Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
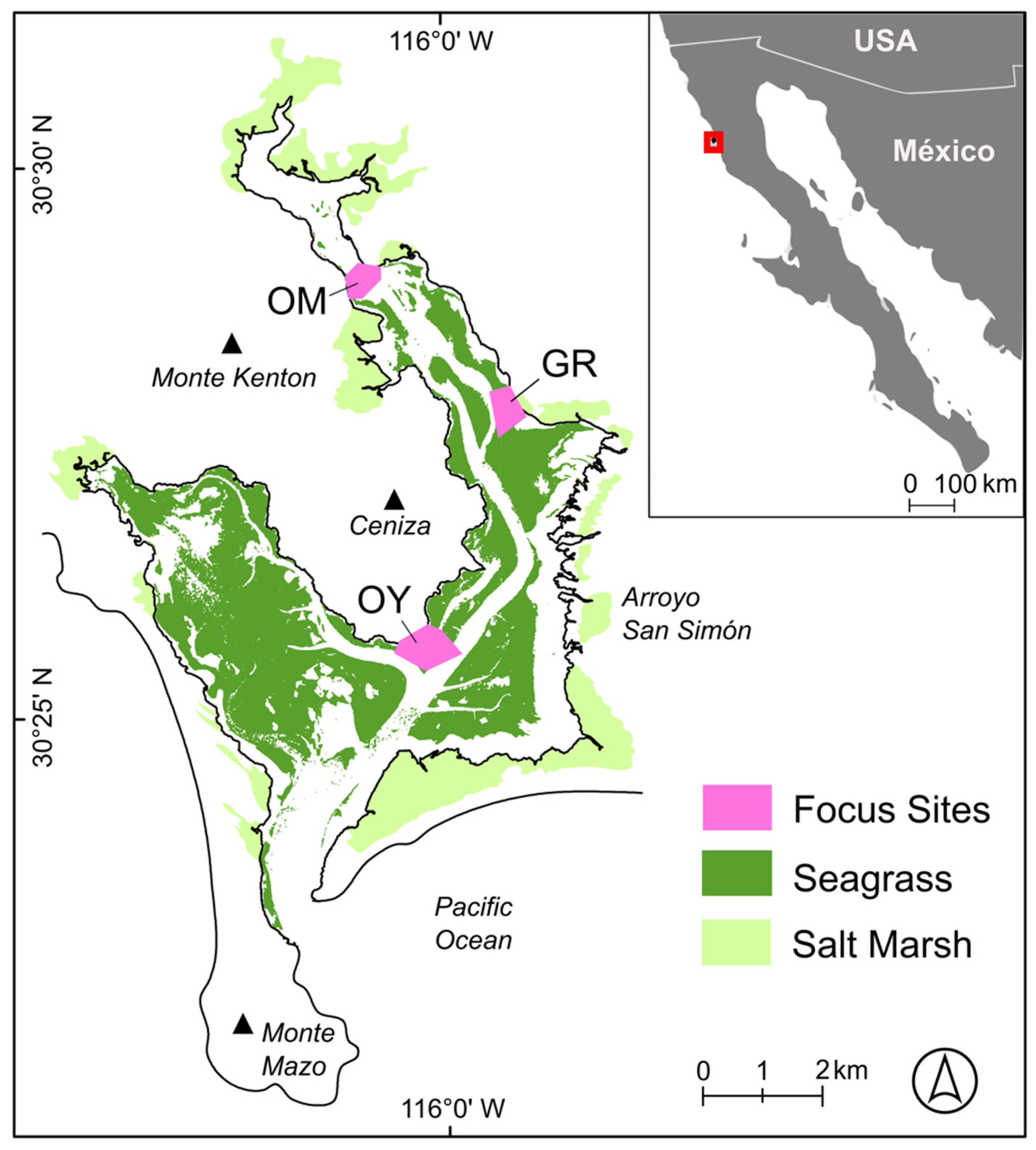
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Image Acquisition and Ground Truthing
2.3. Imagery Pre-Processing
2.4. Object-Based Image Analysis
2.5. Accuracy Assessment
2.6. Trends Analysis
3. Results
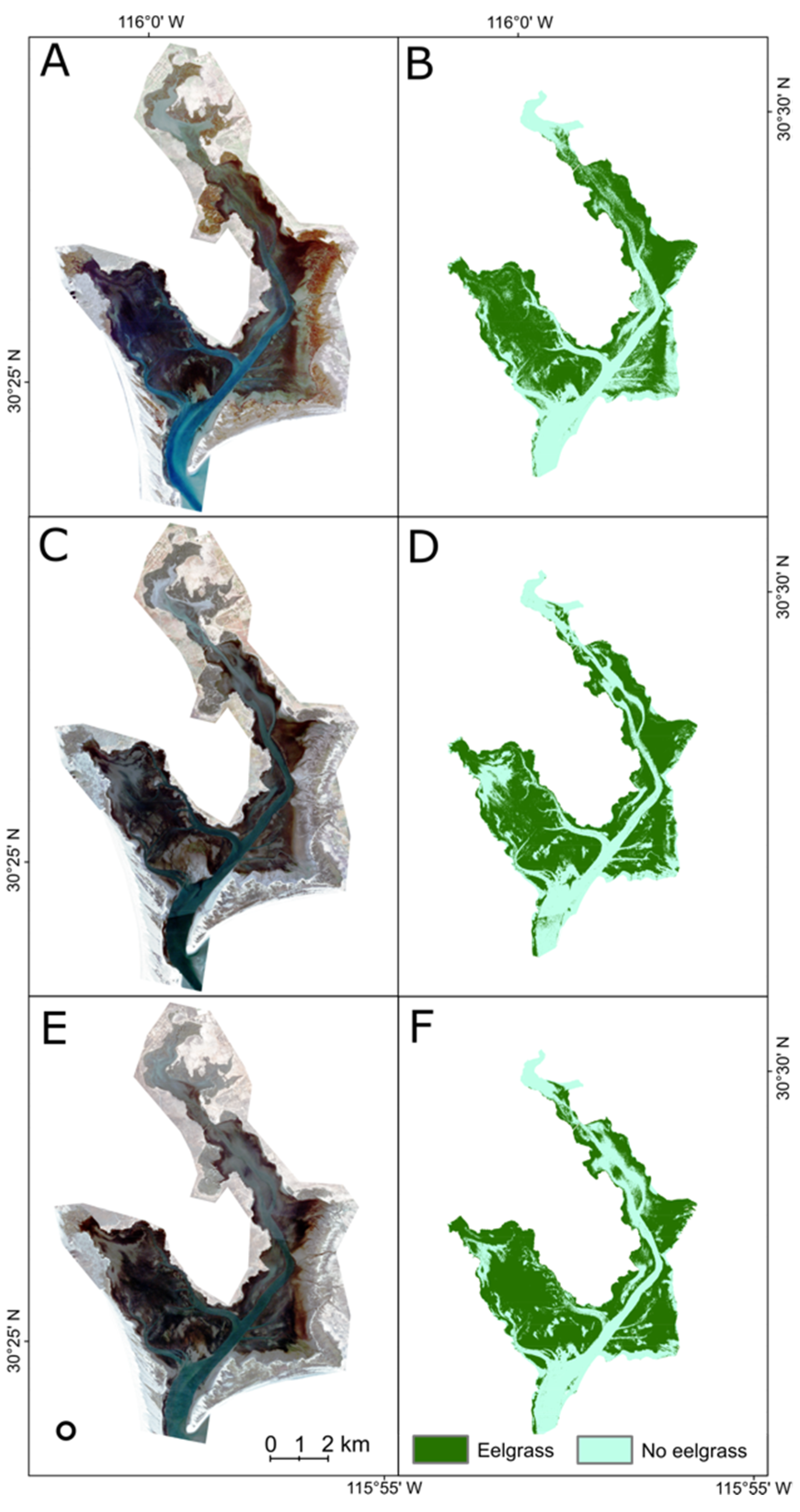
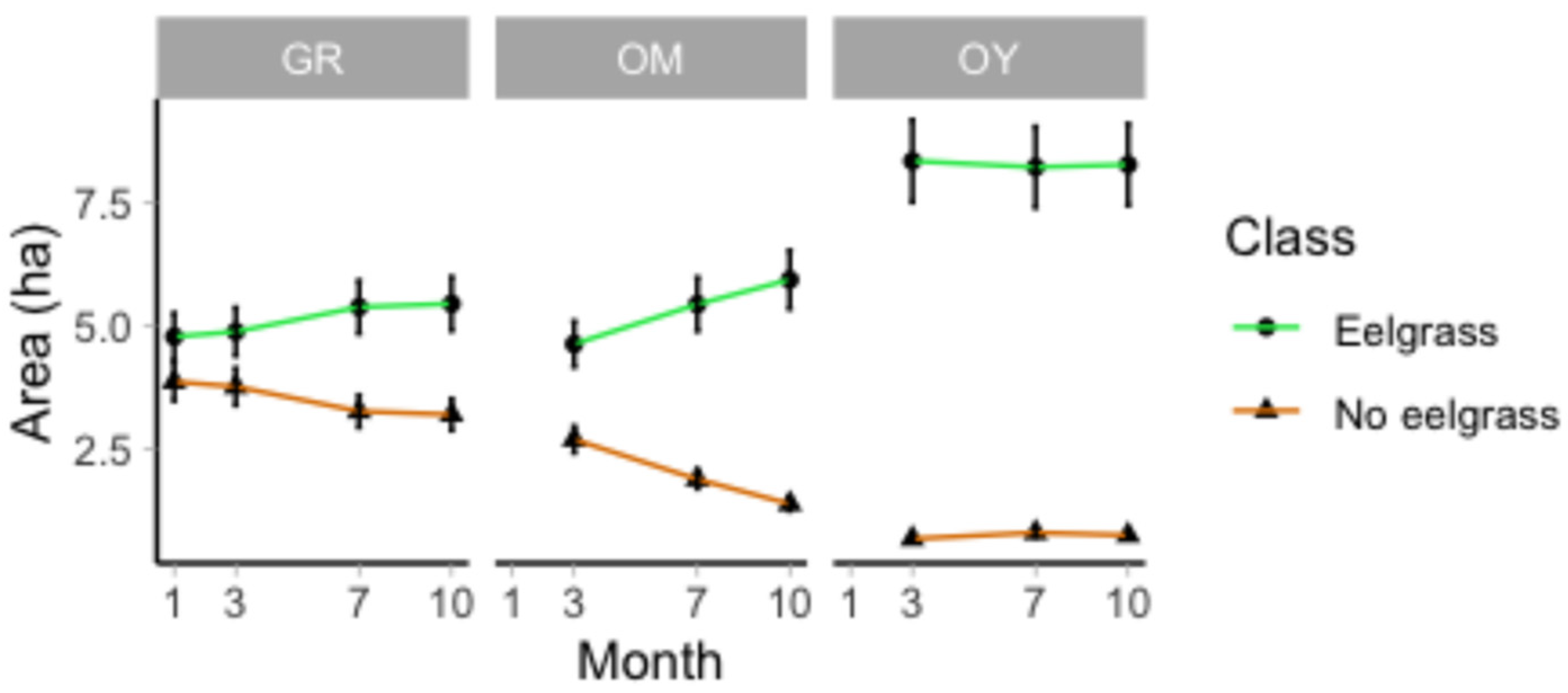
3.1. UAV Image Accuracy Assessment and Trends
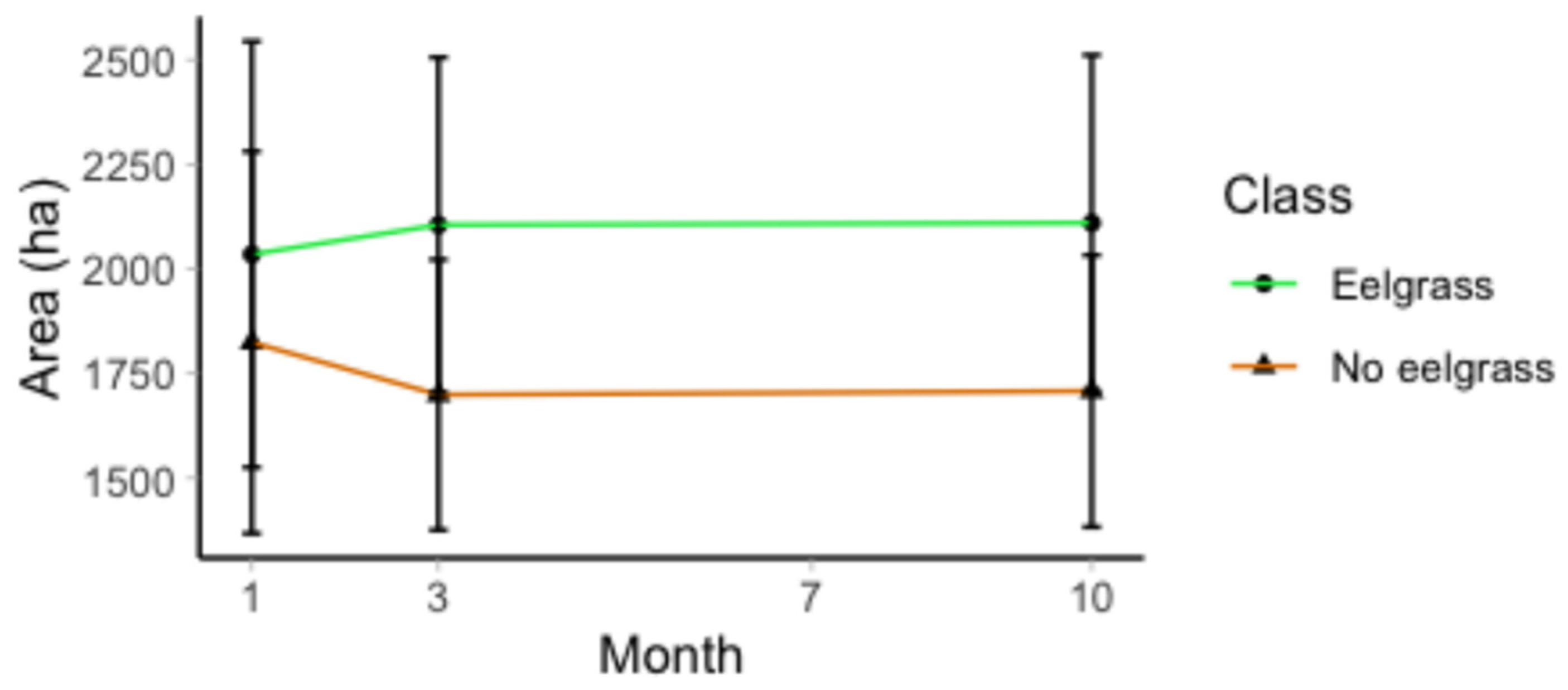
3.2. Satellite Image Accuracy and Trends
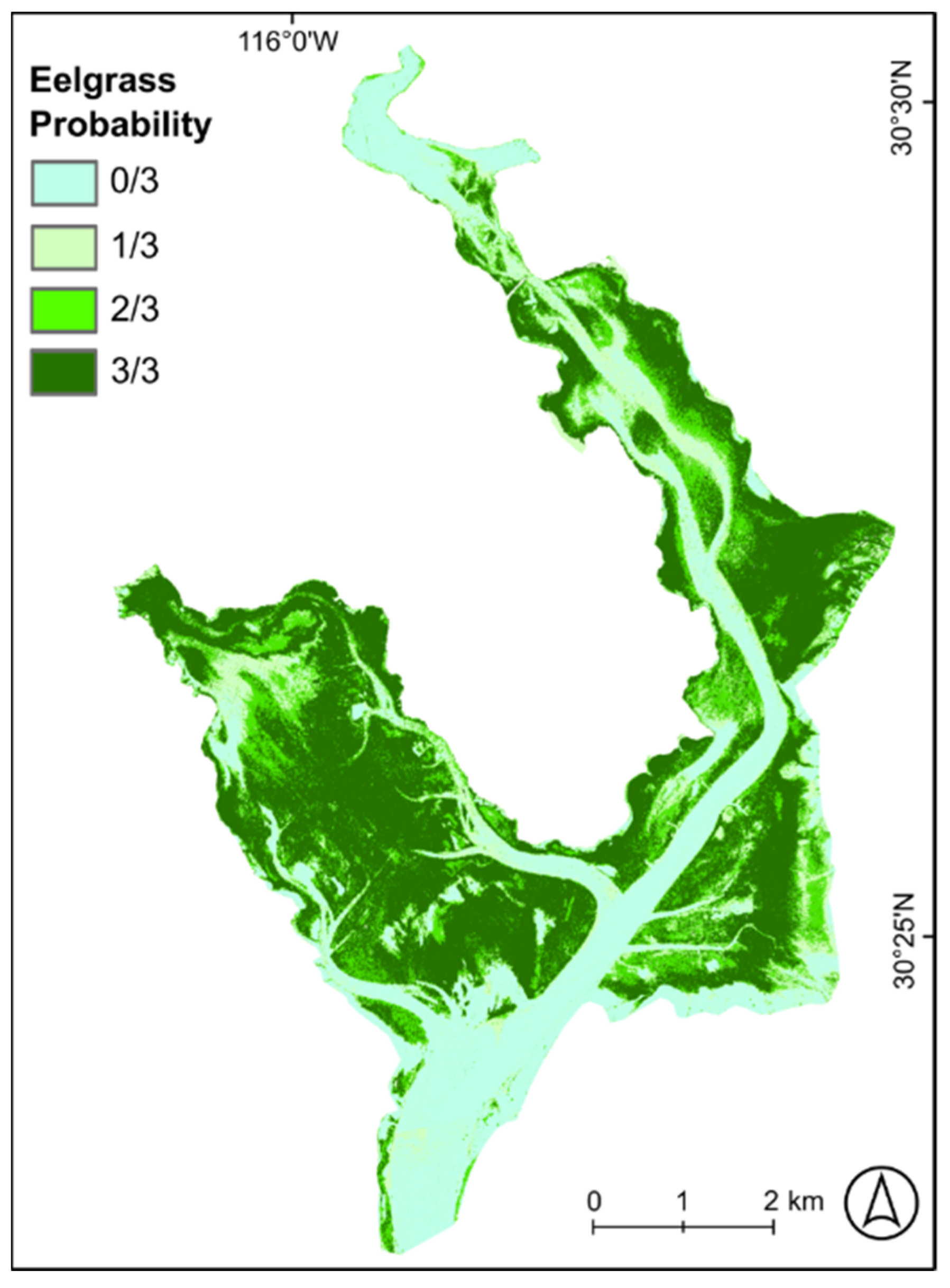
3.3. Eelgrass Probability
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. UAV Surveys Bridge In Situ and Satellite Remote Sensing Observations
4.2. PlanetScope-Daily Revisits but Mixed Image Quality
4.3. Temporal Composite of Satellite Imagery for Eelgrass Probability Mapping
4.4. Mapping Accuracy
4.5. The Seasonality of Eelgrass Growth at San Quintin
4.6. Eelgrass Extent at San Quintin
4.7. Outlook and Lessons Learned
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, C.M.; Marbà, N.; Gacia, E.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Beggins, J.; Barrón, C.; Apostolaki, E.T. Seagrass community metabolism: Assessing the carbon sink capacity of seagrass meadows. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L.; Hays, G.; Orth, R.J. Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 253, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.W.; Barbier, E.B.; Silliman, B.R.; Reed, D.J.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Hacker, S.D.; Granek, E.F.; Primavera, J.H.; Muthiga, N.; Polasky, S.; et al. Non-linearity in ecosystem services: Temporal and spatial variability in coastal protection. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, L.J.; Nordlund, L.M.; Jones, B.L.