Abstract
Boulders on the seabed in coastal marine environments provide key geo- and ecosystem functions and services. They serve as natural coastal protection by dissipating wave energy, and they form an important hard substrate for macroalgae, and hence for coastal marine reefs that serve as important habitats for fish. The aim of this study was to investigate the possibility of developing an automated method to classify boulders from topo-bathymetric LiDAR data in coastal marine environments. The Rødsand lagoon in Denmark was used as study area. A 100 m × 100 m test site was divided into a training and a test set. The classification was performed using the random forest machine learning algorithm. Different tuning parameters were tested. The study resulted in the development of a nearly automated method to classify boulders from topo-bathymetric LiDAR data. Different measure scores were used to evaluate the performance. For the best parameter combination, the recall of the boulders was 57%, precision was 27%, and F-score 37%, while the accuracy of the points was 99%. The most important tuning parameters for boulder classification were the subsampling level, the choice of the neighborhood radius, and the features. Automatic boulder detection will enable transparent, reproducible, and fast detection and mapping of boulders.
1. Introduction
The seabed surface in the Danish waters is diverse regarding abiotic as well as biotic features and functions (e.g., [1,2,3]). The seabed surface geodiversity, i.e., the variety in seabed surface geology, geomorphology, and substrate, is relatively high in Danish waters as a result of the composition of the seabed surface being a combination of a drowned glacial landscape with subsequent and ongoing marine and coastal processes. Accordingly, seabed substrate displays a broad spectrum of soft and hard substrates, including areas specifically designated as stone reefs [4,5]. In coastal environments, stone reefs and boulders act as natural coastal protection, e.g., by dissipating wave energy [6], whereby they provide valuable geosystem services in relation to reducing coastal erosion and coastal hazard risk.
The seabed surface in the Danish waters also displays a high biotic diversity in terms of flora and fauna. An investigation in the southern part of Kattegat identified 67 different species of algae and 167 different animal species within an area of only 4 m2 [7]. Marine animals live, hide, and feed in areas with algae and seaweed growing on hard substrates. Hence, stones on the seabed form an important environment for ecosystems, and stone reefs are considered as important habitats in the Habitat Directive Annex 1 [8]. It has been estimated that ~10,500 km2 of the Danish seabed comprise stone reefs [4,5]. This estimate is based on existing geophysical data in combination with ground truthing data from GEUS’ marine database MARTA (www.geus.dk, accessed on 15 December 2018).
In specific areas of the Danish waters, stones have been removed from the seabed by so-called stone fishing. These stones were used for coastal constructions of dams and harbor piers. Stone fishing stopped in 1999 in Denmark, and it has been illegal since 2009 [9]. Stone fishing destroys the stone reefs and associated ecosystems. Besides, bottom trawling using large trawls and wires can also move stones and destroy stone reefs [7]. Knowledge about the seabed stones (as a hard substrate habitat), their distribution, and spatial extent is an important measure for reef protection and preservation of reef ecosystems. Valuable knowledge of stone reef locations and conditions can be obtained by mapping existing stone reefs, which is also useful for stone reef restoration, and creation of new stone reefs [2].
There is no international common agreement on a quantitative definition of a stone reef with respect to stone size and areal coverage in percentage. The Danish definition of a stone reef is an area with over 25% stones, or an area with >10% adjacent to an area with >25% stones [10]. The most common type of stone reef in Denmark consists of stones originally transported by glaciers and subsequently transported and/or exposed by marine and coastal processes, while seabed consisting of hard bedrock is rarely found in Denmark.
Stone reefs can be identified by mapping the seabed with remote sensing systems and/or with direct visualization. Usually, seabed habitat mapping is based on vessel-borne geophysical surveys using single- and/or multibeam echo sounding in combination with side-scan sonar imaging and sub-bottom profiling. Video documentation, photos, and sediment samples are acquired from remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROVs), divers, or vessels for verification of geophysical mapping [2]. However, full spatial coverage mapping of coastal areas using vessel-borne acoustic systems is a challenging task due to vessel draft limitations in shallow water. Moreover, acoustic measurements with vessel-borne multibeam echo sounder (MBES) systems cover only narrow swathes in shallow waters, which makes full coverage mapping in such areas expensive and time consuming. Side-scan sonar provides seabed imagery in 2D, also with limited spatial coverage in shallow waters. Besides, objects near nadir are difficult to identify unless a 50% overlap is achieved, which is time consuming and may not be economically feasible [11]. On the other hand, divers only collect point data for an area within their visual domain.
An alternative approach for coastal seabed mapping is using airborne LiDAR technology. Recently, topo-bathymetric LiDAR (green wavelength of 532 nm) has made it possible to derive high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) of the bathymetry in coastal zones [12,13]. This technology has successfully been utilized to cover the transition zone between land and water, and the time used in data acquisition is far less than with vessel-borne methods [14]. However, the LiDAR data processing still requires manual decision steps, which makes it rather time consuming and, to some extent, subjective and unrepeatable. The amount of subjectivity in topo-bathymetric LiDAR data processing is continuously decreasing, and improvement in the performance is an ongoing process. Different machine learning approaches have been evaluated to automate the processing steps (e.g., [15,16]).
One of the major challenges in remote sensing is to classify topographic and bathymetric data. A meta-study [17] about classification methods used in satellite-based land-cover mapping demonstrated that the parametric maximum likelihood classifier was the most commonly used approach deployed in over 32% of the studies, even though machine learning methods were routinely found to have notably higher accuracies. This could be due to fewer implementations of advanced algorithms such as traditional ones in conventional remote-sensing image-processing software packages [17]. The general definition of interpretable machine learning is the use of machine learning models for the extraction of relevant knowledge about domain relationships contained in the data. Here, knowledge is relevant if it provides insight for a particular audience to solve a specific problem [18]. Machine learning covers many different approaches to automatically extract information from data. Different machine-leaning algorithms have been applied to LiDAR point cloud data (combined height and intensity data) for land-cover classification [19]. Ref. [20] examined different machine learning approaches for boulder detection in a coastal marine environment using MBES data. The best standalone result was obtained when an object-based random forest method was used. Recent studies have confirmed random forest as a valid machine learning approach for benthic habitat mapping [21]. In [22], stony areas were detected from hydroacoustic data, and automated stone detection is under development. Ref. [23] used the random forest machine learning model for coastal marine habitat mapping based on point cloud data from MBES to detect underwater vegetation. They derived predictive features from the native MBES point cloud in a similar manner to terrestrial LiDAR data analysis. The results were very promising, with an accuracy of 87–96% [23].
Random forest machine learning creates decision trees from a set of features and a predefined classification. Reference [24] tested the performance for different numbers of trees on different datasets and suggest selecting a number of trees between 64 and 128.
As the use of machine learning for habitat classification is increasing quickly, the use of topo-bathymetric LiDAR data is growing rapidly at the same time [25]. Obtaining clean bathymetry data from topo-bathymetric LiDAR data without outliers and correcting for refraction is still a challenging process [26]. Different machine learning approaches have been evaluated for habitat mapping, or to derive clean bathymetric data, including refraction correction [15,16].
Benthic habitat mapping using machine learning on data from topo-bathymetric LiDAR is a new field, where different machine learning models have been tested [27]. Ref. [27] found that the random forest model yielded the best results in accordance with other studies. However, most habitat mapping with topo-bathymetric LiDAR data is carried out on DEMs and not directly on the point cloud [27]. Few point-cloud studies have been made, in which all different kinds of elements on the seabed were found (e.g., boulders, vegetation, shipwreck) [28] and not a single habitat, such as boulders. So far, the random forest algorithm has not been applied to topo-bathymetric LiDAR point clouds for detecting a single habitat type.
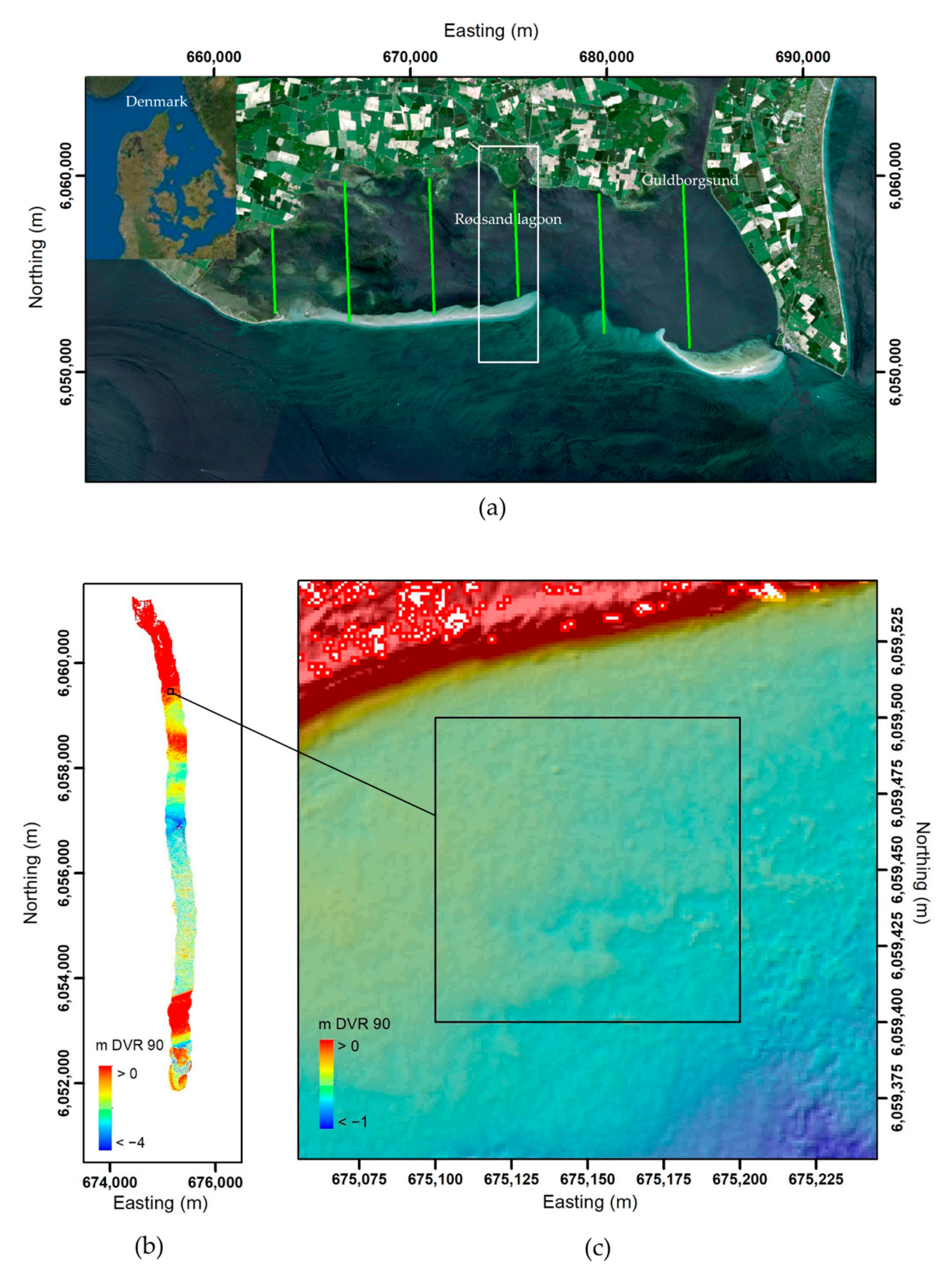
In this study, we aim to develop an automated approach to directly map stand-alone boulders from point clouds derived from topo-bathymetric LiDAR data. The objectives are (1) to process the LiDAR data to generate a point cloud containing only seabed data, (2) to develop a machine learning algorithm for automated boulder detection, (3) to identify the most important tuning parameters and features for boulder detection, and (4) to evaluate the results using relevant performance scores. The study site is the shallow-water Rødsand lagoon in Denmark. It provides an optimal area to study the applicability of our approach on the boundary between land and sea (see Figure 1). The study site was divided into a training and a test area with similar geometrical characteristics.
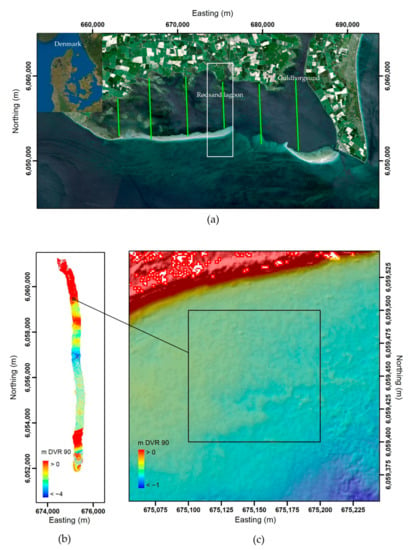
Figure 1.
(a) Rødsand lagoon with flight lines (green lines). Images: Copernicus Sentinel data 2021, processed by ESA, Esri, DigitalGlobe, GeoEye, i-cubed, USDA FSA, USGS, AEX, Getmapping, Aerogrid, IGN, IGP, swisstopo, and the GIS User Community; (b) DEM of the study strip with 1 m × 1 m resolution; (c) DEM of the study area in the northern part of the lagoon, the square defines the training/test area of 100 m × 100 m outlined in the text and the resolution is 1 m × 1 m. Projection is in ETRS89 UTM Zone 32N with units in meters.
2. Study Site
The Rødsand lagoon is located at the southern coast of Lolland and Falster in southern Denmark, adjacent to the Fehmarn Belt in the western Baltic Sea (Figure 1). The narrow strait Guldborgsund connects the lagoon to the northern part of the inner Danish waters. The lagoon is approximately 30 km × 10 km; it is semi-enclosed by a barrier spit and two barrier islands [29]. The water depths range down to 4 m in the western part and down to 8 m in the eastern part of the lagoon. The lagoon is a Natura 2000 and RAMSAR area [30].
The landscape of Lolland and Falster was formed by glacial processes during the Weichselian glaciation [31]. The moraine landscape is made of a WNW–ESE oriented ridge and runnel morphology aligned in the direction of ice shield propagation during the final stages of the glaciation. The adjacent seabed in the lagoon has a similar origin, containing boulders. After deglaciation, a number of sandy barriers formed on top of the elevated ridges of the drowned moraine landscape [32], and the lagoon was established behind those. The seabed of the lagoon is subject to shallow marine and coastal processes.
