Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality and Its Multiscale Relationship with Land Use in the Yangtze River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Water Quality Dataset and Indicators Selection
2.2.2. Land Use Dataset
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Single-Factor Water Quality Identification Index
2.3.2. The Mann–Kendall Trend Test
2.3.3. Spearman Rank Correlation
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality
3.2. Analysis of Annual Trend of Water Quality
3.3. Land Use Change
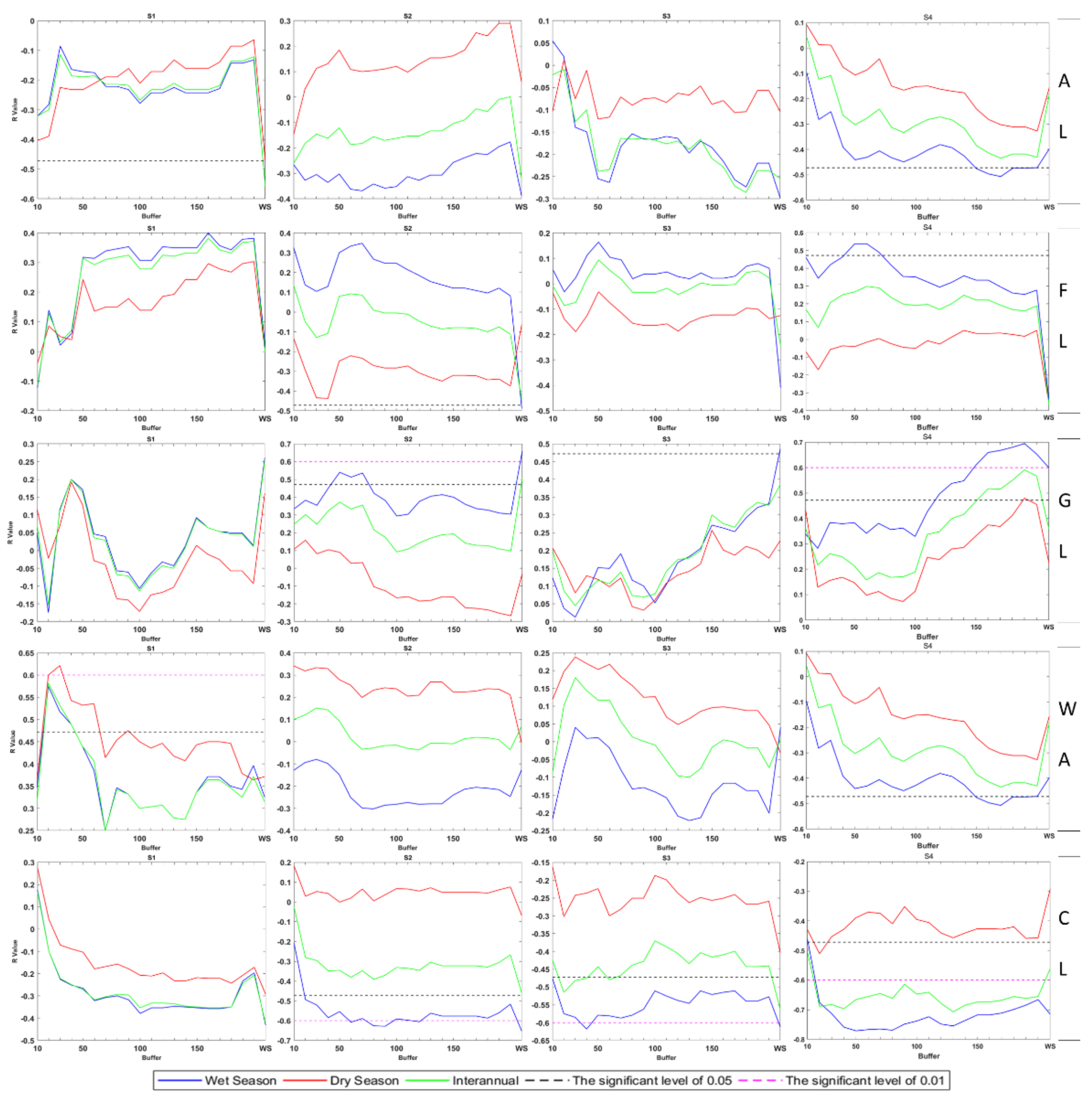
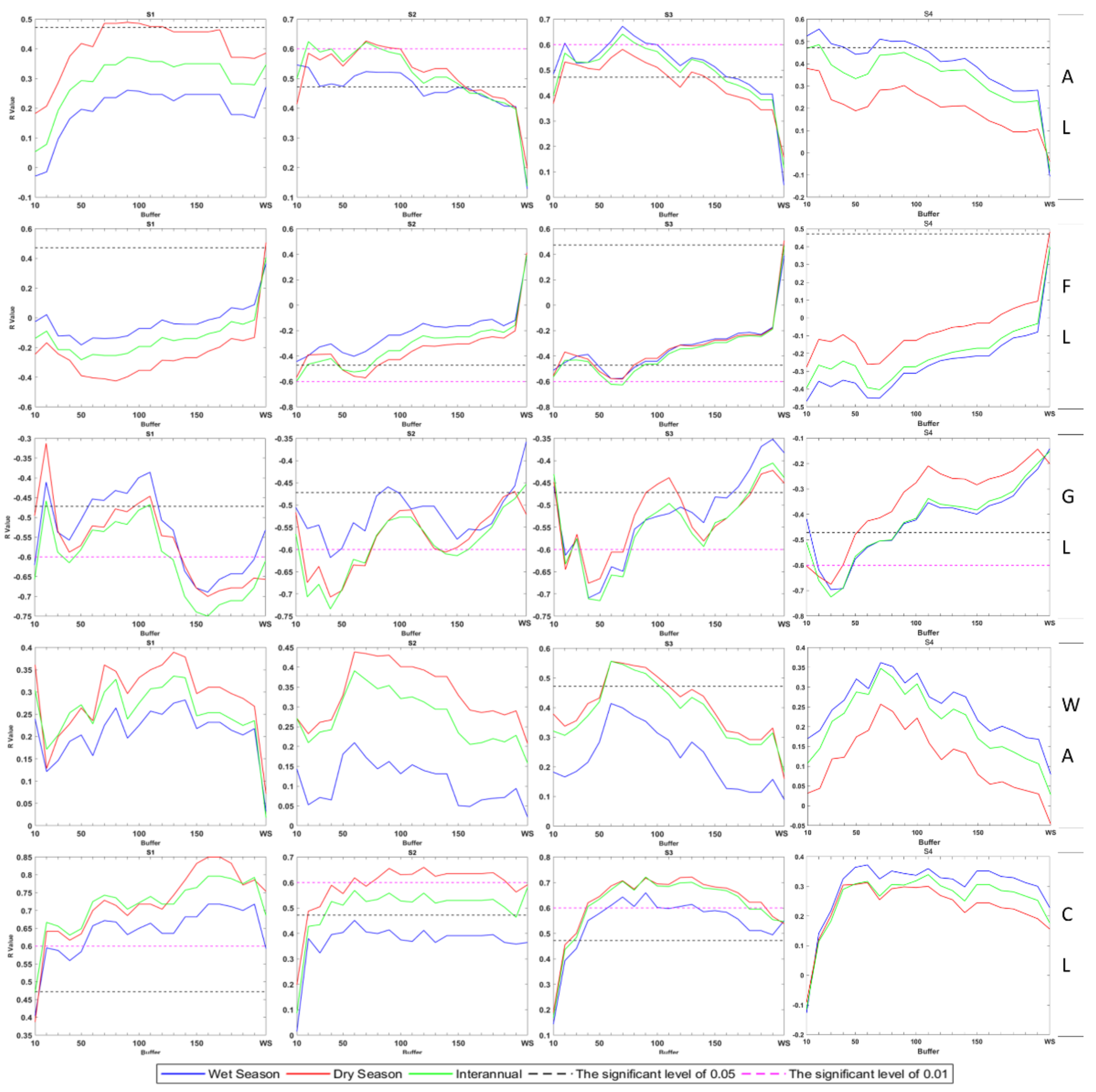
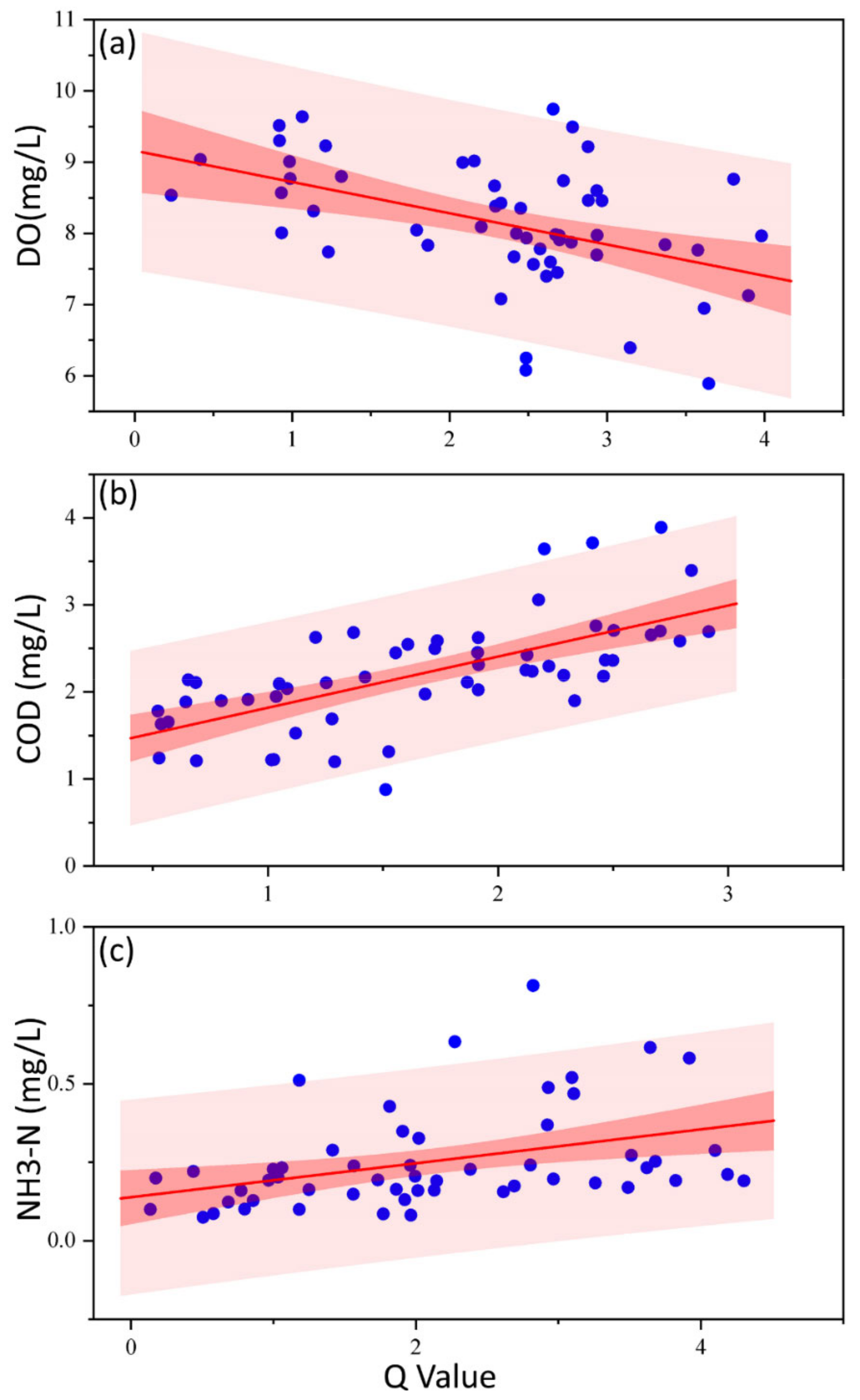
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Water Quality and Land Use
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emergingthreats and persistent conservation challenges for fresh water biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, J.S.; Destouni, G.; Duke-Sylvester, S.M.; Magurran, A.E.; Oberdorff, T.; Reis, R.E.; Winemiller, K.O.; Ripple, W.J. Scientists’ warning to humanity on the freshwater biodiversity crisis. Ambio 2021, 50, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.W. Bidirectional connectivity in rivers and implications for watershed stability and management. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Song, X.; Shao, G.; Hu, T. Effects of Land Use on Stream Water Quality in the Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Multiscale Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabani, A.; Woznicki, S.A.; Mehaffey, M.; Butcher, J.; Wool, T.A.; Whung, P.-Y. A coupled hydrodynamic (HEC-RAS 2D) and water quality model (WASP) for simulating flood-induced soil, sediment, and contaminant transport. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, G.; Kowalczyk, T.; Fischer, T.B.; Szewrański, S.; Chrobak, K.; Kazak, J.K. Ecological state evaluation of lake ecosystems revisited: Latent variables with kSVM algorithm approach for assessment automatization and data comprehension. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, T.; Hou, X. Optimal sampling strategy of water quality monitoring at high dynamic lakes: A remote sensing and spatial simulated annealing integrated approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şandric, I.; Satmari, A.; Zaharia, C.; Petrovici, M.; Cîmpean, M.; Battes, K.