Abstract
Salinization in arid or semiarid regions with water logging limits cropland yield, threatening food security. The highest level of farmland salinization, that is, abandoned salinized farmland, is a tradeoff between inadequate drainage facilities and sustainable farming. The evolution of abandoned salinized farmlands is closely related to the development of cropping systems. However, detecting abandoned salinized farmland using time-series remote sensing data has not been investigated well by previous studies. In this study, a novel approach was proposed to detect the dynamics of abandoned salinized farmland using time-series multispectral and thermal imagery. Thirty-two years of temporal Landsat imagery (from 1988 to 2019) was used to assess the evolution of salinization in Hetao, a two-thousand-year-old irrigation district in northern China. As intermediate variables of the proposed method, the crop-specific planting area was retrieved via its unique temporal vegetation index (VI) pattern, in which the shape-model-fitting technology and the K-means cluster algorithm were used. The desert area was stripped from the clustered non-vegetative area using its distinct features in the thermal band. Subsequently, the abandoned salinized farmland was distinguished from the urban area by the threshold-based saline index (SI). In addition, a regression model between electrical conductance (EC) and SI was established, and the spatial saline degree was evaluated by the SI map in uncropped and unfrozen seasons. The results show that the cropland has constantly been expanding in recent decades (from 4.7 × 105 ha to 7.1 × 105 ha), while the planting area of maize and sunflower has grown and the area of wheat has decreased. Significant desalinization progress was observed in Hetao, where both the area of salt-affected land (salt-free area increased approximately 4 × 105 ha) and the abandoned salinized farmland decreased (reduced from 0.45 × 105 ha to 0.19 × 105 ha). This could be mainly attributed to three reasons: the popularization of water-saving irrigation technology, the construction of artificial drainage facilities, and a shift in cropping patterns. The decrease in irrigation and the increase in drainage have deepened the groundwater table in Hetao, which weakens the salt collection capacity of the abandoned salinized farmland. The results demonstrate the promising possibility of reutilizing abandoned salinized farmland via a leaching campaign where the groundwater table is sufficiently deep to stop salinization.
1. Introduction
Approximately 19.5% of irrigated land worldwide is affected by salt, posing a threat to food security and economic development [1]. Secondary salinity, a direct result of human interaction with the land due to poor management practices, is a prominent land degradation process in agricultural land, especially in arid and semiarid areas with shallow groundwater depth [2,3]. An improper irrigation and fertilization schedule introduces an amount of dissolved salt into the waterlogged area, where salinization occurs due to the capillary ascent of groundwater with high salt content [4]. Salt-affected soil limits growth and reduces the yield of a wide range of crops [5,6]. As the degree of salinization increases without intervention, the salt-affected area may turn into a wasteland, and eventually the soil saline content is beyond the salinity tolerance of crops. As an evaporation sink, abandoned salinized farmland plays an essential role in maintaining sustainable farming by gathering salt from the surrounding cropping area [3]. Traditionally, evaluating the area of salt-affected areas and wasteland areas relies on human surveys, which are laborious and ineffective at the regional scale. Detecting salt-affected farmland in the landscape and monitoring the processes of regional land use by remote sensing are essential for agricultural management, soil improvement, and policy making.
With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, many efforts have been made to classify the land-cover type and degree of soil salinity using mono-temporal and time-series remote sensing products [7,8,9,10,11,12]. In general, methods for land-cover classification can be split into two groups: (1) spectrum-based approaches; and (2) visual-based approaches. Spectrum-based approaches distinguish the land surface based on the difference in reflected spectral signatures or the features of temporal dynamics. For instance, distinguishing vegetation area from bare soil is easy when using a predefined threshold of a vegetation index (VI) (such as the normalized difference vegetation index, NDVI) using mono-temporal imagery. However, classifying similar land types (such as kinds of vegetative areas) using mono-temporal VI information is troublesome. Time-series VI data were used to tackle this problem by introducing the features in the time dimension into the classification task [7]. For example, Yu et al. [13] classified crops using a time-series VI trajectory via the curve-fitting method. Supervised algorithms, such as support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), and neural networks (NNs), have shown superior capability in modelling high-degree nonlinear problems in land-use classification [14,15] and cropland abandonment detection [16,17,18]. Löw et al. [17] used machine learning algorithms (SVM and RF) to successfully distinguish abandoned cropland from a cropland dataset. However, abandoned cropland can be easily confused with spectrally similar land types in a regional task. To address this problem, Yin et al. [18] developed an RF-based model to detect abandoned cropland using several indices such as the bare soil index (BSI), normalized burn ratio (NBR), and NDVI time series as input. With the boom of computer vision technologies, the classification of the land-use type can be achieved by vision-based approaches using merely mono-temporal remote sensing data [19,20]. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), one of the visual-based deep learning approaches, have been widely used to classify Earth’s surface by extracting abstract textural features in imagery [21]. Many successful applications of CNNs have been reported in recent years in crop type classification [22], tree species classification [23], and abandoned cropland detection [24].
However, supervised machine learning algorithms require a wealth of labelled training data which is labor intensive and expensive, and CNNs require remotely sensed imagery with high spatial resolution. The difference in the temporal VI patterns among non-vegetative areas, such as dune area and abandoned salinized farmland, is small. As a result, insufficient training samples can result in the overfitting problem of supervised algorithms, limiting the performance of these methods for abandoned salinized farmland detection. Most previous studies have detected cropland that was abandoned mainly due to its poor topography, long distance to markets, or poor soil fertility. Approaches to detecting abandoned salinized farmland have not been well explored. Wu et al. [10] distinguished saline soil and dune areas using the thermal band because dune areas have higher surface temperatures due to limited evaporation and lower thermal capacity. However, separating the salt-affected soil and other non-vegetative areas (e.g., urban areas) was difficult due to the similar vegetation index value and surface temperature. Strong saline soil shows higher reflectance in the visible and NIR wavelength ranges than less salt-affected areas [11]. Utilizing the reflection characteristics of saline soil, various soil salinity indices (SI) have been designed to assess the degree of soil salinity [12,25,26]. The SI is preferred to quantify the soil salinity in uncropped areas to bypass the influence of vegetation, indicating that it has a limited ability to detect abandoned salinized farmland. Moreover, distinguishing non-vegetative surfaces using the SI has not been discussed much.
Previous studies have mainly focused on limited types of land-use classification or evaluating the soil salinity degree from non-vegetative areas. Most of them failed to identify abandoned salinized farmland, which is crucial in gathering salt from surrounding cropping areas [3]. Wu et al. [10] detected abandoned salinized farmland using mono-temporal imagery via supervision classification. However, mono-temporal data provided limited information for the target and may be influenced by the timing of detection. Therefore, a robust and accurate method that can detect abandoned salinized farmland and evaluate the soil salinity degree simultaneously from temporal remotely sensed data is needed to assess the salinization process over a larger area.
In this study, a method based on the concept of decision trees was developed to monitor the long-term dynamics of salinization in the Hetao Irrigation District, an irrigation system that is over two thousand years old in North China. The direction of the salinization process can be affected by both natural and human factors, while a shallower groundwater table with higher evaporation demands is prone to salinization. In contrast, deeper groundwater levels with sufficient infiltration water (e.g., rainfall and irrigation) show positive signs of desalinization [27,28,29]. Human-related activities may be the dominant factor in determining the direction of salinization for human-dominated land use [30]. However, sometimes the human impacts caused by socioeconomic factors can be spontaneous, making such impacts difficult to predict. For example, a large-scale shift of the cropping structure may disturb the previous balance of the water–salt system, thereby affecting the salinization process. Therefore, the objectives of this study were: (1) to assess the spatio-temporal patterns of the abandoned salinized farmland via remote sensing data backed by a robust and accurate method; and (2) to analyze the influence factors that affect the long-term dynamics of the salinization process in Hetao.
2. Study Area
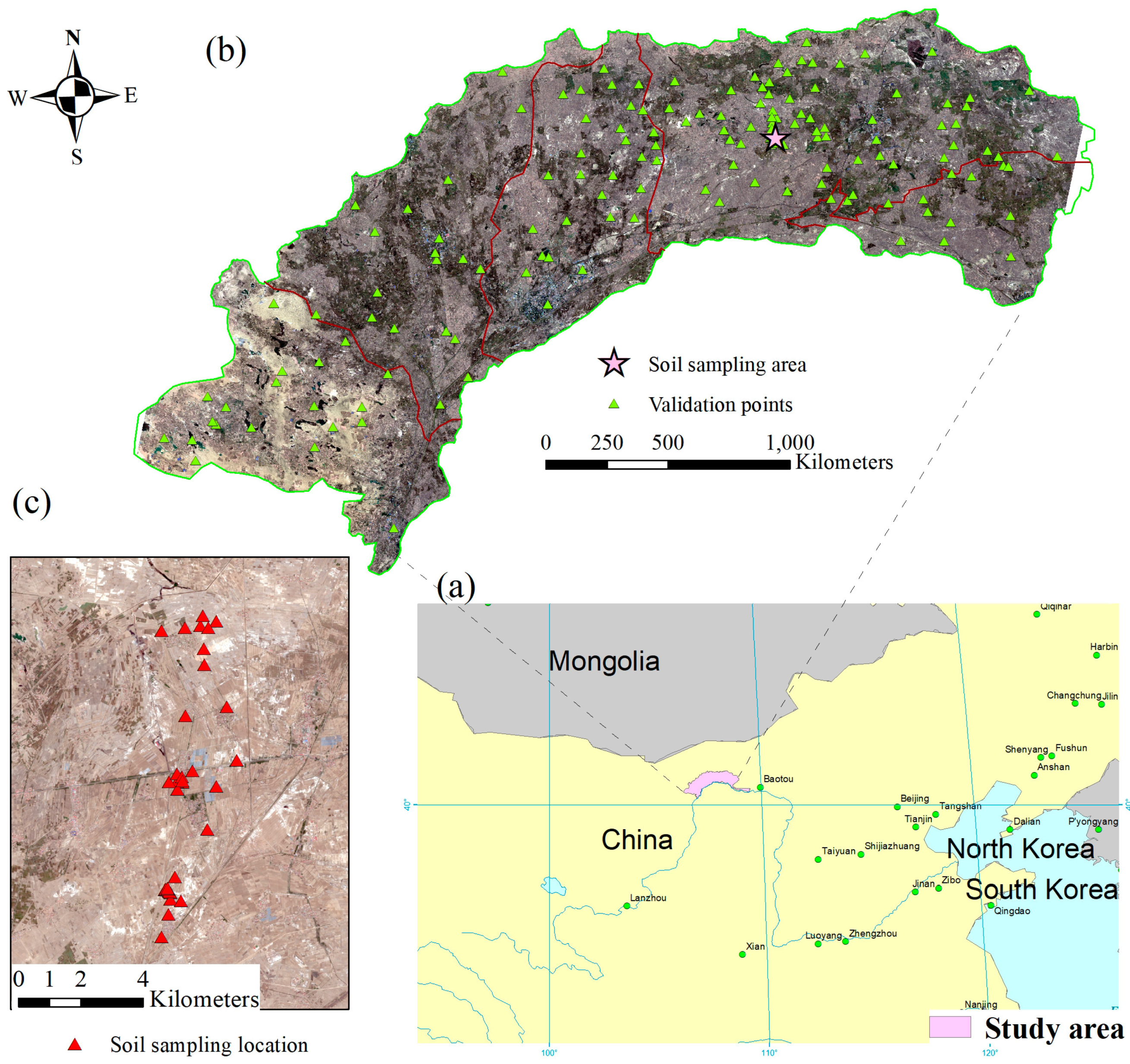
Covering a total area of 1.12 × 106 ha, the Hetao Irrigation District (40.1°–41.4° N, 106.1°–109.4° E) is one of the largest irrigation systems in China (Figure 1). The study area is approximately 250 km in width from west (Wulanbuhe Desert) to east (Wuliangsuhai Lake) and 50 km in length from south (Yellow River) to north (Langshan Mountain). There are mainly five types of surface coverage in the Hetao Irrigation District recorded in the 2020 land cover products provided by GlobeLand30 (http://www.globallandcover.com/, accessed on 31 August 2021). The sand dune area is mainly distributed in the western part, accounting for approximately 7% of the total area. The area with water bodies is approximately 6%. Wuliangsuhai Lake, the largest lake in Hetao, is located in the eastern part of the study area and receives drainage water from the irrigation system. The vegetative area and residential area account for 77% and 8% of the total area, respectively. Spring wheat, maize, and sunflower are the major crops in Hetao, with areas of 4.9 × 104 ha, 3.0 × 105 ha, and 2.8 × 105 ha in 2020, respectively (http://tjj.bynr.gov.cn/, accessed on 31 August 2021). Due to the typical arid and semiarid climate, the Hetao Irrigation District has deficient annual average precipitation (ranging from 60 mm to 280 mm), which is mainly concentrated in July and August, while the potential evaporation reaches 2000–2400 mm per year. The large divide between crop evapotranspiration and actual rainfall provokes high dependence on irrigation water for agriculture.
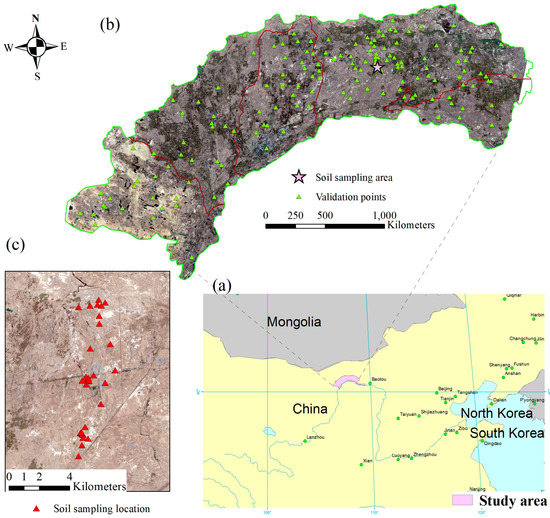
Figure 1.
