Abstract
Deep-learning technologies, especially convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have achieved great success in building extraction from areal images. However, shape details are often lost during the down-sampling process, which results in discontinuous segmentation or inaccurate segmentation boundary. In order to compensate for the loss of shape information, two shape-related auxiliary tasks (i.e., boundary prediction and distance estimation) were jointly learned with building segmentation task in our proposed network. Meanwhile, two consistency constraint losses were designed based on the multi-task network to exploit the duality between the mask prediction and two shape-related information predictions. Specifically, an atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module was appended to the top of the encoder of a U-shaped network to obtain multi-scale features. Based on the multi-scale features, one regression loss and two classification losses were used for predicting the distance-transform map, segmentation, and boundary. Two inter-task consistency-loss functions were constructed to ensure the consistency between distance maps and masks, and the consistency between masks and boundary maps. Experimental results on three public aerial image data sets showed that our method achieved superior performance over the recent state-of-the-art models.
1. Introduction
Automatic building extraction from high-resolution remote-sensing images has important implications in urban planning, disaster monitoring, and 3D building reconstruction [1,2]. Due to the diversity of building characteristics (e.g., shape and size) and the interference of complicated backgrounds in aerial images (e.g., roads and parking lots), it is difficult to achieve intra-class unification and inter-class discrimination simultaneously when extracting buildings automatically [3,4]. Therefore, it is still a challenging task to extract satisfactory buildings from aerial images in an automatic fashion.
Deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) have achieved remarkable success, owing to their great capabilities in learning representative features, which significantly promote the accuracy of semantic segmentation [5,6]. Pooling or convolution striding operations are repeated in DCNNs to increase the receptive field and obtain global-level semantic features; however, the down-sampling process dramatically decreases the initial image resolution, carrying the risk of losing important spatial details, which may result in unsatisfactory segmentation results with inaccurate edges. To alleviate the loss of spatial details and produce accurate segmentation results, computer vision researchers have designed various encoder–decoder structures for better integration of high-level semantic information and low-level spatial information [7,8,9,10]. The idea to fuse feature maps generated from the encoder is also widely applied in DCNN-based building extraction methods, helping to preserve rich spatial details [11,12].
The multi-level features extracted from various encoder–decoder structures are complementary to semantic segmentation. However, low-level features such as edge information directly extracted from a stand-alone mask-segmentation task are redundant and inaccurate, which may clutter dense pixel-wise classification maps. Recently, researchers have begun to look into the potential of joint learning of the semantic segmentation task and shape-related auxiliary tasks. For example, boundary information learned from an individual network or a unified network is used to improve semantic segmentation performance [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Some studies improve the performance via a multi-task network, including a mask-segmentation task and a distance-prediction task that describe the geometric shape of buildings [19,20]. Boundaries reinforce spatial edge information and help produce fine-grained building-extraction results. The distance-transform map measures how far each pixel is from the closest building edge. Its values change smoothly in space, providing the benefit of capturing supplement relationship between neighboring pixels, which are largely ignored by binary boundary maps. Thus, both of the two sources of auxiliary information are helpful to compensate for the loss of shape information for building segmentation. In addition, most existing studies designed various multi-task networks to predict geometric features and segmentation in a parallel manner without consideration of their dual relationship. In fact, distance and boundary maps can be derived from existing building masks for the same image, implying that duality between the mask prediction and two shape-related information predictions can be modeled explicitly if they are put into a joint learning framework.
In this paper, we propose a multi-task convolutional network with distance–mask–boundary consistency constraints (named DMBC-Net) for building extraction from aerial images. The proposed network considered a consistency constraint between distance maps and building masks, and the other constraint between building masks and boundaries. Specifically, an atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module [8] was appended to the top of the encoder of the U-shaped network [7] to obtain contextual information at multiple scales. Based on the multi-scale features, we performed one regression task and two classification tasks, which generated distance transform maps, building masks, and boundary maps, respectively. After obtaining the three predicted maps, two consistency-loss functions were designed: one for modeling the duality between distance maps and building masks, and the other one for modeling the dual relationship between building masks and boundary maps. In order to build the distance–mask consistency, a smooth Heaviside function was utilized to convert the predicted distance map into a building mask. To build the mask–boundary consistency, an edge-detection operator was implemented to transform the predicted building mask into a boundary map. DMBC-Net achieved state-of-the-art performance on three public remote-sensing datasets. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- A multi-scale and multi-task network is proposed for building extraction, consisting of a primary task for building-mask segmentation and two auxiliary tasks for distance and boundary prediction. The proposed network has the advantage of compensating for the loss of shape information by capturing specific geometric features (i.e., distance and boundary information).
- (2)
- The consistency constraints crossing the three tasks (i.e., distance, mask, and boundary predictions) for building information are considered and constructed in the proposed multi-task network. Such consistency constraints exploit the duality between the mask prediction and two shape-related information predictions, and further improve the building segmentation performance.
- (3)
- Compared with existing methods, the proposed method achieves superior performance on both mask- and boundary-based accuracy metrics. Meanwhile, the constructed consistency constraint model can be readily plugged into existing basic segmentation networks.
2. Related Works
2.1. DCNN-Based Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation refers to assigning a class label to each pixel of an image. In recent years, deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) have been widely used in semantic segmentation (e.g., the fully convolutional network (FCN) [21]). Down-sampling operations are repeated in DCNN-based segmentation methods, helping to obtain global-level semantic features, but carrying the risk of losing important spatial details. In order to integrate information from different spatial scales, coarse and fine convolutional features are combined together via channel-wise addition or concatenation operation (e.g., UNet [7], hourglass networks [22], and RefineNet [10]). In order to extract targets with different sizes, multi-scale contexts are integrated through multi-dilated convolutions or multi-scale pooling layers (e.g., DeepLabv3 [23], DeepLabv3+ [24], and PSPNet [25]). Overall, the integration of multi-level features significantly increases semantic segmentation performance. In our work, enhanced multi-scale features were generated by combining the ASPP module with a U-shaped network, and were used for sequential predictions.