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Unsworth, R.K.F. The global distribution of seagrass meadows. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Out of Blue: The Value of Seagrasses to the Environment and to People; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.D.; Xia, J.; Ha, N.T.; Bui, D.T.; Le, N.N.; Tekeuchi, W. A Review of Remote Sensing Approaches for Monitoring Blue Carbon Ecosystems: Mangroves, Seagrasses and Salt Marshes during 2010–2018. Sensors 2019, 19, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Cerra, D.; Reinartz, P. Cubesat-Derived Detection of Seagrasses Using Planet Imagery Following Unmixing-Based Denoising: Is Small the Next Big? ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-1/W1, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Reinartz, P. Interannual Change Detection of Mediterranean Seagrasses Using RapidEye Image Time Series. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckles, H.A.; Kopp, B.S.; Peterson, B.J.; Pooler, P.S. Integrating Scales of Seagrass Monitoring to Meet Conservation Needs. Estuar Coast. 2012, 35, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Trinanes, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Ambo-Rappe, R.; Boström, C.; Buschmann, A.H.; Byrnes, J.; Coles, R.G.; Creed, J.; et al. Toward a coordinated global observing system for seagrasses and marine macroalgae. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.; Roelfsema, C.; Kovacs, E.; Canto, R.; Lyons, M.; Saunders, M.; Maxwell, P. Mapping, monitoring and modelling seagrass using remote sensing techniques. In Seagrasses of Australia: Structure, Ecology and Conservation; Ralph, P., Kendrick, G.A., Larkum, A.W.D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 445–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R. Towards understanding temporal and spatial dynamics of seagrass landscapes using time-series remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 120, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, G.