Overview of the Hetao Irrigation District: (a) geographic location, (b) land surface of the study area depicted by Landsat 8 OLI imagery captured on 30 October 2019, and (c) soil sampling locations for EC measurement.
In Hetao, the main irrigation method is flood irrigation. In response to the national water-saving irrigation policy, drip irrigation has been deployed in Hetao since 2015. However, most areas with drip irrigation are small demonstration areas. Approximately 4.79 billion m3 of water per year (2020, Statistics Bureau of Bayannur City) is diverted into the Hetao area from the Yellow River. The enormous scale of irrigation has lifted the groundwater table of Hetao, which varies between 0.5 and 3.0 m annually. In the meantime, irrigation water transports salt into the groundwater, which makes the salinity of the groundwater increase. Capillary water with high saline content brings salt into the field, and thus, soil salinization occurs.
An artificial drainage system was established to combat the soil salinization process in the Hetao Irrigation District. However, this system operates with low efficiency due to the gentle slope of the terrain in the Hetao area, by which merely thirty percent of the inlet salinity was drained out of the irrigation district. To balance the soil salinity in the field, local farmers deploy a typical irrigation pattern, termed autumn irrigation; that is, irrigating the uncropped field after harvest (usually conducted from mid-October to mid-November). An amount of water is applied in the autumn irrigation to leach the soil salinity downward, which balances the annual soil salinity. Unfortunately, autumn irrigation only leaches the salt-affected surface soil, and there may be an adverse effect if an overdose of irrigation is applied. The soil saline content in the over-irrigated land bounces back in spring after the thawing of the soil water.
3. Methods
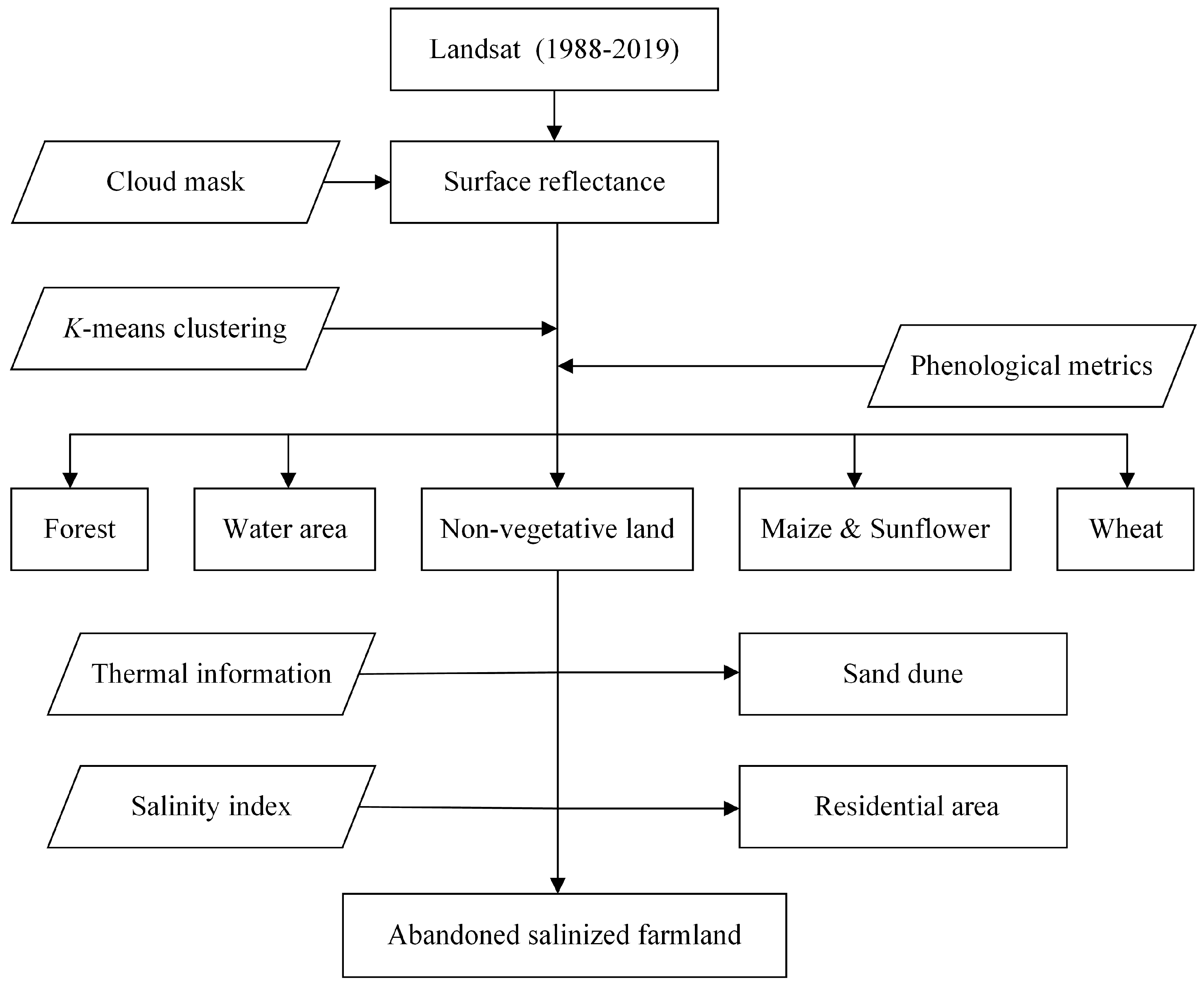
As it is challenging to detect abandoned salinized farmland directly from remote sensing imagery, a method that adopts a step-by-step strategy to exclude the other land types was used in this study. First, all pixels (a pixel is an n-dimensional vector where n is the number of investigated satellite imageries) in the stacked time-series NDVI imagery were classified into 20 unlabeled classes via the K-means clustering algorithm. Then, representative final clusters corresponding to the main land types were manually selected to build a plant shape model. Second, the pixels of non-vegetative areas and water bodies were detected by merging the final clusters based on the predefined threshold; for the vegetative area, the shape-model-fitting method was used to classify each cluster into a specific plant type. Next, sand dunes and residential areas were detected using pixel-based thermal information and the salinity index, and the area of abandoned salinized land was detected after stripping sand dunes and residential areas from non-vegetative areas. Finally, the number of pixels for each land type was counted, and the area was equal to the pixel number multiplied by 30 m × 30 m, where 30 m is the spatial resolution of Landsat imagery. A brief workflow chart is shown in Figure 2, and details of the methodology are described in the following sections.
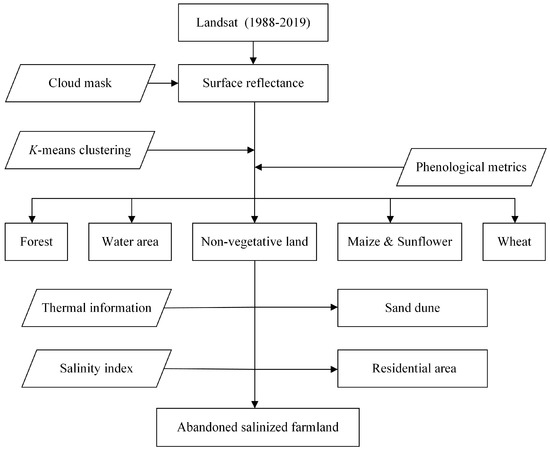
Figure 2.
Methodological workflow.
3.1. Data Processing
3.1.1. Satellite Data
Thirty-two years (1988–2019) of temporal Landsat data (including Landsat 5 TM, Landsat 7 ETM+, and Landsat 8 OLI downloaded from the USGS website: (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/, accessed on 31 August 2021) were used to develop an accurate approach to detect abandoned salinized farmland and to analyze the progress of salinization in Hetao. A total of 207 and 67 cloud-free (rate of cloud cover less than 10%) temporal imageries of Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 8 OLI from 1988 to 2011 and 2013–2019 were investigated, respectively. Due to the failure of the scan line corrector (SLC) in the ETM+ instrument after 2003, the imagery taken by Landsat 7 lost approximately 22% of the information [31]. Consequently, we deployed only six ETM+ imageries for 2012 when the TM instrument was retailed and the OLI was still not online. In addition, high spatial resolution imagery from Sentinel 2 was used to establish a regression model between the salinity index (SI) and measured soil electrical conductivity (EC). Detailed information on the satellite data used is shown in Table 1. Information about acquisition time and identifiers of used data is summarized in Table S1 (Supplementary Material).

Table 1.
Details of the investigated remote sensing data.
The thermal band of the downloaded Landsat level-1 product was radiometrically calibrated with the brightness temperature data using ENVI 5.3 software (Harris Geospatial, Boulder, CO, USA). For other bands, the surface reflectance data were retrieved from the level-2 product. The missing information in the ETM+ imageries was recovered using the interpolation toolbox of ArcGIS 10.3 software (Environmental Systems Research Institute, West Redlands, CA, USA). All thermal imageries were interpolated to 30 m to maintain consistency with VI data For the Sentinel 2 level-1C product (top-of-atmosphere reflectance), the atmospheric correction procedure was conducted by the Sen2Cor toolbox developed by ESA (https://step.esa.int/main/snap-supported-plugins/sen2cor/, accessed on 31 August 2021). The tiles of imageries were mosaicked and subsequently clipped to fit into the predrawn boundary of the study area. The cloud contamination problem is the main obstacle to deploying optical remote sensing products for monitoring Earth’s surface. The simple cloud score algorithm was used to calculate the pixel-based cloud score as follows [32]:
where the cloud_score represents the cloud likelihood. A larger value of cloud_score indicates a greater likelihood of a pixel being cloudy. ρx is the top-of-atmosphere (TOA) reflectance, as shown in Table 1. Tb denotes the brightness temperature. A threshold of 0.3 was used to mask clouds in this study.
3.1.2. Ground Data
Soil samples were collected from the surface at a depth of 0–5 cm. The geolocation for each sampling point was recorded by a GPS device (GPSmap 76, Garmin Company, Olathe, KS, USA) which has an acceptable accuracy (±1.45 m). A total of 133 soil samples were collected from 33 preselected observation sites from May 2018 to October 2019 (Figure 1c). Ten grams of dried and crushed soil sample was weighed and 50 mL of deionized water was added, mixed well, and allowed to stand. After the solution was layered, a conductivity meter (DDSJ-308A, Leici, Yidian Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used to measure the EC value of the supernatant. Then, repeated EC measurements were averaged for each observation site. Linking the soil sampling sites and Landsat imagery was inappropriate due to the high spatio-temporal heterogeneity in the sampling area. As a result, the measured EC values at each site were estimated from the corresponding SI in the high spatial resolution Sentinel 2 imagery collected on 22 April 2019, when the area was uncropped and unfrozen. The statistical crop areas of Bayannur city, including the planting area for spring wheat, corn, and sunflower, were available at the Statistics Bureau of Bayannur City (http://tjj.bynr.gov.cn/, accessed on 31 August 2021). Notably, most cropland in Bayannur City was in the Hetao Irrigation District. Therefore, the statistics of Bayannur city were used to validate the results.
3.2. Analyzing Temporal Remotely Sensed Imageries
Detecting and excluding vegetative areas was the first step in detecting abandoned salinized farmland. The traditional mono-temporal VI threshold-based method is sensitive to the selected threshold, and it may be influenced by the timing of the detection (e.g., flooded irrigation and the variability of the planting schedule may degrade its performance). Therefore, time-series VI was used to analyze the dynamics of the land cover from different years to pursue higher accuracy. Potential land types were classified by the K-means clustering method and the land types of interest were detected and merged via the shape-model-fitting method. The irrigation strategy is determined by cropping structure, which may affect the evolution of abandoned salinized farmland. As a result, the regional cropping structure was additionally detected from clustering results via the shape-model-fitting method [33].
