Mapping China’s Electronic Power Consumption Using Points of Interest and Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
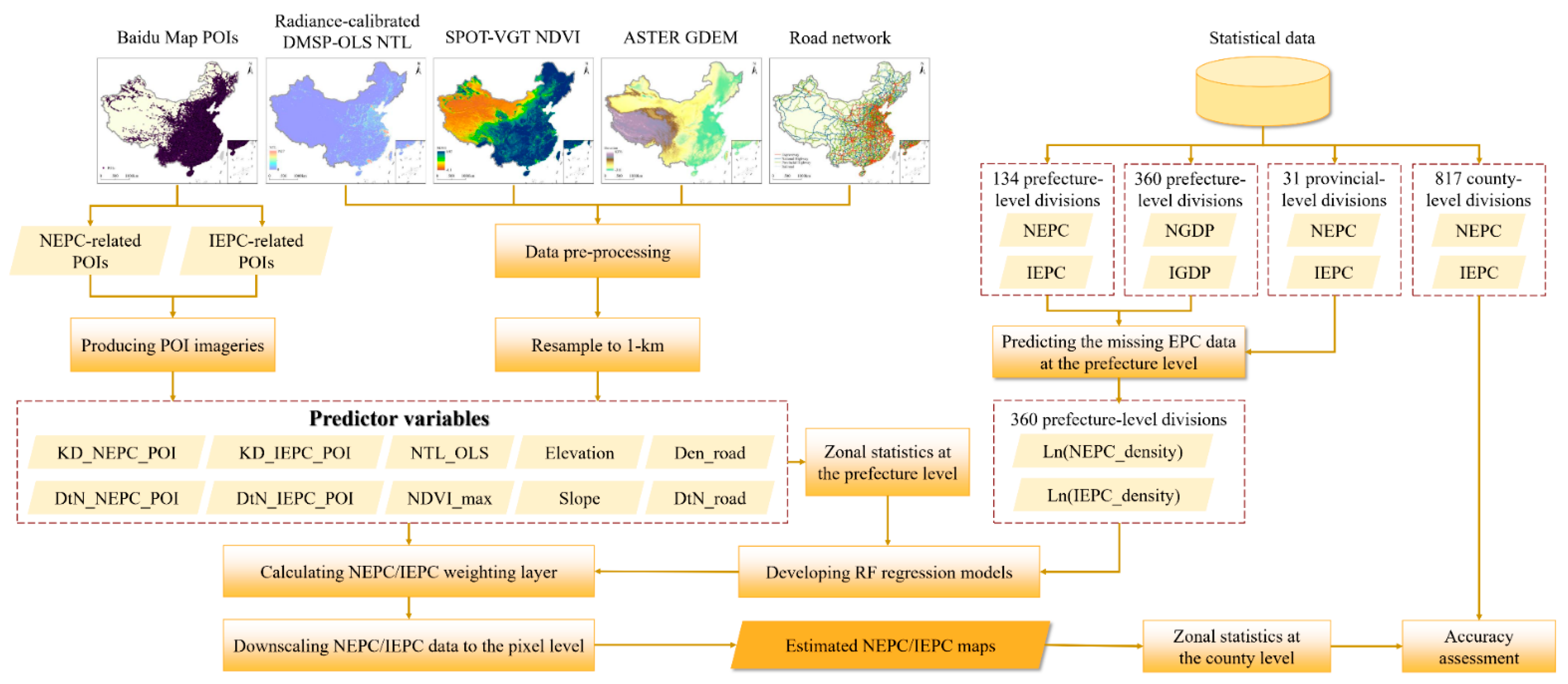
2. Data and Preprocessing
3. Methodology
3.1. Filling the Missing EPC Value at the Prefecture Level
3.2. Producing POIs Imageries
3.3. Building RF Regression Model
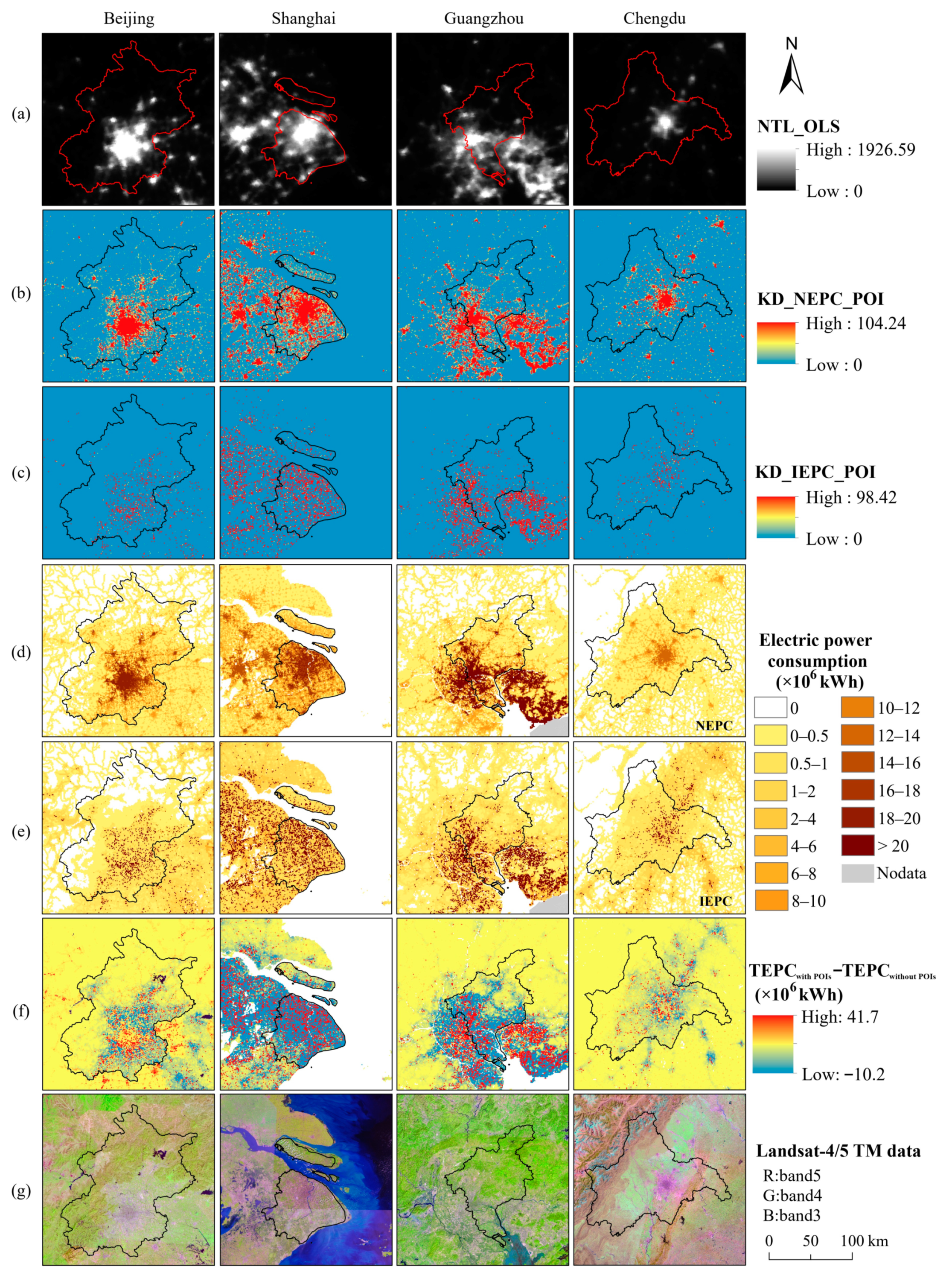
4. Results
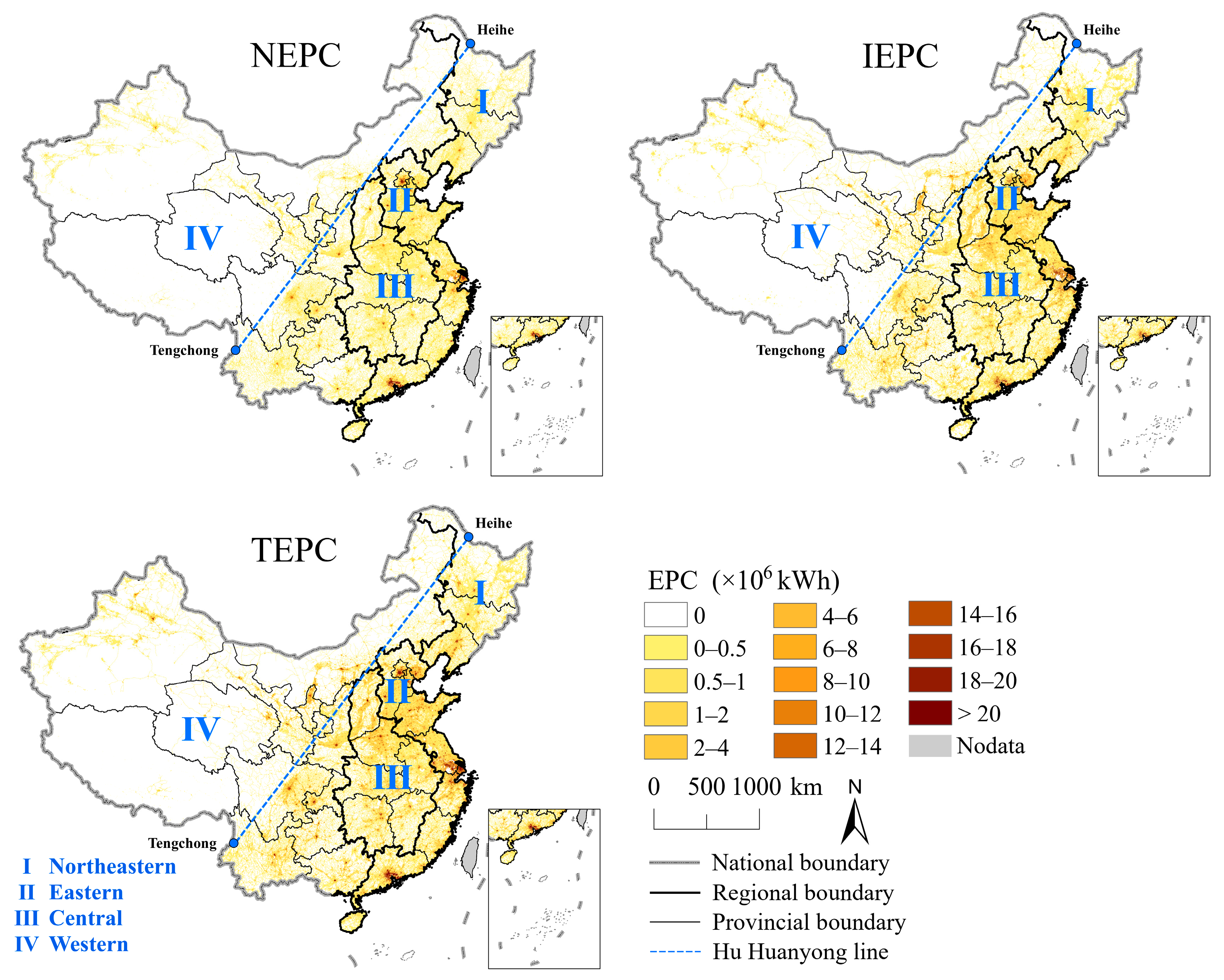
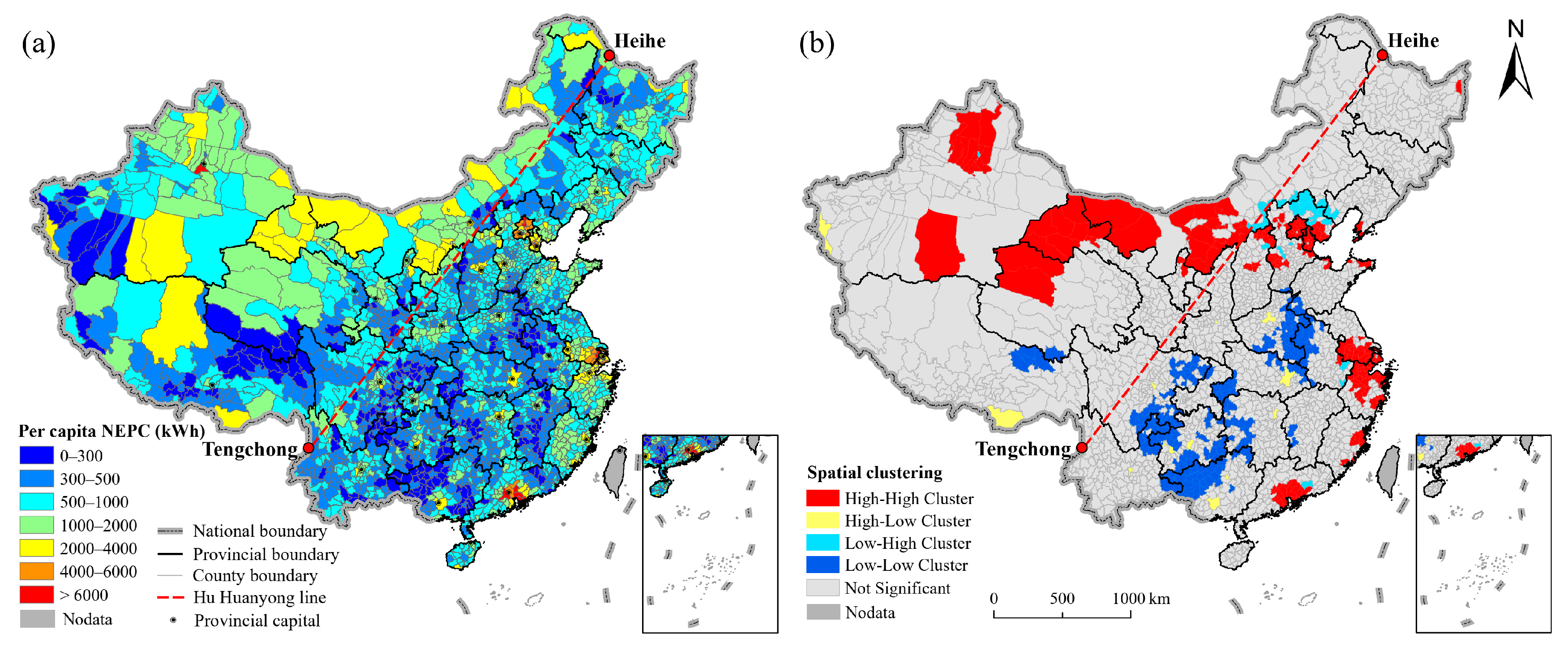
4.1. Gridded EPC Maps for Mainland China
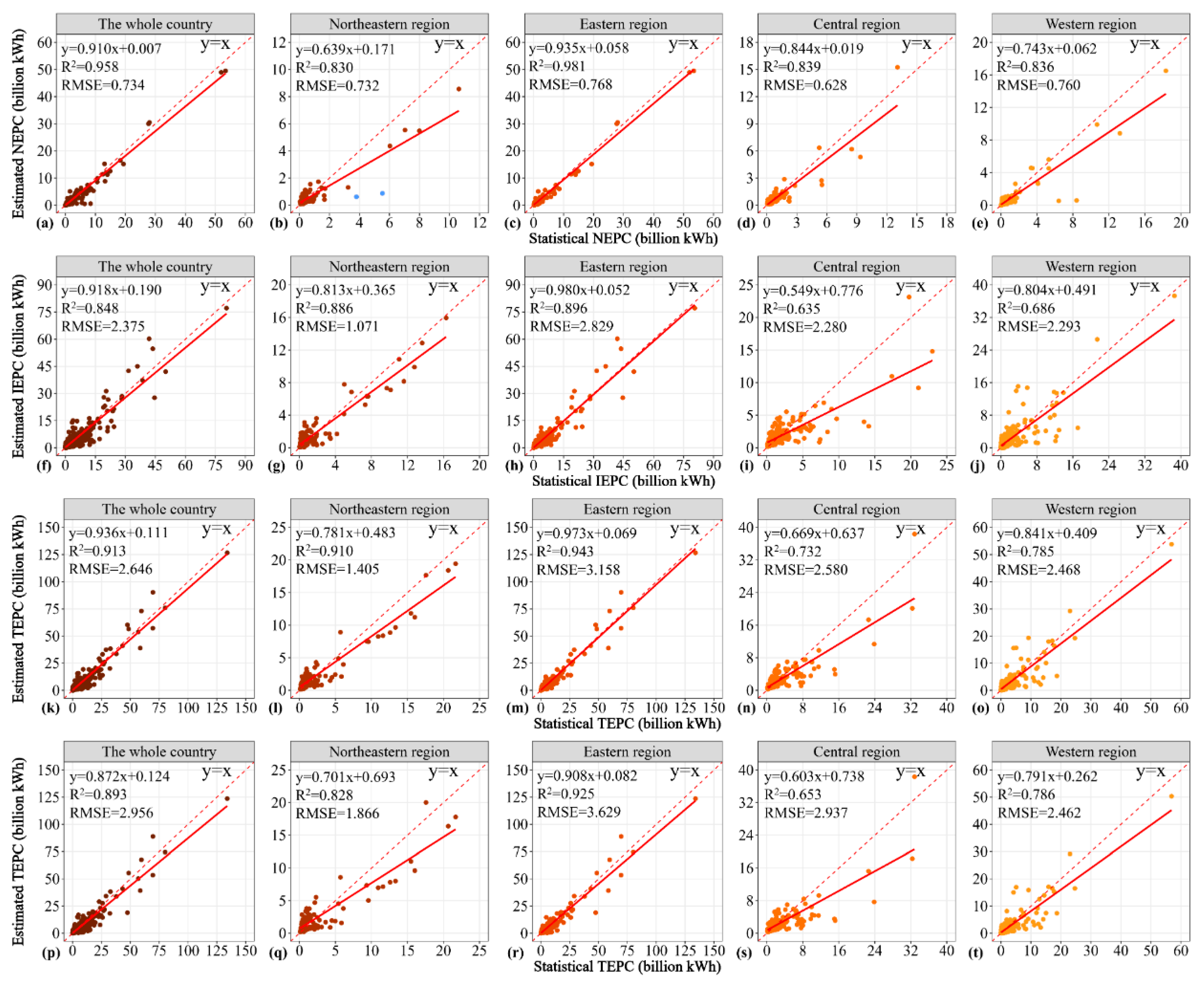
4.2. Accuracy Assessment
4.3. Variable Importance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chand, T.; Badarinath, K.; Elvidge, C.; Tuttle, B. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mulali, U.; Binti Che Sab, C.N.; Fereidouni, H.G. Exploring the bi-directional long run relationship between urbanization, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy 2012, 46, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, F. Spatialization of electricity consumption of China using saturation-corrected DMSP-OLS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in Mainland China using saturation-corrected DMSP/OLS nighttime stable light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 993–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, J. Detecting spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of electric power consumption in countries along the Belt and Road. Energy 2018, 150, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ma, Z.; Mi, Z.; Kelsey, J.; Zheng, J.; Yin, W.; Yan, M. Spatio-temporal simulation of energy consumption in China’s provinces based on satellite night-time light data. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Detecting urban-scale dynamics of electricity consumption at Chinese cities using time-series DMSP-OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program-Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imageries. Energy 2016, 100, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ghosh, T.; Samson, E.L. Mapping spatio-temporal changes of Chinese electric power consumption using night-time imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 6304–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Câmara, G.; Monteiro, A.M.V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Huang, X. A