Abstract
Mangrove forests are important woody plant communities that grow in the intertidal zone between land and sea. They provide important social, ecological and economic services to coastal areas. In recent years, the growth environment of mangrove forests has been threatened. Mangrove forests have become one of the most endangered ecosystems in the world. To better protect mangrove forests, effective monitoring methods are essential. In this study, a spatio-temporal simulation method for mangrove forests was proposed in the mangrove protected areas of Hainan Island, China. This method compared the simulation accuracy of different models in terms of spatial characteristics, evaluated the applicability of driving factors in mangrove simulation and predicted the future spatio-temporal distribution and change trends of mangrove forests under different scenarios. The simulation results of different models showed that AutoRF (random forest with spatial autocorrelation) performs best in spatial characteristic simulation. Driving factors such as the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), various location indices and the spatial autocorrelation factor can significantly improve the accuracy of mangrove simulations. The prediction results for Hainan Island showed that the mangrove area increased slowly under a natural growth scenario (NGS), decreased significantly under an economic development scenario (EDS) and increased significantly under a mangrove protection scenario (MPS) with 4460, 2704 and 5456 ha respectively by 2037. The contraction of mangrove forests is closely related to the expansion of aquaculture ponds, building land and cultivated land. Mangrove contraction is more severe in marginal or fragmented areas. The expansion of mangrove forests is due to the contraction of aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and other forests. The areas around existing mangrove forests and on both sides of the riverbank are typical areas prone to mangrove expansion. The MPS should be the most suitable development direction for the future, as it can reasonably balance economic development with mangrove protection.
1. Introduction
Mangrove forests are important woody plant communities that grow in the intertidal zone between land and sea. They are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world between 30° N and 30° S latitude [1]. Mangrove forests can sequestrate carbon, mitigate climate change, maintain marine and land biodiversity, purify water, protect coastlines and coastal infrastructure and export economic products, thus providing important social, ecological and economic services for surrounding areas [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Mangrove forests are constantly threatened due to natural and anthropogenic factors such as extreme weather events, sea-level rise, aquaculture and urban development, making them one of the most endangered ecosystems in the world [11,12,13,14]. Currently, the world’s mangrove forests have declined by about 40% compared to the middle of the last century [15]. Throughout the 1990s, the annual loss rate of mangrove forests was 1%, which was about twice that of terrestrial forests during the same period [16]. In recent years, with the continuous advancement of protection measures around the world, the loss rate of mangrove forests has slowed, but still remains at 0.26–0.66% per year [17]. If the loss rate of mangrove forests continues, about 40% of the world’s mangrove forests will completely disappear by the end of this century. The services and products provided by mangrove forests will be significantly reduced or lost, which will have a negative impact on human survival and development [1]. Therefore, the protection of mangrove forests is urgent and has reached a broad international consensus. Effective mangrove monitoring methods are very important, which can provide a theoretical basis and decision support for mangrove protection, restoration and utilization.
Mangrove forests grow in the mudflats between land and sea. Traditional field survey methods have difficulty in obtaining accurate, comprehensive and timely mangrove data. In recent years, the rapid development of remote sensing technology has provided a new means for better extraction, analysis and prediction of mangrove forests. At present, mangrove monitoring mainly focuses on mangrove change analysis and time series analysis. Mangrove change analysis is a statistical analysis of the area, extent, conversion and landscape pattern of mangrove forests [8,13,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Although this method can reflect spatial distribution, area change and the causes of changes in mangrove forests, it only statistically analyzes the overall changes, and cannot accurately reveal the spatial trends of each section. Mangrove time series analysis is based on vegetation indices, with short time intervals and long time series. This method explores mangrove trends by linear regression analysis, Theil-Sen median trend analysis, the Mann-Kendall test, the Hurst exponent and so forth. It can reflect the change trends and future trends of mangrove forests, and further reveal the causes and effects of these trends [30,31,32,33]. Although this method accurately reflects the spatial trends of each section, it only analyzes the changes of historical data and cannot predict how long the sustainable trends will continue [34], which poses a challenge for the future continuous monitoring of mangrove forests.
Therefore, it is crucial to conduct spatio-temporal simulation of mangrove forests to predict the future spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests under different scenarios. Land-use change models are the key to spatio-temporal simulation, which can be divided into two categories, non-spatial models and spatial models. Non-spatial models were developed earlier, such as the SAhelian Land-Use model (SALU) [35], linear programming model [36,37], system dynamics model [38,39] and Markov chain model [40]. These models consider only quantity changes and do not measure location changes. Spatial models consist of micromodels (bottom-up) and macromodels (top-down), which consider both quantity and location changes. Micromodels first configure land-use changes according to demands at the microscale and then aggregate the results to the macroscale, with examples including cellular automation (CA) [41,42], SAMBA [43], the Future Land Use Simulation (FLUS) [44] and so forth. Macromodels first configure land-use changes at the macroscale, and then allocate demands to the microscale layer by layer; applications include the Land Use Planning and Analysis System (LUPAS) [45], the Conversion of Land Use and its Effects at Small region extent (CLUE-S) [46] and so forth. At present, few studies address the spatio-temporal simulation of mangrove forests, and these are mainly based on CA-Markov models. This model uses a Markov chain model to calculate the quantity changes, and then brings it into a CA model to simulate location changes. Mukhopadhyay et al. [47] utilized this model to predict the mangrove species of Bangladesh Sundarbans in 2025, 2055 and 2105. Bozkaya et al. [48] compared the CA-Markov and St. Markov models and predicted the distribution of mangrove forests along the northwest coast of Turkey in 2030. DasGupta et al. [49] used Multi-Layer Perceptron-Markov Chain Analysis (MLP-MCA) to predict the distribution of mangrove forests in Sundarbans, India in 2030, under four development scenarios. Tajbakhsh et al. [50] developed a hybrid model (CA-Markov-ANN) to predict the distribution of mangrove forests in Qeshm Island, Southern Iran in 2025. However, the above studies for mangrove forests still have some shortcomings. First, previous studies are mainly based on the CA-Markov model. The CLUE-S model has been widely used in spatio-temporal simulation in different regions [51,52,53]. For long-term simulation with non-stationary change patterns, the CLUE-S model has better stability compared to the CA-Markov model. The statistical significance of the probability values in the CA-Markov model is affected when the number of area changes is small [54]. The CLUE-S model is more accurate in the simulation of the land-use spatial patterns compared to the CA-Markov model [55]. Second, the simulation accuracy of spatial characteristics needs to be improved. Spatial characteristics are key to the CLUE-S model to assess the potential for land-use changes, which was calculated from land-use data and driving factors by logistic regression [51,56], autologistic regression [52,57,58], NE-Logistic regression [56], artificial neural networks [51] and random forest (RF) [53,59], and so forth. Some studies have shown that machine learning methods such as RF have higher simulation accuracy compared to traditional logistic regression [53], but no systematic comparisons have been made. Third, driving factors need to be further refined and selected. Most driving factors in the previous studies are commonly used indices such as elevation, slope and location indices. Vegetation indices such as NDVI and its change trend can well reflect the change trends of vegetation [60], which can provide a reference for simulation and prediction. The spatial autocorrelation factor was proposed to address the spatial autocorrelation effect inherent to spatial statistical analysis [61]. Traditional logistic regression methods can significantly improve the simulation accuracy along with it [57], but machine learning methods have not yet considered it.
Mangrove protected areas in Hainan Island were selected as the study area to explore the spatio-temporal simulation of mangrove forests under different scenarios. The objectives of this study were as follows: (1) compare the simulation accuracy of different models in terms of spatial characteristics and evaluate the applicability of driving factors in mangrove simulation; (2) set different development scenarios and predict the future spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests; and (3) analyze the future change trends of mangrove forests.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
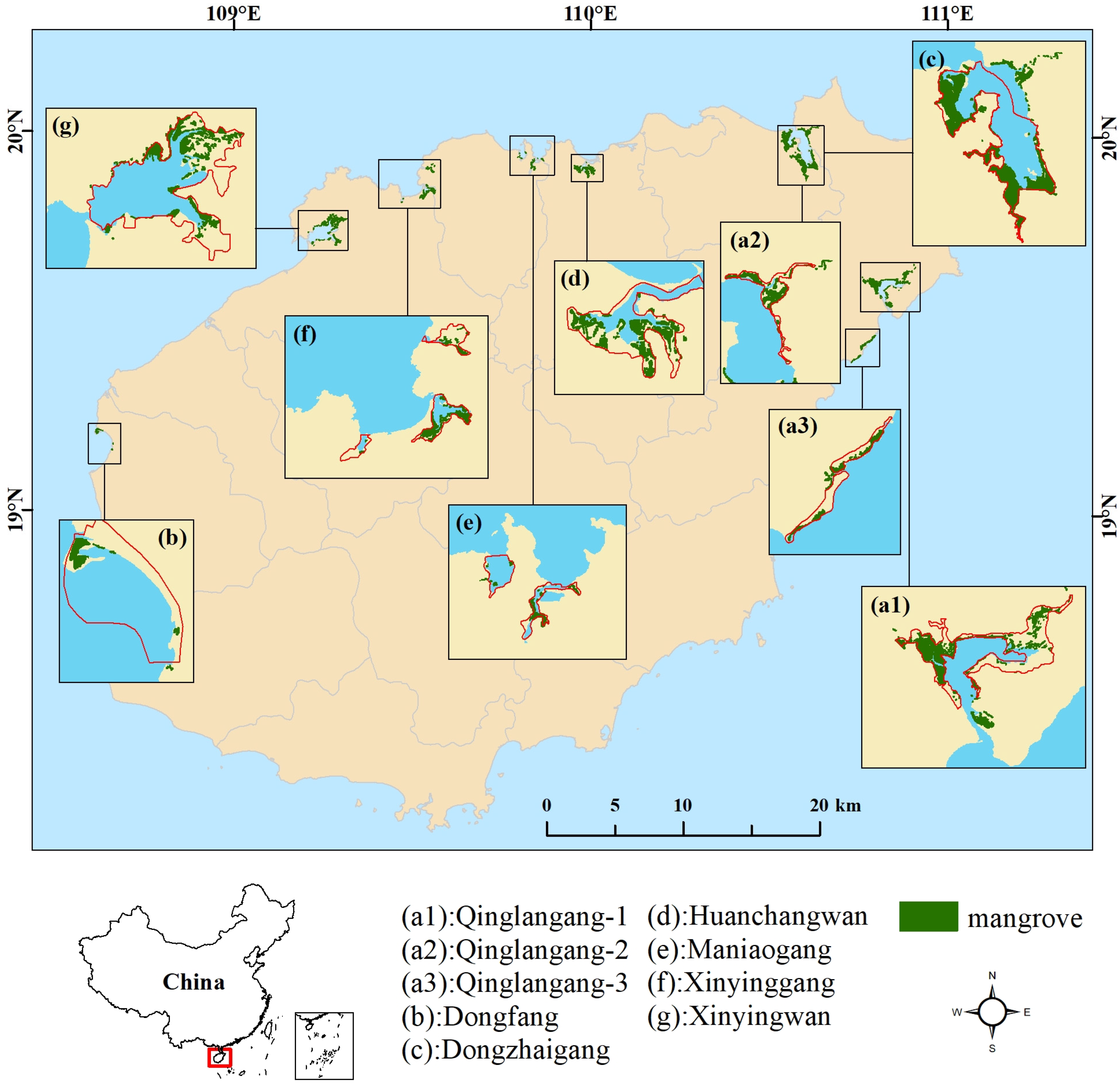
Hainan Island is rich in mangrove species, with 26 species of true mangrove, 12 species of semi-mangrove and more than 40 species of mangrove associates [62], containing almost all of the mangrove species found in China. For more than half a century, the mangrove area in Hainan Island has experienced a developmental process from a sharp decline to a slow increase. In the 1950s, the mangrove area of Hainan Island accounted for about a quarter of China’s mangrove area, reaching 9992 ha [63]. Then, these mangrove forests suffered serious damage due to excessive economic development, such as marine aquaculture, land reclamation and mangrove deforestation. In the 1980s, the mangrove area was reduced by half, to reach 4836 ha [64]. By 2010, the mangrove area in Hainan Island had decreased to 3576 ha [21]. In recent years, as the government began to vigorously implement restrictive measures such as converting cultivated land to wetlands and converting fishponds to wetlands, the public awareness of protecting mangroves has increased significantly. The mangrove area of Hainan Island has responded with a slow increase, recovering to 4278 ha in 2017 [65]. At present, Hainan Island has established 10 mangrove reserves, including one national reserve, two provincial reserves and seven local reserves. Seven of these mangrove reserves were selected for this study (Figure 1 and Table S1). Dongzhaigang National Mangrove Reserve is the best preserved and most abundant mangrove reserve in China. Qinglangang Nature Mangrove Reserve consists of three regions: Huiwen, Puqian and Guannan (a1, a2 and a3 in Figure 1), containing the largest number of mangrove species in China. Dongfang Nature Reserve was established in 2006. Mangrove forests within it provide a good habitat for the international endangered species Platalea minor. The remaining four local protected reserves are located in the northern part of Hainan Island. The study area was selected within the 2 km buffer zone of the reserve boundary [27].