3.2.1. Land Cover Classification via K-Means Clustering
K-means clustering [34], an unsupervised method that accepts arbitrary shapes of input for an individual year, was used to preliminarily classify Earth’s surface. The applicability of unsupervised methods against supervised methods in different situations is discussed in Section 5 This algorithm assumes that the samples have k cluster centers and optimizes the cluster centers by minimizing the within-cluster distances (objective function) as follows:
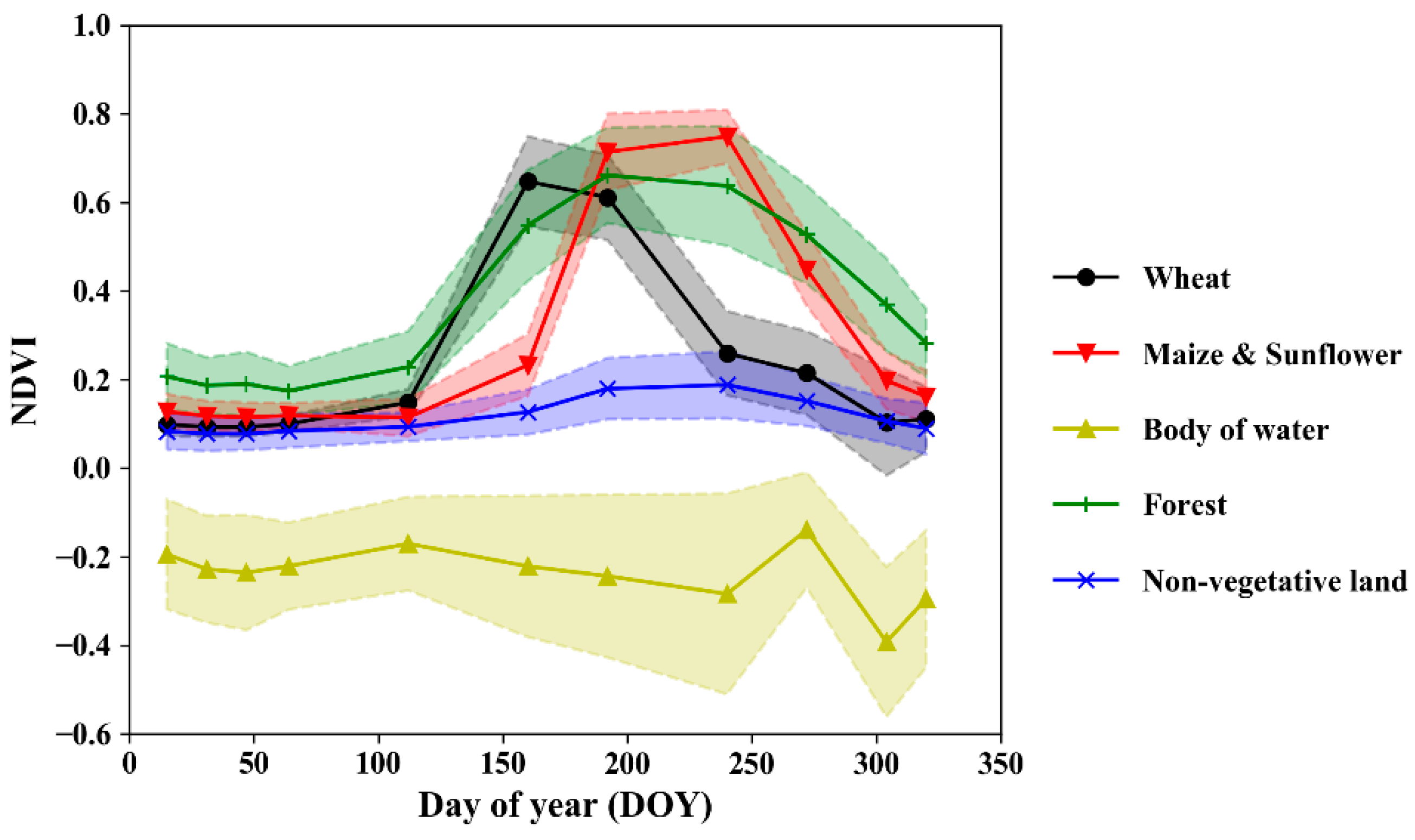
where Ci is the cluster group and μi is the cluster center for Group i. The initial positions in the centroids were randomly selected from the samples. The variation in initial centroids introduced uncertainty into the final result. Therefore, the K-means algorithm was run 10 times with different centroid seeds in this study, and the best case of initial centroids was selected based on its rate of convergence (K-means clustering was deployed by the Python Sklearn package). After clustering, representative final clusters corresponding to main land types were manually selected to analyze their typical VI patterns (Figure 3) and to build a plant shape model to distinguish specific vegetation types (Section 3.2.2). The temporal reflectance dynamics of distinct surfaces are diverse due to the significant differences in the spectral reflectance characteristics of different landscapes. For a planting area, the number of peaks of the VI trajectory was determined by the number of cropping cycles. There is only one growing season in the Hetao Irrigation District due to the extremely low temperature in the winter. As a result, the VI dynamics of a cropping area show a single peak at the maximum leaf area index (LAI) stage (for instance, spring wheat reaches the maximum greenness at the heading stage at approximately DOY 160, while summer maize and sunflower peak at approximately DOY 210). The bodies of water show a negative temporal NDVI throughout the year that makes them easy to identify. The water body area accounts for a small proportion of the total area of the study area, and the spatial variability of water quality is relatively large. As a result, the standard error of NDVI is relatively larger for the body of water. The non-vegetative land has an NDVI with low variability, and the forest shows a long duration in growing season. However, the final classification results were unstable for different random seeds, although the initial centroids were optimized. For this reason, a large k, which is far greater than the actual classes, was used to explore more potential land types. Then the threshold-based method was used to detect and merge the non-vegetative area and water body, and the “shape-model-fitting” method was used to detect and merge specific vegetation types from the final clusters. A higher k allows the algorithm to split the vegetative and non-vegetative areas into land-use types at a fine scale but at the cost of heavy computation. The value of k was determined by the trial-and-error method, and k = 20 was finally applied to make the uncertainty of the final detection of land type small. Then, the types of interest were identified and merged by predefined rules. Specifically, cluster centers with an annual average NDVI (average value of NDVI time series for each year) ranged from 0 to 0.2 were regarded as non-vegetative land, and water bodies were confirmed if the value was negative. For the vegetative area, a shape-model-fitting method is introduced in the next section to identify specific crops based on phenological metrics.
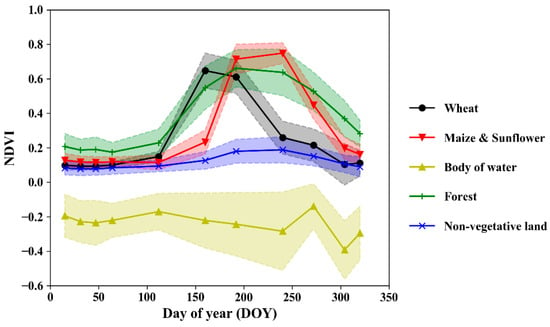
Figure 3.
Examples of cluster centers with annual temporal NDVI in the Hetao Irrigation District in 2019. The shaded width area denotes the standard error (calculated by the NDVI value of all pixels in this class) for each group.
3.2.2. Detecting Cropping Structure Based on Phenological Metrics
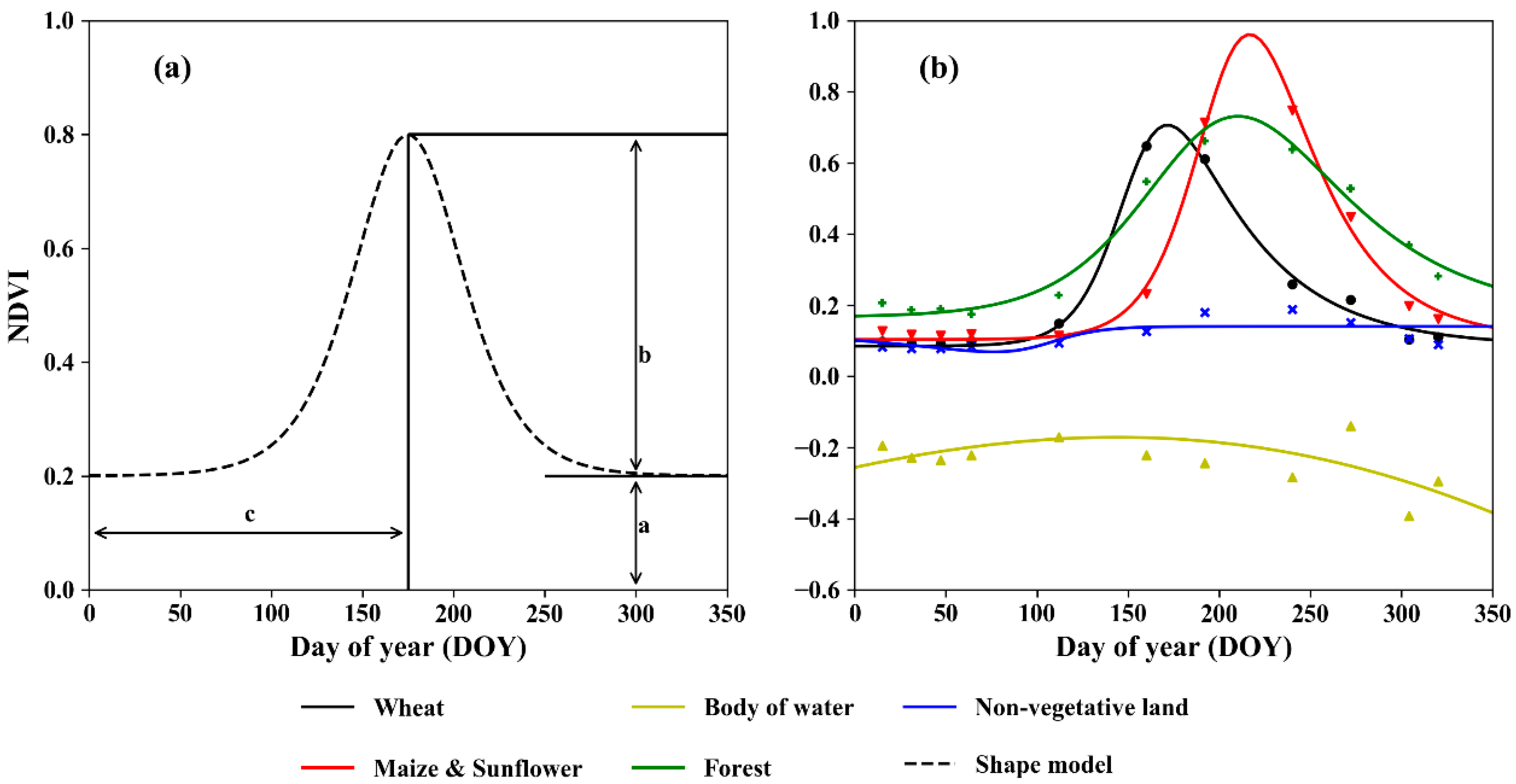
The time-series NDVI for each cluster center was fitted by the shape model (an asymmetric logistic curve in this study) to identify the cropping structure of crops (Equations (9) and (10)).
where f(x) is the shape model with five fitting parameters: a, b, c, d, and k (Figure 4a). The shape model represents the typical temporal VI pattern for a specific crop [33,35]. a refers to the base value of the NDVI. b denotes the difference between the maximal NDVI and a. c is the DOY when the NDVI reaches the peak. d and k control the wideness and the skewness of f(x). The two inflection points of f(x) are:
where the left inflection point denotes the fastest growth stage and the right inflection point corresponds to the senescence stage. Here, we introduced the growth active period (GAP) calculated as follows to represent the growing season length for each plant.
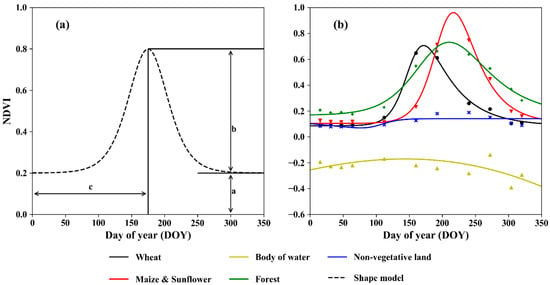
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of phenological metric extraction by shape-model-fitting method.
The optimal fitting parameters were retrieved by fitting f(x) on the discrete VI points via the least square error method using the “scipy.optimize” module in Python. The fitted shape models for the dominant land cover types are shown in Figure 4b. Spring wheat was planted ahead of other crops, and thus, parameter c was significantly smaller. The forest area shows a longer GAP than the crops, and an infinite GAP was observed for non-vegetative land cover types. However, distinguishing corn and sunflower is challenging due to the similar VI dynamics, which require data with a higher temporal resolution [13]. As a result, this study did not distinguish corn from sunflower but only classified them into one category containing plants with tall stems.
3.3. Detecting Sand Dunes and Deserts Using Thermal Information
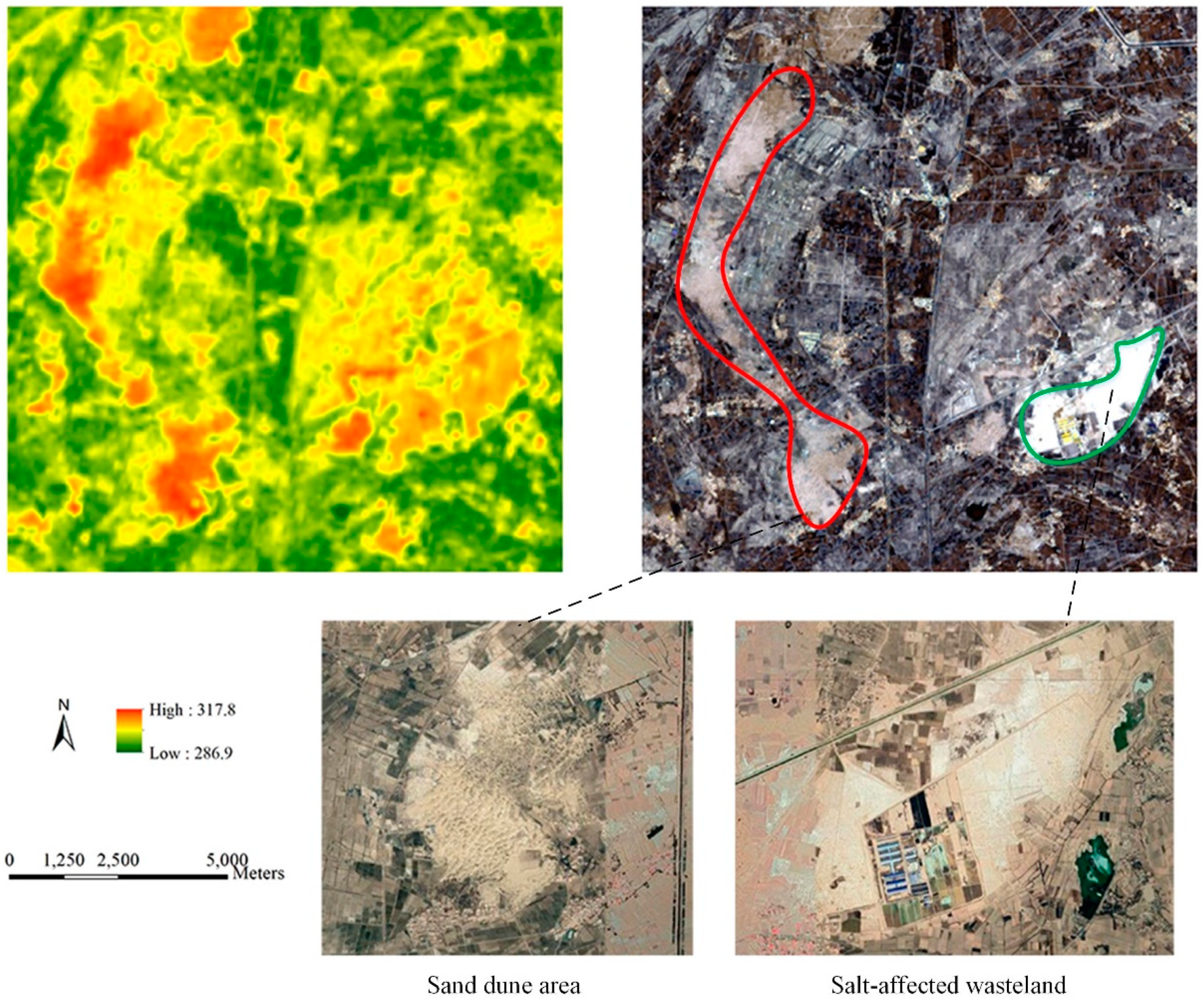
Different crop fields (such as wheat and corn and sunflower) and non-vegetative land (including sand dune area, bare soil area, residential area, and abandoned salinized farmland) in Hetao were successfully detected by the K-means clustering and shape-model-fitting methods. However, the methods failed to subdivide the non-vegetative land with a similar temporal VI pattern. Thermal information was used to mask the sand dune area (or desert) out of the retrieved non-vegetative land using their significant difference in brightness temperature (Figure 5 and Figure 6). Evapotranspiration (ET) of sand dune areas is largely determined by rainfall, resulting in a high-level net radiation (Rn) partition to the sensible heat flux (H). In contrast, abandoned salinized farmland (Figure 5) and residential areas (Figure 6) show lower surface temperatures than sand dune areas due to the higher air-specific humidity and soil moisture.
