On the Assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta Region of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
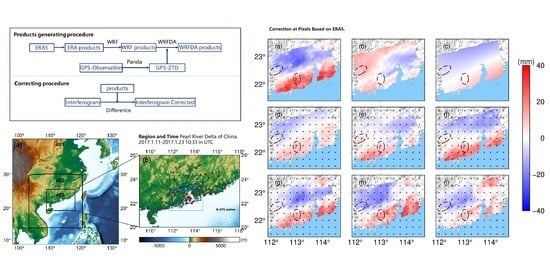
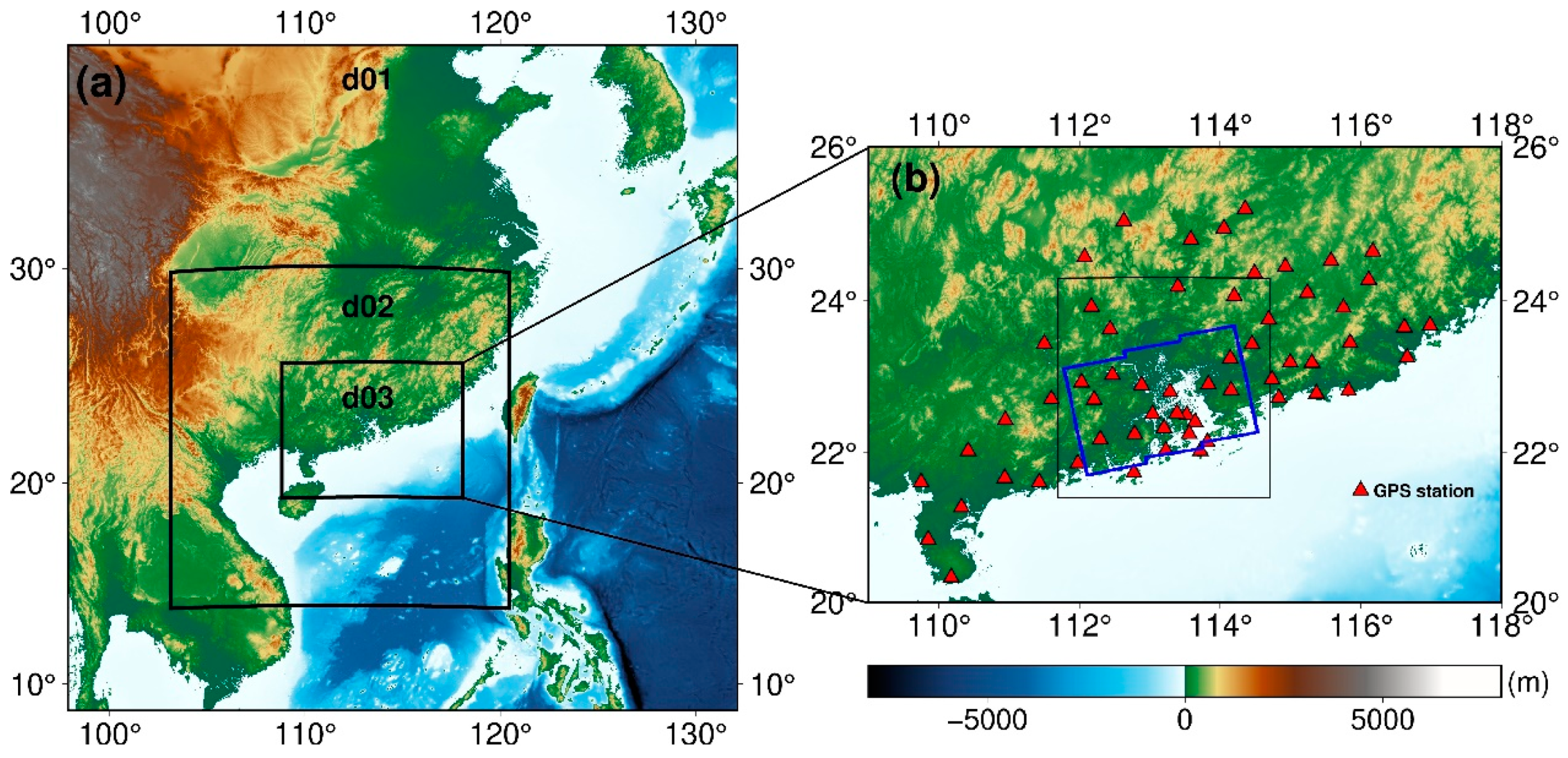
2.1. Study Area and InSAR Data Processing
2.2. Atmospheric Delay in InSAR
2.3. GPS Data Processing
2.4. Reanalysis and Data WRF Simulation
2.5. WRFDA and Configuration
2.6. NWMs-Based ZTD Estimation
3. Results and Comparisons
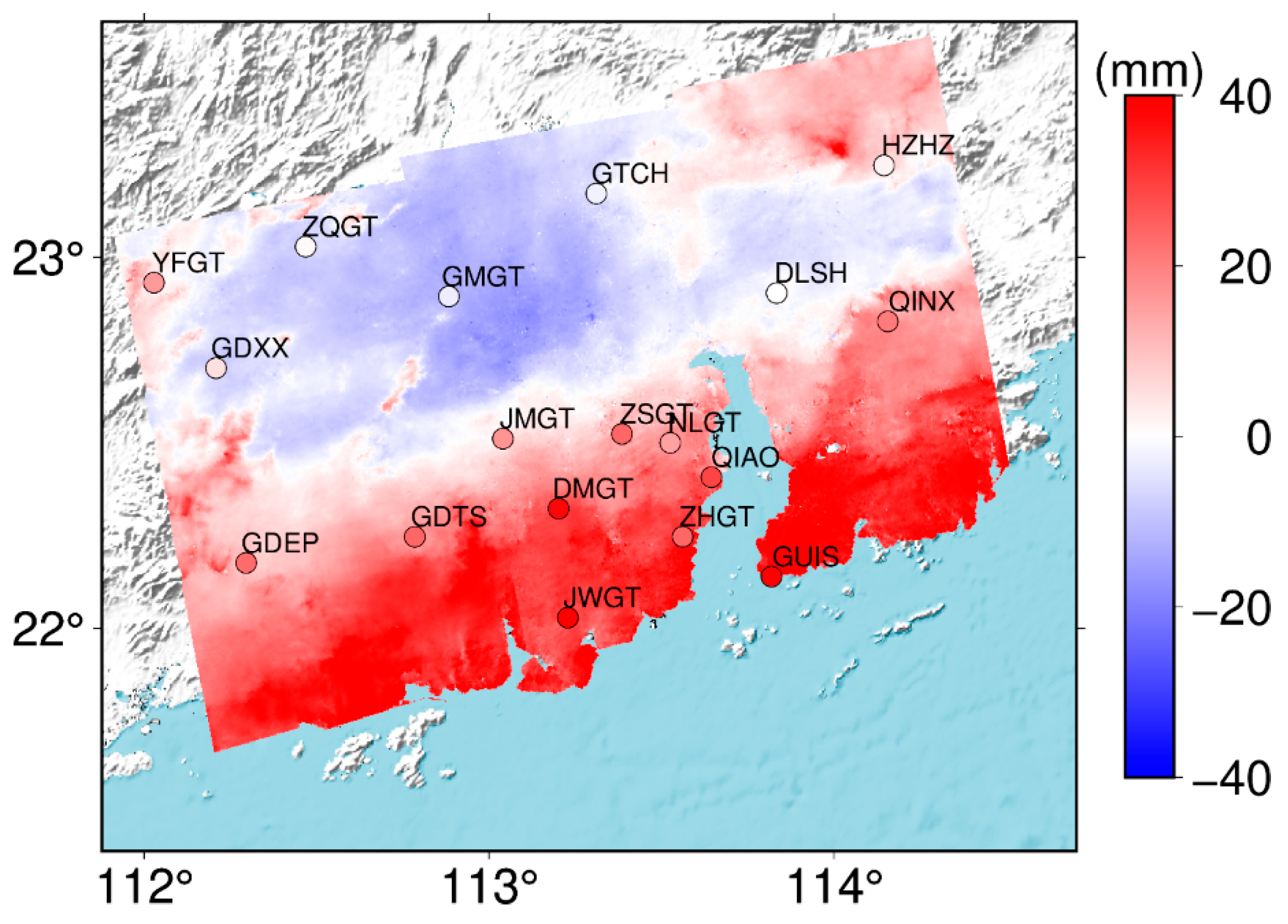
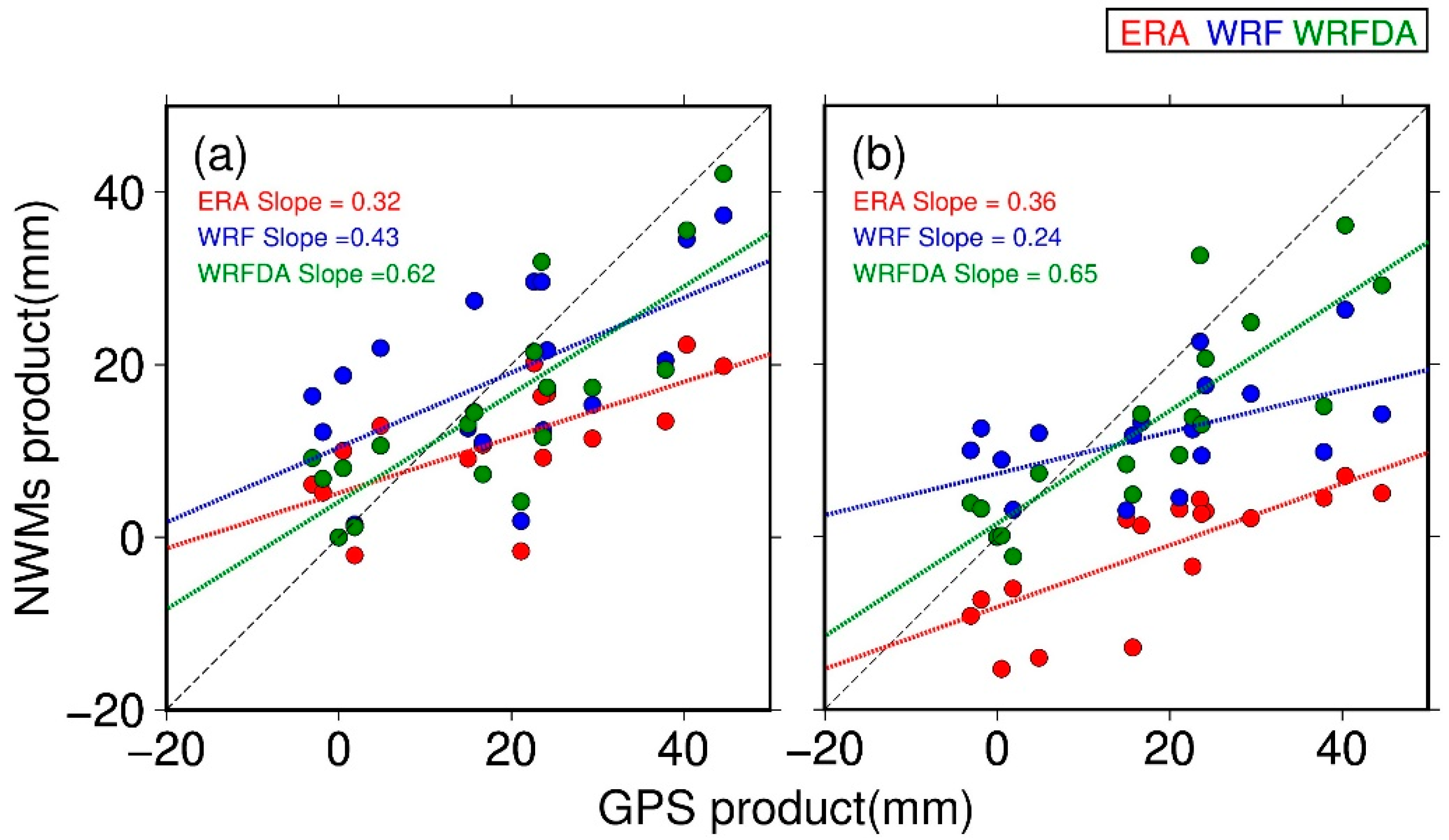
3.1. Comparisons at GPS Stations
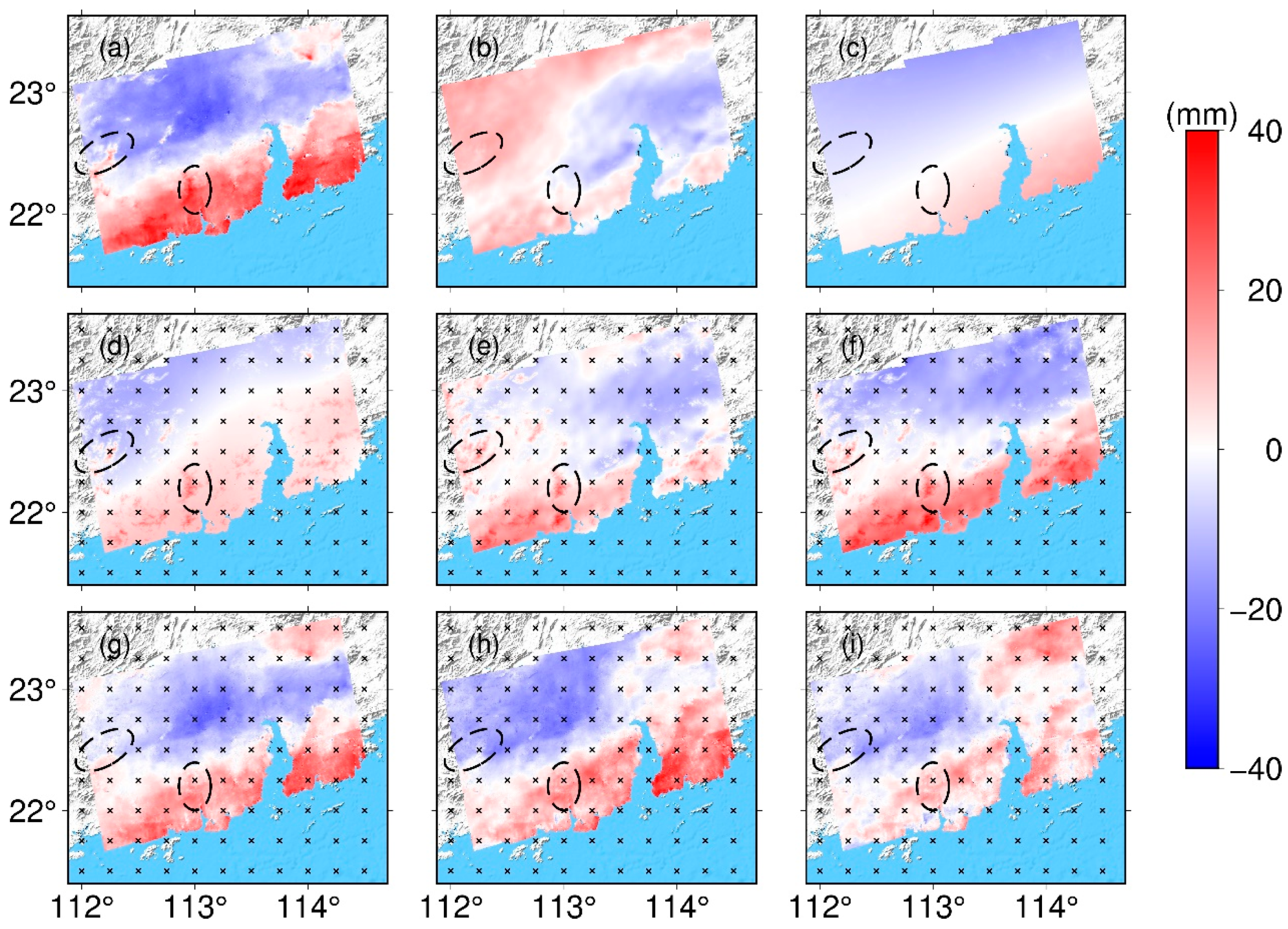
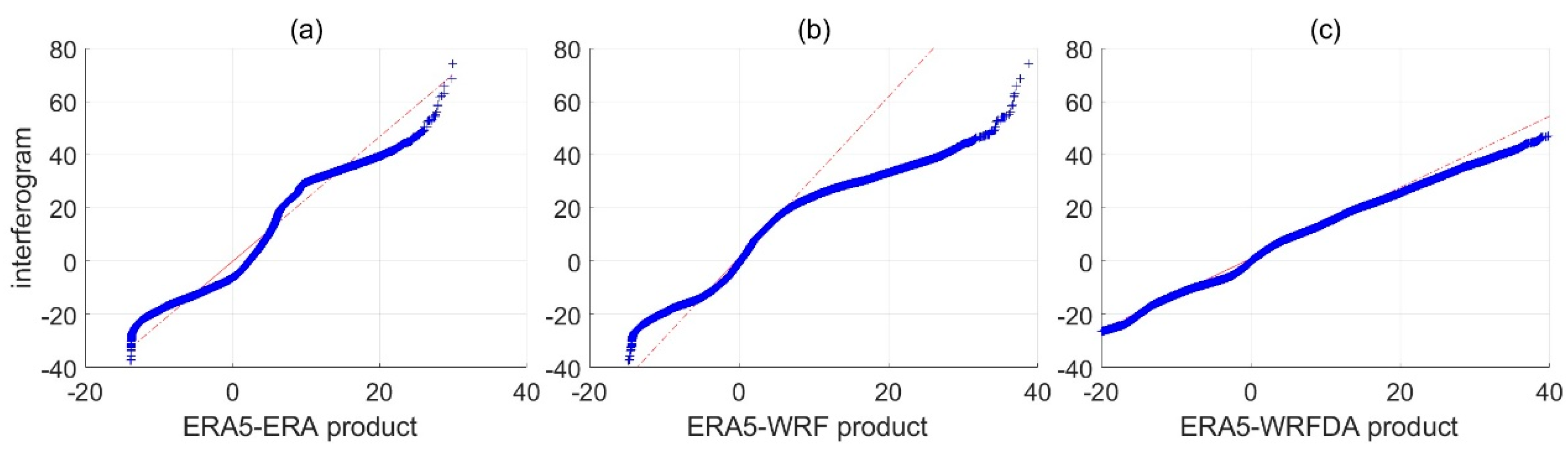
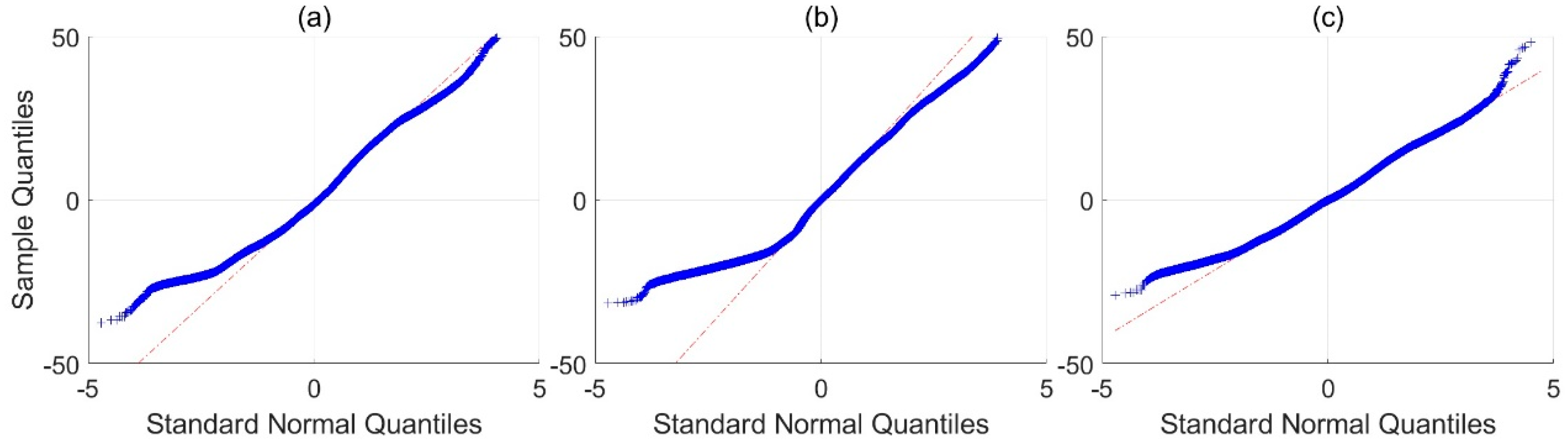
3.2. Comparisons at Interferogram Pixels for ERAI
3.3. Comparisons at Interferogram Pixels for ERA5
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, G.; Hetland, E.A.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Coseismic fault slip of the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake estimated from InSAR and GPS measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L01302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Jónsson, S.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P. Widespread uplift and ‘trapdoor’ faulting on Galápagos volcanoes observed with radar interferometry. Nature 2000, 407, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.E.; Simons, M. A satellite geodetic survey of large-scale deformation of volcanic centres in the central Andes. Nature 2002, 418, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhiwei, L.; Jian-Jun, Z.; Guang-cai, F.; Jiang-ping, L. Atmospheric Effects on InSAR Measurements and Their Mitigation. Sensors 