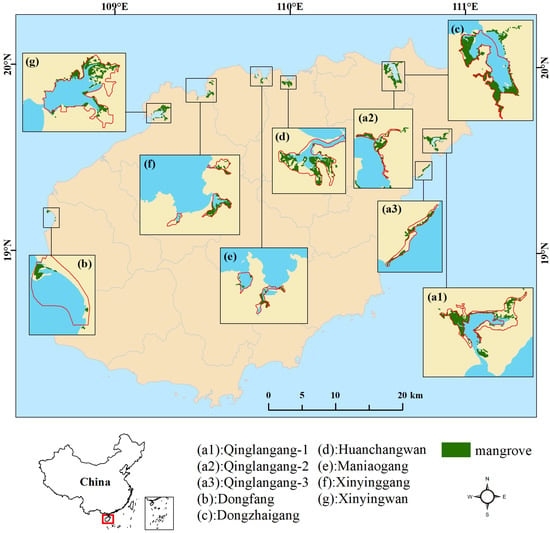
Figure 1.
Location of selected reserves (a1–g) in this study (red lines are the boundary of reserves; green areas indicate the appearance of mangrove forests in 2017).
2.2. Data Sources
The data sources used in this study are land cover data and driving factor data. The land cover data used in the study was based on the classification results of Landsat images in 1987, 1993, 1998, 2003, 2007, 2013 and 2017, with a spatial resolution of 30 m [65]. The 2017 dataset was classified according to the support vector machine method with a high-precision manual correction; the overall accuracy was 98.8%. The classified 2017 image was then used as a reference for the visual interpretation of the remaining images [27]. The land cover types were categorized into 10 classes: mangrove forests (MF), tidal sandflats (TS), aquaculture ponds (AP), water (WT), cultivated land (CL), wetlands (WL), bare land (BL), other forests (OF), suitable land for mangrove (SLM) and building land (BDL).
The driving factor data were mainly selected from 12 indices related to mangrove distribution, including two terrain indices, two vegetation indices, seven location indices and one correlation index (Table 1).

Table 1.
The driving factor data used in this study.
For the terrain indices, the elevation was derived from the 30 m resolution SRTM 1 Arc-Second Global (SRTMGL1) dataset. The slope was then calculated from the elevation gradient.
For the vegetation indices, the EVI was calculated from Landsat images. This index solves the saturation problem under high vegetation coverage [66], and is more suitable for mangrove change studies [33]. In this study, the Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI images with a spatial resolution of 30 m were acquired each year for Huiwen from 1999 to 2003 (for simulation) and for all the study areas from 2013 to 2017 (for prediction). Due to the insignificant phenology effect of mangrove forests, the impacts of cloud cover and tide level were the main parameters considered when screening the images. In this study, the image with the lowest tide level among images, with cloud cover less than 10%, was selected as a representative image for that year. The EVI change trends were calculated by the Theil-Sen median trend analysis using the EVI images of the last five years (Equation 1). It has been proven that this method can well reflect the trends of long time series data, and has been widely used in vegetation studies [33,34,67,68].
where and are the EVI values of years i and j. indicates an increasing trend of the series; all other values indicate a decreasing trend.
The location indices were calculated by the inverse distance weighting method according to the different information. The road information was obtained from OpenStreetMap (OSM). In this study, motorway, trunk, primary, secondary, tertiary and highway links were merged as major roads, while minor roads constituted the remaining residential, pedestrian, cycleways and so forth. The information of sea, river, aquaculture ponds, building land and suitable land for mangrove were obtained from land cover data.
For the correlation index, the spatial autocorrelation factor was selected as follows
where k is the land cover type of pixel i. is the state in which land cover type k exists in pixel j (1 means exists, 0 means does not exist). is the inverse distance weight between pixel i and j, which can be expressed as:
where
is the Euclidean distance between pixels i and j. d is the threshold distance. In this study, d = 500 m is taken according to the pixel size (30 m) of this study.
3. Methods
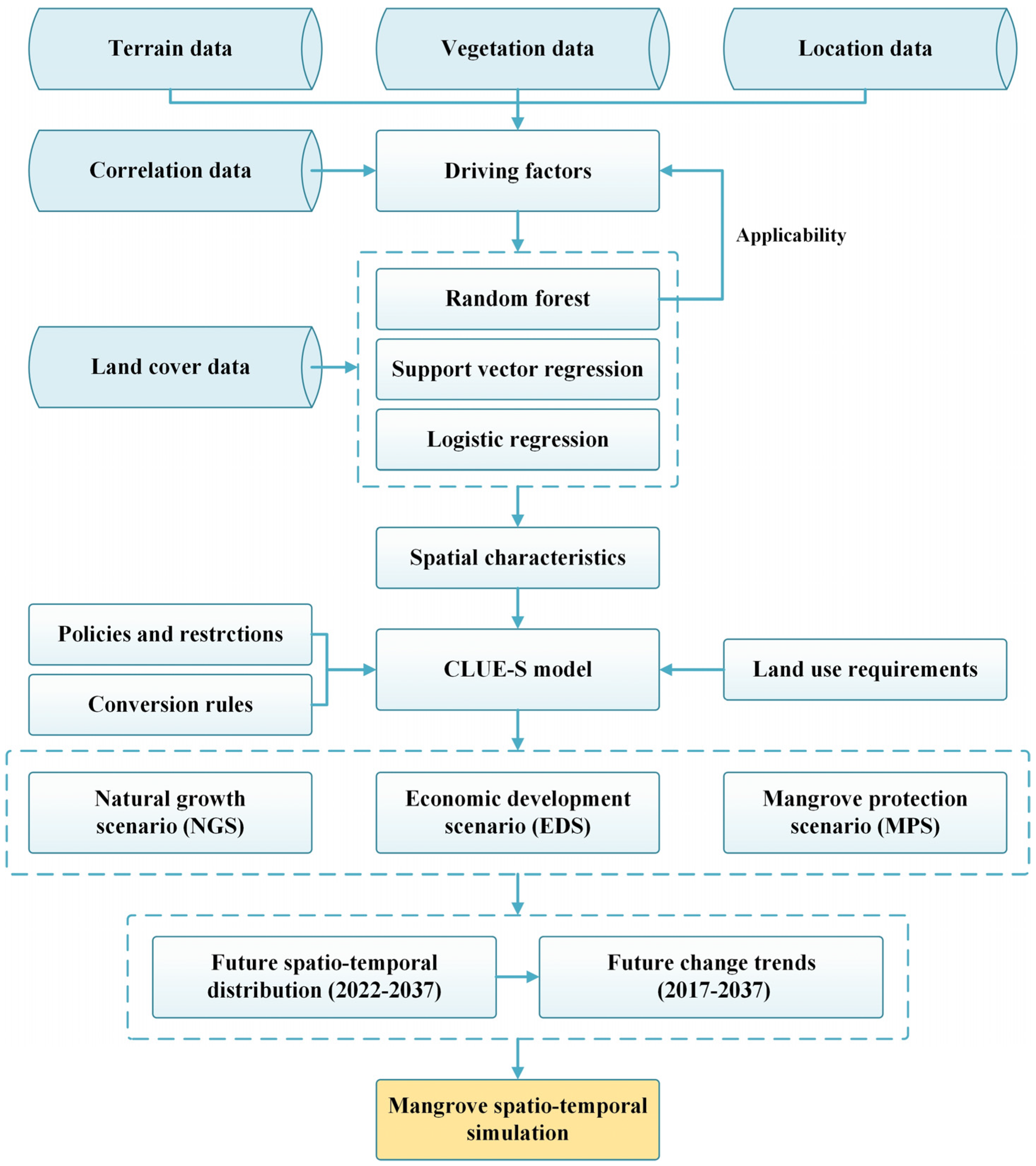
A spatio-temporal simulation method for mangrove forests was proposed (Figure 2). According to the characteristics of mangrove forests, the simulation accuracy of different models such as logistic regression, support vector regression (SVR) and random forest, in terms of spatial characteristics, was compared, and the applicability of driving factors such as vegetation and correlation indices in mangrove simulation were explored. Then, according to the characteristics of the different protected areas, three development scenarios of NGS, EDS and MPS were set. The CLUE-S model was used to predict the spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests from 2022 to 2037 under different scenarios. Finally, based on the prediction results of spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests, the future change trends of mangrove forests from 2017 to 2037 were analyzed.
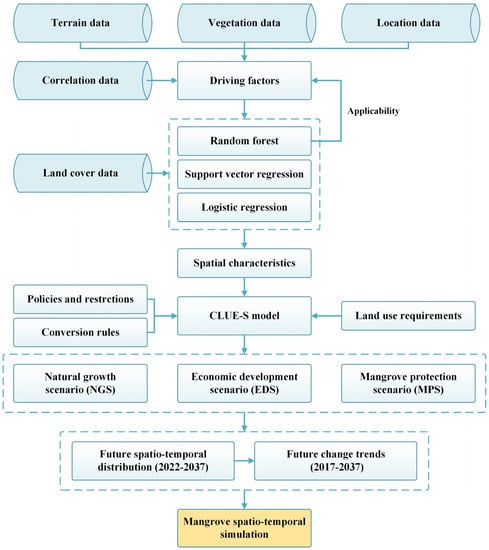
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the spatio-temporal simulation of mangrove forests.
3.1. CLUE-S Model
The CLUE-S model was chosen to simulate mangrove forests in protected areas. It was developed by researchers at Wageningen University based on the CLUE model. Considering the competing mechanisms of land-use changes, this model can effectively link the land-use change processes and environmental driving factors, and is suitable for mesoscale and small-scale land-use simulation studies. The CLUE-S model consists of four input modules (spatial policies and restrictions, land-use type conversion rules, land-use requirements and spatial characteristics) and a spatial allocation module [46].
The spatial policies and restrictions module is used to restrict land-use layout. It refers to areas where land-use changes are not allowed to occur, usually including policy restrictions (nature reserves, national parks and so forth) and spatial restrictions (rivers, oceans and so forth). In this study, rivers and estuaries are usually not encroached upon by other land-use types. Therefore, these areas were set as restricted areas to ensure the connectivity of water bodies.
The land-use type conversion rules module is used to quantify the possibility and intensity of the land-use type conversion, mainly containing conversion sequence and conversion elasticity. Conversion sequence is a parameter that indicates whether conversion can occur between various land-use types. It is represented by a matrix in the CLUE-S model, and the value is 0 (not transferable) or 1 (transferable). The conversion sequence of this study was adjusted according to different scenarios, as described in Section 3.3. Table S2 shows the conversion sequence under different scenarios. Conversion elasticity is a parameter that quantifies the reversibility of land-use changes, with a value range of 0 (easy to transfer) to 1 (not easy to transfer). According to different scenarios, the conversion elasticity of this study was adjusted for different land-use types separately, as described in Section 3.3. Table S3 shows the conversion elasticity under different scenarios.
The land-use requirements module is used to calculate future area demands, which is a key parameter affecting the iterations of the CLUE-S model. It can be estimated by a statistical model [52,53,69,70,71,72], a system dynamics model [73,74], a professional model [75,76] and so forth. In this study, linear regression and scenario analysis were used to predict the future area demands for 2022–2037, as described in Section 3.3.