2.2. Shape-Aware Segmentation
In addition to designing various DCNN-based networks for multi-scale feature integration, some researchers have also explored shape-related auxiliary tasks to improve segmentation performance, such as learning boundary and distance representations.
Applying deep DCNN for boundary detection has been proved to be an effective solution. CEDN [26] formulates the detection of object boundaries as an image-labeling task and uses a fully convolutional encoder–decoder network to detect boundaries in an end-to-end manner. HED [27] and RCF [28] improve boundary-detection performance by combing hierarchical features extracted from DCNN. Learned boundaries can be used to refine segmentation. In [13], boundaries were predicted via an additional network. Then the predicted boundaries were concatenated with images features as inputs for another segmentation network. In addition, some multi-task learning networks have been developed to learn boundary maps and segmentation masks simultaneously. Boundary information was learned using shared semantic features, and was used to construct an edge-aware optimizer to refine segmentation results in [14,29]. A new two-stream CNN structure was developed in [30,31] that consisted of a main stream for segmentation and a shape stream for processing boundary information via attention layers. An auxiliary edge task was added in the head of Mask R-CNN to improve instance-level segmentation performance in [32,33].
Distance representations can also be used to supplement shape information for semantic segmentation. In [34], a signed distance representation was introduced for building extraction. This novel representation with fine-grained labels embeds object boundaries into a high dimensional space, with the benefit of discriminating regions with different spatial relations. Some works [35,36] replaced common region maps with distance representations for segmentation to better preserve object shapes. Ref. [37] introduced a multi-task network to predict a segmentation mask and a distance map simultaneously, and then leveraged the shape prior (i.e., object skeleton) reconstructed from the distance map to refine segmentation masks. The binary boundary map reinforced spatial edge information, while the gray distance map captured the relationship between neighboring pixels. Thus, these two shape-related information (i.e., the boundary and distance information) are helpful to compensate for the lack of shape information for semantic segmentation.
2.3. Building Extraction from Aerial Images
Building extraction from aerial images has been extensively researched in remote sensing over the past decade. Traditionally, shallow features such as color, spectrum, edges, shapes, and shadow are extracted from aerial images. Then one or combination of these features are used to segment buildings via unsupervised technologies (e.g., building hypotheses [38], region growing [39,40], or supervised classifiers such as support vector machine (SVM) [41,42]. Because of the high complexity of building structures in aerial images and confusion with other ground objects like roads, manual features need to be carefully designed and tuned in traditional building-extraction methods, often leading to poor generalization capability.
Recently, most state-of-the-art methods for building extraction are based on deep-learning technologies, especially DCNN due to its capability of learning highly discriminative features. Earlier DCNN-based building extraction methods [43,44] were based on patch classification; i.e., labeling a pixel by classifying a patch around the pixel. The patch-classification process needs to be repeated many times to categorize each pixel in the whole image, which results in high computational cost. To tackle this problem, some FCN-based methods [45,46] have been developed to directly handle images of arbitrary size. In order to alleviate the loss of spatial details and produce accurate building-segmentation results, a series of networks were designed to integrate multi-scale features based on U-shape networks [11,47] or a spatial pyramid pooling strategy [48]. Recently, an attention mechanism [49] was proposed to enhance feature representation for segmentation by capturing rich contextual dependencies in spatial and channel dimensions. Thus, some researchers introduced it into segmentation networks to strengthen learned features for building representation [50,51].
The aforementioned building-extraction methods focus on designing various network structures with only one segmentation task to capture multi-scale features. Recently, some works have been proposed by designing shape-related auxiliary tasks to improve segmentation performance. In [3,4,16,18], researchers develop a multi-task network in which segmentation masks and boundaries were both deeply supervised for building segmentation from remote-sensing images. In [19,20], a distance map was combined with the segmentation map in different encoder–decoder networks in a parallel manner to improve building-segmentation performance. In these works, either boundaries or distance maps were integrated with building masks in a parallel manner without explicit consideration of their relationship. However, in our proposed multi-task network, these three tasks (i.e., distance-map estimation, building-mask segmentation, and boundary extraction) were learned jointly to utilize complementary shape information for building extraction; furthermore, the consistency constraints between the three tasks were explicitly enforced during training, which helped to generate accurate building-segmentation results.
3. Methodology
3.1. Preliminaries
3.1.1. Different Output Representations
A multi-task learning network was constructed in our method that supplements shape information for building semantic segmentation during network learning. Figure 1 shows an example of three different representations of building output results, which were building mask, building boundary, and signed distance map, respectively:

Figure 1.
Example of different building-output representations. (a) Original RGB image; (b) building mask; (c) boundary map; (d) signed distance map.
(1) Building mask: The most essential building output representation is the building mask, in which the class value of a building pixel is labeled as 1, and the value of a non-building pixel is labeled as 0 (see Figure 1b).
(2) Building boundary: The boundary map is one typical type of building-output representation that encodes shape information. The boundary map describes the boundaries of building. As displayed in Figure 1c, the value of building-boundary pixels was assigned 1, and otherwise was 0 in the boundary map.
(3) Signed distance map: Recently, the distance-transform map has been used as an alternate of building-output representation to capture geometric properties of building shapes [34,35,36]. The distance-transform map measures the distance of each pixel to the nearest object boundary in an image. We adopted a variant of the distance-transform map (i.e., the signed distance map, ) in [33], which is defined as follows:
where and are two different pixels in the building mask; and denote the building pixel set and the non-building pixel set, respectively; and represents the pixel set of the building boundary. calculates the Euclidean distance between pixel p and pixel q. In our work, was normalized to the range of [–1, 1]. The normalization was implemented via dividing by the maximum positive value of building pixels or by the absolute value of minimum negative number for non-building pixels. Figure 1d shows an example of the signed distance map.
