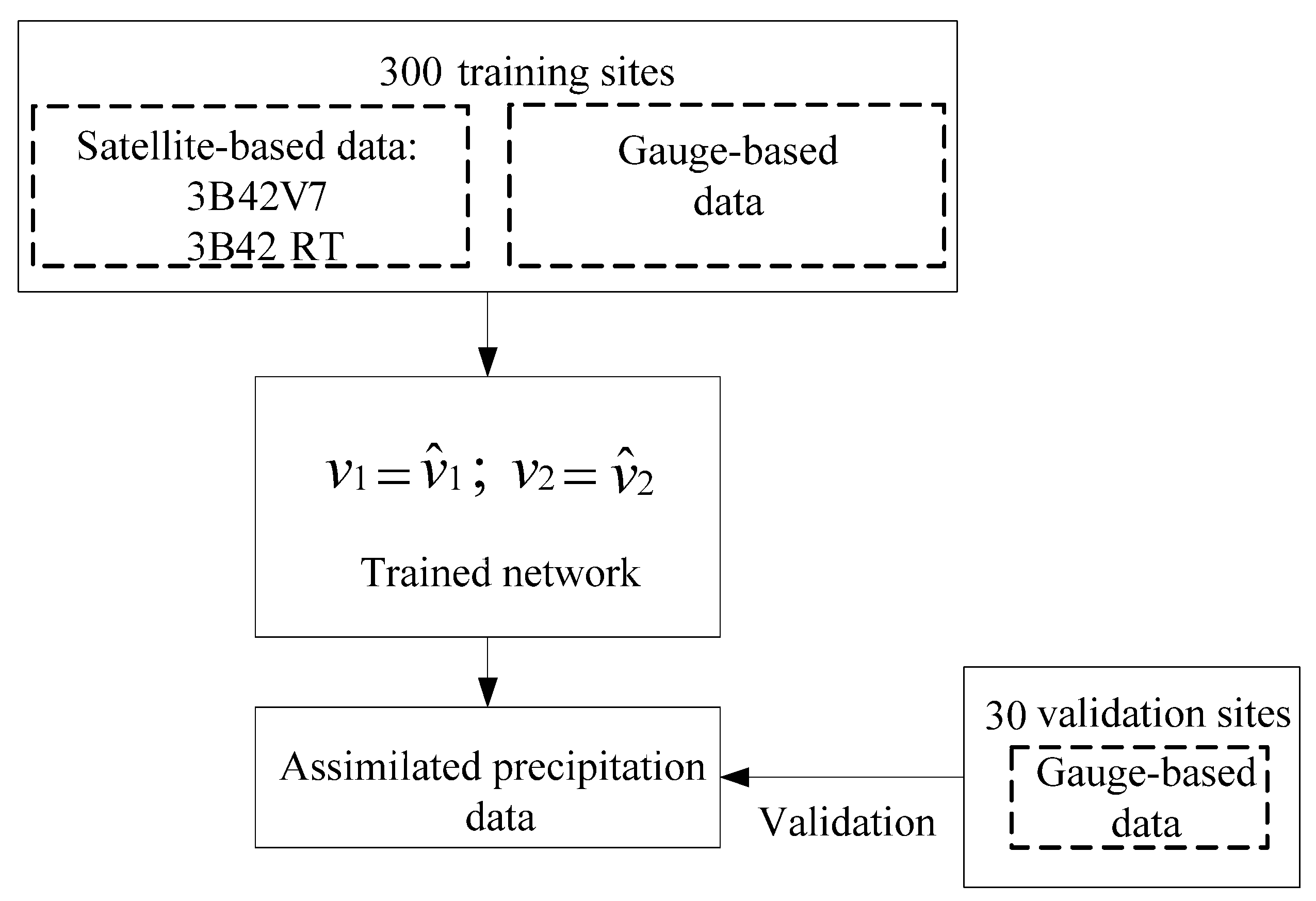
2.3.2. Data Processing for the Framework Validation
2.3.3. Statistical Metrics for Evaluating the Performance of the NGR Framework
2.3.4. Multiple Linear Regression Method
3. Results
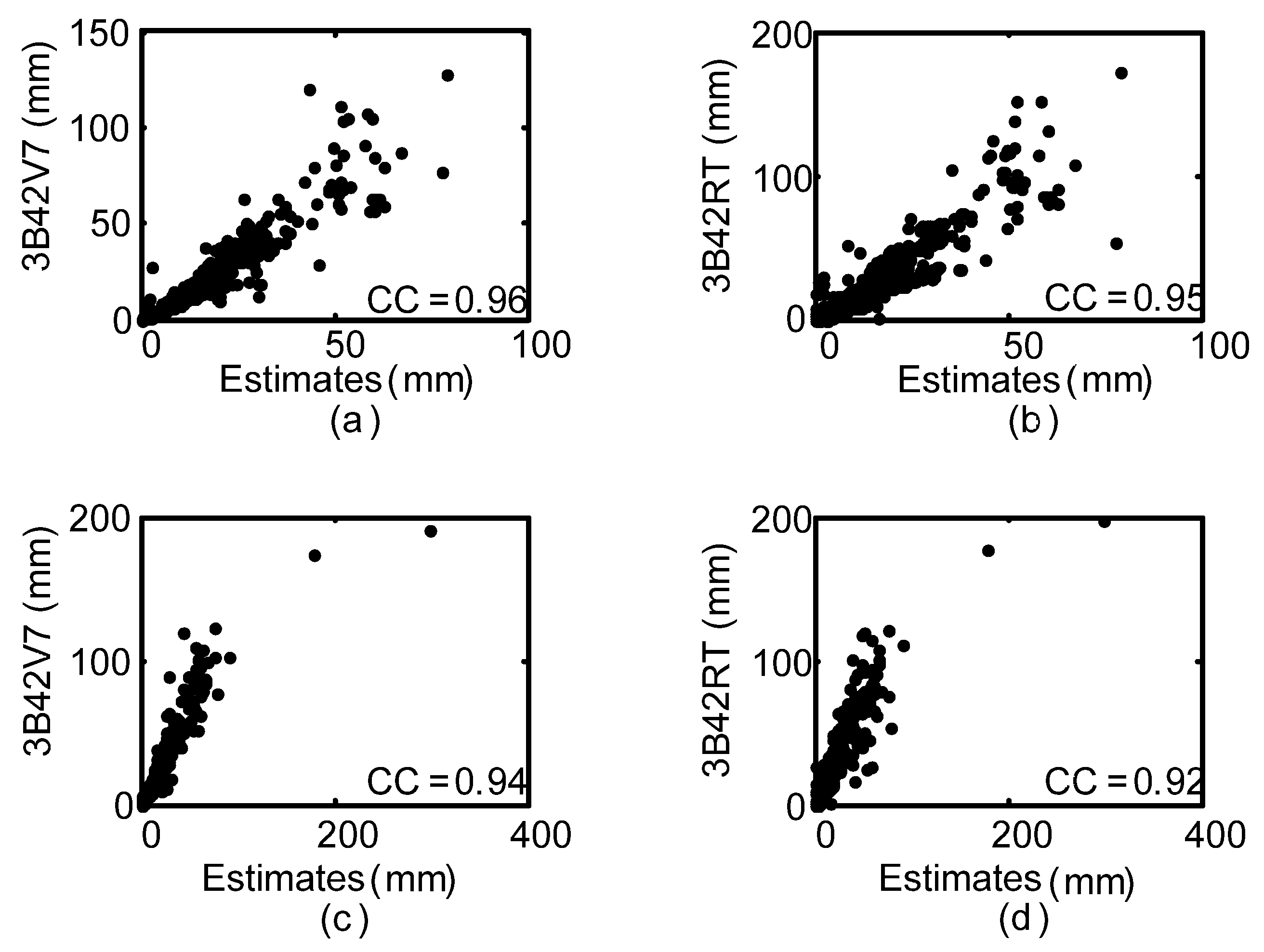