The spatial characteristics module is used to calculate the spatial suitability probability of various land-use types at specific locations. It is key for the CLUE-S model to assess the potential for land-use changes. Spatial suitability probability is generally calculated from land-use data and driving factors by different models. In this study, in addition to the traditional logistic regression, two commonly used machine learning models that support vector regression and random forest methods were added to compare the simulation accuracy in terms of spatial characteristics. Support vector regression uses different kernel functions to nonlinearly map the original low-dimensional feature to the high-dimensional feature space, and then it constructs a linear decision function to solve the nonlinear problem [77]. This method is well suited for solving high-dimensional and nonlinear regression problems. Random forest is based on multiple decision trees. Parts of the features on the tree node are randomly selected for training, and then the optimal feature is selected to divide the node. The final regression result is the average of all the results of the decision tree [78]. This method reduces the generalization error of a single decision tree, and greatly improves the regression accuracy. To reduce the problem of uneven sample selection, both training and validation samples in this study were generated by a stratified random sampling method, where the number of training samples constituted 2% of the total pixels.
The space allocation module is used to calculate the final allocation result. It is based on the results of the four input modules and the land-use map of the starting year. According to the total occurrence probability of various land-use types in each pixel, the space is allocated by several iterations until the land-use requirements are satisfied [46]. The CLUE-S model was implemented through the lulcc-package in R software [79].
3.2. Model Validation Indices
The area under curve (AUC) was chosen to evaluate the simulation accuracy of the different models in terms of spatial characteristics. It represents the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and is commonly used as a performance evaluation index for the classification or fitting algorithms [80]. The value of AUC ranges from 0.5 to 1.0; the closer to 1 the value is, the better performance of the model. An AUC above 0.7 is generally considered as good, and above 0.9 is excellent [51].
Four types of indices were selected to assess the accuracy of the simulation results: the overall accuracy (OA), the Kappa coefficient, the three-dimensional approach and the Figure of Merit (FoM). The OA is the ratio of the number of correctly classified pixels to the total number of pixels, and is often used in the accuracy assessment of classification algorithms. It is also widely used for consistency checking between simulation and observation maps of land-use change models [52,53,72]. The Kappa coefficient represents the proportion of error reduction in the evaluated classification, compared with a completely random classification. It is an index designed for evaluating the accuracy of classification results [81], and is further developed into four different forms that can quantify either quantity error or location error [82]; KQuantity believes that the results have the ability to consider location precision and is applicable to area change evaluation; KLocation believes that the results have the ability to consider quantity precision and is applicable to location change evaluation; and KStandard and KNo consider location and quantity precision together. KNo believes that the results do not have the ability to consider quantity and location precision, which is more objective. KStandard, KNo and KLocation were selected in this study to evaluate the simulation results in terms of location changes. The three-dimensional approach is based on the three-map comparison method, which divides the simulation results into two agreement and three disagreement components [83]. The agreement components are Correct rejections (persistence simulated correctly) and Hits (change simulated correctly). The disagreement components are Misses (change simulated as persistence), Wrong hits (change simulated as change to wrong category) and False alarms (persistence simulated as change). This approach uses a three-dimensional, spatio-temporal comparison method to evaluate results, which is a good supplement to the Kappa coefficient [84]. The FoM is the intersection of the observed change and simulated change divided by the union of the observed change and simulated change [85]. It is often used to compare the consistency of the simulation and observation maps, which is expressed as follows
where a is Misses, b is Hits, c is Wrong hits and d is False alarms.
To explore the contribution of different driving factors to spatial characteristic simulation, the applicability of different driving factors was analyzed using IncNodePurity (Increase in node purity) in random forest. The principle of this index is to calculate the sum of the squares of the residuals. It represents the heterogeneous impact of each feature on the observations of decision tree nodes, reflecting the feature importance in the context of decreasing accuracy. The larger the IncNodePurity, the greater the importance of the driving factor in spatial characteristic simulation.
3.3. Scenario Setting
Three development scenarios, NGS, EDS and MPS, were set up to analyze the impact of different development directions on the future spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests.
The NGS is designed to maintain current development trends. Based on the land cover changes from 2003 to 2017, the conversion sequence (Table S2) and the conversion elasticity (Table S3) were determined. The area demands for 2022–2037 were predicted based on the area of 2003, 2007, 2013 and 2017 by linear regression. The results were appropriately adjusted to ensure the rationality of the changes (Table S4).
The EDS is designed to prioritize economic development. Under this scenario, the area of building land and aquaculture ponds will increase and the area of mangrove forests will decrease. The conversion sequence of aquaculture ponds and building land was restricted. The two types were only allowed to be transferred into economic construction land (aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and building land) (Table S2). The conversion elasticity was adjusted to 0.9 (the highest value) for aquaculture ponds and to 0.35 (the lowest value) for mangrove forests (Table S3). The area demands for 2022–2037 were predicted based on the area changes during the economic development phase (rapid growth of building land and aquaculture ponds) from 1987 to 2017. The results were appropriately adjusted to ensure that the growth rate of building land and aquaculture ponds under this scenario was higher than the NGS (Table S4).
The MPS is designed to prioritize the protection of mangrove forests. Under this scenario, the area of mangrove forests will increase and the area of building land and aquaculture ponds will decrease. The conversion sequence of mangrove forests was restricted. Mangrove forests were not allowed to be transferred into aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and building land (Table S2). The conversion elasticity was adjusted to 0.9 (the highest value) for mangrove forests and to 0.35 (the lowest value) for aquaculture ponds and building land (Table S3). The area demands for 2022–2037 were predicted based on the area changes during the mangrove protection phase (rapid growth of mangrove forests) from 1987 to 2017. The results were appropriately adjusted to ensure that the growth rate of mangrove forests under this scenario was higher than the NGS (Table S4).
4. Results
4.1. Simulation Accuracy of Spatial Characteristic
Based on the observation map and driving factors of Huiwen in 2003, the AUC values of various land cover types in different models were calculated (Table 2). Autologistic, AutoSVR and AutoRF are improved models of Logistic, SVR and RF with the spatial autocorrelation factor. AutoRF had the highest AUC values, with all types of land cover types exceeding 0.95. AutoSVR also achieved excellent accuracy, with all AUC values above 0.9. Autologistic was slightly worse, with AUC values below 0.9 for suitable land for mangrove and cultivated land, but greater than 0.7, indicating that the model also maintained good accuracy. The AUC values of Autologistic, AutoSVR and AutoRF were all higher than those of the unimproved model, indicating that the spatial autocorrelation factor can indeed improve the simulation accuracy. The AUC values of the above six models were greater than 0.7 for all types of land cover types, especially for mangrove forests (above 0.95), showing that the 12 driving factors selected in this study could well simulate the changes in mangrove forests. It is of interest that the AUC values of RF were higher than those of the improved Autologistic and AutoSVR, proving that the random forest had significant advantages in spatial characteristic simulation.

