Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Combined Effect of Aerosol and Water Vapour on Solar Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset and Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
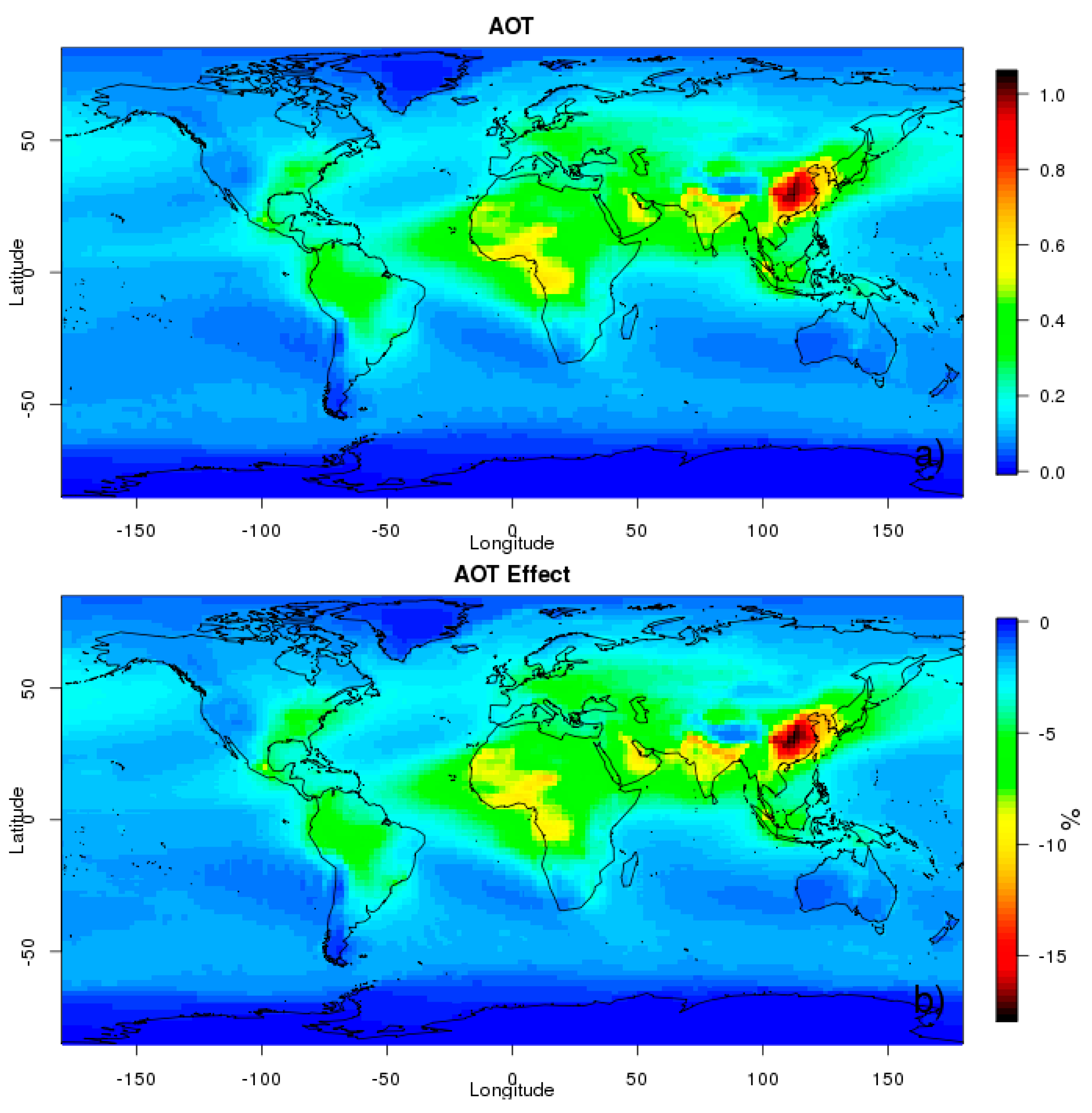
3.1. Spatial Analysis
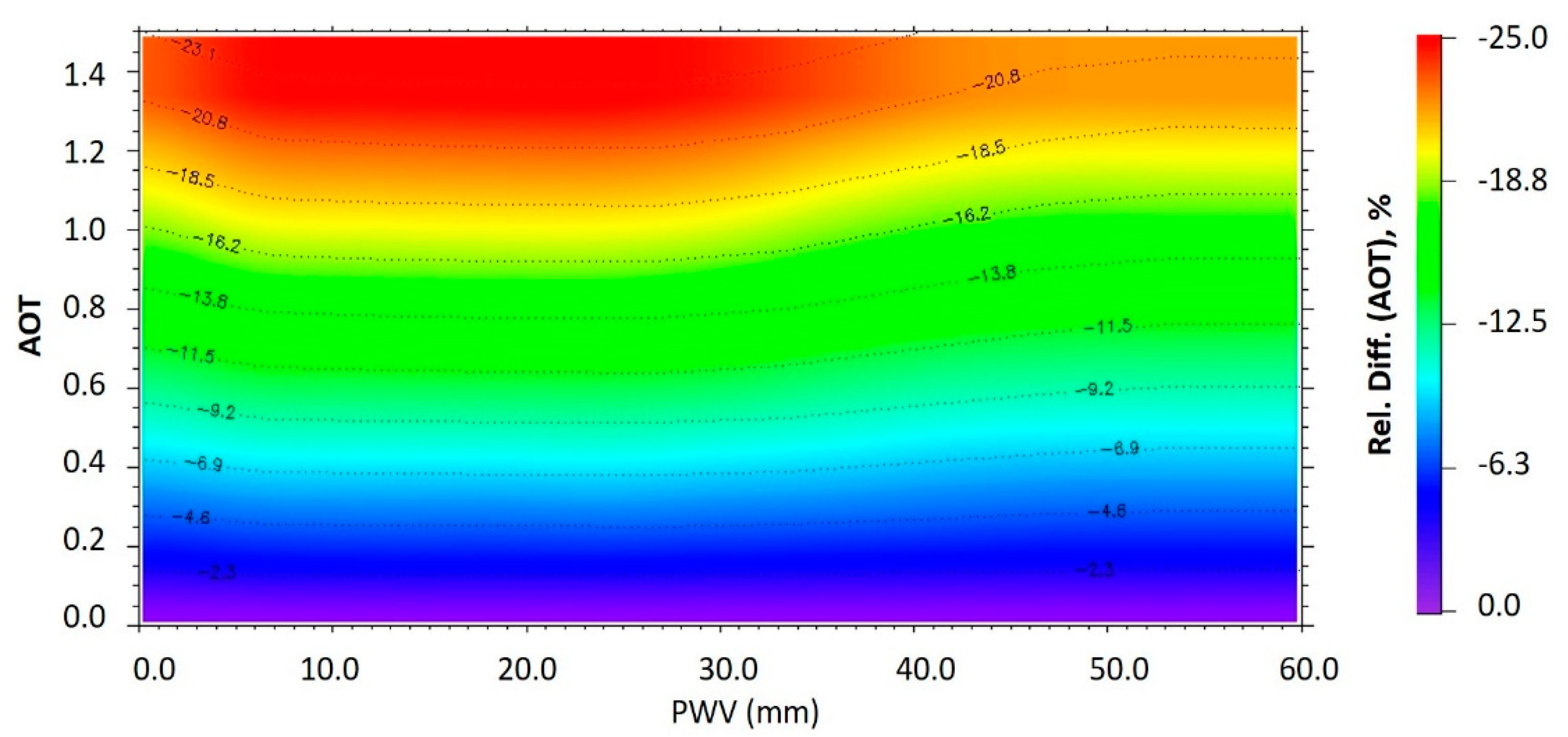
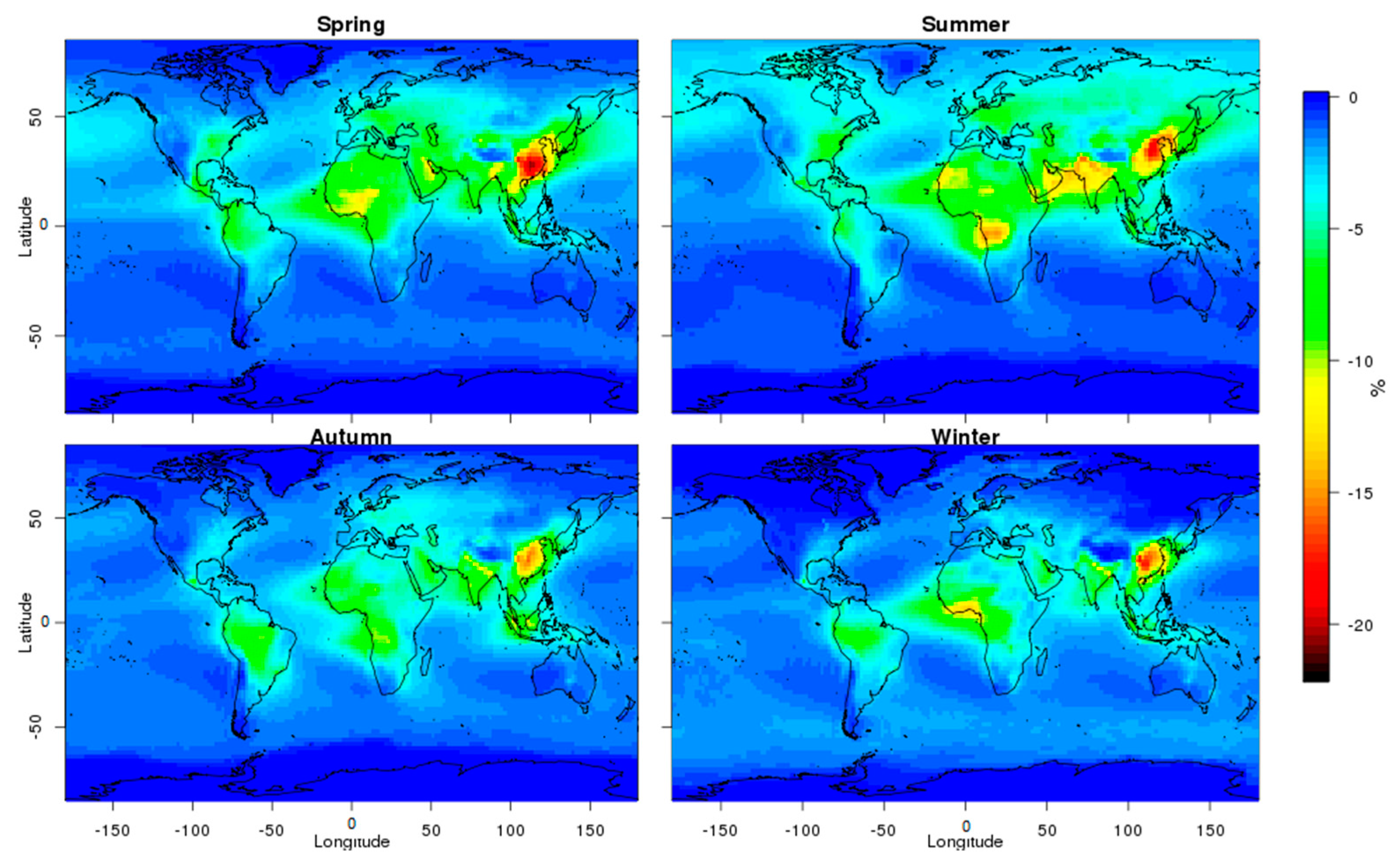
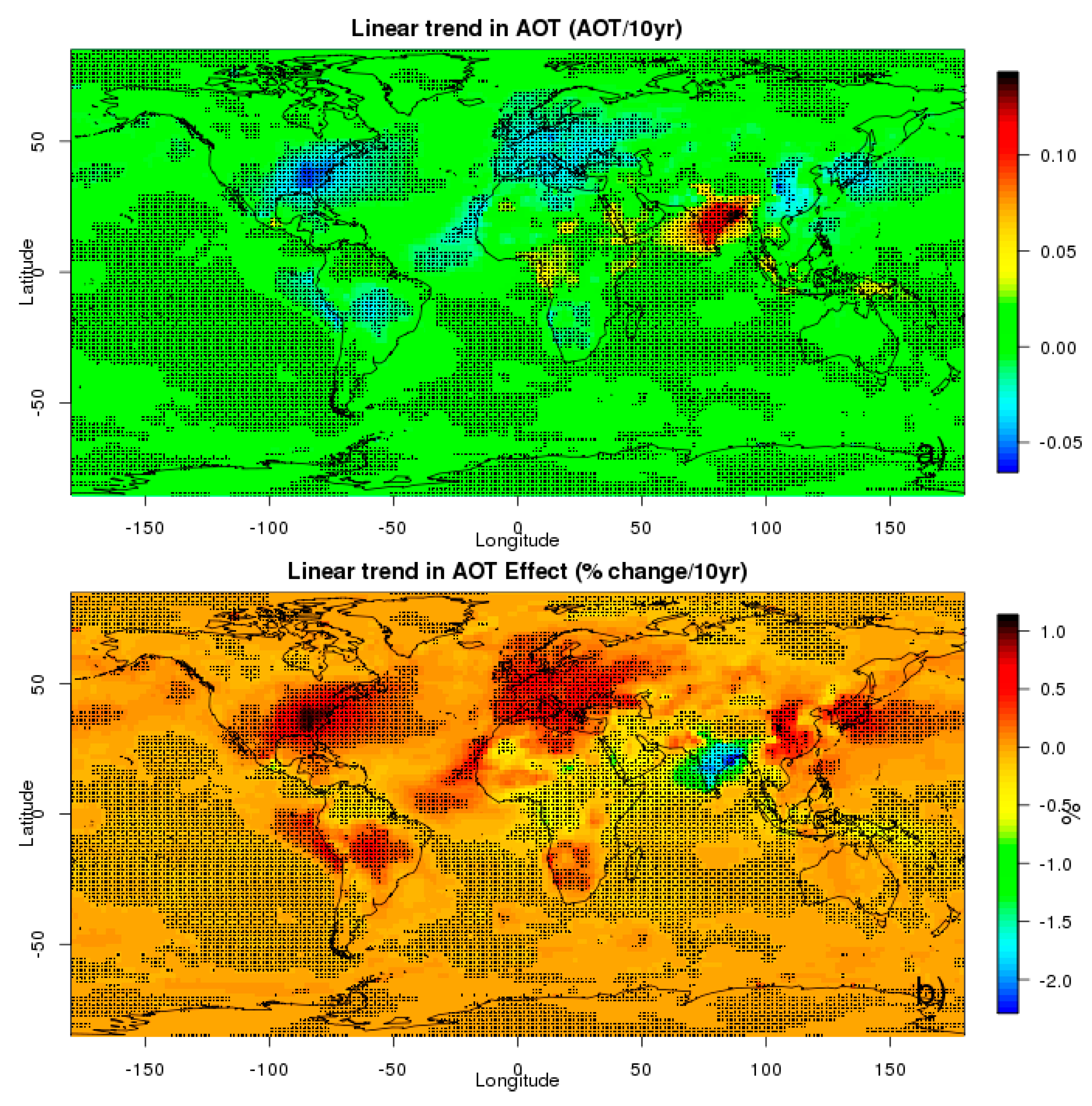
3.1.1. AOT Individual Effect
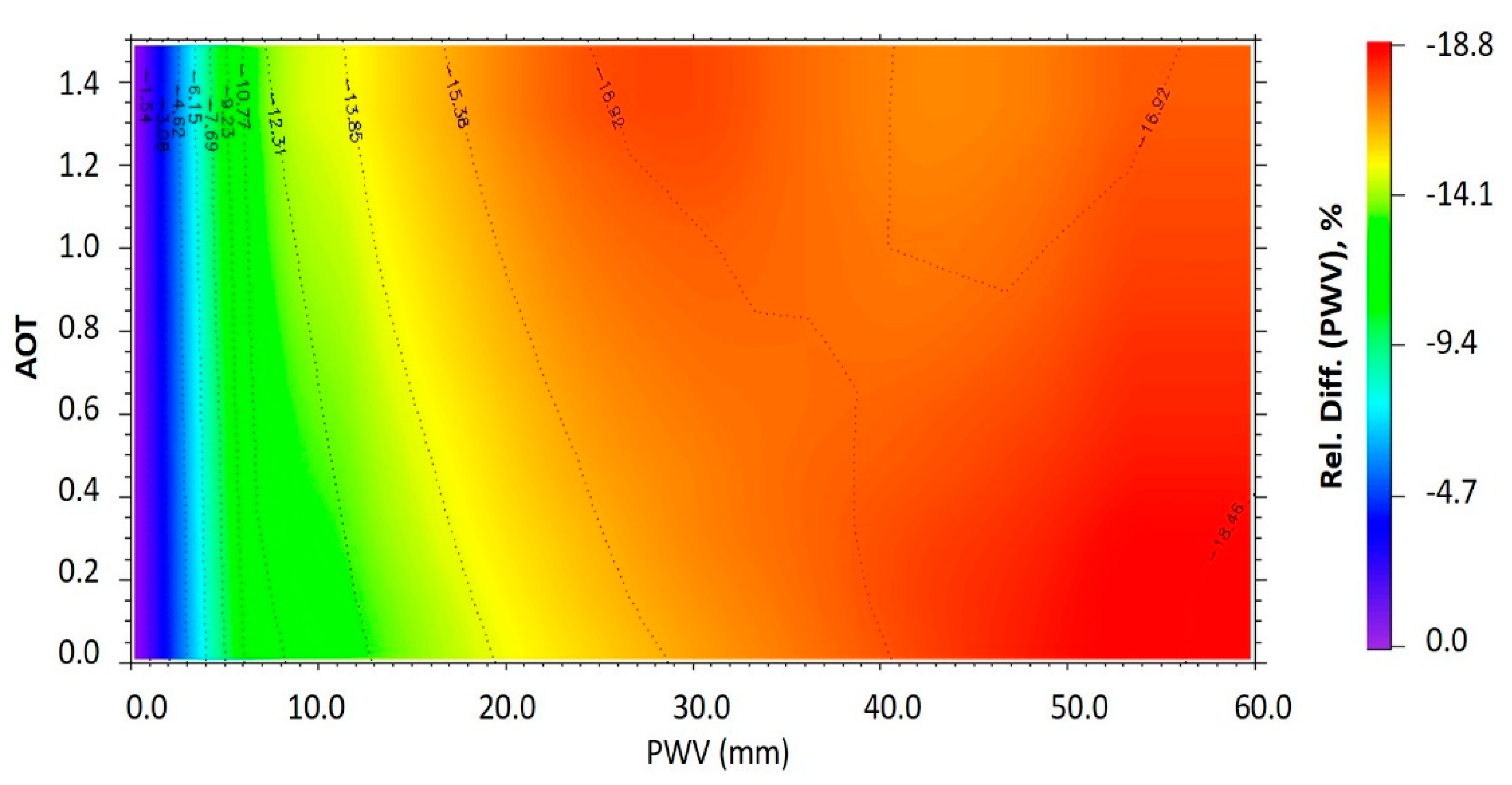
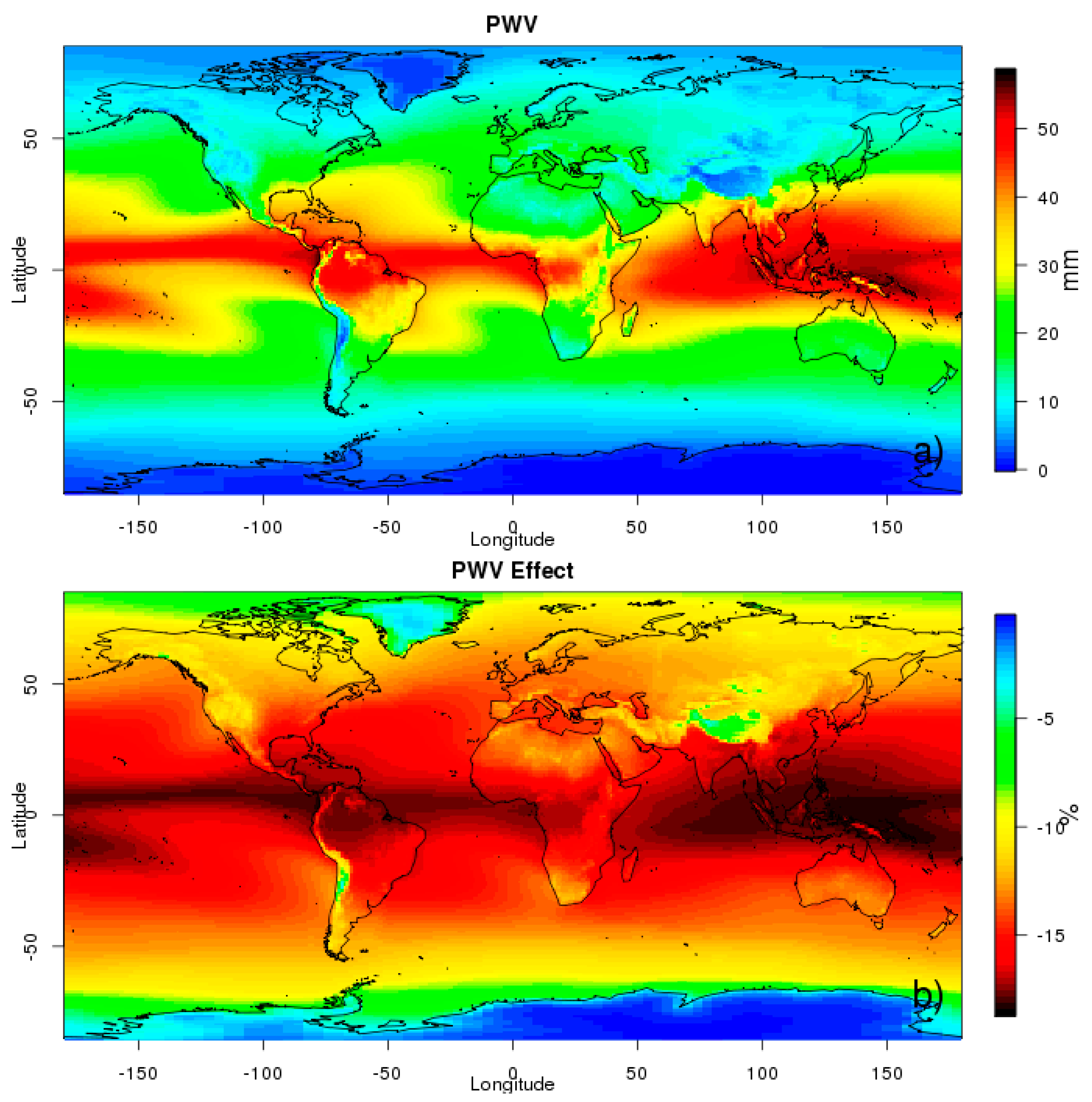
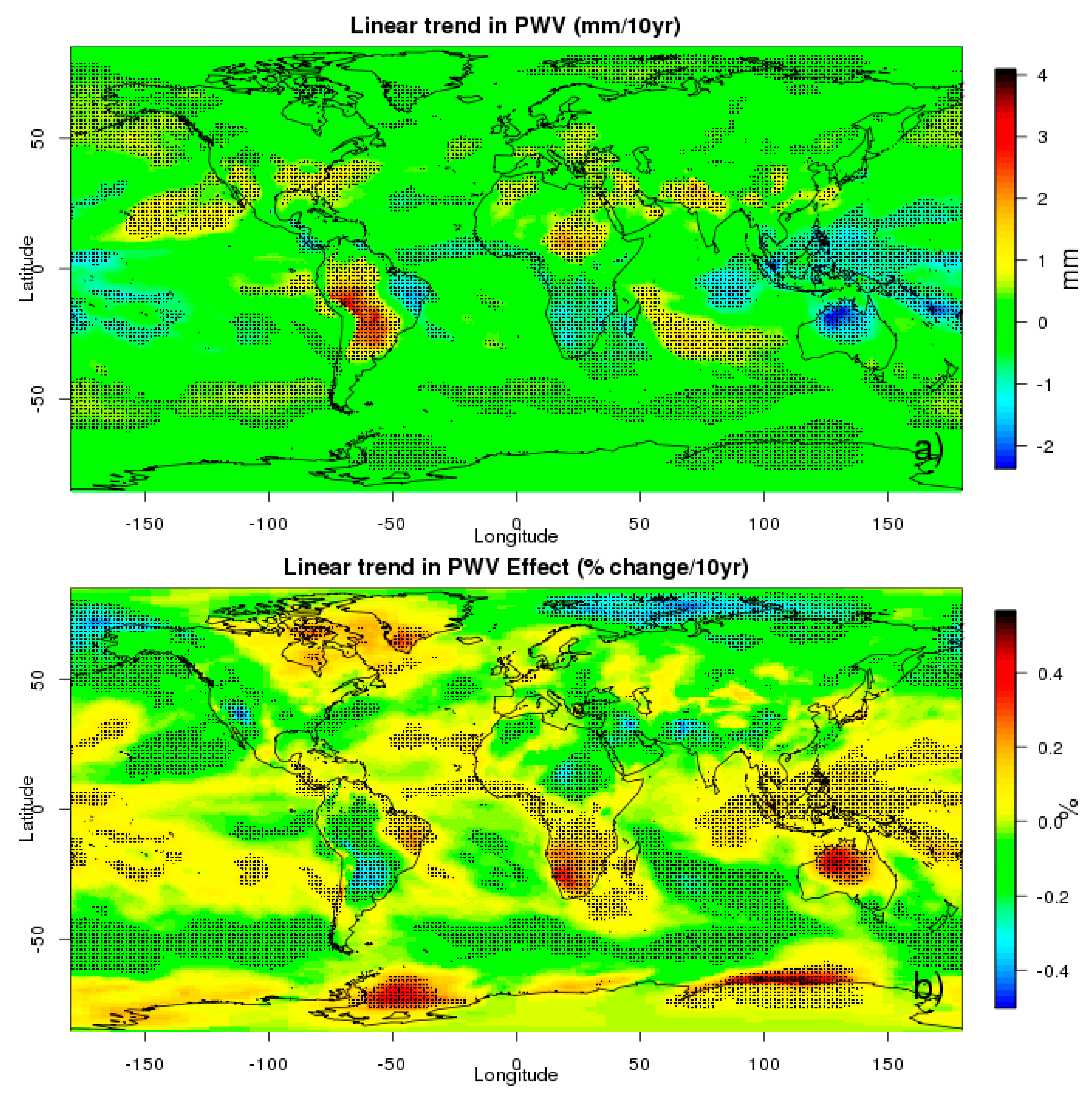
3.1.2. PWV Individual Effect
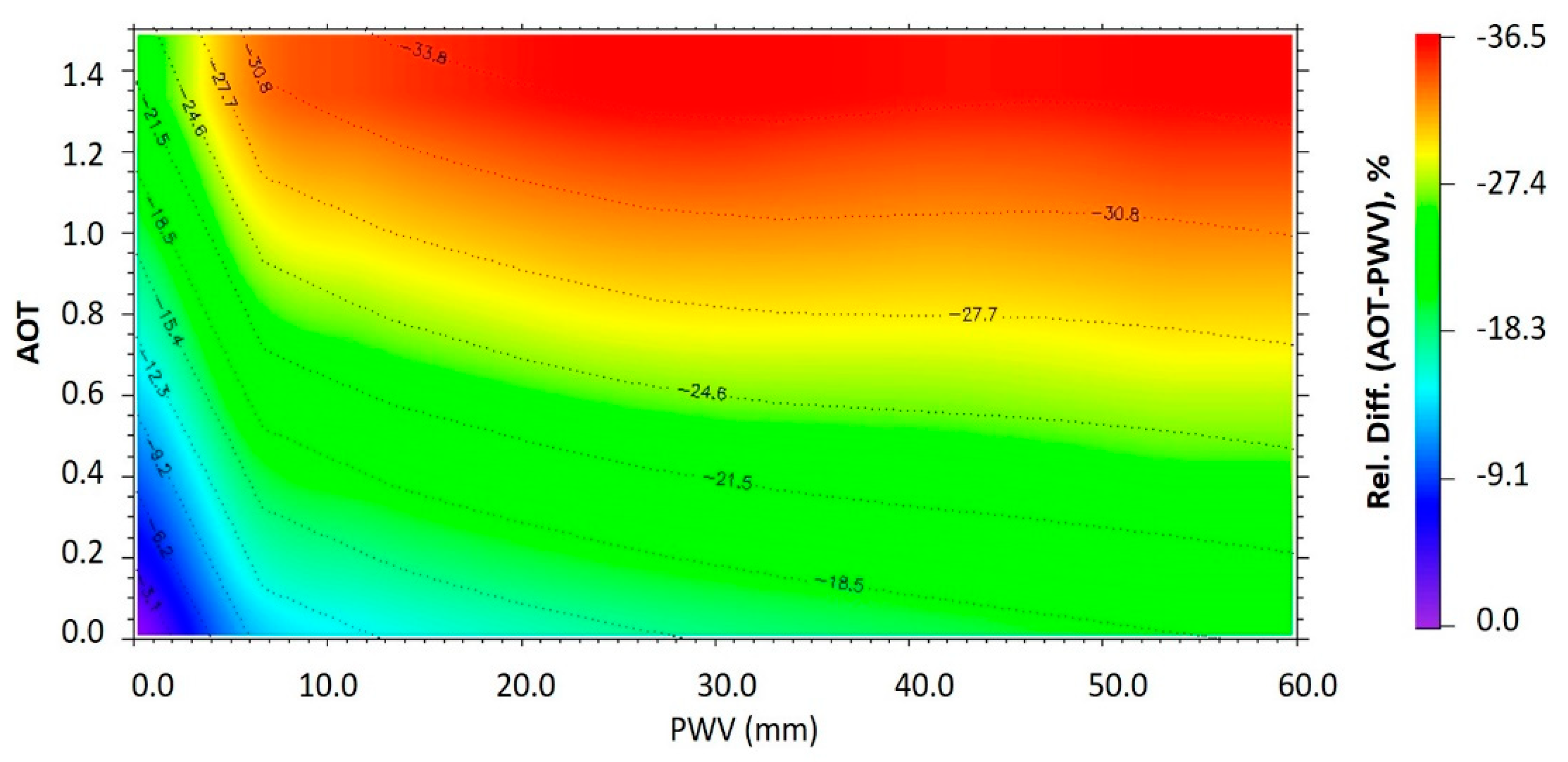
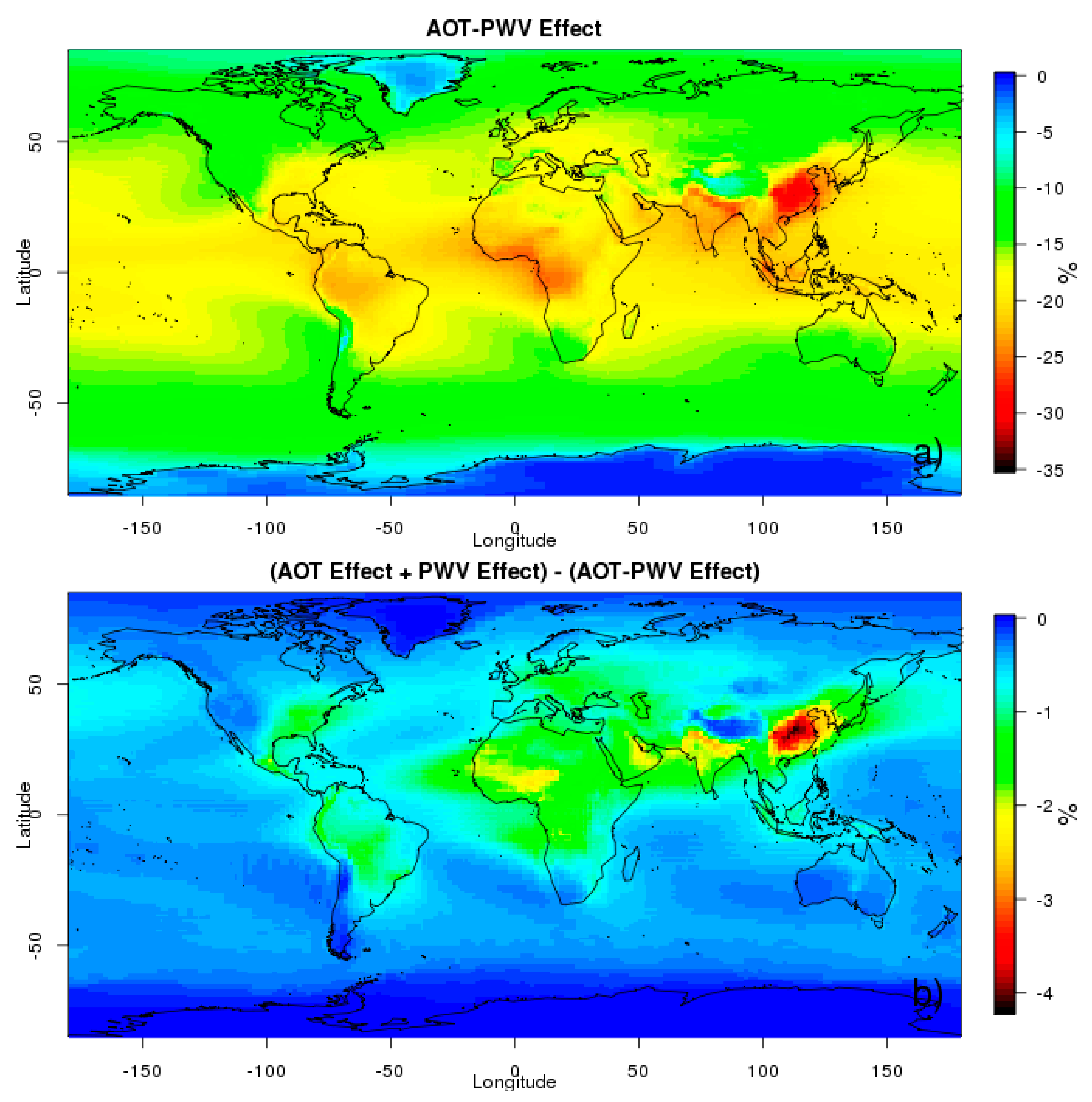
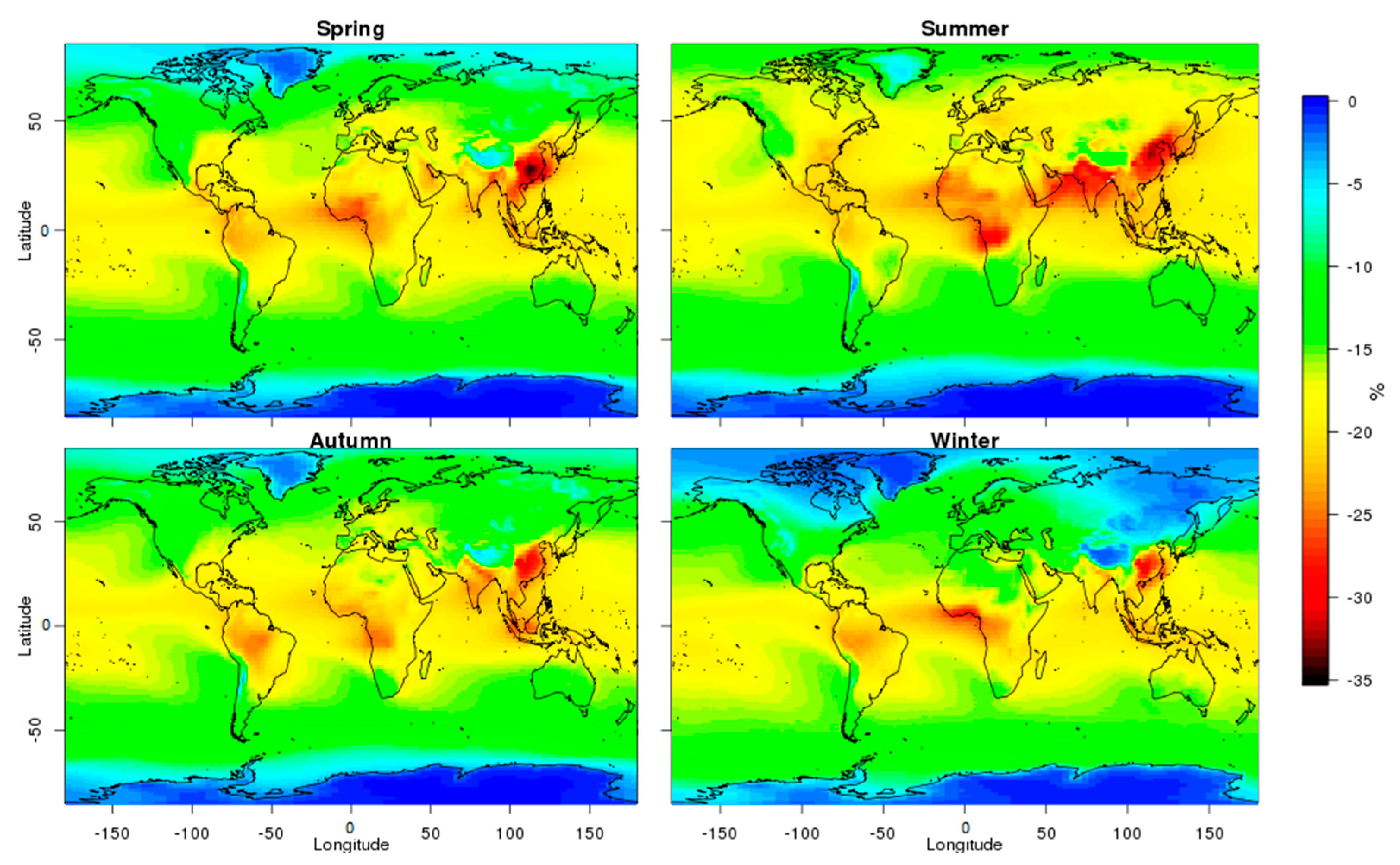
3.1.3. AOT-PWV Combined Effect
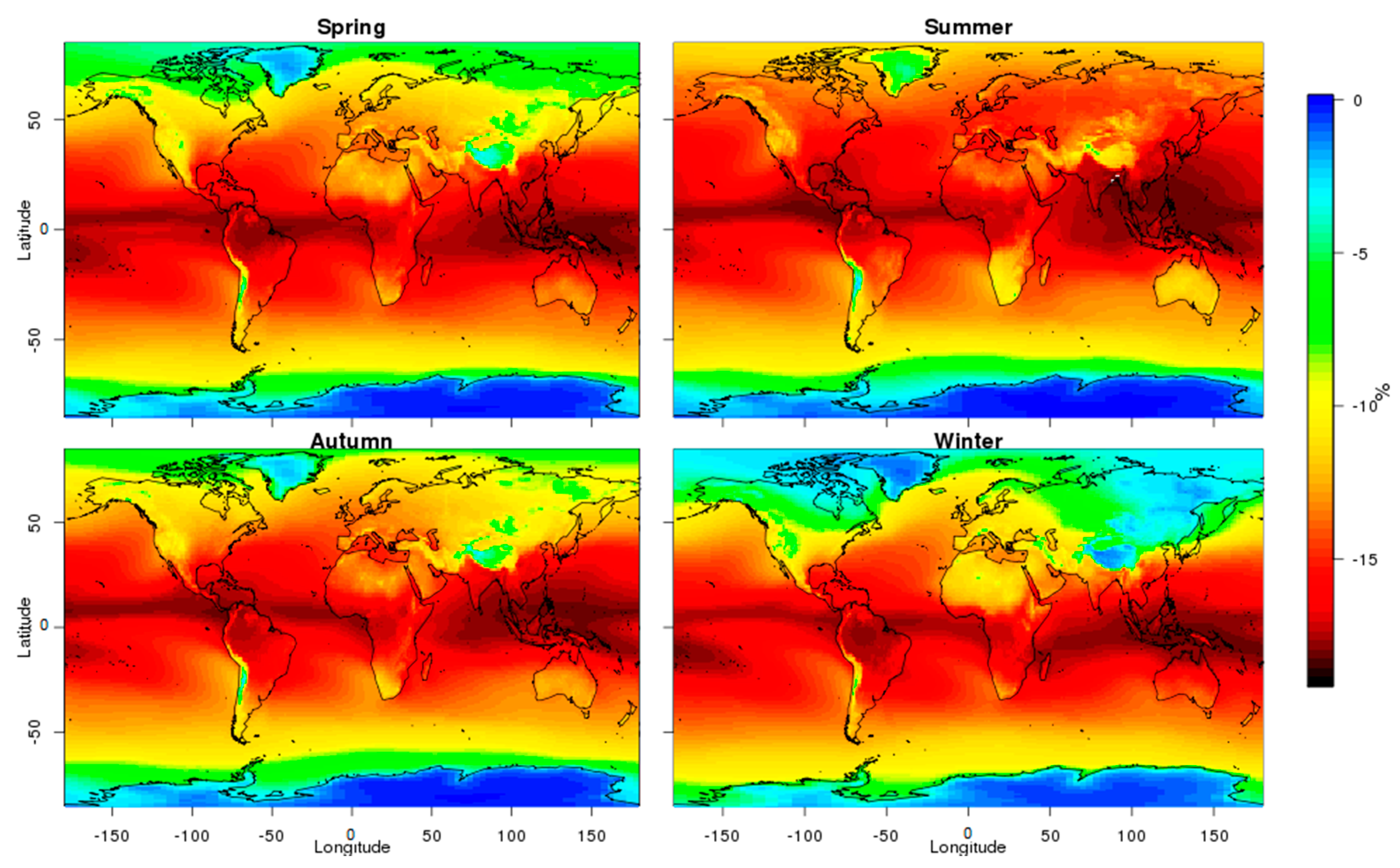
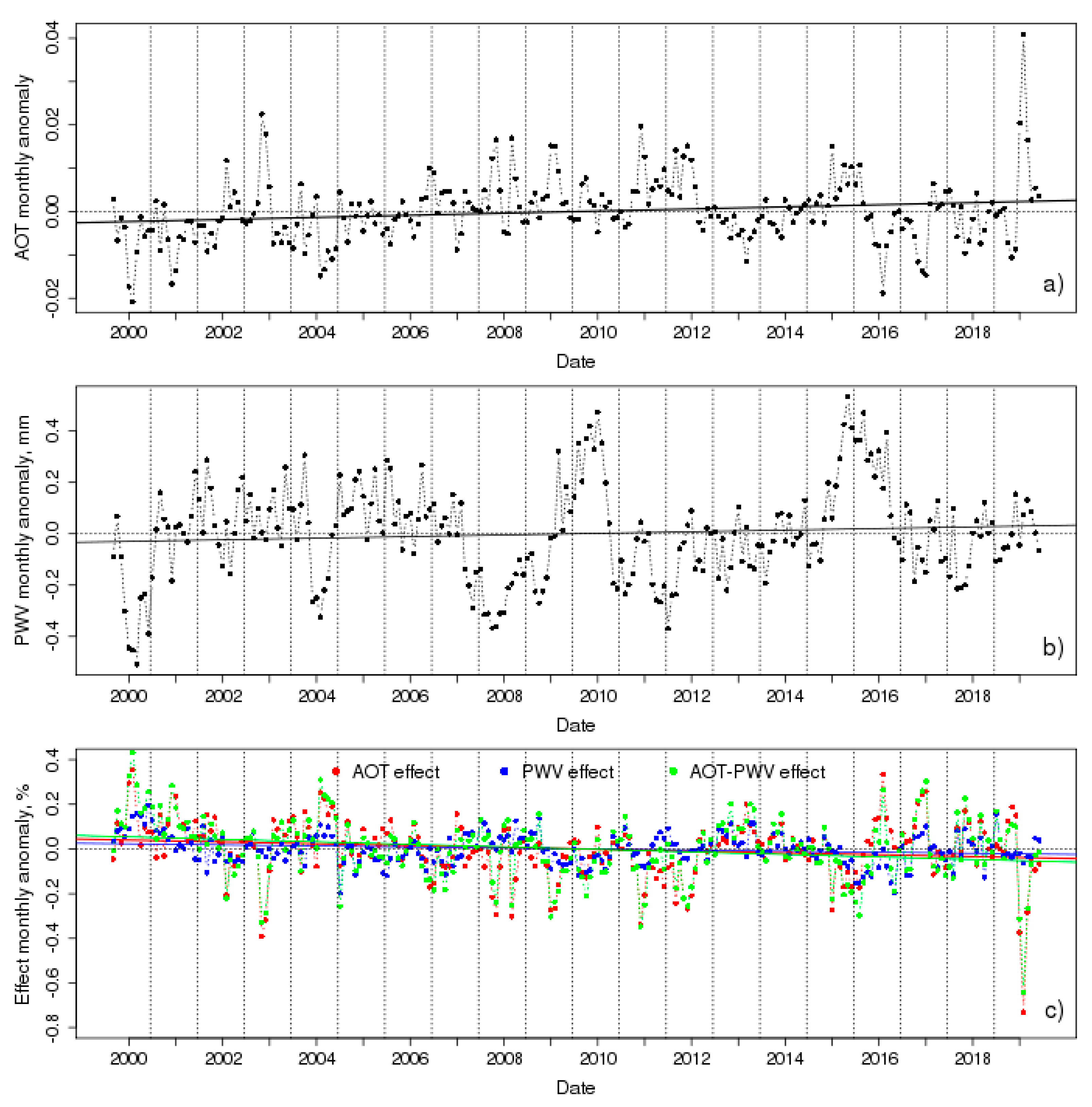
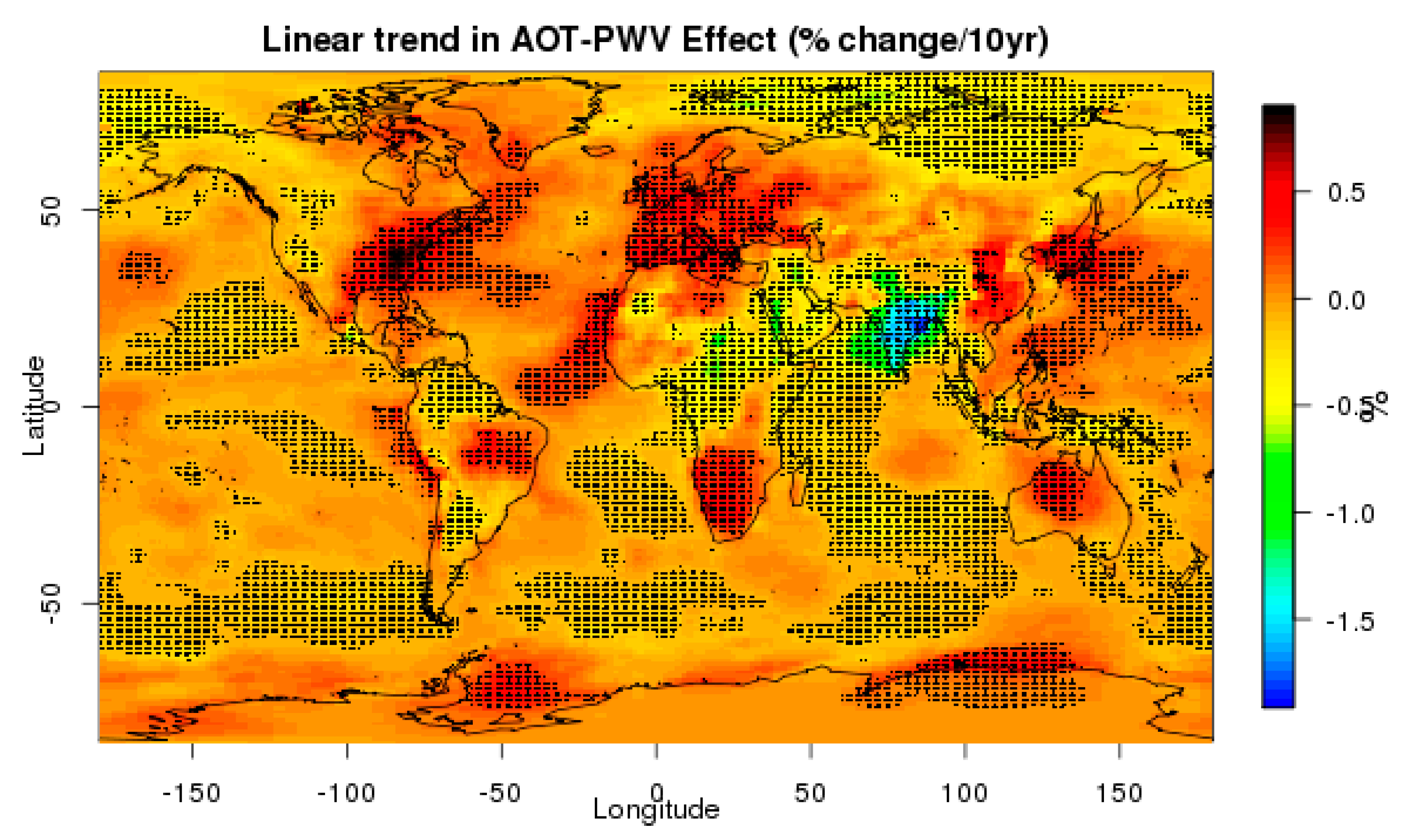
3.2. Temporal Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report 20 of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Yang, S. Wintertime cooling and a potential connection with transported aerosols in Hong Kong during recent decades. Atmos. Res. 2018, 211, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Distinct impact of different types of aerosols on surface solar radiation