-P.; David, D.-C.; Pacioglu, O.; Weiperth, A.; Gál, B.; et al. Integrating catchment land cover data to remotely assess freshwater quality: A step forward in heterogeneity analysis of river networks. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearn, D.S.; Sheibley, R.W.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Anderson, M.; Johnson, J.; Tate, K.W. Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Estrany, J.; Ranzini, M.; Cicco, V.; de Martín-Benito, J.M.T.; Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of land use and seasonality on stream water quality in a small tropical catchment: The headwater of Córrego Água Limpa, São Paulo (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Pontius, R.G.; Klemas, V.; Hong, H. Detecting the dynamic linkage between landscape characteristics and water quality in a subtropical coastal watershed, Southeast China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-R.; Lee, S.-W. Spatially Varying and Scale-Dependent Relationships of Land Use Types with Stream Water Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronvang, B.; Wendland, F.; Kovar, K.; Fraters, D. Land Use and Water Quality. Water 2020, 12, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Response of nitrogen pollution in surface water to land use and social-economic factors in the Weihe River watershed, northwest China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate and planting structure changes on watershed runoff and nitrogen and phosphorus loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 134489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, S.; Jin, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y. Multi-scale relationship between land use/land cover types and water quality in different pollution source areas in Fuxian Lake Basin. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Romero, A.; Rico-Sánchez, A.; Mendoza-Martínez, E.; Gómez-Ruiz, A.