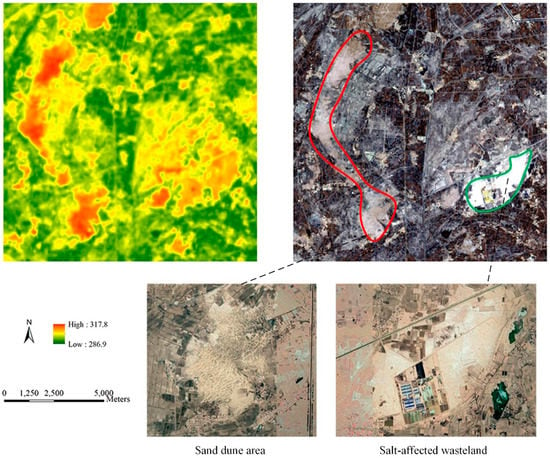
Figure 5.
Example of the difference in brightness temperature between sand dune areas and abandoned salinized farmland. The top left subplot is the brightness temperature data (K) calculated from Landsat 8 OLI imagery (acquired on 10 July 2019). The top right is the corresponding composed RGB imagery. The red area of interest (AOI) denotes the sand dune area, and the green area is the abandoned salinized farmland. The lower subplot is the corresponding Google Earth map that shows the details of AOIs.
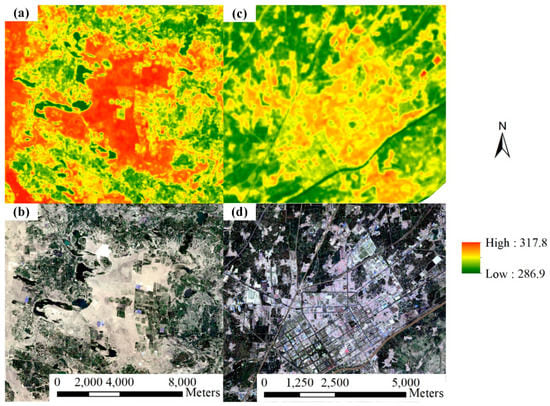
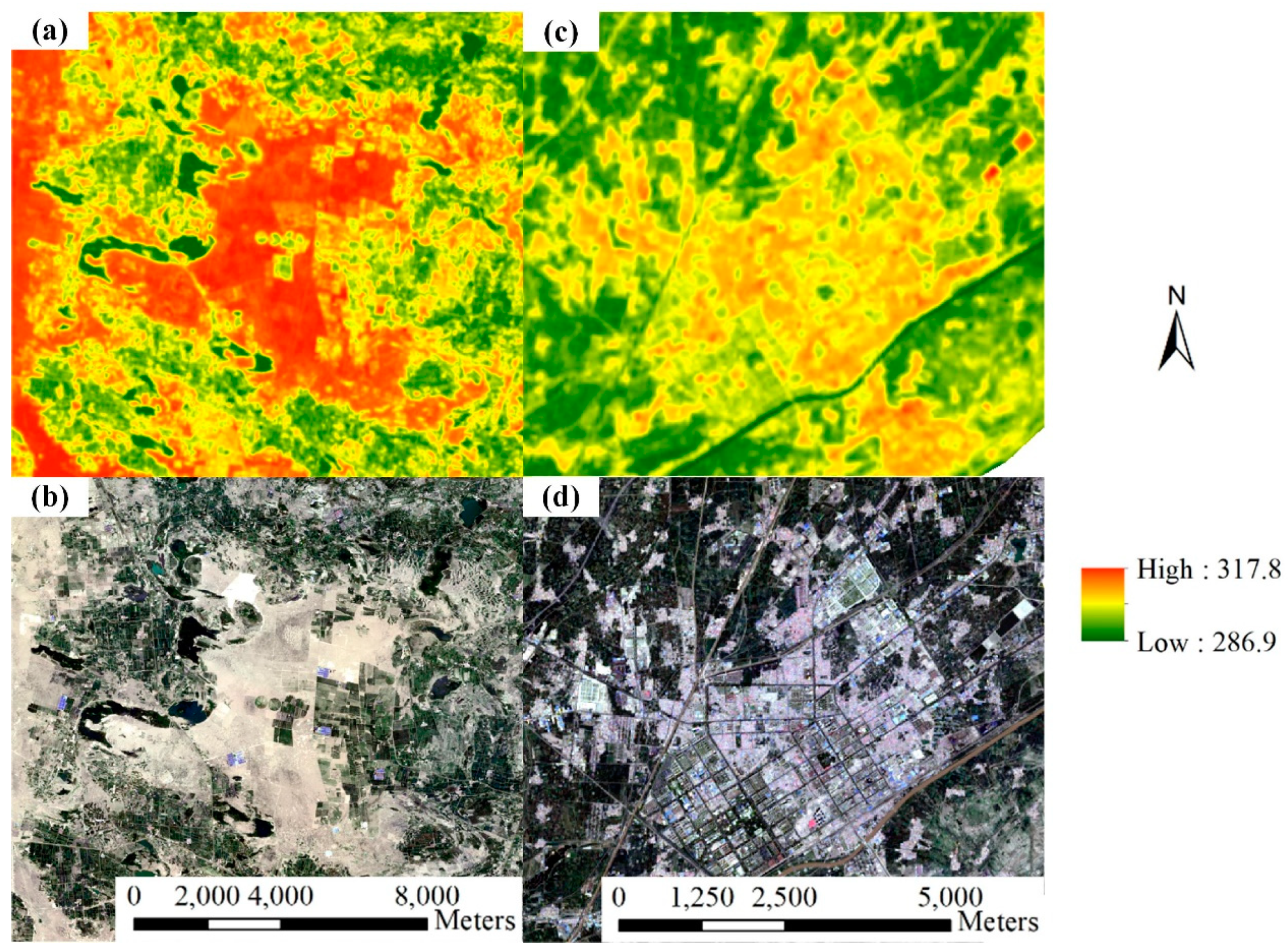
Figure 6.
Example of the difference in brightness temperature (K) between the (a,b) desert and (c,d) residential areas (Landsat OLI imagery collected on 10 April 2019). (a,c): brightness temperature imagery, and (b,d): composed RGB imagery.
Otsu’s method [36], which searches for the threshold by maximizing inter-class variance (between-class variance), was used to distinguish the sand dune area automatically from other non-vegetative surfaces. Specifically, the brightness temperature was calibrated from the Landsat thermal band (band 6 for TM and ETM+, and band 10 for OLI), and optimal threshold k* between two classes was iteratively calculated as follows:
where σ2B is the between-class variance, and L denotes the maximum value of the investigated variable.
3.4. Detecting Abandoned Salinized Farmland
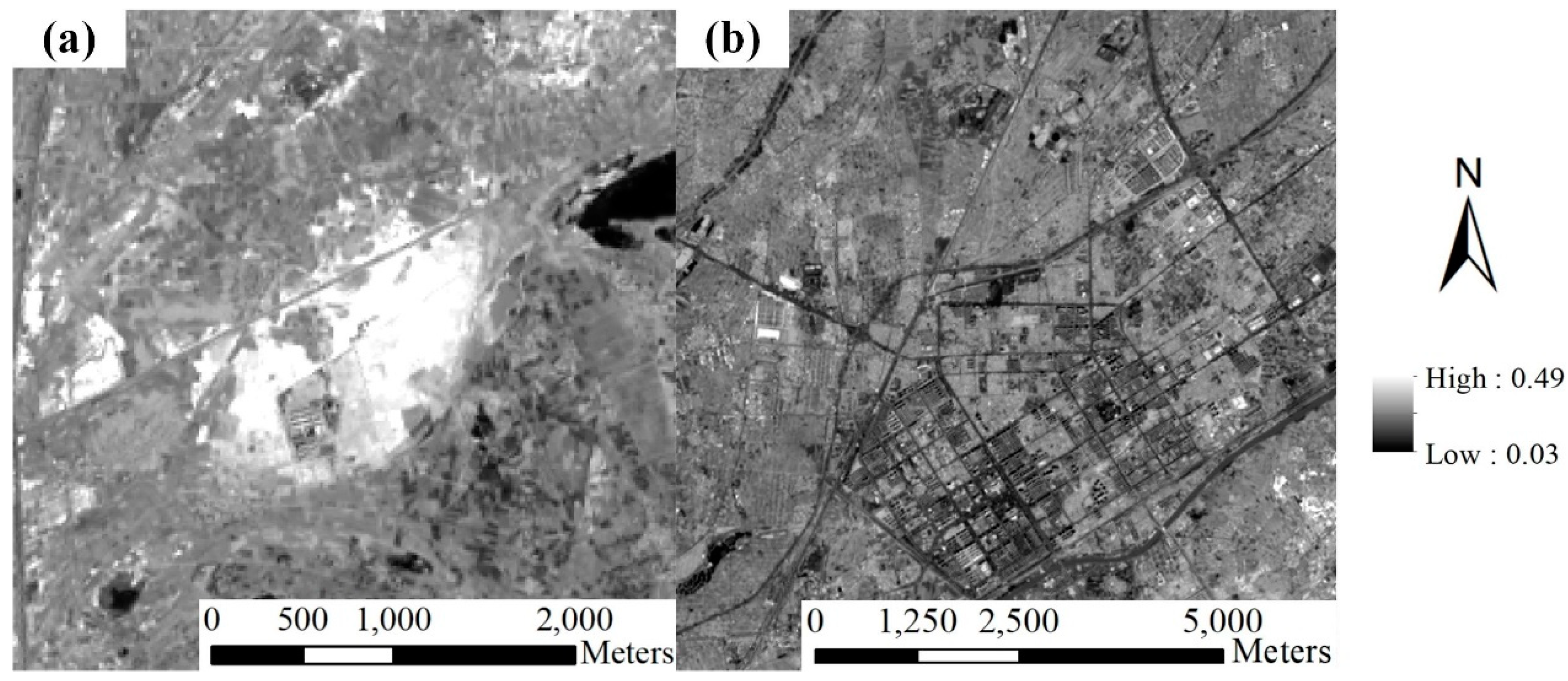
With a similar brightness temperature, the bare soil and residential areas were still mixed with the expected abandoned salinized farmland, although the sand dune area was masked out from the non-vegetative land. The abandoned salinity field showed a bright color in the composed RGB imagery (Figure 5), indicating that it reflected more radiation in the visual bands. The widely used SI calculated as follows was deployed to extract the abandoned salinity field [37,38].
where ρblue and ρred refer to the surface reflectance of the blue band and red band, respectively. The SI difference between abandoned salinized farmland and residential area is shown in Figure 7. Apparently, there was a higher-level SI in abandoned salinized farmland than in residential areas. Similar to the extraction of sand dune areas, the threshold-based method was used for the extraction. Finally, abandoned salinized farmland was detected, combining temporal VI data, thermal imagery, and SI data.
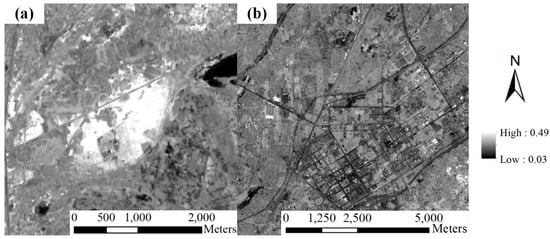
Figure 7.
Example of SI map of (a) the abandoned salinized farmland and (b) the residential area.
3.5. Performance Measures
In this study, a total of 150 validation points (including 22, 37, 23, 12, 15, 13, 16, and 12 points for wheat, corn/sunflower, other crops, forest, water body, sand dune, residential area, and abandoned salinized farmland, respectively) were selected to validate the accuracy of the land-use identification and abandoned salinized farmland identification in 2019 with metrics of precision, recall, F1-scores, and accuracy. The validation points were labelled manually using very high spatial resolution imageries (satellite constellation from Planet Lab Inc. and Google Earth imageries). The spatial distribution of validation points is shown in Figure 1b. Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances, while recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that were retrieved. The F1-score can be understood as a combination of both precision and recall. It should be noted that accuracy takes into account only the total number of samples and thus may be a misleading metric for imbalanced datasets. In contrast, precision, recall, and F1-score consider the total number of samples for each class separately.
where TP, TN, FP, and FN represent the true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative predictions, respectively.