3.1.2. Consistency Constraints
In this study, building information in terms of three output representations (i.e., distance, mask, and boundary maps) were predicted simultaneously through a multi-task learning network. The different building-output representations could be converted to each other. Accordingly, the consistency constraints across different tasks should be considered for the multi-task learning problem. Arguably, explicit enforcement of cross-task consistencies during training has the potential to promote performance of the predicted results for all tasks [52]. Take a two-task learning problem as an example: we use x to denote the input RGB image, , to denote output representations of two different tasks, and to denote learned functions to map x onto y. Next, we give a brief description of the cross-task consistency constraint between and . As described in [52], the triangle loss is the elementary consistency unit, which is defined as follows:
where denotes the distance function such as L1 norm, and denotes a function transforming to . The first two terms in the right-hand side are direct losses for training two tasks. The third term is the consistency term, which enforces that the transformed out of predicted is consistent with directly predicted out of . With the consistency term, the multi-task learning of and are not independent, and the duality between them is exploited. Figure 2a shows the derivation of . The convolutional neural networks are hardly perfect estimators, meaning that the transform function cannot guarantee perfect mapping onto . In order to relax the requirement of an perfect mapping function in the consistency term of the triangle loss, the following triangle inequality is constructed similar to the perceptual loss used in [52]:
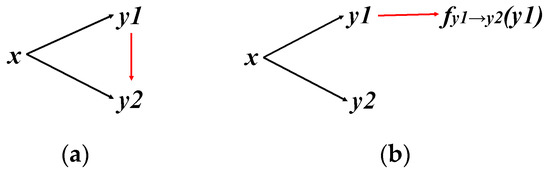
Figure 2.
Illustration of different consistency constraints. (a) The elementary consistency constraint (Equation (2)); (b) the relaxed consistency constraint (Equation (6)).
Applying the triangle inequality for Equation (2), an inequality can be written as follows:
In this inequality, both sides are greater than or equal to 0. We can get the same minimum value when and , thus the upper bound of Equation (5) can replace for optimization. Considering that is constant and closes to 0, and also obtains the same minimum value with the upper bound when and , we can get a relaxed consistency constraint as follows:
The first two terms in the right-hand side in Equation (6) are direct losses for training and . The third term denotes the consistency term, which measures the consistency between and . Compared with Equation (2), the consistency term in Equation (6) does not require transforming into strictly using the transforming function . Figure 2b shows the derivation of .
From Equations (2) and (6), it can be observed that the transforming function is the key to construct consistency constraint, which should be differentiable for the backpropagation of network training. In our network, we constructed two differentiable functions to achieve the conversions between the three different tasks (i.e., distance-map estimation, building segmentation, and boundary extraction) and incorporate the consistency term of Equation (6) into training.
3.2. Overall Architecture
Figure 3 illustrates the overall framework of the proposed DMBC-Net, which consists of one regression head for the distance prediction task and two classification heads for the building-mask-prediction task and the boundary-prediction task, respectively. DMBC-Net employs an enhanced encoder–decoder structure for multi-scale feature extraction, which combines a U-shaped network and an ASPP module. Specifically, the ASPP module, which encodes multi-scale contextual information via parallel atrous convolutions, is plugged into the top of U-shaped network-based encoder to enhance convolutional feature representation. Based on the extracted multi-scale features, DMBC-Net simultaneously predicts distance maps, building masks, and boundary maps via three prediction heads for an input image. As distance and boundary maps can be derived from existing building masks, distance and boundary-prediction tasks should be consistent with the building-segmentation task. In our work, two inter-task consistency constraints were designed based on the three predicted maps (i.e., predicted distance, segmentation, and boundary maps): one inter-task consistency constraint was developed to align the predicted distance and building masks, and the other for guaranteeing the correspondence between predicted masks and boundary maps. To enforce the consistency constraint between the distance and segmentation tasks, a smooth Heaviside function was used to transform distance maps to building masks in a differential way (i.e., DM transforming layer). Similarly, the MB transforming layer transforms building masks to boundary maps via a simple image-difference function, which constructs a mask–boundary consistency constraint. In the following subsections, the two inter-task consistency constraints will be described in detail, and the overall loss function for building extraction with consistency constraints will be introduced.
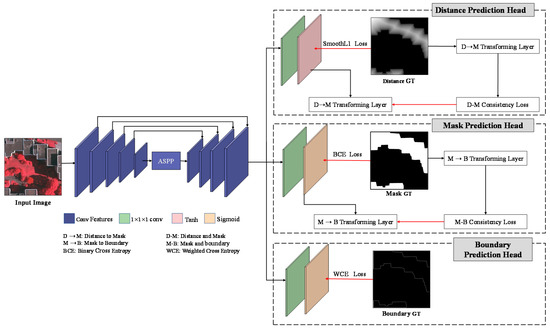
Figure 3.
Overall framework of the proposed method.
3.3. Distance–Mask Consistency Constraint
In order to generate a predicted building mask, a classification head was applied via an convolutional layer along with a sigmoid activated layer after obtaining multi-scale features. To predict the normalized signed distance map, a convolutional layer, along with a tanh activated layer, was applied based on multi-scale features. The ground truth of the normalized signed distance map could be derived from the ground truth of building masks using Equation (1). To integrate the two predicted maps (i.e., normalized signed distance map and building mask) and explore the consistency constraints between them, a smooth Heaviside function was introduced to transform the predicted distance map to the building mask. The smooth Heaviside function ensured that the values of were assigned to 1 and the values of were assigned to 0 for transformed building masks. It is defined as follows:
where represents values in the predicted distance map, and controls the proximity of the smoothed function curve to the exact Heaviside function curve; it was set to 1500 in our study. can be regarded as a sigmoid function with the input multiplied by a factor of k. This function is differentiable and thus could be included in training.
