Research of the Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics for Bathymetry without In-Situ Depth Data in the South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
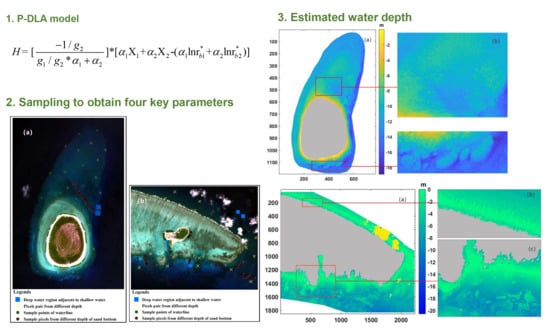
2. Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics (P-DLA)
2.1. Formula Deduction
2.2. Optimal Band Rotation Coefficient Unit Vector
2.3. Bottom Parameters
2.4. Ratio between Diffuse Attenuation Coefficients of the Blue and Green Bands
2.5. Diffuse Attenuation Coefficients of the Green Band Estimated by QAA
3. Study Areas and Data Processing
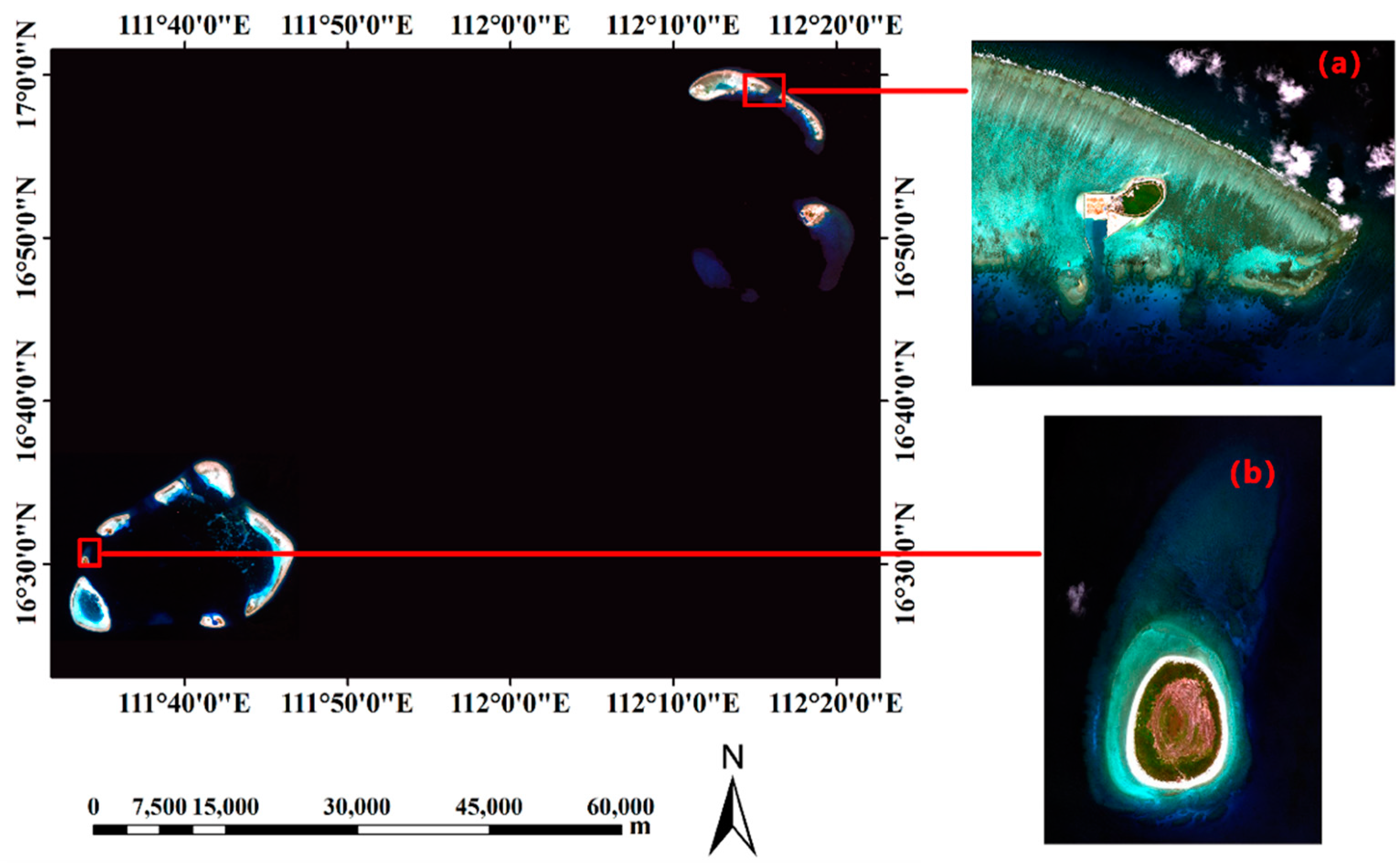
3.1. The Study Areas and Datasets
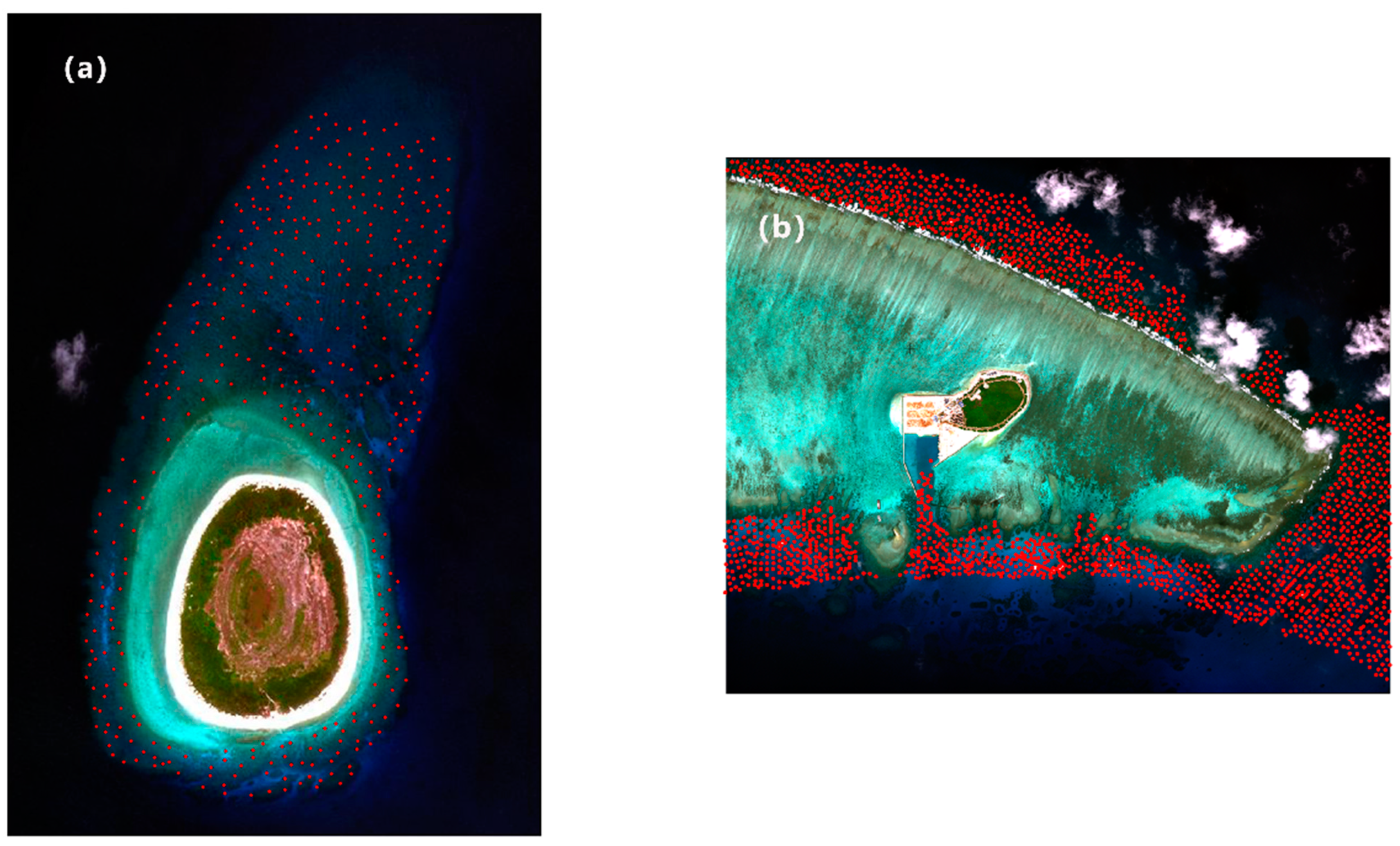
3.2. Collection of Sample Pixels
3.3. Evaluation
4. Results
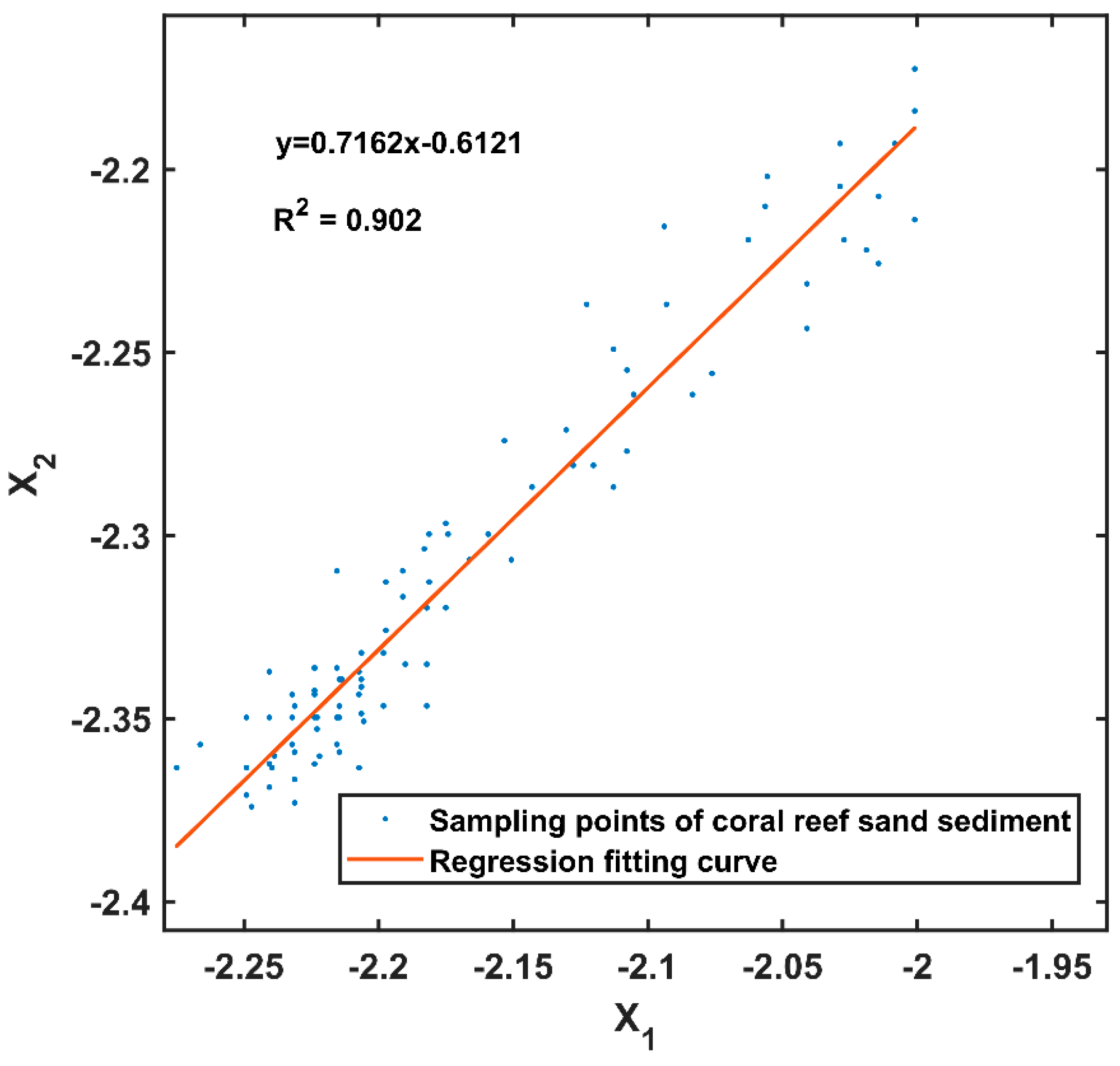
4.1. Estimated Parameters
4.2. Bathymetric Estimated Results
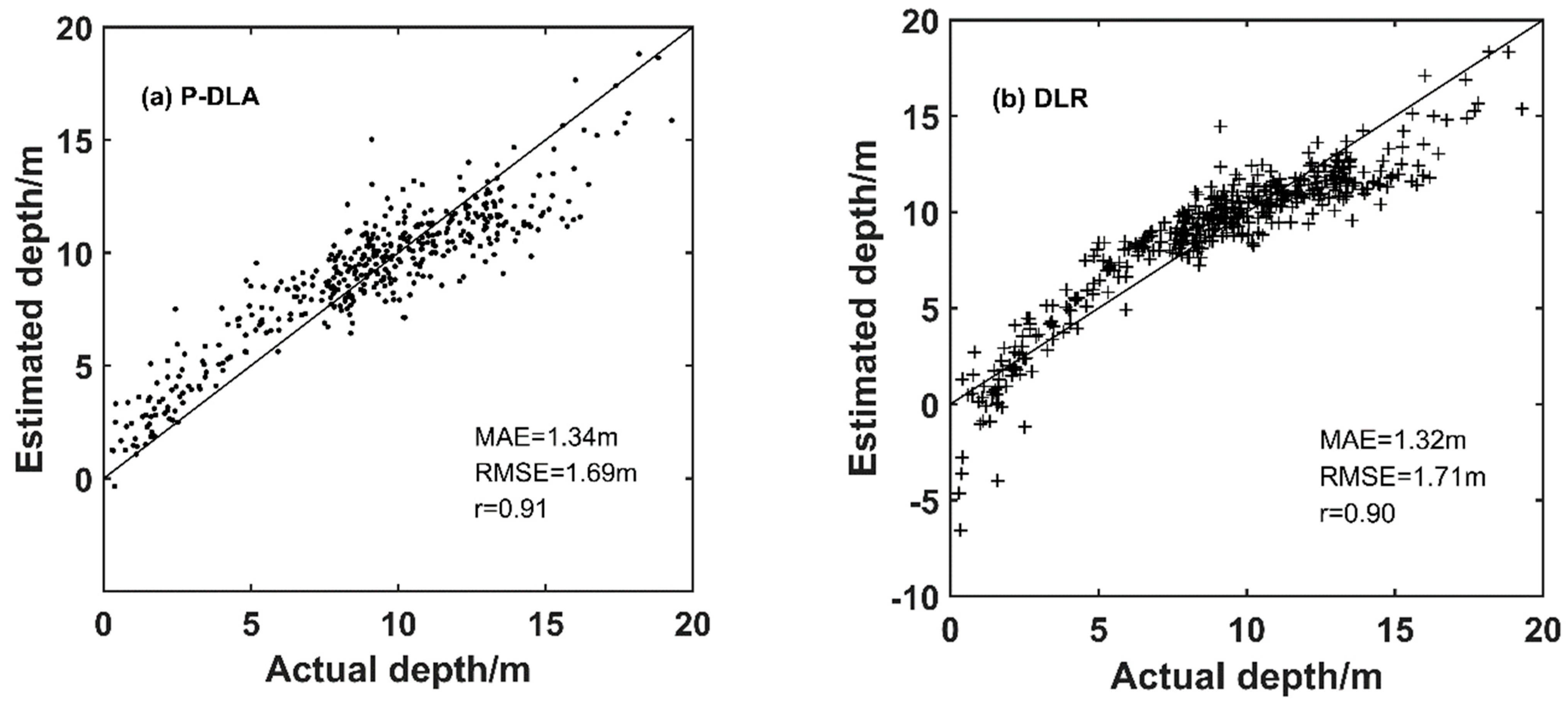
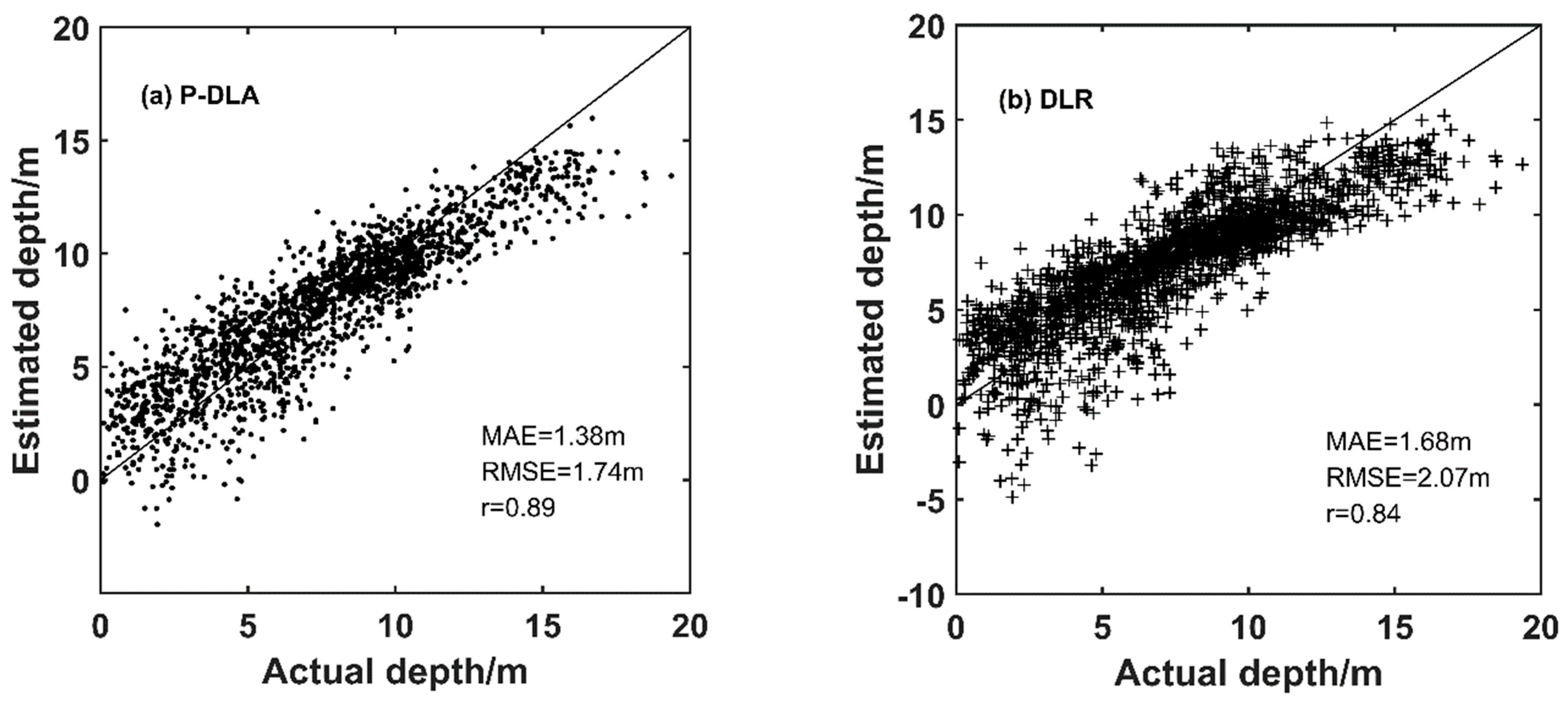
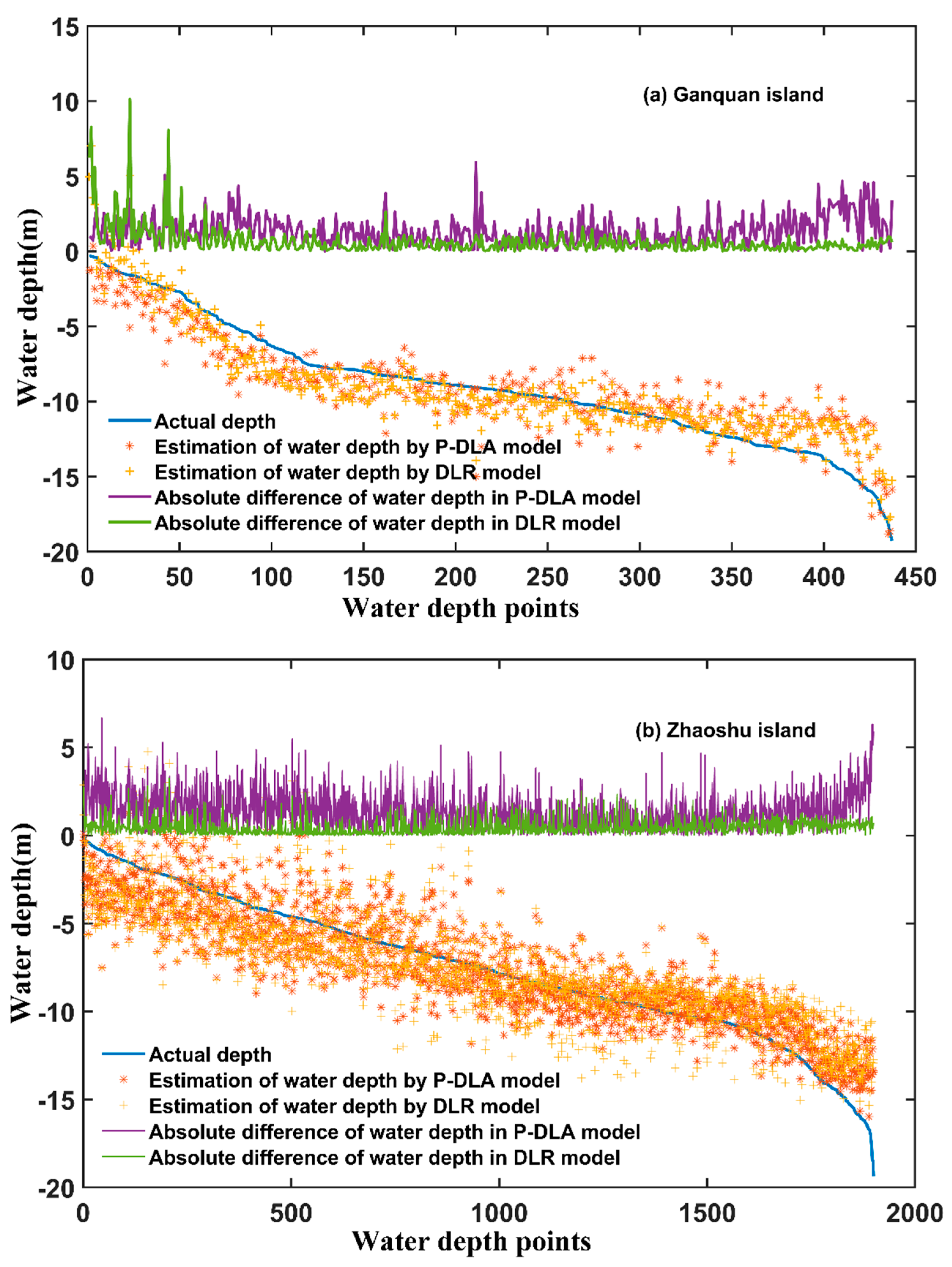
4.3. Accuracy Evaluation