in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6459–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y. Intensification of aerosol pollution associated with its feedback with surface solar radiation and winds in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4093–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M.C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Gong, D.; Huang, J.; Jiang, M.; et al. East Asian study of tropospheric aerosols and their impact on regional clouds, precipitation, and climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13026–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Brunetti, M.; Deser, C. Dimming/brightening over the Iberian Peninsula: Trends in sunshine duration and cloud cover and their relations with atmospheric circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00D09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Folini, D.; Schär, C.; Loeb, N.; Dutton, E.G.; König-Langlo, G. The global energy balance from a surface perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 3107–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; Liepert, B. The earth radiation balance as driver of the global hydrological cycle. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M. Interactions between water vapor and atmospheric aerosols have key roles in air quality and climate change. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S.; Cong, Z.; Letu, H.; Menenti, M. Aerosol characteristics and impacts on weather and climate over the Tibetan Plateau. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C.; Gong, D.; Shi, P. An observational study of the effects of aerosols on diurnal variation of heavy rainfall and associated clouds over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 5211–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, P.; Ramaswamy, V.; Artaxo, P.; Berntsen, T.; Betts, R.; Fahey, D.W.; Haywood, J.; Lean, J.; Lowe, D.C.; Myhre, G.; et al. Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing Chapter 2; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.J.; Sohn, B.J.; Levizzani, V.; Silva, A.M. Radiative forcing of Asian dust determined from the synergized GOME and GMS satellite data—A case study. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 84, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarra, A.; Pace, G.; Meloni, D.; De Silvestri, L.; Piacentino, S.; Monteleone, F. Surface shortwave radiative forcing of different aerosol types in the