Examples of the predicted distance maps and corresponding transformed building masks are displayed in Figure 4. The transforming function aligned the prediction space of the distance task with the space of the mask-segmentation task. The transformed mask map would contain wrongly labeled pixels when the predicted distance map had wrong signs, thus a task-level prediction difference was introduced for the distance and mask-prediction tasks. To enforce the consistency between the transformed building mask of the predicted distance map and the predicted building mask, a distance-mask consistency loss was designed to minimize the difference between them; it is defined as follows:
where represents the predicted distance map, represents the predicted building mask, and represents the ground truth of the distance map. In order to avoid the noise caused by approximate transformation, the distance–mask loss is measured using the consistency term of Equation (6), where the mask ground truth is derived from the ground truth of the normalized signed distance map using the transforming function .
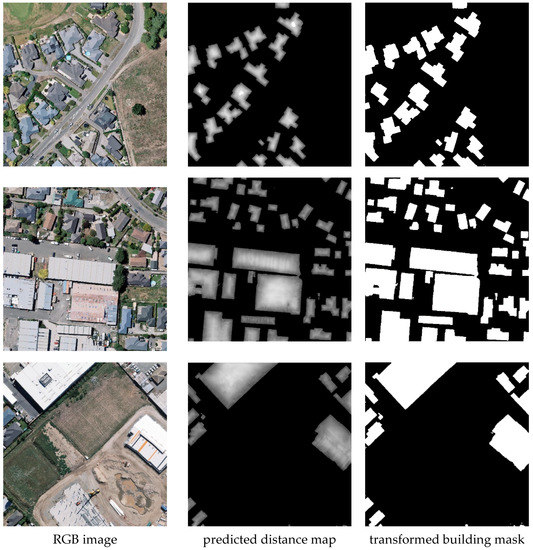
Figure 4.
Examples of predicted distance maps and corresponding transformed building masks via the DM transforming layer (i.e., ).
3.4. Mask–Boundary Consistency Constraint
Boundaries encode critical building-shape information and can be utilized to refine building masks. In our work, the predicted boundary map generated from the convolutional layer was attached to multi-scale features. In order to model the consistency constraint between the mask- and boundary-prediction tasks, predicted building masks were transformed to boundary maps via a difference function. The transformed function calculated the maximum difference between the predicted building mask and its neighboring pixels, ensuring that the values of building boundaries were assigned to 1 and other values were assigned to 0 for the transformed boundary map. The transformed function is defined as follows:
where represents the probability values of buildings in the predicted building mask. The kernel size and the stride of minimum pooling operation were respectively set to 3 and 1 to ensure that the size of the output map was the same as that of the predicted building mask. This function could also be included in training.
As displayed in Figure 5, the transformed boundary maps were generated based on the input building masks using the function, which mapped the predicted building mask to the boundary map. To enforce the consistency between the transformed boundary map derived from the predicted building mask and the directly predicted boundary map, a mask–boundary consistency loss was designed to minimize the difference between them:
where represents the predicted building mask, represents the predicted boundary map, and represents the ground truth of the building mask. In order to avoid the noise caused by approximate transformation, the mask–boundary loss was measured using the consistency term of Equation (6), where the mask ground truth was derived from the ground truth of the building mask using the transforming function .
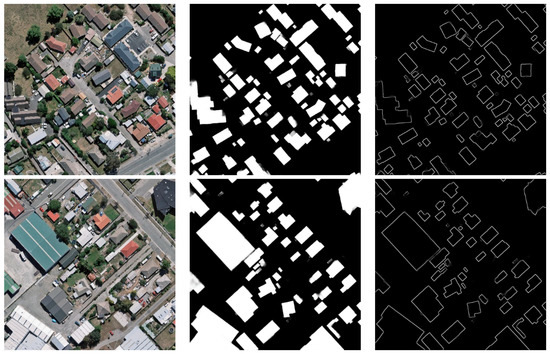

Figure 5.
Examples of predicted building masks and corresponding transformed boundary maps via the MB transforming layer (i.e., ).
3.5. Overall Training Loss Function
As displayed in Figure 3, distance, mask, and boundary prediction tasks were jointly learned with the consideration of their consistency constraints.
The distance-regression task was optimized by two types of loss functions. First, the smoothL1 loss function was formulated on the predicted normalized signed distance map :
where denotes the predicted distance map and denotes the ground truth of the distance map. can be automatically generated from the segmentation ground truth using Equation (1). To penalize the predicted distance map for having wrong signs, the distance–mask consistency loss as described in Section 3.2 also was constructed. The total loss for the distance task is formulated as follows:
For the building-mask-classification task, its loss also consists of two types of loss functions. One is a common binary cross entropy loss based on the predicted building mask , which is defined as follows:
where denotes the predicted building mask and denotes the mask ground truth. The other loss function is the mask–boundary consistency loss, as defined in Section 3.3, which was used to improve the learning of boundary in the predicted building mask. The total loss for the segmentation task is written as:
For the boundary-classification task, a weighted cross entropy was formulated based on the predicted boundary map :
where denotes the predicted boundary map and denotes the boundary ground truth. is the proportion of non-boundary pixels in the boundary ground truth, and is used to alleviate the boundary class imbalance problem.
Putting the distance loss , the mask loss , and the boundary loss together, the overall training loss function for the joint learning of the three tasks is minimized via back-propagation, which is defined as follows:
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Datasets and Implementation Details
The proposed DMBC-Net was evaluated on three public aerial image data sets, namely the WHU aerial building data set [11], the ISPRS Vaihingen data set [53], and the Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set [54].
The WHU aerial building data set was specially designed for building extraction from high-resolution aerial images. The data set was collected from Christchurch, New Zealand, covering an area of more than 450 , containing about 187,000 buildings of different appearance and sizes. It consists of 8189 cropped images sized 512 × 512 pixels with a down-sampled ground resolution of 0.3 m. The whole images in this data set were further divided into a training subset including 4736 images, a validation subset including 2416 images, and a test subset including 1036 images. Our experiments were conducted based on this fixed split data set.