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Water Depth Inversion with and without In-Situ Depth Data
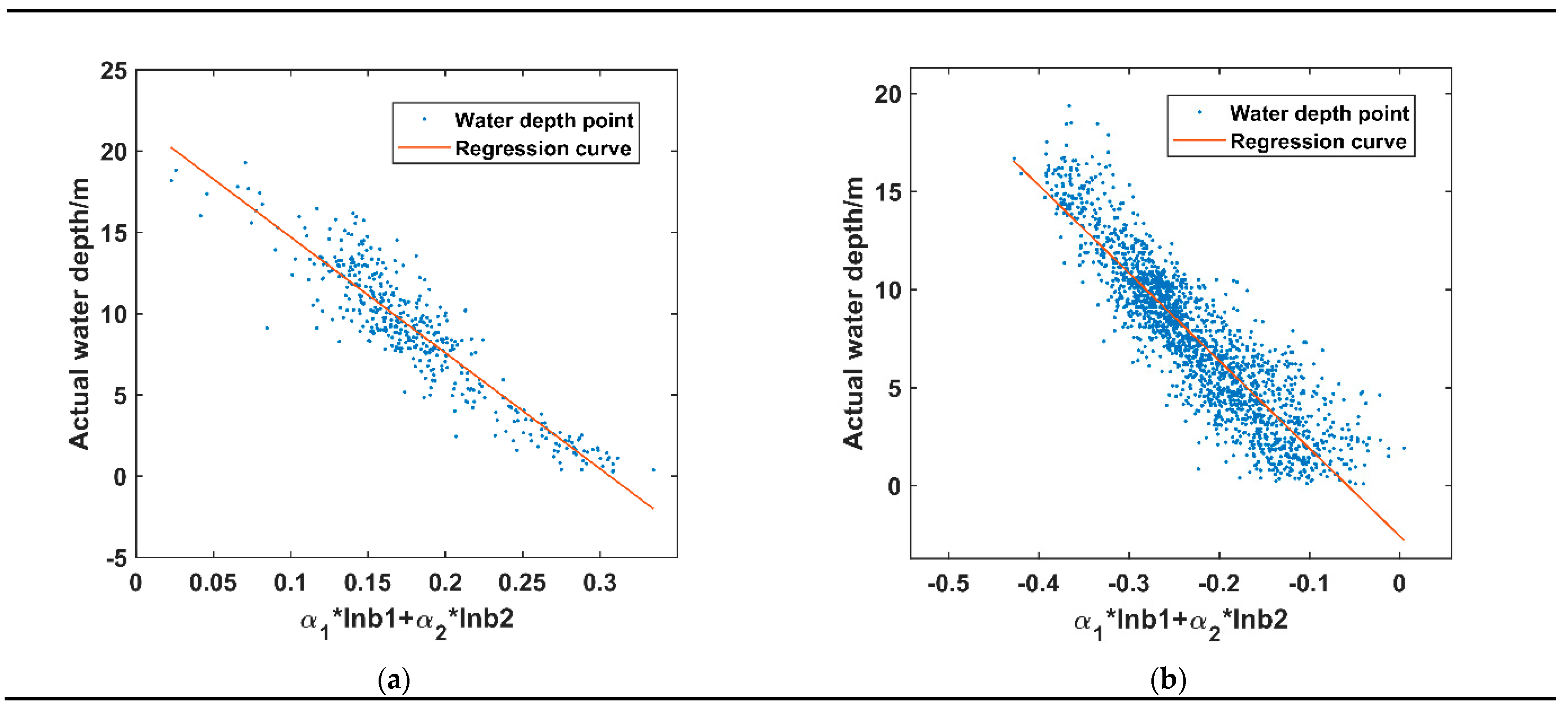
5.2. Relationships between and Actual Water Depth
5.3. Principles of Sample Collection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, R.A.; Lee, Z.; Hochberg, E.J. Hyperspectral Shallow-Water Remote Sensing with an Enhanced Benthic Classifier. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traganos, D.; Reinartz, P. Machine learning-based retrieval of benthic reflectance and Posidonia oceanica seagrass extent using a semi-analytical inversion of Sentinel-2 satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 9428–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Lou, X.; Fan, K.; Shi, A.; Li, D. A Bathymetry Mapping Approach Combining Log-Ratio and Semianalytical Models Using Four-Band Multispectral Imagery Without Ground Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shangguan, M.; Garcia, R.A.; Lai, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Yan, X. Confidence Measure of the Shallow-Water Bathymetry Map Obtained through the Fusion of Lidar and Multiband Image Data. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 9841804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters. I. A semianalytical model. Appl. Optics 1998, 37, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Optics 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, R.; Li, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Multispectral Bathymetry via Linear Unmixing of the Benthic Reflectance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4349–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, R.; Qin, Y.; Cao, B.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, S. Rapid estimation of bathymetry from multispectral imagery without in situ bathymetry data. Appl. Optics 2019, 58, 7538–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, W.; Li, D.; Lou, X.; Fan, K. An Exponential Algorithm for Bottom Reflectance Retrieval in Clear Optically Shallow Waters from Multispectral Imagery without Ground Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Weidemann, A.; Arnone, R. Combined Effect of Reduced Band Number and Increased Bandwidth on Shallow Water Remote Sensing: The Case of WorldView 2. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Lee, Z.; Briceñod, H.O.; Yu, X.; Jiang, L.; Garcia, R.; Wang, J.; Luis, K. Shallow water bathymetry with multi-spectral satellite ocean color sensors: Leveraging temporal variation in image data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Huang, E. A dual band algorithm for shallow water depth retrieval from high spatial resolution imagery with no ground truth. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Morel, A.; Gentili, B. Diffuse reflectance of oceanic shallow waters: Influence of water depth and bottom albedo. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Mobley, C.D. An analytical model for subsurface irradiance and remote sensing reflectance in deep and shallow case-2 waters. Opt. Express. 