novel locally adaptive method for modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption based on DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Weng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Q. An assessment of global electric power consumption using the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program-Operational Linescan System nighttime light imagery. Energy 2019, 189, 116351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Nemani, R.; Longcore, T.; Rich, C.; Safran, J.; et al. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Duke, Y. High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xin, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Xiang, W. Modeling population density based on nighttime light images and land use data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 90, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, E.C.; Seto, K.C. Characterizing urban infrastructural transitions for the Sustainable Development Goals using multi-temporal land, population, and nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111430–111441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Delahunty, T.; Zhao, N.; Cao, G. These lit areas are undeveloped: Delimiting China’s urban extents from thresholded nighttime light imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS “City Lights” Satellite Data to Map Urban Area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Electricity Consumption in China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2019, 12, 395–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.C.; Bruce, D.A. The use of night-time lights satellite imagery as a measure of Australia’s regional electricity consumption and population distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4459–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Tana, G.; Hara, M.; Nishio, F. Monitoring the electric power consumption by lighting from DMSP/OLS nighttime satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2011 IEEE International, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Nishio, F. Regional-Scale Estimation of Electric Power and Power Plant CO2 Emissions Using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Operational Linescan System Nighttime Satellite Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; To, W.; Lo, W.; Choy, Y. Modeling of electricity consumption in the Asian gaming and tourism center—Macao SAR, People’s Republic of China. Energy 2008, 33, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. World energy consumption pattern as revealed by DMSP-OLS nighttime light imagery. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z. On electricity consumption and economic growth in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ma, Q.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in Chinese Mainland from 1995 to 2008 modeled using DMSP/OLS stable nighttime lights data. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, D. Economic growth, regional disparities and energy demand in China. Energy Policy 2014, 71, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiński, T. Modeling electricity consumption using nighttime light images and artificial neural networks. Energy 2019, 179, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongal, H.; Booij, M.J. Simulation and forecasting of streamflows using machine learning models coupled with base flow separation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, A.E.; Stevens, F.R.; Huang, Z.; Nieves, J.J.; Sorichetta, A.; Lai, S.; Ye, X.; Linard, C.; Hornby, G.M.; Hay, S.I.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of population in mainland China, 1990 to 2010. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.R.; Gaughan, A.E.; Linard, C.; Tatem, A.J. Disaggregating census data for population mapping using random forests with remotely-sensed and ancillary data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Hu, K.; Yue, W.; Qi, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Improved population mapping for China using remotely sensed and points-of-interest data within a random forests model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ye, T.; Zhao, N.; Ding, M.; Ouyang, Z.; Jia, P.; Yue, W.; Yang, X. Mapping China’s regional economic activity by integrating points-of-interest and remote sensing data with random forest. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2020, 2399808320951580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Understanding the spatial organization of urban functions based on co-location patterns mining: A comparative analysis for 25 Chinese cities. Cities 2020, 97, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Janowicz, K.; Couclelis, H. Extracting urban functional regions from points of interest and human activities on location-based social networks. Trans. Gis 2017, 21, 446–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Mapping Urban Land Use by Using Landsat Images and Open Social Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Alves, A.; Rodrigues, F.; Ferreira Jr, J.; Pereira, F.C. Mining point-of-interest data from social networks for urban land use classification and disaggregation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 53, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lin, T.; Li, X.; Prishchepov, A.V. Mapping Urban Functional Zones by Integrating Very High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery and Points of Interest: A Case Study of Xiamen, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Shen, Y.; Jin, X. Mapping Block-Level Urban Areas for All Chinese Cities. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2016, 106, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Rutherford, S.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. The temperature–mortality relationship in China: An analysis from 66 Chinese communities. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakillah, M.; Liang, S.; Mobasheri, A.; Jokar Arsanjani, J.; Zipf, A. Fine-resolution population mapping using OpenStreetMap points-of-interest. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 1940–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Mai, K.; Zhang, Y. Mapping fine-scale population distributions at the building level by integrating multisource geospatial big data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1220–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X. Improving the Accuracy of Fine-Grained Population Mapping Using Population-Sensitive POIs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. The Random Forest-Based Method of Fine-Resolution Population Spatialization by Using the International Space Station Nighttime Photography and