3.1. Assimilated Precipitation Data at Meiyu Seasons
3.2. Assimilated Precipitation Data at Typhoon Seasons
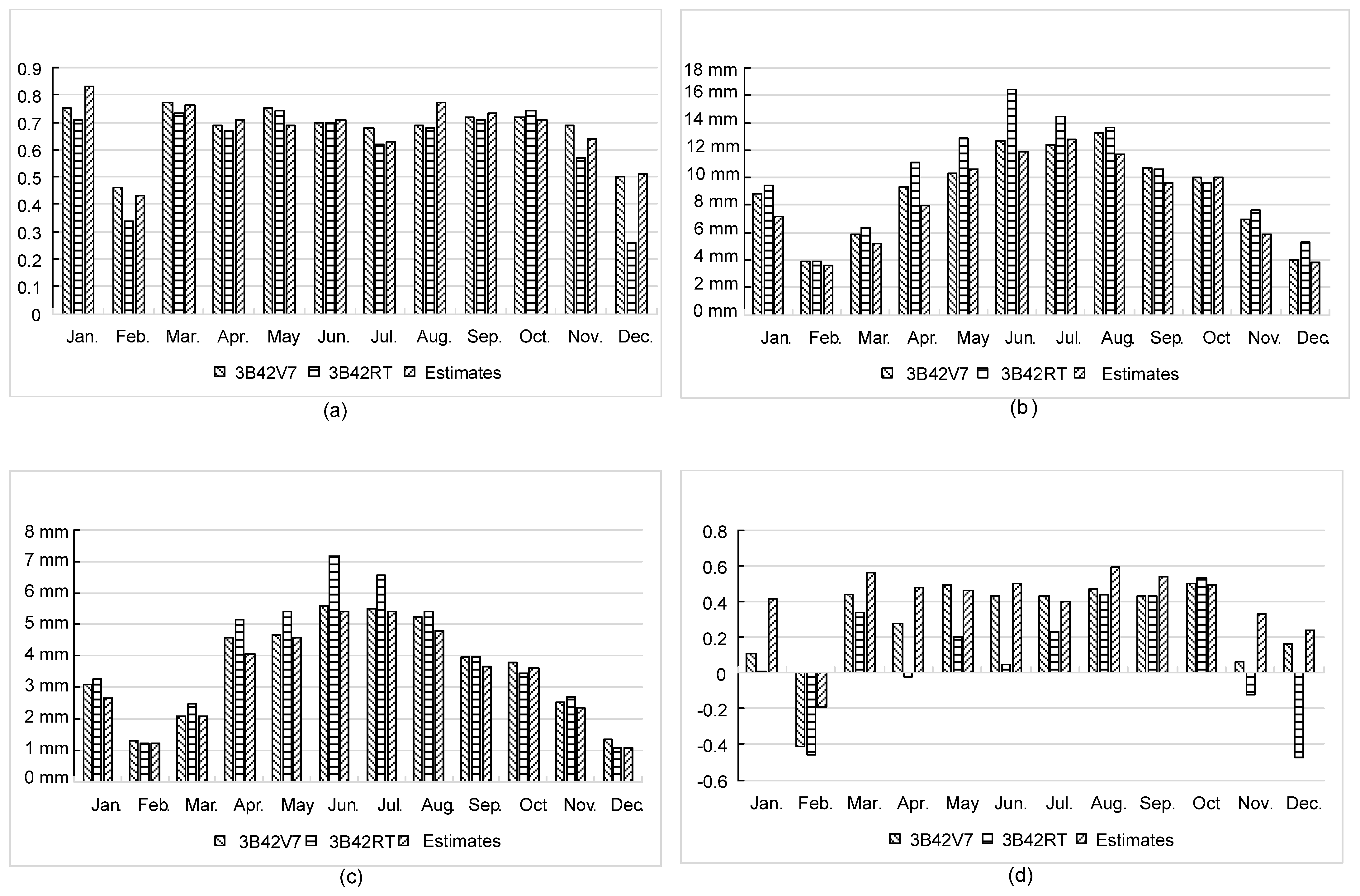
3.3. Assimilated Daily Precipitation at Monthly Scale
3.4. Assimilated Rainfall with Different Intensities