4. Results
4.1. Evolution of Cropping Structure in Hetao
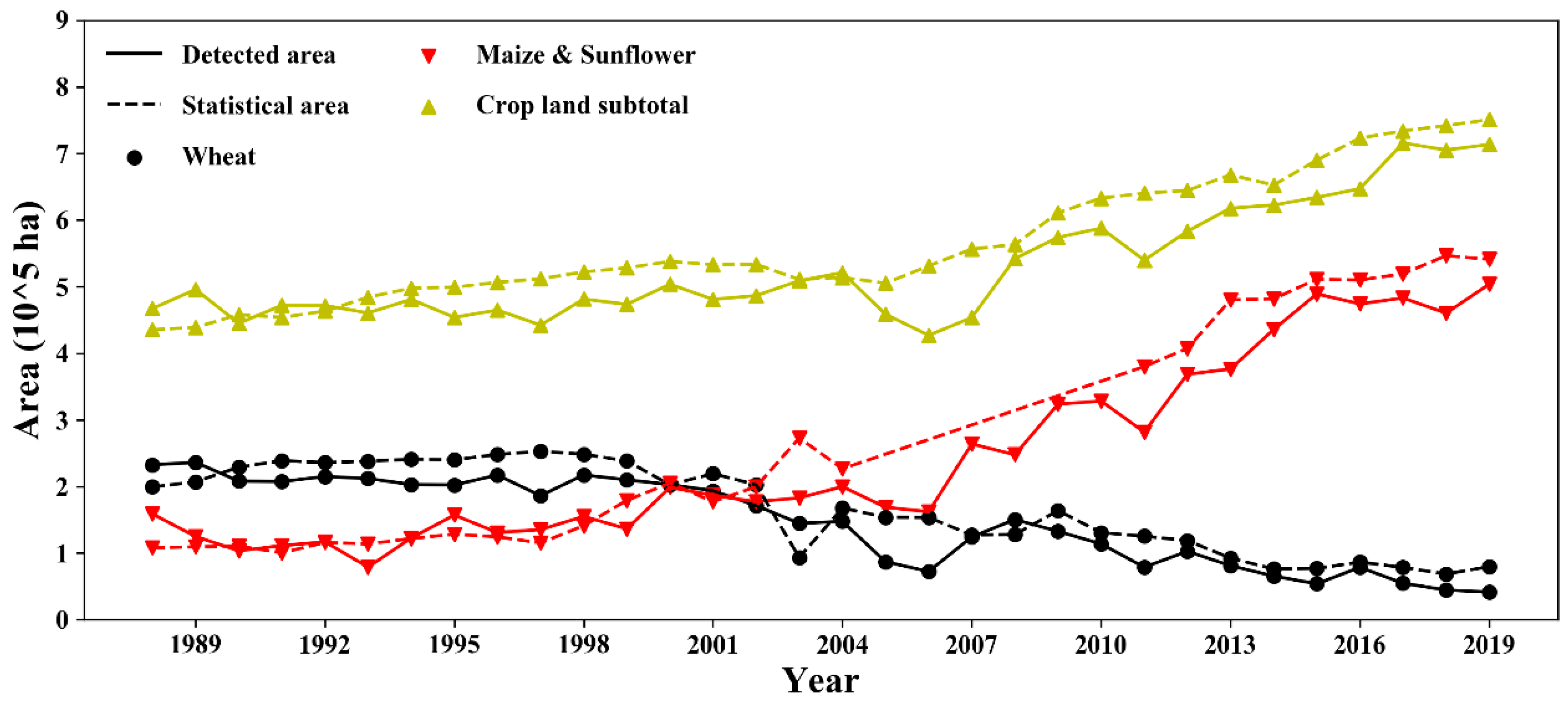
The variation in cropping structure during 1988–2019 is shown in Figure 8. The remote sensing results are in good agreement with the statistical data. The Hetao Irrigation District is included in the administrative region of Bayan Nur city. Consequently, the detection area is generally smaller than the statistical data (statistics include data outside the study area). In general, the results show that the cropland in Hetao has continuously expanded during the last thirty years (area of total cropland has increased from 4.7 × 105 ha to 7.1 × 105 ha). The spring wheat planting area initially accounted for nearly 50% of the crop planting area (1988). However, since 2000, the wheat planting area has shrunk year by year, and in 2019, it was only 6%. This is because an increasing number of local farmers have tended to plant economic crops instead (e.g., sunflower) to make higher profits. As a result, in 2000, the total area of maize and sunflower surpassed the area of wheat (2.0 × 105 ha), and in 2019, the area of maize and sunflower accounted for 70% of the total cropland.
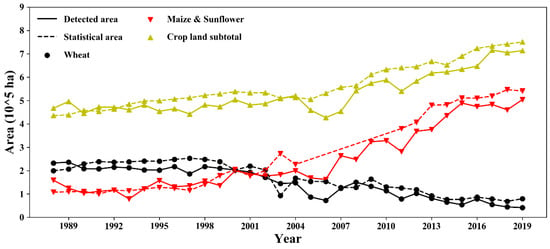
Figure 8.
The evolutionary progress of cropping structure in Hetao from 1988 to 2019. The dashed lines represent the statistical area of Bayan Nur city. The solid lines are the detected cropland area in the Hetao Irrigation District.
The detected area for each crop was significantly underestimated in 2006 and 2011 (residual error between statistics and estimates of the total cropland area up to 10.4 × 105 ha and 10.1 × 105 ha, respectively). This is because the weather conditions of the study area were cloudy in those years; therefore, there were fewer remote sensing data available than in other years.
4.2. Desalinization Progress in Hetao
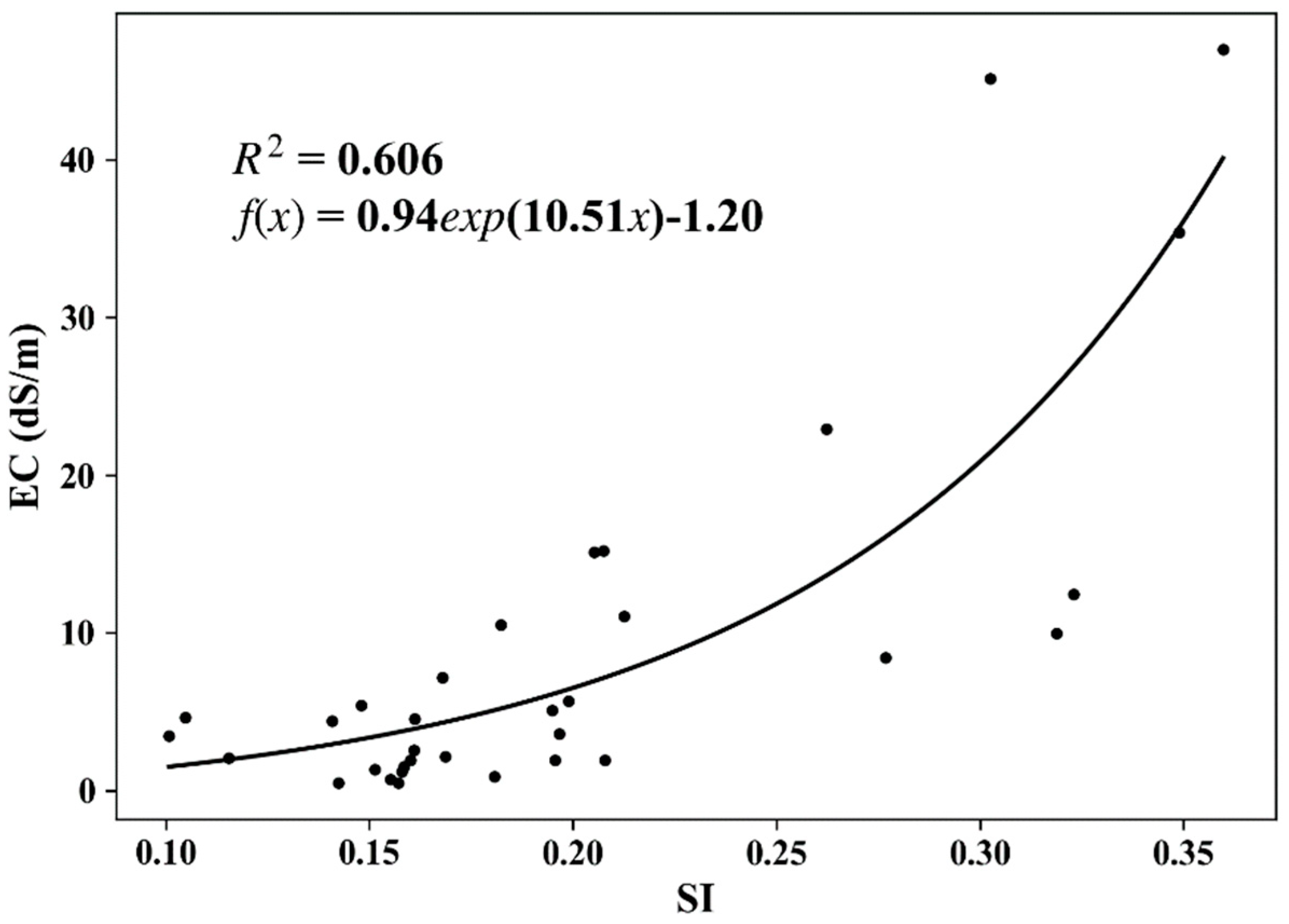
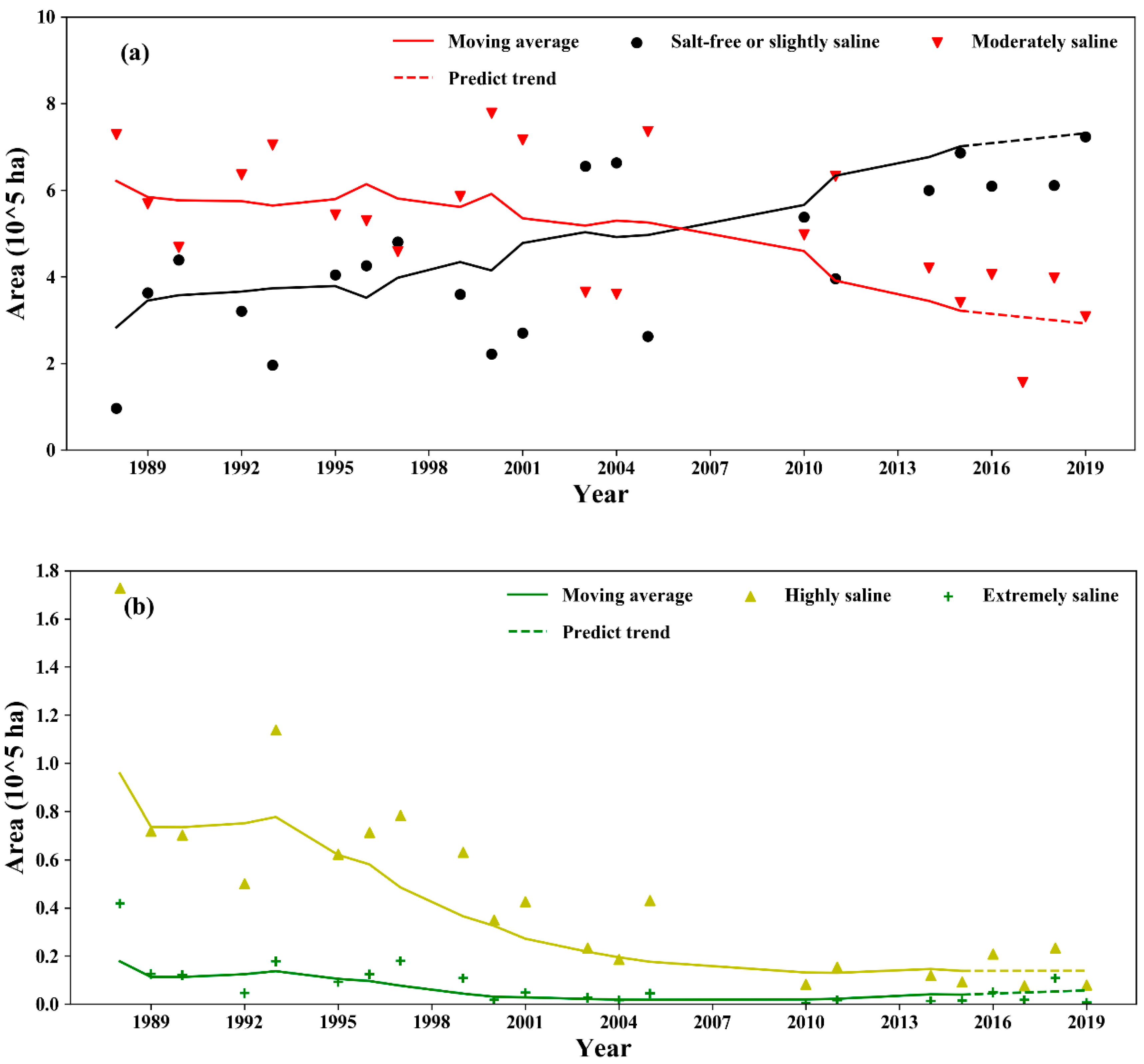
A significant exponential relationship between the SI and measured soil EC values is shown in Figure 9. The EC map was estimated from the SI via the SI–EC relationship in Figure 9, and the salinity classes were determined by EC values using the widely used criteria as follows: (1) 0–4 dS/m: salt-free or slightly saline; (2) 4–8 dS/m: moderately saline; (3) 8–16 dS/m: highly saline; and (4) >16 dS/m: extremely saline [39]. The area was calculated by counting the number of pixels for each saline class (Figure 10). Some research has indicated that the shows the best results [38], while the results of that study were for the entire study area; different degrees of salinity were not studied separately. In the future, more samples should be collected to analyze different degrees of salinization separately. Only imagery collected in March and April was used to calculate the SI when the study area was crop-free and unfrozen. The missing data for specific years indicated that there was no cloud-free imagery available from March to April. The results show that the area of non- (or slightly) saline conditions continued to expand from 1988 to 2019. In contrast, the rate of decline for the moderately saline area has accelerated since 2000, while the highly saline area shrank sharply from 1993 to 2001. The area with extreme salinity decreased to a low level after 2000, indicating the construction of drainage facilities and promoting water-saving irrigation technology, which shows a positive effect on desalinization.