The ISPRS Vaihingen data set is an open benchmark data set for the extraction of various urban targets, including buildings. The data set contains 33 patches with large sizes at a ground sampling distance of 9 cm. Each patch consists of a color infrared orthophoto, a corresponding DSM, and labeled ground truth. In this data set, 16 patches were divided into a training sub-set, and the remaining 17 patches formed a test sub-set. We only utilized the orthophotos and corresponding ground truth for our experiments. Considering computational efficiency, the images in the training set were cropped into 512 × 512 sub-images with an overlap ratio of 0.5. As a result, a new training data set was reconstructed that contained 1046 sub-images and their corresponding ground truths.
The Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set was collected from 10 cities with different urban settlements, ranging from densely populated areas to alpine towns. It consists of 180 orthographic aerial RGB images with public label for training and 180 images without public label for testing. The ground resolution of each image is 0.3 m, and the image size is 5000 × 5000. Similar to the exiting work in [48,55], the first five images of each city in training subset were selected for testing, and the remaining images were used for training. In our experiment, all the images were further divided into 512 × 512 sub-images during training.
The proposed DMBC-Net was implemented on the Keras platform. The backbone of the encoder part was initialized with pre-trained ImageNet weights using the VGG19 network. All models were trained on a single NVIDIA GTX 2080Ti GPU. The Adam optimizer was adopted to optimize the network with a learning rate of 0.0001, beta1 of 0.9, and beta2 of 0.999. Random rotation and flipping and scaling were used for data augmentation. For these data sets, a mini-batch contained 6 images during training, and the training times were set as 200 epochs until training convergence.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
Three typical metrics were used to evaluate the accuracy of the predicted building masks, which were defined as follows:
where denotes true predictions on positive samples, denotes false predictions on positive samples, and denotes false predictions on negative samples. In our work, precision was the proportion of correctly predicted buildings to the total predicted buildings, while recall was the proportion of correctly predicted buildings to the building ground truth. The score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. Intersection over union (IoU) represents the ratio of intersection pixels (i.e., correctly predicted building pixels) over the union pixels between the predicted and ground-truth buildings.
In addition to above-mentioned metrics, a contour-based metric according to the previous studies in [30,56] was adopted to evaluate the quality of the extracted building boundaries. As mentioned in [30], this metric computes the F-score along the boundaries of predicted masks under a small distance tolerance. In our experiments, the distance thresholds were set to pixel widths of 1, 3, 5, and 7.
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
In this section, we report the performance of the proposed DMBC-Net for building extraction and compare its performance with the state-of-the-art methods on three public high-resolution aerial data sets.
(1) The WHU aerial building data set: Seven existing methods were implemented for comparison using this data set, namely FCN [21], UNet [7], DeepLabV3+ [24], SRI-Net [57], EU-Net [48], MA-FCN [47], and MAP-Net [51]. The first three methods are commonly used semantic-segmentation models that achieve satisfactory results on semantic segmentation. The remaining four comparison methods are the most recent building-extraction methods based on CNN. These existing building-extraction methods focus on alleviating the scale effects of buildings in aerial images by designing different multi-scale feature-extraction networks. For SRI-Net, multi-level features are successively fused by a spatial residual-inception module. EU-Net extracts multi-scale dense features for building extraction by applying a dense spatial pyramid pooling module with a compact receptive field. MA-FCN concatenates the output features at different scales in the decoding part. For MAP-Net, a multi-parallel network is constructed to learn localization-preserved multi-scale features.
Table 1 shows the building-extraction performance on the WHU aerial building data set. The first three common semantic segmentation models achieved 86.62%, 88.11%, and 88.26% for the building-mask IoU metric and 51.54%, 52.93%, and 54.63% for the boundary F1-score with a distance threshold of 1 pixel. Compared with the scores for building masks, the F1-scores for building boundaries were relatively low, but were reasonable because it was more difficult to detect accurate building boundaries than building masks because building boundaries have much fewer pixels than masks. By using carefully designed multi-scale feature-extraction networks, the performance of building extraction was further improved. MAP-Net improved building-extraction performance (90.75% for the IoU metric and 58.26% for the boundary F1-score) with the help of an effective multi-scale feature-extraction module and a channel-wise attention-enhancement module. The proposed DMBC-Net made full use of auxiliary shape information. This information can be plugged into any existing encoder–decoder network, such as DeepLabV3+, which will be discussed in the Section 4.5. As displayed in Table 1, DMBC-Net obtained 91.66% for the IoU metric and 61.54% for the boundary F1-score, which outperformed the compared methods.

Table 1.
Quantitative comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the WHU aerial data set.
(2) The ISPRS Vaihingen data set: This data set is a high-resolution aerial dataset of complex urban scenes. It is classified manually into six common land cover classes, including impervious surfaces, building, low vegetation, tree, car, and background. In our experiments, all the objects except buildings were regarded as the background to detect a single building category. It should be noted that only the TOP images and corresponding ground truths were utilized for training the proposed network, and the quality metrics of the building-extraction results were calculated using the ground truths without eroded boundaries.
We compared the proposed DMBC-Net using this data set with three common semantic-segmentation models (i.e., FCN, UNet, and DeepLabV3+) and a specially designed building-extraction model (i.e., MAP-Net). Table 2 shows the building-extraction performance on the ISPRS Vaihingen data set. As indicated in Table 2, FCN obtained lower performance than UNet, DeepLabV3+, MAP-Net, and DMBC-Net, since the multi-scale features were not fully considered in FCN. The proposed DMBC-Net outperformed the other methods, with 89.28% for the IoU metric and 51.43% for the boundary F1-score with a distance threshold of 3 pixels, which was 1.5% and 1.61% higher, respectively, than MAP-Net, the second-best method. The quantitative comparison in this data set further demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method in building extraction.

Table 2.
Quantitative comparison with state-of-the-art methods on the ISPRS Vaihingen data set.