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with the Blended Rainfall Data Obtained by MLR and ANN
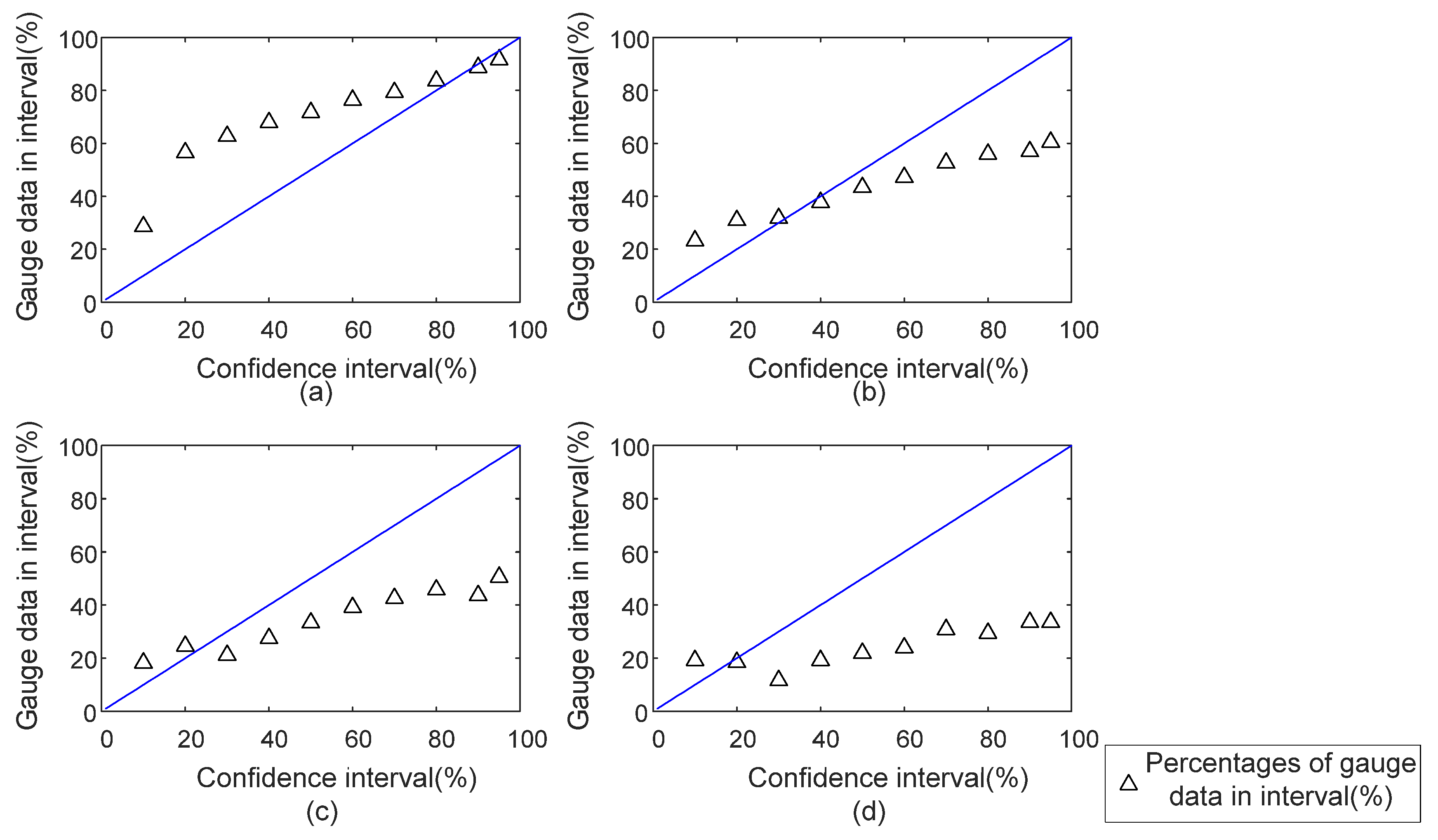
4.2. Uncertainties, Strengths and Weaknesses
5. Conclusions
- (1)
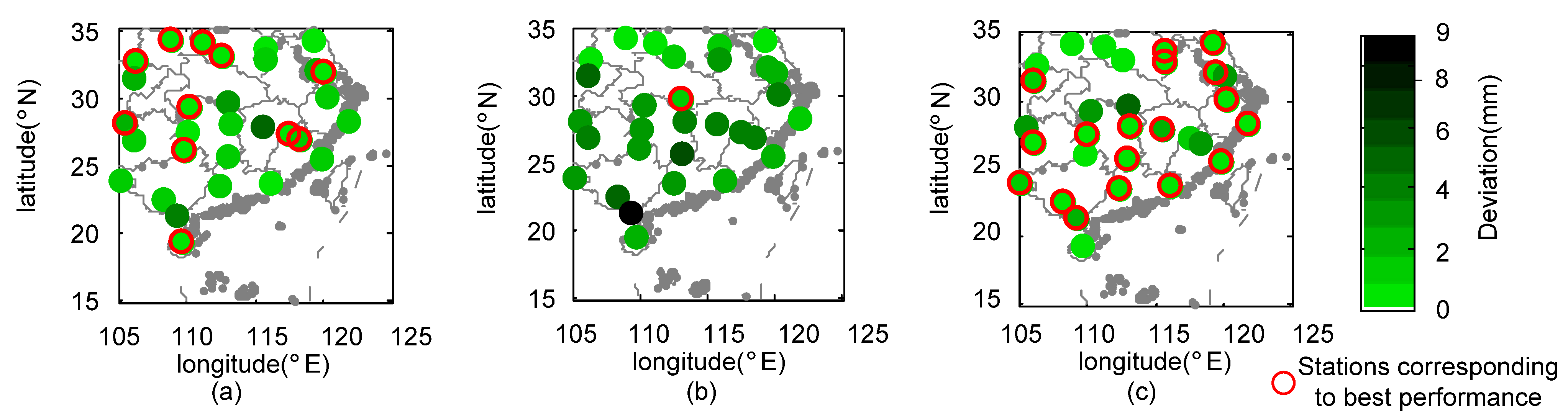
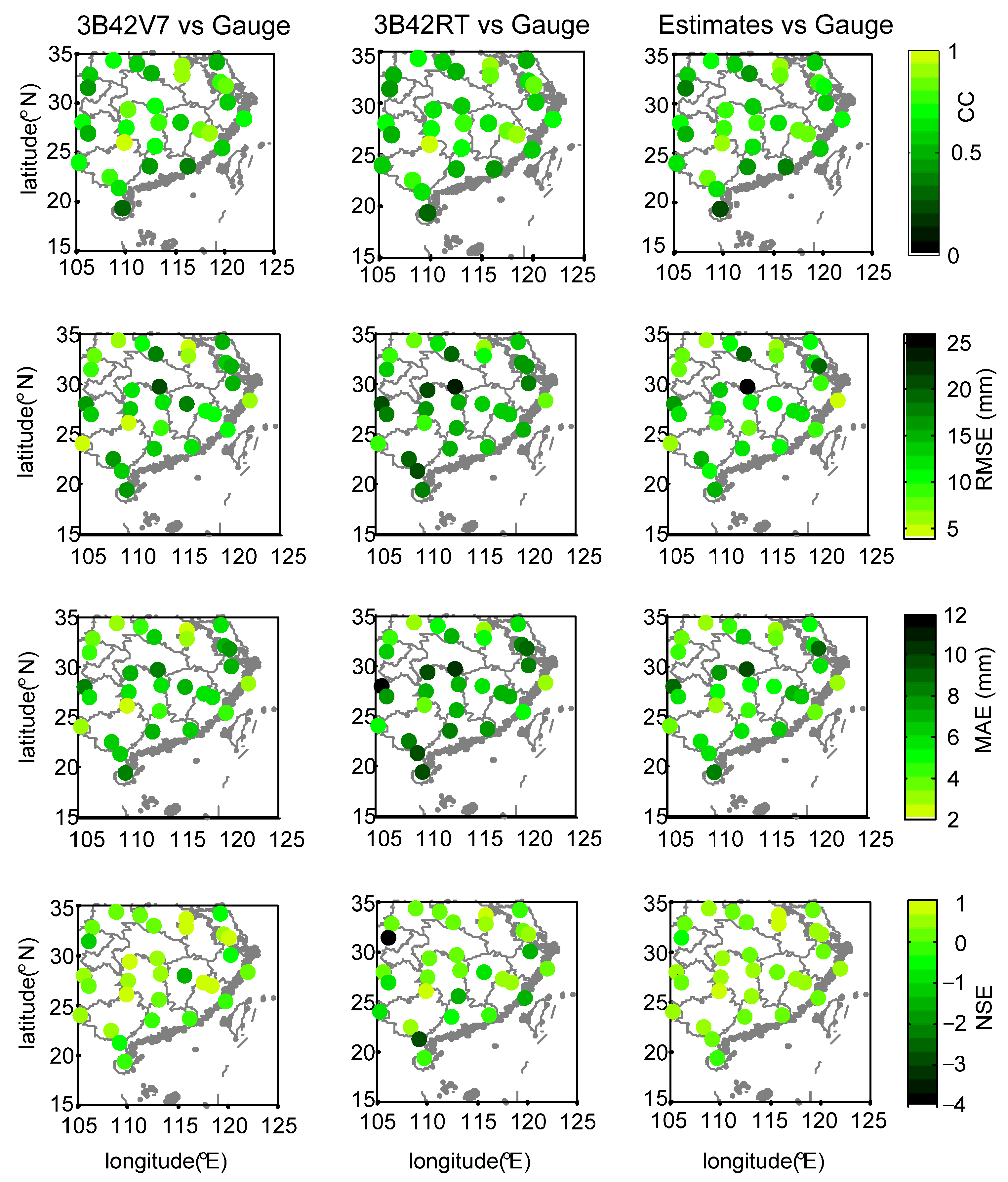