Mediterranean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzianastassiou, N.; Matsoukas, C.; Drakakis, E.; Stackhouse, P.W., Jr.; Koepke, P.; Fotiadi, A.; Pavlakis, K.G.; Vardavas, I. The direct effect of aerosols on solar radiation based on satellite observations, reanalysis datasets, and spectral aerosol optical properties from Global Aerosol Data Set (GADS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2585–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanis, C.; Varotsos, C.A. Tropospheric aerosol forcing of climate: A case study for the greater area of Greece. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 2507–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M. Direct SW aerosol radiative forcing over Portugal. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5771–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Analyses of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over urban and industrial regions in Northeast China. Meteorol Atmos Phys. 2015, 127, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, M.A.; Pereira, S.; Salgueiro, V.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A.; Bortoli, D. Aerosol radiative effects during two desert dust events in August 2012 over the Southwestern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.E.; Chu, J.-E.; Lee, Y.; Van Noije, T.; Jeoung, H.; Ha, K.-J.; Marks, M. Global fine-mode aerosol radiative effect, as constrained by comprehensive observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8071–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, M.A.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A. Thirteen years of aerosol radiative forcing in Southwestern Iberian Peninsula. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Costa, M.J.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bortoli, D.; Olmo, F.J. Solar and thermal radiative effects during the 2011 extreme desert dust episode over Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba, T.; Gogoi, M.M.; Pathak, B.; Bhuyan, P.K.; Babu, S.S. Recent trend in the global distribution of aerosol direct radiative forcing from satellite measurements. Atmos Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Zhang, J. Cloud-free shortwave aerosol radiative effect over oceans: Strategies for identifying anthropogenic forcing from Terra satellite measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L18101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Christopher, S.A.; Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J. Shortwave aerosol radiative forcing over cloud-free oceans from Terra: 2. Seasonal and global distributions. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D10S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, M.A.; Costa, M.J.; Serrano, A.; Silva, A.M. Effect of water vapor in the SW and LW downward irradiance at the surface during a day with low aerosol load. IOP Conf. Ser. 2015, 28, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Pan, Z.; Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Gong, W. Estimating the effects of aerosol, cloud, and water vapor on the recent brightening in India during the monsoon season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero-Martínez, J.; Antón, M.; Ortiz de Galisteo, J.P.; Román, R.; Cachorro, V.E. Water vapor radiative effects on short-wave radiation in Spain. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, M.A.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A. Spatial and temporal variation of aerosol and water vapour effects on solar radiation in the Mediterranean Basin during the last two decades. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, M.A.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A. Impact of aerosol and water vapour on SW radiation at the surface: Sensitivity study and applications. Atmos. Res. 2018, 13, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z. Global water vapour variability and trend from the latest 36 years (1979 to 2014) data of ECMWF and NCEP reanalyses, radiosonde, GPS, and microwave satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11442–11462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelling, D.R.; Sun, M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nordeen, M.L.; Haney, C.O.; Keyes, D.F.; Mlynczak, P.E. Advances in geostationary-derived longwave fluxes for the CERES synoptic (SYN1deg) product. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.; Rasch, P.J.; Eaton, B.E.; Khattatov, B.V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Zender, C. Simulating aerosols using a chemical transport model with assimilation of satellite aerosol retrievals: Methodology for INDOEX. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 7313–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, N.J.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Takacs, L.; Liu, H.-C.; Gu, W.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Koster, R.D.; Gelaro, R.; et al. The GOES-5 Data Assimilation System—Documentation of Versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0; Report No. NASA/TM-2008-105606; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 27.