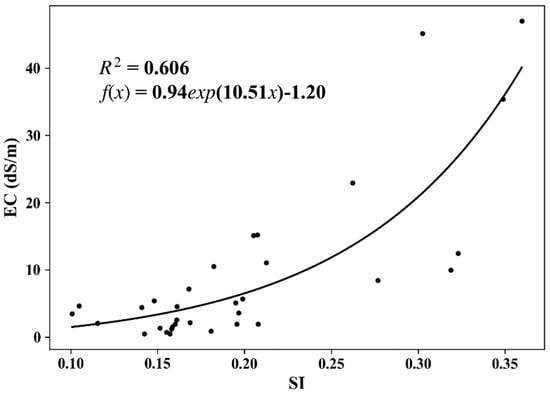
Figure 9.
Exponential relationship between the SI (Sentinel 2) and measured EC. The SI was calculated from Sentinel 2 imagery from 22 April 2019 when the area was uncropped and unfrozen.
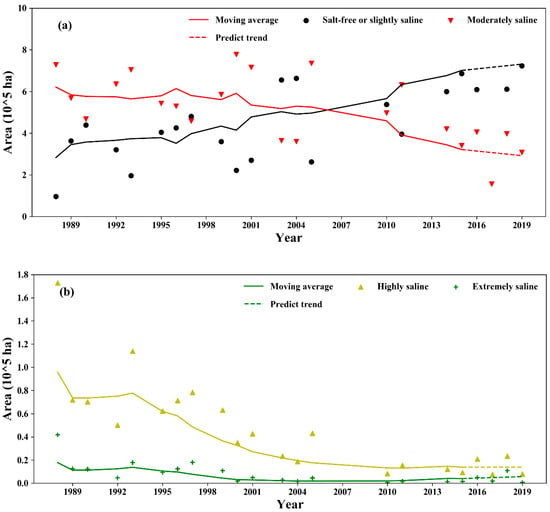
Figure 10.
The dynamics of desalinization in Hetao: (a) salt-free/slightly saline and moderately saline; (b) highly saline and extremely saline. The area for each year was statistically analyzed using mono-temporal SI data from March or April when the study area was uncropped. The trends are depicted by moving average data with a window of 5.
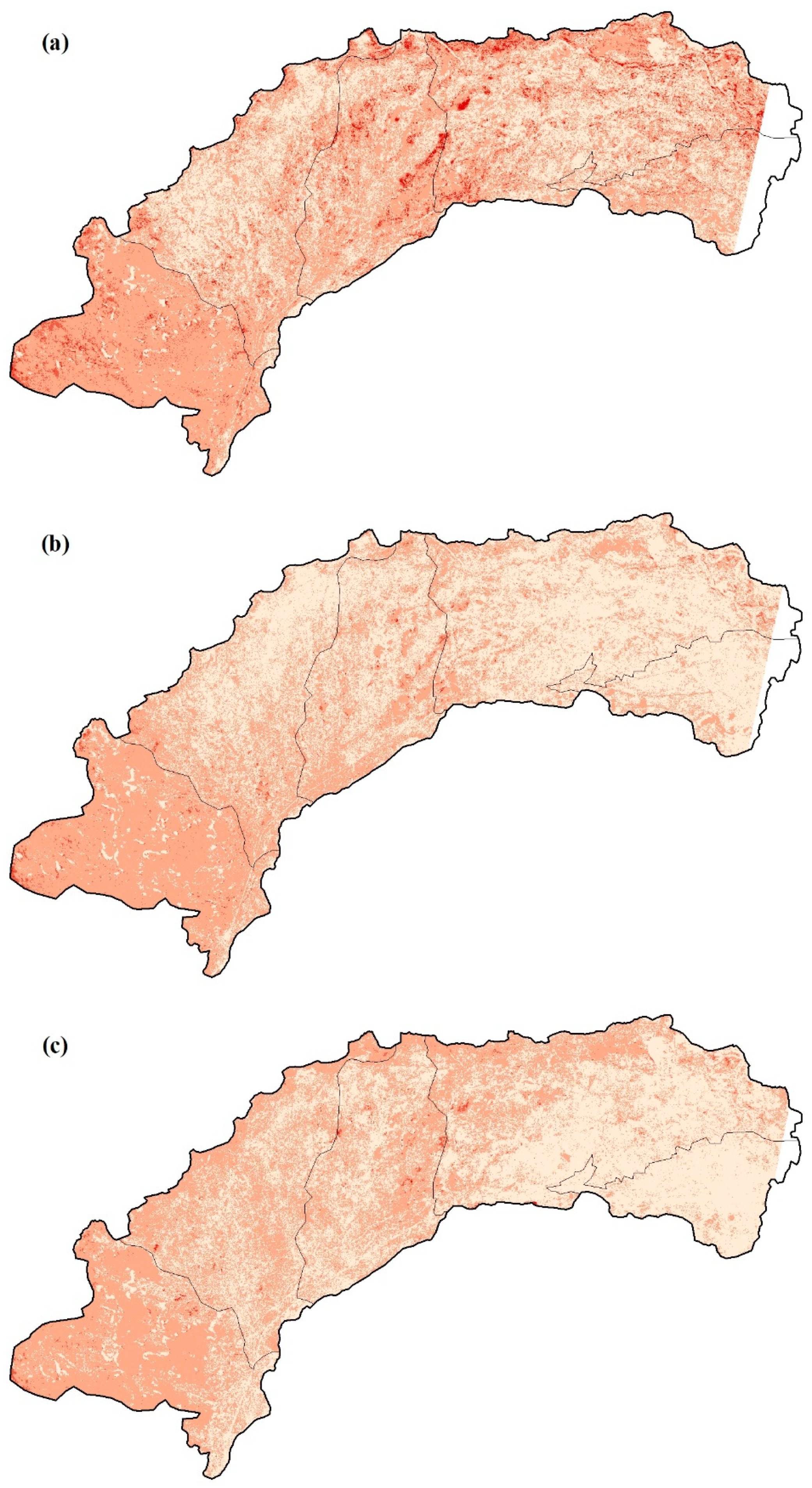
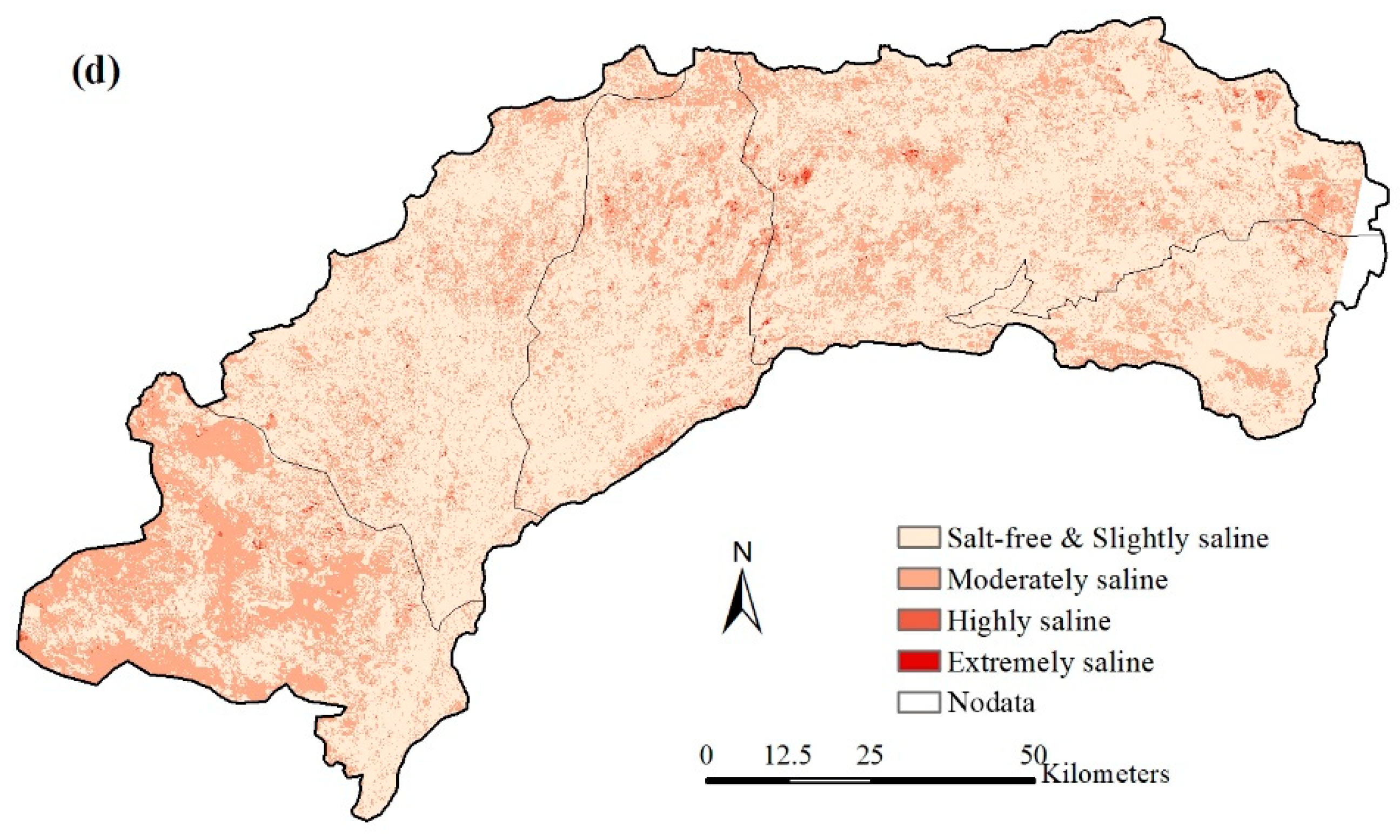
The spatial distribution of saline classes in Hetao from 1988 to 2019 is visualized in Figure 11. In 1988, most lands in Hetao suffered varying degrees of salinity, and the areas with extreme salinity were scattered throughout the study area. Due to the construction of drainage facilities, this situation was relieved in the next two decades. A pumping station was set up at the outlet of the irrigation district (located at the easternmost boundary of Hetao) in 1975, and a field drainage system was built from 1988 to 1996, which drains water into Ulansuhai Nur Lake (east of Hetao). The facilities turned eastern Hetao salt-free (or slightly saline) (Figure 11b,c). However, the drainage system ran at low efficiency in western Hetao due to the flat terrain, which caused western Hetao to still be affected by severe salinity even in 2010 (Figure 11b,c). In the last decade, the changes in the cropping structure (planting more sunflower and corn instead of wheat) required less irrigation. This was because the deeper roots of sunflower and corn enhanced their ability to uptake water from the shallow groundwater table. In addition, the promotion of water-saving techniques reduced the inlet salt from the Yellow River. As a result, the saline situation was significantly mitigated in 2019, when most of western Hetao turned salt-free (or slightly saline) (Figure 11d).
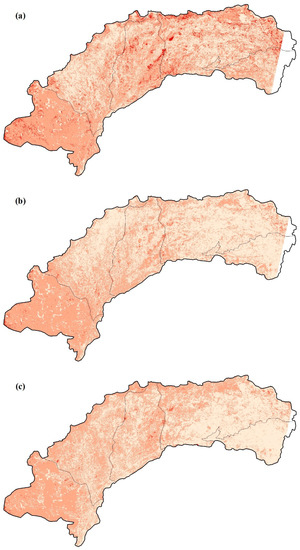
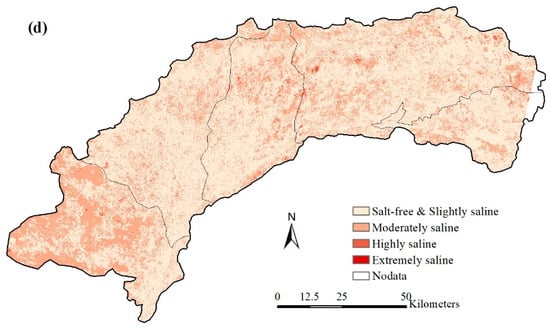
Figure 11.
The spatial distribution of saline classes in Hetao: (a) 1989, (b) 1999, (c) 2010, and (d) 2019.