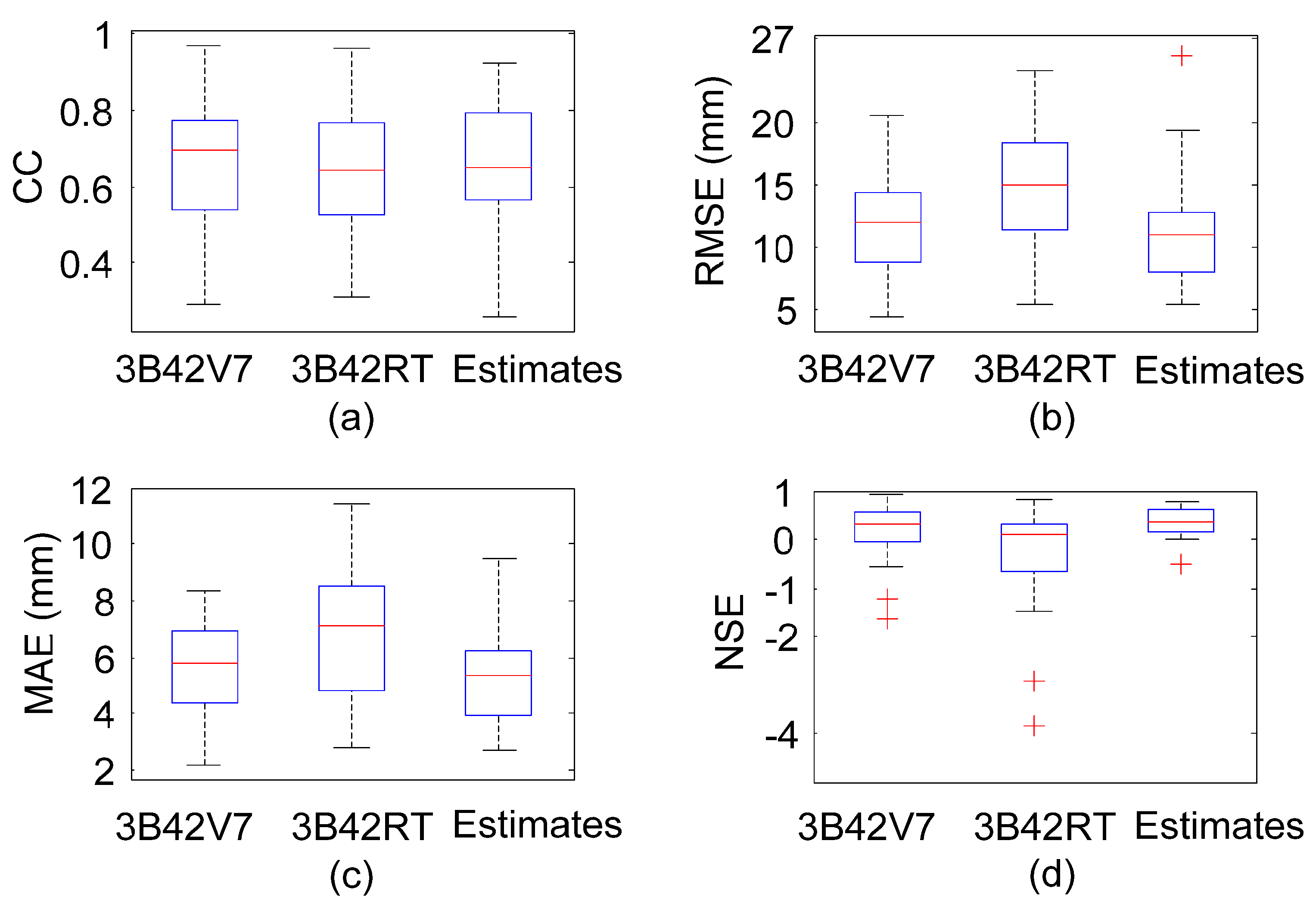
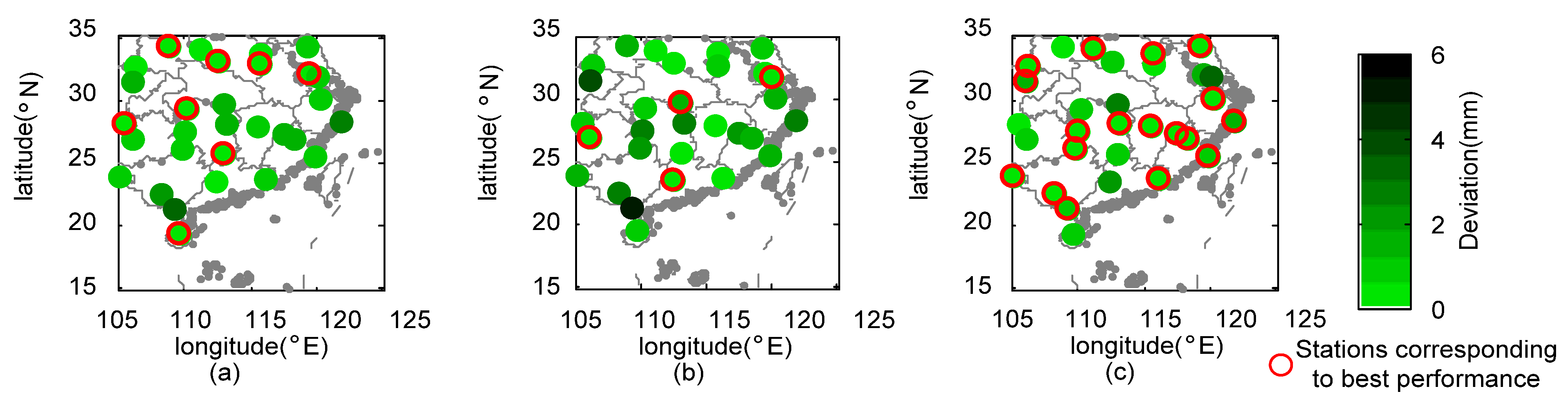
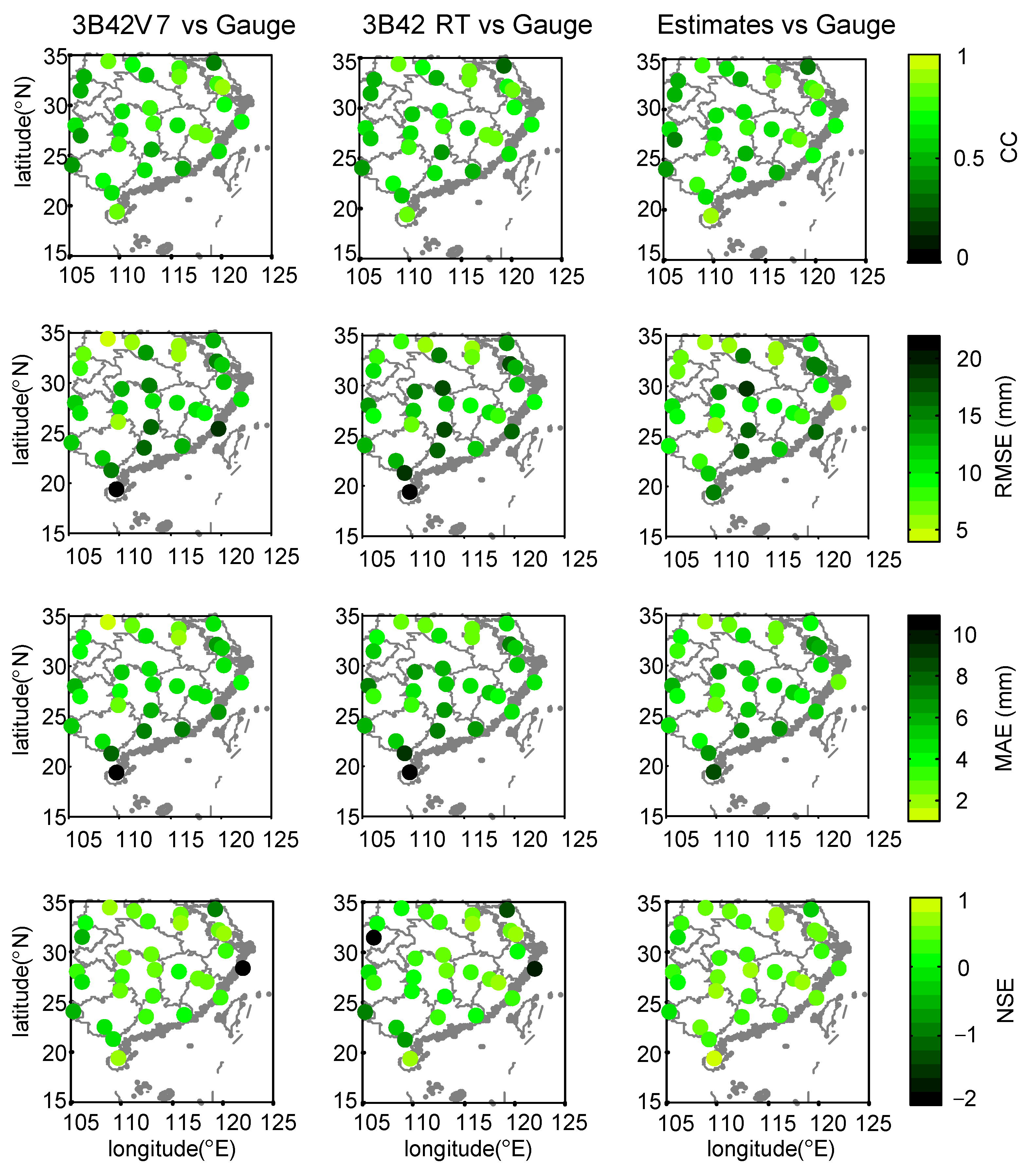
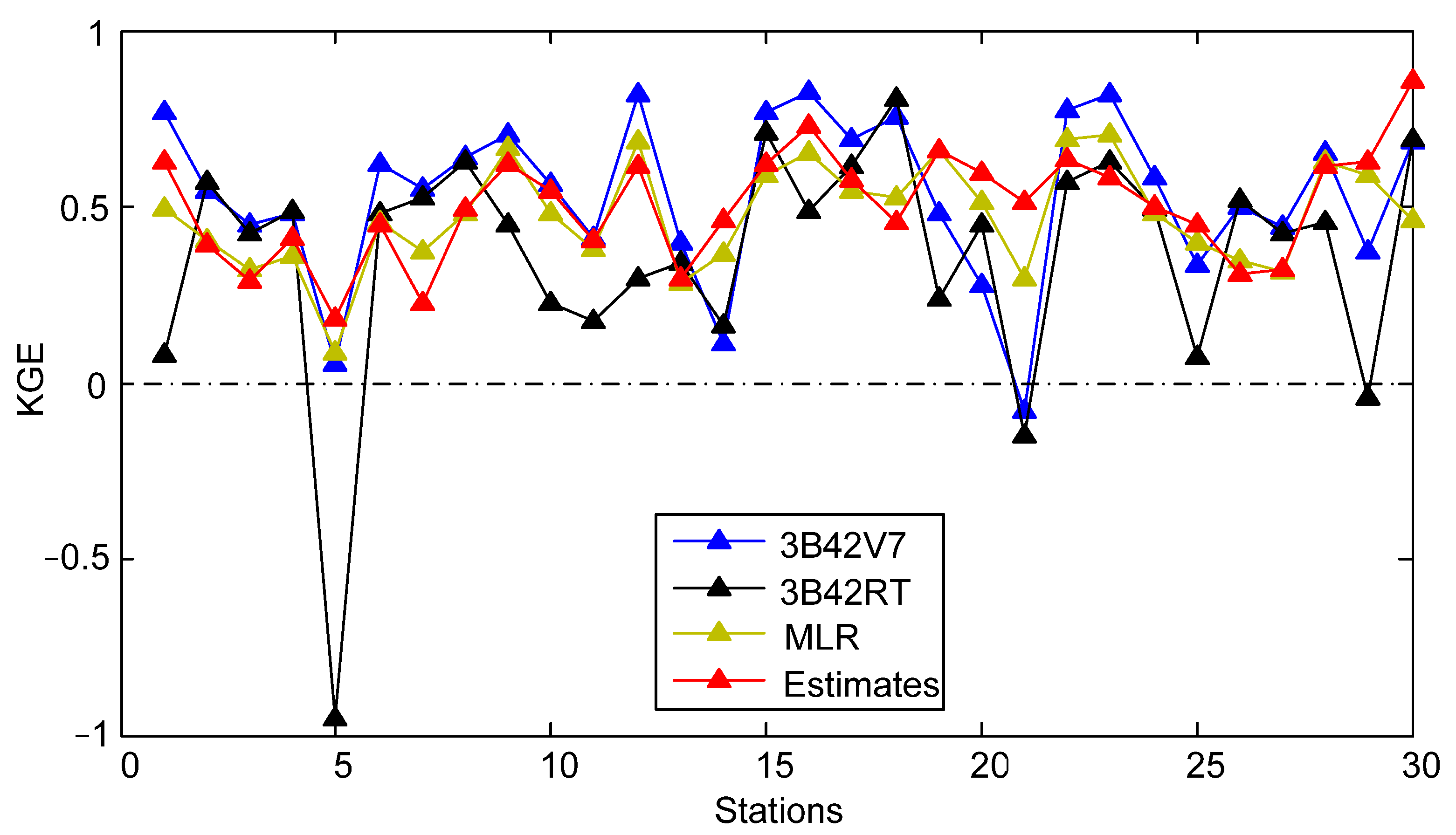
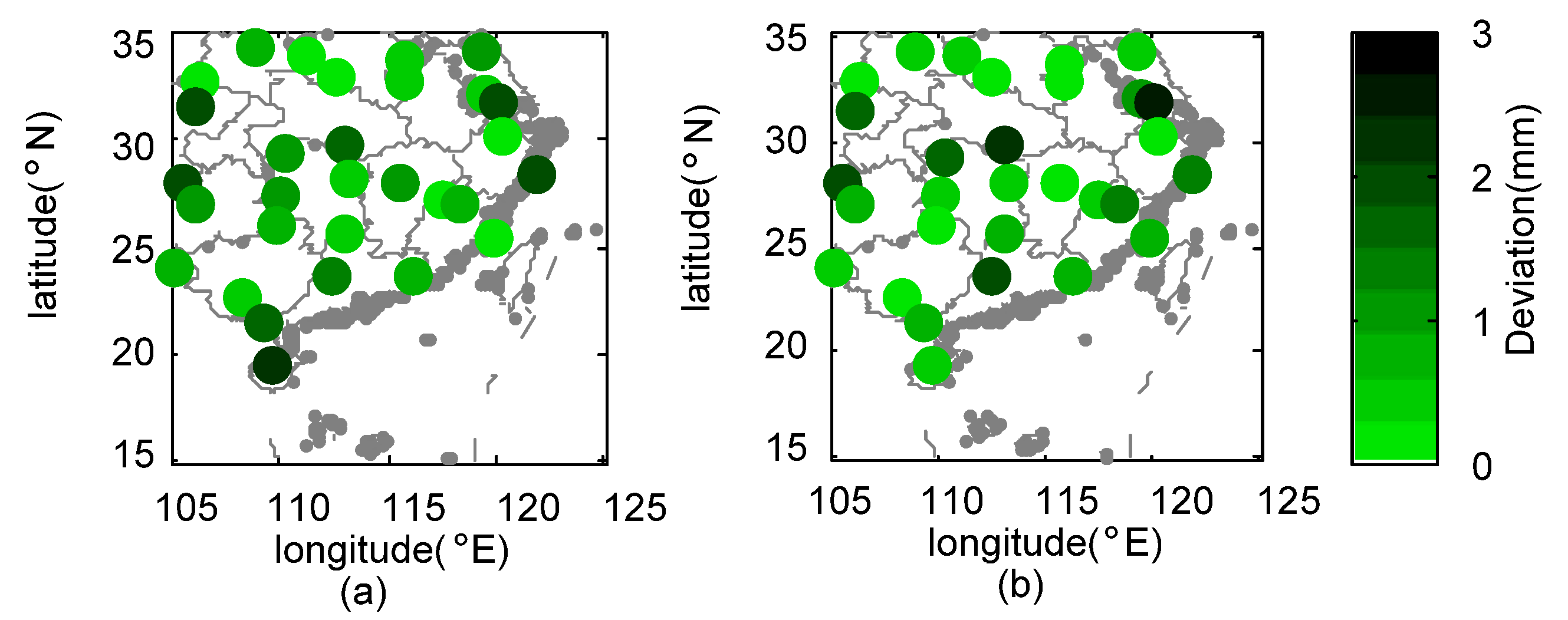
- During Meiyu season, the proposed framework in general outperformed 3B42V7 and 3B42RT on the mean value of the total absolute deviation, with a value of 1.17 mm. NGR exhibited the largest CC values at 40% of validation sites and the minimum RMSE at 19 out of 30 validation sites. For NSE, the estimates from NGR can match the gauge observations much better at 28 validation sites.
- (2)
- During Typhoon season, the total absolute deviation from NGR was smaller than those from satellite-based schemes. Except for similar CC over SEC, NGR exhibited smaller RMSE and MAE, as well as larger NSE at most of the validation sites.