Table 2.
AUC values of various land cover types in different models.
4.2. Simulation Results and Accuracy Assessment
Based on the observation map and spatial characteristics in 2003, the spatial distribution in 2007, 2013 and 2017 were simulated using the CLUE-S model. To assess the accuracy of the simulation results, the OA and Kappa coefficients were calculated for the simulation results of different models based on the observation map of 2007, 2013 and 2017 (Table 3). The simulation accuracy decreased with the increase of simulation time. The highest accuracy was in 2007, the second highest was in 2013 and the lowest was in 2017, all maintaining good levels (OA above 75%). For different models, similar to the results of AUC values, RF is more advantageous than SVR and Logistic and the model with spatial autocorrelation is more ideal than the model without it. AutoRF had the highest simulation accuracy, with an OA of 77.94% in 2017, indicating that the simulation results of this model are in high agreement with the observation. KStandard, Kno and Klocation were 0.7638, 0.7835 and 0.8293, respectively, indicating that the model had high simulation accuracy for location changes.

Table 3.
OA and Kappa coefficients of different models in 2007, 2013 and 2017.
The three-dimensional approach and FoM were also used to further analyze the simulation results of different models in 2017 (Table 4). The results of FoM differed from the previous results. The SVR is more advantageous than RF and Logistic, and the model without spatial autocorrelation is more ideal than a model with it. This is because AutoRF is more conservative in change strategy compared to other models. It ignored some pixels that should have been changed (Misses and Hits) but reduced some false pixels (False alarms + Wrong hits). This led to a lower FoM for AutoRF, but the correct predicted pixels (Correct rejections + Hits) were higher than other models, indicating that AutoRF has some advantages in balancing the overall simulation accuracy.

Table 4.
Three-dimensional approach and FoM of different models in 2017.
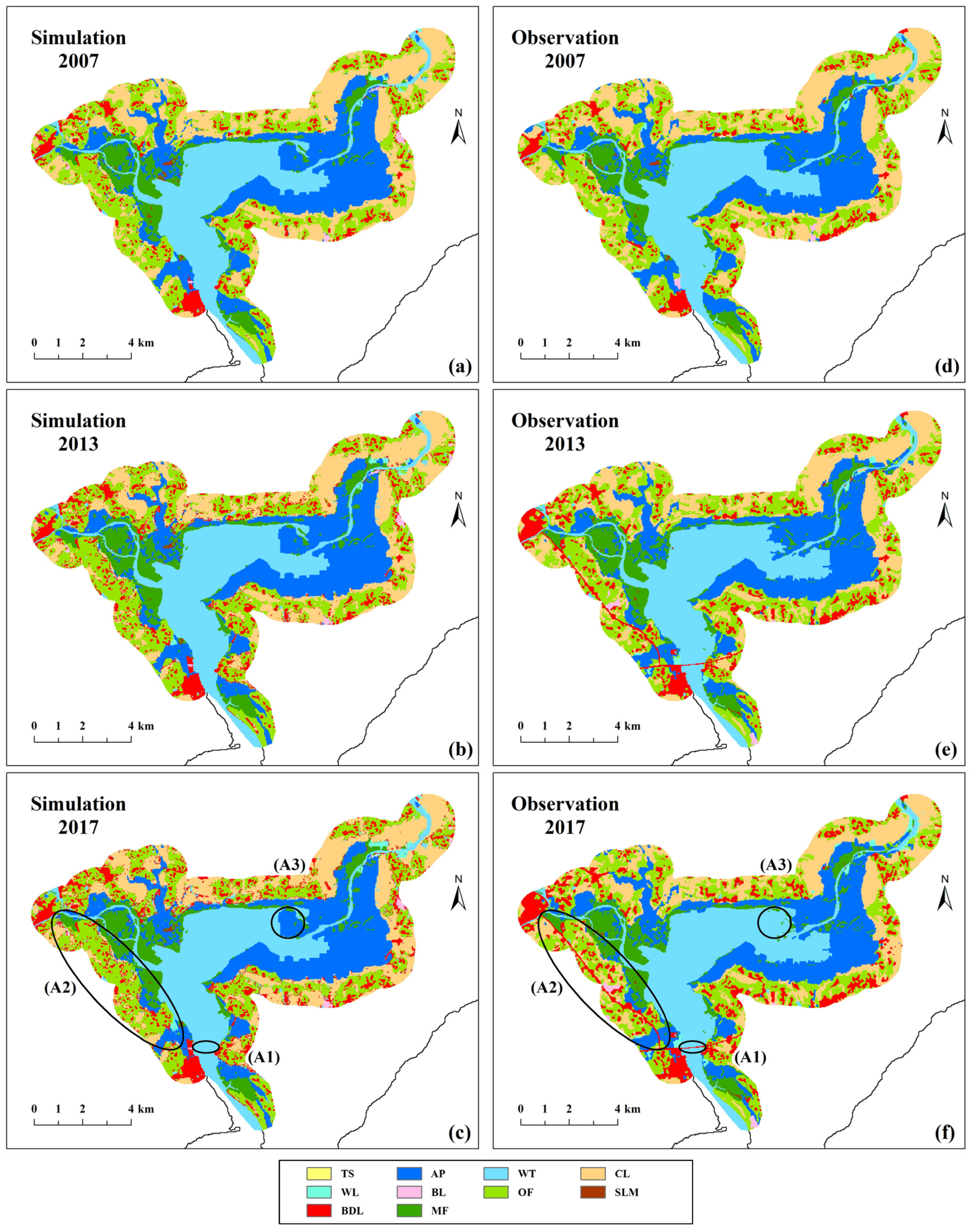
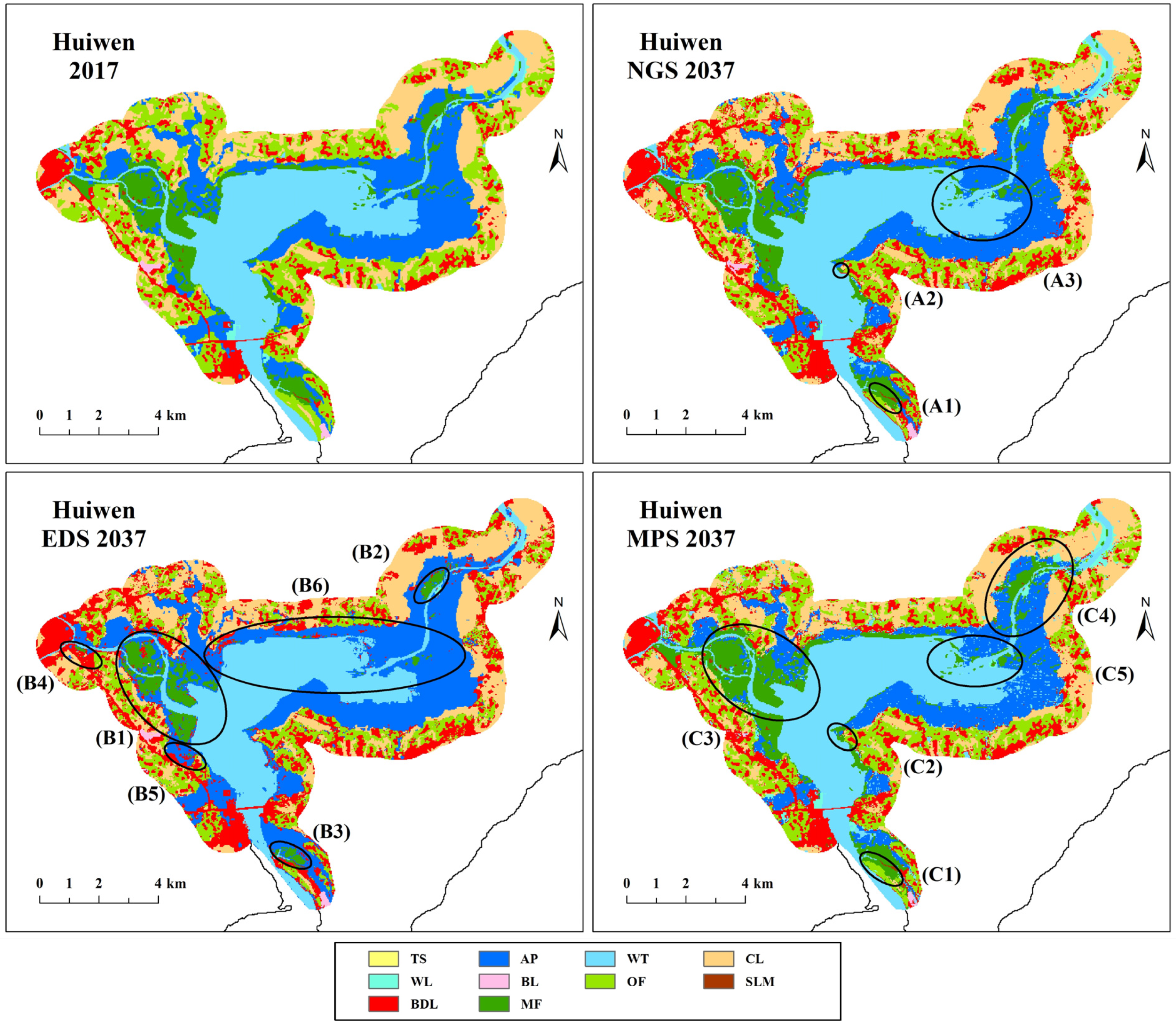
Figure 3 compares the simulation maps and observation maps for AutoRF in 2007, 2013 and 2017. The similarity between the simulation maps and the observation maps was high and both reflected the real spatial distribution of various land cover types. Mangrove forests in simulation maps were all distributed near the sea, which was consistent with the actual growth of mangrove forests. There were also some deviations in simulation maps. The simulation maps were more fragmented compared to the observation maps, which may be related to the high simulation resolution (30 m). The new bridges (Zone A1), new roads (Zone A2) and aquaculture ponds governance (Zone A3), which were greatly affected by policy, were not well simulated. In general, however, the spatial agreement between the simulation maps and observation maps was good.
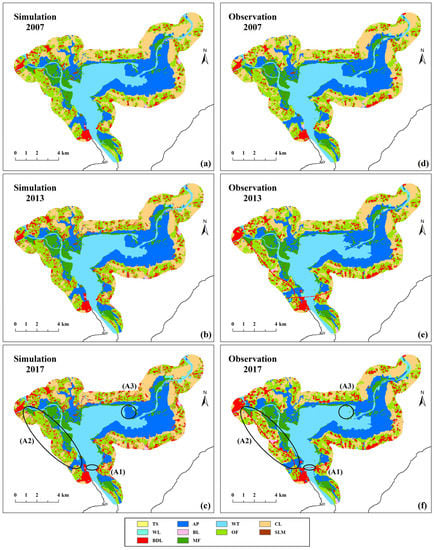
Figure 3.
Comparison between simulation maps (a–c) and observation maps (d–f) for AutoRF.
4.3. Applicability of Driving Factors
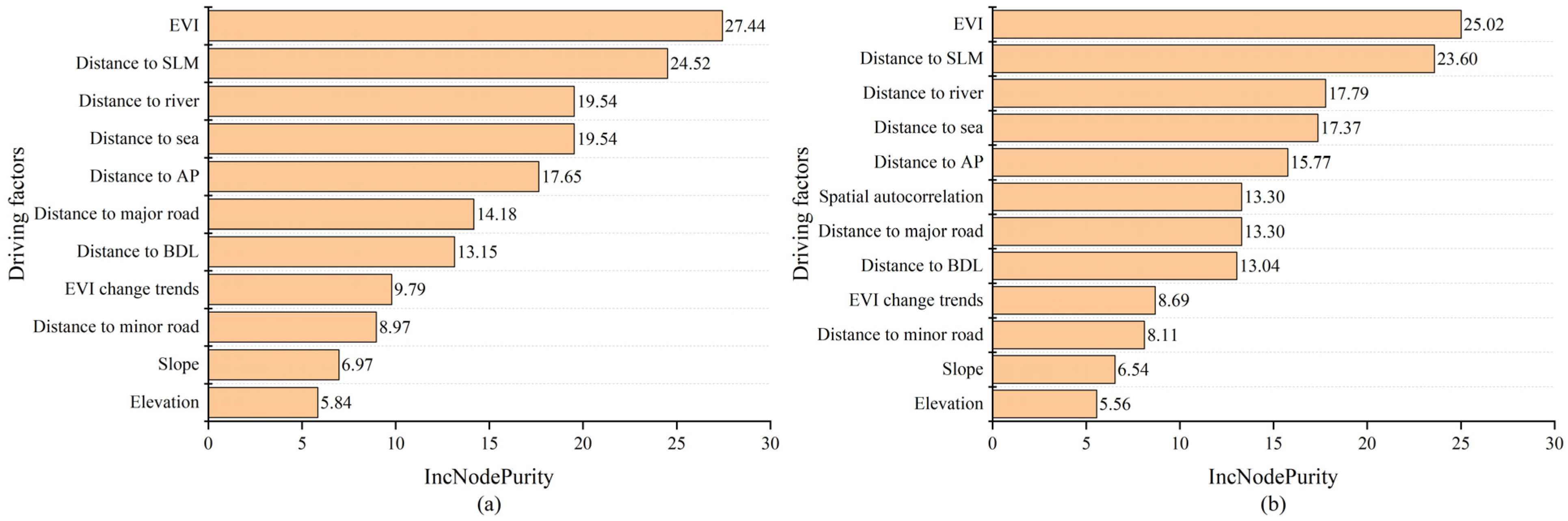
The IncNodePurity was used to evaluate the applicability of driving factors in the mangrove simulation (Figure 4). The results of AutoRF and RF were basically the same. EVI had the greatest importance, indicating that vegetation indices will significantly improve the accuracy of the mangrove simulation. The distance to suitable land for mangrove was the second greatest, suggesting that the changes of mangrove forests are closely related to the distribution of suitable land for mangrove. The importance of the two location indices, distance to river and distance to sea, were also greater, as mangrove forests mostly grow on mudflats between land and sea. The greater importance of the distance to aquaculture ponds and building land indicated that the presence of those two land cover types exerts a strong influence on mangrove growth, which is consistent with the results of previous studies [27]. The spatial autocorrelation factor was equally important, showing that this factor is also essential in machine learning models. The distance to major road was also an important influencing factor, indicating that mangrove growth is closely related to the frequency of human activities. The four indices of EVI change trends, distance to minor road, slope and elevation were weakly related. EVI change trends may better reflect mangrove trends within time spans, and have limited ability to predict future trends. The distance to minor road reflects the impact of residential, pedestrian, cycleway and other trails. The frequency of human activity on these roads is weaker than on major roads, so the impact on mangrove forests was weaker. Since the study area is small and belongs to the coastal area, the two terrain indices, slope and elevation, had little variation, so they were the least important.
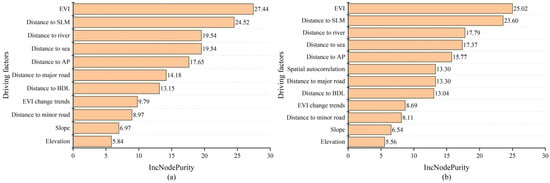
Figure 4.
Applicability of driving factors in mangrove simulation. (a) RF; (b) AutoRF.
4.4. Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Change Trends of Mangrove Forests under Different Scenarios
Based on the observation map and the spatial characteristics of AutoRF in 2017, the spatial distribution of mangrove forests was predicted in all protected areas in 2022, 2027, 2032 and 2037 under different scenarios using the CLUE-S model, and the change trends of mangrove forests were then analyzed.
4.4.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Mangrove Forests
Figure S1 shows the observation maps for 2017 and the prediction maps for 2037 under different scenarios. The results of Huiwen were shown in Figure 5. Mangrove forests in Huiwen were mainly distributed in the junction areas between land and sea along the coast, interlacing with aquaculture ponds. It can be seen that the CLUE-S model used in this study can predict the future spatio-temporal distribution well. The simulation maps in 2037 varied under different scenarios, but the spatial distribution of various land cover types was similar to the observation map in 2017. Under NGS, mangrove forests had few changes as a whole, showing a slow expansion trend. The expansion areas were mainly concentrated in the southern (Zone A1) and central (Zone A2) coastal areas, which were transferred from aquaculture ponds and other forests. Aquaculture ponds showed a contraction trend, especially in the eastern coastal region (Zone A3), which provided a more suitable growth environment for surrounding mangrove forests. Under EDS, mangrove forests showed a significant contraction trend. This is because EDS was designed to ensure economic development. The economic construction land will be aggressively expanded, and the growth areas of mangrove forests will inevitably be occupied. Only three patches of mangrove forests remained in the region, in the west (Zone B1), northeast (Zone B2) and south (Zone B3), noting that the area has been significantly reduced compared to 2017. Mangrove forests in all other areas were severely contracted, and most of them have been developed for building land and aquaculture ponds (Zones B4, B5 and B6). The remaining scattered mangrove forests were surrounded by other land cover types. The quality of the mangrove habitats was worrisome. Under MPS, mangrove forests showed a significant expansion trend. This is because MPS focuses on the protection of mangrove forests. The economic construction land that destroys mangrove habitats will drastically contract, and mangrove forests will inevitably expand. Similar to NGS, the southern (Zone C1) and central (Zone C2) coastal areas were the priority areas for mangrove growth. The two patches of mangrove forests in the west (Zone C3) and northeast (Zone C4) also expanded further outward, which was associated with the contraction of surrounding aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture ponds showed a significant contraction trend, and mangrove forests have begun to dominate the eastern coastal areas (Zone C5).
