Estimation of the PM2.5 and PM10 Mass Concentration over Land from FY-4A Aerosol Optical Depth Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. PM2.5 and PM10 Data
2.3. Fengyun-4 (FY-4A) Data
2.4. Relative Humidity
2.5. (Planetary) Boundary Layer Height
2.6. Land Use Type
2.7. MODIS NDVI Data
3. Methods
4. Results
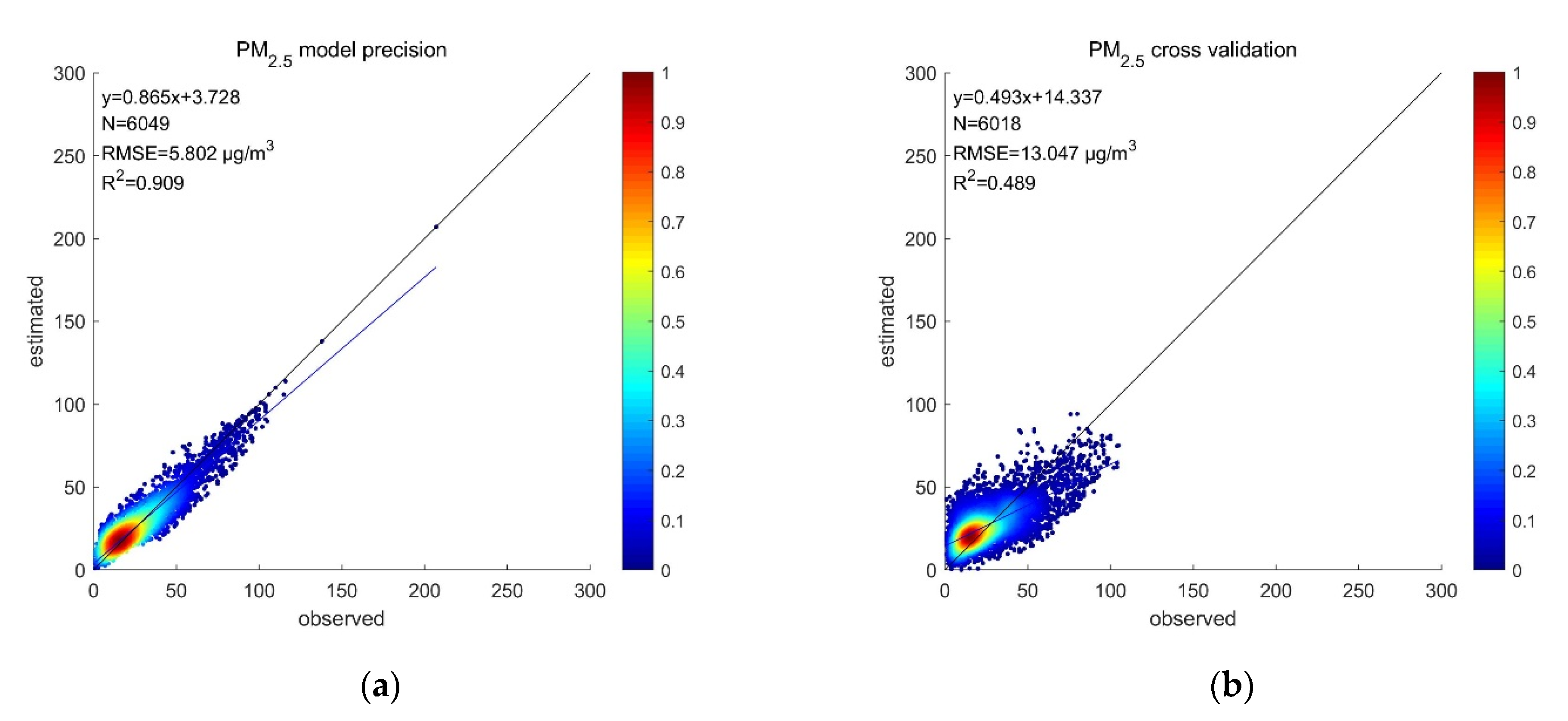
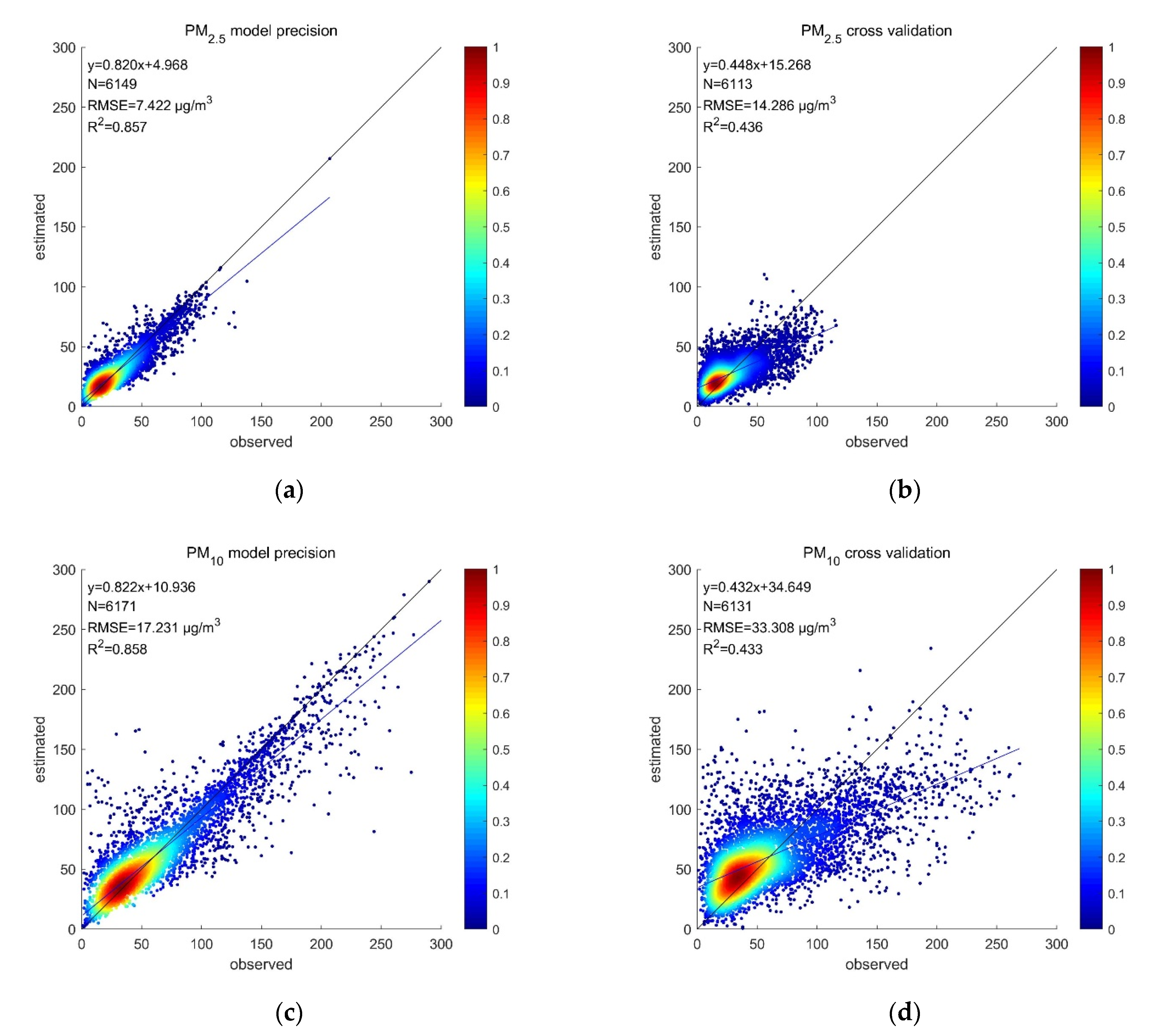
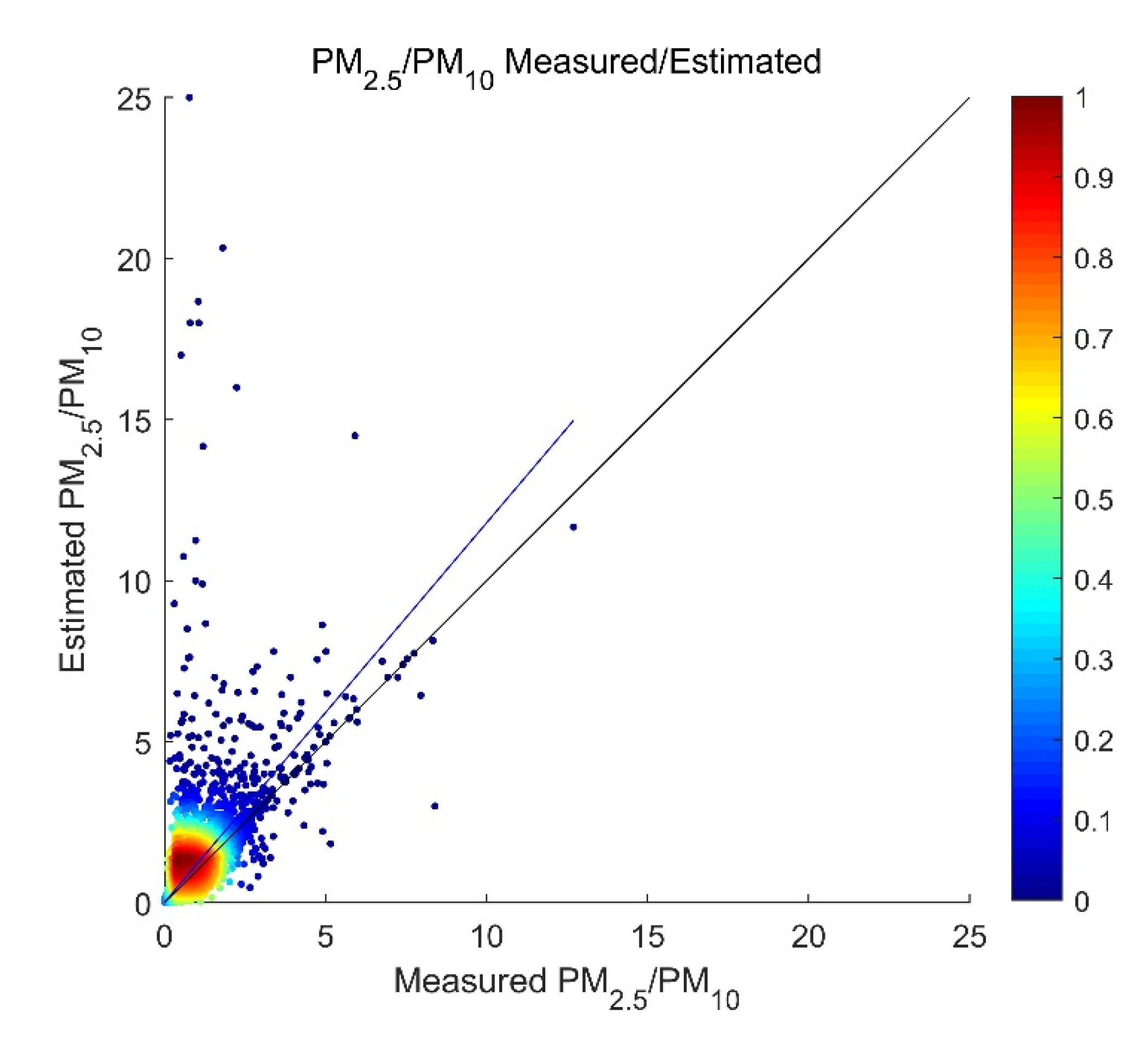
4.1. Evaluation of IGTWR Model Applied to FY-4A
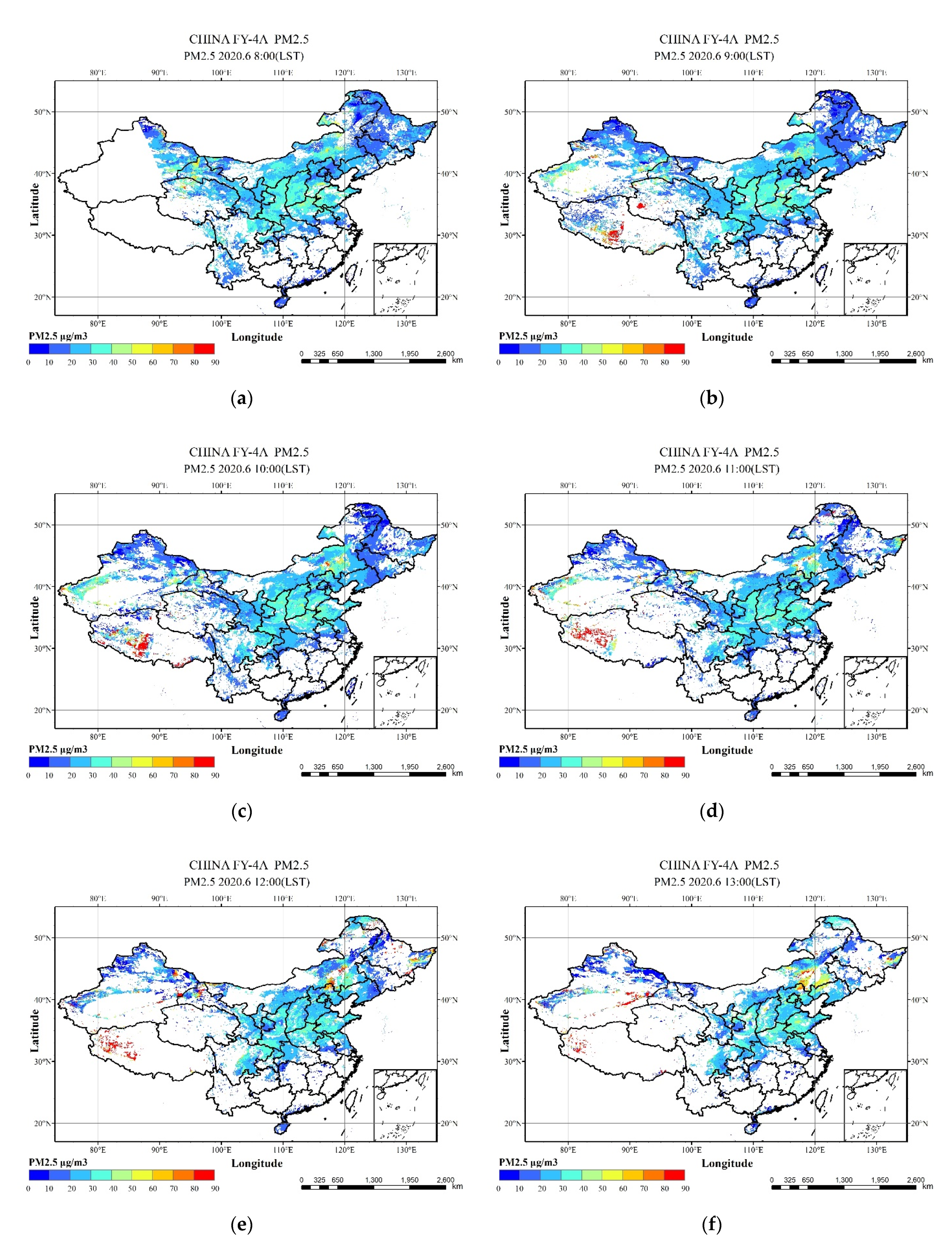
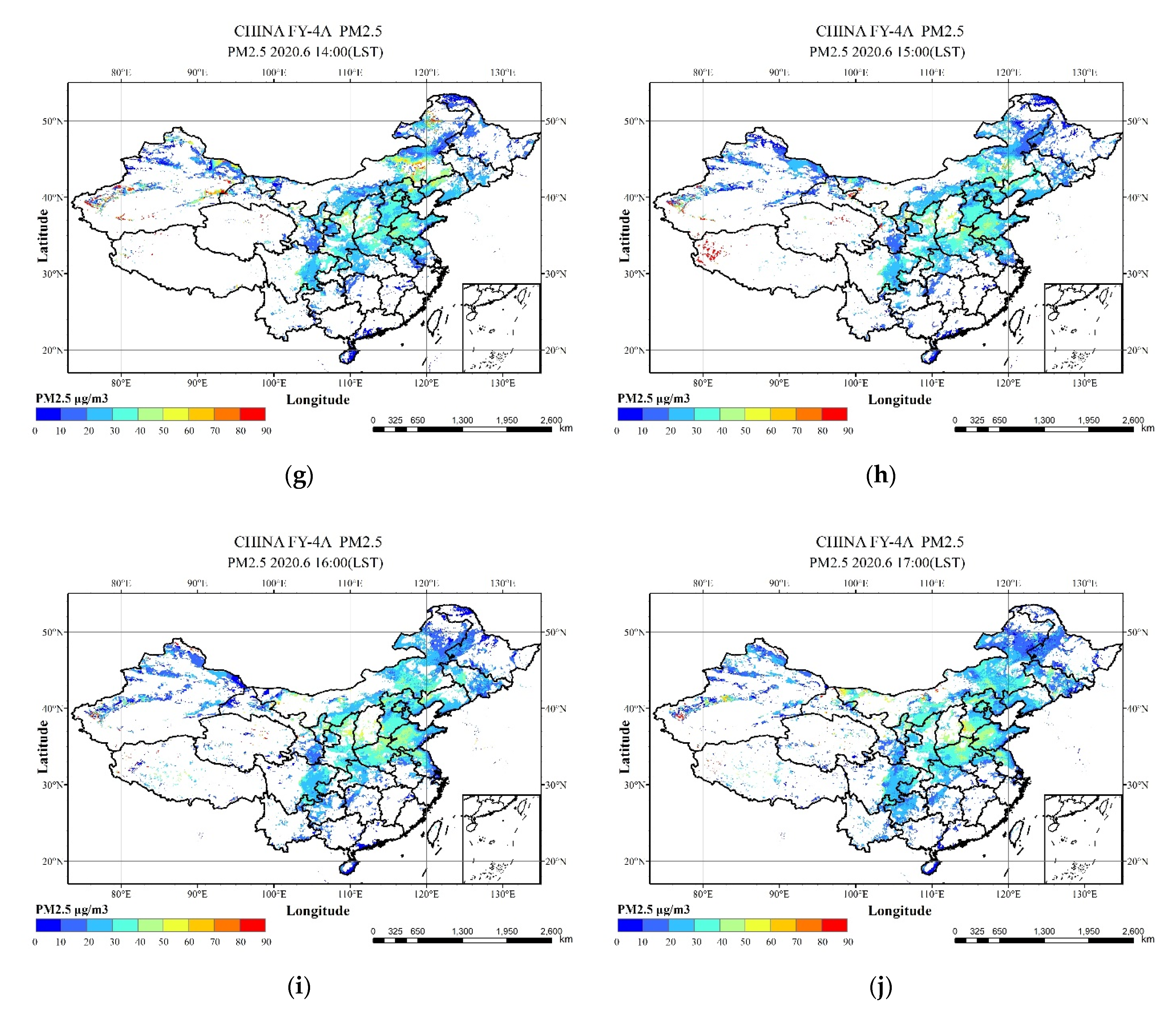
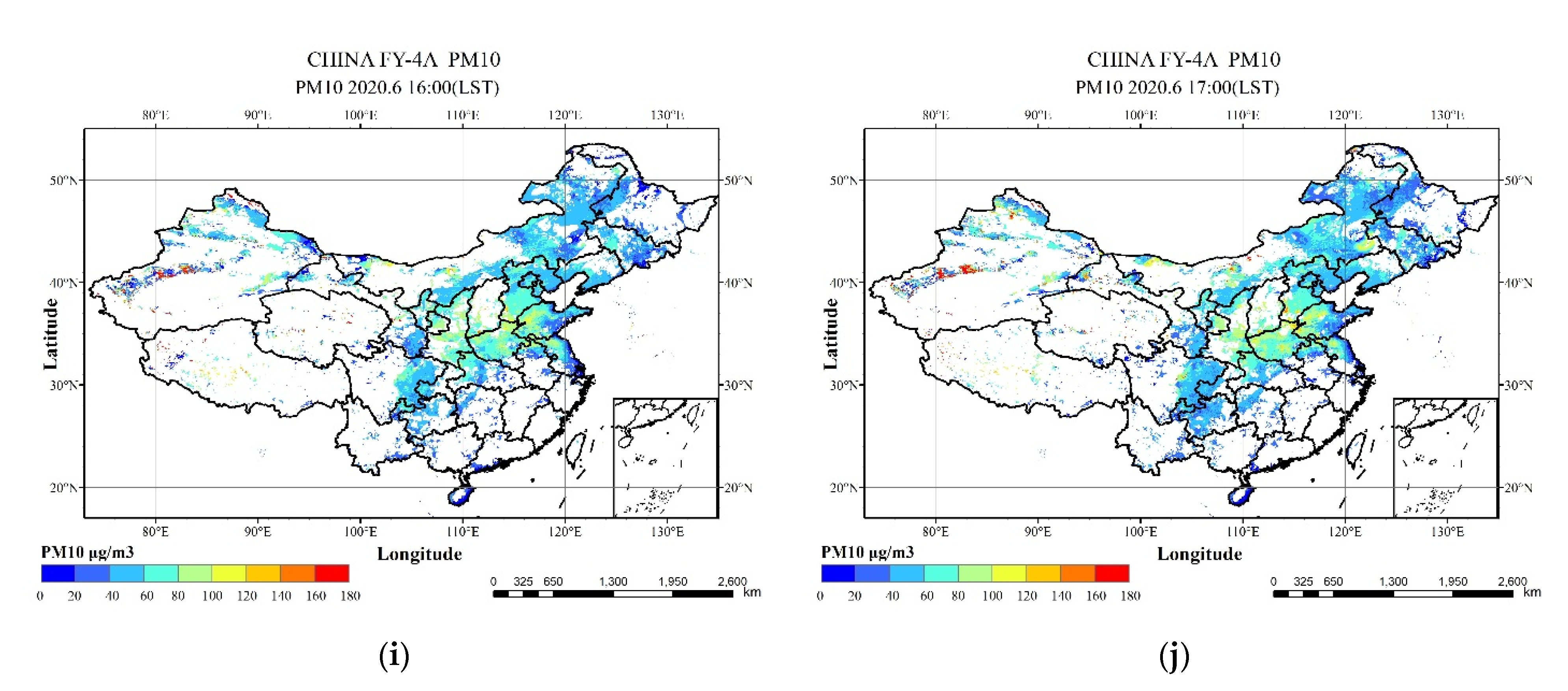
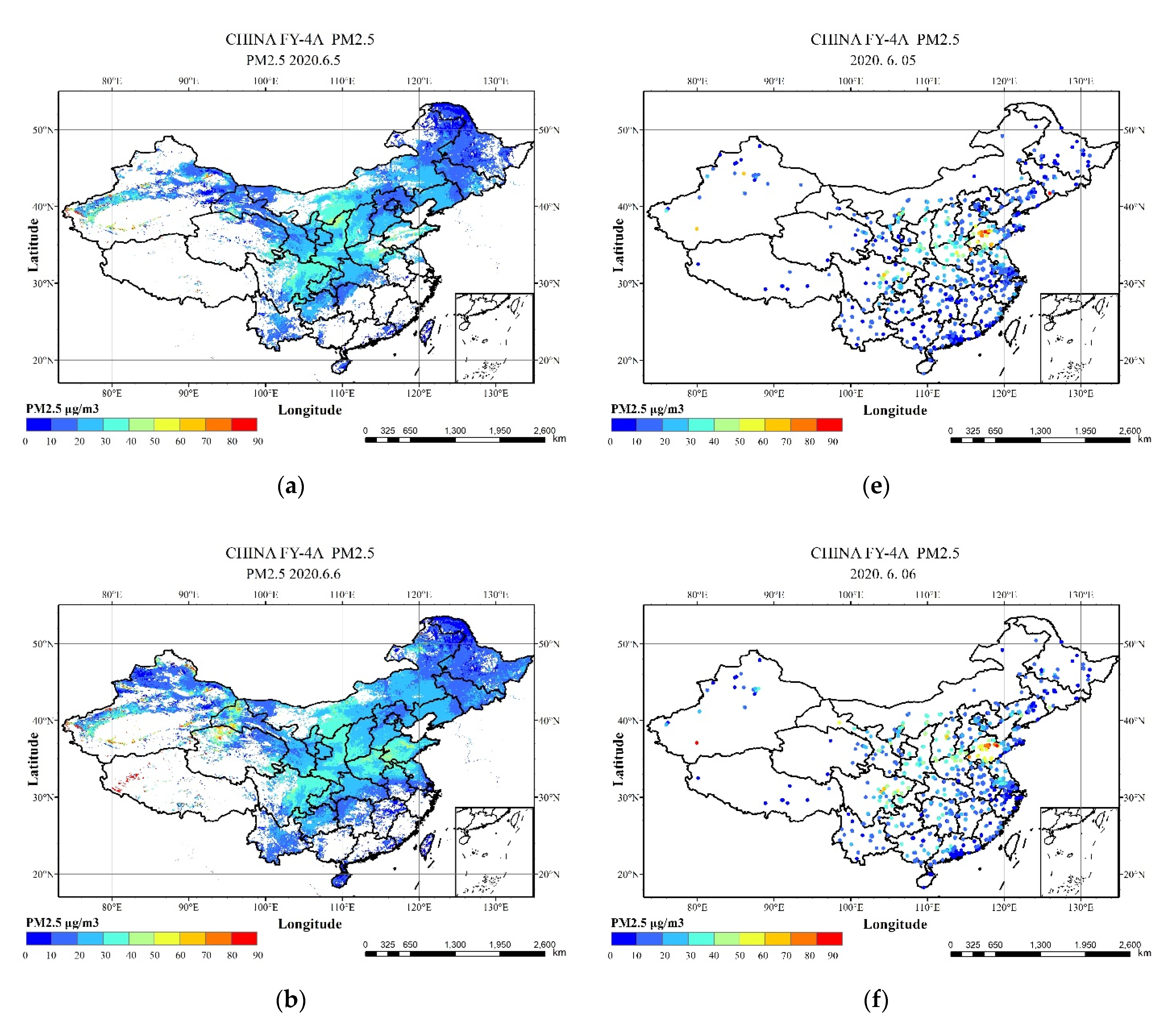
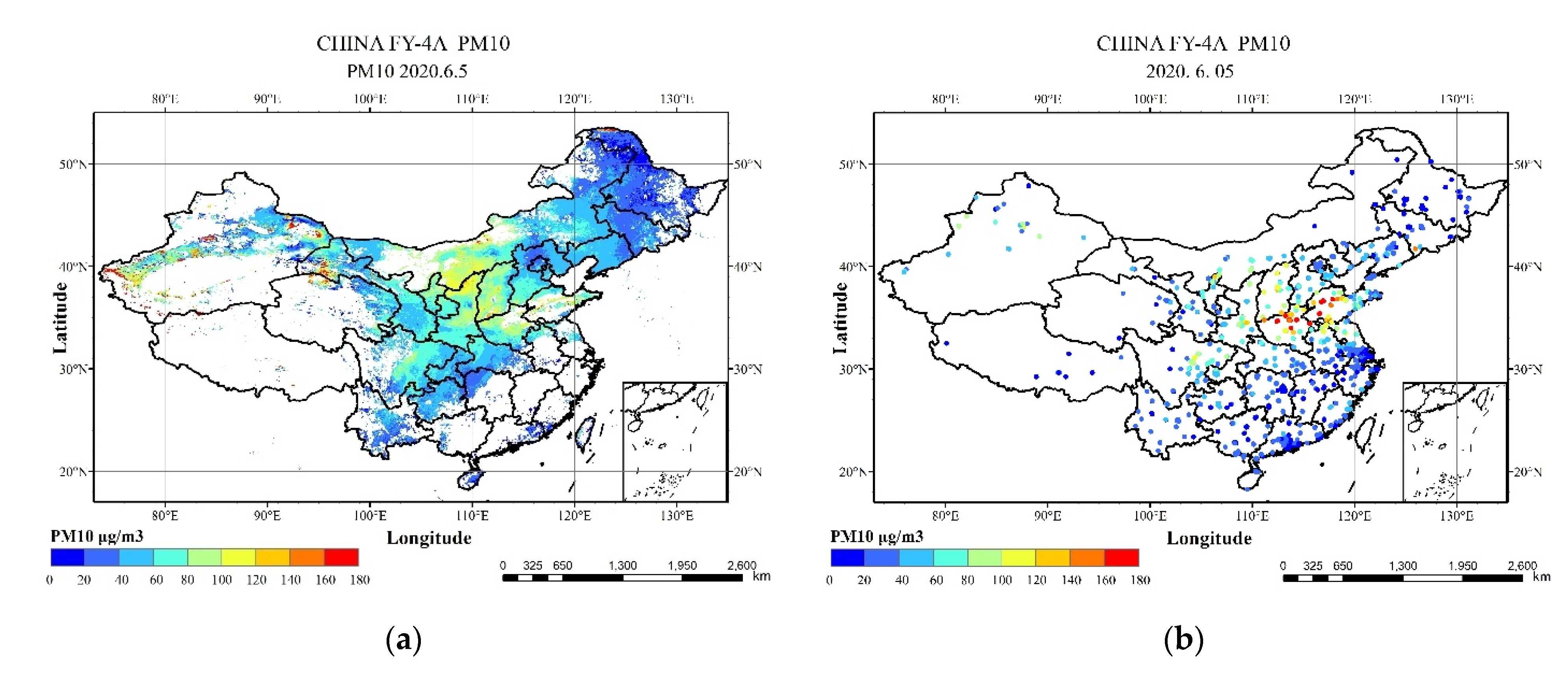
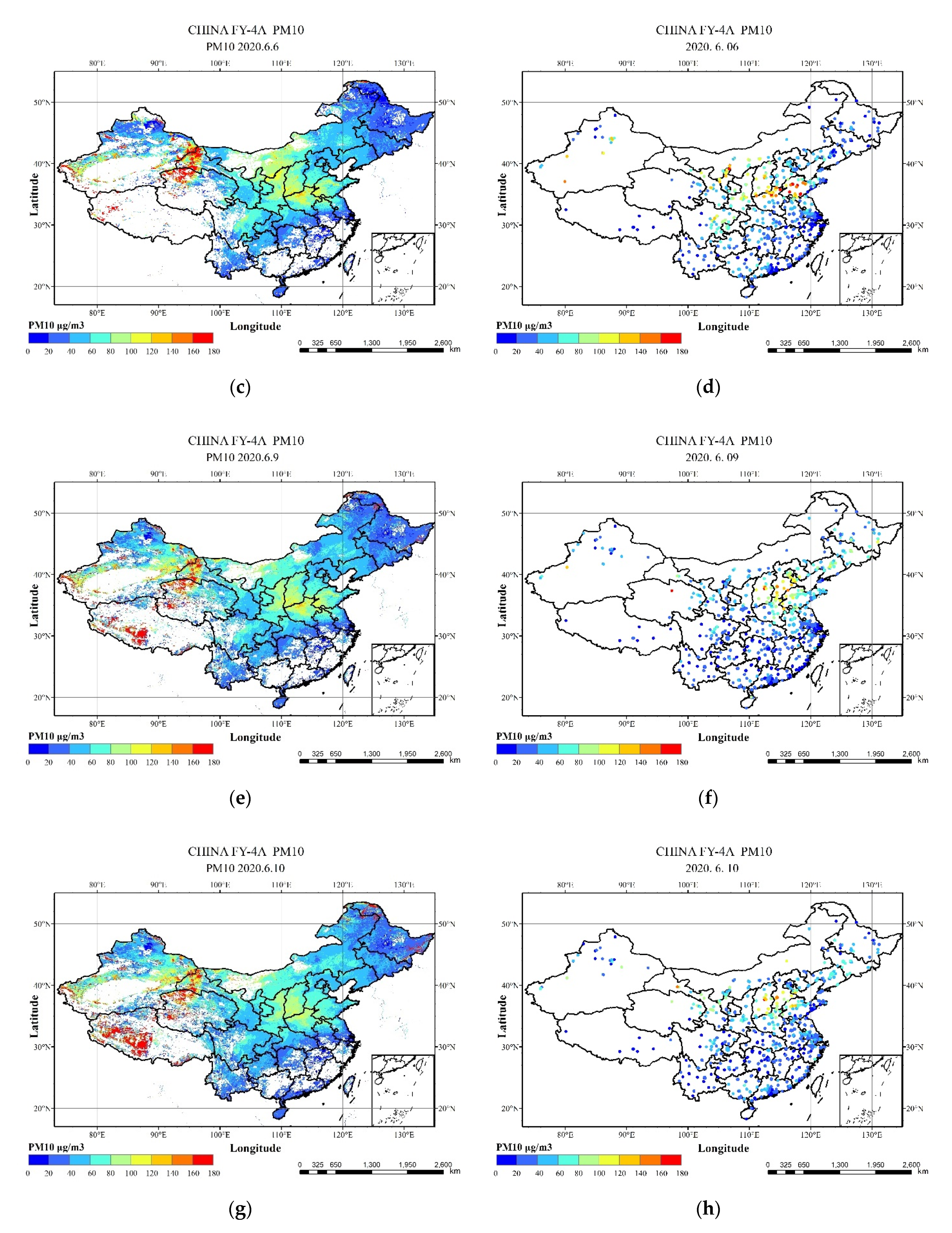
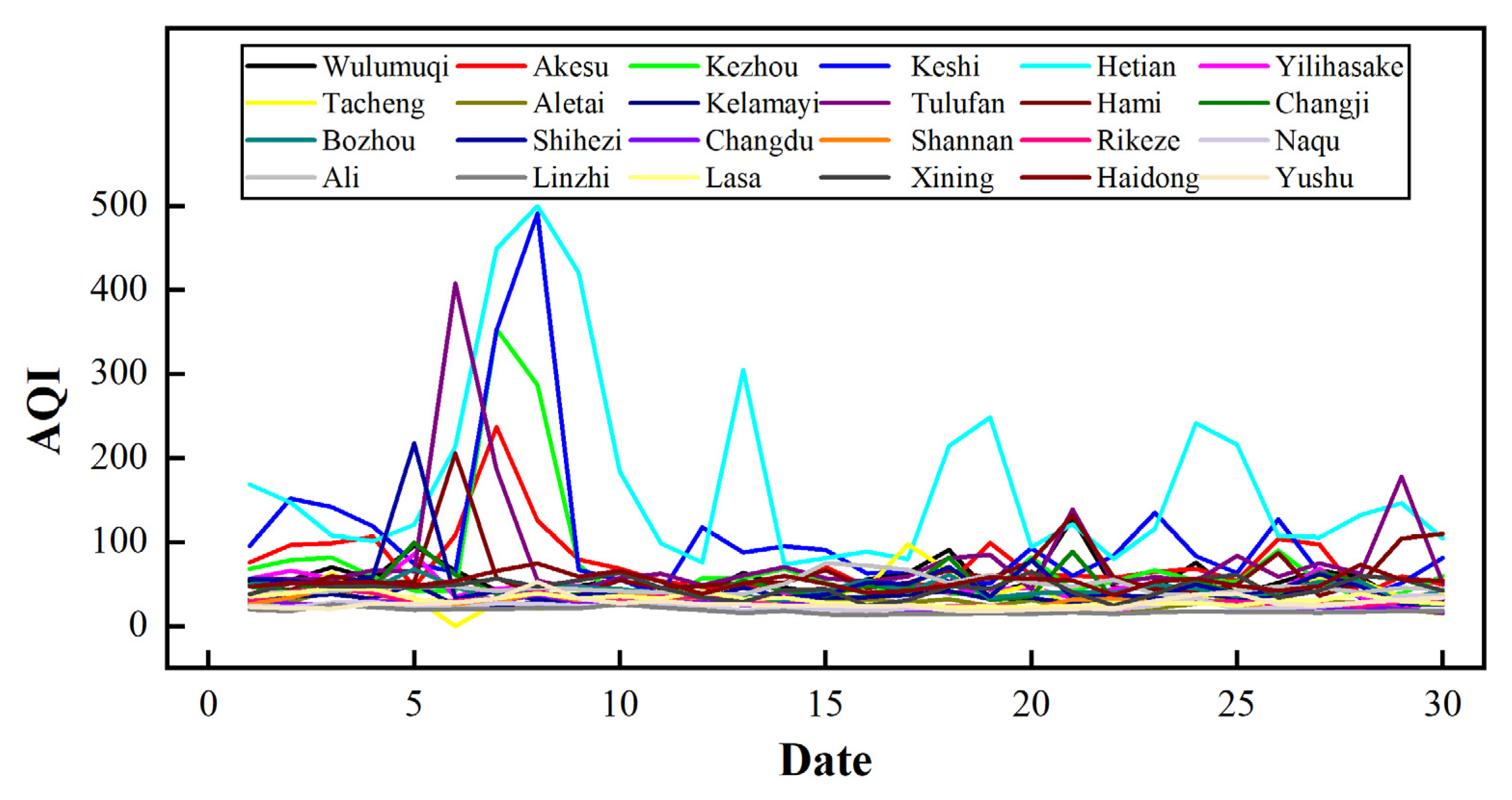
4.2. Hourly PM2.5 and PM10 Concentrations in China
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
5.2. Potential Limitations and Room for Model Improvement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Che, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Jing, J.; Cao, J.; Hsu, S.C. PM2.5 pollution in a megacity of southwest China: Source apportionment and implication. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8679–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015 (vol 389, pg 1907, 2017). Lancet 2018, 391, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Intercomparison between satellite-derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2.5 mass: Implications for air quality studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, N.; Gorai, A.K. Study of aerosol optical depth using satellite data (MODIS Aqua) over Indian Territory and its relation to particulate matter concentration. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Im, J.; Song, C.-K.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, R.; Kim, S.-M.; Yoon, J.; et al. Estimation of spatially continuous daytime particulate matter concentrations under all sky conditions through the synergistic use of satellite-based AOD and numerical models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.H.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.P.; Peng, Y.R.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space-time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- She, L.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Leys, J.; Guang, J.; Che, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y. Joint Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth and Surface Reflectance Over Land Using Geostationary Satellite Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Hong, J.; Min, Q.; Gong, W.; Zang, L.; Yin, J. Estimating hourly full-coverage PM2.5 over China based on TOA reflectance data from the Fengyun-4A satellite. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.B.; Kilaru, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.A.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chen, J.-P.; Chang, S.-C.; Jeng, Y.-J.; Chiang, W.-L.; Lin, N.-H. Interpreting aerosol lidar profiles to better estimate surface PM2.5 for columnar AOD measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) mass concentration near the ground from satellite observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Pan, X.; Li, Y. A nonlinear model for estimating ground-level PM10 concentration in Xi’an using MODIS aerosol optical depth retrieval. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordio, F.; Kloog, I.; Coull, B.A.; Chudnovsky, A.; Grillo, P.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Schwartz, J. Estimating spatio-temporal resolved PM10 aerosol mass concentrations using MODIS satellite data and land use regression over Lombardy, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Shin, M.; Im, J.; Song, C.-K.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.-W.; et al. Estimation of ground-level particulate matter concentrations through the synergistic use of satellite observations and process-based models over South Korea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Wei, P.; Ma, Y. Using support vector regression to predict PM10 and PM2.5. In 35th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment; Guo, H., Ed.; IOP Conference Series-Earth and Environmental Science: Bristol, UK, 2014; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.T.; Chen, B.; Nie, Z.; Ren, Z.H.; Xu, B.; Tang, S.H. Estimation of hourly full-coverage PM2.5 concentrations at 1-km resolution in China using a two-stage random forest model. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ran, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Teng, D.