Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration with InSAR Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cross-Iteration-Based Methodology
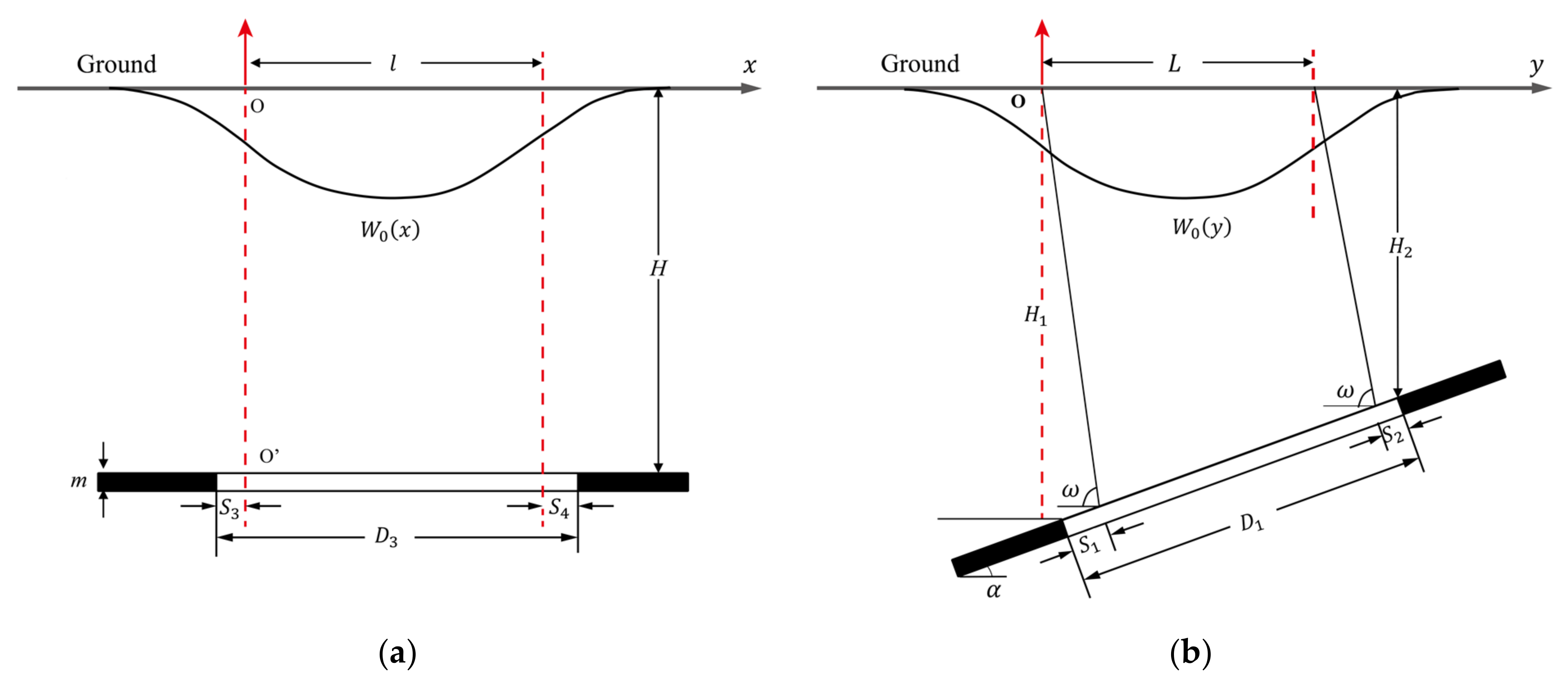
2.1. Principle of the PIM
2.2. Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration
2.2.1. The Function Model Linking InSAR LOS Measurement to Goaf Parameters
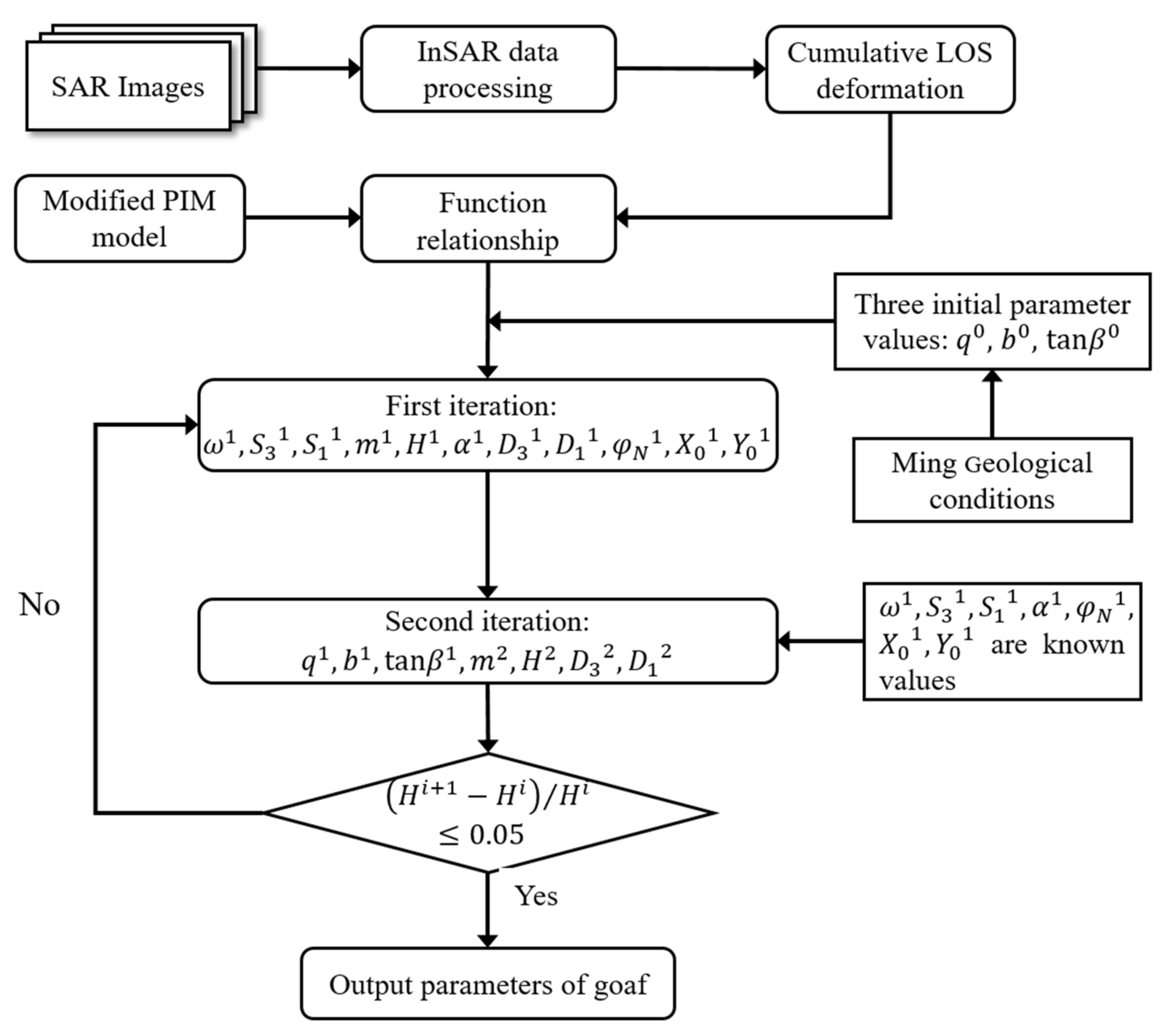
2.2.2. Model Resolution via Cross-Iteration
- (1)
- First Iteration: Determine the empirical values of the three initial model parameters and invert the remaining unknown parameters .
- (2)
- Second Iteration: Treat as known and update the remaining parameters to .
- (3)
- Iteration Termination Judgment: When the condition is satisfied, the iteration is terminated, and the target parameter value is . If the termination condition is not satisfied, the parameter values obtained in the second iteration are used to repeat the two steps (1) and (2) until it is satisfied .
2.2.3. Overall Processing
3. Experiments
3.1. Simulated Experiment
3.2. Real Data Experiment
3.2.1. Study Area
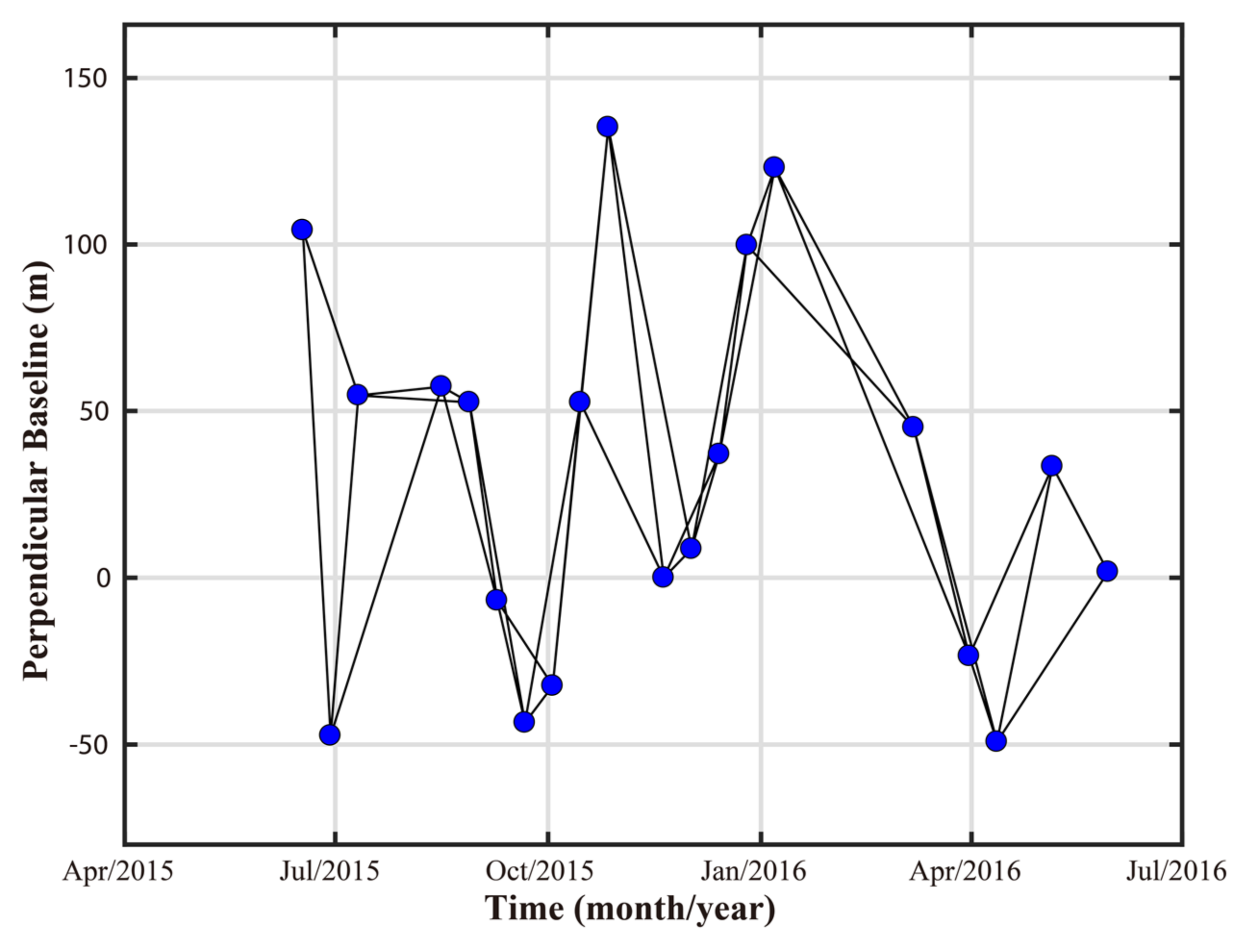
3.2.2. SAR Data Sets and InSAR Processing
4. Results
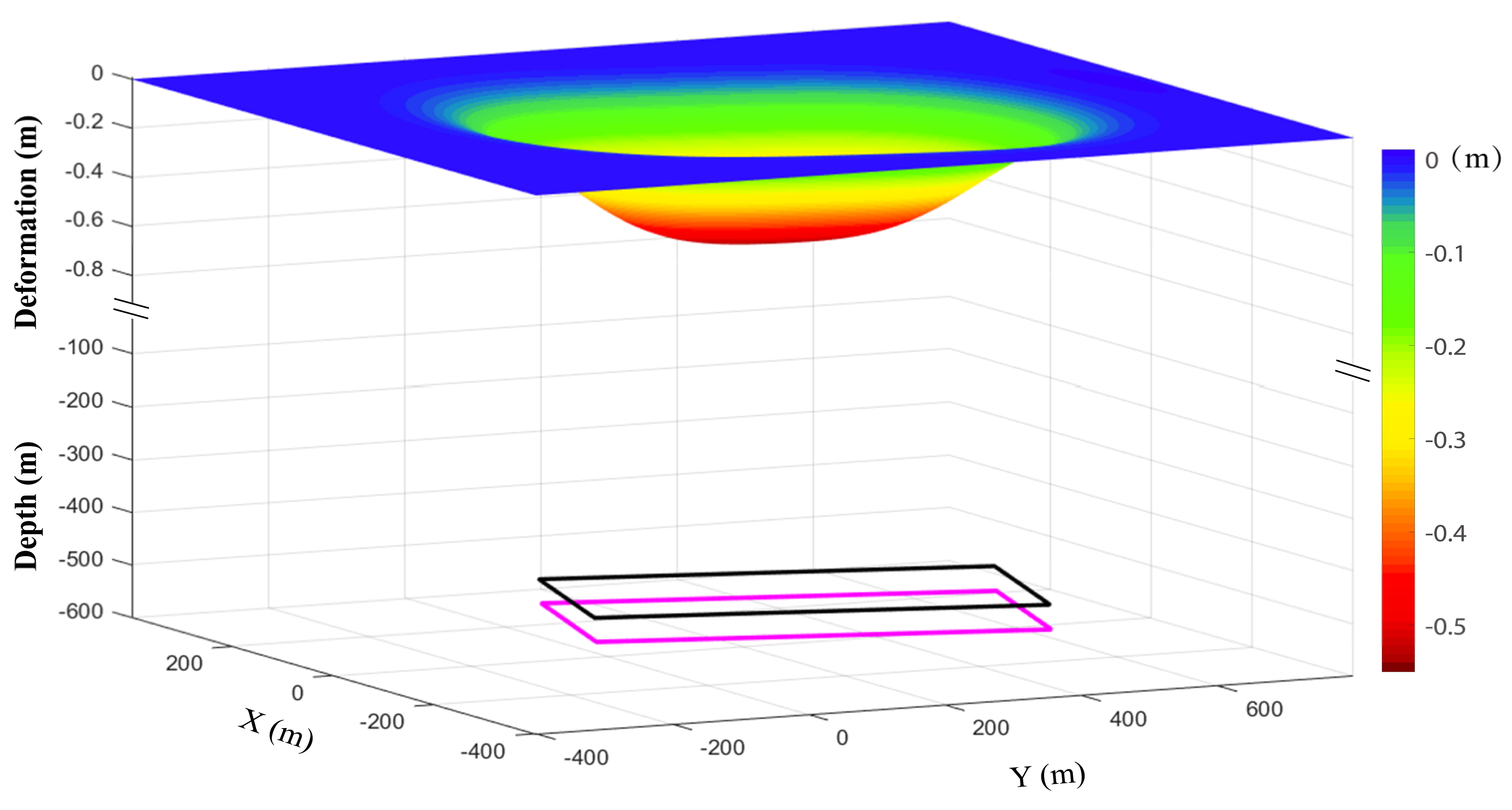
4.1. Simulated Experiment Results
4.1.1. Inversion of Goaf Parameters
4.1.2. Accuracy Evaluation
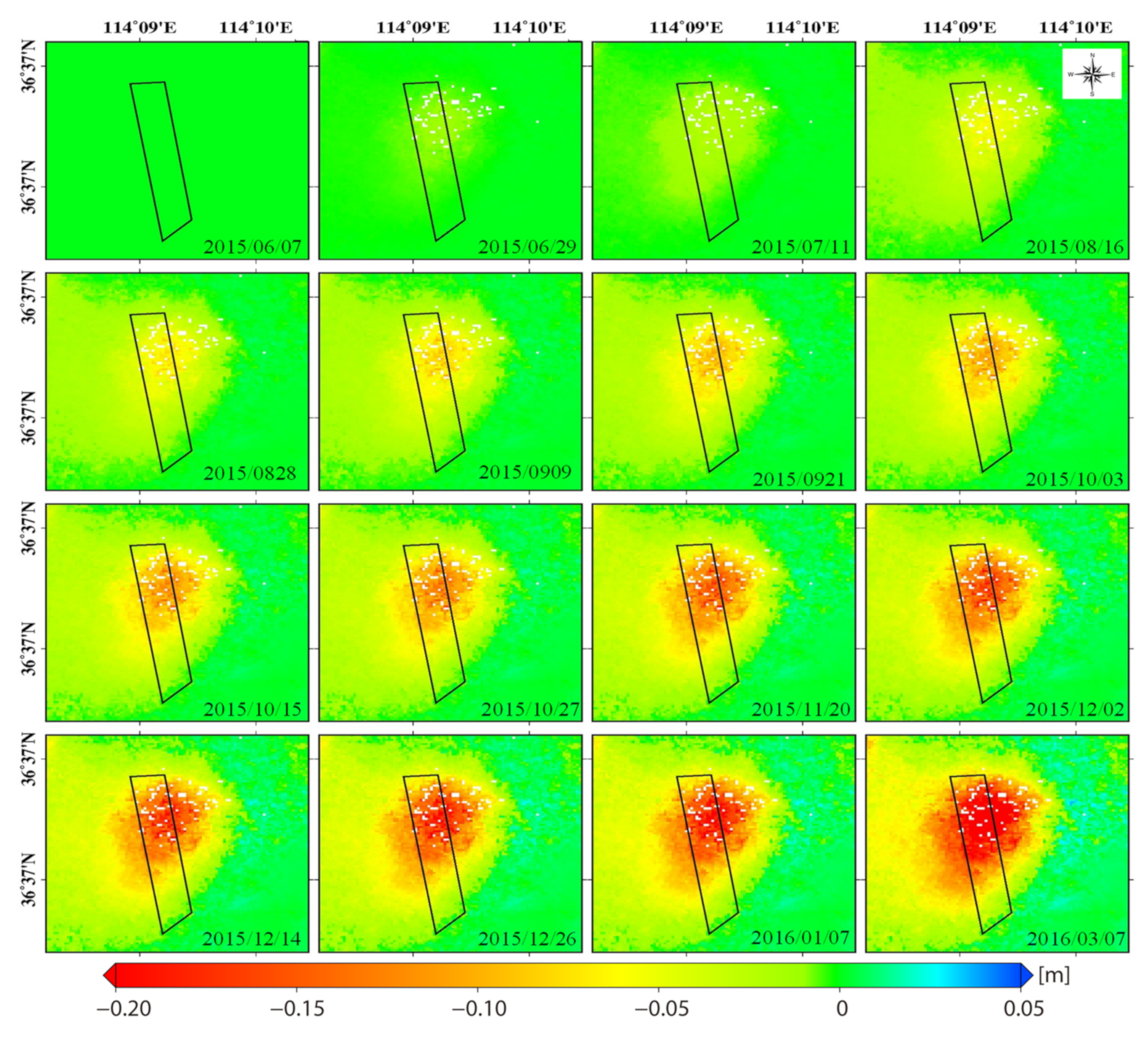
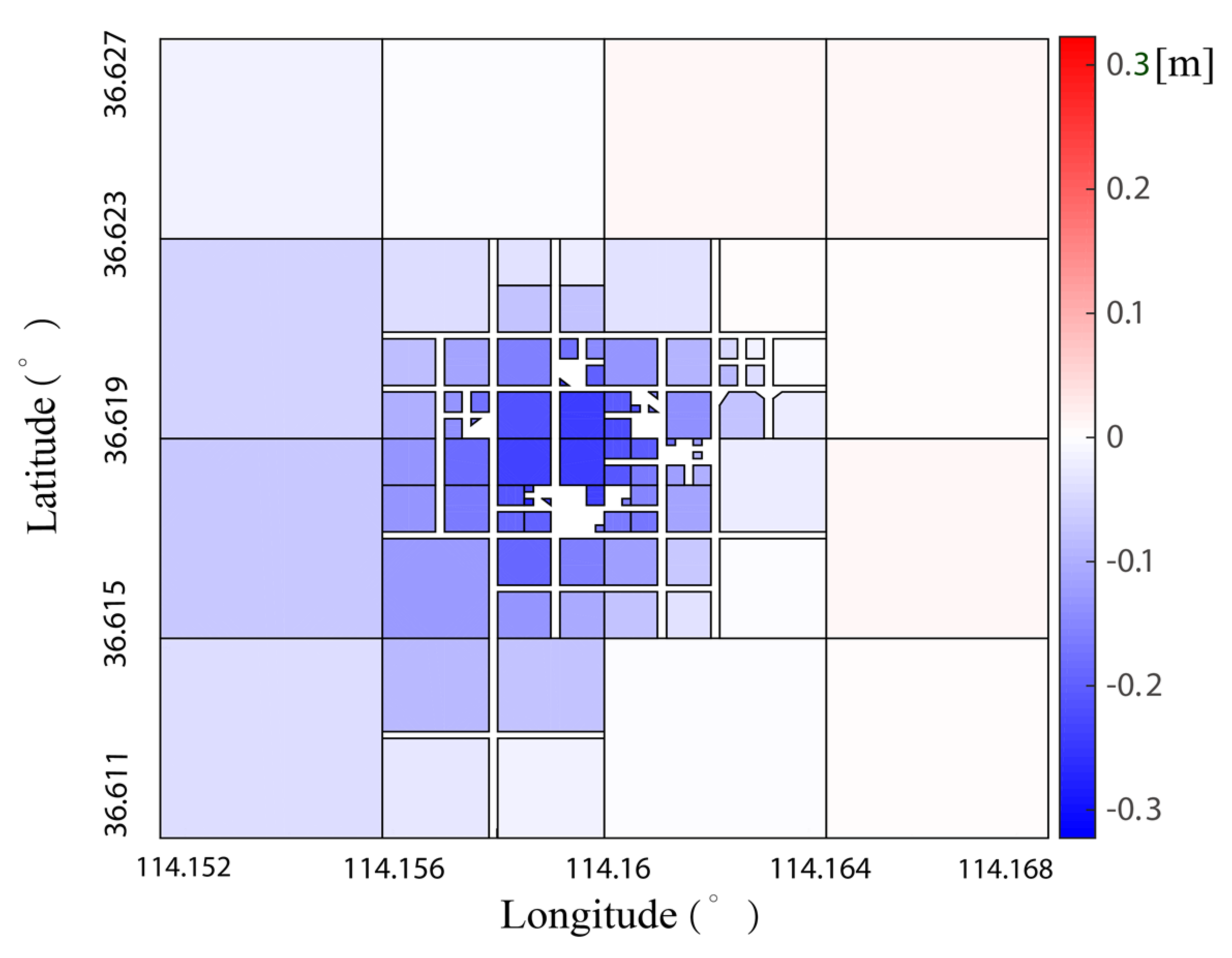
4.2. Real Data Experiment Results
4.2.1. Inversion of Goaf Parameters
4.2.2. Results and Accuracy Evaluation
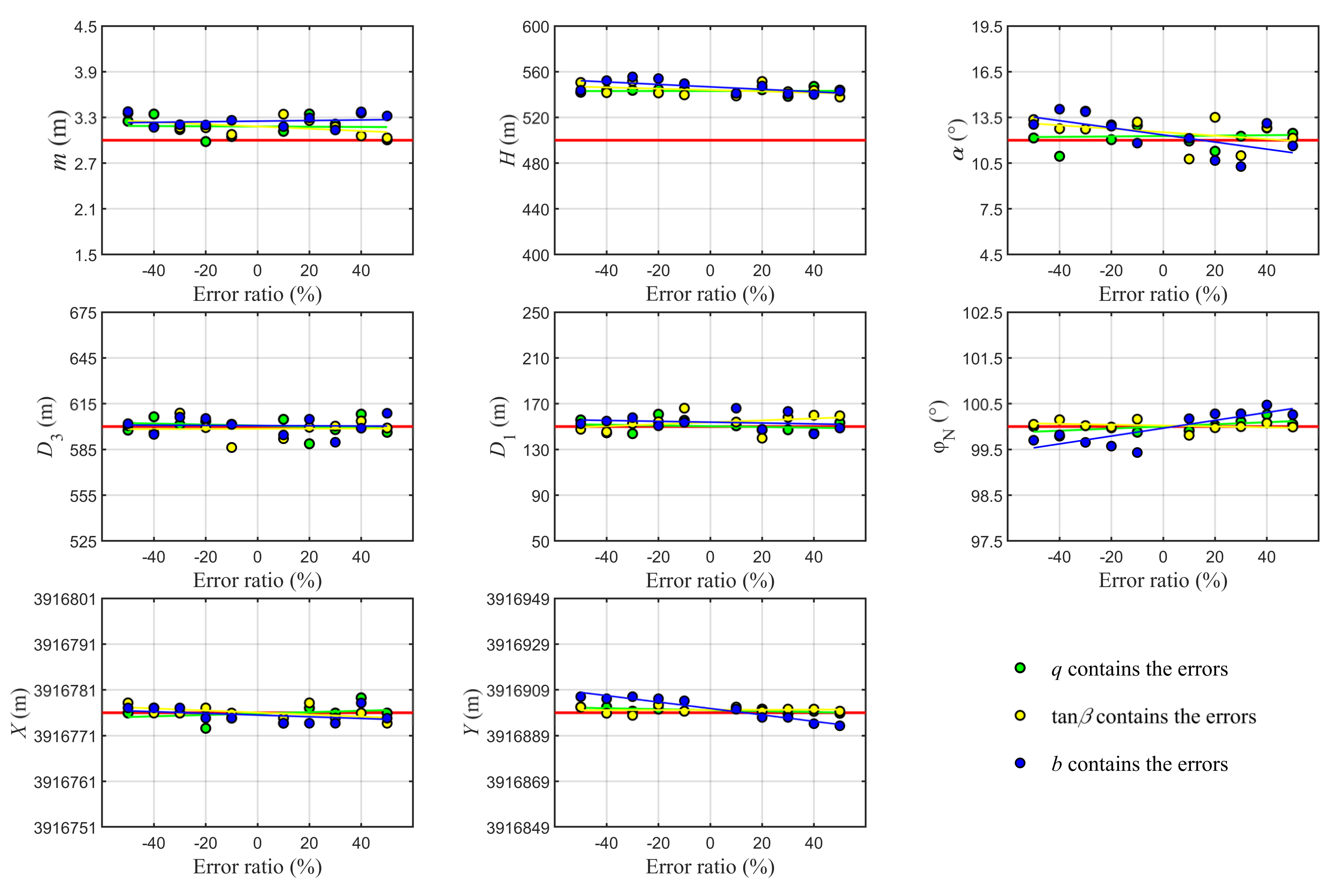
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters Estimation
4.3.1. Impact of the Cross-Iteration Method
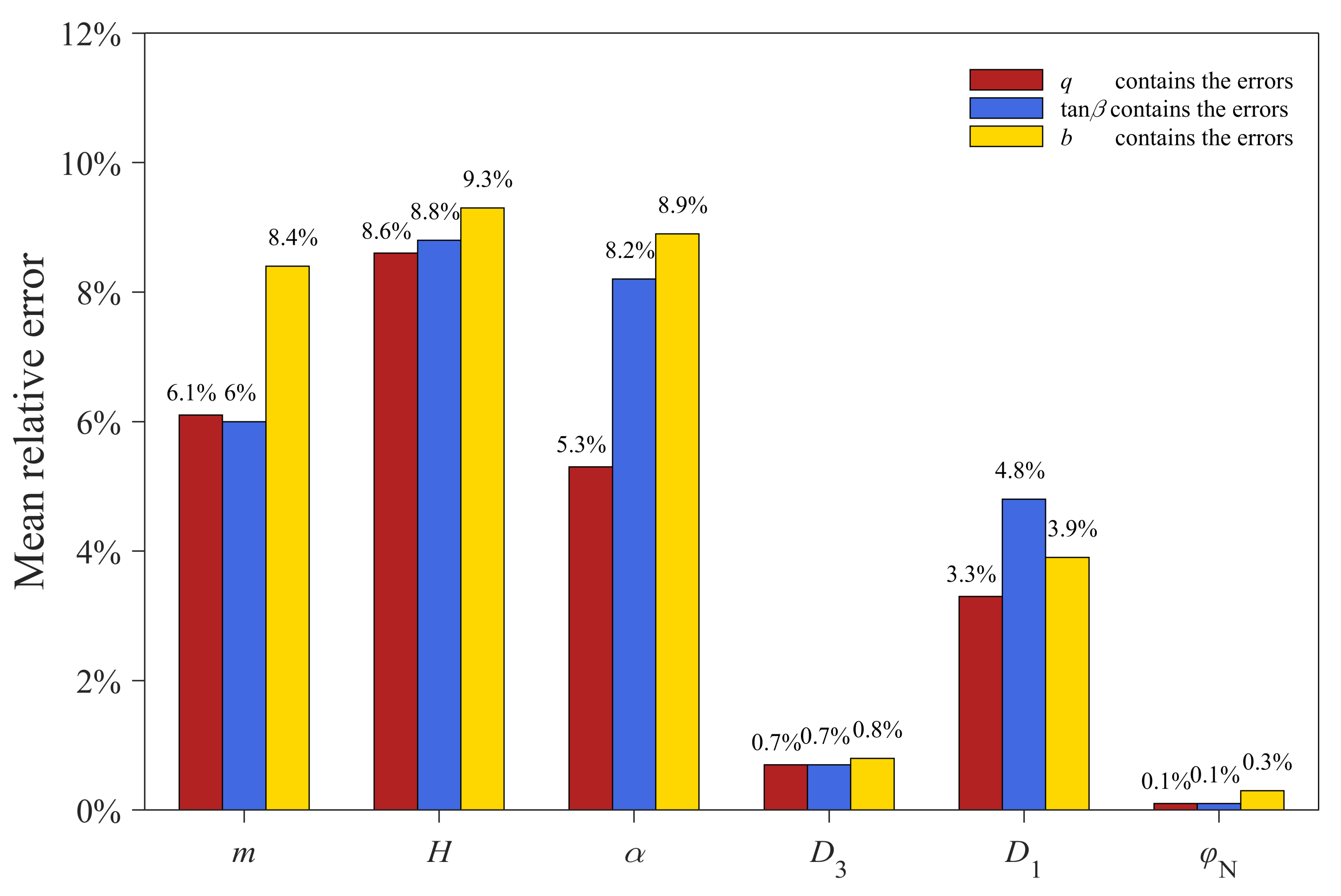
4.3.2. Influence of Deformation Error