(3) The Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set: Using this data set, our proposed network was compared with two popular semantic-segmentation networks (i.e., UNet and DeepLabV3+) and two carefully designed building-extraction networks (i.e., MCFNN [55] and EU-Net [48]). As displayed in Table 3, the proposed DMBC-Net obtained 80.93% for the mask IoU and 39.24% for the boundary F1-score with a distance threshold of 1 pixel. The mask IoU of the proposed network was increased by 4.54%, 3.72%, 1.39%, and 0.24% compared with those of UNet, DeepLabV3+, MCFNN, and EU-Net, respectively. The boundary F1-score was improved by 3.09% and 2.01% compared with UNet and DeepLabV3+, respectively. These results also confirmed that our proposed network with distance–mask–boundary consistency constraints helped improve the performance of building extraction.

Table 3.
Quantitative comparison on the Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set.
4.4. Ablation Experiments for Inter-Task Consistency Constraints
The proposed network jointly learned the building-mask-segmentation task with two shape-related auxiliary tasks (i.e., boundary prediction and distance estimation), and the consistency constraints of the three tasks were modeled in an explicit manner. In order to investigate the effect of inter-task consistency constraint, three different training networks were designed and evaluated using the WHU aerial building data set. The three variants are described as follows:
- (1)
- Mask-Net: Only including the branch for building-mask-prediction task.
- (2)
- DMB-Net (Distance + Mask + Boundary): Including three branches for the distance-, mask-, and boundary-prediction tasks simultaneously.
- (3)
- DMBC-Net (Distance + Mask + Boundary + +): The proposed complete module with two inter-task consistency constraints.
Mask IoU and boundary F1-score comparisons of the above training modules are listed in Table 4. As displayed in Table 4, a 1.07% mask IoU improvement was obtained for building segmentation with the help of the distance task and the boundary task. The inter-task consistency constraints further improved the segmentation results. The proposed DMBC-Net with the inter-task consistency constraints obtained the best IoU score of 91.66%, which was 1.96% higher than that of Mask-Net. In addition to the mask IoU metric, boundary F1-scores with different thresholds also were compared for evaluating boundary alignment. Note that the boundary F1-score was calculated based on the boundary maps, which were derived by extracting the contours of the predicted building masks. As shown in Table 4, with the increase of the distance thresholds, the evaluation region was wider, and the boundary F1-score was higher. Compared with Mask-Net, a 2.24% improvement of the boundary F1-score with a distance threshold of 1 pixel was obtained with the help of the distance and boundary tasks. It also could be also that the use of the inter-task consistency constraints further improved the boundary F1-score. Compared with Mask-Net, the boundary F1-score achieved a 3.69% improvement at the most stringent distance threshold.

Table 4.
Mask IoU and boundary F1-score comparisons for ablation studies of inter-task consistency constraints.
In order to better understand the effect of inter-task consistency constraints, some visual examples are displayed in Figure 6. In the predicted maps of visual examples, white pixels represent correctly predicted building pixels, black pixels represent correctly predicted non-building pixels, red pixels represent falsely predicted building pixels, and green pixels represent missing building pixels. As shown in Figure 6, the segmentation results generated from Mask-Net, DMB-Net, and DMBC-Net were compared. It could be observed that the two shape-related auxiliary tasks helped to generate more complete building masks by filling the holes and discontinuities of buildings, and more accurate building boundaries by adjusting the misclassified pixels around building boundaries, and this effect was further enhanced by the inter-task consistency constraints.
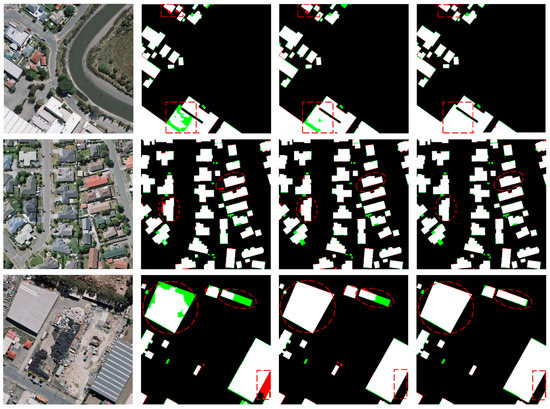

Figure 6.
Comparisons for segmentation results generated from Mask-Net, DMB-Net, and the full model; i.e., DMBC-Net.
4.5. Ablation Experiments for Different Base Networks
The proposed inter-task consistency constraints (i.e., distance–mask consistency constraint and mask–boundary consistency constraint ) can be used as plug-and-play modules and incorporated into existing encoder–decoder networks by inserting two types of auxiliary supervision (i.e., boundary supervision and distance supervision). The modules made use of auxiliary information and enhanced the consistencies between the auxiliary tasks and the primary building-mask-prediction task, thereby improving the performance of building segmentation.
For a more comprehensive evaluation of the inter-task consistency constraints and the adopted base network (which inserted the ASPP module into the top of U-shape network-based encoder), quantitative results of common encoder–decoder networks (including FCN, UNet, and DeepLabV3+) and our proposed base networks with or without the inter-task consistency constraint were compared, as shown in Table 5. The proposed base network achieved a region IoU score of 91.66% and a boundary F1-score with a distance threshold of 1 pixel of 61.54%, which outperformed the compared three common encoder–decoder networks. Furthermore, the performance was improved with the help of the inter-task consistency constraints under different encoder–decoder networks. Take DeepLabV3+ as an example: the IoU and boundary F1-score were improved by 2.03% and 3.74%, respectively. The comparison results demonstrated that the inter-task consistency constraints, which can be easily plugged into the existing encoder–decoder networks, helped to generate more accurate segmentation results.

Table 5.
Comparison of different base networks with or without the inter-task consistency constraints.
4.6. Efficiency Analysis
In order to verify the trade-off between accuracy and model complexity of our proposed network, the IoU metric, trainable parameters, and floating-point operations (FLOPs) were compared among different methods using the WHU data set. In these comparison methods, UNet, PSPNet, and MAPNet were utilized to extract building masks without consideration of shape-related information, while EaNet [17], BARNet [4], and our proposed DMBC-Net combined this information.