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Abandoned Salinized Farmland
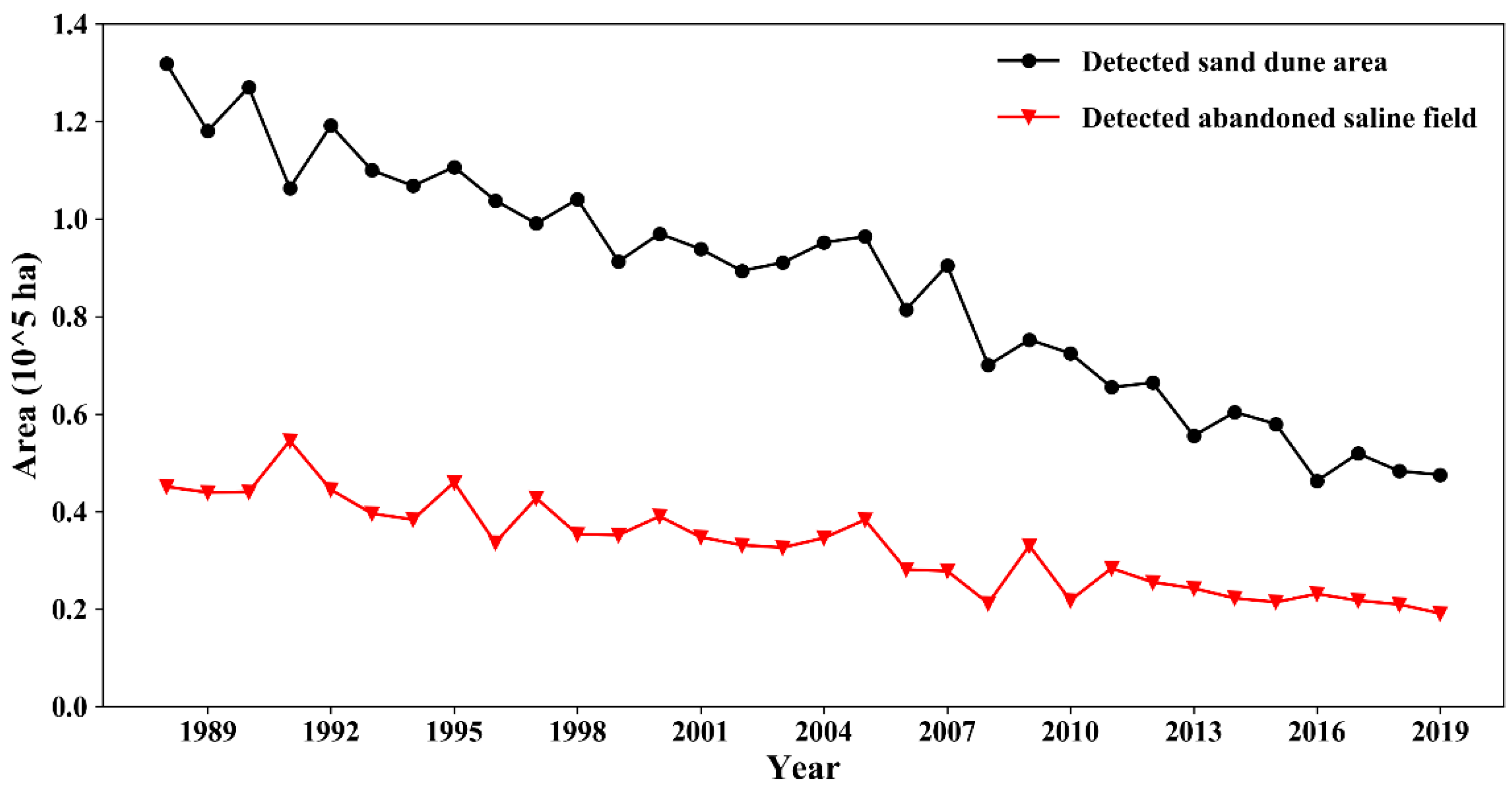
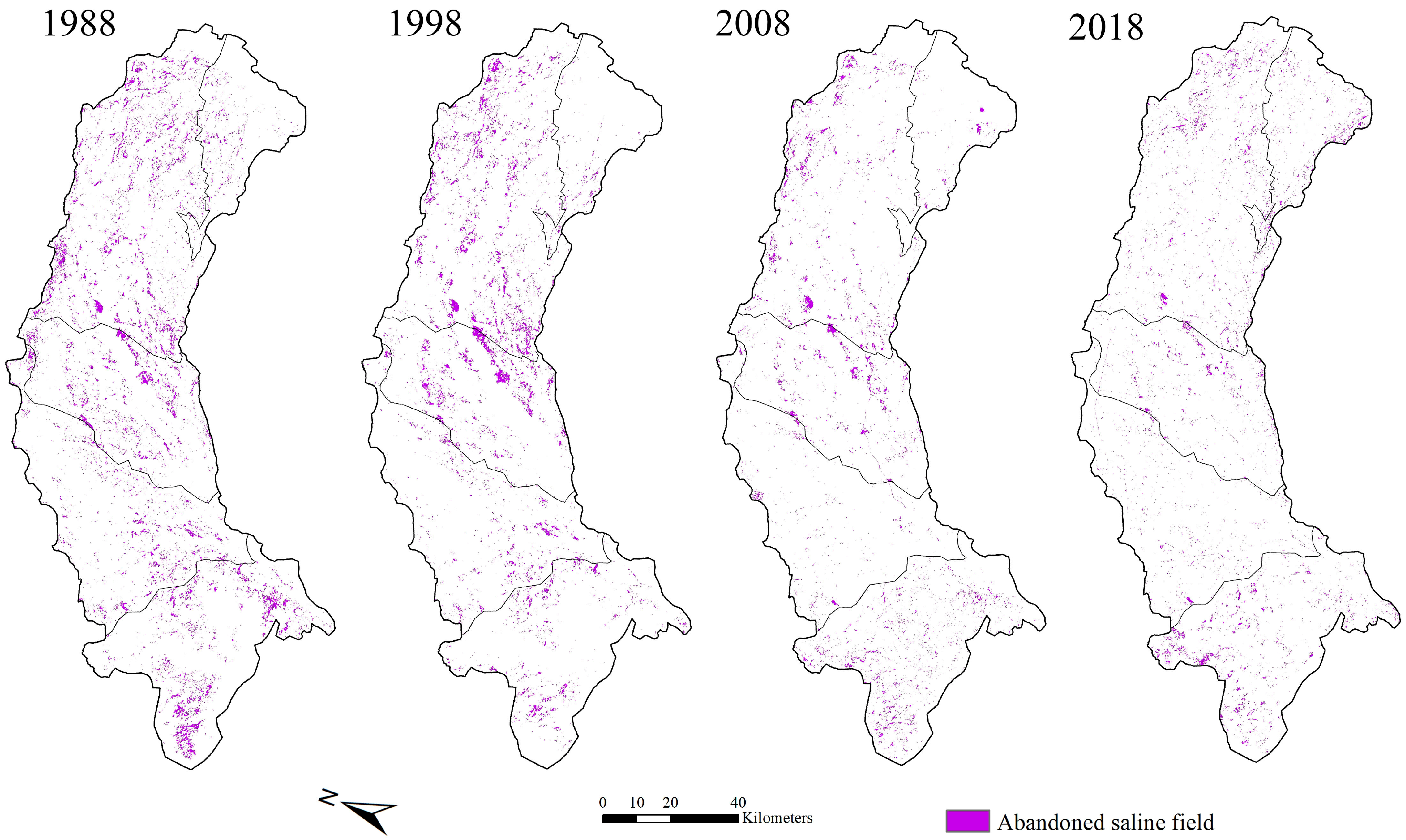
The evolution of the detected area of abandoned salinized farmland from 1988 to 2019 is shown in Figure 12. The results show that both the area of abandoned salinized farmland and sand dunes have declined steadily in recent decades. The tense relationship between food demand and crop yield provoked the installation of irrigation systems (e.g., center-pivot sprinkler irrigation systems, Figure 6b) in the desert area. As a result, an increasing desert area was turned into an oasis in Hetao (area of desert decreased from 1.32 × 105 ha to 0.48 × 105 ha). In addition, the improved irrigation pattern and techniques, drainage system, and optimized cropping structure lowered the saline situation, allowing some of the abandoned salinized farmlands to be cropped again (the area of abandoned saline area was reduced from 0.45 × 105 ha to 0.19 × 105 ha). The spatial distribution of the abandoned salinized farmland in the last three decades is shown in Figure 13. Initially, the abandoned saline area was distributed relatively evenly across the study area. As increasingly highly saline land transformed into non-saline crop field, the abandoned salinized farmland vanished in both eastern and western Hetao. However, it can be seen clearly that there was a group of abandoned salinized farmland that has been in existence for 30 years in central Hetao. These wastelands are usually vast; therefore, it is difficult to leach the salt out of the fields. Moreover, the high potential evaporation in this wasteland made it a groundwater sink, gathering salt from the surrounding cropping area. The incoming salt ascended into the surface soil with the upward water flux, and it might have accumulated in the abandoned salinized farmland if effective leaching had failed to be deployed.
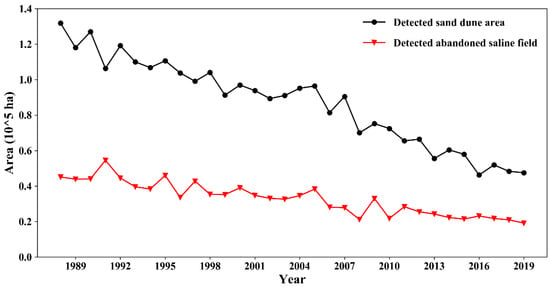
Figure 12.
The trend of the area of sand dunes and deserts and the area of abandoned salinized farmland from 1988 to 2019.
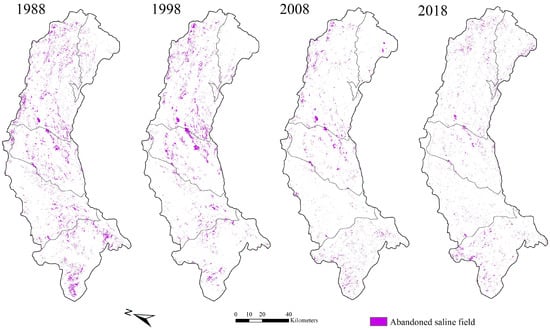
Figure 13.
The spatial distribution of the detected abandoned salinized farmland from 1988 to 2018.
4.4. Validation of Land-Use Classification and Abandoned Farmland Detection
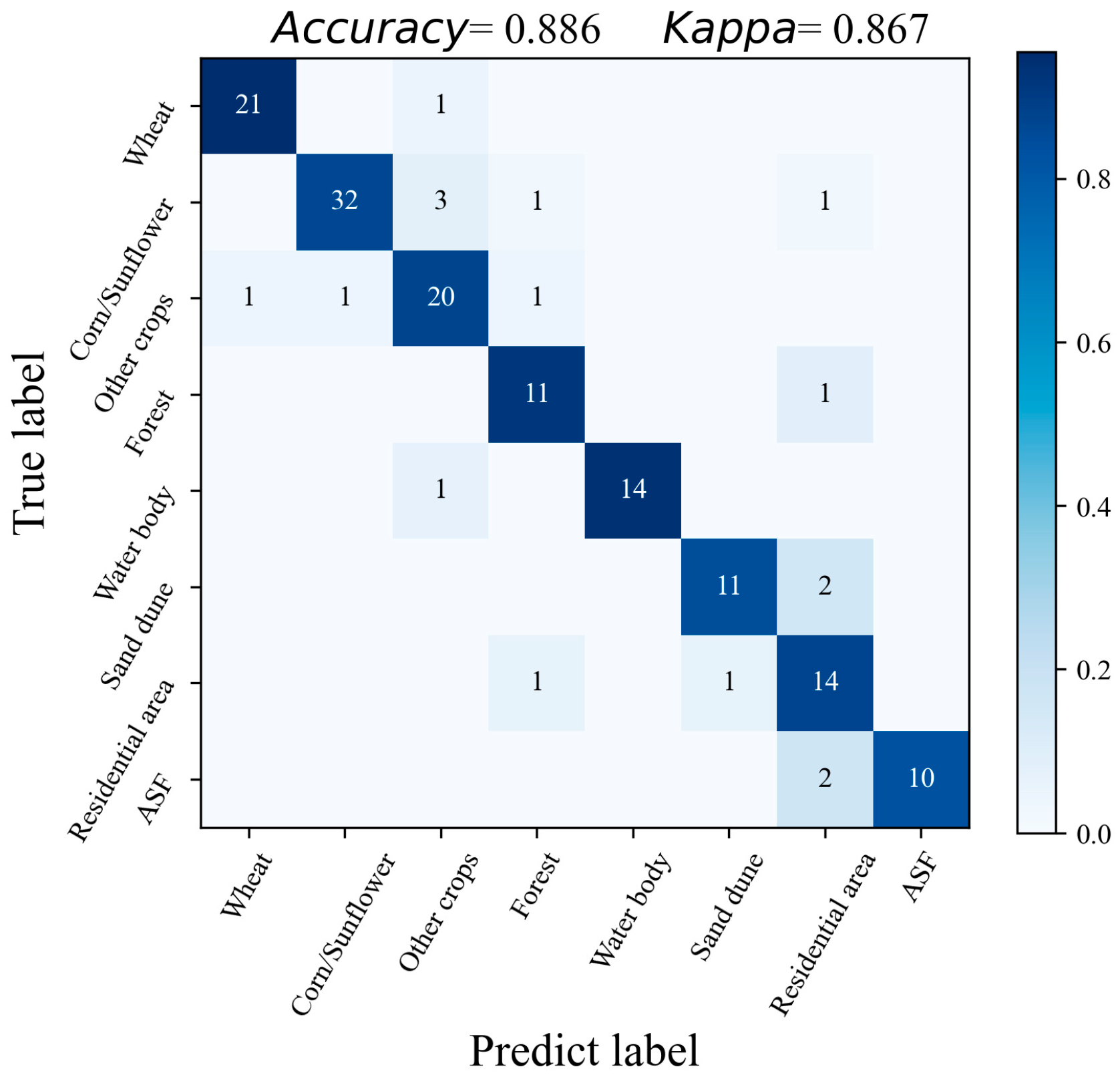
A total of 150 verification points were used to evaluate the performance of the land-use classification and abandoned farmland detection. As seen in Table 2, all metrics reached at least 0.7 and above, within the acceptable range. The proposed method achieved outstanding performance for wheat and water body classification, with all metrics higher than 0.93. This is because the temporal VI patterns of wheat and water bodies are significantly different from those of other land uses, making them easier to classify. The confusion matrix in Figure 14 shows that pixels in residential areas were easily misclassified. This is because the components of the residential area are complex, which makes the pixels in them have a high degree of spatial variability. Overall, the proposed method yielded a feasible result with a kappa coefficient of 0.876.