4.3.3. Effect of the Initial Model Parameter Error of the PIM
5. Discussion
5.1. Impact of the Tangent of the Main Influence Angle on the Average Mining Depth
5.2. Influence of Subcritical Mining
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, G.Q.; Yan, Y.J.; Cheng, J.L. Researches on detection of 3-D underground cave based on TEM technique. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, S. The application of tem and resistivity sounding to the investigation of gob areas near shawu railway. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 35, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, I.; Styles, P.; Emsley, S.J.; Ferguson, N.S. The detection of cavities using the microgravity technique: Case histories from mining and karstic environments. Geol. Soc. Lond. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 1997, 12, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, D.A.; Marsh, S.H.; Gibson, A.; Ager, G.J.; Mcmanus, K.B.; Caunt, S.; Culshaw, M.G. Remote thermal IR surveying to detect abandoned mineshafts in former mining areas. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrog. 2008, 41, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Monti-Guarnieri, A. Distributed Scatterer Interferometry With the Refinement of Spatiotemporal Coherence. IEEE TRANS. Geosci. Remote 2020, 58, 3987–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast Statistically Homogeneous Pixel Selection for Covariance Matrix Estimation for Multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2015, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D.; Biggs, J.; Wicks, C.; Mcnutt, S. Ground surface deformation patterns, magma supply, and magma storage at Okmok volcano, Alaska, from InSAR analysis: 1. Intereruption deformation, 19970–2008. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Shan, W.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, G. Monitoring the Degradation of Island Permafrost Using Time-Series InSAR Technique: A Case Study of Heihe, China. Sensors 2019, 19, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daout, S.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G.; Socquet, A.; Lasserre, C. Large-scale InSAR monitoring of permafrost freeze-thaw cycles on the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Interaction between permafrost and infrastructure along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway detected via jointly analysis of C- and L-band small baseline SAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Z.W.; Feng, G.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Hu, J. Monitoring surface deformation over permafrost with an improved SBAS-InSAR algorithm: With emphasis on climatic factors modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184C, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Balz, T.; Liao, M. Landslide deformation monitoring using point-like target offset tracking with multi-mode high-resolution TerraSAR-X data. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.L.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J. Slope deformation prior to Zhouqu, China landslide from InSAR time series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. 3D coseismic Displacement of 2010 Darfield, New Zealand earthquake estimated from multi-aperture InSAR and D-InSAR measurements. J. Geodesy 2012, 86, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.C.; Hetland, E.A.; Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Lei, Z. Coseismic fault slip of the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake estimated from InSAR and GPS measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, T.; Fielding, E.; Parsons, B. Triggered slip: Observations of the 17 August 1999 Izmit (Turkey) Earthquake using radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, L.; Aoki, Y.; Rivalta, E.; Jónsson, S. Volcano Wide Deformation after the 2017 Erta Ale Dike Intrusion, Ethiopia, Observed with Radar Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB019562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, D.; Palanisamy Vadivel, S.K.; Yun, S. Long-Term Deflection Monitoring for Bridges Using X and C-Band Time-Series SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.; Liao, M.; Lu, Z.; Yang, M. Structural Health and Stability Assessment of High-Speed Railways via Thermal Dilation Mapping With Time-Series InSAR Analysis. IEEE J. Stars 2017, 10, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tosti, F.; Gagliardi, V.; Amico, F.D.; Alani, A.M. Transport infrastructure monitoring by data fusion of GPR and SAR imagery information. Transp. Res. Proc. 2020, 45, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. An Underground-Mining Detection System Based on DInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Peng, G.; Hu, J.; Wu, L.; Preusse, A.; Wang, Y.; Papst, M. Locating and defining underground goaf caused by coal mining from space-borne SAR interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.W.; Chi, K.C.; Troutt, M.D. Application of a mixed simulated annealing-genetic algorithm heuristic for the two-dimensional orthogonal packing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, D.; Xia, Y. Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Y. InSAR- and PIM-Based Inclined Goaf Determination for Illegal Mining Detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwiniszyn, J. Application of the equation of stochastic processes to mechanics of loose bodies. Arch. Mech. 1956, 8, 393–411. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liao, G. Basic Law of Ground Surface Movement Due to Coal Mining; The Industrial Press of China: Beijing, China, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Yang, L.; Ling, G. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Press of China University of Mining and Technology: Xuzhou, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.F.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, G.L. InSAR-Based Model Parameter Estimation of Probability Integral Method and Its Application for Predicting Mining-Induced Horizontal and Vertical Displacements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2016, 54, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnardi, M.; Hooper, A. Inversion of Surface Deformation Data for Rapid Estimates of Source Parameters and Uncertainties: A Bayesian Approach. Geochem. Geophy. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 2194–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decriem, J.; Árnadóttir, T.; Hooper, A.; Geirsson, H.; Sigmundsson, F.; Keiding, M.; Ófeigsson, B.G.; Hreinsdóttir, S.; Einarsson, P.; Lafemina, P. The 2008 May 29 earthquake doublet in SW Iceland. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1128–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WANG, S.; ZUO, M.; KONG, Q.; ZHANG, N. Study on CBM Geological Features and Exploitation, Utilization in Fengfeng Mining Area. Coal Geol. China 2020, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, H.; Huang, P.; Qiao, J.; Liu, D.; Chang, M. Neotectonic character of Handan-Fengfeng mining area and its signifficance for coal resource exploitation. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 32, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhai, P.; Jing, F. Fengfeng Coalfield Gas Occurrence Regularity and Influence Factors. Proc. Eng. 2011, 26, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, X.; Wu, K.; Hu, D.; Li, L.; Zhou, D. Combining differential SAR interferometry and the probability integral method for three-dimensional deformation monitoring of mining areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5196–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Feng, G. Kinematic Coregistration of Sentinel-1 TOPSAR Images Based on Sequential Least Squares Adjustment. IEEE J. Stars 2020, 13, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, Q.J.; Jiang, M. A Refined Strategy for Removing Composite Errors of SAR Interferogram. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Yun, S.H.; Walter, T.R.; Segall, P.; Kim, S.W. Stress Control of Deep Rift Intrusion at Mauna Loa Volcano, Hawaii. Science 2007, 316, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau, C.I.S. Regulations for Coal Pillar Setting and Coal Pressure Mining in Buildings, Water Bodies, Railways and Main Roadways; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C.; Adragna, F.; Peltzer, G.; Feigl, K.; Rabaute, T. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Acquisition Date | Absolute Orbit | Path | Incident Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 June 2015 | 6412 | 40 | 33.7483 |
| 2 | 29 June 2015 | 6587 | 40 | 33.7494 |
| 3 | 11 July 2015 | 6762 | 40 | 33.7483 |
| 4 | 16 August 2015 | 7287 | 40 | 33.7487 |
| 5 | 28 August 2015 | 7462 | 40 | 33.7505 |
| 6 | 9 September 2015 | 7637 | 40 | 33.7506 |
| 7 | 21 September 2015 | 7812 | 40 | 33.7516 |
| 8 | 3 October 2015 | 7987 | 40 | 33.7514 |
| 9 | 15 October 2015 | 8162 | 40 | 33.7510 |
| 10 | 27 October 2015 | 8337 | 40 | 33.7512 |
| 11 | 20 November 2015 | 8687 | 40 | 33.7566 |
| 12 | 2 December 2015 | 8862 | 40 | 33.7566 |
| 13 | 14 December 2015 | 9037 | 40 | 33.7560 |
| 14 | 26 December 2015 | 9212 | 40 | 33.7534 |
| 15 | 7 January 2016 | 9387 | 40 | 33.7533 |
| 16 | 7 March 2016 | 10,262 | 40 | 33.7578 |
| 17 | 31 March 2016 | 10,612 | 40 | 33.7593 |
| 18 | 12 April 2016 | 10,787 | 40 | 33.7623 |
| 19 | 6 May 2016 | 11,137 | 40 | 33.7629 |
| 20 | 30 May 2016 | 11,487 | 40 | 33.7560 |
| Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated | 3 m | 12° | 600 m | 150 m | 100° | 500 m | 3,916,776 m | 520,899 m |
| Inverted | 2.94 m | 11.97° | 596.9 m | 149.8 m | 100.4° | 544.6 m | 3,916,781 m | 520,896 m |
| Absolute error | −0.06 m | −0.03° | −3.1 m | −0.2 m | 0.4° | 44.6 m | −5 m | 3 m |
| Relative error | 2.0% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.1% | 0.4% | 8.9% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
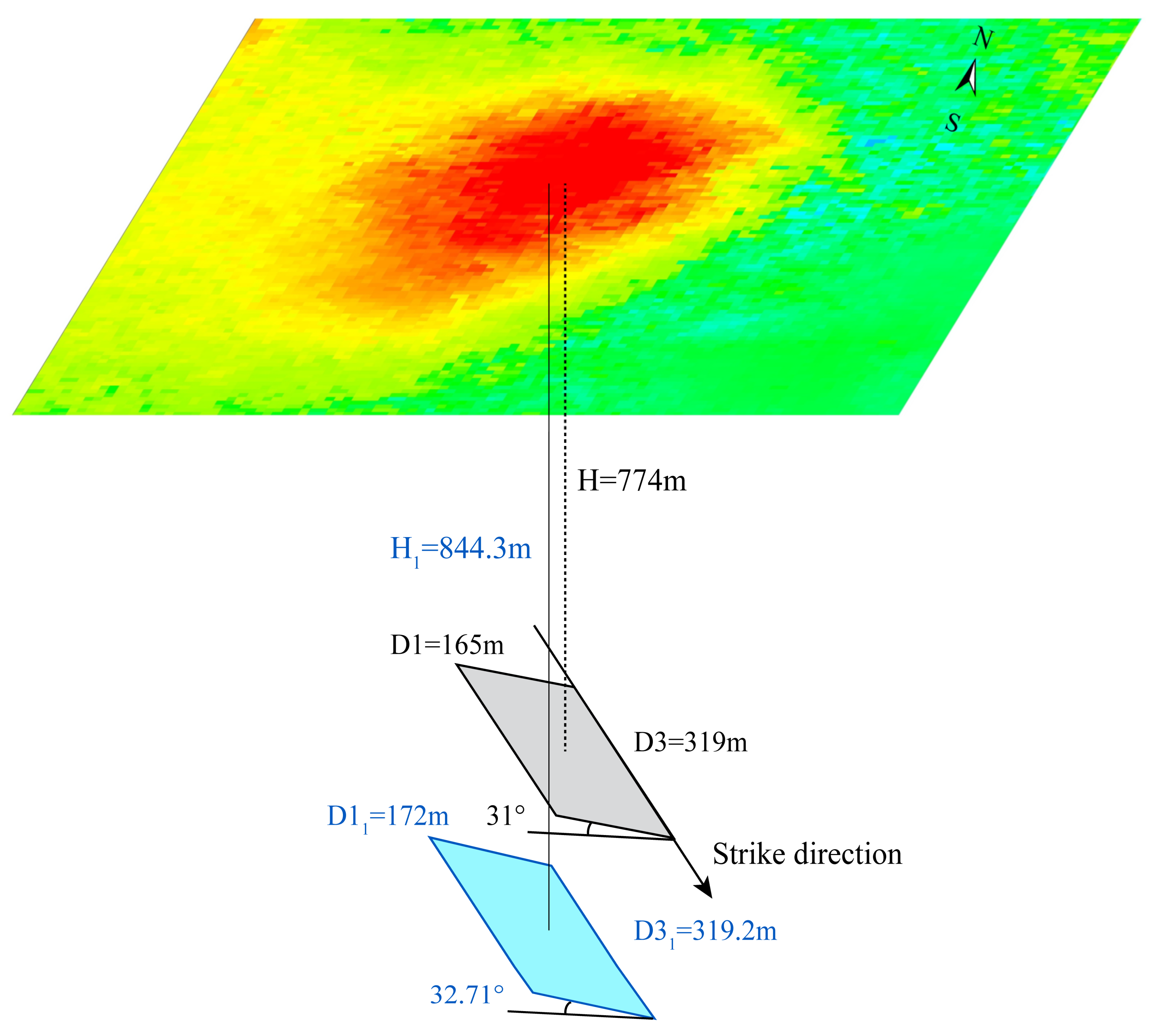
| Measured | 4.5 m | 31° | 319 m | 165 m | 169° | 774 m |
| Inverted | 4.98 m | 32.71° | 319.2 m | 172.0 m | 170.7° | 844.3 m |
| Absolute error | 0.48 m | 1.71° | 0.2 m | 7.0 m | 1.7° | 70.3 m |
| Relative error | 10.7% | 5.5% | 0.0% | 4.2% | 1.0% | 9.1% |
| Relative error in Xia (2020) | - | 6.45% | 7.21% | 16.36% | 3.55% | 1.94% |
| Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured | 4.5 m | 31° | 319 m | 165 m | 169° | 774 m |