As displayed in Table 6, the model complexity of UNet was the lowest, but its accuracy was worse than other methods. MAPNet introduced an attention mechanism for building extraction, which improved accuracy with lower model complexity. Compared with the first three methods, the last three methods generated more accurate building-extraction results by making use of auxiliary shape information and carefully designed feature-extraction networks. EaNet and BARNet had complicated model complexity because that encoder part of the two networks used ResNet-101 as the backbone for feature extraction. DMBC-Net adapted the VGG19 network for feature extraction during the encoder part, thus greatly reducing the complexity of the model. Compared with these methods, our proposed DMBC-Net generated higher accuracy of building-extraction results while maintaining relatively low model complexity.

Table 6.
Accuracy and model-complexity comparison of different methods using the WHU data set.
4.7. Qualitative Results
In order to qualitatively evaluate the performance of our proposed network, visual comparisons of building-extraction results using three public aerial data sets are displayed in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9.

Figure 7.
Visual comparisons of building-extraction results on the WHU building data set by different models. (a) Input image, (b) FCN, (c) Unet, (d) Deeplabv3+, (e) the proposed DMBC-Net, and (f) ground truths of the input image.
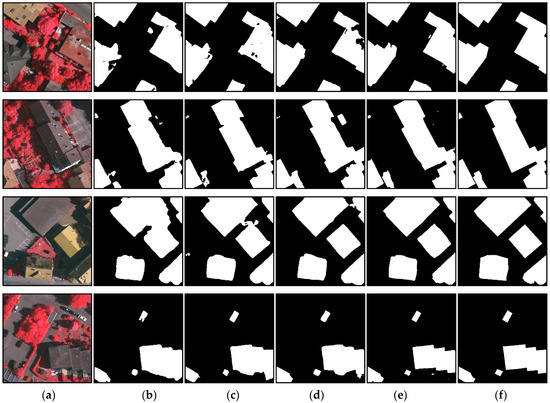

Figure 8.
Visual comparisons of building-extraction results on the ISPRS Vaihingen data set by different models. (a) Input image, (b) FCN, (c) Deeplabv3+, (d) MAPNet, (e) the proposed DMBC-Net, and (f) Ground truths of the input image.
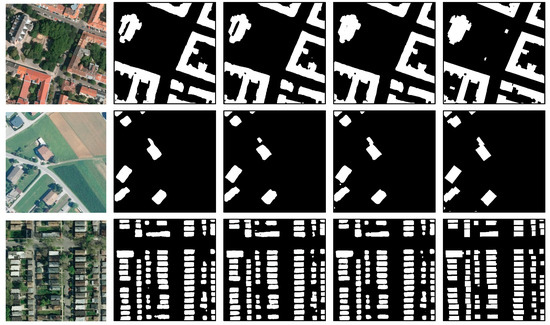
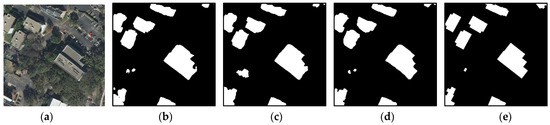
Figure 9.
Visual comparisons of building-extraction results on the Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set by different models. (a) Input image, (b) UNet, (c) Deeplabv3+, (d) the proposed DMBC-Net, and (e) ground truths of the input image.
The first and last columns in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 represent the input images and corresponding ground truths. In Figure 7, buildings-extraction results obtained by FCN, UNet, Deeplabv3+, and the proposed DMBC-Net using the WHU building data set are displayed. Figure 8 compares building-extraction results using the ISPRS Vaihingen data set obtained by FCN, Deeplabv3+, MAPNet, and DMBC-Net. Figure 9 displays building-extraction results using the Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set generated by UNet, DeeplabV3+, and our proposed DMBC-Net. As displayed in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, our proposed method could extract accurate building results, although the buildings in these images varied in size, shape, and appearance. As displayed in the first two rows of Figure 7 and Figure 8, the proposed DMBC-Net extracted more complete results, especially for large buildings. For example, in the first-row image in Figure 7, the large buildings extracted by the compared methods were usually discontinuous, while DMBC-Net extracted relatively complete building results. The images in the third and fourth rows in Figure 7 and Figure 8 show that the proposed DMBC-Net had the capability to separate buildings with adjacent similar backgrounds and generate more accurate building boundaries. For example, in the first-row image in Figure 8, DMBC-Net distinguished buildings from adjacent impervious surfaces with a similar appearance. Building-extraction results for different scenes in the Inria data set are presented in Figure 9, which shows that the proposed DMBC-Net could obtain more complete and accurate building masks with sharp boundaries compared with other methods. For example, in the first row of Figure 9, more complete buildings were extracted by DMBC-Net. These qualitative results further demonstrated the advantage of our proposed method.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have proposed a multi-scale and multi-task network with distance–mask–boundary consistency constraints (i.e., DMBC-Net) for building extraction from high-resolution aerial images. The proposed network consisted of one main task of building-mask prediction and two shape-related tasks of boundary extraction and distance-map estimation. Two inter-task consistency-loss functions were constructed to further improve the performance of building extraction. One loss function ensured the consistency between distance maps and building masks, and the other ensured the consistency between building masks and boundary maps. In order to build the distance–mask consistency, a smooth Heaviside function was utilized to convert the predicted distance-transform map into a segmentation-probability map. To build the mask–boundary consistency, an edge-detection operator was implemented to transform the predicted building mask into a boundary map. The experiments on three public high-resolution aerial image data sets (i.e., the WHU aerial building data set, ISPRS Vaihingen data set, and Inria Aerial Image Labeling data set) showed that the proposed DMBC-Net preserved building shape well with precise boundaries, and improved building-segmentation performance over several state-of-the-art baselines. In addition, it was proved that the proposed inter-task consistency constraints could be incorporated with existing encoder–decoder networks to achieve satisfactory building-extraction results. Currently, the proposed network is implemented to extract buildings at the pixel level. In future work, we will research building extraction at the instance level to delineate each building boundary accurately.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S. and T.Z.; methodology, F.S.; validation, F.S. and T.Z.; formal analysis, F.S.; investigation, F.S; data curation, F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.; writing—review and editing, F.S. and T.Z.; supervision, T.Z.; funding acquisition, T.Z. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41871308) and the National Key R&D Program of China (International Scientific & Technological Cooperation Program, grant no. 2019YFE0106500).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The WHU aerial building [11] and ISPRS Vaihingen [52] data sets presented in this work are openly available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jun, W.; Qiming, Q.; Xin, Y.; Jianhua, W.; Xuebin, Q.; Xiucheng, Y. A Survey of Building Extraction Methods from Optical High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2016, 31, 653–662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, P. Extraction of urban building damage using spectral, height and corner information from VHR satellite images and airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Li, H.; Ge, X.; Chen, M.; Li, C.; Zhu, Q. Joint Learning of Contour and Structure for Boundary-Preserved Building Extraction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Jia, H. Boundary-Aware Refined Network for Automatic Building Extraction in Very High-Resolution Urban Aerial Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Oprea, S.; Villena-Martinez, V.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J. A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.06857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2018, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiasi, G.; Fowlkes, C.C. Laplacian pyramid reconstruction and refinement for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 519–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jian, L.; Min, W.; Haihong, Z. A Multiple-Feature Reuse Network to Extract Buildings from Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar]