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X. Estimating PM2.5 with high-resolution 1-km AOD data and an improved machine learning model over Shenzhen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Kang, Y.; Park, S.; Im, J.; Yoo, C.; Quackenbush, L.J. Estimating ground-level particulate matter concentrations using satellite-based data: A review. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin, C.; Assoc Comp, M. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model for Ground-Level PM2.5 Estimation from Satellite-Derived 500 m Resolution AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gong, D.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, W. National-Scale Estimates of Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentration in China Using Geographically Weighted Regression Based on 3 km Resolution MODIS AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Fan, T.; Liu, L.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. The ChinaHighPM(10) dataset: Generation, validation, and spatiotemporal variations from 2015 to 2019 across China. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The relationships between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth (AOD) in mainland China: About and behind the spatio-temporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Tang, L.; Dong, J. Spatiotemporal relationship between Himawari-8 hourly columnar aerosol optical depth (AOD) and ground-level PM2.5 mass concentration in mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z. Estimation of ground-level dry PM2.5concentrations at 3 km resolution over Beijing using Geostationary Ocean Colour Imager. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Jia, L.; Su, H.; Lin, M. IEEE Estimating PM2.5 concentrations of high-resolution in taiwan island using gf-1 wfv data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 7846–7849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, S.; Li, T. Estimating the daily PM2.5 concentration in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using a random forest model with a 0.01 degrees x 0.01 degrees spatial resolution. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Jeong, J.I.; Park, R.J.; Kim, M.J. Impact of Meteorological Changes on Particulate Matter and Aerosol Optical Depth in Seoul during the Months of June over Recent Decades. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Mei, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Y.; Wei, L. Influence of Spatial Resolution and Retrieval Frequency on Applicability of Satellite-Predicted PM2.5 in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, C. Estimation of ground-level PM2.5concentration using MODIS AOD and corrected regression model over Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Gui, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.; Zhang, B.; Chi, X.; Xu, R. FY-4A satellite data based on grid surface atmospheric particulate concentration estimation in China. Weather 2020, 46, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Tugui, A.; She, L.; Qin, K.; Fan, C.; Che, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wen, Y.; et