2008, 8, 5426–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, R.M. Atmospheric limitations to repeat-track radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 2517–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jehle, M.; Perler, D.; Small, D.; Schubert, A.; Meier, E. Estimation of Atmospheric Path Delays in TerraSAR-X Data using Models vs. Measurements 2008, 8, 8479–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauducel, F.; Briole, P.; Froger, J.-L. Volcano-wide fringes in ERS synthetic aperture radar interferograms of Etna (1992–1998): Deformation or tropospheric effect? J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 16391–16402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, F.; Avallone, A.; Tupin, F.; Briole, P.; Maitre, H. A Multitemporal Method for Correction of Tropospheric Effects in Differential SAR Interferometry: Application to the Gulf of Corinth Earthquake. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2007, 45, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, Y.; Bock, Y.; Tong, X.; Moore, A.W. Calibrating interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) images with regional GPS network atmosphere models. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 2106–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Mallorqui, J. An Accurate Method to Correct Atmospheric Phase Delay for InSAR with the ERA5 Global Atmospheric Model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic Atmospheric Correction Model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.; Brooks, B.; Cherubini, T.; Shacat, C.; Businger, S.; Werner, C.L. Mitigating atmospheric noise for InSAR using a high resolution weather model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L16304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Nico, G.; Catalão, J. Can spaceborne SAR interferometry be used to study the temporal evolution of PWV? Atmos. Res. 2013, 119, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagasio, M.; Parodi, A.; Pulvirenti, L.; Meroni, A.N.; Boni, G.; Pierdicca, N.; Marzano, F.S.; Luini, L.; Venuti, G.; Realini, E.; et al. A Synergistic Use of a High-Resolution Numerical Weather Prediction Model and High-Resolution Earth Observation Products to Improve Precipitation Forecast. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) atmospheric correction: GPS, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), and InSAR integration. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, B03410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Jin, S.; He, X. Assessment of InSAR Atmospheric Correction Using Both MODIS Near-Infrared and Infrared Water Vapor Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5726–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Agram, P.; Lin, Y.n.; Simons, M.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G.; Li, Z. Improving InSAR geodesy using Global Atmospheric Models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, D.; Nutricato, R.; Lorusso, R.; Lombardi, N.; Bovenga, F.; Bruno, M.; Chiaradia, M.; Milillo, G. On the Geolocation Accuracy of COSMO-SkyMed Products; SPIE: Toulouse, France, 2015; Volume 9642. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, X.; Balss, U.; Gonzalez, F.; Eineder, M. Mitigation of Tropospheric Delay in SAR and InSAR Using NWP Data: Its Validation and Application Examples. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nico, G.; Tome, R.; Catalao, J.; Miranda, P.M.A. On the Use of the WRF Model to Mitigate Tropospheric Phase Delay Effects in SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4970–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Furuya, M.; Hobiger, T.; Ichikawa, R. Are numerical weather model outputs helpful to reduce tropospheric delay signals in InSAR data? J. Geod. 2013, 87, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doin, M.P.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G.; Cavalié, O.; Doubre, C. Corrections of stratified tropospheric delays in SAR interferometry: Validation with Global Atmospheric Models. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Green, B.W.; Zhang, F. Mitigating atmospheric effects in InSAR measurements through high-resolution data assimilation and numerical simulations with a weather prediction model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2129–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Herring, T.A.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. GPS Meteorology: Mapping Zenith Wet Delays onto Precipitable Water. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1994, 33, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction using a GPS-based iterative tropospheric decomposition model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Nico, G.; Tome, R.; Catalao, J.; Miranda, P.M.A. Experimental Study on the Atmospheric Delay Based on GPS, SAR Interferometry, and Numerical Weather Model Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.M.A.; Mateus, P.; Nico, G.; Catalão, J.; Tomé, R.; Nogueira, M. InSAR Meteorology: High-Resolution Geodetic Data Can Increase Atmospheric Predictability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateus, P.; Tomé, R.; Nico, G.; Catalão, J. Three-Dimensional Variational Assimilation of InSAR PWV Using the WRFDA Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 7323–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Miranda, P.M.A.; Nico, G.; Catalão, J.; Pinto, P.; Tomé, R. Assimilating InSAR Maps of Water Vapor to Improve Heavy Rainfall Forecasts: A Case Study With Two Successive Storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichelli, E.; Ferretti, R.; Cimini, D.; Panegrossi, G.; Perissin, D.; Pierdicca, N.; Rocca, F.; Rommen, B. InSAR Water Vapor Data Assimilation into Mesoscale Model MM5: Technique and Pilot Study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3859–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.-P.; Peltzer, G. Systematic InSAR tropospheric phase delay corrections from global meteorological reanalysis data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L17311-17311–L17311-17316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.; Sacco, G.F.; Zebker, H. The InSAR scientific computing environment. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 23–26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L. Satellite radar interferometry: Two-dimensional phase unwrapping. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Walters, R.J.; Wright, T.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Parker, D.J. Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, A.L.; Biggs, J.; Walters, R.J.; Ebmeier, S.K.; Wright, T.J.; Teanby, N.A.; Lu, Z. Systematic assessment of atmospheric uncertainties for InSAR data at volcanic arcs using large-scale atmospheric models: Application to the Cascade volcanoes, United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, Q.; Geng, J.; Lou, Y.; Ge, M.; Liu, J. Recent development of PANDA software in GNSS data processing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Earth Observation Data Processing and Analysis (ICEODPA), Wuhan, China, 28–30 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Landskron, D.; Böhm, J. VMF3/GPT3: Refined discrete and empirical troposphere mapping functions. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H. Rapid troposphere tomography using adaptive simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Model Version 4; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, W.-K.; Wu, D.; Lang, S.; Chern, J.-D.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Fridlind, A.; Matsui, T. High-resolution NU-WRF simulations of a deep convective-precipitation system during MC3E: Further improvements and comparisons between Goddard microphysics schemes and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 1278–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Kain, J. The Kain—Fritsch convective parameterization: An update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. J ATMOS SCI 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The NCAR Command Language (Version 6.6.2) [Software]; UCAR/NCAR/CISL/TDD: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.M.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.-R.; Bourgeois, A.J.; Xiao, Q.N. A Three-Dimensional Variational Data Assimilation System for MM5: Implementation and Initial Results. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C. The National Meteorological Center’s spectral statistical-interpolation analysis system. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, J.; Ge, M.; Vedel, H.; Calais, E. Accuracy and Variability of GPS Tropospheric Delay Measurements of Water Vapor in the Western Mediterranean. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric Correction for the Troposphere and the Stratosphere in Radio Ranging Satellites. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1972, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Haase, J.S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J. The Use of Ground-based GPS Precipitable Water Measurements over China to Assess Radiosonde and ERA-Interim Moisture Trends and Errors from 1999–2015. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 7643–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J. Introduction to Atmospheric Chemistry; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F.; Scharroo, R.; Luis, J.; Wobbe, F. Generic Mapping Tools: Improved Version Released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Acquisition Day DD/MM/YY | Number of Stations | Max Scale Factor | Min Scale Factor | Average Scale Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11/01/2017 | 56 | 4.4 | 2.9 | 3.7 |
| 23/01/2017 | 56 | 4.4 | 3.1 | 3.7 |
| Products | ERAI-Based | ERA5-Based | GPS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | ERA | WRF | WRFDA | ERA | WRF | WRFDA | ||
| Amplitude (mm) | 46.48 (18%) | 46.61 (18%) | 34.87 (38%) | 42.41 (25%) | 52.44 (7%) | 31.60 (44%) | 28.48 (50%) | |