- Marmanis, D.; Schindler, K.; Wegner, J.D.; Galliani, S.; Datcu, M.; Stilla, U. Classification with an edge: Improving semantic image segmentation with boundary detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 135, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.; Meng, G.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. FusionNet: Edge aware deep convolutional networks for semantic segmentation of remote sensing harbor images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5769–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ding, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. ERN: Edge loss reinforced semantic segmentation network for remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Jiang, W. Boundary-Assisted Learning for Building Extraction from Optical Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Huan, L.; Xia, G.S.; Gong, J. Parsing very high resolution urban scene images by learning deep ConvNets with edge-aware loss. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 170, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. EANet: Edge-aware network for the extraction of buildings from aerial images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischke, B.; Helber, P.; Folz, J.; Borth, D.; Dengel, A. Multi-task learning for segmentation of building footprints with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1480–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, J.; Du, M.; Ye, X.; Qin, Q.; Sui, J. Effective building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images with multitask driven deep neural network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Price, B.; Cohen, S.; Lee, H.; Yang, M.H. Object contour detection with a fully convolutional encoder-decoder network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-nested edge detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, X. Richer convolutional features for edge detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3000–3009. [Google Scholar]
- Bertasius, G.; Shi, J.; Torresani, L. Semantic segmentation with boundary neural fields. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3602–3610. [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa, T.; Acuna, D.; Jampani, V.; Fidler, S. Gated-SCNN: Gated Shape CNNs for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5229–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Terzopoulos, D.; Myronenko, A. Edge-gated CNNs for volumetric semantic segmentation of medical images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.04207. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, R.S.; Siems, J.N. Faster training of Mask R-CNN by focusing on instance boundaries. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 188, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, W. Boundary-Preserving Mask R-CNN. Trans. Petri Nets Other Models Concurr. XV 2020, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J. Learning building extraction in aerial scenes with convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, D.; Newsam, S.; Huang, J. Aerial image semantic segmentation using DCNN predicted distance maps. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 161, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayder, Z.; He, X.; Salzmann, M. Boundary-aware instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5696–5704. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Fishman, E.K.; Yuille, A.L. Deep distance transform for tubular structure segmentation in CTscans. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3833–3842. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Muller, J.-P. Development of a graph-based approach for building detection. Image Vis. Comput. 1999, 17, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femiani, J.; Li, E.; Razdan, A.; Wonka, P. Shadow-based rooftop segmentation in visible band images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Femiani, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wonka, P. Robust rooftop extraction from visible band images using higher order CRF. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4483–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglada, J. Automatic recognition of man-made objects in high resolution optical remote sensing images by SVM classification of geometric image features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, M.; Koc-San, D. Building extraction from high-resolution optical spaceborne images using the integration of support vector machine (SVM) classification, Hough transformation and perceptual grouping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 34, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Shibasaki, R.; Shao, X. Village building identification based on ensemble convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Shao, X.; Xu, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Ohira, W.; Shibasaki, R. Identification of village building via Google Earth images and supervised machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Pan, C. Building extraction from multi-source remote sensing images via deep deconvolution neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 1835–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. Convolutional neural networks for large-scale remote-sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Ji, S.; Lu, M. Toward automatic building footprint delineation from aerial images using CNN and regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, F.; You, H. EU-net: An efficient fully convolutional network for building extraction from optical remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3141–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Fu, Y.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Comber, A.; Wang, K. Building extraction from very high resolution aerial imagery using joint attention deep neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Mei, X.; Li, H. MAP-Net: Multiple attending path neural network for building footprint extraction from remote sensed imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, A.R.; Sax, A.; Cheerla, N.; Suri, R.; Cao, Z.; Malik, J.; Guibas, L.J. Robust Learning Through Cross-Task Consistency. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11194–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISPRS 2D Semantic Labeling Contest. Available online: http://www2.isprs.org/commissions/comm3/wg4/2d-sem-label-vaihingen.html (accessed on 7 July 2018).
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. Can semantic labeling methods generalize to any city? The inria aerial image labeling benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3226–3229. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Feng, D.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L. Refined extraction of building outlines from high-resolution remote sensing imagery based on a multi feature convolutional neural network and morphological filtering. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1842–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, F.; Pont-Tuset, J.; McWilliams, B.; Van Gool, L.; Gross, M.; Sorkine-Hornung, A. A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 724–732. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Building footprint extraction from high-resolution images via spatial residual inception convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).