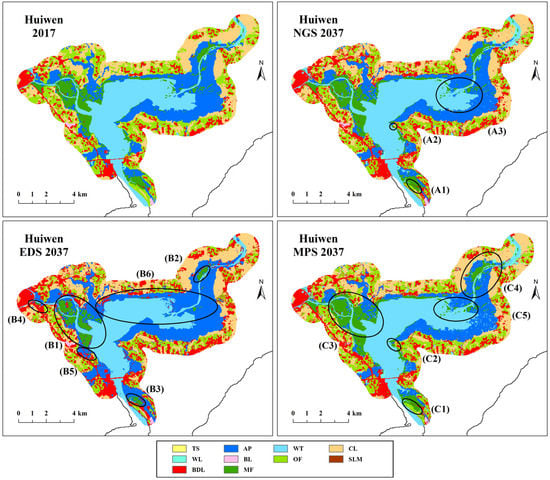
Figure 5.
Comparison between the observation maps for 2017 and the simulation maps for 2037 in Huiwen under different scenarios.
4.4.2. Temporal Change Trends of Mangrove Forests
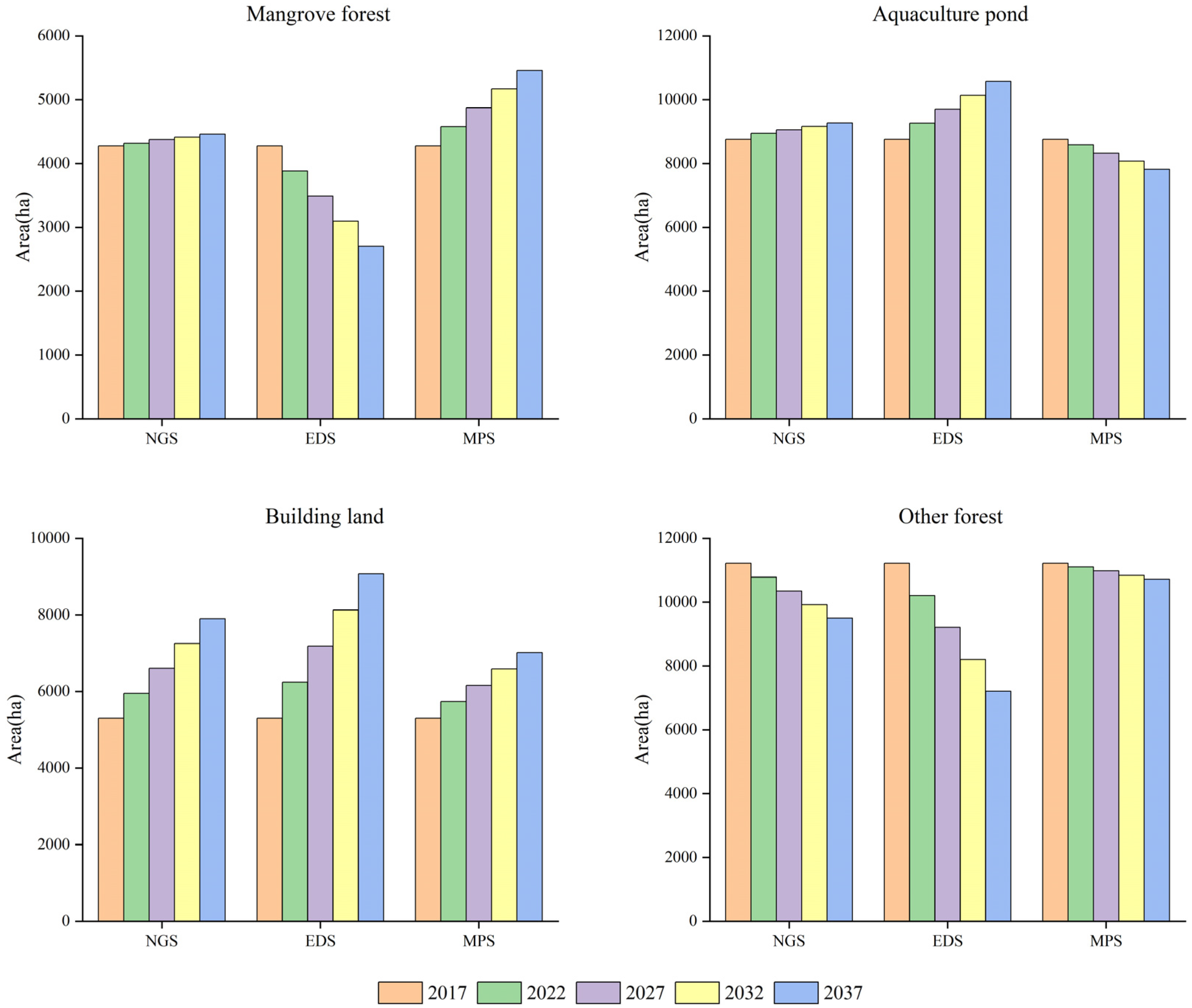
To explore the temporal change trends of mangrove forests under different scenarios, the area changes of mangrove forests and three related land cover types (aquaculture ponds, building land and other forests) were calculated in all protected areas from 2017 to 2037 (Figure 6). By 2037, the mangrove area increased slowly under NGS, decreased significantly under EDS and increased significantly under MPS with 4460, 2704 and 5456 ha respectively. The reasons for different changes of mangrove forests under different scenarios were as follows. Under EDS, the area of aquaculture ponds and building land increased significantly. The decreased area of other forests cannot provide enough space for economic construction land; mangrove forests will be seriously encroached upon. Thus, the mangrove area will decrease significantly. Under NGS, aquaculture ponds and building land still maintained their growth trends, but slowed down significantly compared to EDS. Thus, the impact of economic development on mangrove habitats was greatly reduced and the mangrove area will increase slowly. Under MPS, although the area of building land still increased slightly, the area of aquaculture ponds was reduced significantly, providing enough space for mangrove growth. Thus, the mangrove area will increase significantly.
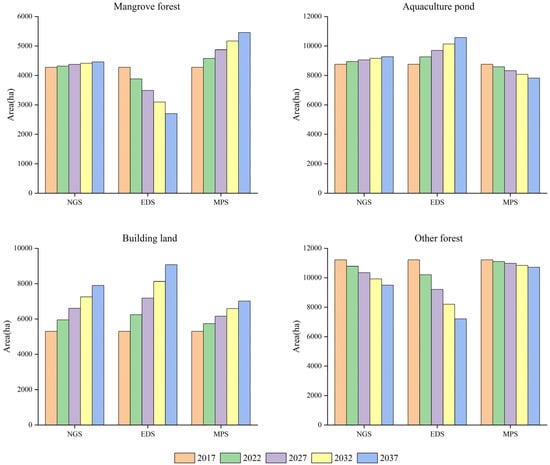
Figure 6.
Area changes of mangrove forests and three related land cover types (aquaculture ponds, building land and other forests) from 2017 to 2037.
4.4.3. Spatial Change Trends of Mangrove Forests
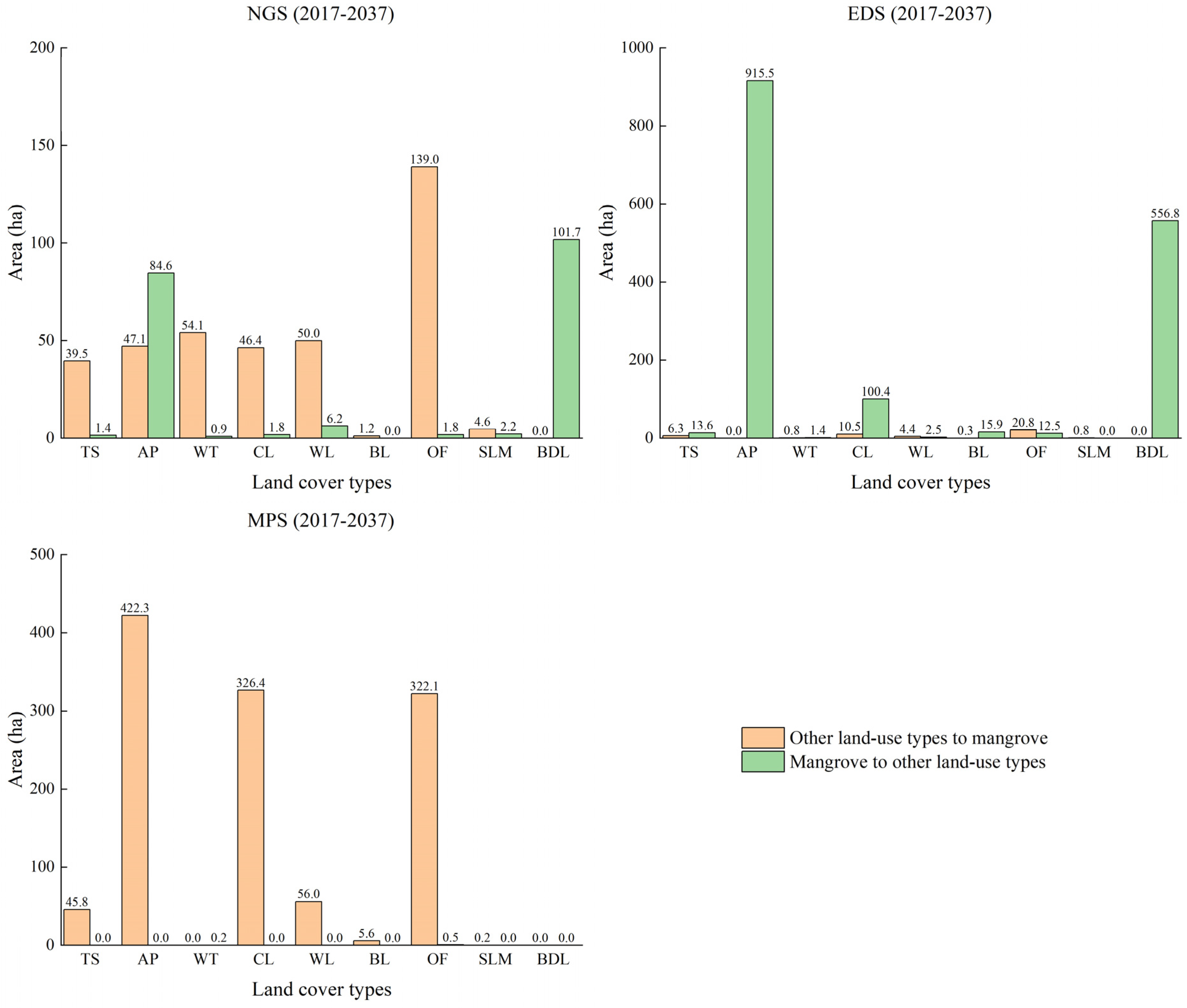
To further analyze the causes of mangrove changes, the conversion between mangrove forests and other land cover types was analyzed from 2017 to 2037 under different scenarios (Figure 7). Under EGS, the two largest land cover types transformed from mangrove forests were aquaculture ponds (916 ha) and building land (557 ha), much higher than other land cover types, indicating that mangrove contraction is indeed closely related to the expansion of economic construction land. Cultivated land also had a larger area (100 ha) transformed from mangrove forests, showing that some mangrove forests were encroached upon for crop production. Under MPS, aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and other forests were the three largest types transformed into mangrove forests with 422, 326 and 322 ha, respectively. The reason for the larger area transformed from aquaculture ponds and cultivated land is due to the strict implementation of the policy of converting fishponds to wetlands and converting cultivated land to wetlands. Other forests can transform into mangrove forests because there is a transformation route: other forests—aquaculture ponds/suitable land for mangrove—mangrove forests. Under NGS, the changes of mangrove forests were between EGS and MPS. Other forests had the largest area (139 ha) transformed into mangrove forests. Water, wetlands, aquaculture ponds and cultivated land also had a larger area (about 50 ha per type). Building land (102 ha) and aquaculture ponds (85 ha) were the two largest land cover types transformed from mangrove forests.
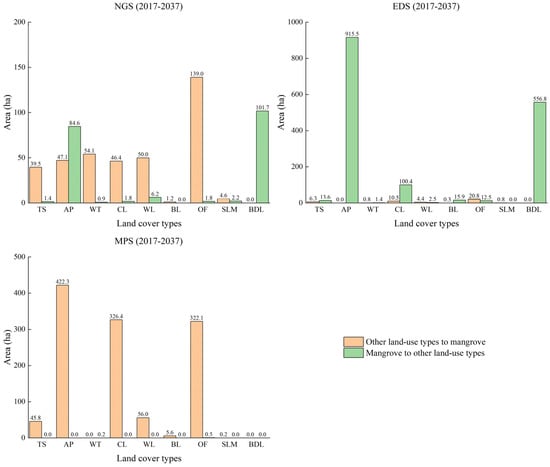
Figure 7.