| stdev (mm) | 14.21 (12%) | 14.64 (9%) | 10.02 (38%) | 11.18 (31%) | 14.54 (10%) | 9.51 (41%) | 7.59 (53%) | |
| Products | ERAI-Based | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | ERA | WRF | WRFDA | |
| Amplitude of Products(mm) | 45.7 | 59.2 | 56.1 | |
| Amplitude after Correction (mm) | 58.2 (11%) | 57.4 (12%) | 45 (31%) | |
| stdev after Correction (mm) | 13.25 (18%) | 13.02 (20%) | 9.21 (43%) | |
| Products | ERA5-Based | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | ERA | WRF | WRFDA | |
| Amplitude of Products(mm) | 33.4 | 40.6 | 53 | |
| Amplitude after Correction (mm) | 58 (11%) | 59.4 (9%) | 44.3 (32%) | |
| stdev after Correction (mm) | 11.76 (28%) | 12.68 (22%) | 8.38 (48%) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, J. On the Assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta Region of China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163280
Zhang Z, Lou Y, Zhang W, Wang H, Zhou Y, Bai J. On the Assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta Region of China. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163280
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenyi, Yidong Lou, Weixing Zhang, Hua Wang, Yaozong Zhou, and Jingna Bai. 2021. "On the Assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta Region of China" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163280
APA StyleZhang, Z., Lou, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Zhou, Y., & Bai, J. (2021). On the Assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta Region of China. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163280