- Trepte, Q.Z.; Minnis, P.; Sun-Mack, S.; Yost, C.R.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Z.; Hong, G.; Chang, F.; Smith, W.L.; Bedka, K.M.; et al. Global cloud detection for CERES Edition 4 using Terra and Aqua MODIS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 57, 9410–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, N.G.; Doelling, D.R.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Nguyen, C.; Corbett, J.G.; Liang, L.; Mitrescu, C.; Rose, F.G.; Kato, S. Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) Top-of-Atmosphere (TOA) edition-4.0 data product. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 895–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Ichoku, C.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Holben, B.N. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval over land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.-R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Rudich, Y.; Koren, I. Spatial boundaries of Aerosol Robotic Network observations over the Mediterranean basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Luo, N.; Zhao, W.; Shi, W.; Yan, X. Evaluation and comparison of Himawari-8 L2 V1.0, V2.1 and MODIS C6.1 aerosol products over Asia and the Oceania regions. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.K.; Singh, R.P. Validation of MODIS Terra, AIRS, NCEP/DOE AMIP-II reanalysis-2, and AERONET sun photometer derived integrated precipitable water vapor using ground-based GPS receivers over India. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D05107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero-Martínez, J.; Antón, M.; de Galisteo, J.P.O.; Cachorro, V.E.; Costa, M.J.; Román, R.; Bennouna, Y.S. Validation of MODIS integrated water vapor product against reference GPS data at the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 63, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vaquero-Martinez, J.; Anton, M.; Ortiz de Galisteo, J.P.; Cachorro, V.E.; Alvarez-Zapatero, P.; Roman, R.; Loyola, D.; Costa, M.J.; Wang, H.; González, A.G.; et al. Inter-comparison of integrated water vapor from satellite instruments using reference GPS data at the Iberian Peninsula. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C.; Kaufman, Y.J. Water vapor retrievals using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) near-infrared channels. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Amer. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, D.A.; Heald, C.L.; Prospero, J.M. What controls the recent changes in African mineral dust aerosol across the Atlantic? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5735–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, C.L.; Butt, E.W.; Ridley, D.A.; Artaxo, P.; Morgan, W.T.; Coe, H.; Spracklen, D.V. Air quality and human health improvements from reductions in deforestation-related fire in Brazil. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.B.; Ma, Y.; Xia, L.; Chen, W.Y.; Shen, X.Y.; He, T.J.; Xu, T.R. Global aerosol change in the last decade: An analysis based on MODIS data. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.; Anshumali. Recent global aerosol optical depth variations and trends—A comparative study using MODIS and MISR level 3 datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 181, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakouri, A.; Korras Carraca, M.B.; Kontos, T.; Matsoukas, C.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Floutsi, A.A.; Kostopoulou, E. Climatology and trends of aerosol optical depth on global scale using CALIOP vertically resolved data during 2007–2017. Geophys. Res. Abst. 2019, 21, EGU2019-10935. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.K.; Sivakumar, V.; Yin, Y.; Reddy, R.R.; Kang, N.; Diao, Y.; Adesina, A.J.; Yu, X. Long-term (2003−2013) climatological trends and variations in aerosol optical parameters retrieved from MODIS over three stations in South Africa. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, Y. A climatological comparison of column-integrated water vapor for the third-generation reanalysis datasets. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.; Smith, L. Trends and variability in column-integrated atmospheric water vapor. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 24, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Grzegorski, M.; Platt, U. Global trends (1996–2003) of total column precipitable water observed by Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME) on ERS-2 and their relation to near-surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D12102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, C. Influence of Saharan Dust on the large-scale meteorological environment for development of tropical cyclone over North Atlantic Ocean Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, JD033454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P. Growth rates of fine aerosol particles at a site near Beijing in June 2013. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M.; Wood, R. The seasonal cycle of planetary boundary layer depth determined using COSMIC radio occultation data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12422–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendry, I.G.; Kamp, D.; Strawbridge, K.B.; Christen, A.; Crawford, B. Simultaneous observations of boundary-layer aerosol layers with CL31 ceilometer and 1064/532 nm lidar. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5847–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, R.C.; Undurraga, A.A. Daytime mixed layer over the Santiago Basin: Description of two years of observations with a lidar ceilometer. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N. Dust storms in Central Asia: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 85, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G.; Újvári, G.; Kovács, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of Saharan dust outbreaks in the Mediterranean Basin. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.; Justice, C.O. Global distribution and seasonality of active fires as observed with the Terra and Aqua Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) sensors. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, G02016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Chen, J.; Wen, Z. Precipitation-surface temperature relationship in the IPCC CMIP5 models. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 30, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Jiménez, C.; Jung, M.; Michel, D.; Ershadi, A.; McCabe, M.F.; Hirschi, M.; Martens, B.; Dolman, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; et al. The WACMOS-ET project—Part 2: Evaluation of global terrestrial evaporation data sets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S. A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and Level 2 MISR aerosol products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10949–10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Gautam, R.; Sayer, A.M.; Bettenhausen, C.; Li, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Tsay, S.C.; Holben, B.N. Global and regional trends of aerosol optical depth over land and ocean using SeaWiFS measurements from 1997 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8037–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Kedia, S.; Srivastava, R. Aerosol optical depth trends over different regions of India. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M. A study of aerosol optical depth variations over the Indian region using thirteen years (2001–2013) of MODIS and MISR level 3 data. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Manoj, M.R.; Moorthy, K.K.; Gogoi, M.M.; Nair, V.S.; Kompalli, S.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Niranjan, K.; Ramagopal, K.; Bhuyan, P.K.; et al. Trends in aerosol optical depth over Indian region: Potential causes and impact indicators. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basart, S.; Pérez, C.; Cuevas, E.; Baldasano, J.M.; Gobbi, G.P. Aerosol characterization in Northern Africa, Northeastern Atlantic, Mediterranean Basin and Middle East from direct-sun AERONET observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8265–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T.; Subhan, F. Changes in aerosol optical properties due to dust storms in the Middle East and Southwest Asia. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Rappenglueck, B.; Eltahir, E.A.B. The climatology of dust aerosol over the Arabian peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 1523–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Diner, D.; Worden, J.; Liou, K.-N.; Su, H.; Xing, J.; Garay, M.; Huang, L. Decadal-scale trends in regional aerosol particle properties and their linkage to emission changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 054021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Y. Atmospheric inverse estimates of CO emissions from Zhengzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wang, B.; Shi, G.; Seyler, B.C.; Qiao, X.; Deng, X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhan, Y. Impact of China’s recent amendments to air quality monitoring protocol on reported trends. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S. Variations in major aerosol components from long-term measurement of columnar aerosol optical properties at a SKYNET site downwind of Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 117991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuliene, L.; Jasineviciene, D.; Garbariene, I.; Andriejauskiene, J.; Ulevicius, V.; Bycenkiene, S. Long-term air pollution trend analysis in the South-eastern Baltic region, 1981–2017. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kharol, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Wild, M. Multi-decadal variation of the net downward shortwave radiation over south Asia: The solar dimming effect. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Recent declines in global water vapor from MODIS products: Artifact or real trend? Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieruch, S.; Noël, S.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P. Analysis of global water vapour trends from satellite measurements in the visible spectral range. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.E. Intensified warming of the Arctic: Causes and impacts on middle latitudes. Global Planet. Chang. 2014, 117, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; Knutti, R.; Arblaster, J.; Dufresne, J.L.; Fichefet, T.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gao, X.; Gutowski, W.J.; Johns, T.; Krinner, G.; et al. Long-term climate change: Projections, commitments and irreversibility. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obregón, M.Á.; Serrano, A.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M. Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Combined Effect of Aerosol and Water Vapour on Solar Radiation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040708
Obregón MÁ, Serrano A, Costa MJ, Silva AM. Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Combined Effect of Aerosol and Water Vapour on Solar Radiation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040708
Chicago/Turabian StyleObregón, María Ángeles, Antonio Serrano, Maria João Costa, and Ana Maria Silva. 2021. "Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Combined Effect of Aerosol and Water Vapour on Solar Radiation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040708
APA StyleObregón, M. Á., Serrano, A., Costa, M. J., & Silva, A. M. (2021). Global Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Combined Effect of Aerosol and Water Vapour on Solar Radiation. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040708