2003, 11, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Shallow-water bathymetry using combined lidar and passive multispectral scanner data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpot, W. Bathymetric mapping with passive multispectral imagery. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Mu, L.; Wang, W. Bathymetry of the Coral Reefs of Weizhou Island Based on Multispectral Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, K.; Mu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Ren, J. Evaluation of the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA) for Estimating Total Absorption Coefficient of Turbid Inland Waters in Northeast China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4022–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.A.; Lee, Z.; Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C.; Dierssen, H.M.; Hochberg, E.J. Benthic classification and IOP retrievals in shallow water environments using MERIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Zibordi, G. Spectral interdependence of remote-sensing reflectance and its implications on the design of ocean color satellite sensors. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenio, F.; Marcello, J.; Martin, J. High-Resolution Maps of Bathymetry and Benthic Habitats in Shallow-Water Environments Using Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Wei, J.; Voss, K.; Lewis, M.; Bricaud, A.; Huot, Y. Hyperspectral absorption coefficient of “pure” seawater in the range of 350–550 nm inverted from remote sensing reflectance. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Qi, L.; Yan, J.; Lin, G. A semi-analytical scheme to estimate Secchi-disk depth from Landsat-8 measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Lubac, B.; Werdell, J.; Arnone, R.A. Update of the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA_v6). Int. Ocean Color Group Softw. Rep. Available online: https://www.ioccg.org/groups/Software_OCA/QAA_v6_2014209.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2013).