Wave processes form the barriers between the Rødsand lagoon and the open water. The sediments comprising the barriers stem from wave-driven onshore transport of sand from the shoreface and alongshore supply of sand from the adjacent coasts by littoral drift [31,33].
The lagoon exhibits a microtidal environment with a mean tidal range of 0.1 m, and tidal currents are very small. The driving forces of the water exchange between the lagoon and the inner Danish waters are basin-scale flushing and meteorological forcing. These driving forces lead to water level fluctuations, which cause flow circulation in the lagoon.
The salinity of the water in the lagoon is about 10–20 PSU. These brackish conditions are caused by the exchange of brackish water from the Baltic Sea and salty water from Kattegat [34]. Waves in the lagoon are fetch limited. The low to moderate waves and currents generate bed shear stresses that can cause bed erosion and suspended sediments in the water column. The latter increases the turbidity of the water.
The top layer of marine sediments in the lagoon is very thin, and the wave-driven processes in the lagoon lead to sediment erosion, transport, and deposition, which may bury the boulders in some areas while exposing the boulders in others.
The seabed contains marine habitats in the form of stone reefs and sandbanks that are suitable as physical foundation for flora, as algae and eelgrass meadows, to grow and flourish provided other environmental parameters are suitable. These habitats serve as food supplies, homes, and hiding places for marine life. Stone reefs were mapped as part of the FEMA baseline studies in relation to the Fehmarnbelt Fixed Link [35], and presented also as part of the marine habitat mapping of the inner Danish waters [1]
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Surveys and Instruments
LiDAR data and RGB images for orthophoto generation were collected by Airborne HydroMapping GmbH (AHM) during a survey on 7 September 2015 (Figure 1a). The weather conditions were of clear sky and average wind velocities of 6–7 ms−1 (DMI, Weather archive).
A twin-engine aircraft (Tecnam P2006T) was used as flight deck with a laser scanner (VQ-880-G, RIEGL LMS) integrated in the frontal part of the aircraft. The laser scanner emits a green laser pulse with a wavelength of 532 nm and a pulse repetition rate of up to 550 kHz. The flight altitude was 400 m, which, combined with a laser beam divergence of 1.1 mrad, yields a laser beam footprint of ~0.4 m.
Aerial images were acquired with an RGB camera (Hasselblad H/39, focal length of 35 mm) integrated in the back of the aircraft. The ground sampling distance (GSD) of the RGB images is ~8 cm at a flight altitude of 400 m. The RGB images showed the reflection from the water and could not serve as ground truth data.
The position and altitude of the aircraft were recorded with a GNSS/IMU navigation system at a rate of 256 Hz, consisting of a compact GNSS antenna (NovAtel 42G1215A-XT-1-1-CERT) mounted on top of the aircraft and an IMU (IGI AEROcontrol-IIe) integrated on top of the laser scanner.
The laser scan pattern is circular, with an incidence angle of 20°, generating curved parallel scanlines with a swath width of ~400 m at a flight altitude of 400 m. The point density is ~20 points/m2 at a flight altitude of 400 m and a flight speed of ~80 kn (~150 km/h). According to the sensor manufacturer, the typical water depth measuring range of the VQ-880-G is about 1.5 Secchi depth. The laser scanner system records full waveform data. Intensity information is provided for each returned signal. For each returned signal, the collected LiDAR data contained the following information: xyz coordinates, GPS time stamp, amplitude, reflectance, return number, and laser beam deviation [14,36].
3.2. Topo-Bathymetric LiDAR Data Processing
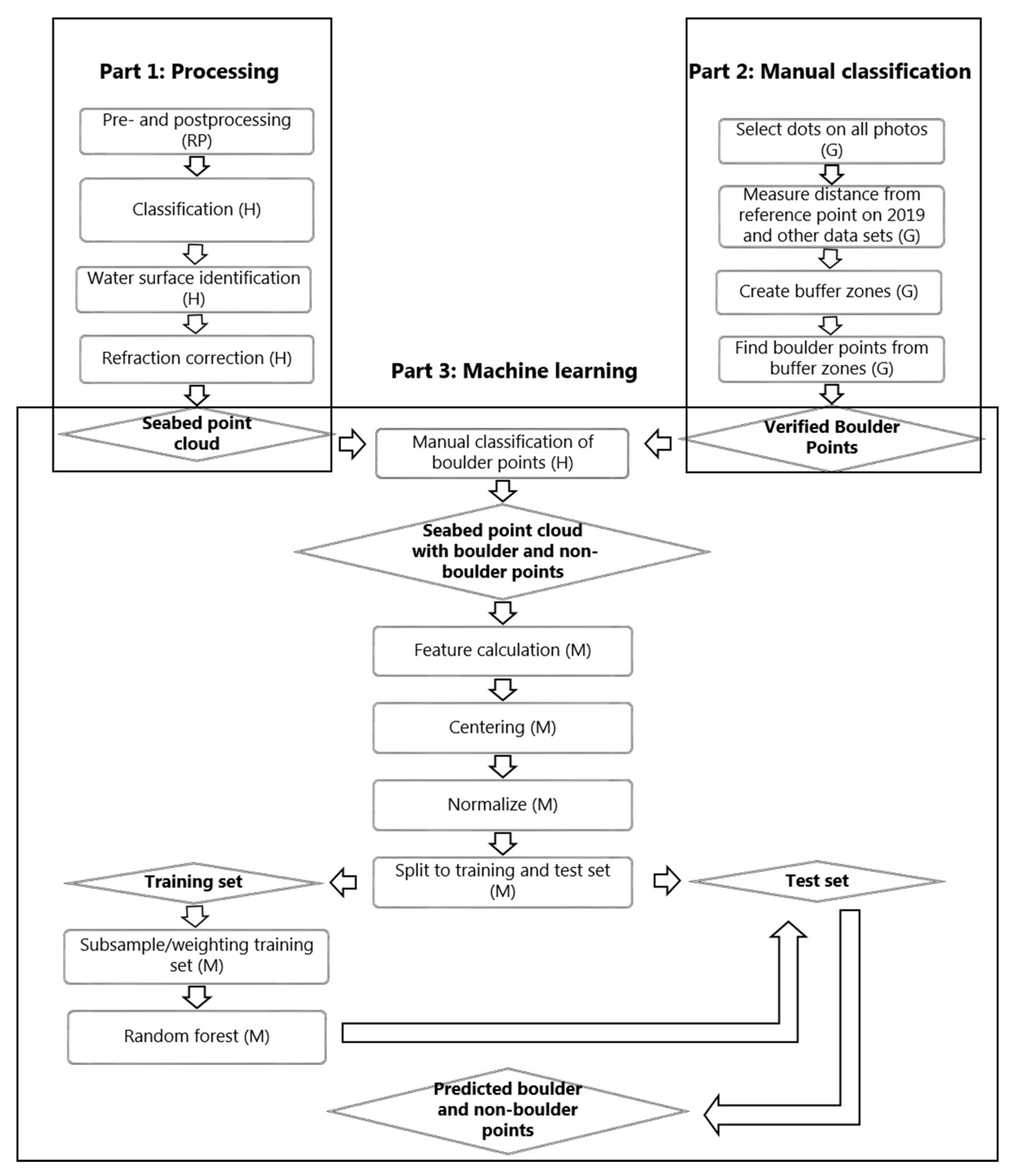
The post-processing steps were carried out using the software RiProcess by RIEGL LMS, and the software HydroVISH developed by AHM (Figure 2). The flight trajectory was calculated using the software packages Aerooffice and GrafNav and incorporating correction data of continuously operated GPS base stations. RiProcess was used for determining the boresight calibration parameters between IMU and laser scanner prior to the data collection, and for strip adjustment after the data collection [14].
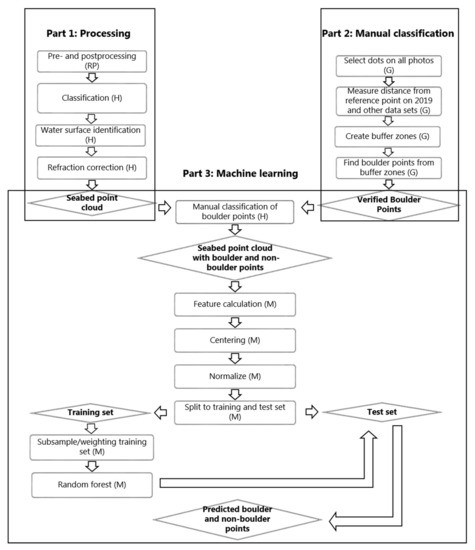
Figure 2.
Workflow of the data processing described in the text. Abbreviations: RP = RiProcess, H = HydroVISH, AM = ArcMap, M = Matlab.
It is necessary to distinguish between points in the water column and points on the seabed, both for detecting objects on the seabed and for performing refraction correction of all points below the water surface. Refraction correction is necessary due to different light velocity in air and water (Figure 2, part 1). The differentiation between seabed and water points was performed first by considering and computing attributes, such as classification, clustering (density), GPS time (time stamp), intensity, last return, number of returns, PointSourceID (strip number), positions (xyz coordinates), and return number. The point density is utilized to ascribe points to certain clusters. For this, the point cloud is further divided into fragments containing clusters to facilitate the data handling. The clusters are then used to remove flaw echoes, especially below the seabed, while a preclassification is carried out to distinguish between seabed and water points.
A triangular mesh representing the water surface was generated based on neighborhood analysis, point density, and the water surface encircling line (equal to water edge line). The encircling line was derived by creating the concave hull of the point cloud using alpha shapes. The refraction correction for the remaining points below water was calculated using the water surface mesh after the removal of flaw echoes (see [14]).
3.3. Manual Classification of Stones on Training and Test Areas
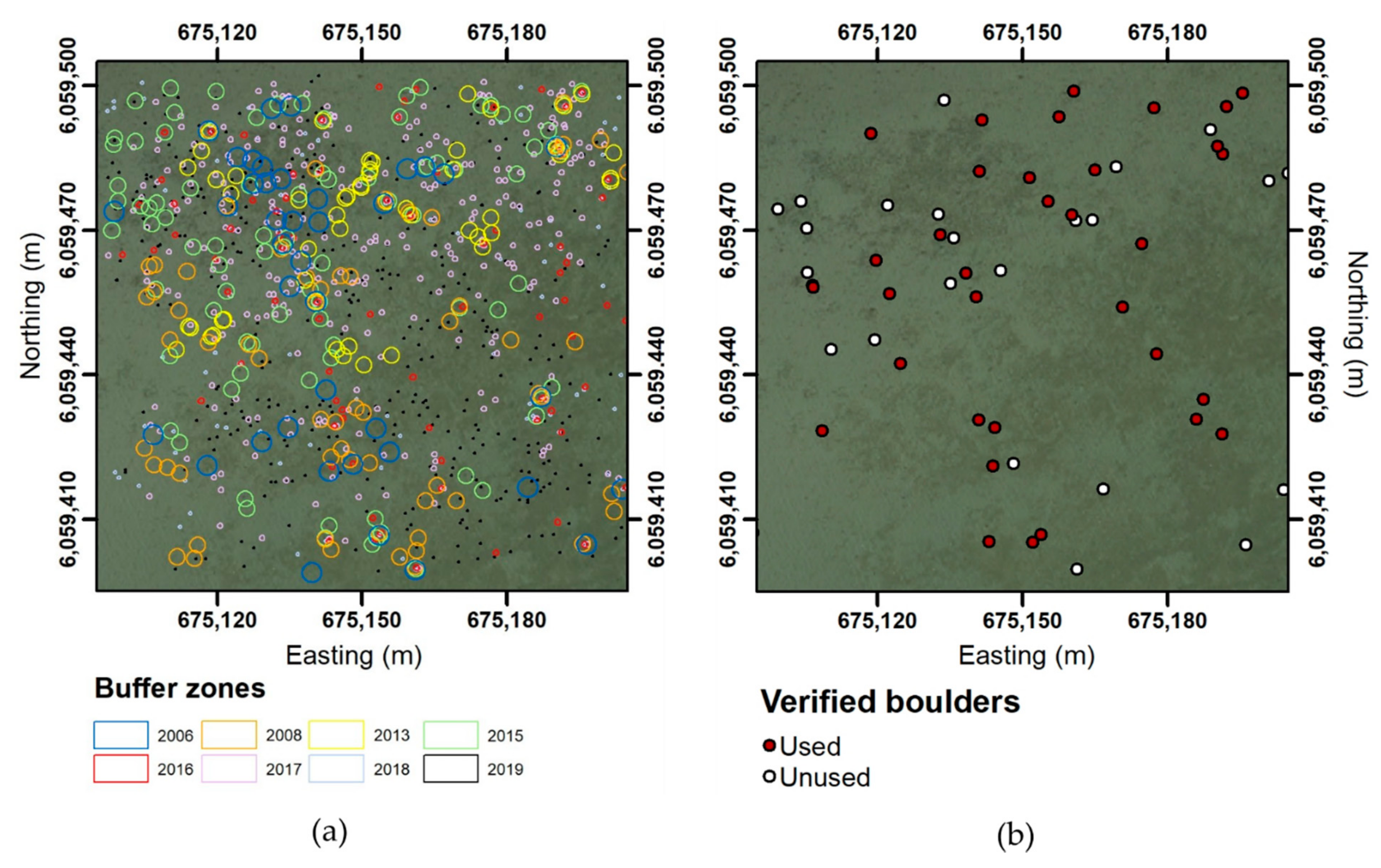
Boulder and non-boulder points need to be classified in the training set and the test dataset. This is manually performed by using RGB orthophotos from the geoDanmark database (Figure 2, part 2) from eight different years: 2006, 2008, 2013, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019 (cf. Table 1). Small black dots that can be either vegetation or boulders, and white dots that can be boulders above water, reflections from the camera, or sea spray were identified on these orthophoto images. All black and white potential boulders were marked in each photo using ArcMap. Since the accuracy of the georeferencing of the orthophotos improved significantly over the years (cf. Table 1), the precise locations of these points might be different on each orthophoto. Thus, we defined a buffer zone around the potential boulders depending on the uncertainty of the georeferencing of each photo. The orthophoto dataset obtained in 2019 was decided to serve as the base line from which uncertainty in georeferencing can be estimated. Fixed points on objects such as houses about 1 km away from the 100 m × 100 m training/test area were used for the georeferencing uncertainty test. For this, the distance was calculated between these fixed points identified in the different photos and the corresponding points of the 2019 dataset, where the longest distance was set to represent the uncertainty. A minimum boulder size of 40 cm diameter was used due to the minimum object size resolved in the LiDAR (footprint size) and the minimum dots size measured in the orthophotos. The buffer zone for each dataset was calculated using a stone radius of 20 cm and adding the georeferencing uncertainty (Table 1).