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.; López-López, E. Impact of Changes of Land Use on Water Quality, from Tropical Forest to Anthropogenic Occupation: A Multivariate Approach. Water 2018, 10, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratt, B.; Chang, H. Effects of land cover, topography, and built structure on seasonal water quality at multiple spatial scales. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson Mwaijengo, G.; Msigwa, A.; Njau, K.N.; Brendonck, L.; Vanschoenwinkel, B. Where does land use matter most? Contrasting land use effects on river quality at different spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 134825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzal-Almeida, S.; Salim, A.; Andrade, M.R.M.; Nascimento, M.d.N.; Bini, L.M.; Bicudo, D.C. Effects of land use and spatial processes in water and surface sediment of tropical reservoirs at local and regional scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J. Spatial scale effects of landscape metrics on stream water quality and their seasonal changes. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Pan, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, S. Spatial scale and seasonal dependence of land use impacts on riverine water quality in the Huai River basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 20995–21010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Xiao, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, B. Effects of farmland conversion on the stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil aggregates on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2019, 351, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Li, L.Z.; Kong, M. Multiple-Scale Analysis of Water Quality Variations and Their Correlation with Land use in Highly Urbanized Taihu Basin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Ni, M. Influences of land use metrics at multi-spatial scales on seasonal water quality: A case study of river systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Water quality in the upper Han River basin, China: The impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Qian, G. Influences of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: A case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2015, 137, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Ni, M.