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Marbà, N. Clonality in seagrasses, emergent properties and seagrass landscapes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 290, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.P.; Pratt, L.; Anderson, K.; Land, P.E.; Shutler, J.D. Spatial assessment of intertidal seagrass meadows using optical imaging systems and a lightweight drone. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 200, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahirnick, N.K.; Reshitnyk, L.; Campbell, M.; Hessing-Lewis, M.; Costa, M.; Yakimishyn, J.; Lee, L.; Horning, N.; Poursanidis, D. Mapping with confidence; delineating seagrass habitats using Unoccupied Aerial Systems (UAS). Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 5, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Martin, R.E.; Mascaro, J. Coral reef atoll assessment in the South China Sea using Planet Dove satellites. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S.; Meyer, C.; Baggett, L.; Zhao, Y. Mapping and Assessing Seagrass along the Western Coast of Florida Using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion Imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 115, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Lyons, M.; Kovacs, E.M.; Maxwell, P.; Saunders, M.I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Phinn, S.R. Multi-temporal mapping of seagrass cover, species and biomass: A semi-automated object based image analysis approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S. Mapping seagrass coverage and spatial patterns with high spatial resolution IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yan, J.; Li, W.; Han, L. Comparing Machine Learning Classifiers for Object-Based Land Cover Classification Using Very High Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Muñoz, A.; Buddemeier, R.W.; Camacho-Ibar, V.; Carriquiry, J.D.; Ibarra-Obando, S.E.; Massey, B.W.; Smith, S.V.; Wulff, F. Sustainability of Coastal Resource Use in San Quintin, Mexico. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2001, 30, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.H.; Morton, A.; Tibbitts, T.L.; Douglas, D.C.; Carrera-Gonzalez, E. Long-Term Change in Eelgrass Distribution at Bahía San Quintín, Baja California, Mexico, Using Satellite Imagery. Estuaries 2003, 26, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas-Ortíz, J.E. Evaluación de la Calidad del Hábitat de Invernación para Branta Bernicla Nigricans en la Bahía de San Quintín. Master’s Thesis, Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada (CICESE), Ensenada, México, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Poumian-Tapia, M.; Ibarra-Obando, S.E. Demography and Biomass of the Seagrass Zostera marina in a Mexican Coastal Lagoon. Estuaries 1999, 22, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakun, A.; Nelson, C.S. The seasonal cycle of wind-stress curl in subtropical eastern boundary current regions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1991, 21, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Carriquiry, J.D.; Smith, S.V. Non-conservative P and N Fluxes and Net Ecosystem Production in San Quintin Bay, Mexico. Estuaries 2003, 26, 1220–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rosas, R.; López-Carrillo, M.; Aguilar-Roses, L.E. Macroalgas Marinas De La Bahía De San Quintín, Baja California, México. Polibotanica 2005, 19, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Aveytua-Alcázar, L.