Table 1.
Orthophoto properties.
Separating potential boulders from vegetation on the photos was performed by assuming that vegetation spots may change their position from year to year, while boulders are stable and show no positional changes over the years, but they could be covered due to sediment transport and deposition. A point was classified as boulder if potential boulder points from three different years were located inside the same buffer zone or in overlapping buffer zones. The classified boulder locations from the orthophotos were subsequently detected in the LiDAR point cloud. Boulder locations that are evident in the orthophoto, but cannot be identified in the point cloud, were disregarded.
3.4. Stone Detection Using Machine Learning
3.4.1. Features
To create input for the machine learning algorithm (Figure 2, part 3), three spectral features (calculated from intensity), five relative position features (calculated from depth), and six geometric features (calculated from the covariance matrix) were determined. Neighborhood analysis was used for feature calculation and the search size was set to a radius of 0.5 m, 1 m, 2 m, or 3 m, respectively. Some of the features were calculated in two different neighborhoods (0.5 m and a larger radii), which resulted in a total set of 19 features (Table 2).

Table 2.
Features and neighborhood radius.
The radius of 0.5 m was chosen as the minimum radius due to the laser footprint size of 0.4 m. The small radius allows to recognize the boundaries between stone and non-stone points, and therefore the geometrical differences between the stones and seabed. Only points with at least four neighbor points within the area of the radius were selected (Table 3). The larger radii were chosen to detect geometrical differences in areas containing multiple stones and areas without stones. The radius of 3 m is sufficient to cover entire boulders, and therefore differences between areas with and without boulders are recognized. By testing with only the small radius and with a large radius of 1 m, 2 m, and 3 m radius, a sensitivity analysis was performed to define the appropriate radius.

Table 3.
Orthophoto properties.
The data were imported and visualized from the custom-built lasdata.m [37] function in Matlab, and the feature extraction algorithm was inspired from the custom-built estimateNormal.m [38] function by using the built-in Matlab functions cov(), eig(), and KDTreeSearcher.
The LiDAR sensor retains the signal amplitude of the returned echo, where the intensity is the strength of the reflected signal [39]. The mean of the intensity was calculated for all neighborhoods as well as the standard deviation. The depth to the seabed points as z coordinate was measured with reference to the Danish Vertical Reference level (DVR90; mean sea level). The elevation change dz is the difference in z of the point and the lowest point in the neighborhood, and it was calculated for all neighborhoods as well as the mean and the standard deviation of the depth.
The best-fitting plane of the neighborhood was calculated from the neighborhood points using the built-in Matlab function pcfitplane. The distance between the point and the plane (Dp) was only calculated for the neighborhoods of the larger radii, because the small neighborhood did not contain enough points to fit a reasonable plane. The Matlab function pcfitplane fits a plane to a point cloud that has a maximum allowable distance from an inlier point to the plane. The function returns a geometrical model that describes the plane [40]. The distance used for this calculation was 0.1 m. The equation for the plane is determined by the pcfitplane function in the form of
where (x,y,z) can be all points that constitute the plane and fulfil the equation, the vector is the normal to the plane and , where is a specific point on the plane.
The distance between the plane and the point cloud point was then determined from the equation:
where are the coordinates of the point, to which the distance is calculated, and A to D are the values from the plane equation.
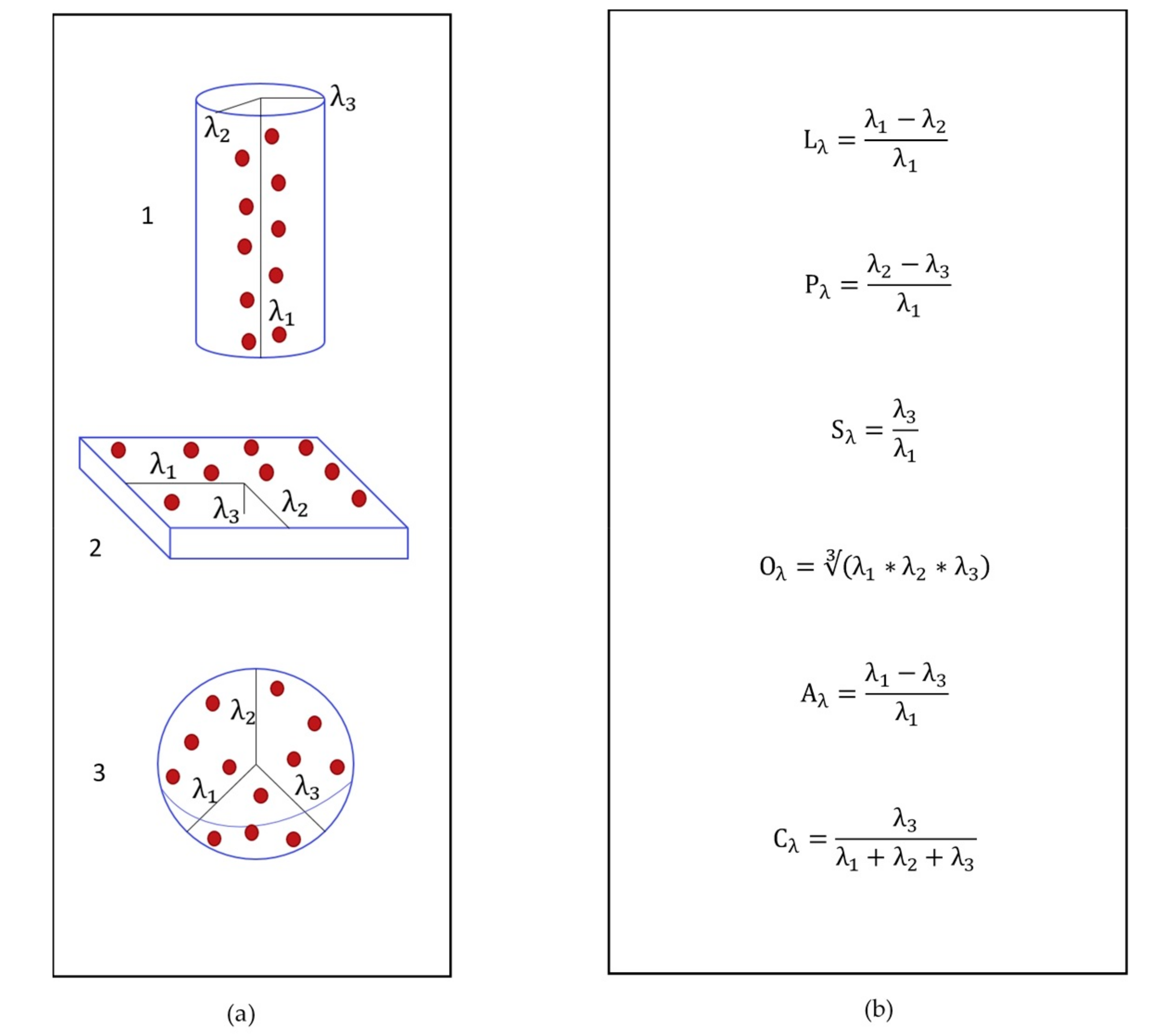
The geometrical distribution of the point cloud is described by tensor field analysis. The representation of anisotropic characteristics such as linearity, planarity, and sphericity was determined for each point in the point cloud by calculating the geometric derivatives in the local neighborhood. This was carried out by calculating the covariance matrix and the eigenvalues of the diagonalized matrix:
where N is the number of observations in the neighborhood, contains all observations in the neighborhood, and is the mean of the observations.
The eigenvalues were calculated according to:
where is the eigenvectors and is the eigenvalues, λ1, λ2, and λ3.
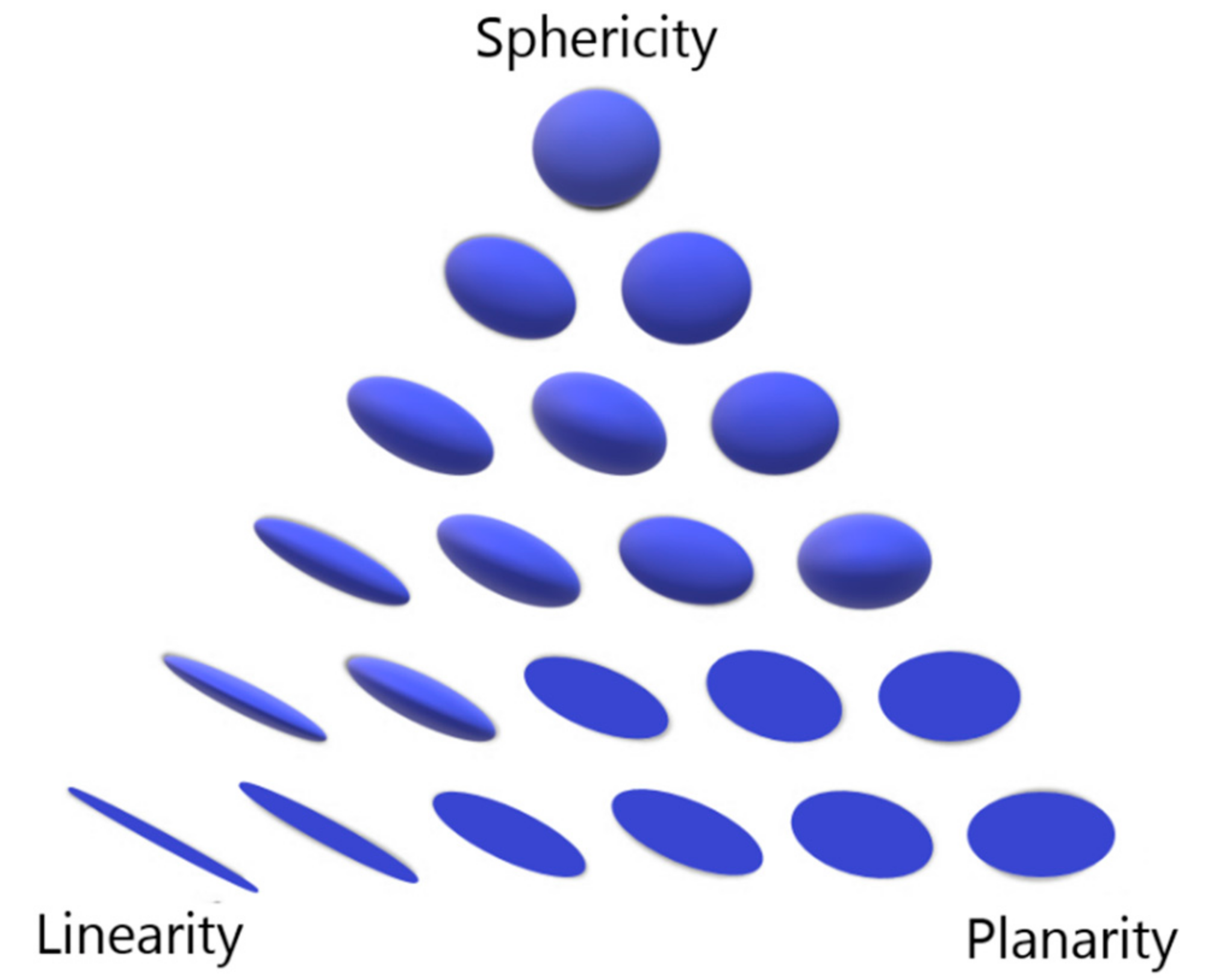
The resulting distribution characteristic of the point and the surrounding points in the neighborhood is represented as an ellipsoid, where the eigenvalues define the proportions of each dimension (Figure 3). The ratio between the values describes how well the points resemble a line, a plane, or a sphere [41].
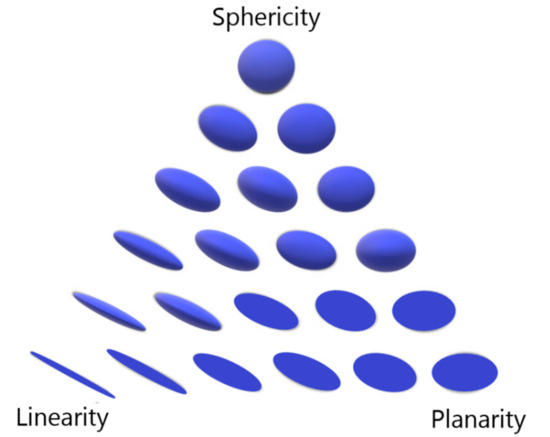
Figure 3.
Ellipsoid representation of relationship between sphericity, linearity, and planarity (after [41]).
The local neighborhood included all points in a sphere with a 0.5 m radius around each point of the point cloud. The eigen-features were calculated by choosing the eigenvalues as λ1 ≥ λ2 ≥ λ3 > 0. Linearity describes points on a line and is high if λ1 is much larger than λ2 and λ3. By calculating the linearity, it can be determined how much the points in the area constitute a line (Figure 4a(1)). The linearity is 1 if the points lie on an exact line, while it is 0 if the distribution is completely random. Planarity describes how well the points constitute a plane (Figure 4a(2)). The planarity is high if λ1 and λ2 are near the same size, while λ3 is much smaller. Sphericity describes how well the points constitute a sphere (Figure 4a(3)). The sphericity is high when all three λ values have almost the same size. Omnivariance describes the geometric mean of the eigenvalues. It describes how much the semi-minor axis differs from the semi-major axis of the ellipsoid defined by the eigenvalues. It describes if the average point density in all directions is high or low. Anisotropy describes whether the points are distributed in a specific direction, or if they are randomly distributed. The change of the curvature describes the degree of bending of a curved line or a plane and is the derivative of the curvature (Figure 4b) [23,42,43].
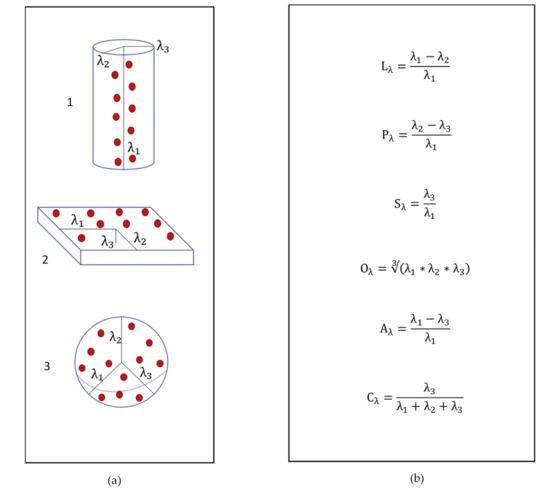
Figure 4.