| Non-iterative | 3.69 m | 41.69° | 353.8 m | 182.7 m | 174.7° | 894.5 m |
| Absolute error | −0.81 m | 10.69° | 34.8 m | 17.7 m | 5.7° | 120.5 m |
| Relative error | 18% | 34.5% | 10.9% | 10.7% | 3.4% | 15.6% |
| Deformation | Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error-free | Inverted | 3.13 m | 12.45° | 600.4 m | 140.7 m | 99.9° | 543.2 m | 3,916,778 m | 520,901 m |
| Absolute error | 0.13 m | 0.45° | 0.4 m | −8.3 m | −0.1° | 43.2 m | 2 m | 2 m | |
| Relative error | 4.3% | 3.8% | 0.1% | 5.5% | 0.1% | 8.6% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Random errors | Inverted | 3.35 m | 13.05° | 591.1 m | 144.1 m | 100.1° | 543.8 m | 3,916,778 m | 520,904 m |
| Absolute error | 0.35 m | 1.05° | −8.9 m | −5.9 m | 0.1° | 43.8 m | 2 m | 5 m | |
| Relative error | 11.7% | 8.8% | 1.5% | 3.9% | 0.1% | 8.8% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Yi, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B. Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration with InSAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163204
Zhang W, Shi J, Yi H, Zhu Y, Xu B. Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration with InSAR Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163204
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weihao, Jiancun Shi, Huiwei Yi, Yan Zhu, and Bing Xu. 2021. "Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration with InSAR Measurements" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163204
APA StyleZhang, W., Shi, J., Yi, H., Zhu, Y., & Xu, B. (2021). Underground Goaf Parameters Estimation by Cross-Iteration with InSAR Measurements. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163204