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Souza, A.J.; Allen, J.I.; Torres, R. Modelling Zostera marina and Ulva spp. in a coastal lagoon. Ecol. Model. 2008, 218, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zertuche-González, J.; Camacho-Ibar, V.; Pacheco-Ruíz, I.; Cabello-Pasini, A.; Galindo-Bect, L.; Guzmán-Calderón, J.; Macias-Carranza, V.; Espinoza-Avalos, J. The role of Ulva spp. as a temporary nutrient sink in a coastal lagoon with oyster cultivation and upwelling influence. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REDNOM: Red Géodesica Del Noroeste de México, Departamento de Sismología Del Centro de Investigación Científica y Educación Superior de Ensenada. Baja California, México. Available online: http://regnom.cicese.mx (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Planet Team. Planet Application Program Interface: In Space for Life on Earth. Available online: http://planet.com (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- USGS National Unmanned Aircraft Systems Project Office. Umanned Aircraft Systems Data Post-Processing—Structure-from-motion Photogrammetry. Available online: https://uas.usgs.gov/nupo/pdf/PhotoScanProcessingDSLRMar2017.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Christianini, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An. Introduction to Support. Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods, 16th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data. Principles and Practices, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M. Building predictive models in R using the caret package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebesma, E.; Bivand, R.S. S Classes and Methods for Spatial Data: The sp Package. Econ. Geogr. 