(a) Visualization of (1) linearity, (2) planarity, and (3) sphericity (after [43]). (b) Equation for linearity (Lλ), planarity (Pλ), sphericity (Sλ), omnivariance (Oλ), anisotropy (Aλ), and change of curvature (Cλ).
All features outlined above were calculated for each point in the point cloud. All feature values were subsequently centered by subtraction of the mean value of each feature and normalized using minimum–maximum feature scaling to avoid predefined feature preferences prior to the tuning process in the random forest algorithm (Figure 2, part 3).
3.4.2. Random Forest Automatic Stone Detection
Random forest is a machine learning model creating decision trees from a set of features and a predefined classification. The algorithm creates trees by randomly choosing between the features and their values. To avoid overfitting, the most likely class for the classification is chosen from a subset of randomly generated trees. The classification is made by using the most represented class for all trees [44].
The used random forest model is point-based. Each boulder can consist of several boulder points, and the mentioned features are calculated for each of those points using the values from the surrounding points in the neighborhoods. The in-built Matlab function TreeBagger was utilized for the stone detection. Bootstrap-aggregated decision trees were created by using a random subset of predictors for each decision split in each tree as in the common random forest algorithm [45]. A new training set was developed with a random set of features for each node in each tree. Features were chosen from the original feature set but with replacement, so that the same feature can be represented multiple times in the new training set. For each node, the same number of features were represented, but not all features. Two split criteria were evaluated: standard CART and curvature. The standard CART algorithm selects the split predictor that maximizes the split-criterion gain over all possible splits of all predictors [45]. For the CART criterion, the best splitting value was found by Gini impurity [46].
The curvature criteria select the split predictor that minimizes the p-value of chi-square tests of independence between each predictor and the response [45].
The 100 m × 100 m study area (Figure 1) was divided into a training and a test set by a diagonal line across the area to avoid large geometrical differences and to have a similar heterogeneity in the two areas (Figure 2, part 3). The random forest algorithm was used on the test set with features calculated for the small neighborhood radius of only 0.5 m, and with both 0.5 m and a large neighborhood radius of 1 m, 2 m, and 3 m.
The 100 m × 100 m area contained nearly 255,000 points, of which about 2000 points (0.8%) were classified as boulder points. The dataset is imbalanced with a large overrepresentation of non-boulder points. Combinations of subsampling and classification cost were tested to avoid the algorithm’s tendency to classify as non-boulder points. Randomly distributed non-boulder points were selected along with all boulder points. Different datasets were created with a ratio between boulders and non-boulders of 1:1–1:12 and 1:343 (all the points).
An equivalent classification cost was used, weighting boulder points to be equally as important as the overrepresentation of non-boulder points. All features calculated from the 0.5 m radius, 0.5 m, and 1 m radius, 0.5 m and 2 m radius, and 0.5 m and 3 m radius were individually tested for all subsampling/weighting levels and with the two split criteria. These tests yielded 104 different combinations. The results were evaluated using the F-score, by which the best radius/subsampling combinations were found (Figure 2, part 3).
The feature importance score was determined for the best radius/subsampling combinations using the feature selection Matlab function: OOBPredictorImportance. The function was used to detect the order of the out-of-bag feature importance, and it calculates the out-of-bag permuted delta error, which is the error for the prediction when all values for one feature are permuted compared to using the correct values for all features. This error was calculated for each feature. By using enough trees for the TreeBagger algorithm, the feature importance value will no longer depend on each created tree. For this process, 10,000 trees were created (Figure 2, part 3).
3.4.3. Performance and Accuracy Assessment
Statistical measures were applied to evaluate the performance. The predicted data points fell into four categories, for which the performance was evaluated from: TP = true positive, FP = false positive, TN = true negative and FN = false negative. These categories were used to describe the performance of the model. However, different performance measures were found depending on how the categories were handled. Accuracy indicates the percentage of correctly classified points. However, with an imbalanced dataset, the accuracy can be good even though the model is not able to predict any stones correctly. Therefore, other additional measures are required. Cohen’s kappa coefficient evaluates whether the predicted result has occurred by chance. The precision shows the percentage of the predicted boulder points that are classified correctly. The recall gives the percentage of correct boulder points that are predicted. The F-factor is the harmonic mean between the recall and precision, considering both measures [47]:
All these performance measures are point-based. They determine the accuracy of each boulder point even though each boulder consists of several points. A cluster analysis was further utilized to determine how well the model is suited to detect each boulder. The Matlab clustering algorithm, i.e., the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), was used to group the points from each boulder. All non-boulder points were removed, and only the boulder points were clustered. The algorithm was used to group the points from each stone. All boulder points are part of a cluster, while only one point is sufficient to constitute a cluster. The algorithm detects clusters with a high density of points from a neighborhood defined by a radius. By using the algorithm on the test set with the manually classified boulder points, a minimum and maximum radius were determined, which created exactly the same clusters as the boulders in the test set. The average of these two radii was used as radius for the DBSCAN algorithm.
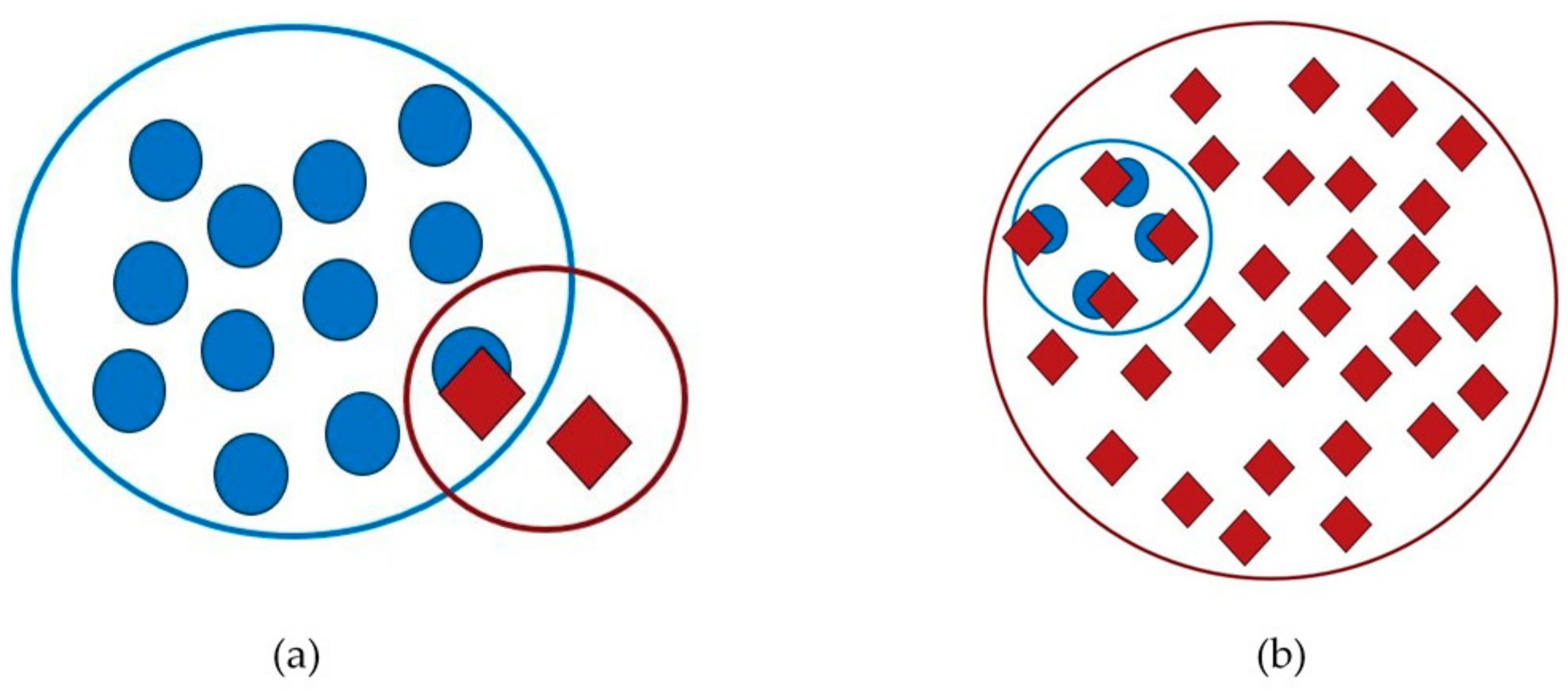
The detected boulders in the predicted set were coupled with the boulders in the verified set. By comparing the equivalent clusters in the predicted and verified sets, the percentage of overlapping points was determined, and it was used to evaluate the success in boulder detection. A 50% overlap between predicted and verified points was found to be sufficient. This corresponds to situation a (Figure 5a), which would be determined as a predicted boulder, while it would not be determined as a predicted boulder in situation b (Figure 5b).
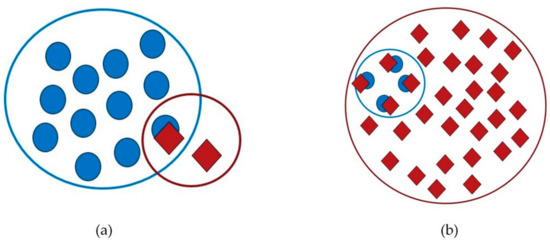
Figure 5.
Blue is verified boulder points and red is predicted boulder points. (a) A 50% overlap of the predicted boulder points. (b) Less than 50% overlap of the predicted boulder points.
The clusters in the verified and in the predicted set were used to determine the recall, precision, and F-score for the boulders by determining the number of correctly predicted boulders (I), the number of predicted boulders (S), and the number of boulders in the test set (T).
4. Results
4.1. Manually Classified Boulder Points
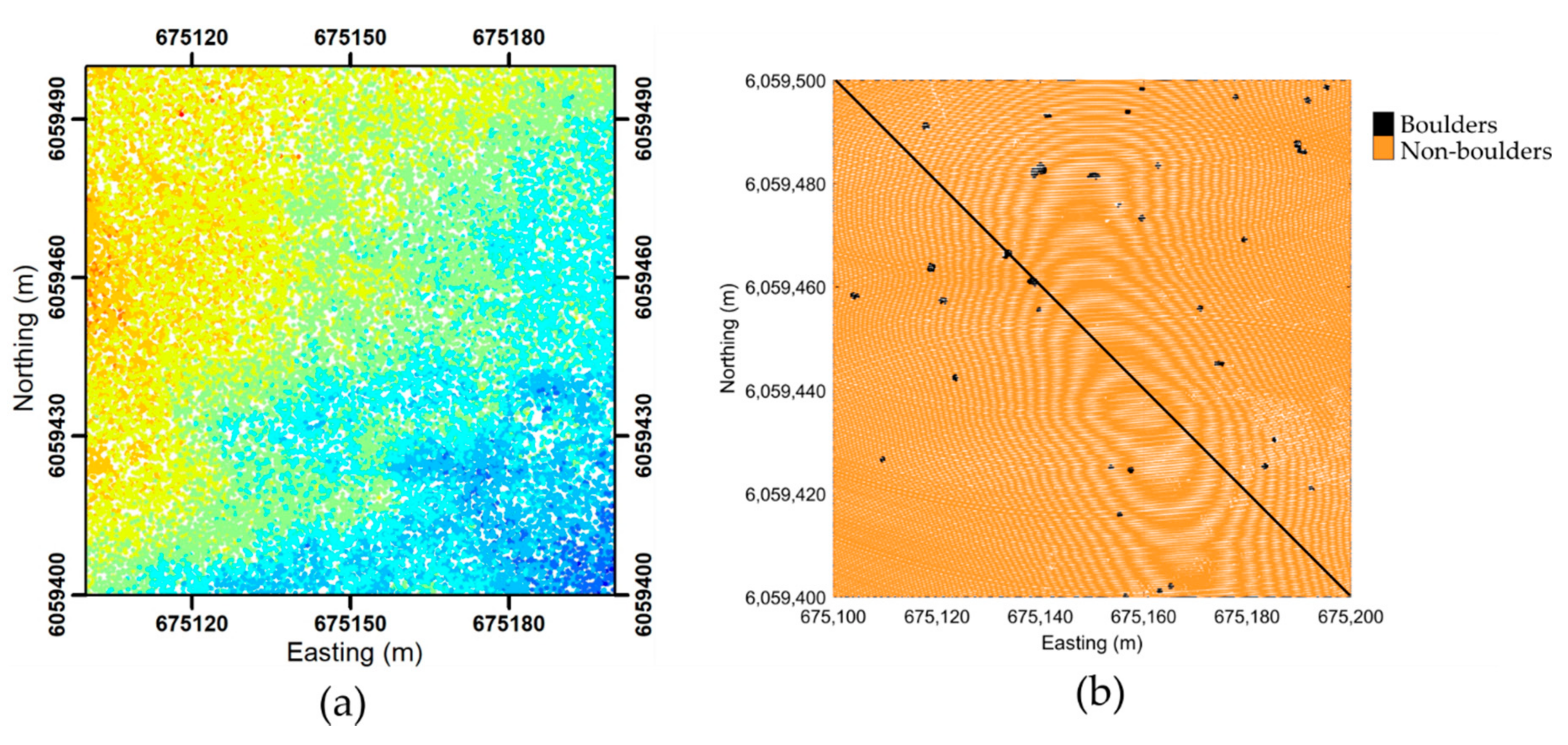
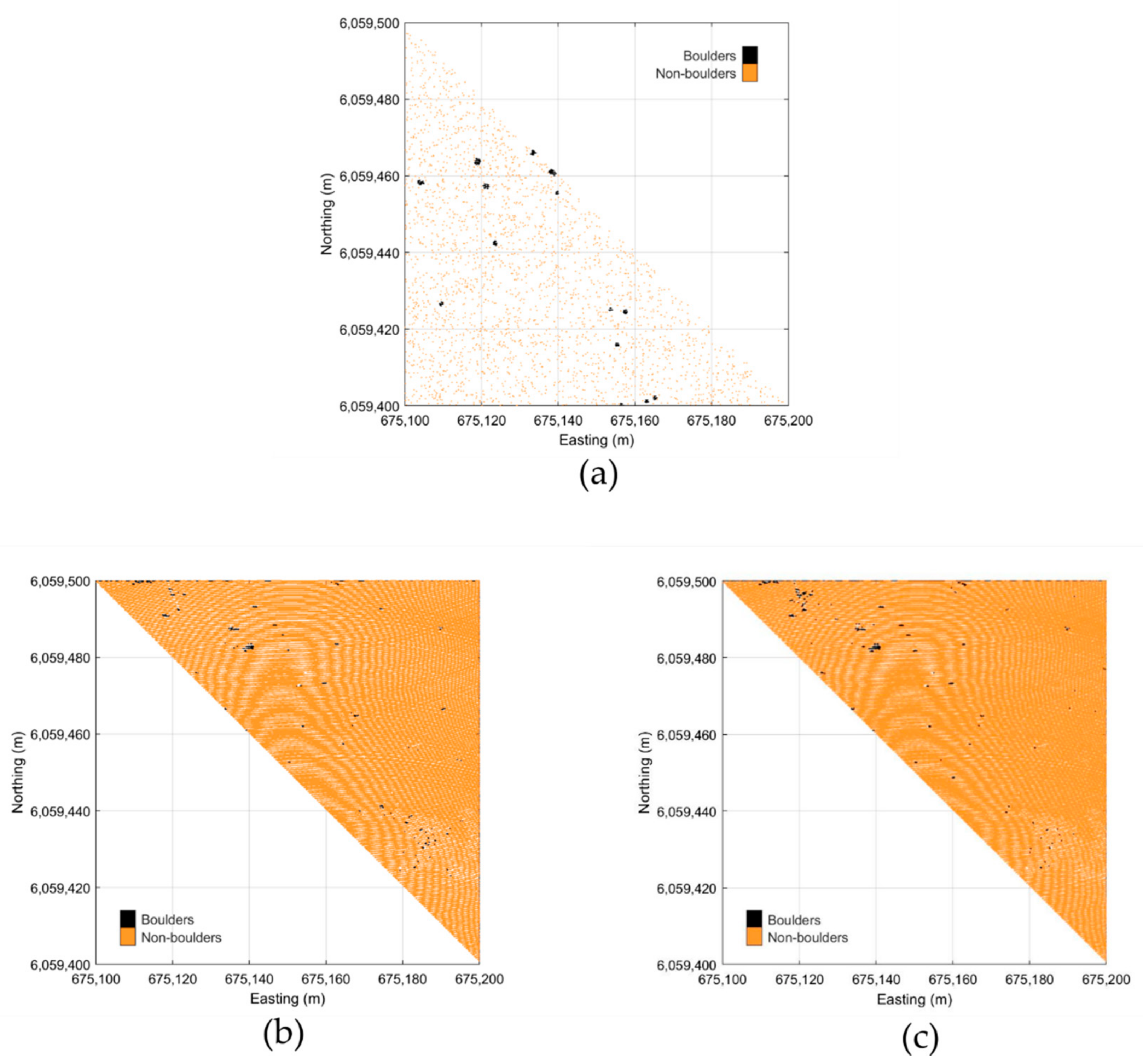
The potential boulders identified on the orthophotos from 2006 to 2019 are indicated in Figure 6a, including uncertainty buffers (Table 1). They exhibit a decrease in uncertainty from 2.0 m in 2006 to 0.2 m in 2019. The resulting spatial distribution of boulders (Figure 6b) was determined by assuming that any overlapping buffer zones in three subsequent years constituted verified boulders (cf. Section 3.3). The locations of the verified boulders are visualized in the seabed point cloud, where the individual seabed points constituting boulders are shown in black, while the non-boulder seabed points are shown in orange (Figure 7b).