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Xiao, Z. Seasonal variations of water quality response to land use metrics at multi-spatial scales in the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Ji, R.; Dolf, R.; Gu, X. Water Quality Analysis of the Yangtze and the Rhine River: A Comparative Study Based on Monitoring Data from 2007 to 2018. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Gardner, C.; Wu, F. Threats and protection policies of the aquatic biodiversity in the Yangtze River. J. Nat. Conserv. 2020, 58, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Wang, Y.; Nover, D.; Chen, W.; Yang, G. Identification of long-term trends and seasonality in high-frequency water quality data from the Yangtze River basin, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0188889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Qian, H.; Huang, M.; Xu, N. Monitoring Temporal Change of River Islands in the Yangtze River by Remotely Sensed Data. Water 2018, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Li, N.; Gong, C. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China. Water 2020, 12, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods. Biometrika 1957, 44, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, N.; Luo, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, K. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Land Marketization and Its Driving Forces for Sustainable Urban–Rural Development in Shaanxi Province in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Spearman Rank Correlation. In Encyclopedia of Biostatistics; Armitage, P., Colton, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; ISBN 047084907X. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Zhong, M.; Gan, Q.; Liu, Y. A Novel Calendar-Based Method for Visualizing Water Quality Change: The Case of the Yangtze River 2006–2015. Water 2017, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, R.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Nie, X. Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, H.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, K.B.; Christopher, S.F.; Mitchell, M.J. Spatial and temporal dynamics of stream chemistry in a forested watershed. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-H.; Inam, E.; Abdullah, M.H.; Agustiyani, D.; Duan, L.; Hoang, T.T.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, S.D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Pekthong, T.; et al. Implications of rainfall variability for seasonality and climate-induced risks concerning surface water quality in East Asia. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G.; Hong, H. New insight into the correlations between land use and water quality in a coastal watershed of China: Does point source pollution weaken it? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, P.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z. Effect of irrigation amount and fertilization on agriculture non-point source pollution in the paddy field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 10363–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fu, Y.; Ruan, B.; Ge, H.; Zhao, N. Agricultural non-point source pollution in the Yongding River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, A.; Bayraktar, H.D. Assessment of lake water quality using multivariate statistical techniques and chlorophyll-nutrient relationships: A case study of the Göksu Lake. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.; Lye, L.; Khan, A.; Paterson, R. The Influence of Air Temperature on Water Temperature and the Concentration of Dissolved Oxygen in Newfoundland Rivers. Can. Water Resour. J. 2011, 36, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhao, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J. Control and remediation methods for eutrophic lakes in the past 30 years. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, M.S.; Heggem, D.T.; Ebert, D.; Wade, T.G.; Hall, R.K. Multi-scale landscape factors influencing stream water quality in the state of Oregon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 156, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miserendino, M.L.; Casaux, R.; Archangelsky, M.; Di Prinzio, C.Y.; Brand, C.; Kutschker, A.M. Assessing land-use effects on water quality, in-stream habitat, riparian ecosystems and biodiversity in Patagonian