2005, 50, 1–21. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.160.9361&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Hijmans, R.J.; van Etten, J.; Sumner, M.; Cheng, J.; Bevan, A.; Bivand, R.; Busetto, L.; Canty, M.; Forrest, D.; Golicher, D.; et al. Package ‘Raster’. R Topics Documented. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/raster/raster.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D.; Georgopoulos, A.; Karantzalos, K. Shallowwater bathymetry mapping from UAV imagery based on machine learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, D.; Bonifazi, A.; Gravina, M.F.; Belluscio, A.; Ardizzone, G. Mapping and classification of ecologically sensitive marine habitats using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery and Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P.; Lazuardi, W. Assessment of PlanetScope images for benthic habitat and seagrass species mapping in a complex optically shallow water environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5739–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Knapp, D.E.; Fabina, N.S.; Kennedy, E.V.; Larsen, K.; Lyons, M.B.; Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Asner, G.P. A global coral reef probability map generated using convolutional neural networks. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 1805–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelestov, A.; Lavreniuk, M.; Kussul, N.; Novikov, A.; Skakun, S. Exploring Google earth engine platform for big data processing: Classification of multi-temporal satellite imagery for crop mapping. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, R.K.F.; McKenzie, L.J.; Collier, C.J.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Eklöf, J.S.; Jarvis, J.C.; Jones, B.L.; Nordlund, N.L. Global Challenges for Seagrass Conservation. Ambio 2019, 48, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello-Pasini, A.; Muñiz-Salazar, R.; Ward, D.H. Annual variations of biomass and photosynthesis in Zostera marina at its southern end of distribution in the North Pacific. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 76, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana-Arellano, M.E.; Echavarria-Heras, H.A.; Ibarra-Obando, S.E. Leaf-size Dynamics for Zostera marina L. in San Quintin Bay, México: A Theoretical Study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveytua-Alcazar, L.; Melaku Canu, D.; Camacho-Ibar, V.F.; Solidoro, C. Changes in upwelling regimes in a Mediterranean-type lagoon: A model application. Ecol. Model. 2020, 418, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Obando, S.E.; Solana Arellano, M.E.; Poumian-Tapia, M. El papel de Zostera marina en el ciclo del carbono en Bahía San Quintín, Baja California. In Carbono en Ecosistemas Acuáticos de México; Hernández-de-la-Torre, B., Gaxiola-Castro, G., Eds.; CICESE: Ensenada, Mexico, 2007; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Eugenio, F.; Marcello, J.; Martin, J.; Rodríguez-Esparragón, D. Benthic habitat mapping using multispectral high-resolution imagery: Evaluation of shallow water atmospheric correction techniques. Sensors 2017, 17, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.H. Use of digital multispectral videography to assess seagrass distribution in San Quintín Bay, Baja California, Mexico. Cienc. Mar. 2004, 30, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
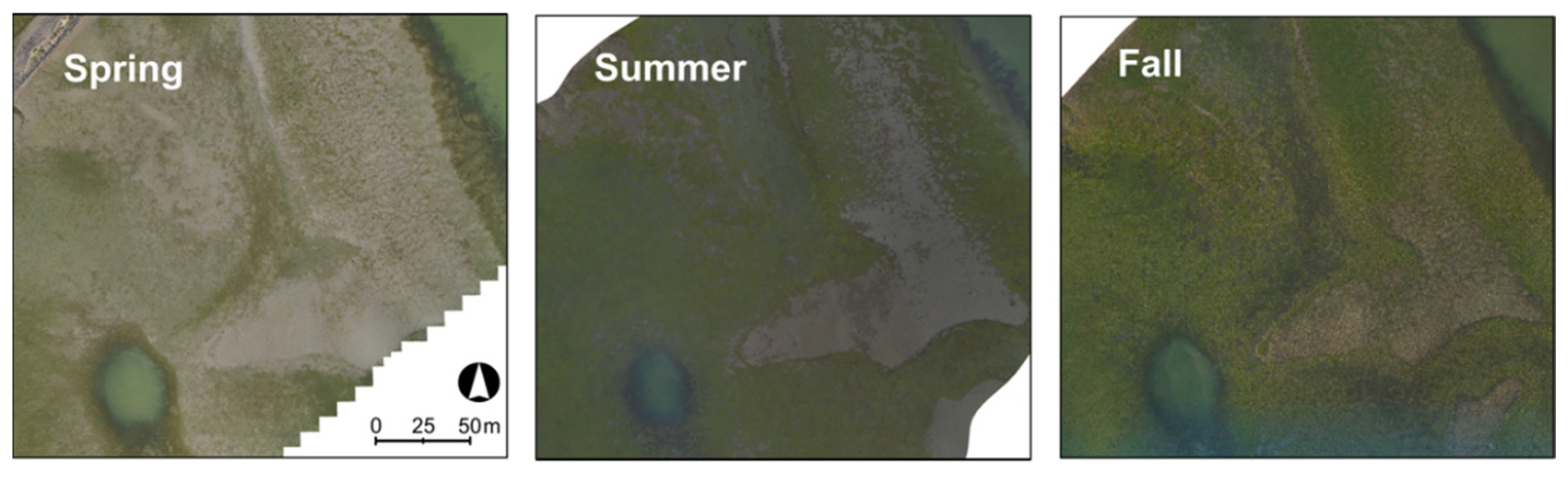