Social Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, T.; Zhao, N.; Chen, Q.; Yue, W.; Qi, J.; Zeng, B.; Jia, P. Population mapping with multisensor remote sensing images and point-of-interest data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemacher, T.; Frieling, H.; Wilhelm, J.; Heberlein, A.; Karagülle, D.; Bleich, S.; Lenz, B.; Kornhuber, J. Indicators for elevated risk factors for alcohol-withdrawal seizures: An analysis using a random forest algorithm. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Elvidge, C. DMSP-OLS Radiance Calibrated Nighttime Lights Time Series with Intercalibration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1855–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Trigg, M.A.; Ikeshima, D. Development of a global ~90 m water body map using multi-temporal Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Hu, Y. The Impact of Financial Crisis on Electricity Demand: A Case Study of North China. Energies 2016, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Liu, C. Why is electricity consumption inconsistent with economic growth in China? Energy Policy 2016, 88, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.R.; Sajjad, H.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ting, Y.; Pandey, P.C.; Rani, M.; Kumar, P. Modeling of Electric Demand for Sustainable Energy and Management in India Using Spatio-Temporal DMSP-OLS Night-Time Data. Environ. Manag. 2018, 61, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, B.P.Y.; Yao, S.; Wu, J. Spatial point analysis of road crashes in Shanghai: A GIS-based network kernel density method. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Yan, J. Kernel Density Estimation of traffic accidents in a network space. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2008, 32, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Wong, D.W.S. A Surface-Based Approach to Measuring Spatial Segregation. Geogr. Anal. 2007, 39, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorichetta, A.; Hornby, G.M.; Stevens, F.R.; Gaughan, A.E.; Linard, C.; Tatem, A.J. High-resolution gridded population datasets for Latin America and the Caribbean in 2010, 2015, and 2020. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M.J.R.n. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H. The distribution of population in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1935, 2, 33–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D. An index of inequality in China. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zheng, X.; Wei, C. Measurement of inequality using household energy consumption data in rural China. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fan, C.; Yao, W.; Huang, R.; Mostafavi, A. Exploring the emergence of influential users on social media during natural disasters. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 38, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, A.; Zhang, A. Recent development of energy supply and demand in China, and energy sector prospects through 2030. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 6745–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, L.; Liu, X.; Mao, J.; Wu, J.; Li, M. City type-oriented modeling electric power consumption in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime stable light data. Energy 2019, 189, 116040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, D.; Xiang, B. Spatiotemporal dynamics of impervious surface areas across China during the early 21st century. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Okada, S.; Yagi, H.; Moriyama, T.; Shigehara, K.; Sugimori, Y. Progress for stable artificial lights distribution extraction accuracy and estimation of electric power consumption by means of DMSP/OLS nighttime Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. Earth Sci. 2004, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The Vegetation Adjusted NTL Urban Index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschken, H.L. Global Cities Are Coastal Cities Too: Paradox in Sustainability? Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 1760–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F. Estimating the Energy Consumption with Nighttime City Light from the DMSP/OLS imagery. In Proceedings of the 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Shanghai, China, 20–22 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Samson, E.L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, G. Improving Nighttime Light Imagery With Location-Based Social Media Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wei, Y.H.D.; Pan, F. Geographical Concentration of Manufacturing Industries in China: The Importance of Spatial and Industrial Scales. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2007, 48, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, W.; Michael, D. State land policy, land markets and geographies of manufacturing: The case of Beijing, China. Land Use Policy 2014, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P.; Wei, Y.D. Suburban industrial land development in transitional China: Spatial restructuring and determinants. Cities 2018, 78, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Cao, G.; Zhang, W.; Samson, E.L. Tweets or nighttime lights: Comparison for preeminence in estimating socioeconomic factors. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Cao, G.; Zhang, W.; Samson, E.L.; Chen, Y. Remote sensing and social sensing for socioeconomic systems: A comparison study between nighttime lights and location-based social media at the 500 m spatial resolution. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 87, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shahtahmassebi, A.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K. Characterizing spatial patterns and driving forces of expansion and regeneration of industrial regions in the Hangzhou megacity, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wang, S.; Hwang, M.; Padmanabhan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Soltani, K. A scalable framework for spatiotemporal analysis of location-based social media data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 51, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Vohland, M. Downscaling land surface temperatures at regional scales with random forest regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| OB (km) | PCC | %IncMSE | Weight | %IncMSE | Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEPC-related | Airport | 2.0 | 0.682 | 5.860 | 0.050 | 4.415 | 0.035 |
| Auto service | 1.1 | 0.924 | 5.287 | 0.045 | 4.922 | 0.039 | |
| Bank | 1.0 | 0.938 | 14.887 | 0.126 | 9.122 | 0.072 | |
| Commercial building | 1.2 | 0.954 | 7.306 | 0.062 | 5.371 | 0.043 | |
| Education facility | 0.4 | 0.919 | 7.432 | 0.063 | 5.939 | 0.047 | |
| Gas station | 1.1 | 0.618 | 8.104 | 0.069 | 8.962 | 0.071 | |