al. Hourly PM2.5 Estimation over Central and Eastern China Based on Himawari-8 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D. Remote sensing Monitoring methods of land use/cover changes in national scale. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wei, C.Y.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the New Generation of Chinese Geostationary Weather Satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Min, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P. Aerosol data assimilation using data from Fengyun-4A, a next-generation geostationary meteorological satellite. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lou, M. Unraveling the relationships between boundary layer height and PM2.5 pollution in China based on four-year radiosonde measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego Rodriguez, J.; Perez, A.; Antonio Lozano, J. Sensitivity Analysis of k-Fold Cross Validation in Prediction Error Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Kahn, R. Relationships between the planetary boundary layer height and surface pollutants derived from lidar observations over China: Regional pattern and influencing factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15921–15935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (on Trial): HJ, 633–2012; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Shen, H.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 by Fusing Satellite and Station Observations: A Geo-Intelligent Deep Learning Approach. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 11985–11993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Weng, F.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.C. Hourly PM2.5 Estimates from a Geostationary Satellite Based on an Ensemble Learning Algorithm and Their Spatiotemporal Patterns over Central East China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Wang, Z.; Luo, M.; Zhang, L.; Liao, T.; Zhao, H.; et al. Construction of a virtual PM2.5 observation network in China based on high-density surface meteorological observations using the Extreme Gradient Boosting model. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Mao, F.; Zang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Hong, J. Retrieving PM2.5 with high spatio-temporal coverage by TOA reflectance of Himawari-8. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G., Jr.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern US using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, L.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Guang, J.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y. Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Primary Types | Secondary Types | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Designation | Number | Designation |
| 1 | Cultivated land | 11 | Paddy field |
| 12 | Dry land | ||
| 2 | Forest | 21 | Woodland |
| 22 | Shrub wood | ||
| 23 | Sparse woodland | ||
| 24 | Other woodlands | ||
| 3 | Lawn | 31 | High-coverage grassland |