Conversion between mangrove forests and other land cover types from 2017 to 2037 under different scenarios.
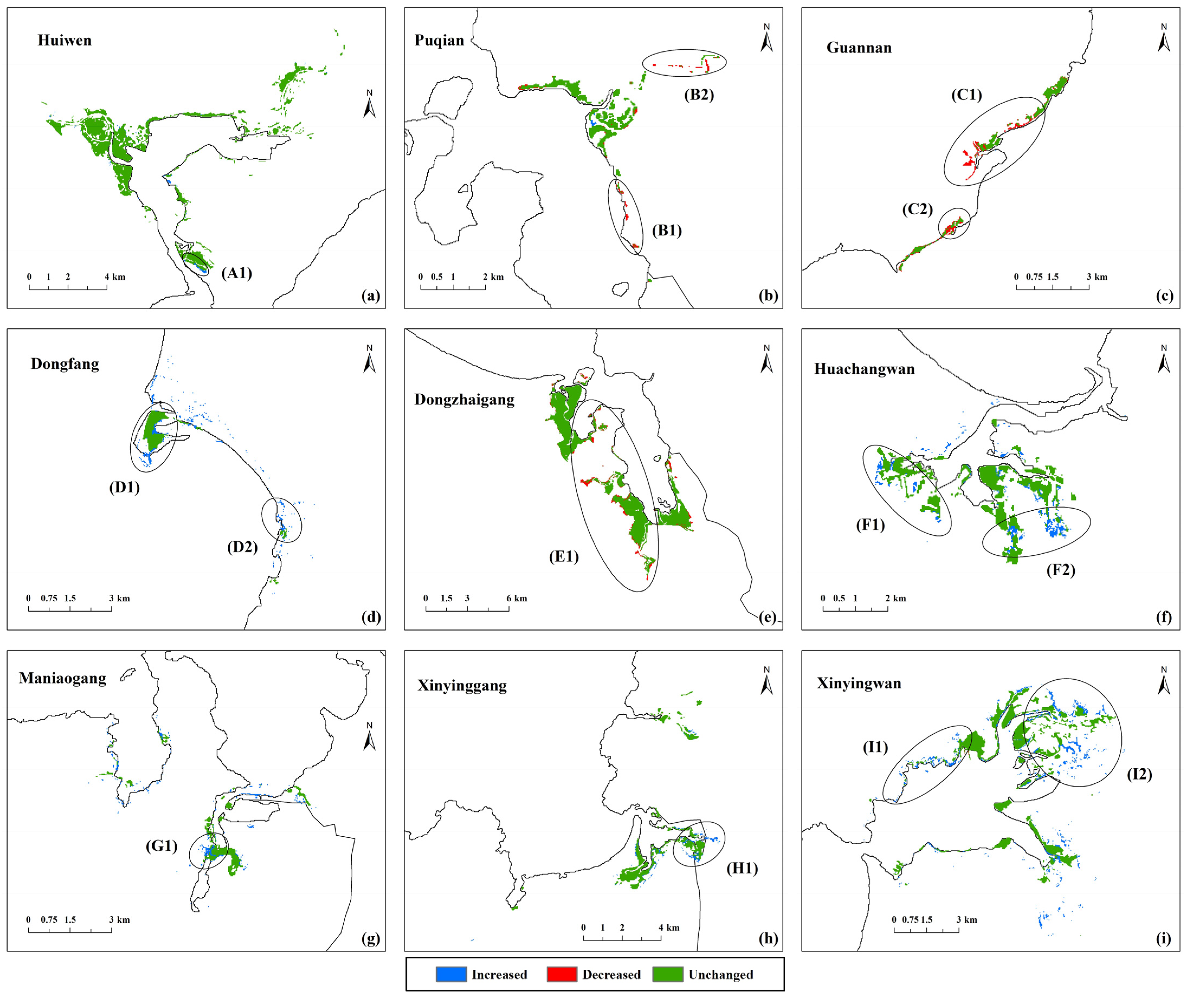
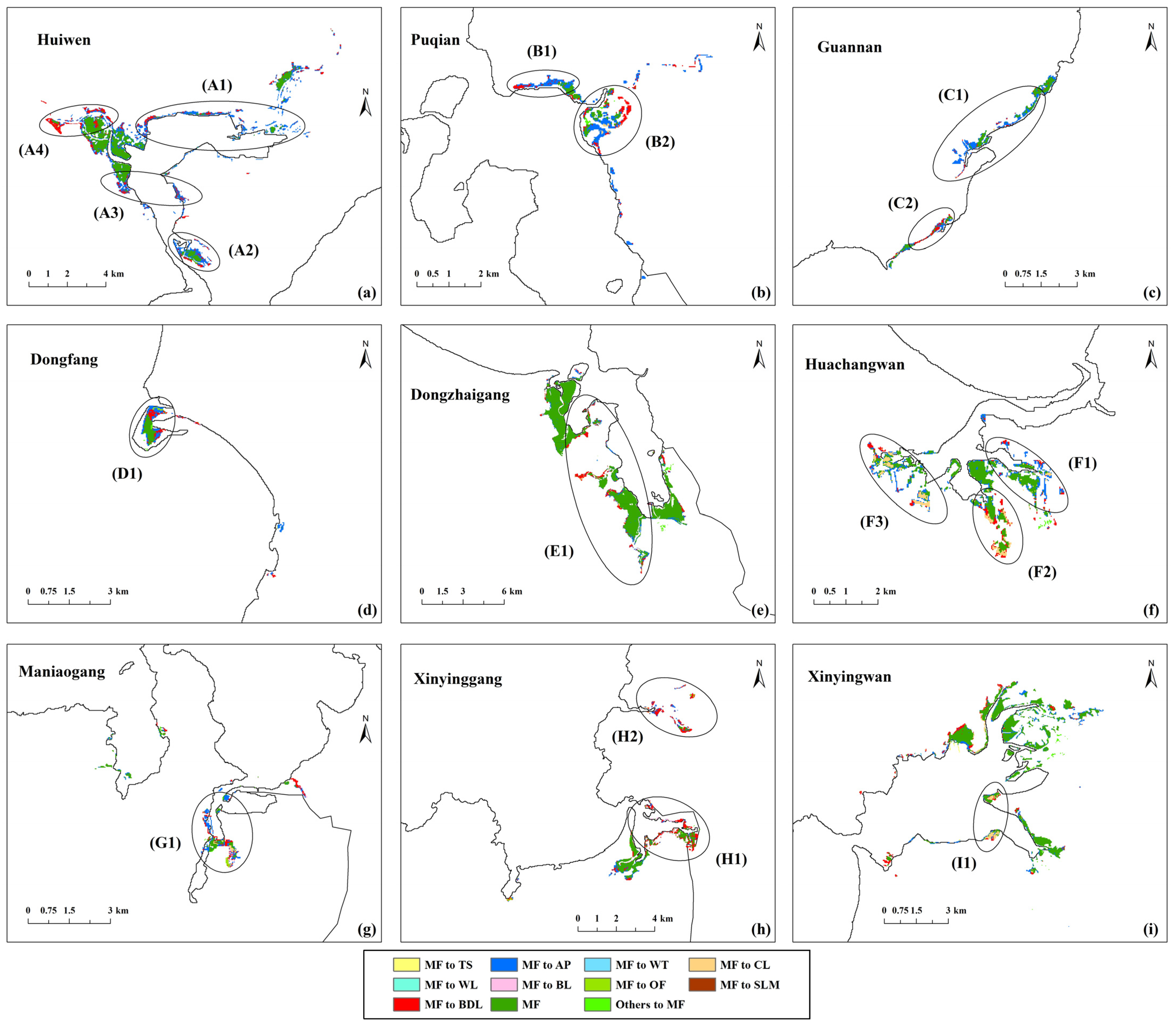
Figure 8 shows the land cover changes of mangrove forests from 2017 to 2037 under NGS. The mangrove area of all protected areas generally increased. Only the coastal of Puqian (Zones B1 and B2), the central of Guanan (Zones C1 and C2) and the western of Dongzhaigang (Zone E1) decreased significantly. Most of the mangrove growth areas were around existing mangrove forests (Zones A1, D1, D2, F1, F2, G1, H1 and I1) or along the riverbank (Zone I2).
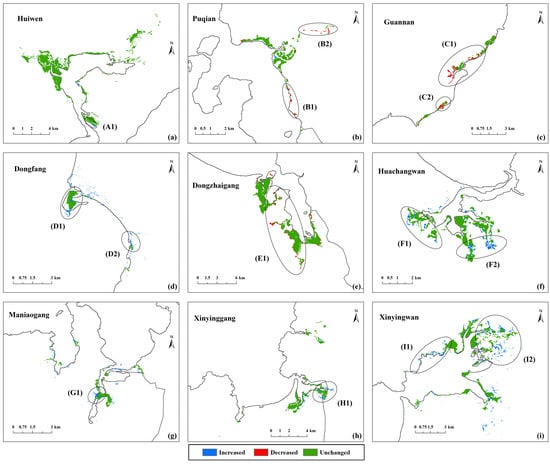
Figure 8.
Land cover changes of mangrove forests (a–i) from 2017 to 2037 under NGS.
Figure 9 shows the land cover changes of mangrove forests from 2017 to 2037 under EDS. The mangrove area of all protected areas showed a significant decrease. The main types transformed from mangrove forests are aquaculture ponds (Zones A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, C1, D1, F1 and G1), building land (Zones A4, B2, C2, D1, E1, H1 and H2) and cultivated land (Zones F2, F3 and I1). Most of the contraction areas are comprised of marginal mangrove forests, as mangrove forests here are vulnerable to external disturbances. Their health conditions were worse compared to the interior mangrove forests. Therefore, these areas are more easily transformed into economic construction land, and will be the priority encroachment area during the economic development phase. The fragmented and scattered mangrove forests (Zones A1, B1, B2 and C2) contracted more than the intact and contiguous mangrove forests. Since these mangrove forests are mostly surrounded by other land cover types, their ability to resist stress is weak. With the decline of the habitat quality, the growth areas of fragmented and scattered mangrove forests will be rapidly encroached upon.
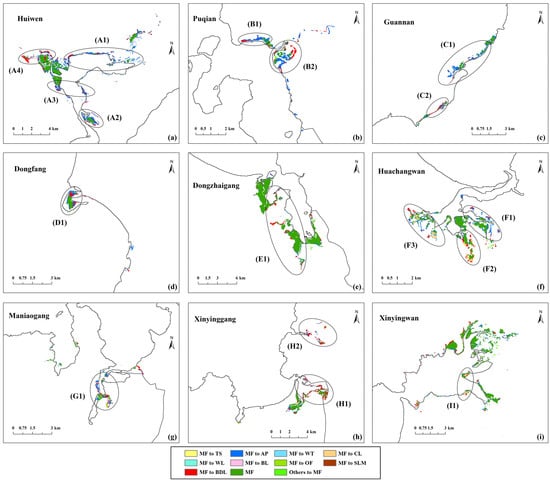
Figure 9.
Land cover changes of mangrove forests (a–i) from 2017 to 2037 under EDS.