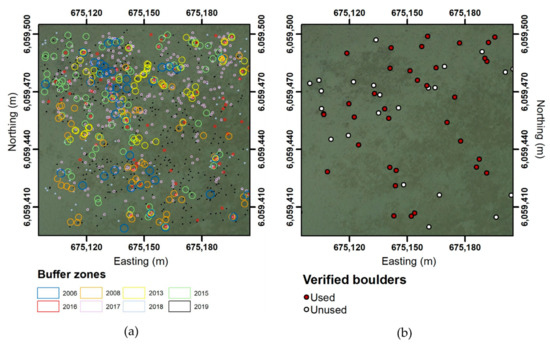
Figure 6.
(a) Potential boulders from orthophoto mapping with buffer zones. (b) Boulders found from three overlapping buffer zones. Red dots are boulders used for machine learning and white dots are boulders that were not used for machine learning. Projection is in ETRS89 UTM Zone 32N with units in meters.
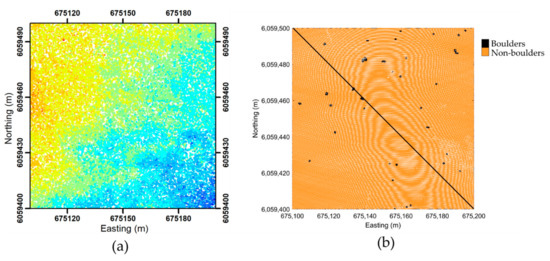
Figure 7.
(a) Point cloud of the study area colored by depth. (b) Point cloud with boulder (black)/non-boulder (orange) classification divided into training set (left half) and test set (right half). Projection is in ETRS89 UTM Zone 32N with units in meters.
4.2. Features in the Training and Test Set
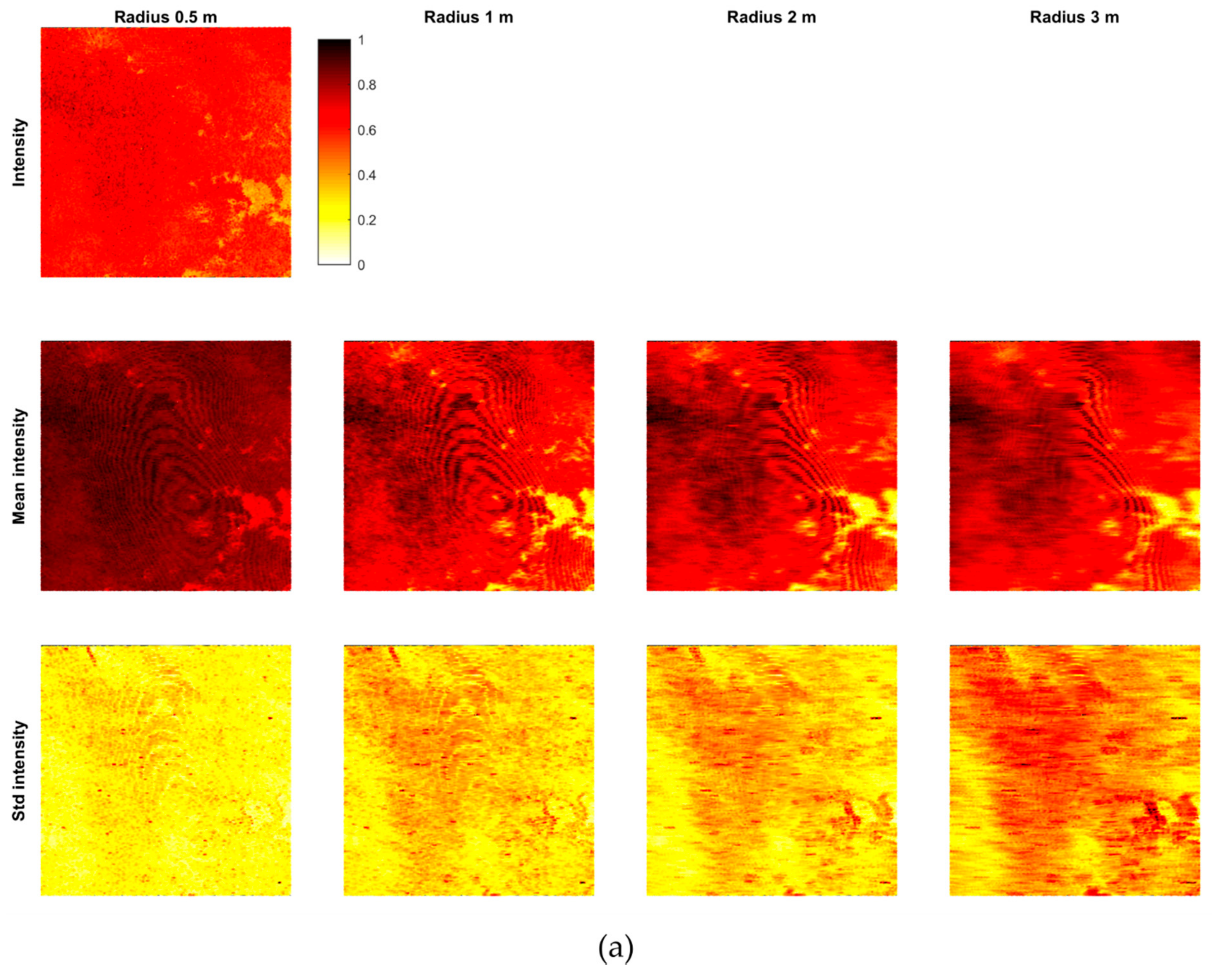
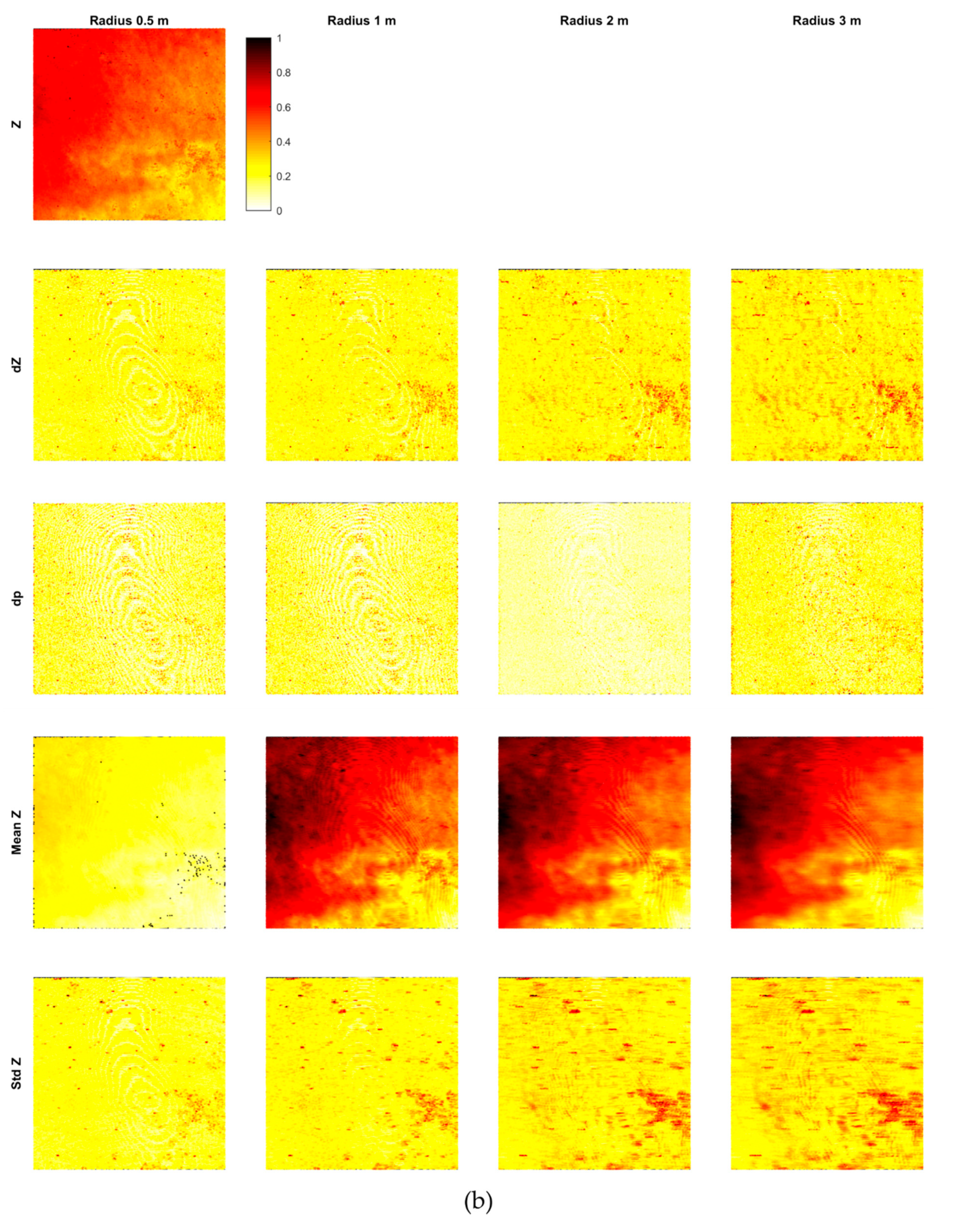
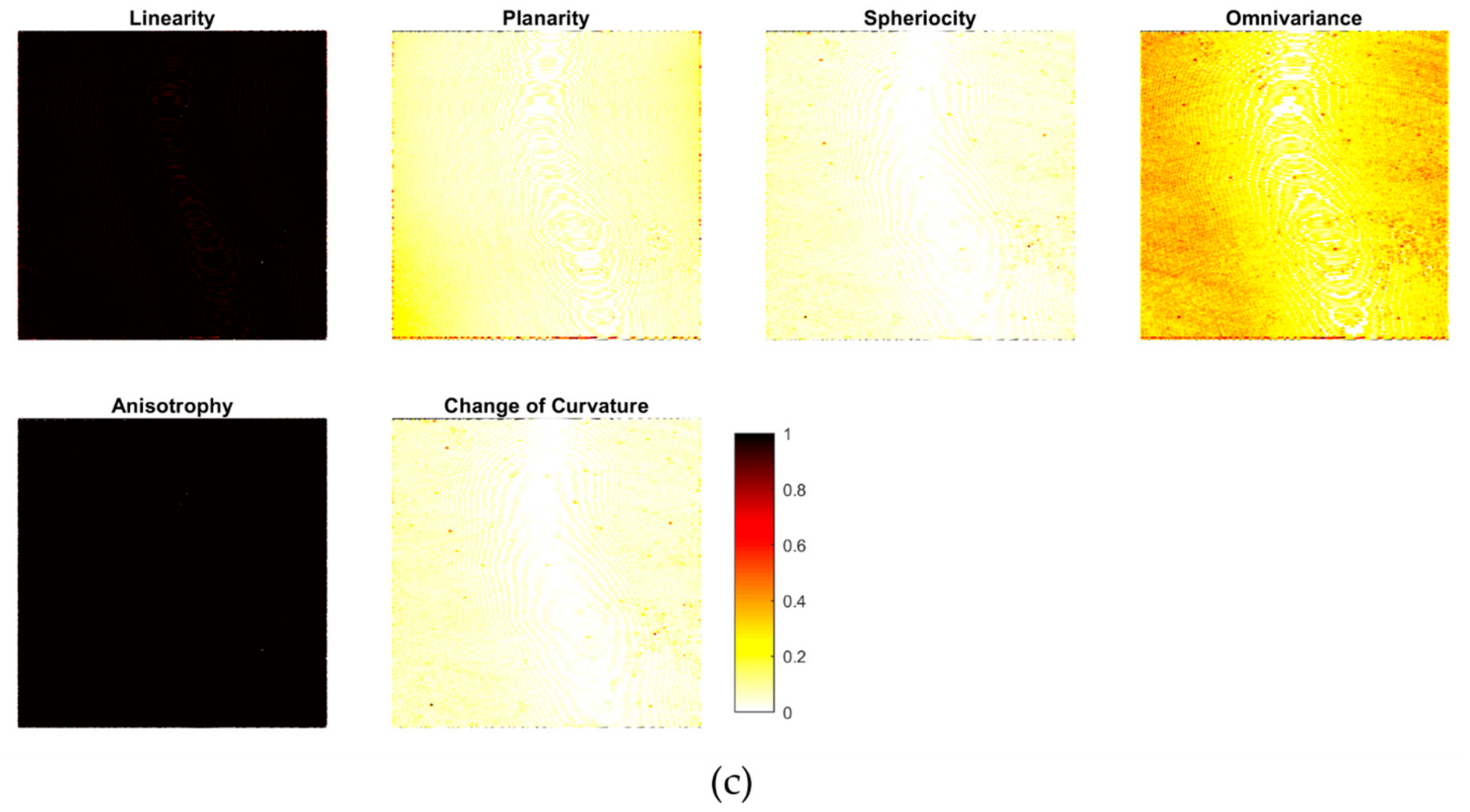
Figure 8 shows the results for calculating the three spectral features (a), the five relative position features for different neighborhoods (b), and the six covariance features for 0.5 m neighborhood (c) (cf. Section 3.3). Very few points were removed in the feature calculation due to a minimum number of only four points in the neighborhood (cf. Table 3). Some large-scale patterns in the signal, showing geometrical or structural (material/color) variations for the entire area, are visible in the intensity, mean intensity, std intensity (large neighborhood), Z, mean Z (larger neighborhood), and omnivariance; while small, separated dots are evident on std intensity, Z, dZ, mean Z (small neighborhood), std Z, and omnivariance.