| Government agency | 1.0 | 0.793 | 4.240 | 0.036 | 4.119 | 0.033 | |
| Hospital and clinic | 1.1 | 0.901 | 6.003 | 0.051 | 4.107 | 0.033 | |
| Hotel | 1.2 | 0.898 | 3.578 | 0.030 | 6.123 | 0.048 | |
| Motor passenger station | 1.2 | 0.467 | 0.963 | 0.008 | 11.606 | 0.092 | |
| Non-industrial enterprise | 0.2 | 0.794 | 1.679 | 0.014 | 8.175 | 0.065 | |
| Park | 0.6 | 0.948 | 7.125 | 0.060 | 5.438 | 0.043 | |
| Railway station | 1.4 | 0.474 | −0.070 | 0.000 | 8.828 | 0.070 | |
| Residential community | 0.6 | 0.925 | 9.230 | 0.078 | 5.683 | 0.045 | |
| Restaurant and entertainment | 0.2 | 0.941 | 6.861 | 0.058 | 8.728 | 0.069 | |
| Retail | 0.5 | 0.911 | 6.681 | 0.057 | 5.311 | 0.042 | |
| Service zone of highway | 1.1 | 0.924 | 7.863 | 0.067 | 6.685 | 0.053 | |
| Toll station | 0.5 | 0.858 | 7.329 | 0.062 | 7.993 | 0.063 | |
| Others | 0.6 | 0.928 | 7.541 | 0.064 | 4.740 | 0.038 | |
| IEPC-related | Industrial enterprise | 0.4 | 0.718 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Year for Validation | Level for Validation | Number of Samples | Validation Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE (Billion kWh) | Slope | ||||
| [3] | 2009 | City | 101 | 0.490 | 6.152 | / |
| [8] | 2010 | Urban district | 255 | 0.750 | / | 0.744 |
| With POIs | 2011 | County | 817 | 0.913 | 2.646 | 0.936 |
| Without POIs | 2011 | County | 817 | 0.893 | 2.956 | 0.872 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, N.; Ouyang, Z.; Yue, W. Mapping China’s Electronic Power Consumption Using Points of Interest and Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061058
Jin C, Zhang Y, Yang X, Zhao N, Ouyang Z, Yue W. Mapping China’s Electronic Power Consumption Using Points of Interest and Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061058
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Cheng, Yili Zhang, Xuchao Yang, Naizhuo Zhao, Zutao Ouyang, and Wenze Yue. 2021. "Mapping China’s Electronic Power Consumption Using Points of Interest and Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061058
APA StyleJin, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Zhao, N., Ouyang, Z., & Yue, W. (2021). Mapping China’s Electronic Power Consumption Using Points of Interest and Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061058