| Winter | Spring | Fall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 20190104_17 3541_0f2a | 20190314_17 2554_0f33 | 20191005_18 0405_0f35 |
| Date | 4 January 2019 | 14 March 2019 | 5 October 2019 |
| Time (UTM) | 17:35:41 | 17:25:54 | 18:04:05 |
| Tidal stage (m MLLW) | 1.50 | 0.19 | 0.96 |
| Sun elevation | 28.1 | 42 | 48.8 |
| Sun azimuth | 145 | 126 | 145 |
| Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction | Eelgrass | No Eelgrass | |
| Eelgrass | 30 | 4 | PPV: 0.88 |
| No eelgrass | 2 | 21 | NPV: 0.91 |
| Sensitivity: 0.94 | Specificity: 0.84 | Accuracy: 0.90 |
| Accuracy Metrics | Winter | Spring | Fall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| Sensitivity | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.82 |
| Specificity | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.80 |
| PPV | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.80 |
| NPV | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krause, J.R.; Hinojosa-Corona, A.; Gray, A.B.; Burke Watson, E. Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183681
Krause JR, Hinojosa-Corona A, Gray AB, Burke Watson E. Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(18):3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183681
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrause, Johannes R., Alejandro Hinojosa-Corona, Andrew B. Gray, and Elizabeth Burke Watson. 2021. "Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale" Remote Sensing 13, no. 18: 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183681
APA StyleKrause, J. R., Hinojosa-Corona, A., Gray, A. B., & Burke Watson, E. (2021). Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale. Remote Sensing, 13(18), 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183681