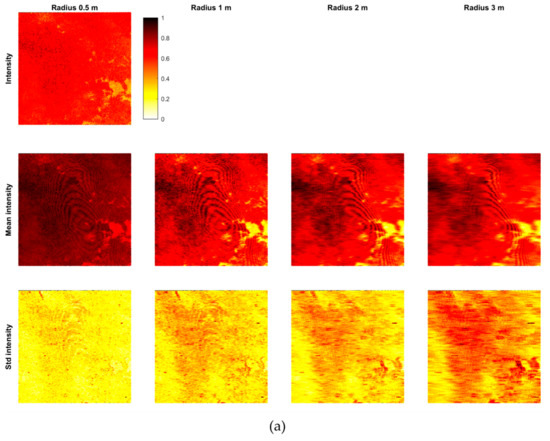
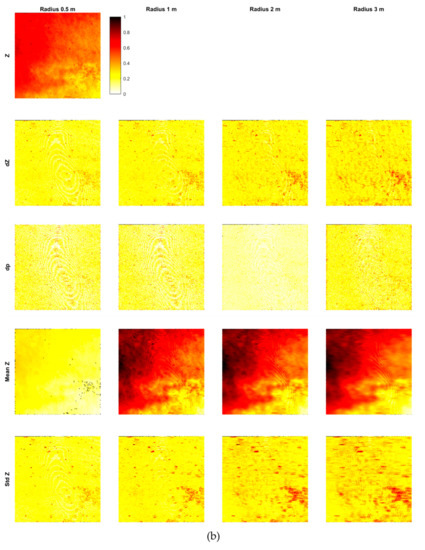
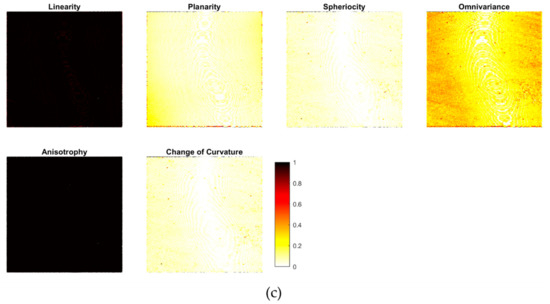
Figure 8.
Features in the area: (a) spectral features, (b) relative position features, and (c) covariance features.
4.2.1. Boulder Density and Size—Subsampling and Radius
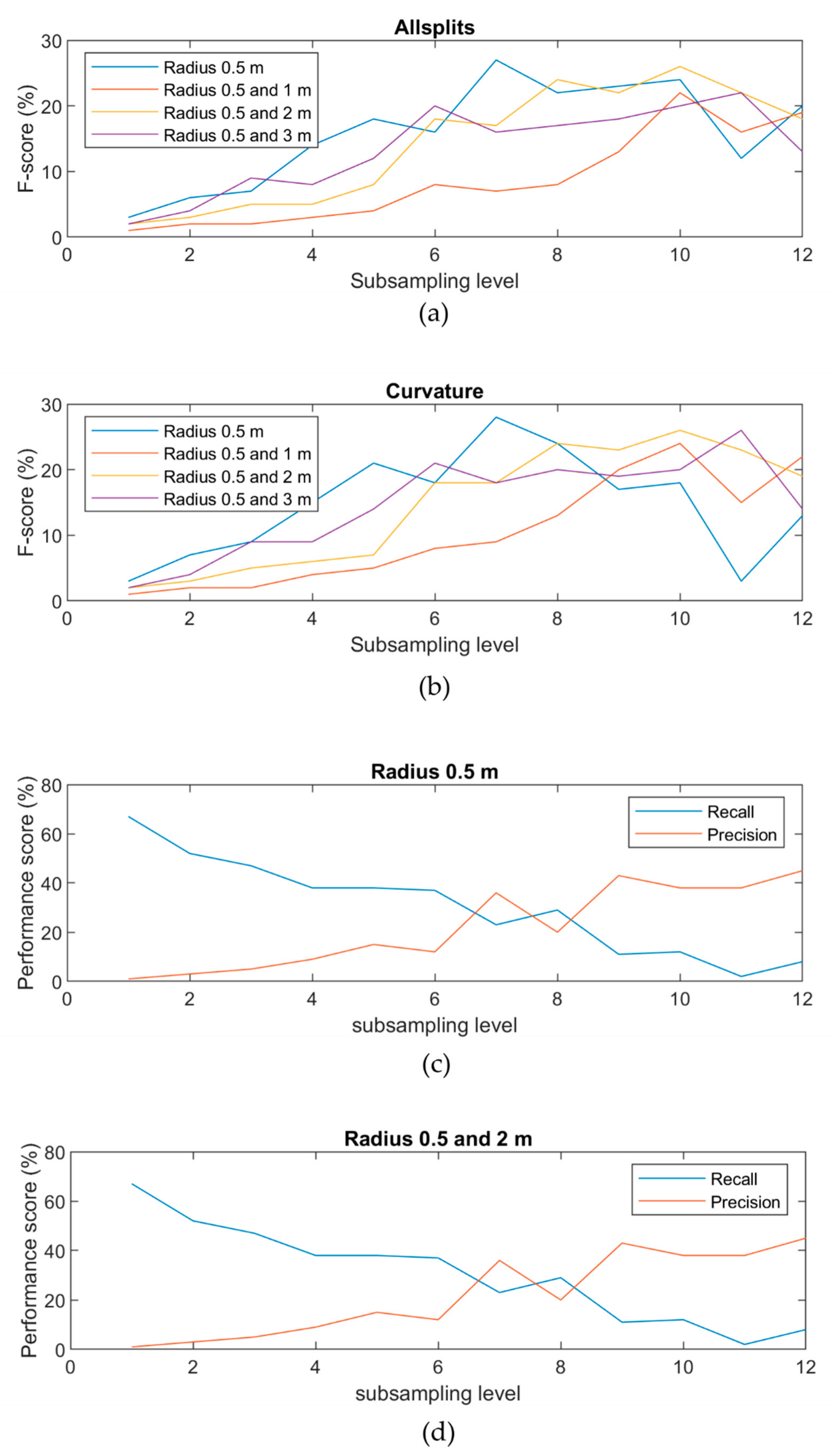
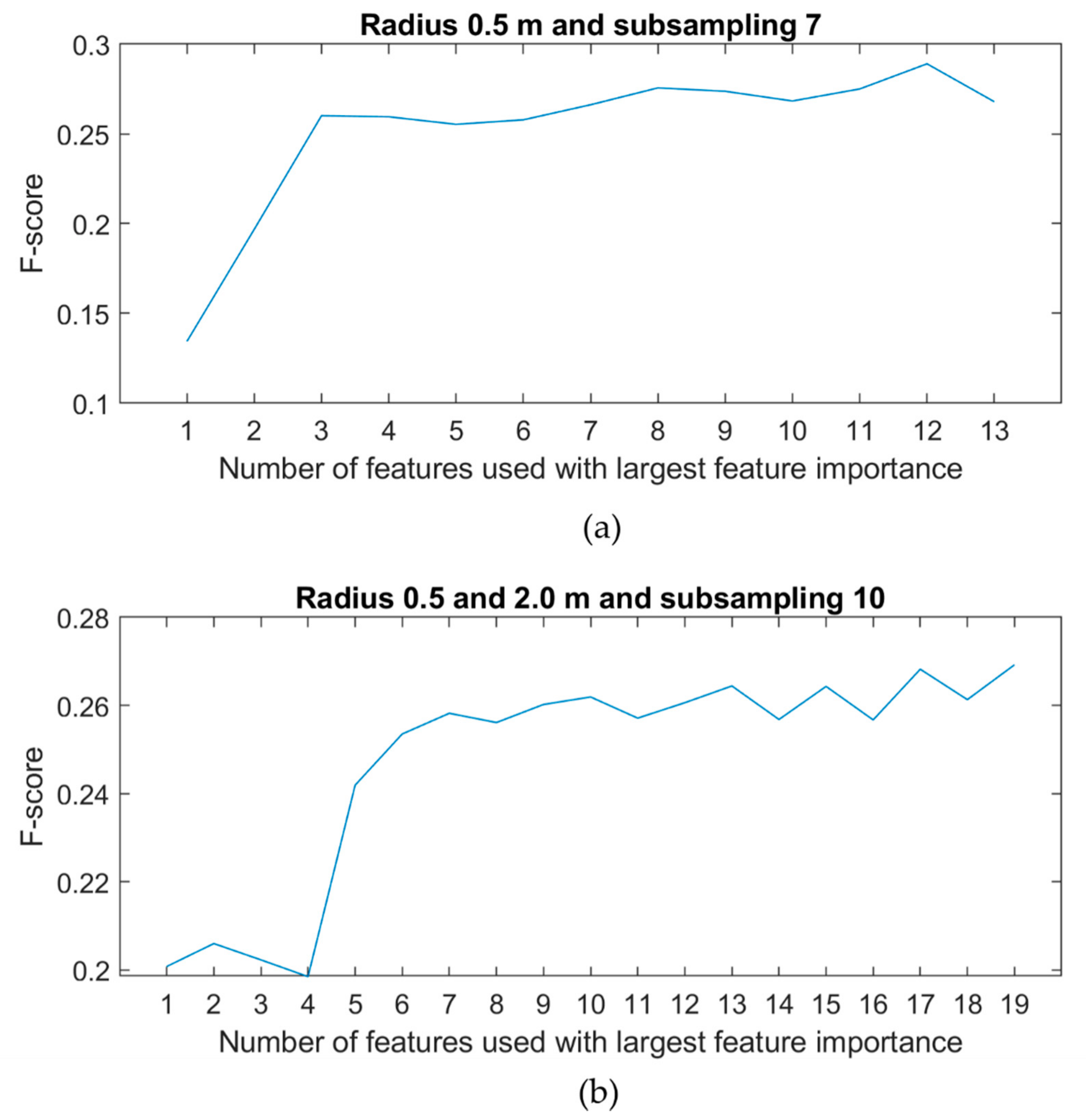
Features were calculated with different subsampling levels, neighborhood sizes, and split selectors, resulting in 104 different combinations (cf. Section 3.4.2). The F-score was used to evaluate subsampling/neighborhood combinations for both split selectors. Subsampling level 7 was best when only using the 0.5 m radius, while subsampling level 10 was best for the 1 m and 2 m radius, and subsampling level 11 was best for the 3 m radius (Figure 9). The curvature split predictor was the best split predictor (comparison Figure 9a,b). Based on the F-score evaluation, the case with no large radius is best, and the 2 m large radius is second-best (Figure 9b).
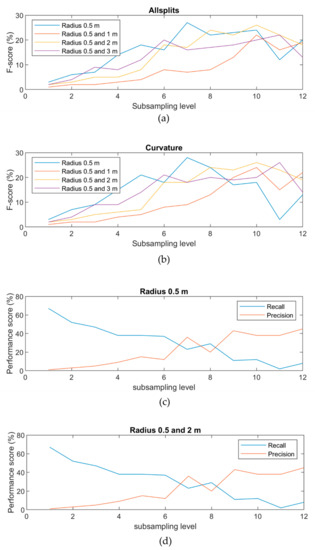
Figure 9.
F-scores and performance scores. (a) F-score for all radii with all split predictors. (b) F-score for all radii with curvature split predictor. (c) Recall and precision for radius 0.5 m. (d) Recall and precision for radius 0.5 m and 2 m.