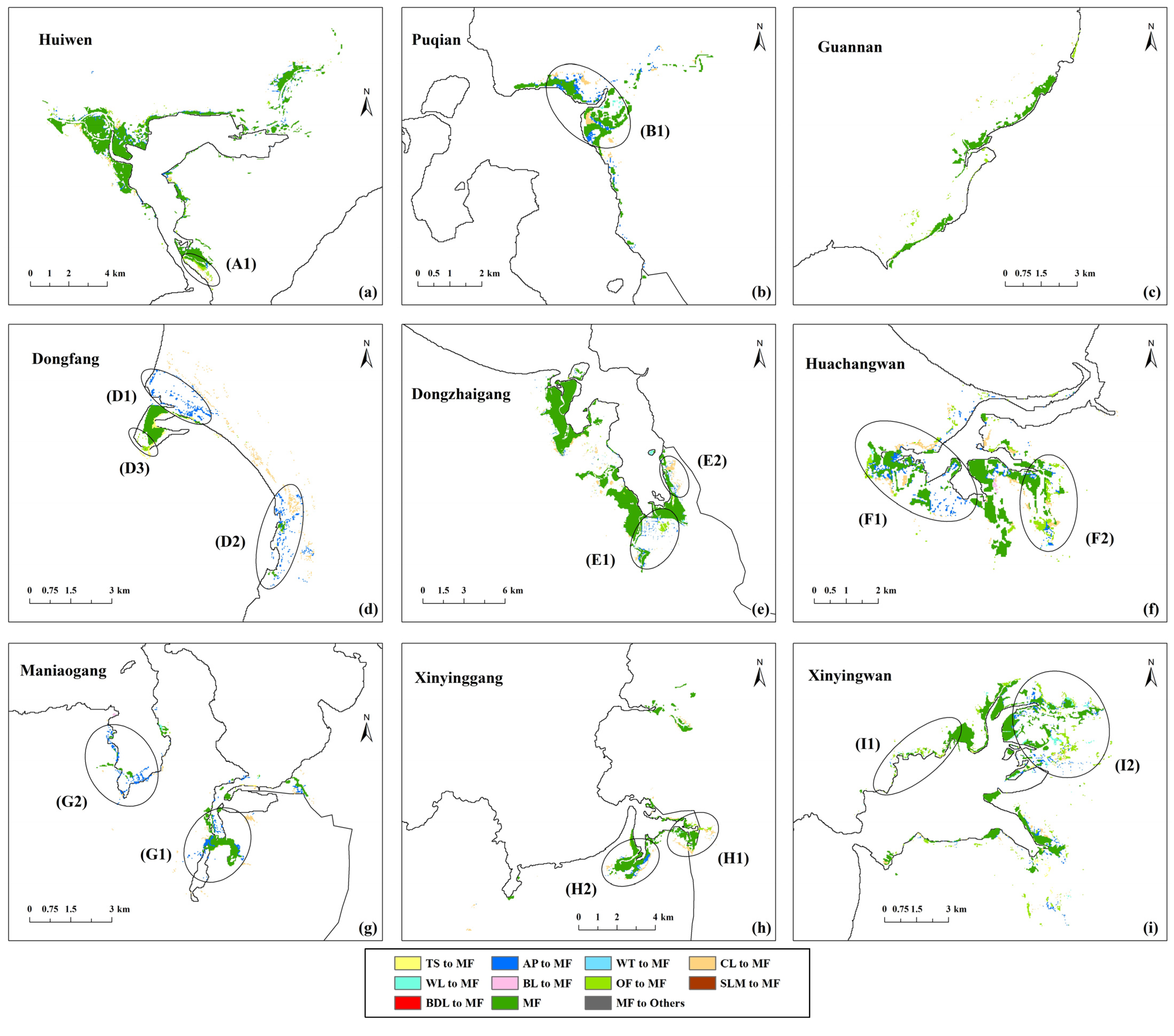
Figure 10 shows the land cover changes of mangrove forests under MPS from 2017 to 2037. The mangrove area of the most protected areas showed a significant increase. The main types transformed into mangrove forests were aquaculture ponds (Zones B1, D1, D2, F1, G1, G2 and H2), cultivated land (Zones B1, D2, E2, F1 and H1) and other forests (Zones A1, D3, E1, F2, I1 and I2). Most of these expansion areas were located around existing mangrove forests, as the habitat quality there is better. Therefore, after the governance of economic construction land, these areas are more easily transformed into mangrove forests, and will be the priority restoration area during the mangrove protection phase. Other expansion areas were along the riverbank (Zones E1 and I2). This is because these areas are close to water and away from other land cover types, which are conducive to mangrove growth, especially for mangrove seedlings [33]. Only the mangrove area in Guannan did not increase significantly under this scenario, as the ecological management of this region has always been poor. Aquaculture ponds have been threatening surrounding mangrove forests [65].
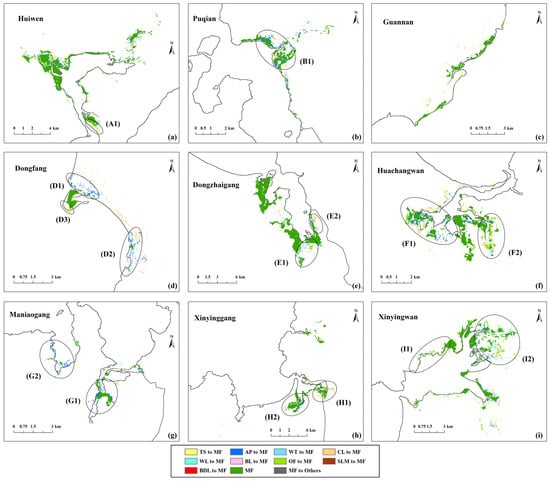
Figure 10.
Land cover changes of mangrove forests (a–i) from 2017 to 2037 under MPS.
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of the Spatio-Temporal Simulation Methods of Mangrove Forests
In this study, the simulation accuracy of logistic regression, support vector regression and random forest were first compared in terms of spatial characteristics, and the simulation potential of different models was evaluated. The results showed that: (1) RF is more advantageous than SVR and Logistic; (2) the model with spatial autocorrelation is more ideal than the model without it; and (3) AutoRF performs the best in spatial characteristic simulation. AutoRF was then combined with the CLUE-S model to simulate the spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests. The results showed that the simulation maps of the model are in good spatial agreement with the observation maps, and the OA (77.94%) is better compared to the other models. This indicated that AutoRF proposed in this study has significant advantages for mangrove simulation. Driving factors reflecting the characteristics of mangrove forests were also explored in this study, and the applicability of mangrove simulation was assessed. The results showed that the vegetation index EVI can significantly improve the accuracy of mangrove simulation; location indices such as distance to suitable land for mangrove, river, sea, aquaculture ponds, major road and building land are also very important constraints; and the spatial autocorrelation factor is also indispensable in machine learning models. This indicated that the driving factors selected in this study play an important role in mangrove simulation. Overall, the spatio-temporal simulation method proposed in this study can effectively simulate the relationship between mangrove change processes and environmental driving factors, accurately predict the future spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests, and provide a theoretical basis and decision support for mangrove protection, restoration and utilization.
5.2. Future Changes of Mangrove Forests in Hainan Island
The future changes of mangrove forests in Hainan Island from 2022 to 2037 vary under different scenarios. By 2037, the mangrove area increased slowly under NGS, decreased significantly under EDS and increased significantly under MPS occupying 4460, 2704 and 5456 ha, respectively. The changes in area are associated with changes in aquaculture ponds, building land, cultivated land and other forests. The contraction of mangrove forests is closely related to the expansion of aquaculture ponds, building land and cultivated land. The marginal mangrove forests are more prone to contraction than the interior mangrove forests and the fragmented mangrove forests contracted more than the intact mangrove forests. Mangrove forests in these areas should be protected as a priority in the future. The expansion of mangrove forests is attributed to the contraction of aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and other forests. The areas around existing mangrove forests and on both sides of the riverbank are typical areas for mangrove expansion; these areas are preferable for artificial planting. Comparing different development scenarios, the MPS should be the most suitable development direction in the future. The reason is that this scenario maintains a steady growth of economic construction land and significant growth of mangrove forests, which reasonably balances the relationship between economic development and mangrove protection.
5.3. Limitations and Future Perspective of the Study
The potential of land cover changes was assessed in this study through spatial suitability probability, considering only the relationship between land cover types and driving factors from a mono-temporal perspective. Although this model may be more stable for long-term simulation with non-stationary change patterns, it is difficult to capture and distinguish different change processes, as the spatial configuration of past changes is not considered [54]. Therefore, other forests can directly transform into mangrove forests in this study. This is because the transformation route of other forests-aquaculture ponds/suitable land for mangrove-mangrove forests was simplified to other forests-mangrove forests. Another similar phenomenon was that only a small area of suitable land for mangrove was transformed into mangrove forests. This is because the transformation route of aquaculture ponds-suitable land for mangrove-mangrove forests was simplified to aquaculture ponds-mangrove forests. Another limitation of this method is the difficulty in predicting changes affected by policy such as new bridges, new roads and aquaculture ponds governance (Zones A1, A2 and A3 in Figure 3). Meanwhile, the future area demands under different scenarios were predicted by linear regression and scenario analysis. Although these methods are simple and effective [53], they cannot reflect the complex processes in land-use changes. This study also found that the simulated maps were more fragmented compared to the observation maps, which may be related to the high simulation resolution (30 m).
Therefore, models that consider the relationship between past changes and driving factors, such as DINAMICA and the Land Change Modeler (LCM), should be combined in future studies to better capture the actual process of land cover changes [54]. Future planning data should be added to the model to reduce the uncertainty of simulation results caused by policy. At the same time, system dynamics models or artificial neural networks should also be used to estimate area demands. Finally, it is also the goal of future efforts to explore the simulation accuracy of models and the applicability of driving factors under different resolutions, especially for high resolutions (integrated with Sentinel-1/2), and select the optimal resolution applicable to mangrove spatio-temporal simulation.
6. Conclusions
Mangrove forests are important wetland ecosystems that grow in the intertidal zone between land and sea. They provide important social, ecological and economic services to coastal areas. In recent years, mangrove protection has reached a broad international consensus and effective mangrove monitoring methods are essential. A spatio-temporal simulation method for mangrove forests was proposed in this study. This method compared the simulation accuracy of different models in terms of spatial characteristics, evaluated the applicability of driving factors in mangrove simulation and predicted the future spatio-temporal distribution and change trends of mangrove forests under different scenarios.
The simulation results of different models reveal that for spatial characteristic simulation: (1) RF is more advantageous than SVR and Logistic; (2) the model with spatial autocorrelation is more ideal than the model without it; and (3) AutoRF performs the best. For different driving factors, knowledge of vegetation index EVI, various location indices and the spatial autocorrelation factor can significantly improve the accuracy of mangrove simulation. The prediction results of Hainan Island showed that the future spatio-temporal distribution of mangrove forests varies under different scenarios. The mangrove area increased slowly under NGS, decreased significantly under EDS and increased significantly under MPS. The contraction of mangrove forests is closely related to the expansion of aquaculture ponds, building land and cultivated land. Mangrove contraction is more severe in marginal or fragmented areas. The expansion of mangrove forests is due to the contraction of aquaculture ponds, cultivated land and other forests. The areas around existing mangrove forests and on both sides of the riverbank are typical areas of mangrove expansion. The MPS should be the most suitable development direction for the future, as it can reasonably balance economic development with mangrove protection. This will provide a theoretical basis and decision support for mangrove protection, restoration and utilization.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs13204059/s1, Figure S1: Comparison between the observation maps for 2017 and the simulation maps for 2037 under different scenarios, Table S1: The details of the selected reserves in this study, Table S2: The conversion sequence under different scenarios, Table S3: The conversion elasticity under different scenarios, and Table S4: The annual area changes under different scenarios (pixel/y).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; methodology, B.Z. and J.L.; software, B.Z.; validation, B.Z.; formal analysis, B.Z., J.L. and G.S.; investigation, B.Z. and J.L.; resources, J.L.; data curation, B.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z., J.L. and G.S.; writing—review and editing, B.Z., J.L. and G.S.; visualization, B.Z.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, J.L.; and funding acquisition, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hainan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. ZDKJ2019006) and Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA19030302).