| 32 | Medium-coverage grassland | ||
| 33 | Low-coverage grassland | ||
| 4 | Water area | 41 | Channel |
| 42 | Lake | ||
| 43 | Reservoir pond | ||
| 44 | Permanent glacier and snow | ||
| 45 | Tidal flat | ||
| 46 | Beach land | ||
| 5 | Urban, rural, industrial, mining and residential land | 51 | Urban land use |
| 52 | Rural settlements | ||
| 53 | Other construction land | ||
| 6 | Unused land | 61 | Sand |
| 62 | Gobi | ||
| 63 | Saline alkali soil | ||
| 64 | Swamp land | ||
| 65 | Bare land | ||
| 66 | Bare rock texture | ||
| 67 | Other | ||
| 9 | 99 | undefined | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, X.; Jin, C.; Wu, S.; Zhou, X. Estimation of the PM2.5 and PM10 Mass Concentration over Land from FY-4A Aerosol Optical Depth Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214276
Sun Y, Xue Y, Jiang X, Jin C, Wu S, Zhou X. Estimation of the PM2.5 and PM10 Mass Concentration over Land from FY-4A Aerosol Optical Depth Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214276
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yuxin, Yong Xue, Xingxing Jiang, Chunlin Jin, Shuhui Wu, and Xiran Zhou. 2021. "Estimation of the PM2.5 and PM10 Mass Concentration over Land from FY-4A Aerosol Optical Depth Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214276
APA StyleSun, Y., Xue, Y., Jiang, X., Jin, C., Wu, S., & Zhou, X. (2021). Estimation of the PM2.5 and PM10 Mass Concentration over Land from FY-4A Aerosol Optical Depth Data. Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214276