Table 2.
Metrics of land-use classification and abandoned salinized farmland detection results.
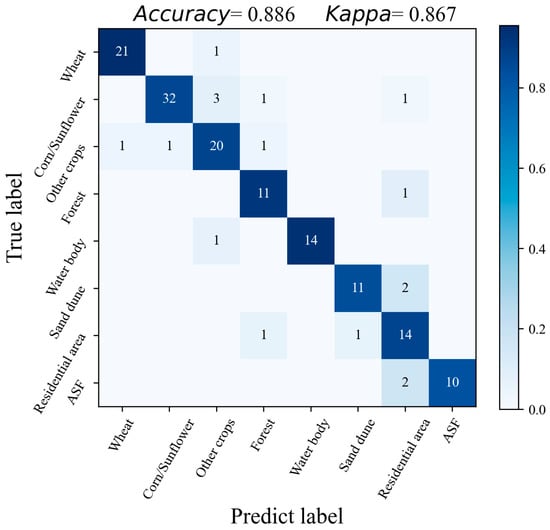
Figure 14.
The confusion matrix of land-use classification and abandoned salinized farmland detection results. The ASF represents the abandoned salinized farmland.
5. Discussion
Supervised machine learning algorithms have shown a solid capability to learn abstract features in nonlinear systems [40]. However, the input of these algorithms should be a uniformly formatted array. In other words, the shape of the input should be the same in the training and the testing phases [21]. Formatting the time-series input for remote sensing data with high temporal resolution (e.g., MODIS-based products) is applicable via cloud and cloud shadow compensation technology [41]. For high spatial resolution products (e.g., Landsat-based products), contamination from clouds heavily affects the consistency of formatted VI time series in different years (the number of available imageries varied depending on the climate condition of that year). Directly extending the short time-series data through time interpolation introduces large uncertainty in the testing phase, which hampers the performance of fine-scale surface classification by the supervised method. To test the applicability of the supervised algorithms for land cover classification using time-series data with varying lengths (Landsat imageries), we examined one of the widely used algorithms, the random forest, to perform the task. The training samples were manually selected in specific years (years with more cloud-free data available) and tested in other years (results not shown). The trained model indeed performed well for years with more available time-series data. Unfortunately, it failed for years with short time series.
In contrast, unsupervised algorithms, such as K-means clustering, classify the samples by learning the distinct features from the samples themselves instead of the training set. Then, the clustering results are labelled automatically by prior rules. The advantages of K-means clustering make it deployable on any dataset with different lengths of time series. The results confirmed that this method showed stable performance and worked well in both cloudy years and less cloudy years.
A significant desalinization process was observed during the last thirty years, while the area of extremely saline conditions was reduced by approximately 50% and the area of highly saline conditions was reduced by approximately 70% (Figure 10). These results were deduced from the EC estimates of bare soil during the fallow season based on an established SI–EC relationship. However, the distribution of collected soil samples was imbalanced where the samples with extremely high EC were sparse. As a result, the prediction error of the established SI–EC relationship may be large in extremely saline areas. The only way to improve the robustness of the SI–EC relationship is to involve more available data. Therefore, more soil samples will be collected in the study area in future studies. In addition, Sentinel-2 imageries were used to build the EC estimation model because of the high spatial heterogeneity of the surface of the study area; therefore, remote sensing data with high resolution are needed to match the ground samples. However, the scale effect may reduce model performance when the SI–EC relationship is used in imagery with a lower resolution relationship (caused by the mixed pixels). Therefore, EC estimates may be more accurate on relatively uniform land with a smaller scale effect.
When a field is affected by high-level salinity, this reduces the yield of most crops and causes the field to be abandoned. Abandoned salinized farmland acts as an evaporative sink, resulting in a lower groundwater depth than the cropped area where constant irrigation increases the water table. Consequently, the salty water is drained from the cropped area into the abandoned salinized farmland, which mitigates the salinity in the cropping area. This is the concept of “dry drainage” [42]. The higher gradient of the water table in the dry drainage system transforms more salt into abandoned salinized farmland, which may increase its saline degree. The soil hardens in the abandoned salinized farmland when its saline degree is extremely high. The hardened soil layer reduces the capillary effect of soil water and decreases the efficiency of the dry drainage system. The tug-of-war between the efficiency of salt drainage and the evaporation capability of the abandoned salinized farmland creates a long-term salt balance in the dry drainage system [3]. In other words, the soil in the abandoned salinized farmland is difficult to improve due to the dry drainage effect, which has resulted in a thousand-year-old codependent relationship between the cropping system and the dry drainage system in Hetao.
The results show that the area of abandoned salinized farmlands has declined steadily in recent decades. The continuous decrease in the area of abandoned salinized farmland weakens the codependent relationship between the cropping system and the dry drainage system. There were three main reasons for the decline: (1) drainage facilities and water-saving irrigation techniques reduced the groundwater table [43]; (2) the inlet salt was reduced while the well-irrigation facilities were set up to pump groundwater for irrigation; (3) the introduced salt-tolerant crops that could grow in the salt-affected field not only lowered the area of the abandoned salinized farmland but also removed salt from the field [44]. The desalinization progress relaxed the tight connection inside the dry drainage system, where the deeper water table staggered the evaporation capability of the fallow area, and the shrinking abandoned saline area reduced the scale of the system. The soil salt content of wasteland decreased as the salt was leached by rainfall, while less salt was transferred into the area. The salt of the cropping area was directly leached into the deeper groundwater with irrigation and rainfall. This provided a moment to reutilize abandoned salinized farmland after artificial leaching campaigns. However, the risk of salinization bounce back still exists due to the rising groundwater table during rainy years. Therefore, a leaching project should be thoroughly designed and conducted step by step after evaluating the environmental conditions and the future climate.
6. Conclusions
In arid and semiarid water-logged areas, abandoned salinized farmland plays an essential role in acting as an evaporation sink gathering salt from the surrounding cropping area. However, traditional methods for land-use (land cover) classification fail to detect these wastelands. This study introduced a robust approach to detect abandoned saline land in the Hetao Irrigation District using 32-year time-series remotely sensed data. The proposed method is based on the idea of “elimination” to detect abandoned saline land step by step, which provides inspiration for monitoring the planting pattern of specific crops, or progress such as desertification or urbanization. At the same time, the dynamics of the cropping structure were monitored. The combination of the K-means cluster algorithm and the shape-model-fitting method successfully identified the specific crop, where the estimates agreed well with the statistics. The results show that the cropland in Hetao has continuously expanded during the last thirty years. An increasing number of farmers in Hetao have tended to plant high stem crops (maize and sunflower) instead of spring wheat from 1988 to 2019. The salinization degree was evaluated by the SI using an established exponential relationship between the SI and measured soil EC. The saline situation has been mitigated during recent decades, indicating that water-saving techniques, drainage facilities, and optimized cropping structures represent desalinization progress. Thermal information and the SI were used to distinguish the abandoned salinized farmland from other non-vegetative lands. The detected area of abandoned salinized farmland has continuously decreased, while many small wastelands have vanished in eastern and western Hetao. However, in central Hetao, a group of large-area abandoned salinized farmland has existed for 30 years. The strong effect of the dry drainage system has slowed the reutilization progress in these wastelands. However, a decrease in the groundwater table and salt-tolerant plants have created an opportunity to launch a saline field improvement project to reutilize the abandoned salinized farmland where the dry drainage system has already collapsed.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs13204057/s1, Table S1: Acquisition Time and Identifiers of Used Satellite Data.
Author Contributions
L.Z. performed data collection and processing; L.Z. and Q.Y. analyzed the data and interpreted the results; L.Z. and Q.Y. supported the writing, review and editing; J.W. and Q.Z. provided the suggestions and reviews. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51790532).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and others who contributed to this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soil-management/management-of-some-problem-soils/salt-affected-soils/more-information-on-salt-affected-soils/en/ (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Thomas, D.S.G.; Middleton, N.J. Salinization: New perspectives on a major desertification issue. J. Arid Environ. 1993, 24, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W.; Rose, D.A. Dry drainage: A sustainable solution to waterlogging and salinity problems in irrigation areas? Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 83, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A. Salinization and Saline. Environ. Geochem. 2005, 9, 333. [Google Scholar]
- De Pascale, S.; Maggio, A.; Barbieri, G. Soil salinization affects growth, yield and mineral composition of cauliflower and broccoli. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.M.A.; Serralheiro, R.P. Soil salinity: Effect on vegetable crop growth. Management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Sawaya, K.E.; Loeffelholz, B.C.; Bauer, M.E. Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) metropolitan area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrão, H.; Gonçalves, P.; Caetano, M. Contribution of multispectral and multitemporal information from MODIS images to land cover classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Van Der Wiele, C.F.; Khorram, S. An automated artificial neural network system for land use/land cover classification from landsat TM imagery. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Vincent, B.; Yang, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. Remote sensing monitoring of changes in soil salinity: A case study in inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2008, 8, 7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Aldakheel, Y.Y. Assessing soil salinity using soil salinity and vegetation indices derived from IKONOS high-spatial resolution imageries: Applications in a date palm dominated region. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Jamil, R. Soil salinity detection from satellite image analysis: An integrated approach of salinity indices and field data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shang, S. Multi-year mapping of maize and sunflower in hetao irrigation district of china with high spatial and temporal resolution vegetation index series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukawattanavijit, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H. GA-SVM Algorithm for Improving Land-Cover Classification Using SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, A.; Baumann, M.; Kuemmerle, T.; Pflugmacher, D.; Rabe, A.; Griffiths, P.; Hölzel, N.; Kamp, J.; Freitag, M.; Hostert, P. Mapping the timing of cropland abandonment and recultivation in northern Kazakhstan using annual Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 213, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, F.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Waldner, F.; Dubovyk, O.; Akramkhanov, A.; Biradar, C.; Lamers, J.P.A. Mapping Cropland Abandonment in the Aral Sea Basin with MODIS Time Series. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Brandão, A.; Buchner, J.; Helmers, D.; Iuliano, B.G.; Kimambo, N.E.; Lewińska, K.E.; Razenkova, E.; Rizayeva, A.; Rogova, N.; et al. Monitoring cropland abandonment with Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetano, R.; Ienco, D.; Ose, K.; Cresson, R. A two-branch CNN architecture for land cover classification of PAN and MS imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kussul, N.; Lavreniuk, M.; Skakun, S.; Shelestov, A. Deep Learning Classification of Land Cover and Crop Types Using Remote Sensing Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, U.; von Rekowski, C.S.; Stecklina, M.; Krokotsch, T.; Minh, T.P.; Hauffe, V.; Kilias, D.; Ehrhardt, I.; Sagischewski, H.; Chmara, S.; et al. Tree species classification based on hybrid ensembles of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and random forest classifiers. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portalés-Julià, E.; Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Gilabert, M.A. Assessing the sentinel-2 capabilities to identify abandoned crops using deep learning. Agronomy 2021, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting salinity hazards within a semiarid context by means of combining soil and remote-sensing data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehni, A.; Lounis, M. Remote sensing techniques for salt affected soil mapping: Application to the Oran region of Algeria. Procedia Eng. 2012, 33, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.N.; Sheng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, H.Q.; Liu, Y. Desalination of saline farmland drainage water through wetland plants. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 156, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishida, J.; Kojima, T.; Kumar, S. Solar desalination of saline soil for afforestation in arid areas: Numerical and experimental investigation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.L.; Herrero, J.; Weindorf, D.C. Multivariate analysis of soil salination-desalination in a semi-arid irrigated district of Spain. Geoderma 2017, 291, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.W.; Fan, Y.H.; Tiyip, T. The Research of Soil Salinization Human Impact Based on Remote Sensing Classification in Oasis Irrigation Area. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Barsi, J. Landsat 7 scan line corrector-off gap-filled product development. In Proceedings of the Pecora, Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 23–27 October 2005; Volume 16, pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lobell, D.B.; Thau, D.; Seifert, C.; Engle, E.; Little, B. A scalable satellite-based crop yield mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Wardlow, B.D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.E.; Arkebauer, T.J. A Two-Step Filtering approach for detecting maize and soybean phenology with time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likas, A.; Vlassis, N.; Verbeek, J.J. The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Shi, L.; Han, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, K. A near real-time deep learning approach for detecting rice phenology based on UAV images. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Sato, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Assessment of hydrosaline land degradation by using a simple approach of remote sensing indicators. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, T.; Sertel, E.; Tanik, A. Monitoring soil salinity via remote sensing technology under data scarce conditions: A case study from Turkey. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, I.P.; Yadav, J.S.P.; Massoud, F.I. Salt-Affected Soils and Their Management; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1988; ISBN 9251026866. [Google Scholar]
- Crisci, C.; Ghattas, B.; Perera, G. A review of supervised machine learning algorithms and their applications to ecological data. Ecol. Modell. 2012, 240, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Vermote, E.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Defries, R.; Roy, D.P.; Hall, D.K.; Salomonson, V.V.; Privette, J.L.; Riggs, G.; Strahler, A.; et al. The moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS): Land remote sensing for global change research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1228–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowing, J.W.; Wyseure, G.C.L. Dry-drainage a sustainable and cost-effective solution to waterlogging and salinisation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Drainage Workshop, Lahore, Pakistan, 8–15 February 1992; Volume 3, pp. 6–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Qu, Z.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blumwald, E. Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: Challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).