northwest streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.D.F.; de Souza, A.L.T.; Tanaka, M.O. Can the structure of a riparian forest remnant influence stream water quality? A tropical case study. Hydrobiologia 2014, 724, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Duan, L.; Si, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Mulder, J. Long-Term 15 N Balance After Single-Dose Input of 15 N-Labeled NH 4+ and NO3− in a Subtropical Forest Under Reducing N Deposition. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, 35, e2021GB006959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Effect of soil conservation measures and slope on runoff, soil, TN, and TP losses from cultivated lands in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Dong, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Gu, X.; Guo, Y. Spatiotemporal Coupling Coordination Analysis of Social Economy and Resource Environment of Central Cities in the Yellow River Basin. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
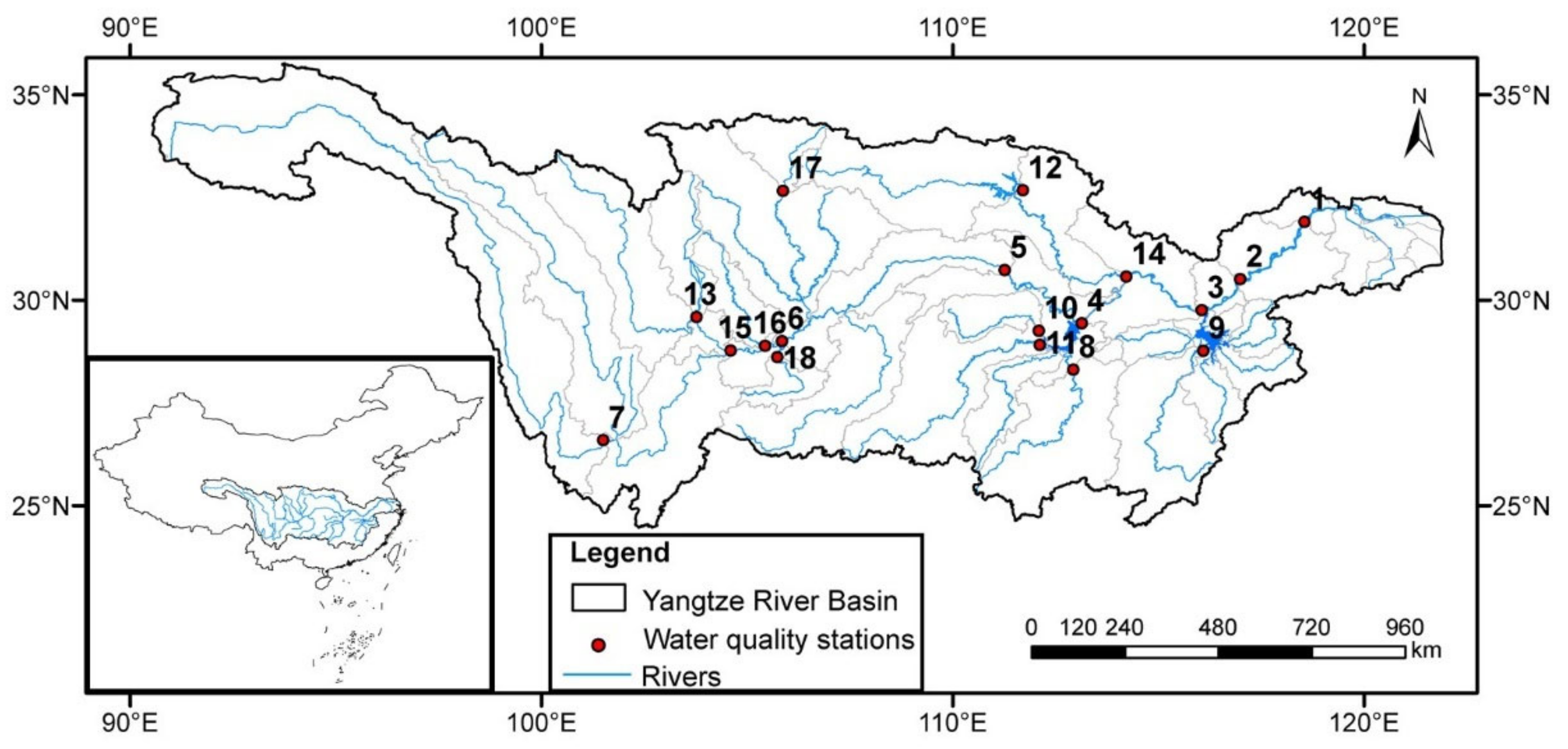
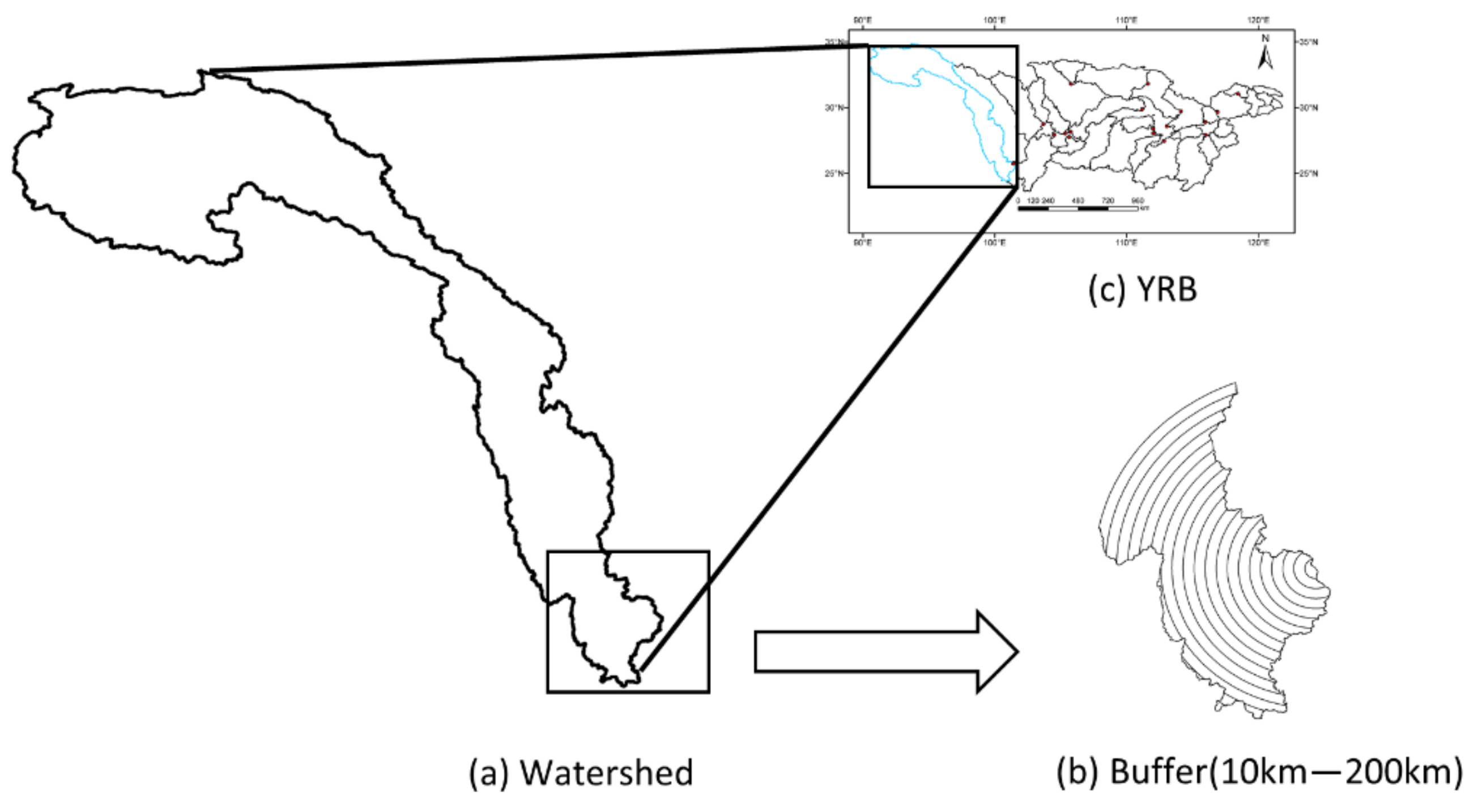

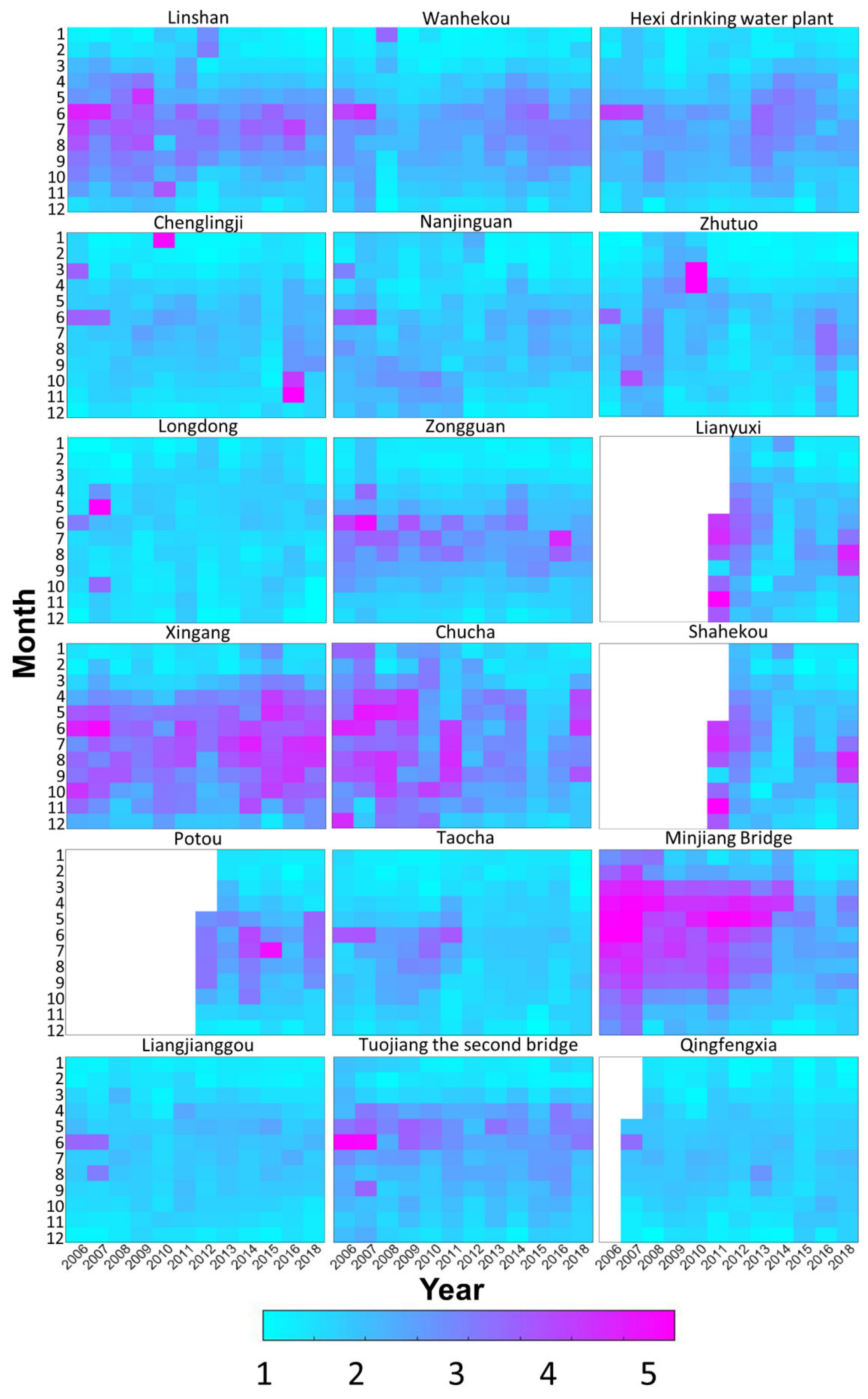
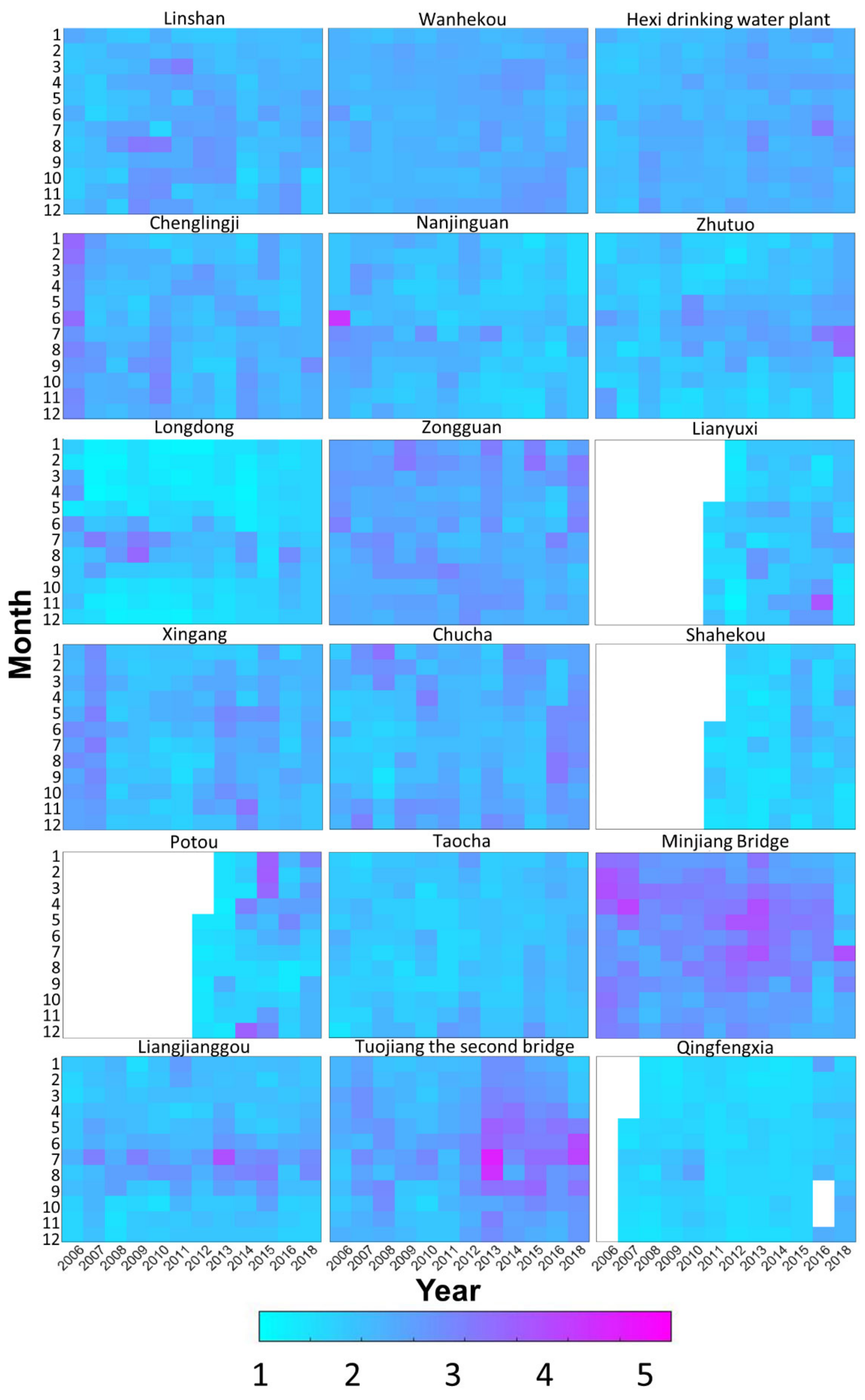
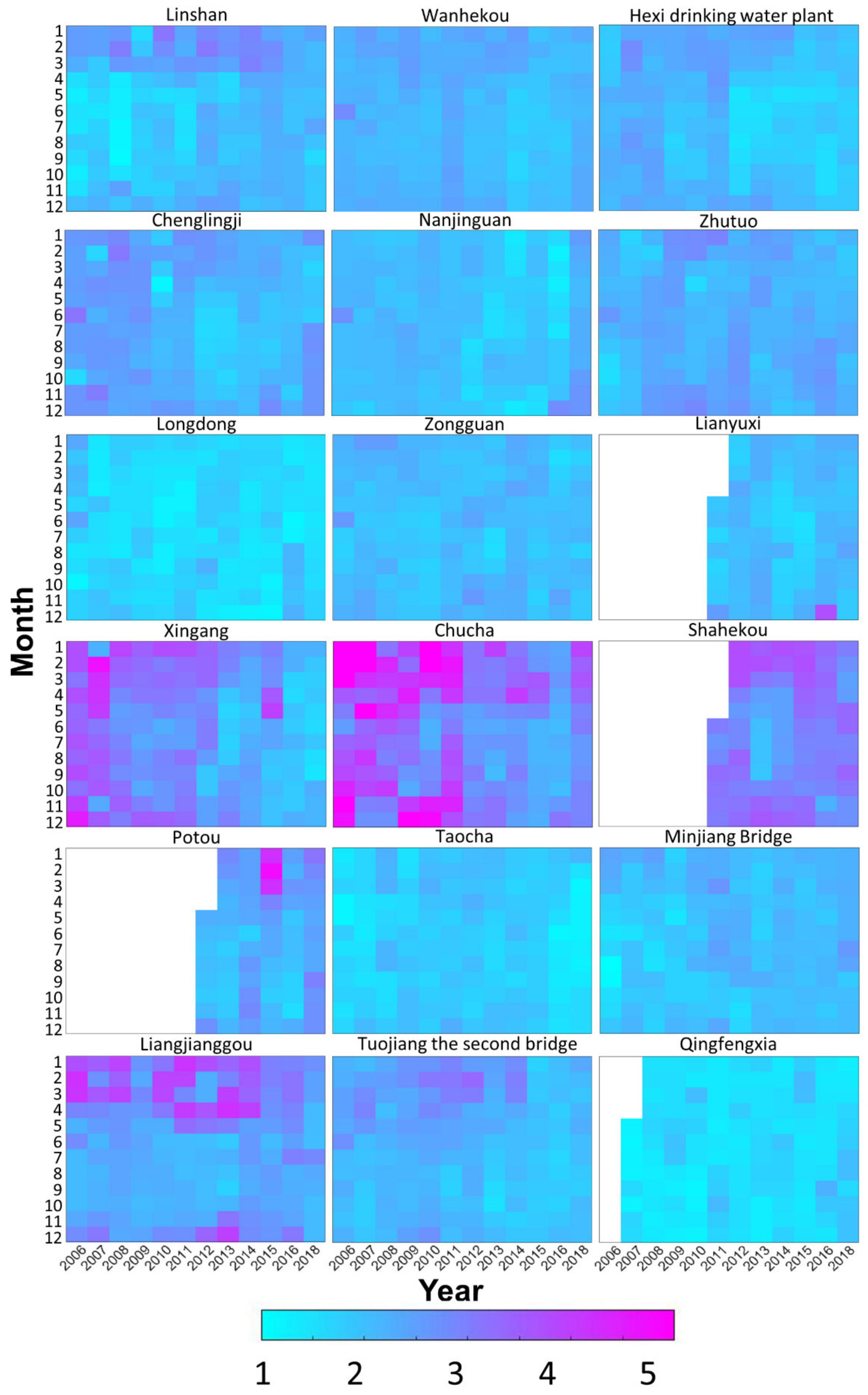
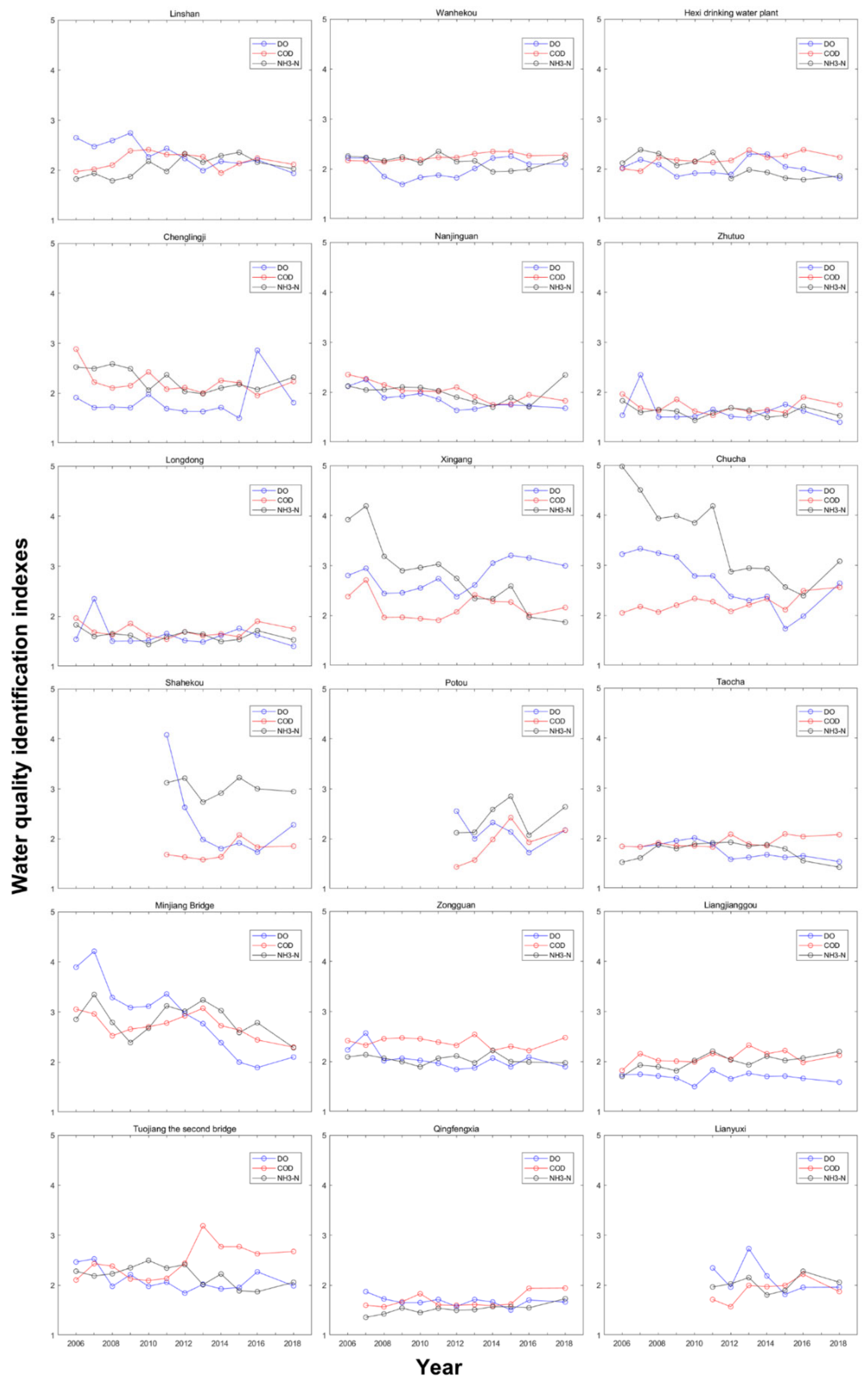
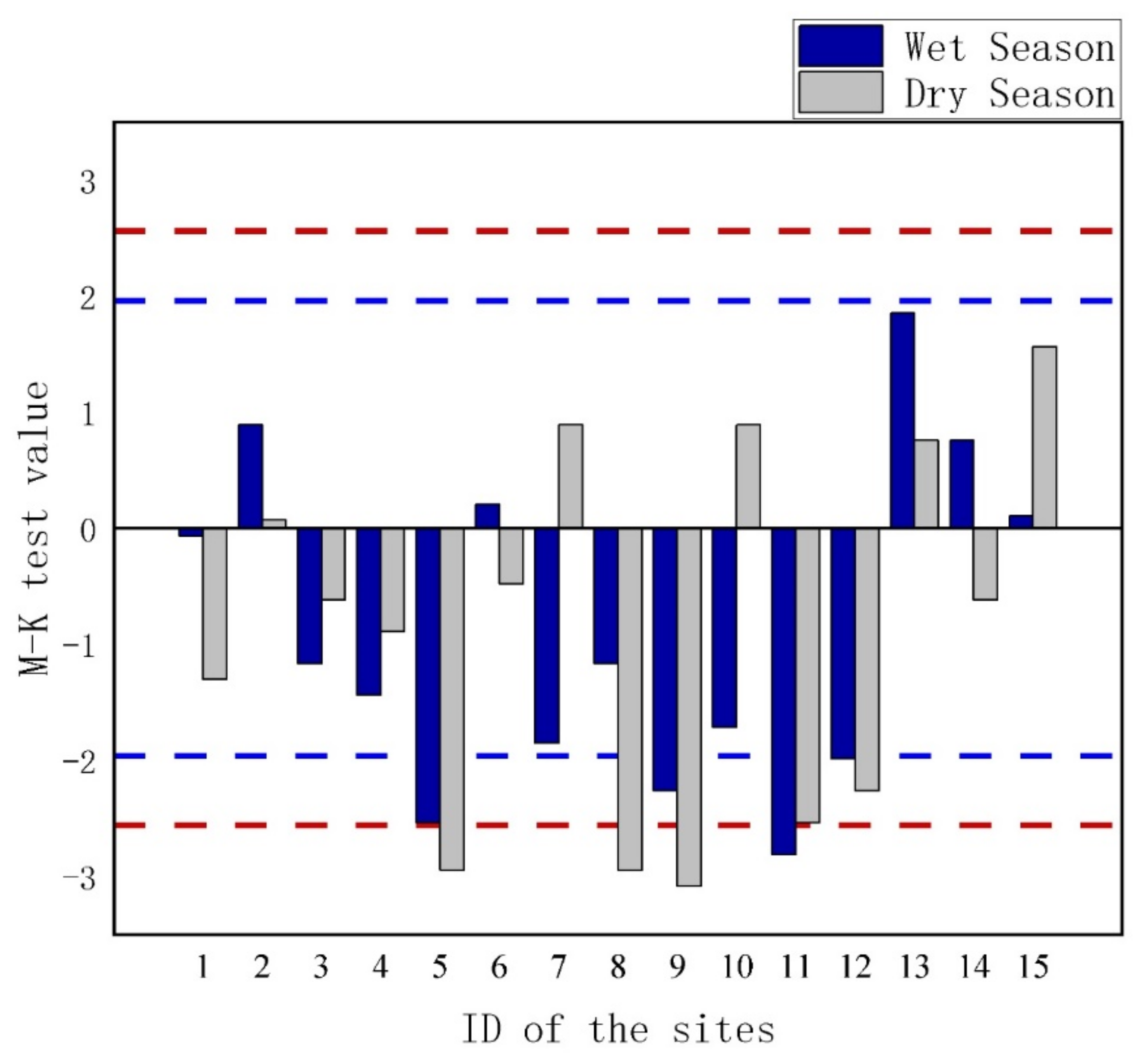

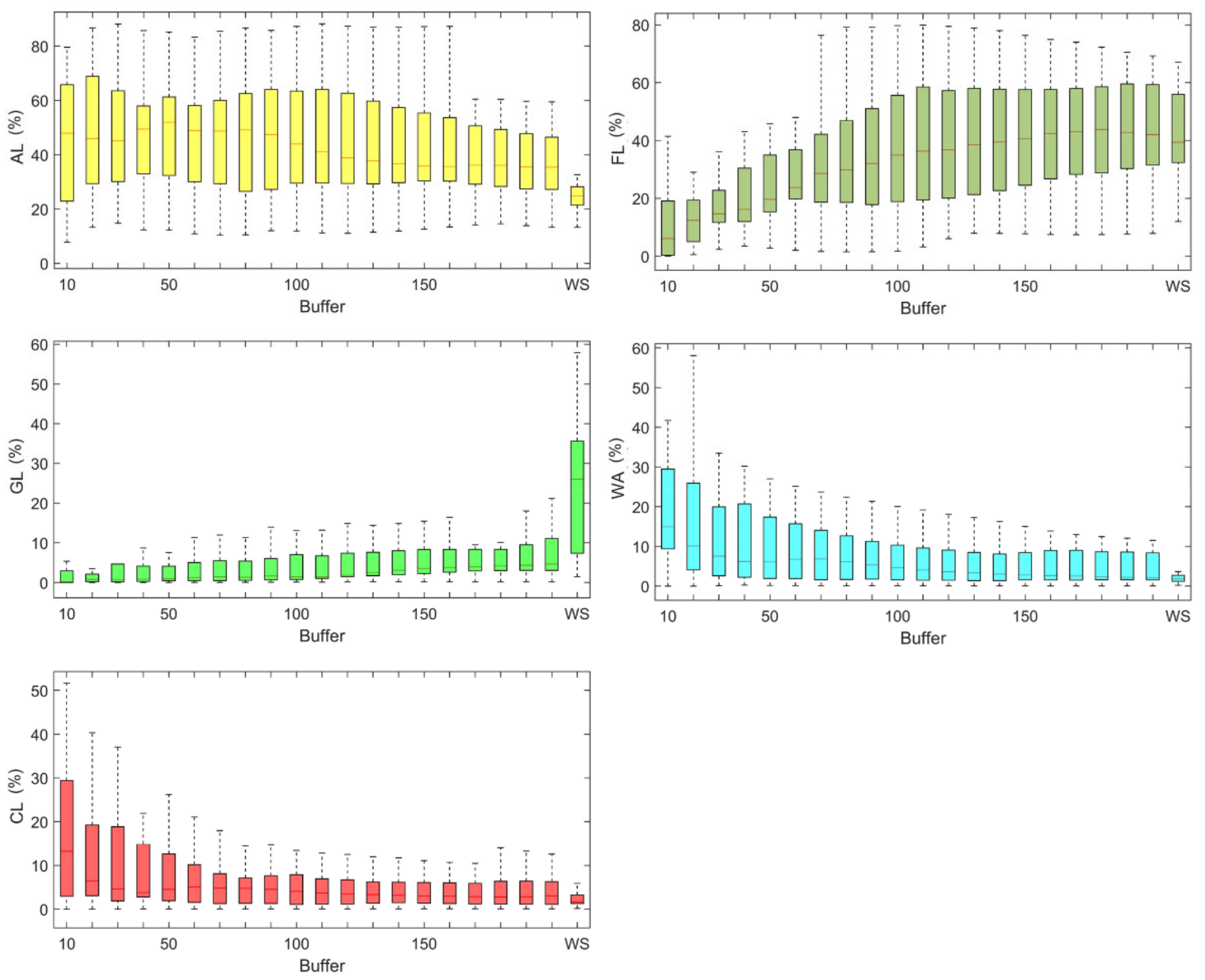

| ID | Station Name | River | NS | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linshan | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 2 | Wanhekou | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 3 | Hexi Drinking Water Plant | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 4 | Chenglingji | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 5 | Nanjinguan | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 6 | Zhutuo | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 7 | Longdong | Yangtze River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 8 | Xingang | Xiangjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 9 | Chucha | Ganjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 10 | Shahekou | Lishui River | 84 | 2011–2018 |
| 11 | Potou | Yuanjiang River | 72 | 2012–2018 |