- (3)
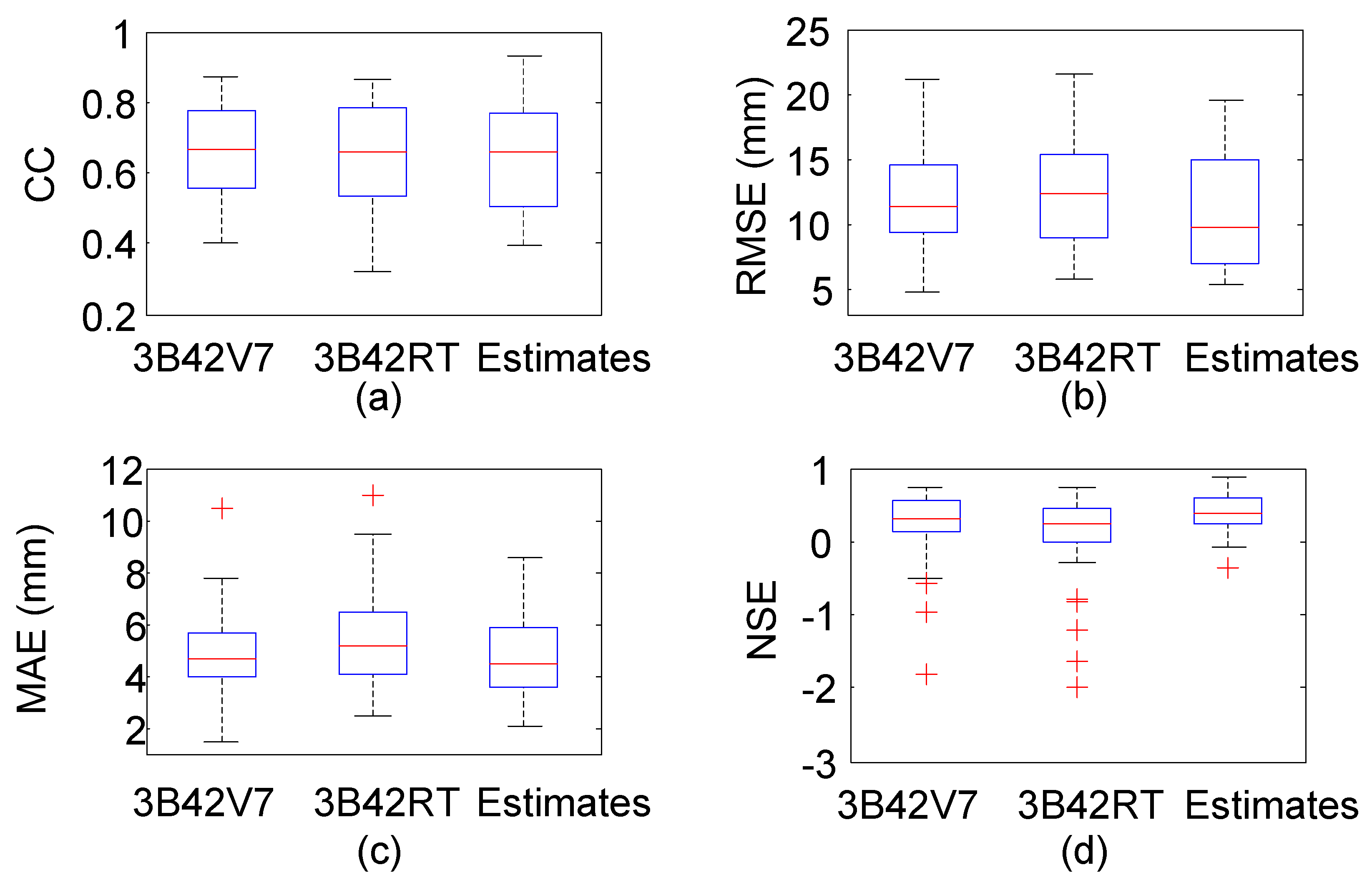
- At a monthly scale, NGR performed better on CC in 6 months, RMSE in 9 months and MAE in 10 months, as well as NSE in 9 months. Compared with 3B42V7 and 3B42RT, NGR yielded estimates with larger CC, smaller RMSE and MAE, as well as larger NSE, when the rainfall intensity was less than 50 mm/day.
- (4)
- The 3B42V7 data, in general, performed better than 3B42RT data at 30 validation sites across SEC in 2016, which contributed more to the assimilated rainfall data than those from 3B42RT. The NGR framework is capable of automatically selecting the original satellite-based dataset with better performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J. Analyzing the Water Budget and Hydrological Characteristics and Responses to Land Use in a Monsoonal Climate River Basin in South China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Long, D.; Yong, B.; Zhong, L.; Wan, W.; Hong, Y. Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M. Characterizing the spatial variations and correlations of large rainstorms for landslide study. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4573–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.M.; Cheung, R.W.M. Relationships between natural terrain landslide magnitudes and triggering rainfall based on a large landslide inventory in Hong Kong. Landslides 2018, 15, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. Evaluating Metropolitan Flood Coping Capabilities under Heavy Storms. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 05019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nakagami, K.; Takara, K.; Nover, D. Historical assessment and future sustainability challenges of Egyptian water resources management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Hydrological Variations and Their Impacts on Vegetation in Semiarid Areas from Multiple Satellite Data. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and Its Utility in Hydrologic Prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J. Long-term prediction of precipitation and hydrologic extremes with nonstationary oscillation processes. J. Geophys. Res. Athmos. 2010, 115, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.-L.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S.I. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic prediction in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Luo, P.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Huo, A.; Duan, W.; Nover, D.; He, B.; Zhao, X. Impact of temporal rainfall patterns on flash floods in Hue City, Vietnam. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, e12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Shi, X. Evaluation and hydrological application of satellite-based precipitation datasets in driving hydrological models over the Huifa river basin in Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 207, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh-Tuan, L.; Matsumoto, J.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Nodzu, M.I.; Inoue, T. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products over Central Vietnam. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. The TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) in Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 3–22. ISBN 978-90-481-2914-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S. Comparison of TMPA-3B42RT Legacy Product and the Equivalent IMERG Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W. Evaluation of TRMM 3B43 data over the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, D. Bayesian Assimilation of Multiscale Precipitation Data and Sparse Ground Gauge Observations in Mountainous Areas. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 1473–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Yang, F.; Biswas, N.K.; Rahat, S.H.; Neelam, T.J. Machine Learning-Based Error Modeling to Improve GPM IMERG Precipitation Product over the Brahmaputra River Basin. Forecast 2020, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Ma, M.; Liu, R.; Wen, Y.; Hong, Y. Can Near-Real-Time Satellite Precipitation Products Capture Rainstorms and Guide Flood Warning for the 2016 Summer in South China? IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Geographically weighted regression based methods for merging satellite and gauge precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation of satellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Y. Merging multiple satellite-based precipitation products and gauge observations using a novel double machine learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y. A two-stage blending approach for merging multiple satellite precipitation estimates and rain gauge observations: An experiment in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N. Machine Learning—Based Blending of Satellite and Reanalysis Precipitation Datasets: A Multiregional Tropical Complex Terrain Evaluation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guo, S.; Gu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.-Y. Blending multi-satellite, atmospheric reanalysis and gauge precipitation products to facilitate hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiong, L.; Ma, Q.; Kim, J.-S.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.-Y. Improving daily spatial precipitation estimates by merging gauge observation with multiple satellite-based precipitation products based on the geographically weighted ridge regression method. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metered, H.; Bonello, P.; Oyadiji, S. Nonparametric Identification Modeling of Magnetorheological Damper Using Chebyshev Polynomials Fits. SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars Mech. Syst. 2009, 2, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuok, S.C.; Yuen, K.V. Broad learning for nonparametric spatial modeling with application to seismic attenuation. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Huang, L.-S. Goodness-of-Fit Tests for Parametric Regression Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2001, 96, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.L. Bayesian Nonparametric Modeling for Causal Inference. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2011, 20, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Barella-Ortiz, A. A nonparametric statistical technique for combining global precipitation datasets: Development and hydrological evaluation over the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1371–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yao, Y.; Long, D.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, R. Performance of Optimally Merged Multisatellite Precipitation Products Using the Dynamic Bayesian Model Averaging Scheme Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 814–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsoukas, C.; Islam, S.; Kothari, R. Fusion of radar and rain gage measurements for an accurate estimation of rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31437–31450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, T. Mapping Areal Precipitation with Fusion Data by ANN Machine Learning in Sparse Gauged Region. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, Y.; Temimi, M.; Adler, R.F. Enhancing Precipitation Estimates Through the Fusion of Weather Radar, Satellite Retrievals, and Surface Parameters. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, K.-V.; Ortiz, G.A. Bayesian Nonparametric General Regression. Int. J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2016, 6, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Yiou, P. Simulation of regional climate change under the IPCC A2 scenario in southeast China. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Shi, Y.; Song, R.; Giorgi, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D. Reduction of future monsoon precipitation over China: Comparison between a high resolution RCM simulation and the driving GCM. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 100, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Han, W.; Jiang, B.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y. Infectious Diseases and Tropical Cyclones in Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J. Investigating the effects of point source and nonpoint source pollution on the water quality of the East River (Dongjiang) in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 32, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Scheffran, J.; Qin, H.; You, Q. Climate-related flood risks and urban responses in the Pearl River Delta, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Niu, R. Similarities and differences of summer persistent heavy rainfall and atmospheric circulation characteristics in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River between 2016 and 1998. Torrential Rain Disasters 2019, 38, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mu, D.; Xue, H.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Dang-Dinh, K.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Schladow, G. Flood inundation assessment for the Hanoi Central Area, Vietnam under historical and extreme rainfall conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham Stewart, A.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. GWR and Spatial Autocorrelation in Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 103–124. ISBN 0-471-49616-2. [Google Scholar]
- Giarno, G.; Hadi, M.P.; Suprayogi, S.; Murti, S.H. Suitable Proportion Sample of Holdout Validation for Spatial Rainfall Interpolation in Surrounding the Makassar Strait. Forum Geogr. 2020, 33, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian Model Averaging to Calibrate Forecast Ensembles. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Technical note: Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash-Sutcliffe and Kling-Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda-Gonzalez, M.; Poulin, A.; Romero-Lopez, R.; Arsenault, R.; Brissette, F.; Chaumont, D.; Paquin, D. Impacts of Regional Climate Model Spatial Resolution on Summer Flood Simulation. EPiC Ser. Eng. 2018, 3, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.C.; Arheimer, B.; Traoré, F.; Gustafsson, D.; Ali, A. Process refinements improve a hydrological model concept applied to the Niger River basin. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4540–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S. Simple Linear Regression in Applied Linear Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 19–33. ISBN 0-471-66379-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Li, X. Evaluation of IMERG and TRMM 3B43 Monthly Precipitation Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Yang, D.; Ding, Y.; Han, T.; Koike, T. A Bias-Corrected Precipitation Climatology for China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Products | Spatial/Temporal Resolution | Time Period Available | Coverage | Source of Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3B42V7 | 0.25°/3 h | January 1998 to January 2020 | 50° S to 50° N | Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) |
| 3B42RT | 0.25°/3 h | February 2000 to January 2020 | 60° S to 60° N | GSFC |
| PERSIANN | 0.25°/3 h | March 2000 to present | 60° S to 60° N | Center for Hydrometeorology and Remote Sensing (CHRS) |
| Rain gauge observation | Point/Daily | 1951 to present | China | China Meteorological Data Service Center (CMDC) |
| Products | CC | RMSE (mm) | MAE (mm) | NSE | KGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimates | 0.68 | 9.76 | 3.61 | 0.45 | 0.58 |
| 3B42V7 | 0.70 | 9.98 | 3.78 | 0.43 | 0.70 |
| 3B42RT | 0.67 | 11.38 | 4.19 | 0.25 | 0.63 |
| Statistical Metrics | Products | Number of Stations (Meiyu) | Number of Stations (Typhoon) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3B42V7 | 11 | 12 | |
| CC | 3B42RT | 7 | 6 |
| Estimates | 12 | 12 | |
| 3B42V7 | 11 | 8 | |
| RMSE | 3B42RT | 0 | 2 |
| Estimates | 19 | 20 | |
| 3B42V7 | 14 | 10 | |
| MAE | 3B42RT | 0 | 3 |
| Estimates | 16 | 17 | |
| 3B42V7 | 11 | 8 | |
| NSE | 3B42RT | 0 | 2 |
| Estimates | 19 | 20 | |
| 3B42V7 | 11 | 8 | |
| Deviation | 3B42RT | 1 | 4 |
| Estimates | 18 | 18 |
| Classification of Rainfall Intensities | Products | CC | RMSE (mm) | MAE (mm) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light rain | 3B42V7 | 0.284 | 8.75 | 4.61 | −9.86 |
| 3B42RT | 0.263 | 9.99 | 5.01 | −13.16 | |
| Estimates | 0.295 | 6.77 | 4.01 | −5.45 | |
| Moderate rain | 3B42V7 | 0.161 | 17.01 | 13.00 | −14.41 |
| 3B42RT | 0.124 | 20.27 | 14.45 | −20.90 | |
| Estimates | 0.163 | 12.63 | 10.28 | −7.49 | |
| Heavy rain | 3B42V7 | 0.148 | 24.09 | 19.79 | −11.95 |
| 3B42RT | 0.150 | 27.42 | 22.23 | –15.79 | |
| Estimates | 0.152 | 21.47 | 18.77 | −9.29 | |
| Rainstorm | 3B42V7 | 0.541 | 44.88 | 34.89 | −0.33 |
| 3B42RT | 0.501 | 47.05 | 37.38 | −0.46 | |
| Estimates | 0.600 | 53.11 | 43.88 | −0.86 |
| Products | CC | RMSE (mm) | MAE (mm) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimates | 0.715 | 11.54 | 4.83 | 0.51 |
| MLR | 0.701 | 11.79 | 4.76 | 0.49 |
| 3B42V7 | 0.700 | 12.31 | 5.08 | 0.44 |
| 3B42RT | 0.673 | 13.94 | 5.78 | 0.29 |
| PERSIANN | 0.571 | 13.73 | 5.49 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Qin, N.; Tang, Q.; Shi, H.; Gao, L. Assimilation of Multi-Source Precipitation Data over Southeast China Using a Nonparametric Framework. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061057
Zhou Y, Qin N, Tang Q, Shi H, Gao L. Assimilation of Multi-Source Precipitation Data over Southeast China Using a Nonparametric Framework. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061057
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuanyuan, Nianxiu Qin, Qiuhong Tang, Huabin Shi, and Liang Gao. 2021. "Assimilation of Multi-Source Precipitation Data over Southeast China Using a Nonparametric Framework" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061057
APA StyleZhou, Y., Qin, N., Tang, Q., Shi, H., & Gao, L. (2021). Assimilation of Multi-Source Precipitation Data over Southeast China Using a Nonparametric Framework. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061057