4.2.2. Feature Selection
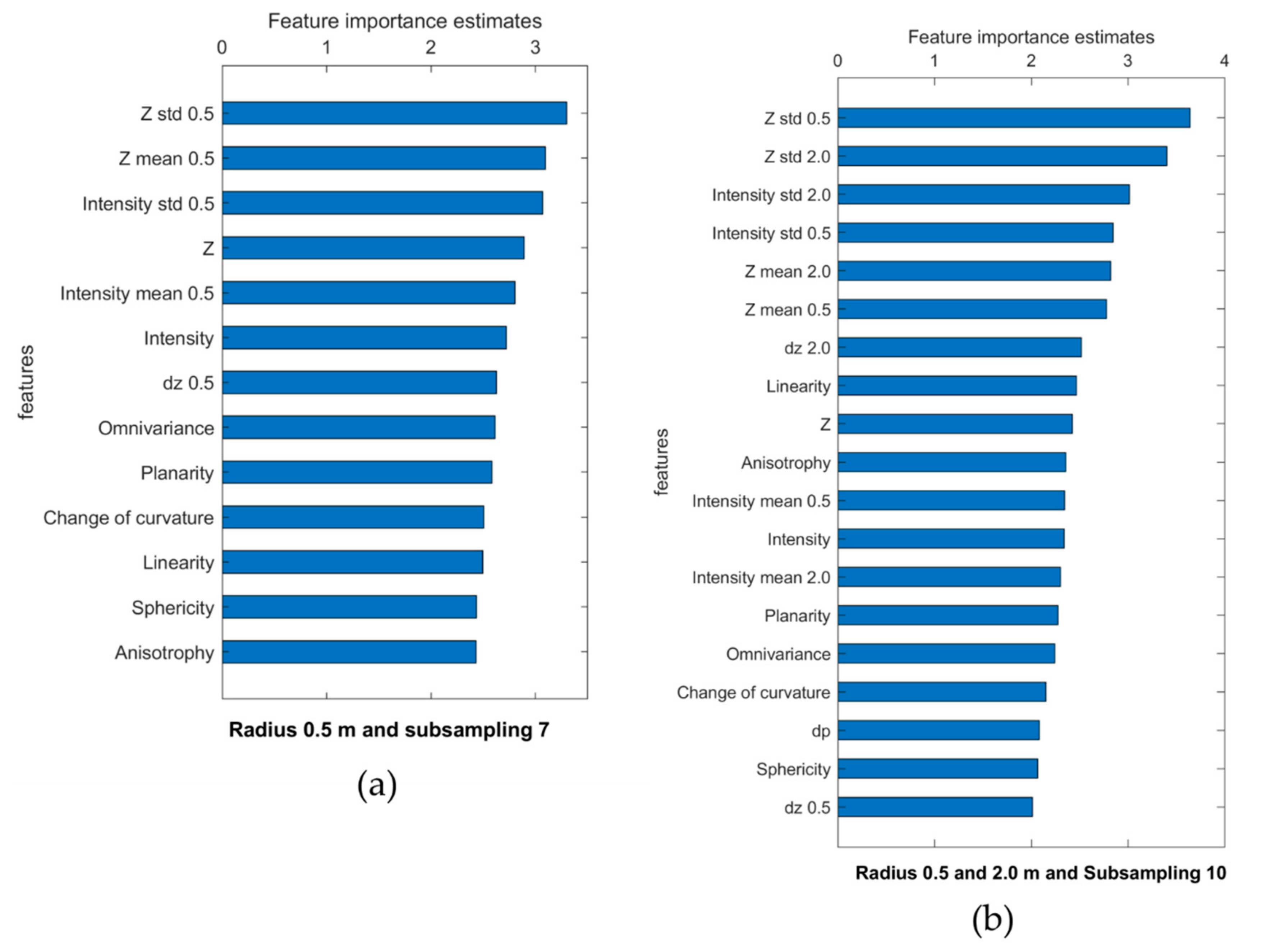
The most relevant features were the standard deviation of the depth, the standard deviation of the intensity, and the mean of the depth (Figure 10). The spectral and relative position features were the most important groups, while the geometric features were least important. From the first two groups, the least relevant features were dz for the 0.5 m radius, distance to plane, and intensity.
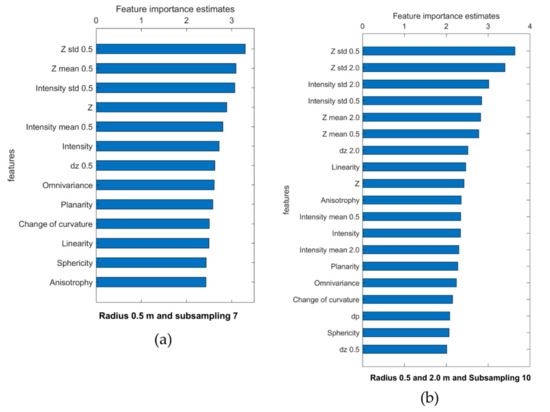
Figure 10.
Estimates of feature importance for (a) radius 0.5 m with subsampling 7, and for (b) radius 0.5 m and 2 m with subsampling 10.
The best threshold for feature selection uses the F-score that was calculated using only the single best feature, then the two best features, and so on up to all features. For both radius/subsampling situations, the best result was found based on all features. However, a threshold was found using only the first three features for radius 0.5 m and subsampling 7 (Z std 0.5 m, Z mean 0.5 m, and intensity std 0.5 m; Figure 11a). For radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m at subsampling 10, a threshold was found by using the seven best features (Z std 0.5 m, Z std 2.0 m, intensity std 0.5 m, intensity std 2.0 m, Z mean 0.5 m, Z mean 2.0 m, and dz 2.0 m; Figure 11b).
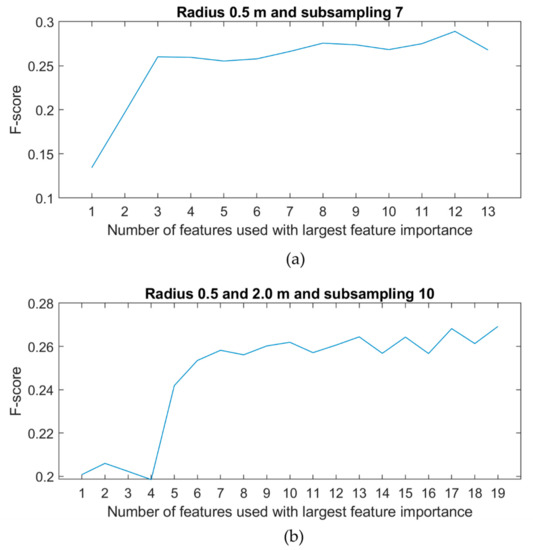
Figure 11.
Test of all best feature thresholds for (a) radius 0.5 m and subsampling 7 and (b) for radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m and subsampling 10.
4.3. Boulder Prediction Using Random Forest
The best random forest result depends on subsampling level, choice of large radius, the selected features, and the predictor selection algorithm. In the curvature prediction algorithm, only radius 0.5 m was chosen to determine the best subsampling level, which was 7 (Figure 12a) and with all features (Figure 12b). Good results can still be obtained by using only the best three features. The second-best result was achieved using curvature, radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m, and subsampling 10, as well as all features (Figure 12c). Using only the best seven features still yielded good results.
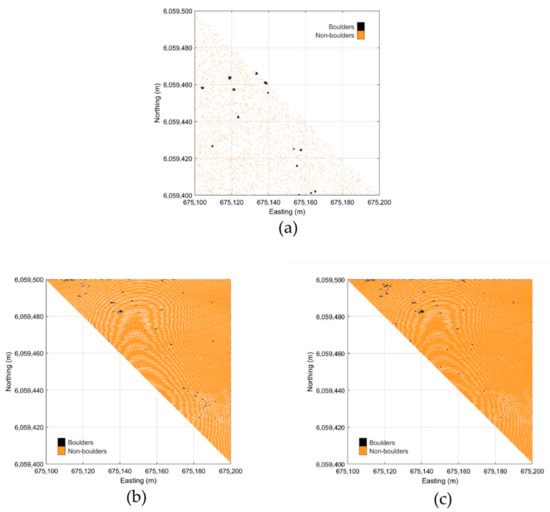
Figure 12.
(a) Boulder and non-boulder points for test set using subsampling level 7. (b) Predicted boulders with random forest using radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m and subsampling level 10, all features; (c) predicted boulders with random forest using radius 0.5 m and subsampling 7, all features.
4.4. Performance and Accuracy Assessment
Performance scores were calculated for the best two results using point-based (Table 4) and object-based (Table 5) analysis. A radius of 2 m was used for the clustering analysis due to a minimum and maximum radius of 0.6 m and 3.4 m (cf. Section 3.4.3). The best result with radius 0.5 m, subsampling level 7, and curvature split selector had a point-based recall (R) of 23%, precision (P) of 32%, and F-score of 27%, while the object-based recall was 57%, precision 27%, and F-score 37% (Table 4 and Table 5). The second-best result with radius 0.5 m and 2 m, subsampling level 10, and curvature split selector had a point-based recall of 22%, precision of 36%, and F-score of 27%, while the object-based recall was 43%, precision 21%, and F-score 28% (Table 4 and Table 5).

Table 4.
Accuracy assessment with different performance scores for point-based analysis.

Table 5.
Accuracy assessment with different performance scores for object-based analysis.
5. Discussion
5.1. Evaluation of Methods to Identify Boulders and Verified Boulder Points
Automated procedure yields reproducible results. The input data for an automated machine learning procedure are crucial for algorithm performance. Two steps are necessary to generate classification input data for a 3D point cloud: (1) the verification of boulder positions, and (2) marking of boulder points in the point cloud. For this, the identification of boulders from orthophotos is faster and less expensive than in situ boulder detection in the field from diving or video imaging. However, exposure, overturning, and migration of boulders may introduce errors in the boulder verification in the orthophoto images.
Ref. [48] concluded that exposure of cobbles and boulders from glacial till by erosion is the main driver for stone habitat dynamics. However, the timescale in their study was of decades. The study area in this work has similar bed sediments and wave heights as in [48], but boulders could be more susceptible to sediment transport in the present study area due to the shallow water depth conditions in Rødsand lagoon. Yet, it is unlikely to find boulders exposed after 2015, though two boulders that were identified only on orthophotos after 2015 may have been unexposed prior to 2015. In [48], overturning and migration occurred only to cobbles, but not to boulders. The definition of boulders applied by [48] is 60 cm, instead of 40 cm, as used in the present study following the Udden–Wentworth grain size classification. However, the identified boulders are generally larger than one meter in the present study. In [48], the overturning of cobbles occurred instantaneously after storm events. Shallow water depth or difference in boulder size classification could cause overturning to happen for boulders in Rødsand lagoon during storm events.
The misclassification of boulder and non-boulder points in the point cloud will lead to errors in the prediction. Some of the identified boulders were difficult to extract in the point cloud. In such cases, the points were classified as non-boulders. This category contains all different types of non-boulder points, e.g., algae, eelgrass, or sand.
The exclusive classification of boulders (>40 cm) and the exclusion of cobbles (<40 cm) from the classification can affect the results. Predicted stone points in areas without boulders may be due to the presence of smaller stones, which were too small for correct identification in the orthophotos dependent on the image resolution.
5.2. Evaluation of Selected Training Area
A 100 m × 100 m area was chosen as test and training set due to data amount and processing time. The separation of the training and test set affects the prediction. The algorithm performance is best in areas with similar depth and seabed properties as in the training set. A diversity in the properties of the training set improves the model to predict boulders better in different settings. The choice of the test set affects the evaluation of the algorithm. A test set of very similar characteristics to the training set can yield good results, while the algorithm may perform worse in areas that are differing from the training set. Therefore, the diversity of the classification area needs to be considered when defining the training and test sets.
One way to ensure the diversity of the training set is to use the same area as training and test set. Using random points distributed over the area for the training set and other random points for the test set results in a very diverse training set [23]. If more than one point represents the same boulder, this approach can lead to one boulder represented in both the test and training set, so that the points in the training and test set have very similar properties. In this case, the evaluation is good but not representative. Therefore, separate training and test sets were set up in this study. An area with boulders, sand, and vegetation was selected to ensure the diversity in both sets with similar distributions.
5.3. Prediction Errors and Possible Algorithm Improvements
Vegetation cover and geometrical irregularities appear in the lower right and upper left corners of the test set. The prediction is poorer in these areas compared to areas where boulders are exposed on a bare sandy seabed. This difference in algorithm performance is probably due to clearer distinguished feature properties between sand and boulders than between vegetation and boulders. Smaller stones in vegetated areas can also lead to prediction errors.
Ref. [49] applied a probability threshold approach to predict boulders and non-boulders. In the random forest standard setting, the splitting probability between two classes is 50%. A probability threshold analysis can be applied as an additional tuning parameter after radius, subsampling level, and feature selection.
5.4. Performance Evaluation
The evaluation of the prediction depends on the choice of the performance measure for the random forest model. A standard accuracy measure evaluating all boulder and non-boulder points as equally important can lead to a high accuracy with no predicted boulder points at all, in the case of an imbalanced dataset. The purpose of the prediction is relevant for the choice of the performance measure. The importance of predicting all boulders (recall) or of avoiding prediction errors (precision) requires specific consideration. In this study, the purpose is to detect boulder locations. Therefore, predicting non-boulder points are irrelevant and the accuracy is an irrelevant measure despite the very high measure score. Thus, we chose the F-score as the most important measure, because it takes both recall and precision into account.
The most relevant features are the mean and the standard deviation of the depth (neighborhood radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m), the depth change (neighborhood radius 2 m), and the standard deviation of the intensity (neighborhood radius 0.5 m and 2.0 m). Furthermore, the derivatives of the depth and intensity data are more important than the depth and intensity data itself. This may be due to the fact that distinguishing between boulder and non-boulder points requires knowledge about the change of feature properties between boulder and non-boulder points. The difference between feature values for boulder and non-boulder points is not sufficient for the model. This could be due to derivatives being more sensitive to changes than the values themselves. None of the geometric covariance features were of relevance for the boulder prediction. This can be due to the geometrical diversity in the boulder appearance compared to other habitats, such as submerged aquatic vegetation [23] or sandbanks showing more uniform geometric characteristics.