| 12 | Taocha | Hanjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 13 | Minjiang Bridge | Minjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 14 | Zongguan | Hanjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 15 | Liangjianggou | Minjiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 16 | Tuojiang Second Bridge | Tuojiang River | 144 | 2006–2018 |
| 17 | Qingfengxia | Jialing River | 132 | 2007–2018 |
| 18 | Lianyuxi | Chishui River | 84 | 2011–2018 |
| ID | Station Name | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Stage 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linshan | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 2 | Wanhekou | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 3 | Hexi Drinking Water Plant | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 4 | Chenglingji | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 5 | Nanjinguan | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 6 | Zhutuo | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 7 | Longdong | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 8 | Xingang | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 9 | Chucha | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 10 | Shahekou | – | 2011–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 11 | Potou | – | 2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 12 | Taocha | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 13 | Minjiang Bridge | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 14 | Zongguan | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 15 | Liangjianggou | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 16 | Tuojiang Second Bridge | 2006–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 17 | Qingfengxia | 2007–2008 | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| 18 | Lianyuxi | – | 2010–2012 | 2013–2015 | 2016,2018 |
| Land Use Type | Year | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | |||||
| AP | GR | AP | GR | AP | GR | AP | GR | |
| Agricultural land | 26.91% | – | 27.54% | 2.28% | 27.19% | −1.28% | 26.76% | −1.52% |
| Forest land | 43.48% | – | 40.86% | −6.04% | 40.75% | −0.28% | 41.27% | 1.32% |