- Howard, R.G.; Otis, B.B.; Robert, H.E.; James, W.B.; Raymond, C.S.; Karen, S.B.; Dennis, K.C. A Semianalytic Radiance Model of Ocean Color. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, R.M.; Fry, E.S. Absorption spectrum (380–700 nm) of pure water. II. Integrating cavity measurements. Appl. Optics 1997, 36, 8710–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.G.; Otis, B.B.; Michael, M.J. Remote sensing of ocean color: A methodology for dealing with broad spectral bands and significant out-of-band response. Appl. Optics 1995, 34, 8363–8374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Shallow Water Bathymetry Based on Inherent Optical Properties Using High Spatial Resolution Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Shen, D.; Shen, J. Formation Mechanism of Beach Rocks and Its Controlling Factors in Coral Reef Area, Qilian Islets and Cays, Xisha Islands, China. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 30, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, H.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; Xu, J.; Lei, S.; et al. Inland Water Atmospheric Correction Based on Turbidity Classification Using OLCI and SLSTR Synergistic Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products. Reports and Monographs of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group. Available online: https://www.ioccg.org/reports/report10.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Wang, D.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S.A. The Assessment of Landsat-8 OLI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Holderied, K.; Sinclair, M. Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R.; Malinas, N.P.; Tanis, F.J. Multispectral bathymetry using a simple physically based algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Knapp, D.E.; Schill, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.; Phinn, S.; Silman, M.; Mascaro, J.; Asner, G.P. Adaptive bathymetry estimation for shallow coastal waters using Planet Dove satellites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


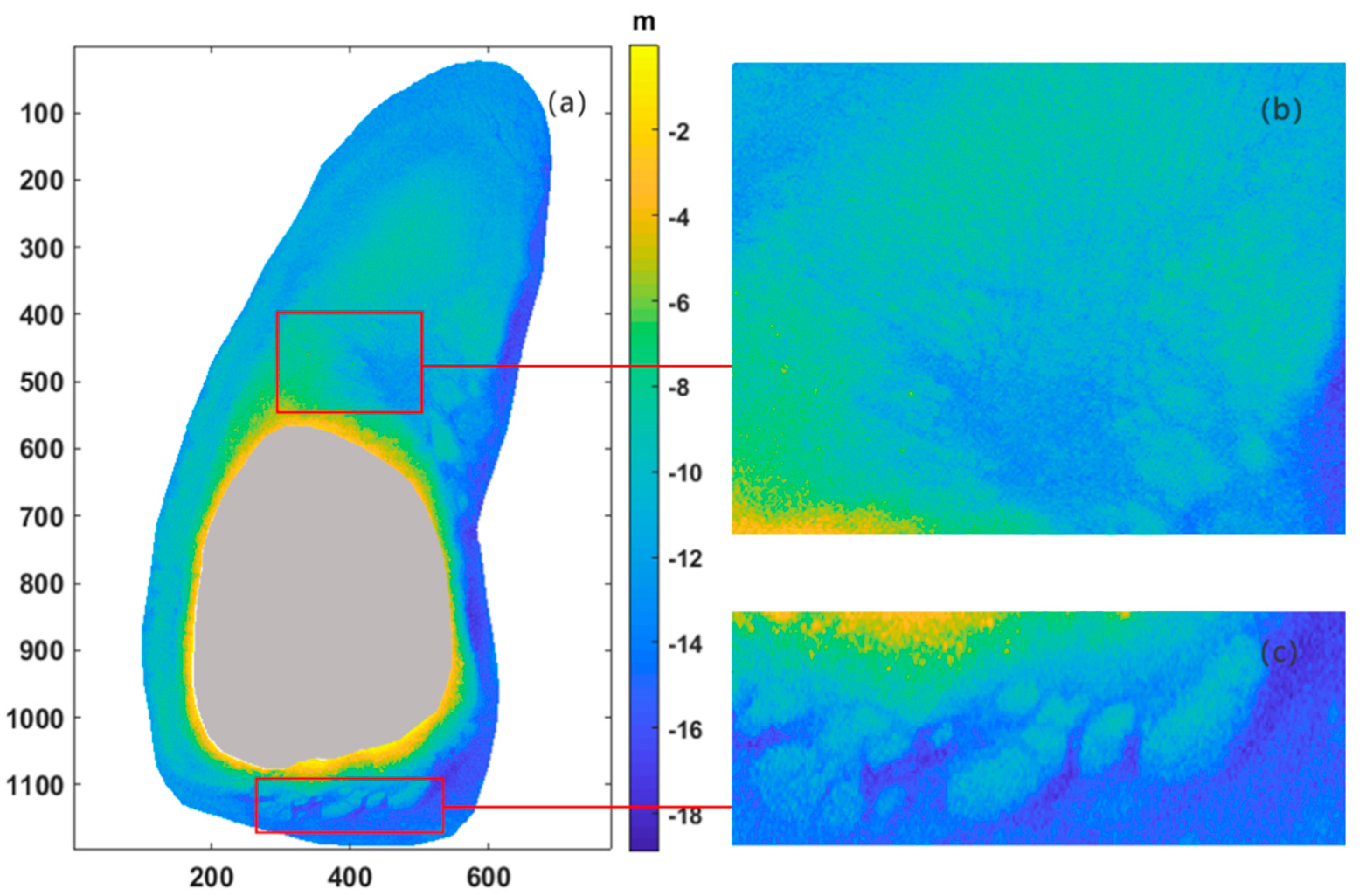
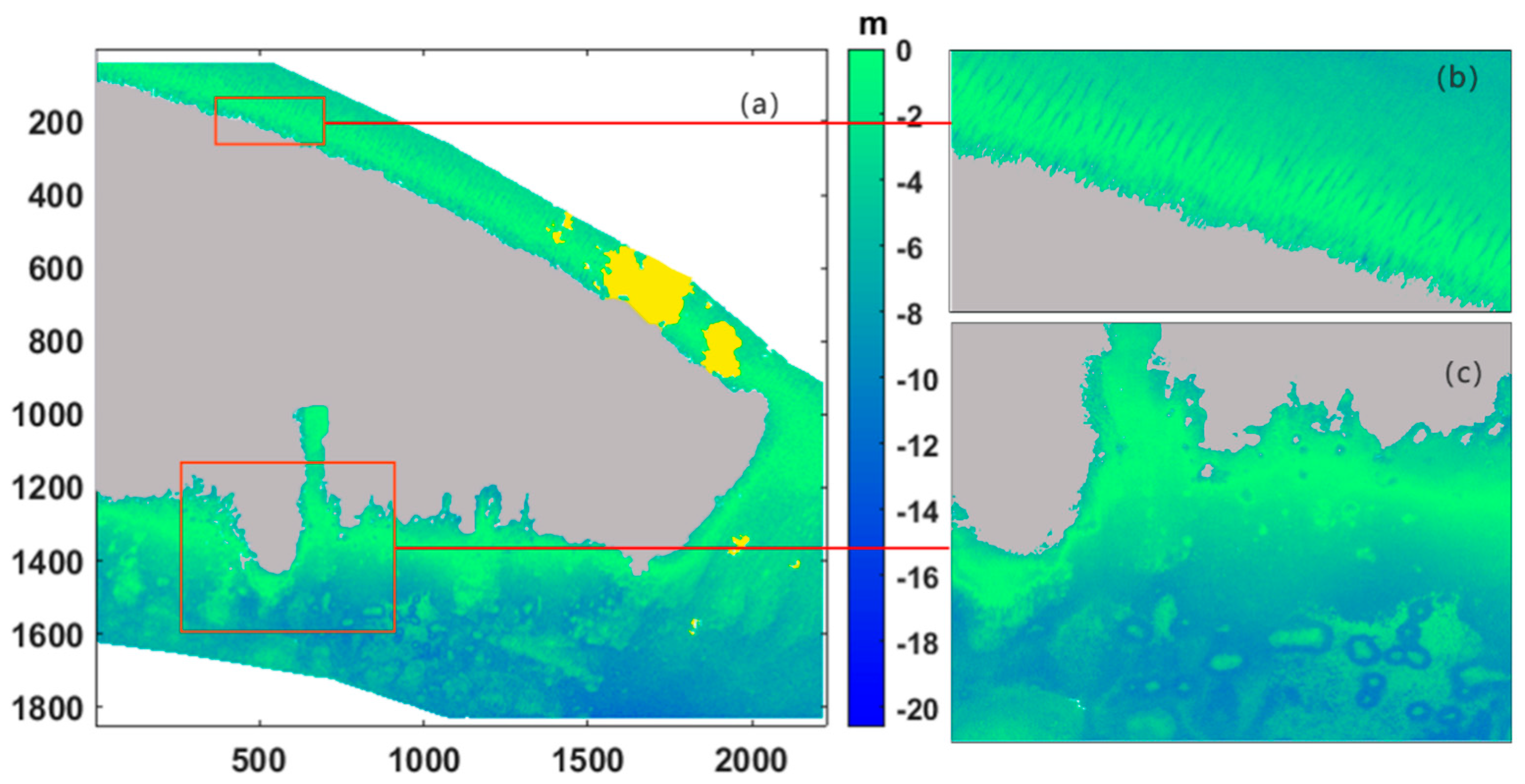

| Research Regions | Acquisition Date | Cloud Fraction | Solar Zenith Angle | Satellite Zenith Angle | Tidal Height/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganquan Island | 2 April 2014 | 0.1% | 19.4° | 36.3° | 0.78 |
| Zhaoshu Island | 11 March 2017 | 0.6% | 31.6° | 27.6° | 0.21 |