5.5. Processing Time and Upscaling
The TreeBagger algorithm is the most time-consuming part of the point-based analysis. The time depends on the number of trees and the number of points for the analysis and the computer power. For the 100 m × 100 m area in this study, the time consumption was minutes to hours, depending on subsampling level and number of trees. The size of the area was chosen so that all points could be processed without subsampling and still not reach the maximum level of Matlab memory. If the maximum level of Matlab memory is reached, the processing velocity will be reduced significantly, and the process is difficult to run. This problem could be solved by using a random forest algorithm in another programming language such as Python. Using a low subsampling level, e.g., 7, which led to the best result in this study, enables upscaling the area.
5.6. Boulder Dynamics
Mapping stone reefs in the same area over years makes it possible to detect potential changes in the stone reefs, which is requested in relation to the EU MSFD with loss and disturbance of seafloor integrity [50]. For decades, cobbles and boulders have been seen as immobile and stable. However, new studies show how natural dynamics of boulders and cobbles need to be considered in the marine habitat mapping directives [48]. Ref. [51] observed boulders in the western Baltic Sea for 22 years, and they noticed that, despite stone fishing in the area until 1974, the number of boulders had increased in the observation period. The study concludes that natural processes of boulder exposure should be considered in regeneration of marine habitats. Exposure of boulders depends on abrasion rate, which is dependent on water depth, wave climate, and resistance of the glacial till against erosion [48]. Climate change and, especially, sea level rise can affect the distribution of macroalgae living on hard substrate [52]. To preserve ecological stability and the functioning of ecosystems, it is important to study the dynamics in the coastal areas by observing how the climate affects the stone reefs and the vegetation on hard substrate.
6. Conclusions
We developed a semi-automated method to map boulders from topo-bathymetric LiDAR point cloud data. First, the LiDAR data were processed to generate a point cloud containing only seabed information by an unsupervised classification of the point cloud without any manual classification correction of seabed points. Second, a random forest machine learning algorithm was developed for automated boulder detection. Third, the most important tuning parameters for the random forest algorithm were the subsampling level, the choice of the neighborhood radius, and the choice of features.
The best combinations for boulder prediction in the study area were (i) subsampling level 7, neighborhood radius 0.5 m, all features and curvature split selection algorithm, and (ii) subsampling level 10, neighborhood radius 0.5 m, and 2.0 m, all features and curvature split selection algorithm. For the parameter combination listed in (i), a threshold can be set by using the best three features, which are Z std 0.5 m, Z mean 0.5 m, and intensity std 0.5 m. For the parameter combination listed in (ii), a threshold can be set by using the best seven features (Z std 0.5 m, Z std 2.0 m, intensity std 0.5 m, intensity std 2.0 m, Z mean 0.5 m, Z mean 2.0 m, and dz 2.0 m).
Fourth, the results were evaluated using performance scores. For the best parameter combination (i), the recall of the boulders was 57%, precision 27%, and F-score 37%, while the accuracy of the points was 99%. For the best parameter combination (ii), the recall of the boulders was 43%, precision 21%, and F-score 28%, while the accuracy of the points was 99% with a kappa coefficient on 0.27.
Automatic boulder detection will enable transparent, reproducible, and fast detection and mapping of boulders. Furthermore, it will allow to detect potential dynamics of boulder assemblages and stone reefs over time. Quantification of the spatial distribution of boulders and boulder sizes, as well as their dynamics, will also provide valuable knowledge in relation to stone reef management and restoration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.H., V.B.E., and Z.A.-H.; methodology, S.S.H.; software, S.S.H. and M.N.; validation, S.S.H.; formal analysis, S.S.H.; investigation (LiDAR data collection), F.S. and R.B.; data curation, R.B., M.S.A., M.N., and S.S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.H.; writing—review and editing, V.B.E., A.K., Z.A.-H., R.B., and M.S.A.; visualization, S.S.H. and M.S.A.; supervision, V.B.E., A.K., and Z.A.-H.; project administration, V.B.E.; funding acquisition, V.B.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work is part of the project “ECOMAP-Baltic Sea environmental assessments by innovative opto-acoustic remote sensing, mapping, and monitoring”, supported by BONUS (Art 185), funded jointly by the EU and the Innovation Fund Denmark.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that supports the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank divers Paul Christiansen and Per Freiberg and master’s student Sebastian Marker Westh for their help in the field. Finally, we thank the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Al-Hamdani, Z.; Jensen, J.B.; Skar, S.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, N.; Leth, J.O.; Lomholt, S.; Bennike, O.; Granat, H.; Andersen, M.S.; Rödel, L.G.; et al. Marin Habitatkortlægning I De Indre Danske Farvande; Naturstyrelsen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani, Z.; Skar, S.; Jensen, J.B.; Rödel, L.G.; Pjetursson, B.; Bennike, O.; Oxfeldt Jensen, G.C.; Rasmussen, M.B.; Dahl, K.; Koefoed Rømer, J.; et al. Marin Habitatkortlægning i Skagerrak og Nordsøen 2015; Naturstyrelsen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani, Z.; Owen, M.; Rödel, L.G.; Witt, N.; Nørgaard-Petersen, N.; Bennike, O.; Sabra, H.; Eriksen, L.N.; Kragh, S.; Jensen, J.B.; et al. Kortlægning af Natura 2000-Områder Marin Habitatkortlægning i Skagerrak Og Nordsøen 2017–2018; Miljøstyrelsen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019; ISBN 978-87-7038-027-0. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani, Z. Analyse af 1170 Stenrev Henholdsvis Indenfor og Udenfor Marine Habitatområder; GEUS: Århus, Denmark, 2018. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani, Z.; Skar, S. Analyse af Naturtype 1170 Stenrev Henholdsvis Indenfor og Udenfor de Marine Habitatområder; GEUS: Århus, Denmak, 2017. (In Dansih) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. Artificial Reefs for Ecosystem Restoration and Coastal Erosion Protection with Aquaculture and Recreational Amenities. Reef J. 2009, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.; Lundsteen, S.; Helmig, S.A. Stenrev—Havets oaser. Danmarks Miljøundersøgelser, G.E.C. Gads Forlag. 2003. Available online: https://www2.dmu.dk/1_Viden/2_Publikationer/3_miljobib/rapporter/MB02.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021). (In Danish).
- Interpretation Manual of European Union Habitats. European Commission dg Environment. Nature, ENV B.3. 2013. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/legislation/habitatsdirective/docs/Int_Manual_EU28.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Helmig, S.A.; Nielsen, M.M.; Petersen, J.K. Andre Presfaktorer end Næringsstoffer og Klimaforandringer—Vurdering af Omfanget af Stenfiskeri i Kystnære Marine Områder; DTU Aqua-rapport; DTU Aqua: Lyngby, Denmark, 2020. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani, Z.; Jensen, J.B.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, N.; Skar, S.; Rödel, L.G.; Paradeisis-Stathis, S. Investigating the Potential of Stone Reefs in Reducing Nutrient Loads, as an Input to There-Establishing of a Stone Reef in the Natura 2000-Area “Løgstør Bredning, Vejlerne and Bulbjerg”; GEUS: Århus, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, A.; Rahman, A.F.; Kline, R.; Rahman, M.S. Side scan sonar: A cost-efficient alternative method for measuring seagrass cover in shallow environments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 207, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlburger, G. A review of airborne laser bathymetry for mapping of inland and coastal waters. Hydrogr. Nachr. 2020, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, H.; Mader, D.; Richter, K.; Westfeld, P. Improvements in LiDAR bathymetry data analysis. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, M.S.; Gergely, Á.; Al-Hamdani, Z.K.; Steinbacher, F.; Larsen, L.R.; Ernstsen, V.B. Processing and performance of topobathymetric lidar data for geomorphometric and morphological classification in a high-energy tidal environment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Karantzalos, K.; Georgopoulos, A.; Skarlatos, D. Correcting Image Refraction: Towards Accurate Aerial Image-Based Bathymetry Mapping in Shallow Waters. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagawa, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Okumura, T.; Yamanokuchi, T. Satellite Derived Bathymetry Using Machine Learning and Multi-Temporal Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Liang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, P.; et al. Meta-discoveries from a synthesis of satellite-based land-cover mapping research. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2014, 35, 4573–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, W.J.; Singh, C.; Kumbier, K.; Abbasi-Asl, R.; Yu, B. Definitions, methods, and applications in interpretable machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22071–22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A.; El-Ashmawy, N. Urban land cover classification using airborne LiDAR data: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, L.; Trzcinska, K.; Tegowski, J.; Kruss, A.; Rucinska-Zjadacz, M.; Pocwiardowski, P. Nearshore Benthic Habitat Mapping Based on Multi-Frequency, Multibeam Echosounder Data Using a Combined Object-Based Approach: A Case Study from the Rowy Site in the Southern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janowski, Ł.; Wróblewski, R.; Dworniczak, J.; Kolakowski, M.; Rogowska, K.; Wojcik, M.; Gajewski, J. Offshore benthic habitat mapping based on object-based image analysis and geomorphometric approach. A case study from the Slupsk Bank, Southern Baltic Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 801, 149712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenmeier, S.; Hass, H.C. Detection of Stones in Marine Habitats Combining Simultaneous Hydroacoustic Surveys. Geosciences 2018, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Held, P.; Deimling, J.S.V. New Feature Classes for Acoustic Habitat Mapping—A Multibeam Echosounder Point Cloud Analysis for Mapping Submerged Aquatic Vegetation (SAV). Geosciences 2019, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshiro, T.M.; Perez, P.S.; Baranauskas, J.A. How Many Trees in a Random Forest? In Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. MLDM 2012. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Perner, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; Volume 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, K.; Calder, B. Extracting Shallow-Water Bathymetry from Lidar Point Clouds Using Pulse Attribute Data: Merging Density-Based and Machine Learning Approaches. Mar. Geod. 2021, 44, 259–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlburger, G.; Pfennigbauer, M.; Schwarz, R.; Flöry, S.; Nussbaumer, L. Concept and Performance Evaluation of a Novel UAV-Borne Topo-Bathymetric LiDAR Sensor. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collin, A.; Archambault, P.; Long, B. Predicting species diversity of benthic communities within turbid nearshore using full-waveform bathymetric LiDAR and machine learners. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kogut, T.; Weistock, M.; Bakuła, K. Classification of data from airborne lidar bathymetry with random forest algorithm based on different feature vectors. Isprs—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W16, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsberg, P.L.; Lumborg, U.; Bundgaard, K.; Ernstsen, V.B. Impact of mussel bioengineering on fine-grained sediment dynamics in a coastal lagoon: A numerical modelling investigation. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, P.; Lumborg, U.; Andersen, T.; Kroon, A.; Ernstsen, V. The relative impact of future storminess versus offshore dredging on suspended sediment concentration in a shallow coastal embayment: Rødsand lagoon, western Baltic Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, O.; Drønen, N.; Kroon, A. Barrier morphodynamics under micro-tidal and low to moderate wave conditions, Rødsand, Denmark. Dynamics 2017, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar]
- FEHY. Fehmarnbelt Fixed Link EIA. Marine Soil—Baseline. In Coastal Morphology along Fehmarn and Lolland; Raport no. E1TR0056—2013; FEHY Consortium/Co DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2013; Volume III, p. 212. ISBN 978-87-92416-34-6. [Google Scholar]
- DHI. Rødsand 2. Waves and Sediment Transport. Littoral Transport and Coastal Morphology; Final Rapport prepared for Dong Energy; DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg, P.L.; Ernstsen, V.B.; Andersen, T.J.; Winter, C.; Becker, M.; Kroon, A. The effect of successive storm events and seagrass coverage on sediment suspension in a coastal lagoon. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 212, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA. Fehmarnbelt Fixed Link EIA. Marine Fauna and Flora—Baseline; Habitat Mapping of the Fehmarnbelt Area Report No. E2TR0020; FEMA Consortium/Co DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2013; Volume III, p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Riegl: LASextrabytes implementation in RIEGL software—Whitepaper, Riegl Laser Measurement Systems GmbH. Available online: http://www.riegl.com/uploads/tx_pxpriegldownloads/Whitepaper_LAS_extrabytes_implementation_in_RIEGL_Software_2019-04-15.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Kumpumäki, T. Lasdata. 2021. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/48073-lasdata (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Beksi, W. Estimate Surface Normals. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/46757-estimate-surface-normals (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Höfle, B.; Vetter, M.; Pfeifer, N.; Mandlburger, G.; Stötter, J. Water surface mapping from airborne laser scanning using signal intensity and elevation data. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. Computer Vision Toolbox (R2021a). Available online: https://se.mathworks.com/help/vision/index.html?s_tid=CRUX_lftnav (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Bi, C.; Yang, L.; Duan, Y.; Shi, Y. A survey on visualization of tensor field. J. Vis. 2019, 22, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chen, J.; Su, P.L.; Chen, C. Eigen-feature analysis of weighted covariance matrices for LiDAR point cloud classification. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, G.; Lei, J.; Fan, F.; Ye, X.; Mei, Q. A Novel Method of Autonomous Inspection for Transmission Line based on Cable Inspection Robot LiDAR Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MathWorks. Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox (R2021a). 2021. Available online: https://se.mathworks.com/help/stats/index.html?s_tid=CRUX_lftnav (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Loh, W.; Shih, Y. Split selection methods for classification trees. Stat. Sin. 1997, 7, 815–840. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Using Random Forest to Learn Imbalanced Data; Department of Statistics, UC Berkley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Von Rönn, G.A.; Krämer, K.; Franz, M.; Schwarzer, K.; Reimers, H.-C.; Winter, C. Dynamics of Stone Habitats in Coastal Waters of the Southwestern Baltic Sea (Hohwacht Bay). Geosciences 2021, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiuk, B.; Diesing, M.; Aitken, A.; Brown, C.J.; Edinger, E.N.; Bell, T. A Spatially Explicit Comparison of Quantitative and Categorical Modelling Approaches for Mapping Seabed Sediments Using Random Forest. Geosciences 2019, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Report from the commission to the council and the european parliament The first phase of implementation of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (2008/56/EC) The European Commission’s assessment and guidance/*COM/2014/097 final*. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A52014DC0097 (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Schwarzer, K.; Bohling, B.; Heinrich, C. Submarine hard-bottom substrates in the western Baltic Sea—human impact versus natural development. J. Coast. Res. Spec. Issue 2014, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torn, K.; Peterson, A.; Herkül, K. Predicting the Impact of Climate Change on the Distribution of the Key Habitat-Forming Species in the Ne Baltic Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).