| Grassland | 23.32% | – | 23.31% | −0.05% | 23.31% | −0.03% | 23.05% | −1.06% |
| Water area | 2.42% | – | 3.08% | 26.95% | 3.11% | 1.18% | 3.23% | 3.78% |
| Construction land | 0.81% | – | 1.96% | 143.03% | 2.40% | 22.47% | 3.00% | 25.16% |
| Unused land | 3.06% | – | 3.25% | 5.98% | 3.25% | −0.05% | 2.68% | −17.43% |
| Land Use | Wet Season | |||||
| DO | CODMn | NH3-N | ||||
| Max. R | Buffer | Max. R | Buffer | Max. R | Buffer | |
| AL | −0.51 | 17 | 0.83 | 17 | 0.56 | 2 |
| FL | 0.54 | 5 | −0.63 | 14 | −0.47 | 1 |
| GL | 0.69 | 19 | −0.55 | 19 | −0.7 | 3 |
| WA | −0.45 | 13 | 0.28 | 14 | 0.36 | 7 |
| CL | −0.77 | 5 | 0.7 | 20 | 0.37 | 6 |
| Land Use | Dry Season | |||||
| DO | CODMn | NH3-N | ||||
| Max. R | Buffer | Max. R | Buffer | Max. R | Buffer | |
| AL | −0.33 | 20 | 0.58 | 17 | 0.38 | 1 |
| FL | −0.17 | 2 | −0.63 | 4 | −0.28 | 1 |
| GL | 0.48 | 19 | −0.68 | 20 | −0.68 | 3 |
| WA | −0.22 | 13 | 0.62 | 14 | 0.26 | 7 |
| CL | −0.51 | 2 | 0.76 | 13 | 0.31 | 6 |
| Water Quality Indexes | Spearman R | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| DO | −0.44 | <0.01 |
| CODMn | 0.73 | <0.01 |
| NH3-N | 0.46 | <0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zeng, S.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Xia, J. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality and Its Multiscale Relationship with Land Use in the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163309
Wu J, Zeng S, Yang L, Ren Y, Xia J. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality and Its Multiscale Relationship with Land Use in the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163309
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jian, Sidong Zeng, Linhan Yang, Yuanxin Ren, and Jun Xia. 2021. "Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality and Its Multiscale Relationship with Land Use in the Yangtze River Basin" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163309
APA StyleWu, J., Zeng, S., Yang, L., Ren, Y., & Xia, J. (2021). Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Water Quality and Its Multiscale Relationship with Land Use in the Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3309. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163309