| Research Regions | Data Source | Acquisition Date | Data Precision | Number of Points with In-Situ Depth Data | Mean Water Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganquan Island | Airborne Lidar detection system | 9 January 2013 | 0.15 m | 437 | −8.95 m |
| Zhaoshu Island | Combination of single-beam and manual measurements | 2 March 2014 | 1% above the Precision of Water Depth | 1900 | −7.45 m |
| Ganquan Island | −0.755 | 0.655 | 0.329 | 0.716 | 0.143 |
| Zhaoshu Island | −0.674 | 0.738 | −0.043 | 0.894 | 0.178 |
| RMSE/m | MAE/m | MRE | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganquan Island | 1.692 | 1.348 | 0.148 | 0.914 |
| Zhaoshu Island | 1.744 | 1.385 | 0.183 | 0.895 |
| Research Regions | Indicators for Evaluation | 0–5 m | 5–10 m | 10–15 m | 15–20 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganquan Island | RMSE/m | 1.805 | 1.456 | 1.708 | 2.674 |
| MAE/m | 1.493 | 1.165 | 1.362 | 2.238 | |
| MRE | 0.375 | 0.129 | 0.123 | 0.154 | |
| Zhaoshu Island | RMSE/m | 2.084 | 1.416 | 1.477 | 3.230 |
| MAE/m | 1.755 | 1.098 | 1.204 | 2.962 | |
| MRE | 0.426 | 0.141 | 0.113 | 0.225 |
| Research Regions | Number of Training Samples | Number of Validation Samples | Bathymetric Inversion Model | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganquan Island | 305 | 132 | −10.84 + 366.53 * log(B1) + 410.87 * log(B2) | 0.900 |
| Zhaoshu Island | 1330 | 570 | −8.9 + (−276.18) * log(B1) + (322.21) * log(B2) | 0.843 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, W.; Ye, L.; Qiu, Z.; Luan, K.; He, N.; Wei, Z.; Yang, F.; Yue, Z.; Zhao, S.; Yang, F. Research of the Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics for Bathymetry without In-Situ Depth Data in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214331
Zhu W, Ye L, Qiu Z, Luan K, He N, Wei Z, Yang F, Yue Z, Zhao S, Yang F. Research of the Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics for Bathymetry without In-Situ Depth Data in the South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Weidong, Li Ye, Zhenge Qiu, Kuifeng Luan, Naiying He, Zheng Wei, Fan Yang, Zilin Yue, Shubing Zhao, and Fei Yang. 2021. "Research of the Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics for Bathymetry without In-Situ Depth Data in the South China Sea" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214331
APA StyleZhu, W., Ye, L., Qiu, Z., Luan, K., He, N., Wei, Z., Yang, F., Yue, Z., Zhao, S., & Yang, F. (2021). Research of the Dual-Band Log-Linear Analysis Model Based on Physics for Bathymetry without In-Situ Depth Data in the South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214331