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to the confidentiality of the research projects.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express thanks to the anonymous reviewers for their voluntary work and the constructive comments to improve this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Giri, C. Recent Advancement in Mangrove Forests Mapping and Monitoring of the World Using Earth Observation Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.J.; Edwards, A.J.; Arias-Gonzalez, J.E.; Lindeman, K.C.; Blackwell, P.G.; Gall, A.; Gorczynska, M.I.; Harborne, A.R.; Pescod, C.L.; Renken, H.; et al. Mangroves enhance the biomass of coral reef fish communities in the Caribbean. Nature 2004, 427, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbier, E.B. Natural barriers to natural disasters: Replanting mangroves after the tsunami. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, B.B.; Ronnback, P.; Kovacs, J.M.; Crona, B.; Hussain, S.A.; Badola, R.; Primavera, J.H.; Barbier, E.; Dahdouh-Guebas, F. Ethnobiology, socio-economics and management of mangrove forests: A review. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 89, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Kauffman, J.B.; Murdiyarso, D.; Kurnianto, S.; Stidham, M.; Kanninen, M. Mangroves among the most carbon-rich forests in the tropics. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, Q.T.; Kuenzer, C.; Vo, Q.M.; Moder, F.; Oppelt, N. Review of valuation methods for mangrove ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.; Lagomasino, D.; Thomas, N.; Fatoyinbo, T. Global declines in human-driven mangrove loss. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5844–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirga, A.; Addisu Legesse, S.; Mekuriaw, A. Carbon Stock and Mitigation Potentials of Zeghie Natural Forest for Climate Change Disaster Reduction, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Bateni, S.M.; Jun, C. Global Surface Temperature: A New Insight. Climate 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.R.; Friess, D.A. Rates and drivers of mangrove deforestation in Southeast Asia, 2000-2012. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friess, D.A.; Thompson, B.S.; Brown, B.; Amir, A.A.; Cameron, C.; Koldewey, H.J.; Sasmito, S.D.; Sidik, F. Policy challenges and approaches for the conservation of mangrove forests in Southeast Asia. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P.; Hardy, A.; Rosenqvist, A.; Simard, M. Distribution and drivers of global mangrove forest change, 1996–2010. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, H.; Delworth, T.L.; Cooke, W.F.; Zhao, M.; Xiang, B.Q.; Hsu, P.C. Detected climatic change in global distribution of tropical cyclones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10706–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, D.M. Present state and future of the world’s mangrove forests. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayaux, P.; Holmgren, P.; Achard, F.; Eva, H.; Stibig, H.; Branthomme, A. Tropical forest cover change in the 1990s and options for future monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Casey, D. Creation of a high spatio-temporal resolution global database of continuous mangrove forest cover for the 21st century (CGMFC-21). Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 25, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conchedda, G.; Durieux, L.; Mayaux, P. An object-based method for mapping and change analysis in mangrove ecosystems. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Ochieng, E.; Tieszen, L.L.; Zhu, Z.; Singh, A.; Loveland, T.; Masek, J.; Duke, N. Status and distribution of mangrove forests of the world using earth observation satellite data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, W.R.; Souza, P.W.M.; Proisy, C.; Lucas, R.M.; Rosenqvist, A. Mapping changes in the largest continuous Amazonian mangrove belt using object-based classification of multisensor satellite imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 117, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.M. Remote Sensing Analysis of China’ Mangrove Forests Dynamic During 1973 to 2013; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.Q.; Xiao, X.M.; Li, X.P.; Pan, L.H.; Doughty, R.; Ma, J.; Dong, J.W.; Qin, Y.W.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Z.X.; et al. A mangrove forest map of China in 2015: Analysis of time series Landsat 7/8 and Sentinel-1A imagery in Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, P.; Rosenqvist, A.; Lucas, R.M.; Rebelo, L.M.; Hilarides, L.; Thomas, N.; Hardy, A.; Itoh, T.; Shimada, M.; Finlayson, C.M. The Global Mangrove WatchA New 2010 Global Baseline of Mangrove Extent. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suyadi; Gao, J.; Lundquist, C.J.; Schwendenmann, L. Characterizing landscape patterns in changing mangrove ecosystems at high, latitudes using spatial metrics. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.M.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Mao, D.H.; Wang, C. Monitoring loss and recovery of mangrove forests during 42 years: The achievements of mangrove conservation in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Buitre, M.J.C.; Zhang, H.S.; Lin, H. The Mangrove Forests Change and Impacts from Tropical Cyclones in the Philippines Using Time Series Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.J.; Zhen, J.N.; Zhang, L.; Metternicht, G. Understanding Dynamics of Mangrove Forest on Protected Areas of Hainan Island, China: 30 Years of Evidence from Remote Sensing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamberlain, D.; Phinn, S.; Possingham, H. Remote Sensing of Mangroves and Estuarine Communities in Central Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.J.; Liao, J.J.; Shen, G.Z. Mapping Large-Scale Mangroves along the Maritime Silk Road from 1990 to 2015 Using a Novel Deep Learning Model and Landsat Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.S.; Takewaka, S. Analyses on phenological and morphological variations of mangrove forests along the southwest coast of Bangladesh. J. Coast. Conserv. 2014, 18, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga-Robles, C.A.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Villanueva, M.R.N. Seasonal trend analysis (STA) of MODIS vegetation index time series for the mangrove canopy of the Teacapan-Agua Brava lagoon system, Mexico. Giscience Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 338–361. [Google Scholar]
- Le, H.T.; Tran, T.V.; Gyeltshen, S.; Nguyen, C.P.T.; Tran, D.X.; Luu, T.H.; Duong, M.B. Characterizing Spatiotemporal Patterns of Mangrove Forests in Can Gio Biosphere Reserve Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Appl. Sci. Basel 2020, 10, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Liao, J.; Shen, G. Combining time series and land cover data for analyzing spatio-temporal changes in mangrove forests: A case study of Qinglangang Nature Reserve, Hainan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Yuan, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shen, W.M. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenne, N.; Lambin, E.F. A dynamic simulation model of land-use changes in Sudano-sahelian countries of Africa (SALU). Agric. Ecosyst Env. 2001, 85, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Matas, C.; Pukkala, T. Optimisation of the traditional land-use system in the Angolan highlands using linear programming. Int J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2014, 21, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taromi, R.; DuRoss, M.; Chen, B.T.; Faghri, A.; Li, M.X.; DeLiberty, T. A multiobjective land development optimization model: The case of New Castle County, Delaware. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2015, 38, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saysel, A.K.; Barlas, Y.; Yenigun, O. Environmental sustainability in an agricultural development project: A system dynamics approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.P.; Ou, J.P.; Li, X.; Ai, B. Combining system dynamics and hybrid particle swarm optimization for land use allocation. Ecol. Model. 2013, 257, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Son, N.T.; Chang, N.B.; Chen, C.R.; Chang, L.Y.; Valdez, M.; Centeno, G.; Thompson, C.A.; Aceituno, J.L. Multi-Decadal Mangrove Forest Change Detection and Prediction in Honduras, Central America, with Landsat Imagery and a Markov Chain Model. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6408–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.S.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.Q. Incorporating spatial autocorrelation into cellular automata model: An application to the dynamics of Chinese tamarisk (Tamarix chinensis Lour.). Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3490–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basse, R.M.; Omrani, H.; Charif, O.; Gerber, P.; Bodis, K. Land use changes modelling using advanced methods: Cellular automata and artificial neural networks. The spatial and explicit representation of land cover dynamics at the cross-border region scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, J.C.; Verburg, P.H. Combination of process-oriented and pattern-oriented models of land-use change in a mountain area of Vietnam. Ecol. Model. 2007, 202, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.C.; Ou, J.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Pei, F.S. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetter, R.P.; Hoanh, C.T.; Laborte, A.G.; Van Keulen, H.; Van Ittersum, M.K.; Dreiser, C.; Van Diepen, C.A.; De Ridder, N.; Van Laar, H.H. Integration of Systems Network (SysNet) tools for regional land use scenario analysis in Asia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V.; Mastura, S.S.A. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Mondal, P.; Barik, J.; Chowdhury, S.M.; Ghosh, T.; Hazra, S. Changes in mangrove species assemblages and future prediction of the Bangladesh Sundarbans using Markov chain model and cellular automata. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkaya, A.G.; Balcik, F.B.; Goksel, C.; Esbah, H. Forecasting land-cover growth using remotely sensed data: A case study of the Igneada protection area in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasGupta, R.; Hashimoto, S.; Okuro, T.; Basu, M. Scenario-based land change modelling in the Indian Sundarban delta: An exploratory analysis of plausible alternative regional futures. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, A.; Karimi, A.; Zhang, A.L. Modeling land cover change dynamic using a hybrid model approach in Qeshm Island, Southern Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-P.; Chu, H.-J.; Wu, C.-F.; Verburg, P.H. Predictive ability of logistic regression, auto-logistic regression and neural network models in empirical land-use change modeling—A case study. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.G.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; He, B.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Y.F. Simulation of urban agglomeration ecosystem spatial distributions under different scenarios: A case study of the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.F.; Jiang, W.G.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Chen, Z. Simulating wetland changes under different scenarios based on integrating the random forest and CLUE-S models: A case study of Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.F.; Kolb, M.; Paegelow, M.; Olmedo, M.T.C.; Houet, T. Inductive pattern-based land use/cover change models: A comparison of four software packages. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 51, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, F.; Fu, M.C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.T. Land-use change in Changli County, China: Predicting its spatio-temporal evolution in habitat quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.X.; Wu, H.; Li, S.Y. Simulating land-use changes by incorporating spatial autocorrelation and self-organization in CLUE-S modeling: A case study in Zengcheng District, Guangzhou, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 12, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Jia, K.; Wu, Y.F. Simulating urban land use change by incorporating an autologistic regression model into a CLUE-S model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, W.G.; Wang, W.J.; Lei, X.; Deng, Y. Exploring spatial-temporal change and gravity center movement of construction land in the Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1363–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, K.F.; Jiang, W.G.; Ling, Z.Y.; Hou, P.; Deng, Y.W. Evaluating the potential impacts of land use changes on ecosystem service value under multiple scenarios in support of SDG reporting: A case study of the Wuhan urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y. Dynamic vegetation cover change over the last 18 years in China. Quat. Sci. 2001, 21, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Besag, J.E. Nearest-Neighbour Systems and the Auto-Logistic Model for Binary Data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1972, 34, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Wang, M. The Mangroves of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Song, X.Q.; Lei, J.R.; Fang, Z.S.; Meng, Q.W. Mangrove Plants Resources and Its Conservation Strategies on Hainan. J. Trop. Biol. 2016, 7, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.X.; Chen, E.Y. Distribution of Mangrove in Hainan Island at Present. J. Trop Oceanogr. 1985, 1985, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.N. Monitoring and Dynamic Analysis of Mangrove Forests in Hainan Island using Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. ITGRS 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Jiang, W.G.; Yuan, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Lv, Z.L.; Chen, Z. Inter-annual variations in vegetation and their response to climatic factors in the upper catchments of the Yellow River from 2000 to 2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.X.; Jiang, W.G.; Wang, W.J.; Wu, Z.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Z. Wetland Loss Identification and Evaluation Based on Landscape and Remote Sensing Indices in Xiong’an New Area. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Su, W.; Li, Y. Simulating the optimal land-use pattern in the farming-pastoral transitional zone of Northern China. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2008, 32, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, S.W.; Huang, Y.J.; Cao, M.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Exploring an Ecologically Sustainable Scheme for Landscape Restoration of Abandoned Mine Land: Scenario-Based Simulation Integrated Linear Programming and CLUE-S Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Pu, J.; Miao, P.; Wang, Q.; Tan, K. Optimization of the National Land Space Based on the Coordination of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Functions in the Karst Areas of Southwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, B.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, H. Identification and scenario prediction of degree of wetland damage in Guangxi based on the CA-Markov model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ren, X.; Che, Y.; Yang, K. A Coupled SD and CLUE-S Model for Exploring the Impact of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study in Baoshan District, Shanghai, China. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Mai, X.; Shen, G. Delineation of Urban Growth Boundaries with SD and CLUE-s Models under Multi-Scenarios in Chengdu Metropolitan Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourdes Lima, M.; Romanelli, A.; Massone, H.E. Assessing groundwater pollution hazard changes under different socio-economic and environmental scenarios in an agricultural watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.K.; Mohanasundaram, S.; Shrestha, S. Impacts of land-use changes on the groundwater recharge in the Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. MLear 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. MLear 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Moulds, S.; Buytaert, W.; Mijic, A. An open and extensible framework for spatially explicit land use change modelling: The lulcc R package. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2015, 8, 3215–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, A.P. The use of the area under the roc curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.A. Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G. Quantification error versus location error in comparison of categorical maps. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Peethambaram, S.; Castella, J.-C. Comparison of Three Maps at Multiple Resolutions: A Case Study of Land Change Simulation in Cho Don District, Vietnam. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2011, 101, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, O.G.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Szabo, Z.; Szabo, S. Effects of Category Aggregation on Land Change Simulation Based on Corine Land Cover Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Boersma, W.; Castella, J.-C.; Clarke, K.; de Nijs, T.; Dietzel, C.; Duan, Z.; Fotsing, E.; Goldstein, N.; Kok, K.; et al. Comparing the input, output, and validation maps for several models of land change. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2008, 42, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).